|
Sambhu Nath De
Sambhunath De ; (1 February 1915 – 15 April 1985) was an Indian medical scientist and researcher, who discovered the cholera toxin, the ''animal model of cholera'', and successfully demonstrated the method of transmission of cholera pathogen ''Vibrio cholerae''. Early career Shambhu Nath De was born in Hooghly District, West Bengal, India. His father Mr Dasarathi De was a not so successful businessman. Supported by his uncle Asutosh De, De completed the Matriculation examination with distinction from Garbati High School that helped him to get the District scholarship as well as to pursue further education in Hooghly Mohsin College, which was then affiliated with the prestigious University of Calcutta. His higher education was supported by Kestodhan Seth, who identified De as an extraordinary student. De passed his M.B. examination in 1939 from Calcutta Medical College and completed a Diploma in Tropical Medicine (DTM) in 1942. Soon after graduation he joined Calcutta Medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fellow Of The Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the judges of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural science, natural knowledge, including mathematics, engineering science, and medical science". Fellow, Fellowship of the Society, the oldest known scientific academy in continuous existence, is a significant honour. It has been awarded to many eminent scientists throughout history, including Isaac Newton (1672), Michael Faraday (1824), Charles Darwin (1839), Ernest Rutherford (1903), Srinivasa Ramanujan (1918), Albert Einstein (1921), Paul Dirac (1930), Winston Churchill (1941), Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar (1944), Dorothy Hodgkin (1947), Alan Turing (1951), Lise Meitner (1955) and Francis Crick (1959). More recently, fellowship has been awarded to Stephen Hawking (1974), David Attenborough (1983), Tim Hunt (1991), Elizabeth Blackburn (1992), Tim Berners-Lee (2001), Venki R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
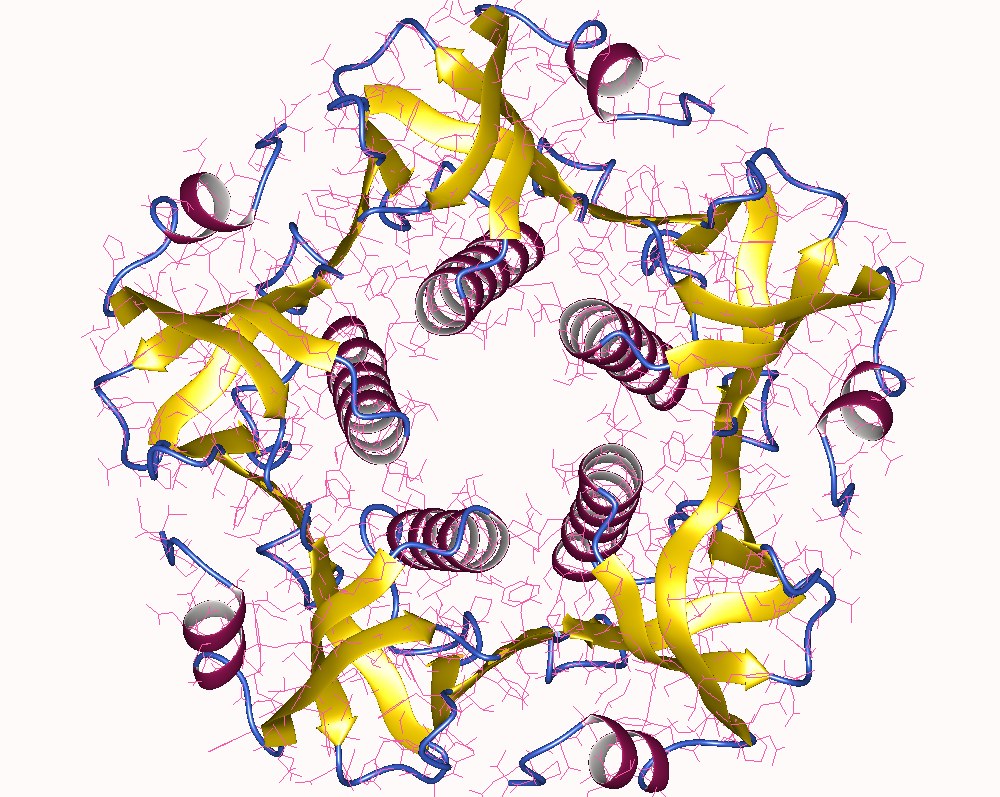
Cholera Toxin
Cholera toxin (also known as choleragen and sometimes abbreviated to CTX, Ctx or CT) is AB5 multimeric protein complex secreted by the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. CTX is responsible for the massive, watery diarrhea characteristic of cholera infection. It is a member of the Heat-labile enterotoxin family. History Cholera toxin was discovered in 1959 by Indian microbiologist Sambhu Nath De. Structure The complete toxin is a hexamer made up of a single copy of the A subunit (part A, enzymatic, ), and five copies of the B subunit (part B, receptor binding, ), denoted as AB5. Subunit B binds while subunit A activates the G protein which activates adenylate cyclase. The three-dimensional structure of the toxin was determined using X-ray crystallography by Zhang ''et al.'' in 1995. The five B subunits—each weighing 11 kDa, form a five-membered ring. The A subunit which is 28 kDa, has two important segments. The A1 portion of the chain (CTA1) is a globular enzyme payload t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
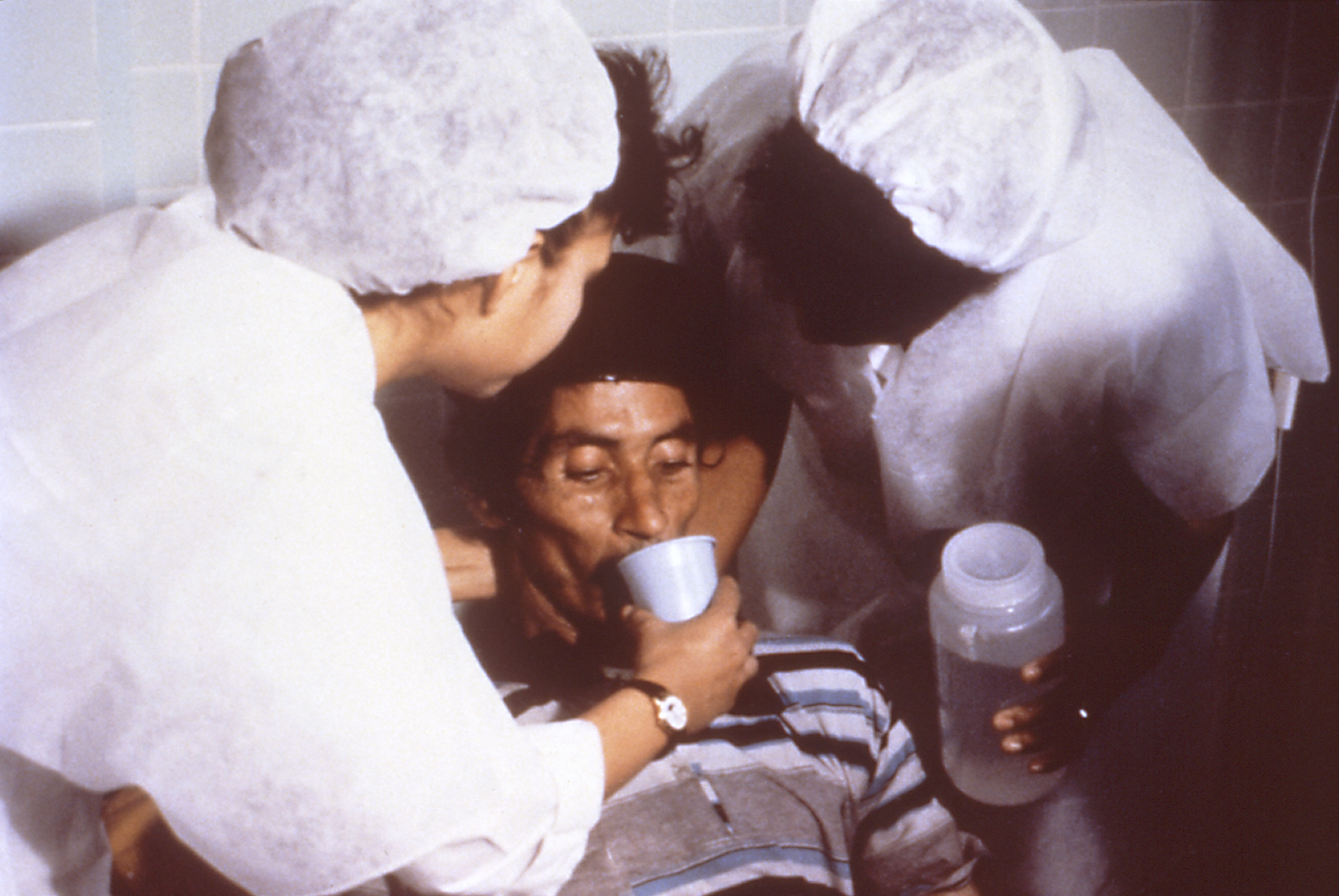
Oral Rehydration Therapy
Oral rehydration therapy (ORT) is a type of fluid replacement used to prevent and treat dehydration, especially due to diarrhea. It involves drinking water with modest amounts of sugar and salts, specifically sodium and potassium. Oral rehydration therapy can also be given by a nasogastric tube. Therapy should routinely include the use of zinc supplements. Use of oral rehydration therapy has been estimated to decrease the risk of death from diarrhea by up to 93%. Side effects may include vomiting, high blood sodium, or high blood potassium. If vomiting occurs, it is recommended that use be paused for 10 minutes and then gradually restarted. The recommended formulation includes sodium chloride, sodium citrate, potassium chloride, and glucose. Glucose may be replaced by sucrose and sodium citrate may be replaced by sodium bicarbonate, if not available. It works as glucose increases the uptake of sodium and thus water by the intestines. A number of other formulations are also ava ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hooghly District
Hooghly district () is one of the districts of the Indian state of West Bengal. It can alternatively be spelt ''Hoogli'' or ''Hugli''. The district is named after the Hooghly River. The headquarters of the district are at Hooghly-Chinsura (''Chuchura''). There are four subdivisions: Chinsurah Sadar, Srirampore, Chandannagore, and Arambagh. History The district of Hooghly derived its name from the town of Hooghly on the west bank of the Hugli River about 40 km north of Kolkata. This town was a major river port for trade in India before colonialism. The district has thousands of years of rich heritage as part of the Bengali kingdom of Bhurshut. The first European to reach this area was the Portuguese sailor Vasco da Gama. In 1536 Portuguese traders obtained a permit from Sultan Mahmud Shah to trade in this area. In those days the Hooghly River was the main route for transportation and Hooghly served as an excellent trading port. Within a few decades, the town of Hoog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibrio Cholerae
''Vibrio cholerae'' is a species of Gram-negative, facultative anaerobe and comma-shaped bacteria. The bacteria naturally live in brackish or saltwater where they attach themselves easily to the chitin-containing shells of crabs, shrimps, and other shellfish. Some strains of ''V. cholerae'' are pathogenic to humans and cause a deadly disease cholera, which can be derived from the consumption of undercooked or raw marine life species. ''V. cholerae'' was first described by Félix-Archimède Pouchet in 1849 as some kind of protozoa. Filippo Pacini correctly identified it as a bacterium and from him, the scientific name is adopted. The bacterium as the cause of cholera was discovered by Robert Koch in 1884. Sambhu Nath De isolated the cholera toxin and demonstrated the toxin as the cause of cholera in 1959. The bacterium has a flagellum at one pole and several pili throughout its cell surface. It undergoes respiratory and fermentative metabolism. Two serogroups called O1 and O139 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholera Toxin
Cholera toxin (also known as choleragen and sometimes abbreviated to CTX, Ctx or CT) is AB5 multimeric protein complex secreted by the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. CTX is responsible for the massive, watery diarrhea characteristic of cholera infection. It is a member of the Heat-labile enterotoxin family. History Cholera toxin was discovered in 1959 by Indian microbiologist Sambhu Nath De. Structure The complete toxin is a hexamer made up of a single copy of the A subunit (part A, enzymatic, ), and five copies of the B subunit (part B, receptor binding, ), denoted as AB5. Subunit B binds while subunit A activates the G protein which activates adenylate cyclase. The three-dimensional structure of the toxin was determined using X-ray crystallography by Zhang ''et al.'' in 1995. The five B subunits—each weighing 11 kDa, form a five-membered ring. The A subunit which is 28 kDa, has two important segments. The A1 portion of the chain (CTA1) is a globular enzyme payload t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathological Society Of Great Britain And Ireland
The Pathological Society is a professional organisation of Great Britain and Ireland whose mission is stated as 'understanding disease'. Membership and profile The membership of the society is mainly drawn from the UK and includes an international membership. Members are clinical and experimental pathologists. There is a strong representation of academic pathologists within the membership. A flourishing Trainees Group operates within the membership and represents those who are in the process of training in the discipline of pathology. More recently, in parallel with the Royal College of Pathologists, the society introduced an undergraduate membership scheme as part of an initiative to increase undergraduate engagement in pathology and research. The society is run by a committee elected from its membership. A group of Officers of the Society manage executive functions. These include a President (Ian Ellis), a General Secretary (Richard Byers), a Treasurer (Nicholas Rooney) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of London
The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in post-nominals) is a federal public research university located in London, England, United Kingdom. The university was established by royal charter in 1836 as a degree-awarding examination board for students holding certificates from University College London and King's College London and "other such other Institutions, corporate or unincorporated, as shall be established for the purpose of Education, whether within the Metropolis or elsewhere within our United Kingdom". This fact allows it to be one of three institutions to claim the title of the third-oldest university in England, and moved to a federal structure in 1900. It is now incorporated by its fourth (1863) royal charter and governed by the University of London Act 2018. It was the first university in the United Kingdom to introduce examinations for women in 1869 and, a decade later, the first to admit women to degrees. In 1913, it appointe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcutta University
The University of Calcutta (informally known as Calcutta University; CU) is a public collegiate state university in India, located in Kolkata, West Bengal, India. Considered one of best state research university all over India every year, CU has topped among India's best universities several times. It has 151 affiliated undergraduate colleges and 16 institutes in Kolkata and nearby areas. It was established on 24 January 1857 and is the oldest multidisciplinary and European-style institution in Asia. Today, the university's jurisdiction is limited to a few districts of West Bengal, but at the time of establishment it had a catchment area, ranging from Lahore to Myanmar. Within India, it is recognized as a "Five-Star University" and accredited an "A+" grade by the National Assessment and Accreditation Council (NAAC). The University of Calcutta was awarded the status of "Centre with Potential for Excellence in Particular Area" and "University with potential for excellence" by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coates Medal , a village and civil pari ...
Coates may refer to: *Coates (surname) Places United Kingdom *Coates, Cambridgeshire *Coates, Gloucestershire * Coates, Lancashire * Coates, Nottinghamshire *Coates, West Sussex *Coates by Stow, in Lincolnshire *Coates Castle, a Grade II listed manor in West Sussex United States *Coates, Minnesota Other * Coates graph, a kind of flow graph associated with the solution of a system of linear equations * Coates Hire, an Australian equipment hire company * Coates (supercomputer), a supercomputer at Purdue University * Coates' disease, occasional spelling for Coats' disease, a rare human eye disorder See also * Coate (other) * Cotes (other) * Coats (other) * Great Coates Great Coates is a village and civil parish in North East Lincolnshire, England. It is to the north-west and adjoins the Grimsby urban area, and is served by Great Coates railway station. The northern part of the parish extends to the Humber Es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |