|
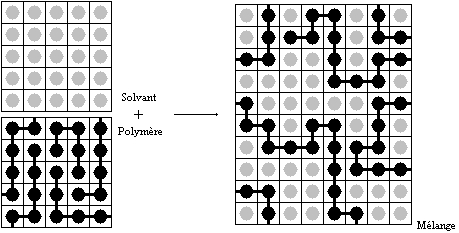
Flory–Huggins Solution Theory
Flory–Huggins solution theory is a lattice model of the thermodynamics of polymer solutions which takes account of the great dissimilarity in molecular sizes in adapting the usual expression for the entropy of mixing. The result is an equation for the Gibbs free energy change \Delta G_m for mixing a polymer with a solvent. Although it makes simplifying assumptions, it generates useful results for interpreting experiments. Theory The thermodynamic equation for the Gibbs energy change accompanying mixing at constant temperature and (external) pressure is :\Delta G_m = \Delta H_m - T\Delta S_m \, A change, denoted by \Delta, is the value of a variable for a solution or mixture minus the values for the pure components considered separately. The objective is to find explicit formulas for \Delta H_m and \Delta S_m, the enthalpy and entropy increments associated with the mixing process. The result obtained by Flory and Huggins is :\Delta G_m = RT ,n_1\ln\phi_1 + n_2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Component (thermodynamics)
In thermodynamics, a component is one of a collection of chemically independent constituents of a system. The number of components represents the minimum number of independent chemical species necessary to define the composition of all phases of the system. Calculating the number of components in a system is necessary when applying Gibbs' phase rule in determination of the number of degrees of freedom of a system. The number of components is equal to the number of distinct chemical species (constituents), minus the number of chemical reactions between them, minus the number of any constraints (like charge neutrality or balance of molar quantities). Calculation Suppose that a chemical system has elements and chemical species (elements or compounds). The latter are combinations of the former, and each species can be represented as a sum of elements: : A_i = \sum_j a_E_j, where are the integers denoting number of atoms of element in molecule . Each species is determined by a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entropy
Entropy is a scientific concept, as well as a measurable physical property, that is most commonly associated with a state of disorder, randomness, or uncertainty. The term and the concept are used in diverse fields, from classical thermodynamics, where it was first recognized, to the microscopic description of nature in statistical physics, and to the principles of information theory. It has found far-ranging applications in chemistry and physics, in biological systems and their relation to life, in cosmology, economics, sociology, weather science, climate change, and information systems including the transmission of information in telecommunication. The thermodynamic concept was referred to by Scottish scientist and engineer William Rankine in 1850 with the names ''thermodynamic function'' and ''heat-potential''. In 1865, German physicist Rudolf Clausius, one of the leading founders of the field of thermodynamics, defined it as the quotient of an infinitesimal amount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole Fraction
In chemistry, the mole fraction or molar fraction (''xi'' or ) is defined as unit of the amount of a constituent (expressed in moles), ''ni'', divided by the total amount of all constituents in a mixture (also expressed in moles), ''n''tot. This expression is given below: :x_i = \frac The sum of all the mole fractions is equal to 1: :\sum_^ n_i = n_\mathrm ; \ \sum_^ x_i = 1. The same concept expressed with a denominator of 100 is the mole percent, molar percentage or molar proportion (mol%). The mole fraction is also called the amount fraction. It is identical to the number fraction, which is defined as the number of molecules of a constituent ''Ni'' divided by the total number of all molecules ''N''tot. The mole fraction is sometimes denoted by the lowercase Greek letter (chi) instead of a Roman ''x''. For mixtures of gases, IUPAC recommends the letter ''y''. The National Institute of Standards and Technology of the United States prefers the term amount-of-substance fract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermodynamic Temperature
Thermodynamic temperature is a quantity defined in thermodynamics as distinct from kinetic theory or statistical mechanics. Historically, thermodynamic temperature was defined by Kelvin in terms of a macroscopic relation between thermodynamic work and heat transfer as defined in thermodynamics, but the kelvin was redefined by international agreement in 2019 in terms of phenomena that are now understood as manifestations of the kinetic energy of free motion of microscopic particles such as atoms, molecules, and electrons. From the thermodynamic viewpoint, for historical reasons, because of how it is defined and measured, this microscopic kinetic definition is regarded as an "empirical" temperature. It was adopted because in practice it can generally be measured more precisely than can Kelvin's thermodynamic temperature. A thermodynamic temperature reading of zero is of particular importance for the third law of thermodynamics. By convention, it is reported on the '' Kelvin sca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gas Constant
The molar gas constant (also known as the gas constant, universal gas constant, or ideal gas constant) is denoted by the symbol or . It is the molar equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, expressed in units of energy per temperature increment per amount of substance, i.e. the pressure–volume product, rather than energy per temperature increment per ''particle''. The constant is also a combination of the constants from Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law. It is a physical constant that is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law, the Arrhenius equation, and the Nernst equation. The gas constant is the constant of proportionality that relates the energy scale in physics to the temperature scale and the scale used for amount of substance. Thus, the value of the gas constant ultimately derives from historical decisions and accidents in the setting of units of energy, temperature and amount of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of heat and light. Energy is a conserved quantity—the law of conservation of energy states that energy can be converted in form, but not created or destroyed. The unit of measurement for energy in the International System of Units (SI) is the joule (J). Common forms of energy include the kinetic energy of a moving object, the potential energy stored by an object (for instance due to its position in a field), the elastic energy stored in a solid object, chemical energy associated with chemical reactions, the radiant energy carried by electromagnetic radiation, and the internal energy contained within a thermodynamic system. All living organisms constantly take in and release energy. Due to mass–energy equivalence, any object that h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mole (unit)
The mole, symbol mol, is the unit of amount of substance in the International System of Units (SI). The quantity amount of substance is a measure of how many elementary entities of a given substance are in an object or sample. The mole is defined as containing exactly elementary entities. Depending on what the substance is, an elementary entity may be an atom, a molecule, an ion, an ion pair, or a subatomic particle such as an electron. For example, 10 moles of water (a chemical compound) and 10 moles of mercury (a chemical element), contain equal amounts of substance and the mercury contains exactly one atom for each molecule of the water, despite the two having different volumes and different masses. The number of elementary entities in one mole is known as the Avogadro number, which is the approximate number of nucleons ( protons or neutrons) in one gram of ordinary matter. The previous definition of a mole was simply the number of elementary entities equal to that of 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function from a set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words map, mapping, transformation, correspondence, and operator are often used synonymously. The set is called the domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function.Codomain ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'Codomain. ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics''/ref> The earliest known approach to the notion of function can be traced back to works of Persian mathematicians Al-Biruni and Sharaf al-Din al-Tusi. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice Loyal Huggins
Maurice Loyal Huggins (19 September 1897, Berkeley County, West Virginia – 17 December 1981) was a scientist who independently conceived the idea of hydrogen bonding and who was an early advocate for their role in stabilizing protein secondary structure. An important polymer theory, Flory–Huggins theory, is also named after him. Controversies over the hydrogen bond Huggins believed that he had been the first to suggest the concept of the hydrogen bond, while he was a student under G. N. Lewis at the Chemical Laboratory of the University of California, Berkeley. According to his account, he wrote a thesis in 1919 in which the H-bond was introduced and applied to tautomerism in acetoacetic acid. Unfortunately, no hard copy of the thesis remains. The first extant publication of the H-bond was that of Wendell Latimer and Worth Rodebush in 1920, who cite Huggins' unpublished work in a footnote. (They were fellow scientists at the Chemical Laboratory.) Structure of the pepti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Flory
Paul John Flory (June 19, 1910 – September 9, 1985) was an American chemist and Nobel laureate who was known for his work in the field of polymers, or macromolecules. He was a leading pioneer in understanding the behavior of polymers in solution, and won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1974 "for his fundamental achievements, both theoretical and experimental, in the physical chemistry of macromolecules". Biography Personal life Flory was born in Sterling, Illinois, on June 19, 1910. He was raised by Ezra Flory and Nee Martha Brumbaugh. His father worked as a clergyman-educator, and his mother was a school teacher. He first gained his interest in science from Carl W Holl, who was a professor in chemistry. Holl was employed in Indiana at Manchester College as a chemistry professor. In 1936, he married Emily Catherine Tabor. He and Emily had three children together; Susan Springer, Melinda Groom and Paul John Flory jr. They also had five grandchildren. All of his children purs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process (science)
The scientific method is an Empirical evidence, empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientific method for additional detail.) It involves careful observation, applying rigorous skepticism about what is observed, given that Philosophy of science#Observation inseparable from theory, cognitive assumptions can distort how one interprets the Perception#Process and terminology, observation. It involves formulating Hypothesis, hypotheses, via Inductive reasoning, induction, based on such observations; the testability of hypotheses, experimental and the measurement-based statistical testing of Deductive reasoning, deductions drawn from the hypotheses; and refinement (or elimination) of the hypotheses based on the experimental findings. These are ''principles'' of the scientific method, as distinguished from a definitive ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |