|
WASH
WASH (or Watsan, WaSH) is an acronym that stands for "water, sanitation and hygiene". It is used widely by non-governmental organizations and aid agencies in developing countries. The purposes of providing access to WASH services include achieving public health gains, improving human dignity in the case of sanitation, implementing the human right to water and sanitation, reducing the burden of collecting drinking water for women, reducing risks of violence against women, improving education and health outcomes at schools and health facilities, and reducing water pollution. Access to WASH services is also an important component of water security. Universal, affordable and sustainable access to WASH is a key issue within international development and is the focus of the first two targets of Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6). Targets 6.1 and 6.2 aim at equitable and accessible water and sanitation for all. In 2017, it was estimated that 2.3 billion people live without basic san ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neglected Tropical Diseases
Neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) are a diverse group of tropical disease, tropical infections that are common in low-income populations in Developing country, developing regions of Africa, Asia, and the Americas. They are caused by a variety of Pathogen, pathogens, such as viruses, bacteria, protozoa, and parasitic worms (helminths). These diseases are contrasted with the "big three" infectious diseases (HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria), which generally receive greater treatment and research funding. In sub-Saharan Africa, disease burden, the effect of neglected tropical diseases as a group is comparable to that of malaria and tuberculosis. NTD co-infection can also make HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis more deadly. Some treatments for NTDs are relatively inexpensive. For example, the treatment for schistosomiasis is US$0.20 per child per year. Nevertheless, in 2010 it was estimated that control of neglected diseases would require funding of between US$2 billion and $3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
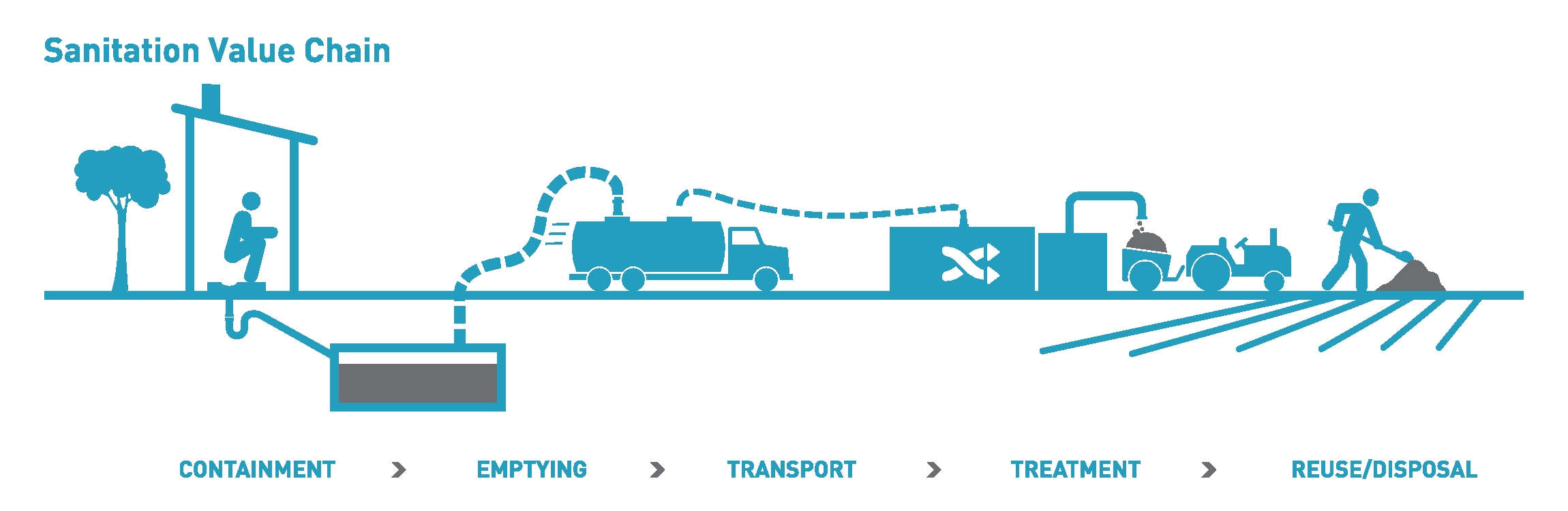
Sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems aim to protect human health by providing a clean environment that will stop the transmission of disease, especially through the fecal–oral route.SuSanA (2008)Towards more sustainable sanitation solutions Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) For example, diarrhea, a main cause of malnutrition and stunted growth in children, can be reduced through adequate sanitation. There are many other diseases which are easily transmitted in communities that have low levels of sanitation, such as ascariasis (a type of intestinal worm infection or helminthiasis), cholera, hepatitis, polio, schistosomiasis, and trachoma, to name just a few. A range of sanitation technologies and approaches exists. Some examples are community-led total sanitation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menstrual Hygiene Management
Menstrual hygiene management (MHM) or menstrual health and hygiene (MHH) refers to access to menstrual hygiene products to absorb or collect the flow of blood during menstruation, privacy to change the materials, and access to facilities to dispose of used menstrual management materials. It can also include the "broader systemic factors that link menstruation with health, well-being, gender equality, education, equity, empowerment, and rights".UNICEF (2019)Guidance on Menstrual Health and Hygiene UNICEF, New York, USA Menstrual hygiene management can be particularly challenging for girls and women in developing countries, where clean water and toilet facilities are often inadequate. Menstrual waste is largely ignored in schools in developing countries, despite it being a significant problem. Menstruation can be a barrier to education for many girls, as a lack of effective sanitary products restricts girls' involvement in educational and social activities. Terminology An accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stunted Growth
Stunted growth is a reduced growth rate in human development. It is a primary manifestation of malnutrition (or more precisely undernutrition) and recurrent infections, such as diarrhea and helminthiasis, in early childhood and even before birth, due to malnutrition during fetal development brought on by a malnourished mother. The definition of stunting according to the World Health Organization (WHO) is for the "height for age" value to be less than two standard deviations of the WHO Child Growth Standards median. As of 2012 an estimated 162 million children under 5 years of age, or 25%, were stunted. More than 90% of the world's stunted children live in Africa and Asia, where respectively 36% and 56% of children are affected. Once established, stunting and its effects typically become permanent. Stunted children may never regain the height lost as a result of stunting, and most children will never gain the corresponding body weight. Living in an environment where many people de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Security
Water security is the focused goal of water policy and water management. A society with a high level of water security makes the most of water's benefits for humans and ecosystems and limits the risk of destructive impacts associated with water. These include too much water (flood), too little water (drought and water scarcity) or poor quality (polluted) water. A widely accepted definition of water security is: "Water security is the reliable availability of an acceptable quantity and quality of water for health, livelihoods and production, coupled with an acceptable level of water-related risks". Water security is framed as a situation where water-related risks are managed and water-related opportunities are captured but it is difficult to provide a set of indicators to quantify this. Policy-makers and water managers seek to achieve a variety of water security outcomes related to economic, environmental and social equity concerns. These outcomes can include increasing economic we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustainable Development Goal 6
Sustainable Development Goal 6 (SDG 6 or Global Goal 6) is about "clean water and sanitation for all". It is one of 17 Sustainable Development Goals established by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015, the official wording is: "Ensure availability and sustainable management of water and sanitation for all." The goal has eight targets to be achieved by 2030. Progress toward the targets will be measured by using eleven indicators. The six "outcome-oriented targets" include: Safe and affordable drinking water; end open defecation and provide access to sanitation, and hygiene, improve water quality, wastewater treatment and safe reuse, increase water-use efficiency and ensure freshwater supplies, implement IWRM, protect and restore water-related ecosystems. The two "means of achieving" targets are to expand water and sanitation support to developing countries, and to support local engagement in water and sanitation management. In 2017, 2.2 billion people lacked safely mana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
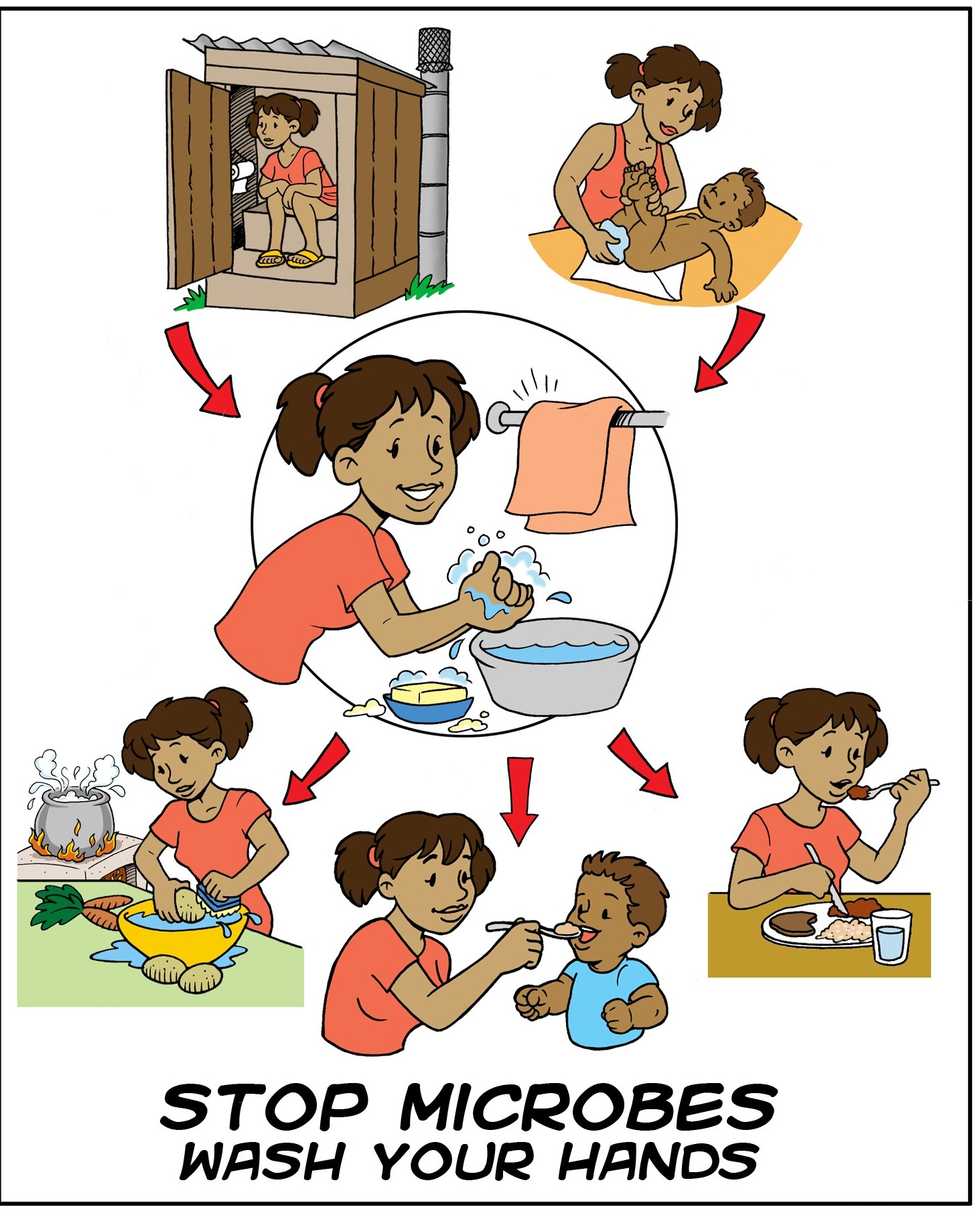
Hand Washing
Hand washing (or handwashing), also known as hand hygiene, is the act of cleaning one's hands with soap, soap or handwash and water to remove viruses/bacteria/microorganisms, dirt, grease, or other harmful and unwanted substances stuck to the hands. Drying of the washed hands is part of the process as wet and moist hands are more easily recontaminated. If soap and water are unavailable, hand sanitizer that is at least 60% (v/v) Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol in water can be used as long as hands are not visibly excessively dirty or greasy. Hand hygiene is central to preventing the spread of Infection, infectious diseases in home and everyday life settings. The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends washing hands for at least 20 seconds before and after certain activities. These include the five critical times during the day where washing hands with soap is important to reduce Fecal–oral route, fecal-oral transmission of disease: after using the Toilet (room), toilet (for ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diarrhea
Diarrhea, also spelled diarrhoea, is the condition of having at least three loose, liquid, or watery bowel movements each day. It often lasts for a few days and can result in dehydration due to fluid loss. Signs of dehydration often begin with loss of the normal stretchiness of the skin and irritable behaviour. This can progress to decreased urination, loss of skin color, a fast heart rate, and a decrease in responsiveness as it becomes more severe. Loose but non-watery stools in babies who are exclusively breastfed, however, are normal. The most common cause is an infection of the intestines due to either a virus, bacterium, or parasite—a condition also known as gastroenteritis. These infections are often acquired from food or water that has been contaminated by feces, or directly from another person who is infected. The three types of diarrhea are: short duration watery diarrhea, short duration bloody diarrhea, and persistent diarrhea (lasting more than two weeks, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Developing Country
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. The term low and middle-income country (LMIC) is often used interchangeably but refers only to the economy of the countries. The World Bank classifies the world's economies into four groups, based on gross national income per capita: high, upper-middle, lower-middle, and low income countries. Least developed countries, landlocked developing countries and small island developing states are all sub-groupings of developing countries. Countries on the other end of the spectrum are usually referred to as high-income countries or developed countries. There are controversies over this term's use, which some feel it perpetuates an outdated concept of "us" and "them". In 2015, the World Bank declared that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Right To Water And Sanitation
The human right to water and sanitation (HRWS) is a principle stating that clean drinking water and sanitation are a universal human right because of their high importance in sustaining every person's life. It was recognized as a human right by the United Nations General Assembly on 28 July 2010. The HRWS has been recognized in international law through human rights treaties, declarations and other standards. Some commentators have based an argument for the existence of a universal human right to water on grounds independent of the 2010 General Assembly resolution, such as Article 11.1 of the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights (ICESCR); among those commentators, those who accept the existence of international ''ius cogens'' and consider it to include the Covenant's provisions hold that such a right is a universally binding principle of international law. Other treaties that explicitly recognize the HRWS include the 1979 Convention on the Elimination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, so that it negatively affects its uses. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. Water pollution results when contaminants are introduced into these water bodies. Water pollution can be attributed to one of four sources: sewage discharges, industrial activities, agricultural activities, and urban runoff including stormwater. It can be grouped into surface water pollution (either fresh water pollution or marine pollution) or groundwater pollution. For example, releasing inadequately treated wastewater into natural waters can lead to degradation of these aquatic ecosystems. Water pollution can also lead to water-borne diseases for people using polluted water for drinking, bathing, washing or irrigation. Water pollution reduces the ability of the body of water to provide the ecosystem services (such as drinking water) that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
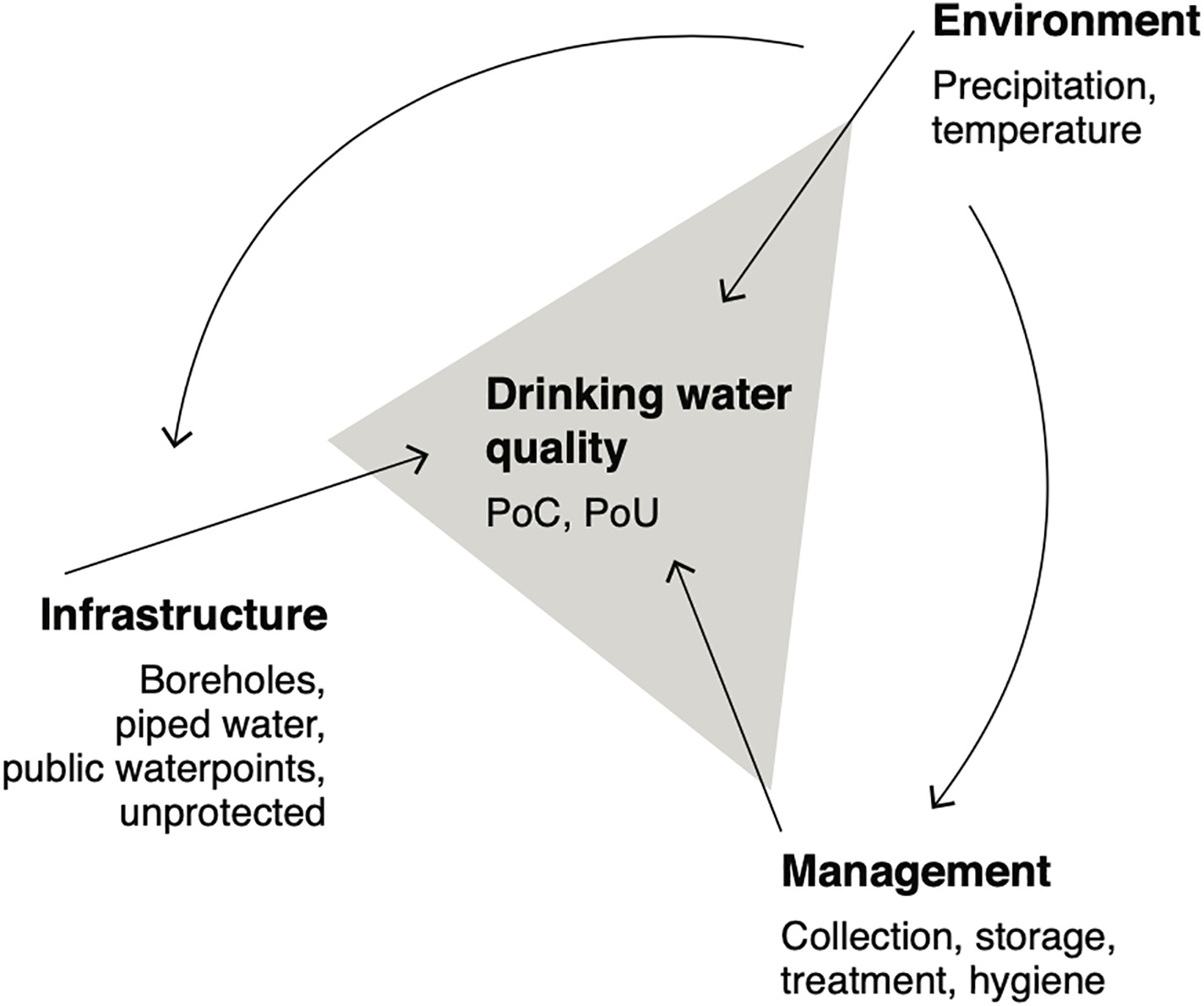
Water Supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. These systems are what supply drinking water to populations around the globe. Aspects of service quality include continuity of supply, water quality and water pressure. The institutional responsibility for water supply is arranged differently in different countries and regions (urban versus rural). It usually includes issues surrounding policy and regulation, service provision and standardization. The cost of supplying water consists, to a very large extent, of fixed costs (capital costs and personnel costs) and only to a small extent of variable costs that depend on the amount of water consumed (mainly energy and chemicals). Almost all service providers in the world charge tariffs to recover part of their costs. Water supply is a separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)
.jpg)