Asiatic cholera on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cholera () is an


, World Health Organization, Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean, undated but citing sources from '07, '04, '03, '04, and '05. Any individual, even a healthy adult in middle age, can undergo a severe case, and each person's case should be measured by the loss of fluids, preferably in consultation with a professional
 When consumed, most bacteria do not survive the
When consumed, most bacteria do not survive the
who.int
. Retrieved November 5, 2013. By inserting separate, successive sections of ''V. cholerae'' DNA into the DNA of other bacteria, such as ''
File:Unsafe disposal of faecal sludge or sewage in Haiti (6458176073).jpg, Dumping of
 Spanish physician Jaume Ferran i Clua developed the first successful cholera inoculation in 1885, the first to immunize humans against a bacterial disease. His vaccine and inoculation was rather controversial and was rejected by his peers and several investigation commissions but it ended up demonstrating its effectiveness and being recognized for it: out of the 30 thousand people he vaccinated only 54 died. Russian-French bacteriologist Waldemar Haffkine also developed a human cholera vaccine in July 1892. He conducted a massive inoculation program in
Spanish physician Jaume Ferran i Clua developed the first successful cholera inoculation in 1885, the first to immunize humans against a bacterial disease. His vaccine and inoculation was rather controversial and was rejected by his peers and several investigation commissions but it ended up demonstrating its effectiveness and being recognized for it: out of the 30 thousand people he vaccinated only 54 died. Russian-French bacteriologist Waldemar Haffkine also developed a human cholera vaccine in July 1892. He conducted a massive inoculation program in
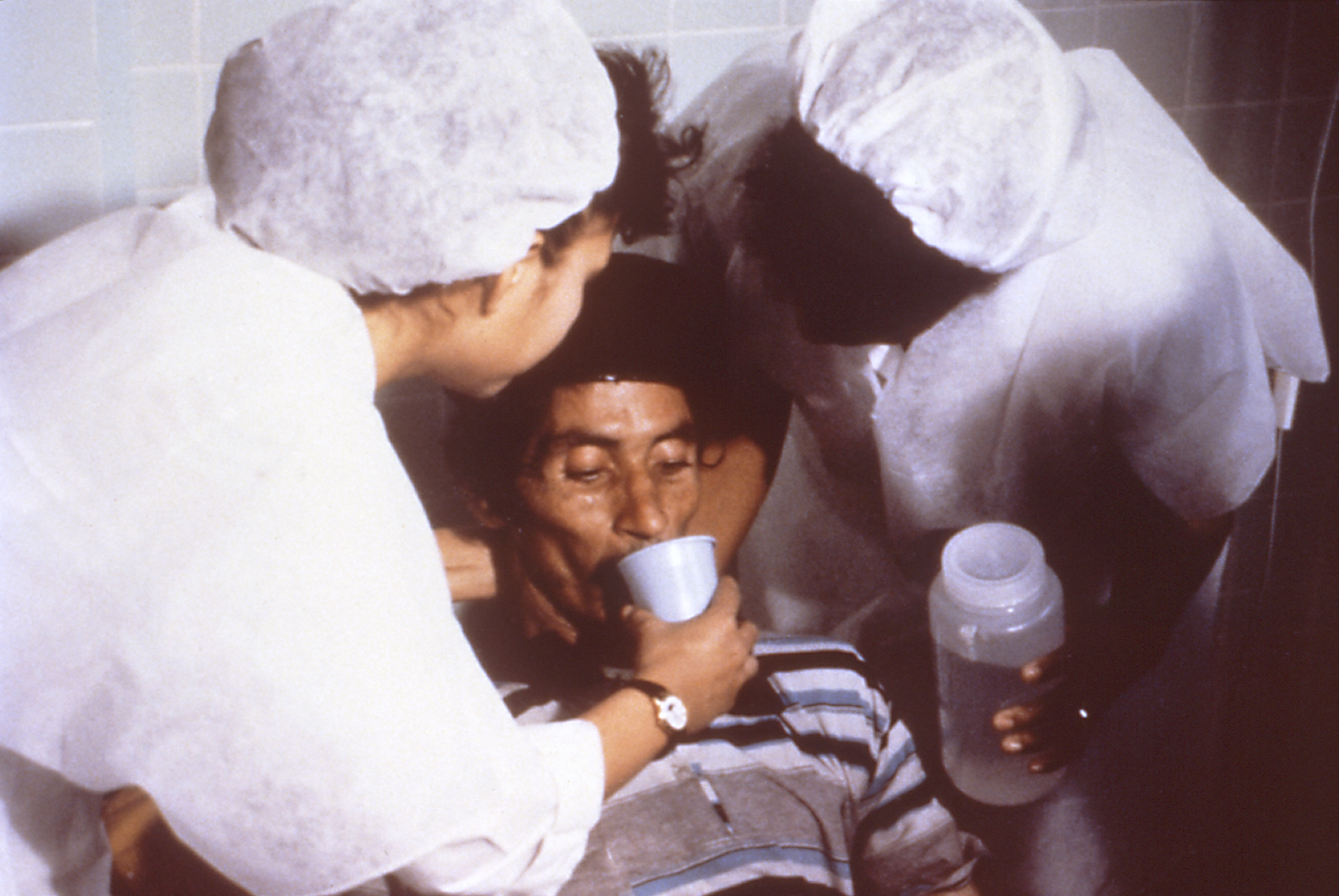 Continued eating speeds the recovery of normal intestinal function. The WHO recommends this generally for cases of diarrhea no matter what the underlying cause. A CDC training manual specifically for cholera states: "Continue to breastfeed your baby if the baby has watery diarrhea, even when traveling to get treatment. Adults and older children should continue to eat frequently."
Continued eating speeds the recovery of normal intestinal function. The WHO recommends this generally for cases of diarrhea no matter what the underlying cause. A CDC training manual specifically for cholera states: "Continue to breastfeed your baby if the baby has watery diarrhea, even when traveling to get treatment. Adults and older children should continue to eat frequently."

 The word cholera is from ''kholera'' from χολή ''kholē'' "bile". Cholera likely has its origins in the
The word cholera is from ''kholera'' from χολή ''kholē'' "bile". Cholera likely has its origins in the
File:Cholera.jpg,
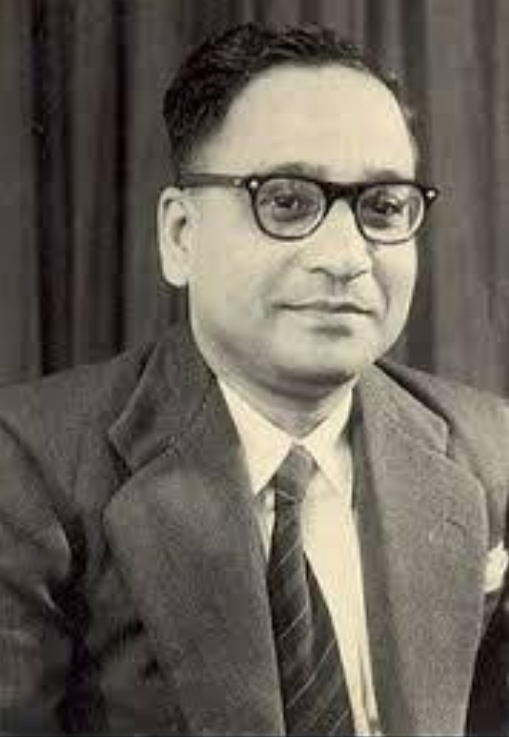 Indian medical scientist Sambhu Nath De discovered the
Indian medical scientist Sambhu Nath De discovered the
 The city of
The city of
online
* * * * Gilbert, Pamela K. "Cholera and Nation: Doctoring the Social Body in Victorian England" (SUNY Press, 2008). *
online
* * * *
online
* * * Longmate, Norman. ''King Cholera: The biography of a disease'' (1966), in British history. * * Pollitzer, R. "Cholera studies: History of the disease," ''Bulletin of the World Health Organization'' (1954) 10: 421- 461
online
worldwide coverage in 18th century; also India before 1800. * * * Snowden, Frank M. ''Naples in the Time of Cholera, 1884–1911'' (Cambridge UP, 1995). * Vinten-Johansen, Peter, ed. ''Investigating Cholera in Broad Street: A History in Documents'' (Broadview Press, 2020). regarding 1850s in England. * Vinten-Johansen, Peter, et al. ''Cholera, chloroform, and the science of medicine: a life of John Snow'' (2003).
Prevention and control of cholera outbreaks: WHO policy and recommendations
Cholera
orld Health Organization
Cholera – ''Vibrio cholerae'' infection
enters for Disease Control and Prevention * {{Authority control Diarrhea Foodborne illnesses Gastrointestinal tract disorders Intestinal infectious diseases Tropical diseases Epidemics Pandemics Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Sanitation Waterborne diseases Vaccine-preventable diseases
infection
An infection is the invasion of tissue (biology), tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host (biology), host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmis ...
of the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intes ...
by some strains of the bacterium
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the ...
''Vibrio cholerae
''Vibrio cholerae'' is a species of Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Facultative anaerobic organism, facultative anaerobe and Vibrio, comma-shaped bacteria. The bacteria naturally live in Brackish water, brackish or saltwater where they att ...
''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
lasting a few days. Vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
and muscle cramps
A cramp is a sudden, involuntary, painful skeletal muscle contraction or overshortening associated with electrical activity. While generally temporary and non-damaging, they can cause significant pain and a paralysis-like immobility of the affe ...
may also occur. Diarrhea can be so severe that it leads within hours to severe dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
and electrolyte imbalance
Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function ...
. This can in turn result in sunken eyes, cold or cyanotic
Cyanosis is the change of tissue color to a bluish-purple hue, as a result of decrease in the amount of oxygen bound to the hemoglobin in the red blood cells of the capillary bed. Cyanosis is apparent usually in the body tissues covered with ...
skin, decreased skin elasticity, wrinkling of the hands and feet, and, in severe cases, death. Symptoms start two hours to five days after exposure.
Cholera is caused by a number of types
Type may refer to:
Science and technology Computing
* Typing, producing text via a keyboard, typewriter, etc.
* Data type, collection of values used for computations.
* File type
* TYPE (DOS command), a command to display contents of a file.
* Ty ...
of ''Vibrio cholerae'', with some types producing more severe disease than others. It is spread mostly by unsafe water and unsafe food that has been contaminated with human feces
Human feces (American English) or faeces (British English), commonly and in medical literature more often called stool, are the solid or semisolid remains of food that could not be digested or absorbed in the small intestine of humans, but has b ...
containing the bacteria. Undercooked shellfish
Shellfish, in colloquial and fisheries usage, are exoskeleton-bearing Aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrates used as Human food, food, including various species of Mollusca, molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish ...
is a common source. Humans are the only known host for the bacteria
Bacteria (; : bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of Prokaryote, prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micr ...
. Risk factors
In epidemiology, a risk factor or determinant is a variable associated with an increased risk of disease or infection.
Due to a lack of harmonization across disciplines, determinant, in its more widely accepted scientific meaning, is often ...
for the disease include poor sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
, insufficient clean drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water that is safe for ingestion, either when drunk directly in liquid form or consumed indirectly through food preparation. It is often (but not always) supplied through taps, in which case it is also calle ...
, and poverty
Poverty is a state or condition in which an individual lacks the financial resources and essentials for a basic standard of living. Poverty can have diverse Biophysical environmen ...
. Cholera can be diagnosed by a stool test
A stool test is a medical diagnostic technique that involves the collection and analysis of fecal matter. Microbial analysis (culturing), microscopy and chemical tests are among the tests performed on stool samples.
Collection
Stool samples shou ...
, or a rapid dipstick test, although the dipstick test is less accurate.
Prevention methods against cholera include improved sanitation and access to clean water
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. ...
. Cholera vaccine
A cholera vaccine is a vaccine that is effective at reducing the risk of contracting cholera. The recommended cholera vaccines are administered orally to elicit local immune responses in the gut, where the intestinal cells produce antibodies ...
s that are given by mouth provide reasonable protection for about six months, and confer the added benefit of protecting against another type of diarrhea caused by '' E. coli''. In 2017, the US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
(FDA) approved a single-dose, live, oral cholera vaccine called Vaxchora for adults aged 18–64 who are travelling to an area of active cholera transmission. It offers limited protection to young children. People who survive an episode of cholera have long-lasting immunity for at least three years (the period tested).
The primary treatment for affected individuals is oral rehydration salts (ORS), the replacement of fluids and electrolytes by using slightly sweet and salty solutions. Rice-based solutions are preferred. In children, zinc supplementation
Zinc deficiency is defined either as insufficient body levels of zinc to meet the needs of the body, or as a zinc blood level below the normal range. However, since a decrease in blood concentration is only detectable after long-term or severe ...
has also been found to improve outcomes. In severe cases, intravenous fluid
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
s, such as Ringer's lactate
Ringer's lactate solution (RL), also known as sodium lactate solution, Lactated Ringer's (LR), and Hartmann's solution, is a mixture of sodium chloride, sodium lactate, potassium chloride, and calcium chloride in water. It is used for repla ...
, may be required, and antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
s may be beneficial. The choice of antibiotic is aided by antibiotic sensitivity testing.
Cholera continues to affect an estimated 3–5 million people worldwide and causes 28,800–130,000 deaths a year. To date, seven cholera pandemics have occurred, with the most recent beginning in 1961, and continuing today. The illness is rare in high-income countries, and affects children most severely. Cholera occurs as both outbreaks
In epidemiology, an outbreak is a sudden increase in occurrences of a disease when cases are in excess of normal expectancy for the location or season. It may affect a small and localized group or impact upon thousands of people across an entire ...
and chronically in certain areas. Areas with an ongoing risk of disease include Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent after Asia. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 20% of Earth's land area and 6% of its total surfac ...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia is the geographical United Nations geoscheme for Asia#South-eastern Asia, southeastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of China, east of the Indian subcontinent, and northwest of the Mainland Au ...
. The risk of death among those affected is usually less than 5%, given improved treatment, but may be as high as 50% without such access to treatment. Descriptions of cholera are found as early as the 5th century BCE in Sanskrit literature
Sanskrit literature is a broad term for all literature composed in Sanskrit. This includes texts composed in the earliest attested descendant of the Proto-Indo-Aryan language known as Vedic Sanskrit, texts in Classical Sanskrit as well as some ...
. In Europe, cholera was a term initially used to describe any kind of gastroenteritis, and was not used for this disease until the early 19th century. The study of cholera in England by John Snow
John Snow (15 March 1813 – 16 June 1858) was an English physician and a leader in the development of anaesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered one of the founders of modern epidemiology and early germ theory, in part because of hi ...
between 1849 and 1854 led to significant advances in the field of epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent dise ...
because of his insights about transmission via contaminated water, and a map of the same was the first recorded incidence of epidemiological tracking.
Signs and symptoms
The primary symptoms of cholera are profusediarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
and vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
of clear fluid. These symptoms usually start suddenly, half a day to five days after ingestion of the bacteria. The diarrhea is frequently described as "rice water" in nature and may have a fishy odor. An untreated person with cholera may produce of diarrhea a day. Severe cholera, without treatment, kills about half of affected individuals. If the severe diarrhea is not treated, it can result in life-threatening dehydration
In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild deh ...
and electrolyte
An electrolyte is a substance that conducts electricity through the movement of ions, but not through the movement of electrons. This includes most soluble Salt (chemistry), salts, acids, and Base (chemistry), bases, dissolved in a polar solven ...
imbalances. Estimates of the ratio of asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test).
P ...
to symptomatic infections have ranged from 3 to 100. Cholera has been nicknamed the "blue death" because a person's skin may turn bluish-gray from extreme loss of fluids.
Fever is rare and should raise suspicion for secondary infection. Patients can be lethargic and might have sunken eyes, dry mouth, cold clammy skin, or wrinkled hands and feet. Kussmaul breathing
Kussmaul breathing is a deep and labored breathing pattern often associated with severe metabolic acidosis, particularly diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) but also kidney failure. It is a form of hyperventilation, which is any breathing pattern that ...
, a deep and labored breathing pattern, can occur because of acidosis
Acidosis is a biological process producing hydrogen ions and increasing their concentration in blood or body fluids. pH is the negative log of hydrogen ion concentration and so it is decreased by a process of acidosis.
Acidemia
The term ac ...
from stool bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula .
Bicarbonate serves a crucial bioche ...
losses and lactic acidosis
Lactic acidosis refers to the process leading to the production of lactate by anaerobic metabolism. It increases hydrogen ion concentration tending to the state of acidemia or low pH. The result can be detected with high levels of lactate and lo ...
associated with poor perfusion
Perfusion is the passage of fluid through the circulatory system or lymphatic system to an organ (anatomy), organ or a tissue (biology), tissue, usually referring to the delivery of blood to a capillary bed in tissue. Perfusion may also refer t ...
. Blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term ...
drops due to dehydration, peripheral pulse is rapid and thready, and urine output decreases with time. Muscle cramping and weakness, altered consciousness, seizures
A seizure is a sudden, brief disruption of brain activity caused by abnormal, excessive, or synchronous neuronal firing. Depending on the regions of the brain involved, seizures can lead to changes in movement, sensation, behavior, awareness, o ...
, or even coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to Nociception, respond normally to Pain, painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal Circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate ...
due to electrolyte imbalance
Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function ...
s are common, especially in children.
Cause


Transmission
Cholera bacteria have been found inshellfish
Shellfish, in colloquial and fisheries usage, are exoskeleton-bearing Aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrates used as Human food, food, including various species of Mollusca, molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish ...
and plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are ca ...
.
Transmission
Transmission or transmit may refer to:
Science and technology
* Power transmission
** Electric power transmission
** Transmission (mechanical device), technology that allows controlled application of power
*** Automatic transmission
*** Manual tra ...
is usually through the fecal-oral route of contaminated food or water caused by poor sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
. Most cholera cases in developed countries
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
are a result of transmission by food, while in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed Secondary sector of the economy, industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. ...
it is more often water. Food transmission can occur when people harvest seafood such as oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but no ...
s in waters infected with sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewerage, sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged fro ...
, as ''Vibrio cholerae'' accumulates in plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms that drift in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) but are unable to actively propel themselves against ocean current, currents (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are ca ...
ic crustaceans
Crustaceans (from Latin meaning: "those with shells" or "crusted ones") are invertebrate animals that constitute one group of Arthropod, arthropods that are traditionally a part of the subphylum Crustacea (), a large, diverse group of mainly aquat ...
and the oysters eat the zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequent ...
.
People infected with cholera often have diarrhea, and disease transmission may occur if this highly liquid stool, colloquially referred to as "rice-water", contaminates water used by others. A single diarrheal event can cause a one-million fold increase in numbers of ''V. cholerae'' in the environment. The source of the contamination is typically other people with cholera when their untreated diarrheal discharge is allowed to get into waterways, groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and Pore space in soil, soil pore spaces and in the fractures of stratum, rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available fresh water in the world is groundwater. A unit ...
or drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water that is safe for ingestion, either when drunk directly in liquid form or consumed indirectly through food preparation. It is often (but not always) supplied through taps, in which case it is also calle ...
supplies. Drinking any contaminated water and eating any foods washed in the water, as well as shellfish
Shellfish, in colloquial and fisheries usage, are exoskeleton-bearing Aquatic animal, aquatic invertebrates used as Human food, food, including various species of Mollusca, molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish ...
living in the affected waterway
A waterway is any Navigability, navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other ways. A first distinction is ...
, can cause a person to contract an infection. Cholera is rarely spread directly from person to person.According to CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the national public health agency of the United States. It is a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and is headquartered in Atlanta, ...
,"The infection holerais not likely to spread directly from one person to another; therefore, casual contact with an infected person is not a risk factor for becoming ill."
''V. cholerae'' also exists outside the human body in natural water sources, either by itself or through interacting with phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater Aquatic ecosystem, ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek language, Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), mea ...
, zooplankton
Zooplankton are the heterotrophic component of the planktonic community (the " zoo-" prefix comes from ), having to consume other organisms to thrive. Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents. Consequent ...
, or biotic and abiotic
In biology and ecology, abiotic components or abiotic factors are non-living chemical and physical parts of the environment that affect living organisms and the functioning of ecosystems. Abiotic factors and the phenomena associated with them und ...
detritus. Drinking such water can also result in the disease, even without prior contamination through fecal matter. Selective pressures exist however in the aquatic environment that may reduce the virulence of ''V. cholerae''. Specifically, animal models indicate that the transcriptional profile of the pathogen changes as it prepares to enter an aquatic environment. This transcriptional change results in a loss of ability of ''V. cholerae'' to be cultured on standard media, a phenotype referred to as 'viable but non-culturable
Viable but nonculturable (VBNC) bacteria refers as to bacteria that are in a state of very low metabolic activity and do not divide, but are alive and have the ability to become culturable once resuscitated.
Bacteria in a VBNC state cannot grow on ...
' (VBNC) or more conservatively 'active but non-culturable
Active may refer to:
Music
* ''Active'' (album), a 1992 album by Casiopea
* "Active" (song), a 2024 song by Asake and Travis Scott from Asake's album ''Lungu Boy''
* Active Records, a record label
Ships
* ''Active'' (ship), several com ...
' (ABNC). One study indicates that the culturability of ''V. cholerae'' drops 90% within 24 hours of entering the water, and furthermore that this loss in culturability is associated with a loss in virulence.
Both toxic and non-toxic strains exist. Non-toxic strains can acquire toxicity
Toxicity is the degree to which a chemical substance or a particular mixture of substances can damage an organism. Toxicity can refer to the effect on a whole organism, such as an animal, bacteria, bacterium, or plant, as well as the effect o ...
through a temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ran ...
bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a phage (), is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria. The term is derived . Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that Capsid, encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structu ...
.
Susceptibility
About 100million bacteria must typically be ingested to cause cholera in a normal healthy adult. This dose, however, is less in those with loweredgastric acid
Gastric acid or stomach acid is the acidic component – hydrochloric acid – of gastric juice, produced by parietal cells in the gastric glands of the stomach lining. In humans, the pH is between one and three, much lower than most other a ...
ity (for instance those using proton pump inhibitors
Proton-pump inhibitors (PPIs) are a class of medications that cause a profound and prolonged reduction of gastric acid, stomach acid production. They do so by irreversibly inhibiting the stomach's H+/K+ ATPase, H+/K+ ATPase proton pump. The body ...
). Children are also more susceptible, with two- to four-year-olds having the highest rates of infection. Individuals' susceptibility to cholera is also affected by their blood type
A blood type (also known as a blood group) is based on the presence and absence of antibody, antibodies and Heredity, inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells (RBCs). These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycop ...
, with those with type O blood being the most susceptible. Persons with lowered immunity, such as persons with AIDS
The HIV, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is a retrovirus that attacks the immune system. Without treatment, it can lead to a spectrum of conditions including acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). It is a Preventive healthcare, pr ...
or malnourished
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
children, are more likely to develop a severe case if they become infected.Prevention and control of cholera outbreaks: WHO policy and recommendations, World Health Organization, Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean, undated but citing sources from '07, '04, '03, '04, and '05. Any individual, even a healthy adult in middle age, can undergo a severe case, and each person's case should be measured by the loss of fluids, preferably in consultation with a professional
health care provider
A health care provider is an individual health professional or a health facility organization licensed to provide health care diagnosis and treatment services including medication, surgery and medical devices. Health care providers often rece ...
.
The cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is a genetic disorder inherited in an autosomal recessive manner that impairs the normal clearance of Sputum, mucus from the lungs, which facilitates the colonization and infection of the lungs by bacteria, notably ''Staphy ...
genetic mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, ...
known as delta-F508 in humans has been said to maintain a selective heterozygous advantage: heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mos ...
carriers of the mutation (who are not affected by cystic fibrosis) are more resistant to ''V. cholerae'' infections. In this model, the genetic deficiency in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) is a membrane protein and anion channel in vertebrates that is encoded by the ''CFTR'' gene.
Geneticist Lap-Chee Tsui and his team identified the ''CFTR'' gene in 1989 as the gene lin ...
channel proteins interferes with bacteria binding to the intestinal epithelium
The intestinal epithelium is the single cell layer that forms the luminal surface (lining) of both the small and large intestine (colon) of the gastrointestinal tract. Composed of simple columnar epithelium its main functions are absorptio ...
, thus reducing the effects of an infection.
Mechanism
 When consumed, most bacteria do not survive the
When consumed, most bacteria do not survive the acidic
An acid is a molecule or ion capable of either donating a proton (i.e. hydrogen cation, H+), known as a Brønsted–Lowry acid, or forming a covalent bond with an electron pair, known as a Lewis acid.
The first category of acids are the ...
conditions of the human stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical terms re ...
. The few surviving bacteria conserve their energy and stored nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s during the passage through the stomach by shutting down protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metab ...
production. When the surviving bacteria exit the stomach and reach the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ (anatomy), organ in the human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract where most of the #Absorption, absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intes ...
, they must propel themselves through the thick mucus
Mucus (, ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both Serous fluid, serous and muc ...
that lines the small intestine to reach the intestinal walls where they can attach and thrive.
Once the cholera bacteria reach the intestinal wall, they no longer need the flagella
A flagellum (; : flagella) (Latin for 'whip' or 'scourge') is a hair-like appendage that protrudes from certain plant and animal sperm cells, from fungal spores ( zoospores), and from a wide range of microorganisms to provide motility. Many pr ...
to move. The bacteria stop producing the protein flagellin
Flagellins are a family of proteins present in flagellated bacteria which arrange themselves in a hollow cylinder to form the filament in a bacterial flagellum. Flagellin has a mass on average of about 40,000 daltons. Flagellins are the princi ...
to conserve energy and nutrients by changing the mix of proteins that they express in response to the changed chemical surroundings. On reaching the intestinal wall, ''V. cholerae'' start producing the toxic proteins that give the infected person a watery diarrhea. This carries the multiplying new generations of ''V. cholerae'' bacteria out into the drinking water of the next host if proper sanitation measures are not in place.
The cholera toxin
Cholera toxin (also known as choleragen, CTX, CTx and CT) is a potent enterotoxin produced by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae which causes severe watery diarrhea and dehydration that define cholera infections. The toxin is a member of the heat-l ...
(CTX or CT) is an oligomer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relativ ...
ic complex made up of six protein subunit
In structural biology, a protein subunit is a polypeptide chain or single protein molecule that assembles (or "''coassembles''") with others to form a protein complex.
Large assemblies of proteins such as viruses often use a small number of t ...
s: a single copy of the A subunit (part A), and five copies of the B subunit (part B), connected by a disulfide bond
In chemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) is a compound containing a functional group or the anion. The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and usually derived from two thiol groups.
In inor ...
. The five B subunits form a five-membered ring that binds to GM1 ganglioside
A ganglioside is a molecule composed of a glycosphingolipid (ceramide and oligosaccharide) with one or more sialic acids (e.g. N-acetylneuraminic acid, ''N''-acetylneuraminic acid, NANA) linked on the sugar chain. NeuNAc, an acetylated derivative ...
s on the surface of the intestinal epithelium cells. The A1 portion of the A subunit is an enzyme that ADP-ribosylates G protein
G proteins, also known as guanine nucleotide-binding proteins, are a Protein family, family of proteins that act as molecular switches inside cells, and are involved in transmitting signals from a variety of stimuli outside a cell (biology), ...
s, while the A2 chain fits into the central pore of the B subunit ring. Upon binding, the complex is taken into the cell via receptor-mediated endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which Chemical substance, substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a Vesicle (biology and chem ...
. Once inside the cell, the disulfide bond is reduced, and the A1 subunit is freed to bind with a human partner protein called ADP-ribosylation factor 6 (Arf6). Binding exposes its active site, allowing it to permanently ribosylate the Gs alpha subunit
The Gs alpha subunit (Gαs, Gsα) is a subunit of the heterotrimeric G protein Gs that stimulates the cAMP-dependent pathway by activating adenylyl cyclase. Gsα is a GTPase that functions as a cellular signaling protein.
Gsα is the founding m ...
of the heterotrimeric G protein
Heterotrimeric G protein, also sometimes referred to as the ''"large" G proteins'' (as opposed to the subclass of smaller, monomeric small GTPases) are membrane-associated G proteins that form a Heteromer, heterotrimeric complex. The biggest no ...
. This results in constitutive cAMP
Camp may refer to:
Areas of confinement, imprisonment, or for execution
* Concentration camp, an internment camp for political prisoners or politically targeted demographics, such as members of national or minority ethnic groups
* Extermination ...
production, which in turn leads to the secretion of water, sodium, potassium, and bicarbonate into the lumen of the small intestine and rapid dehydration. The gene encoding the cholera toxin was introduced into ''V. cholerae'' by horizontal gene transfer
Horizontal gene transfer (HGT) or lateral gene transfer (LGT) is the movement of genetic material between organisms other than by the ("vertical") transmission of DNA from parent to offspring (reproduction). HGT is an important factor in the e ...
. Virulent strains of ''V. cholerae'' carry a variant of a temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (approximately 23.5° to 66.5° N/S of the Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ran ...
bacteriophage
A bacteriophage (), also known informally as a phage (), is a virus that infects and replicates within bacteria. The term is derived . Bacteriophages are composed of proteins that Capsid, encapsulate a DNA or RNA genome, and may have structu ...
called CTXφ.
Microbiologists have studied the genetic mechanisms by which the ''V. cholerae'' bacteria turn off the production of some proteins and turn on the production of other proteins as they respond to the series of chemical environments they encounter, passing through the stomach, through the mucous layer of the small intestine, and on to the intestinal wall. Of particular interest have been the genetic mechanisms by which cholera bacteria turn on the protein production of the toxins that interact with host cell mechanisms to pump chloride
The term chloride refers to a compound or molecule that contains either a chlorine anion (), which is a negatively charged chlorine atom, or a non-charged chlorine atom covalently bonded to the rest of the molecule by a single bond (). The pr ...
ions into the small intestine, creating an ionic pressure which prevents sodium ions from entering the cell. The chloride and sodium ions create a salt-water environment in the small intestines, which through osmosis can pull up to six liters of water per day through the intestinal cells, creating the massive amounts of diarrhea. The host can become rapidly dehydrated unless treated properly."Cholera Fact Sheet", World Health Organizationwho.int
. Retrieved November 5, 2013. By inserting separate, successive sections of ''V. cholerae'' DNA into the DNA of other bacteria, such as ''
E. coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly foun ...
'' that would not naturally produce the protein toxins, researchers have investigated the mechanisms by which ''V. cholerae'' responds to the changing chemical environments of the stomach, mucous layers, and intestinal wall. Researchers have discovered a complex cascade of regulatory proteins controls expression of ''V. cholerae'' virulence
Virulence is a pathogen's or microorganism's ability to cause damage to a host.
In most cases, especially in animal systems, virulence refers to the degree of damage caused by a microbe to its host. The pathogenicity of an organism—its abili ...
determinants. In responding to the chemical environment at the intestinal wall, the ''V. cholerae'' bacteria produce the TcpP/TcpH proteins, which, together with the ToxR/ToxS proteins, activate the expression of the ToxT regulatory protein. ToxT then directly activates expression of virulence
Virulence is a pathogen's or microorganism's ability to cause damage to a host.
In most cases, especially in animal systems, virulence refers to the degree of damage caused by a microbe to its host. The pathogenicity of an organism—its abili ...
genes that produce the toxins, causing diarrhea in the infected person and allowing the bacteria to colonize the intestine. Current research aims at discovering "the signal that makes the cholera bacteria stop swimming and start to colonize (that is, adhere to the cells of) the small intestine."
Genetic structure
Amplified fragment length polymorphism
Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP-PCR or AFLP) is a PCR-based tool used in genetics research, DNA fingerprinting, and in the practice of genetic engineering. Developed in the early 1990s by Pieter Vos, AFLP uses restriction enzymes t ...
fingerprinting
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfa ...
of the pandemic isolates of ''V. cholerae'' has revealed variation in the genetic structure. Two clusters
may refer to:
Science and technology Astronomy
* Cluster (spacecraft), constellation of four European Space Agency spacecraft
* Cluster II (spacecraft), a European Space Agency mission to study the magnetosphere
* Asteroid cluster, a small ...
have been identified: Cluster I and Cluster II. For the most part, Cluster I consists of strains from the 1960s and 1970s, while Cluster II largely contains strains from the 1980s and 1990s, based on the change in the clone structure. This grouping of strains is best seen in the strains from the African continent.
Antibiotic resistance
In many areas of the world,antibiotic resistance
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR or AR) occurs when microbes evolve mechanisms that protect them from antimicrobials, which are drugs used to treat infections. This resistance affects all classes of microbes, including bacteria (antibiotic resis ...
is increasing within cholera bacteria. In Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, for example, most cases are resistant to tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. It is available in oral an ...
, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole, sold under the trade names Bactrim, Cotrim (a short form of the British Approved Name, Co-trimoxazole) and Septra, among others, is a fixed-dose combination antibiotic medication used to treat a variety of bacte ...
, and erythromycin
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used ...
. Rapid diagnostic assay
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity ...
methods are available for the identification of multi-drug resistant cases. New generation antimicrobials have been discovered which are effective against cholera bacteria in ''in vitro'' studies.
Diagnosis
A rapiddipstick
A dipstick is one of several measurement devices.
Some dipsticks are dipped into a liquid to perform a chemical test or to provide a measure of quantity of the liquid.
Since the late 20th century, a flatness/levelness measuring device trademark ...
test is available to determine the presence of ''V. cholerae''. In those samples that test positive, further testing should be done to determine antibiotic resistance. In epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infection ...
situations, a clinical diagnosis may be made by taking a patient history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is a set of information the physicians collect over medical interviews. It involves the patient, and even ...
and doing a brief examination. Treatment via hydration and over-the-counter hydration solutions can be started without or before confirmation by laboratory analysis, especially where cholera is a common problem.
Stool and swab samples collected in the acute stage of the disease, before antibiotics have been administered, are the most useful specimens for laboratory diagnosis. If an epidemic of cholera is suspected, the most common causative agent is ''V. cholerae'' O1. If ''V. cholerae'' serogroup O1 is not isolated, the laboratory should test for ''V. cholerae'' O139. However, if neither of these organisms is isolated, it is necessary to send stool specimens to a reference laboratory.
Infection with ''V. cholerae'' O139 should be reported and handled in the same manner as that caused by ''V. cholerae'' O1. The associated diarrheal illness should be referred to as cholera and must be reported in the United States.
Prevention
TheWorld Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a list of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Gen ...
(WHO) recommends focusing on prevention, preparedness, and response to combat the spread of cholera. They also stress the importance of an effective surveillance system. Governments can play a role in all of these areas.
Water, sanitation and hygiene
Although cholera may be life-threatening, prevention of the disease is normally straightforward if propersanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
practices are followed. In developed countries
A developed country, or advanced country, is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy, and advanced technological infrastructure relative to other less industrialized nations. Most commonly, the criteria for eval ...
, due to their nearly universal advanced water treatment
Water treatment is any process that improves the quality of water to make it appropriate for a specific end-use. The end use may be drinking, industrial water supply, irrigation, river flow maintenance, water recreation or many other uses, ...
and sanitation practices, cholera is rare. For example, the last major outbreak of cholera in the United States occurred in 1910–1911. Cholera is mainly a risk in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed Secondary sector of the economy, industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. ...
in those areas where access to WASH (water, sanitation and hygiene) infrastructure is still inadequate.
Effective sanitation practices, if instituted and adhered to in time, are usually sufficient to stop an epidemic. There are several points along the cholera transmission path at which its spread may be halted:
* Sterilization: Proper disposal and treatment of all materials that may have come into contact with the feces of other people with cholera (e.g., clothing, bedding, etc.) are essential. These should be sanitized by washing in hot water, using chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between ...
bleach
Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove color from (i.e. to whiten) fabric or fiber (in a process called bleaching) or to disinfect after cleaning. It often refers specifically t ...
if possible. Hands that touch cholera patients or their clothing, bedding, etc., should be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected with chlorinated water or other effective antimicrobial agents.
* Sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewerage, sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged fro ...
and fecal sludge management
Fecal sludge management (FSM) (or faecal sludge management in British English) is the storage, collection, transport, treatment and safe end use or disposal of fecal sludge. Together, the collection, transport, treatment and end use of fecal slud ...
: In cholera-affected areas, sewage and fecal sludge need to be treated and managed carefully in order to stop the spread of this disease via human excreta
Human waste (or human excreta) refers to the waste products of the human digestive system, menses, and human metabolism including urine and feces. As part of a sanitation system that is in place, human waste is collected, transported, treated an ...
. Provision of sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems ...
and hygiene
Hygiene is a set of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
is an important preventative measure. Open defecation
Open defecation is the human practice of defecating outside ("in the open") rather than into a toilet. People may choose fields, bushes, forests, ditches, streets, canals, or other open spaces for defecation. They do so either because they do ...
, release of untreated sewage, or dumping of fecal sludge from pit latrine
A pit latrine, also known as pit toilet, is a type of toilet that collects human waste in a hole in the ground. Urine and feces enter the pit through a drop hole in the floor, which might be connected to a toilet seat or squatting pan for user ...
s or septic tank
A septic tank is an underground chamber made of concrete, fiberglass, or plastic through which domestic wastewater (sewage) flows for basic sewage treatment. Settling and anaerobic digestion processes reduce solids and organics, but the treatment ...
s into the environment need to be prevented. In many cholera affected zones, there is a low degree of sewage treatment
Sewage treatment is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable to discharge to the surrounding environment or an intended reuse application, thereby preventing water p ...
. Therefore, the implementation of dry toilet
A dry toilet (or non-flush toilet, no flush toilet or toilet without a flush) is a toilet which, unlike a flush toilet, does not use flush water. Dry toilets do not use water to move excreta along or block odors. They do not produce sewage, and a ...
s that do not contribute to water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of Body of water, water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and ...
, as they do not flush with water, may be an interesting alternative to flush toilets.
* Sources: Warnings about possible cholera contamination should be posted around contaminated water sources with directions on how to decontaminate the water (boiling, chlorination etc.) for possible use.
* Water purification
Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids, and gases from water. The goal is to produce water that is fit for specific purposes. Most water is purified and disinfected for hu ...
: All water used for drinking, washing, or cooking should be sterilized by either boiling, chlorination, ozone water treatment, ultraviolet light sterilization (e.g., by solar water disinfection
Solar water disinfection, in short SODIS, is a type of portable water purification that uses solar energy to make biologically-contaminated (e.g. bacteria, viruses, protozoa and worms) water safe to drink. Water contaminated with non-biological a ...
), or antimicrobial filtration in any area where cholera may be present. Chlorination and boiling are often the least expensive and most effective means of halting transmission. Cloth filter
A cloth filter is a simple and cost-effective appropriate technology method for reducing the contamination of drinking water, developed for use mainly in Bangladesh. Water collected in this way has a greatly reduced pathogen count. Though not a ...
s or sari filtration, though very basic, have significantly reduced the occurrence of cholera when used in poor villages in Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
that rely on untreated surface water. Better antimicrobial filters, like those present in advanced individual water treatment hiking kits, are most effective. Public health education and adherence to appropriate sanitation practices are of primary importance to help prevent and control transmission of cholera and other diseases.
Handwashing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap or handwash and water to remove viruses, bacteria, microorganisms, dirt, grease, and other harmful or unwanted substances stuck to the han ...
with soap or ash after using a toilet
A toilet is a piece of sanitary hardware that collects human waste (urine and feces) and sometimes toilet paper, usually for disposal. Flush toilets use water, while dry or non-flush toilets do not. They can be designed for a sitting p ...
and before handling food or eating is also recommended for cholera prevention by WHO Africa.
sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewerage, sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged fro ...
or fecal sludge from a UN camp into a lake in the surroundings of Port-au-Prince
Port-au-Prince ( ; ; , ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Haiti, most populous city of Haiti. The city's population was estimated at 1,200,000 in 2022 with the metropolitan area estimated at a population of 2,618,894. The me ...
is thought to have contributed to the spread of cholera after the Haiti earthquake in 2010, killing thousands.
File:A SOIL EkoLakay toilet customer. (15921409131).jpg, Example of a urine-diverting dry toilet
A urine-diverting dry toilet (UDDT) is a type of dry toilet with urine diversion that can be used to provide safe, affordable sanitation in a variety of contexts worldwide. The separate collection of feces and urine without any flush water has ...
in a cholera-affected area in Haiti
Haiti, officially the Republic of Haiti, is a country on the island of Hispaniola in the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and south of the Bahamas. It occupies the western three-eighths of the island, which it shares with the Dominican ...
. This type of toilet stops transmission of disease via the fecal-oral route due to water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of Body of water, water bodies, with a negative impact on their uses. It is usually a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and ...
.
File:Cholera hospital in Dhaka.jpg, Cholera hospital in Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; , ), List of renamed places in Bangladesh, formerly known as Dacca, is the capital city, capital and list of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city of Bangladesh. It is one of the list of largest cities, largest and list o ...
, showing typical "cholera beds"
Surveillance
Surveillance and prompt reporting allow for containing cholera epidemics rapidly. Cholera exists as a seasonal disease in many endemic countries, occurring annually mostly during rainy seasons. Surveillance systems can provide early alerts to outbreaks, therefore leading to coordinated response and assist in preparation of preparedness plans. Efficient surveillance systems can also improve the risk assessment for potential cholera outbreaks. Understanding the seasonality and location of outbreaks provides guidance for improving cholera control activities for the most vulnerable. For prevention to be effective, it is important that cases be reported to national health authorities.Vaccination
 Spanish physician Jaume Ferran i Clua developed the first successful cholera inoculation in 1885, the first to immunize humans against a bacterial disease. His vaccine and inoculation was rather controversial and was rejected by his peers and several investigation commissions but it ended up demonstrating its effectiveness and being recognized for it: out of the 30 thousand people he vaccinated only 54 died. Russian-French bacteriologist Waldemar Haffkine also developed a human cholera vaccine in July 1892. He conducted a massive inoculation program in
Spanish physician Jaume Ferran i Clua developed the first successful cholera inoculation in 1885, the first to immunize humans against a bacterial disease. His vaccine and inoculation was rather controversial and was rejected by his peers and several investigation commissions but it ended up demonstrating its effectiveness and being recognized for it: out of the 30 thousand people he vaccinated only 54 died. Russian-French bacteriologist Waldemar Haffkine also developed a human cholera vaccine in July 1892. He conducted a massive inoculation program in British India
The provinces of India, earlier presidencies of British India and still earlier, presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in South Asia. Collectively, they have been called British India. In one form or another ...
.
Persons who survive an episode of cholera have long-lasting immunity for at least 3 years (the period tested). A number of safe and effective oral vaccines for cholera are available. The World Health Organization (WHO) has three prequalified oral cholera vaccines (OCVs): Dukoral, Sanchol, and Euvichol. Dukoral, an orally administered, inactivated whole-cell vaccine, has an overall efficacy of about 52% during the first year after being given and 62% in the second year, with minimal side effects. It is available in over 60 countries. However, it is not currently recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) is the National public health institutes, national public health agency of the United States. It is a Federal agencies of the United States, United States federal agency under the United S ...
(CDC) for most people traveling from the United States to endemic countries. The vaccine that the US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
(FDA) recommends, Vaxchora, is an oral attenuated live vaccine, that is effective for adults aged 18–64 as a single dose.
One injectable vaccine was found to be effective for two to three years. The protective efficacy was 28% lower in children less than five years old. However, , it has limited availability. Work is under way to investigate the role of mass vaccination. The WHO recommends immunization of high-risk groups, such as children and people with HIV
The human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) are two species of '' Lentivirus'' (a subgroup of retrovirus) that infect humans. Over time, they cause acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), a condition in which progressive failure of the im ...
, in countries where this disease is endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
. If people are immunized broadly, herd immunity
Herd immunity (also called herd effect, community immunity, population immunity, or mass immunity) is a form of indirect protection that applies only to contagious diseases. It occurs when a sufficient percentage of a population has become i ...
results, with a decrease in the amount of contamination in the environment.
WHO recommends that oral cholera vaccination be considered in areas where the disease is endemic (with seasonal peaks), as part of the response to outbreaks, or in a humanitarian crisis during which the risk of cholera is high. OCV has been recognized as an adjunct tool for prevention and control of cholera. The WHO has prequalified three bivalent cholera vaccines—Dukoral (SBL Vaccines), containing a non-toxic B-subunit of cholera toxin and providing protection against ''V. cholerae'' O1; and two vaccines developed using the same transfer of technology—ShanChol (Shantha Biotec) and Euvichol (EuBiologics Co.), which have bivalent O1 and O139 oral killed cholera vaccines. Oral cholera vaccination could be deployed in a diverse range of situations from cholera-endemic areas and locations of humanitarian crises, but no clear consensus exists.
Sari filtration
Developed for use inBangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by ...
, the "sari filter" is a simple and cost-effective appropriate technology
Appropriate technology is a movement (and its manifestations) encompassing technology, technological choice and application that is small-scale, affordable by its users, labor-intensive, efficient energy use, energy-efficient, environmentally sust ...
method for reducing the contamination of drinking water. Used sari
A sari (also called sharee, saree or sadi)The name of the garment in various regional languages include:
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
* is a drape (cloth) and a women's garment in the Indian subcontinent. It consists of an un-sti ...
cloth is preferable but other types of used cloth can be used with some effect, though the effectiveness will vary significantly. Used cloth is more effective than new cloth, as the repeated washing reduces the space between the fibers. Water collected in this way has a greatly reduced pathogen
In biology, a pathogen (, "suffering", "passion" and , "producer of"), in the oldest and broadest sense, is any organism or agent that can produce disease. A pathogen may also be referred to as an infectious agent, or simply a Germ theory of d ...
count—though it will not necessarily be perfectly safe, it is an improvement for poor people with limited options. In Bangladesh this practice was found to decrease rates of cholera by nearly half. It involves folding a ''sari'' four to eight times. Between uses the cloth should be rinsed in clean water and dried in the sun to kill any bacteria on it. A nylon
Nylon is a family of synthetic polymers characterised by amide linkages, typically connecting aliphatic or Polyamide#Classification, semi-aromatic groups.
Nylons are generally brownish in color and can possess a soft texture, with some varieti ...
cloth appears to work as well but is not as affordable.
Treatment
 Continued eating speeds the recovery of normal intestinal function. The WHO recommends this generally for cases of diarrhea no matter what the underlying cause. A CDC training manual specifically for cholera states: "Continue to breastfeed your baby if the baby has watery diarrhea, even when traveling to get treatment. Adults and older children should continue to eat frequently."
Continued eating speeds the recovery of normal intestinal function. The WHO recommends this generally for cases of diarrhea no matter what the underlying cause. A CDC training manual specifically for cholera states: "Continue to breastfeed your baby if the baby has watery diarrhea, even when traveling to get treatment. Adults and older children should continue to eat frequently."
Fluids
The most common error in caring for patients with cholera is to underestimate the speed and volume of fluids required. In most cases, cholera can be successfully treated withoral rehydration therapy
Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) also officially known as Oral Rehydration Solution is a type of fluid replacement used to prevent and treat dehydration, especially due to diarrhea. It involves drinking water with modest amounts of sugar and salt ...
(ORT), which is highly effective, safe, and simple to administer. Rice-based solutions are preferred to glucose-based ones due to greater efficiency. In severe cases with significant dehydration, intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutr ...
rehydration may be necessary. Ringer's lactate
Ringer's lactate solution (RL), also known as sodium lactate solution, Lactated Ringer's (LR), and Hartmann's solution, is a mixture of sodium chloride, sodium lactate, potassium chloride, and calcium chloride in water. It is used for repla ...
is the preferred solution, often with added potassium. Large volumes and continued replacement until diarrhea has subsided may be needed. Ten percent of a person's body weight in fluid may need to be given in the first two to four hours. This method was first tried on a mass scale during the Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War (, ), also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, was an War, armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalism, Bengali nationalist and self-determination movement in East Pakistan, which res ...
, and was found to have much success. Despite widespread beliefs, fruit juices and commercial fizzy drinks like cola are not ideal for rehydration of people with serious infections of the intestines, and their excessive sugar content may even harm water uptake.
If commercially produced oral rehydration solutions are too expensive or difficult to obtain, solutions can be made. One such recipe calls for 1 liter of boiled water, 1/2 teaspoon of salt, 6 teaspoons of sugar, and added mashed banana for potassium and to improve taste.
Electrolytes
As there frequently is initiallyacidosis
Acidosis is a biological process producing hydrogen ions and increasing their concentration in blood or body fluids. pH is the negative log of hydrogen ion concentration and so it is decreased by a process of acidosis.
Acidemia
The term ac ...
, the potassium
Potassium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol K (from Neo-Latin ) and atomic number19. It is a silvery white metal that is soft enough to easily cut with a knife. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmospheric oxygen to ...
level may be normal, even though large losses have occurred. As the dehydration is corrected, potassium levels may decrease rapidly, and thus need to be replaced. This is best done by Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS).
Antibiotics
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy ...
treatments for one to three days shorten the course of the disease and reduce the severity of the symptoms. Use of antibiotics also reduces fluid requirements. People will recover without them, however, if sufficient hydration is maintained. The WHO only recommends antibiotics in those with severe dehydration.
Doxycycline
Doxycycline is a Broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum antibiotic of the Tetracycline antibiotics, tetracycline class used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat pneumonia, bacterial p ...
is typically used first line, although some strains of ''V. cholerae'' have shown resistance. Testing for resistance during an outbreak can help determine appropriate future choices. Other antibiotics proven to be effective include cotrimoxazole, erythromycin
Erythromycin is an antibiotic used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes respiratory tract infections, skin infections, chlamydia infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, and syphilis. It may also be used ...
, tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. It is available in oral an ...
, chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, pl ...
, and furazolidone. Fluoroquinolone
Quinolone antibiotics constitute a large group of broad-spectrum bacteriocidals that share a bicyclic core structure related to the substance 4-quinolone. They are used in human and veterinary medicine to treat bacterial infections, as well ...
s, such as ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin ...
, also may be used, but resistance has been reported.
Antibiotics improve outcomes in those who are both severely and not severely dehydrated. Azithromycin
Azithromycin, sold under the brand names Zithromax (in oral form) and Azasite (as an eye drop), is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of several bacterial infections. This includes otitis media, middle ear infections, strep throa ...
and tetracycline
Tetracycline, sold under various brand names, is an antibiotic in the tetracyclines family of medications, used to treat a number of infections, including acne, cholera, brucellosis, plague, malaria, and syphilis. It is available in oral an ...
may work better than doxycycline
Doxycycline is a Broad-spectrum antibiotic, broad-spectrum antibiotic of the Tetracycline antibiotics, tetracycline class used in the treatment of infections caused by bacteria and certain parasites. It is used to treat pneumonia, bacterial p ...
or ciprofloxacin
Ciprofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic used to treat a number of bacterial infections. This includes bone and joint infections, intra-abdominal infections, certain types of infectious diarrhea, respiratory tract infections, skin ...
.
Zinc supplementation
In Bangladeshzinc
Zinc is a chemical element; it has symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodic tabl ...
supplementation reduced the duration and severity of diarrhea in children with cholera when given with antibiotics and rehydration therapy as needed. It reduced the length of disease by eight hours and the amount of diarrhea stool by 10%. Supplementation appears to be also effective in both treating and preventing infectious diarrhea due to other causes among children in the developing world.
Prognosis
If people with cholera are treated quickly and properly, the mortality rate is less than 1%; however, with untreated cholera, the mortality rate rises to 50–60%. For certain genetic strains of cholera, such as the one present during the 2010 epidemic in Haiti and the 2004 outbreak in India, death can occur within two hours of becoming ill.Epidemiology
Cholera affects an estimated 2.8 million people worldwide, and causes approximately 95,000 deaths a year (uncertainty range: 21,000–143,000) . This occurs mainly in the developing world. In the early 1980s, death rates are believed to have still been higher than three million a year. It is difficult to calculate exact numbers of cases, as many go unreported due to concerns that an outbreak may have a negative impact on the tourism of a country. As of 2004, cholera remained bothepidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of hosts in a given population within a short period of time. For example, in meningococcal infection ...
and endemic in many areas of the world.
Recent major outbreaks are the 2010s Haiti cholera outbreak and the 2016–2022 Yemen cholera outbreak. In October 2016, an outbreak of cholera began in war-ravaged Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
. WHO
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations which coordinates responses to international public health issues and emergencies. It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland, and has 6 regional offices and 15 ...
called it "the worst cholera outbreak in the world". In 2019, 93% of the reported 923,037 cholera cases were from Yemen
Yemen, officially the Republic of Yemen, is a country in West Asia. Located in South Arabia, southern Arabia, it borders Saudi Arabia to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the north, Oman to Oman–Yemen border, the northeast, the south-eastern part ...
(with 1911 deaths reported). Between September 2019 and September 2020, a global total of over 450,000 cases and over 900 deaths was reported; however, the accuracy of these numbers suffer from over-reporting from countries that report suspected cases (and not laboratory confirmed cases), as well as under-reporting from countries that do not report official cases (such as Bangladesh, India and Philippines).
Although much is known about the mechanisms behind the spread of cholera, researchers still do not have a full understanding of what makes cholera outbreaks happen in some places and not others. Lack of treatment of human feces
Feces (also known as faeces American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, or fæces; : faex) are the solid or semi-solid remains of food that was not digested in the small intestine, and has been broken down by bacteria in the ...
and lack of treatment of drinking water greatly facilitate its spread. Bodies of water have been found to serve as a reservoir
A reservoir (; ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam, usually built to water storage, store fresh water, often doubling for hydroelectric power generation.
Reservoirs are created by controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of wa ...
of infection, and seafood shipped long distances can spread the disease.
Cholera had disappeared from the Americas
The Americas, sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America and South America.''Webster's New World College Dictionary'', 2010 by Wiley Publishing, Inc., Cleveland, Ohio. When viewed as a sing ...
for most of the 20th century, but it reappeared toward the end of that century, beginning with a severe outbreak in Peru. This was followed by the 2010s Haiti cholera outbreak and another outbreak of cholera in Haiti amid the 2018–2023 Haitian crisis. the disease is endemic in Africa and some areas of eastern and western Asia (Bangladesh, India and Yemen). Cholera is not endemic in Europe; all reported cases had a travel history to endemic areas.
History of outbreaks

 The word cholera is from ''kholera'' from χολή ''kholē'' "bile". Cholera likely has its origins in the
The word cholera is from ''kholera'' from χολή ''kholē'' "bile". Cholera likely has its origins in the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakista ...
as evidenced by its prevalence in the region for centuries.
References to cholera appear in the European literature as early as 1642, from the Dutch physician Jakob de Bondt's description in his De Medicina Indorum. (The "Indorum" of the title refers to the East Indies. He also gave first European descriptions of other diseases.) But at the time, the word "cholera" was historically used by European physicians to refer to any gastrointestinal upset resulting in yellow diarrhea. De Bondt thus used a common word already in regular use to describe the new disease. This was a frequent practice of the time. It was not until the 1830s that the name for severe yellow diarrhea changed in English from "cholera" to "cholera morbus" to differentiate it from what was then known as "Asiatic cholera", or that associated with origins in India and the East.
Early outbreaks in the Indian subcontinent are believed to have been the result of crowded, poor living conditions, as well as the presence of pools of still water, both of which provide ideal conditions for cholera to thrive. The disease first spread by travelers along trade route
A trade route is a logistical network identified as a series of pathways and stoppages used for the commercial transport of cargo. The term can also be used to refer to trade over land or water. Allowing goods to reach distant markets, a singl ...
s (land and sea) to Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
in 1817, later to the rest of Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east ...
, and from Europe to North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South Ameri ...
and the rest of the world, (hence the name "Asiatic cholera"). Seven cholera pandemics have occurred since the early 19th century; the first one did not reach the Americas. The seventh pandemic
A pandemic ( ) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has a sudden increase in cases and spreads across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic (epi ...
originated in Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, ...
in 1961.
The first cholera pandemic occurred in the Bengal region of India, near Calcutta starting in 1817 through 1824. The disease dispersed from India to Southeast Asia, the Middle East, Europe, and Eastern Africa. The movement of British Army and Navy ships and personnel is believed to have contributed to the range of the pandemic, since the ships carried people with the disease to the shores of the Indian Ocean, from Africa to Indonesia, and north to China and Japan.
The second pandemic lasted from 1826 to 1837 and particularly affected North America and Europe. Advancements in transport and global trade, and increased human migration, including soldiers, meant that more people were carrying the disease more widely.
The third pandemic erupted in 1846, persisted until 1860, extended to North Africa, and reached North and South America. It was introduced to North America at Quebec, Canada
Quebec is Canada's largest province by area. Located in Central Canada, the province shares borders with the provinces of Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast and a coastal border ...
, via Irish immigrants from the Great Famine. In this pandemic, Brazil was affected for the first time.
The fourth pandemic lasted from 1863 to 1875, spreading from India to Naples and Spain, and reaching the United States at New Orleans, Louisiana
New Orleans (commonly known as NOLA or The Big Easy among other nicknames) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 at the 2020 ...
in 1873. It spread throughout the Mississippi River system on the continent.
The fifth pandemic was from 1881 to 1896. It started in India and spread to Europe, Asia, and South America. The sixth pandemic ran from 1899 to 1923. These epidemics had a lower number of fatalities because physicians and researchers had a greater understanding of the cholera bacteria. Egypt, the Arabian peninsula, Persia, India, and the Philippines were hit hardest during these epidemics. Other areas, such as Germany in 1892 (primarily the city of Hamburg, where more than 8,600 people died) and Naples from 1910 to 1911, also had severe outbreaks.
The seventh pandemic originated in 1961 in Indonesia and is marked by the emergence of a new strain, nicknamed ''El Tor'', which still persists () in developing countries. This pandemic had initially subsided about 1975 and was thought to have ended, but, as noted, it has persisted. There were a rise in cases in the 1990s and since.
Cholera became widespread in the 19th century. Since then it has killed tens of millions of people. In Russia
Russia, or the Russian Federation, is a country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia. It is the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the world, and extends across Time in Russia, eleven time zones, sharing Borders ...
alone, between 1847 and 1851, more than one million people died from the disease. It killed 150,000 Americans during the second pandemic. Between 1900 and 1920, perhaps eight million people died of cholera in India. Cholera officially became the first reportable disease in the United States due to the significant effects it had on health. John Snow
John Snow (15 March 1813 – 16 June 1858) was an English physician and a leader in the development of anaesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered one of the founders of modern epidemiology and early germ theory, in part because of hi ...
, in England
England is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is located on the island of Great Britain, of which it covers about 62%, and List of islands of England, more than 100 smaller adjacent islands. It ...
, in 1854 was the first to identify the importance of contaminated water as its source of transmission. Cholera is now no longer considered a pressing health threat in Europe and North America due to filtering
Filtration is a physical process that separates solid matter and fluid from a mixture.
Filter, filtering, filters or filtration may also refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Fil ...
and chlorination of water supplies, but it still strongly affects populations in developing countries
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less-developed Secondary sector of the economy, industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to developed countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. ...
.
In the past, vessels flew a yellow quarantine
A quarantine is a restriction on the movement of people, animals, and goods which is intended to prevent the spread of disease or pests. It is often used in connection to disease and illness, preventing the movement of those who may have bee ...
flag if any crew members or passengers had cholera. No one aboard a vessel flying a yellow flag would be allowed ashore for an extended period, typically 30 to 40 days.
Historically many different claimed remedies have existed in folklore. Many of the older remedies were based on the miasma theory
The miasma theory (also called the miasmic theory) is an abandoned medical theory that held that diseases—such as cholera, chlamydia, or plague—were caused by a ''miasma'' (, Ancient Greek for 'pollution'), a noxious form of "bad air", a ...
, that the disease was transmitted by bad air. Some believed that abdominal chilling made one more susceptible, and flannel and cholera belts were included in army kits. In the 1854–1855 outbreak in Naples, homeopathic camphor
Camphor () is a waxy, colorless solid with a strong aroma. It is classified as a terpenoid and a cyclic ketone. It is found in the wood of the camphor laurel (''Cinnamomum camphora''), a large evergreen tree found in East Asia; and in the kapu ...
was used according to Hahnemann. Dr. Hahnemann laid down three main remedies that would be curative in that disease; in early and simple cases camphor; in later stages with excessive cramping, cuprum or with excessive evacuations and profuse cold sweat, veratrum album. These are the Trio Cholera remedies used by homoeopaths around the world.
T. J. Ritter's ''Mother's Remedies'' book lists tomato syrup as a home remedy from northern America. Elecampane was recommended in the United Kingdom, according to William Thomas Fernie. The first effective human vaccine was developed in 1885, and the first effective antibiotic was developed in 1948.
Cholera cases are much less frequent in developed countries where governments have helped to establish water sanitation practices and effective medical treatments. In the 19th century the United States, for example, had a severe cholera problem similar to those in some developing countries. It had three large cholera outbreaks in the 1800s, which can be attributed to ''Vibrio cholerae'' spread through interior waterways such as the Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east–west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigability, navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, ...
and the extensive Mississippi River valley system, as well as the major ports along the Eastern Seaboard and their cities upriver. The island of Manhattan in New York City touches the Atlantic Ocean, where cholera collected from river waters and ship discharges just off the coast. At this time, New York City did not have as effective a sanitation system as it developed in the later 20th century, so cholera spread through the city's water supply.
Cholera morbus is a historical term that was used to refer to gastroenteritis
Gastroenteritis, also known as infectious diarrhea, is an inflammation of the Human gastrointestinal tract, gastrointestinal tract including the stomach and intestine. Symptoms may include diarrhea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Fever, lack of ...
rather than specifically to what is now defined as the disease of cholera.
Drawing
Drawing is a Visual arts, visual art that uses an instrument to mark paper or another two-dimensional surface, or a digital representation of such. Traditionally, the instruments used to make a drawing include pencils, crayons, and ink pens, some ...
of Death
Death is the end of life; the irreversible cessation of all biological functions that sustain a living organism. Death eventually and inevitably occurs in all organisms. The remains of a former organism normally begin to decompose sh ...
bringing cholera, in '' Le Petit Journal'' (1912)
File:Pedro II of Brazil and ministers of state.JPG, Emperor Pedro II of Brazil
''Don (honorific), Dom'' PedroII (Pedro de Alcântara João Carlos Leopoldo Salvador Bibiano Francisco Xavier de Paula Leocádio Miguel Gabriel Rafael Gonzaga; 2 December 1825 – 5 December 1891), nicknamed the Magnanimous (), was the List o ...
visiting people with cholera in 1855
File:Cholera 395.1.jpg, Hand bill from the New York City Board of Health, 1832—the outdated public health advice demonstrates the lack of understanding of the disease and its causative factors.
Research
One of the major contributions to fighting cholera was made by the physician and pioneer medical scientistJohn Snow
John Snow (15 March 1813 – 16 June 1858) was an English physician and a leader in the development of anaesthesia and medical hygiene. He is considered one of the founders of modern epidemiology and early germ theory, in part because of hi ...
(1813–1858), who in 1854 found a link between cholera and contaminated drinking water. Dr. Snow proposed a microbial origin for epidemic cholera in 1849. In his major "state of the art" review of 1855, he proposed a substantially complete and correct model for the cause of the disease. In two pioneering epidemiological field studies, he was able to demonstrate human sewage
Sewage (or domestic sewage, domestic wastewater, municipal wastewater) is a type of wastewater that is produced by a community of people. It is typically transported through a sewerage, sewer system. Sewage consists of wastewater discharged fro ...
contamination was the most probable disease vector in two major epidemics in London in 1854. His model was not immediately accepted, but it was increasingly seen as plausible as medical microbiology developed over the next 30 years or so. For his work on cholera, John Snow is often regarded as the "Father of Epidemiology".
The bacterium was isolated in 1854 by Italian anatomist Filippo Pacini, but its exact nature and his results were not widely known. In the same year, the Catalan Joaquim Balcells i Pascual discovered the bacterium. In 1856 António Augusto da Costa Simões and José Ferreira de Macedo Pinto, two Portuguese researchers, are believed to have done the same.
Between the mid-1850s and the 1900s, cities in developed nations made massive investment in clean water supply and well-separated sewage treatment infrastructures. This eliminated the threat of cholera epidemics from the major developed cities in the world. In 1883, Robert Koch
Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch ( ; ; 11 December 1843 – 27 May 1910) was a German physician and microbiologist. As the discoverer of the specific causative agents of deadly infectious diseases including tuberculosis, cholera and anthrax, he i ...
identified ''V. cholerae'' with a microscope as the bacillus causing the disease.
Hemendra Nath Chatterjee, a Bengali scientist, was the first to formulate and demonstrate the effectiveness of oral rehydration salt (ORS) to treat diarrhea
Diarrhea (American English), also spelled diarrhoea or diarrhœa (British English), is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements in a day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration d ...
. In his 1953 paper, published in ''The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal, founded in England in 1823. It is one of the world's highest-impact academic journals and also one of the oldest medical journals still in publication.
The journal publishes ...
'', he states that promethazine
Promethazine, sold under the brand name Phenergan among others, is a first-generation antihistamine, sedative, and antiemetic used to treat allergies, insomnia, and nausea. It may also help with some symptoms associated with the common cold a ...
can stop vomiting
Vomiting (also known as emesis, puking and throwing up) is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenteritis, pre ...
during cholera and then oral rehydration is possible. The formulation of the fluid replacement solution was 4 g of sodium chloride
Sodium chloride , commonly known as Salt#Edible salt, edible salt, is an ionic compound with the chemical formula NaCl, representing a 1:1 ratio of sodium and chloride ions. It is transparent or translucent, brittle, hygroscopic, and occurs a ...
, 25 g of glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
and 1000 ml of water
Water is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance. It is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known liv ...
.
 Indian medical scientist Sambhu Nath De discovered the
Indian medical scientist Sambhu Nath De discovered the cholera toxin
Cholera toxin (also known as choleragen, CTX, CTx and CT) is a potent enterotoxin produced by the bacterium Vibrio cholerae which causes severe watery diarrhea and dehydration that define cholera infections. The toxin is a member of the heat-l ...
, the ''animal model
An animal model (short for animal disease model) is a living, non-human, often genetic-engineered animal used during the research and investigation of human disease, for the purpose of better understanding the disease process without the risk of ha ...
of cholera'', and successfully demonstrated the method of transmission of cholera pathogen ''Vibrio cholerae''.
Robert Allan Phillips, working at US Naval Medical Research Unit Two in Southeast Asia, evaluated the pathophysiology of the disease using modern laboratory chemistry techniques. He developed a protocol for rehydration. His research led the Lasker Foundation to award him its prize in 1967.
More recently, in 2002, Alam, ''et al.'', studied stool samples from patients at the International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease in Dhaka, Bangladesh
Dhaka ( or ; , ), List of renamed places in Bangladesh, formerly known as Dacca, is the capital city, capital and list of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city of Bangladesh. It is one of the list of largest cities, largest and list o ...
. From the various experiments they conducted, the researchers found a correlation between the passage of ''V. cholerae'' through the human digestive system and an increased infectivity state. Furthermore, the researchers found the bacterium creates a hyperinfected state where gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protei ...
s that control biosynthesis of amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although over 500 amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the 22 α-amino acids incorporated into proteins. Only these 22 a ...
s, iron
Iron is a chemical element; it has symbol Fe () and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, forming much of Earth's o ...
uptake systems, and formation of periplasmic nitrate reductase complexes were induced just before defecation. These induced characteristics allow the cholera vibrios to survive in the "rice water" stools, an environment of limited oxygen and iron, of patients with a cholera infection.
Global Strategy
In 2017, the WHO launched the "Ending Cholera: a global roadmap to 2030" strategy which aims to reduce cholera deaths by 90% by 2030. The strategy was developed by the Global Task Force on Cholera Control (GTFCC) which develops country-specific plans and monitors progress. The approach to achieve this goal combines surveillance, water sanitation, rehydration treatment and oral vaccines. Specifically, the control strategy focuses on three approaches: i) early detection and response to outbreaks to contain outbreaks, ii) stopping cholera transmission through improved sanitation and vaccines in hotspots, and iii) a global framework for cholera control through the GTFCC. The WHO and the GTFCC do not consider global cholera eradication a viable goal. Even though humans are the only host of cholera, the bacterium can persist in the environment without a human host. While global eradication is not possible, elimination of human to human transmission may be possible. Local elimination is possible, which has been underway most recently during the 2010s Haiti cholera outbreak. Haiti aims to achieve certification of elimination by 2022. The GTFCC targets 47 countries, 13 of which have established vaccination campaigns.Society and culture
Health policy
In many developing countries, cholera still reaches its victims through contaminated water sources, and countries without proper sanitation techniques have greater incidence of the disease. Governments can play a role in this. In 2008, for example, the Zimbabwean cholera outbreak was due partly to the government's role, according to a report from theJames Baker Institute
The Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy (formerly known as the James A. Baker III Institute for Public Policy) is an American think tank housed on the campus of Rice University in Houston, Texas. Founded in 1993, it functions as a ...
. The Haitian government's inability to provide safe drinking water after the 2010 earthquake led to an increase in cholera cases as well.
Similarly, South Africa's cholera outbreak was exacerbated by the government's policy of privatizing water programs. The wealthy elite of the country were able to afford safe water while others had to use water from cholera-infected rivers.
According to Rita R. Colwell
Rita Rossi Colwell (born November 23, 1934) is an American environmental microbiologist and scientific administrator. Colwell holds degrees in bacteriology, genetics, and oceanography and studies infectious diseases. Colwell is the founder and C ...
of the James Baker Institute
The Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy (formerly known as the James A. Baker III Institute for Public Policy) is an American think tank housed on the campus of Rice University in Houston, Texas. Founded in 1993, it functions as a ...
, if cholera does begin to spread, government preparedness is crucial. A government's ability to contain the disease before it extends to other areas can prevent a high death toll and the development of an epidemic or even pandemic. Effective disease surveillance can ensure that cholera outbreaks are recognized as soon as possible and dealt with appropriately. Oftentimes, this will allow public health programs to determine and control the cause of the cases, whether it is unsanitary water or seafood that have accumulated a lot of ''Vibrio cholerae'' specimens. Having an effective surveillance program contributes to a government's ability to prevent cholera from spreading. In the year 2000 in the state of Kerala in India, the Kottayam district was determined to be "Cholera-affected"; this pronouncement led to task forces that concentrated on educating citizens with 13,670 information sessions about human health. These task forces promoted the boiling of water to obtain safe water, and provided chlorine and oral rehydration salts. Ultimately, this helped to control the spread of the disease to other areas and minimize deaths. On the other hand, researchers have shown that most of the citizens infected during the 1991 cholera outbreak in Bangladesh lived in rural areas, and were not recognized by the government's surveillance program. This inhibited physicians' abilities to detect cholera cases early.
According to Colwell, the quality and inclusiveness of a country's health care system affects the control of cholera, as it did in the Zimbabwean cholera outbreak. While sanitation practices are important, when governments respond quickly and have readily available vaccines, the country will have a lower cholera death toll. Affordability of vaccines can be a problem; if the governments do not provide vaccinations, only the wealthy may be able to afford them and there will be a greater toll on the country's poor. The speed with which government leaders respond to cholera outbreaks is important.
Besides contributing to an effective or declining public health care system and water sanitation treatments, government can have indirect effects on cholera control and the effectiveness of a response to cholera. A country's government can impact its ability to prevent disease and control its spread. A speedy government response backed by a fully functioning health care system and financial resources can prevent cholera's spread. This limits cholera's ability to cause death, or at the very least a decline in education, as children are kept out of school to minimize the risk of infection. Inversely, poor government response can lead to civil unrest and cholera riots.
Notable cases
*Tchaikovsky
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky ( ; 7 May 1840 – 6 November 1893) was a Russian composer during the Romantic period. He was the first Russian composer whose music made a lasting impression internationally. Tchaikovsky wrote some of the most popular ...
's death has traditionally been attributed to cholera, most probably contracted through drinking contaminated water several days earlier. Tchaikovsky's mother died of cholera, and his father became sick with cholera at this time but made a full recovery. Some scholars, however, including English musicologist and Tchaikovsky authority David Brown and biographer Anthony Holden
Anthony Ivan Holden (22 May 1947 – 7 October 2023) was an English writer, broadcaster and literary critic, particularly known as a biographer of artists including Shakespeare, Tchaikovsky, the essayist Leigh Hunt, the opera librettist Lorenzo ...
, have theorized that his death was a suicide.
* 2010s Haiti cholera outbreak. Ten months after the 2010 earthquake, an outbreak swept over Haiti, traced to a United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is the Earth, global intergovernmental organization established by the signing of the Charter of the United Nations, UN Charter on 26 June 1945 with the stated purpose of maintaining international peace and internationa ...
base of peacekeepers from Nepal
Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also includes parts of the Indo-Gangetic Plain. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China Ch ...
. This marks the worst cholera outbreak in recent history, as well as the best documented cholera outbreak in modern public health.
* Adam Mickiewicz
Adam Bernard Mickiewicz (24 December 179826 November 1855) was a Polish poet, dramatist, essayist, publicist, translator and political activist. He is regarded as national poet in Poland, Lithuania and Belarus. He also largely influenced Ukra ...
, Polish poet and novelist, is thought to have died of cholera in Istanbul in 1855.
* Sadi Carnot, physicist, a pioneer of thermodynamics (d. 1832)
* Charles X Charles X may refer to:
* Charles X of France (1757–1836)
* Charles X Gustav (1622–1660), King of Sweden
* Charles, Cardinal de Bourbon (1523–1590), recognized as Charles X of France but renounced the royal title
See also
*
* King Charle ...
, King of France
France was ruled by monarchs from the establishment of the kingdom of West Francia in 843 until the end of the Second French Empire in 1870, with several interruptions.
Classical French historiography usually regards Clovis I, king of the Fra ...
(d. 1836)
* James K. Polk
James Knox Polk (; November 2, 1795 – June 15, 1849) was the 11th president of the United States, serving from 1845 to 1849. A protégé of Andrew Jackson and a member of the Democratic Party, he was an advocate of Jacksonian democracy and ...
, eleventh president of the United States
The president of the United States (POTUS) is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president directs the Federal government of the United States#Executive branch, executive branch of the Federal government of t ...
(d. 1849)
* Carl von Clausewitz
Carl Philipp Gottlieb von Clausewitz ( , ; born Carl Philipp Gottlieb Clauswitz; 1 July 1780 – 16 November 1831) was a Kingdom of Prussia, Prussian general and Military theory, military theorist who stressed the "moral" (in modern terms meani ...
, Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
n soldier and German military theorist (d. 1831)
* Elliot Bovill
Sir Elliot Charles Bovill (23 April 1848 – 24 March 1893) was a British lawyer and judge. He served as Chief Justice of Cyprus and the Straits Settlements in the late 19th century.
Early life
Bovill was born in Clapham, at that time in Surre ...
, Chief Justice of the Straits Settlements (1893)
*Nikola Tesla
Nikola Tesla (;"Tesla"
. ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; 10 July 1856 – 7 ...
, Serbian-American . ''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. ; 10 July 1856 – 7 ...
inventor
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea, or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an ...
, engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who Invention, invent, design, build, maintain and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials. They aim to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while ...
and futurist
Futurists (also known as futurologists, prospectivists, foresight practitioners and horizon scanners) are people whose specialty or interest is futures studies or futurology or the attempt to systematically explore predictions and possibilities ...
known for his contributions to the design of the modern alternating current
Alternating current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction and changes its magnitude continuously with time, in contrast to direct current (DC), which flows only in one direction. Alternating current is the form in w ...
(AC) electricity supply
Mains electricity, utility power, grid power, domestic power, wall power, household current, or, in some parts of Canada, hydro, is a general-purpose alternating-current (AC) electric power supply. It is the form of electrical power that is de ...
system, contracted cholera in 1873 at the age of 17. He was bedridden for nine months, and near death multiple times, but survived and fully recovered.
In popular culture
Unliketuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can al ...
("consumption") which in literature and the arts was often romanticized as a disease of denizens of the demimonde
is a French 19th-century term referring to women on the fringes of respectable society, and specifically to courtesans supported by wealthy lovers. The term is French for "half-world", and derives from an 1855 play called , by Alexandre Dumas ...
or those with an artistic temperament, cholera is a disease which almost entirely affects the poor living in unsanitary conditions. This, and the unpleasant course of the disease – which includes voluminous "rice-water" diarrhea, the hemorrhaging of liquids from the mouth, and violent muscle contractions which continue even after death – has discouraged the disease from being romanticized, or even being factually presented in popular culture.
* The 1889 novel '' Mastro-don Gesualdo'' by Giovanni Verga
Giovanni Carmelo Verga di Fontanabianca (; 2 September 1840 – 27 January 1922) was an Italian Literary realism, realist (''Verismo (literature), verista'') writer. His novels ''I Malavoglia'' (1881) and ''Mastro-don Gesualdo'' (1889) are widel ...
presents the course of a cholera epidemic across the island of Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
, but does not show the suffering of those affected.
* Cholera is a major plot device in The Painted Veil, a 1925 novel by W. Somerset Maugham
William Somerset Maugham ( ; 25 January 1874 – 16 December 1965) was an English writer, known for his plays, novels and short stories. Born in Paris, where he spent his first ten years, Maugham was schooled in England and went to a German un ...
. The story concerns a shy bacteriologist who discovers his young, pretty wife is having an adulterous affair. The doctor exacts revenge on his wife by inducing her to travel with him to mainland China which is in the grips of an horrific cholera outbreak. The ravages of the disease are frankly described in the novel.
* In Thomas Mann
Paul Thomas Mann ( , ; ; 6 June 1875 – 12 August 1955) was a German novelist, short story writer, social critic, philanthropist, essayist, and the 1929 Nobel Prize in Literature laureate. His highly symbolic and ironic epic novels and novell ...
's novella
A novella is a narrative prose fiction whose length is shorter than most novels, but longer than most novelettes and short stories. The English word ''novella'' derives from the Italian meaning a short story related to true (or apparently so) ...
''Death in Venice
''Death in Venice ''() is a novella by German author Thomas Mann, published in 1912. It presents an ennobled writer who visits Venice and is liberated, uplifted, and then increasingly obsessed by the sight of a boy in a family of Polish tourist ...
'', first published in 1912 as ''Der Tod in Venedig'', Mann "presented the disease as emblematic of the final 'bestial degradation' of the sexually transgressive author Gustav von Aschenbach." Contrary to the actual facts of how violently cholera kills, Mann has his protagonist die peacefully on a beach in a deck chair. Luchino Visconti
Luchino Visconti di Modrone, Count of Lonate Pozzolo (; 2 November 1906 – 17 March 1976) was an Italian filmmaker, theatre and opera director, and screenwriter. He was one of the fathers of Italian neorealism, cinematic neorealism, but later ...
's 1971 film version also hid from the audience the actual course of the disease. Mann's novella was also made into an opera by Benjamin Britten
Edward Benjamin Britten, Baron Britten of Aldeburgh (22 November 1913 – 4 December 1976) was an English composer, conductor, and pianist. He was a central figure of 20th-century British music, with a range of works including opera, o ...
in 1973, his last one, and into a ballet by John Neumeier for his Hamburg Ballet company, in December 2003.*
* '' The Horseman on the Roof'' (orig. French ''Le Hussard sur le toit'') is a 1951 adventure novel written by Jean Giono
Jean Giono (30 March 1895 – 8 October 1970) was a French writer who wrote works of fiction mostly set in the Provence region of France.
First period
Jean Giono was born to a family of modest means, his father a cobbler of Piedmontese descent a ...
. It tells the story of Angelo Pardi, a young Italian carbonaro colonel of hussars
A hussar, ; ; ; ; . was a member of a class of light cavalry, originally from the Kingdom of Hungary during the 15th and 16th centuries. The title and distinctive dress of these horsemen were subsequently widely adopted by light cavalry ...
, caught up in the 1832 cholera epidemic in Provence
Provence is a geographical region and historical province of southeastern France, which stretches from the left bank of the lower Rhône to the west to the France–Italy border, Italian border to the east; it is bordered by the Mediterrane ...
. In 1995, it was made into a film of the same name directed by Jean-Paul Rappeneau
Jean-Paul Rappeneau (; born 8 April 1932) is a French film director and screenwriter.
Career
He started out in film as an assistant and screenwriter collaborating with Louis Malle on ''Zazie dans le métro'' in 1960 and ''Vie privée'' in 1961. ...
.
* In Gabriel Garcia Márquez's 1985 novel '' Love in the Time of Cholera'', cholera is "a looming background presence rather than a central figure requiring vile description." The novel was adapted in 2007 for the film of the same name directed by Mike Newell.
* In ''The Secret Garden
''The Secret Garden'' is a children's novel by Frances Hodgson Burnett first published in book form in 1911, after serialisation in ''The American Magazine'' (November 1910 – August 1911). Set in England, it is seen as a classic of English c ...
'', Mary Lennox's parents die from cholera.
Country examples
Zambia
InZambia
Zambia, officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central Africa, Central, Southern Africa, Southern and East Africa. It is typically referred to being in South-Central Africa or Southern Africa. It is bor ...
, widespread cholera outbreaks have occurred since 1977, most commonly in the capital city of Lusaka
Lusaka ( ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Zambia. It is one of the fastest-developing cities in southern Africa. Lusaka is in the southern part of the central plateau at an elevation of about . , the city's population was abo ...
. In 2017, an outbreak of cholera was declared in Zambia after laboratory confirmation of ''Vibrio cholerae
''Vibrio cholerae'' is a species of Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Facultative anaerobic organism, facultative anaerobe and Vibrio, comma-shaped bacteria. The bacteria naturally live in Brackish water, brackish or saltwater where they att ...
'' O1, biotype El Tor, serotype Ogawa, from stool samples from two patients with acute watery diarrhea. There was a rapid increase in the number of cases from several hundred cases in early December 2017 to approximately 2,000 by early January 2018. With intensification of the rains, new cases increased on a daily basis reaching a peak on the first week of January 2018 with over 700 cases reported.
In collaboration with partners, the Zambia Ministry of Health (MoH) launched a multifaceted public health response that included increased chlorination of the Lusaka municipal water supply, provision of emergency water supplies, water quality monitoring and testing, enhanced surveillance, epidemiologic investigations, a cholera vaccination campaign, aggressive case management and health care worker training, and laboratory testing of clinical samples.
The Zambian Ministry of Health implemented a reactive one-dose Oral Cholera Vaccine (OCV) campaign in April 2016 in three Lusaka compounds, followed by a pre-emptive second-round in December.
Nigeria
In June 2024, the Nigeria Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (NCDC) announced a total of 1,141 suspected and 65 confirmed cases of cholera with 30 deaths from 96 Local Government Areas (LGAs) in 30 states of the country. NCDC, in its public health advisory, said Abia, Bayelsa, Bauchi, Cross River, Delta, Imo, Katsina, Lagos, Nasarawa and Zamfara states were the 10 states that contributed 90 percent of the burden of cholera in the country at the time.
India
 The city of
The city of Kolkata
Kolkata, also known as Calcutta ( its official name until 2001), is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of West Bengal. It lies on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River, west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, seventh-largest country by area; the List of countries by population (United Nations), most populous country since ...
, in the state of West Bengal
West Bengal (; Bengali language, Bengali: , , abbr. WB) is a States and union territories of India, state in the East India, eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabi ...
in the Ganges delta
The Ganges Delta (also known the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, the Sundarbans Delta or the Bengal Delta) is a river delta predominantly covering the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent, consisting of Bangladesh and the Indian state of West Be ...
, has been described as the "homeland of cholera", with regular outbreaks and pronounced seasonality. In India, where the disease is endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found only in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also foun ...
, cholera outbreaks occur every year between dry season
The dry season is a yearly period of low rainfall, especially in the tropics. The weather in the tropics is dominated by the tropical rain belt, which moves from the northern to the southern tropics and back over the course of the year. The t ...
s and rainy seasons. India is also characterized by high population density, unsafe drinking water, open drains, and poor sanitation, which provide an optimal niche for survival, sustenance, and transmission of ''Vibrio cholerae''.
Democratic Republic of Congo
InGoma
Goma is a city in the eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo. It is the Capital city, capital and largest city of the North Kivu, North Kivu Province; it is located on the northern shore of Lake Kivu and shares borders with the Bukumu Chiefdo ...
in the Democratic Republic of Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), also known as the DR Congo, Congo-Kinshasa, or simply the Congo (the last ambiguously also referring to the neighbouring Republic of the Congo), is a country in Central Africa. By land area, it is t ...
, cholera has left an enduring mark on human and medical history. Cholera pandemics in the 19th and 20th centuries led to the growth of epidemiology as a science and in recent years it has continued to press advances in the concepts of disease ecology
Disease ecology is a sub-discipline of ecology concerned with the mechanisms, patterns, and effects of host-pathogen interactions, particularly those of infectious diseases. For example, it examines how parasites spread through and influence wildl ...
, basic membrane biology, and transmembrane signaling and in the use of scientific information and treatment design.
Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
* * * Bilson, Geoffrey. ''A Darkened House: Cholera in Nineteenth-Century Canada'' (U of Toronto Press, 1980). * * Delaporte, François. ''Disease and Civilization: The Cholera in Paris, 1832'' (MIT Press, 1986) * Duffy, John. "The history of Asiatic cholera in the United States," ''Bulletin of the New York Academy of Medicine'' (1971) 47#10: pp. 1152-68; PMID: 4939340, ISSN: 0028-709online
* * * * Gilbert, Pamela K. "Cholera and Nation: Doctoring the Social Body in Victorian England" (SUNY Press, 2008). *
online
* * * *
online
* * * Longmate, Norman. ''King Cholera: The biography of a disease'' (1966), in British history. * * Pollitzer, R. "Cholera studies: History of the disease," ''Bulletin of the World Health Organization'' (1954) 10: 421- 461
online
worldwide coverage in 18th century; also India before 1800. * * * Snowden, Frank M. ''Naples in the Time of Cholera, 1884–1911'' (Cambridge UP, 1995). * Vinten-Johansen, Peter, ed. ''Investigating Cholera in Broad Street: A History in Documents'' (Broadview Press, 2020). regarding 1850s in England. * Vinten-Johansen, Peter, et al. ''Cholera, chloroform, and the science of medicine: a life of John Snow'' (2003).
External links
Prevention and control of cholera outbreaks: WHO policy and recommendations
Cholera
orld Health Organization
Cholera – ''Vibrio cholerae'' infection
enters for Disease Control and Prevention * {{Authority control Diarrhea Foodborne illnesses Gastrointestinal tract disorders Intestinal infectious diseases Tropical diseases Epidemics Pandemics Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia emergency medicine articles ready to translate Sanitation Waterborne diseases Vaccine-preventable diseases