esophagus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The esophagus (
 The esophagus has four points of constriction. When a corrosive substance, or a solid object is swallowed, it is most likely to lodge and damage one of these four points. These constrictions arise from particular structures that compress the esophagus. These constrictions are:
* At the start of the esophagus, where the
The esophagus has four points of constriction. When a corrosive substance, or a solid object is swallowed, it is most likely to lodge and damage one of these four points. These constrictions arise from particular structures that compress the esophagus. These constrictions are:
* At the start of the esophagus, where the
 An
An
"The occurrence, bionomics and potential impacts of the invasive freshwater snail ''Tarebia granifera'' (Lamarck, 1822) (Gastropoda: Thiaridae) in South Africa"
. ''Zoologische Mededelingen'' 83. In the
American English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lan ...
) or oesophagus (British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet, is an organ in vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
s through which food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is inge ...
passes, aided by peristaltic contractions, from the pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its st ...
to the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
. The esophagus is a fibromuscular tube, about long in adults, that travels behind the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a Cartilage, cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends ...
and heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide t ...
, passes through the diaphragm, and empties into the uppermost region of the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
. During swallowing, the epiglottis
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food in ...
tilts backwards to prevent food from going down the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
and lungs. The word ''oesophagus'' is from Ancient Greek οἰσοφάγος (oisophágos), from οἴσω (oísō), future form of φέρω (phérō, “I carry”) + ἔφαγον (éphagon, “I ate”).
The wall of the esophagus from the lumen outwards consists of mucosa, submucosa (connective tissue), layers of muscle fibers between layers of fibrous tissue
Fiber or fibre (from la, fibra, links=no) is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate ...
, and an outer layer of connective tissue. The mucosa is a stratified squamous epithelium of around three layers of squamous cells, which contrasts to the single layer of columnar cells of the stomach. The transition between these two types of epithelium is visible as a zig-zag line. Most of the muscle is smooth muscle although striated muscle
Striations means a series of ridges, furrows or linear marks, and is used in several ways:
* Glacial striation
* Striation (fatigue), in material
* Striation (geology), a ''striation'' as a result of a geological fault
* Striation Valley, in An ...
predominates in its upper third. It has two muscular rings or sphincter
A sphincter is a circular muscle that normally maintains constriction of a natural body passage or orifice and which relaxes as required by normal physiological functioning. Sphincters are found in many animals. There are over 60 types in the h ...
s in its wall, one at the top and one at the bottom. The lower sphincter helps to prevent reflux of acidic stomach content. The esophagus has a rich blood supply and venous drainage. Its smooth muscle is innervated by involuntary nerves (sympathetic nerve
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the ...
s via the sympathetic trunk
The sympathetic trunks (sympathetic chain, gangliated cord) are a paired bundle of nerve fibers that run from the base of the skull to the coccyx. They are a major component of the sympathetic nervous system.
Structure
The sympathetic trunk lies j ...
and parasympathetic nerve
The parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS) is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of ...
s via the vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right ...
) and in addition voluntary nerves (lower motor neurons
Lower motor neurons (LMNs) are motor neurons located in either the anterior grey column, anterior nerve roots (spinal lower motor neurons) or the cranial nerve nuclei of the brainstem and cranial nerves with motor function (cranial nerve lower m ...
) which are carried in the vagus nerve to innervate its striated muscle.
The esophagus passes through the thoracic cavity into the diaphragm into the stomach.
The esophagus may be affected by gastric reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the upper gastrointestinal chronic diseases where stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/ ...
, cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, prominent dilated blood vessels called varices
A varix (pl. varices) is an abnormally dilated vessel with a tortuous course. Varices usually occur in the venous system, but may also occur in arterial or lymphatic vessels.
Examples of varices include:
* Varicose veins, large tortuous veins usua ...
that can bleed heavily, tears
Tears are a clear liquid secreted by the lacrimal glands (tear gland) found in the eyes of all land mammals. Tears are made up of water, electrolytes, proteins, lipids, and mucins that form layers on the surface of eyes. The different types of ...
, constrictions, and disorders of motility. Diseases may cause difficulty swallowing (dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liq ...
), painful swallowing (odynophagia
Odynophagia is pain when swallowing. The pain may be felt in the mouth or throat and can occur with or without difficulty swallowing. The pain may be described as an ache, burning sensation, or occasionally a stabbing pain that radiates to the b ...
), chest pain, or cause no symptoms at all. Clinical investigations include X-rays
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nbs ...
when swallowing barium sulfate
Barium sulfate (or sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ba SO4. It is a white crystalline solid that is odorless and insoluble in water. It occurs as the mineral barite, which is the main commercial source of barium an ...
, endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
, and CT scans. Surgically,
the esophagus is difficult to access in part due to its position between critical organs and directly between the sternum and spinal column.
Structure
The esophagus is one of the upper parts of the digestive system. There aretaste bud
Taste buds contain the taste receptor cells, which are also known as gustatory cells. The taste receptors are located around the small structures known as lingual papillae, papillae found on the upper surface of the tongue, soft palate, upper e ...
s on its upper part. It begins at the back of the mouth, passing downward through the rear part of the mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagu ...
, through the diaphragm, and into the stomach. In humans, the esophagus generally starts around the level of the sixth cervical vertebra
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (singular: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In sa ...
behind the cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
of the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a Cartilage, cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends ...
, enters the diaphragm at about the level of the tenth thoracic vertebra
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical ...
, and ends at the cardia of the stomach, at the level of the eleventh thoracic vertebra
In vertebrates, thoracic vertebrae compose the middle segment of the vertebral column, between the cervical vertebrae and the lumbar vertebrae. In humans, there are twelve thoracic vertebrae and they are intermediate in size between the cervical ...
. The esophagus is usually about 25 cm (10 in) in length.
Many blood vessel
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients, and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide away ...
s serve the esophagus, with blood supply varying along its course. The upper parts of the esophagus and the upper esophageal sphincter receive blood from the inferior thyroid artery
The inferior thyroid artery is an artery in the neck. It arises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes upward, in front of the vertebral artery and longus colli muscle. It then turns medially behind the carotid sheath and its contents, and als ...
, the parts of the esophagus in the thorax from the bronchial arteries
In human anatomy, the bronchial arteries supply the lungs with nutrition and oxygenated blood. Although there is much variation, there are usually two bronchial arteries that run to the left lung, and one to the right lung and are a vital part o ...
and branches directly from the thoracic aorta
The descending thoracic aorta is a part of the aorta located in the thorax. It is a continuation of the aortic arch. It is located within the posterior mediastinal cavity, but frequently bulges into the left pleural cavity. The descending thoracic ...
, and the lower parts of the esophagus and the lower esophageal sphincter receive blood from the left gastric artery
In human anatomy, the left gastric artery arises from the celiac artery and runs along the superior portion of the lesser curvature of the stomach. Branches also supply the lower esophagus. The left gastric artery anastomoses with the right gas ...
and the left inferior phrenic artery
The inferior phrenic arteries are two small vessels which supply the diaphragm. They present much variety in their origin.
Structure
Origin
The inferior phrenic arteries usually arise between T12 and L2 vertebrae. They may arise separately ...
. The venous drainage also differs along the course of the esophagus. The upper and middle parts of the esophagus drain into the azygos and hemiazygos vein
The hemiazygos vein (vena azygos minor inferior) is a vein running superiorly in the lower thoracic region, just to the left side of the vertebral column.
Structure
The hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein, when taken together, essen ...
s, and blood from the lower part drains into the left gastric vein
The left gastric vein (or coronary vein) is a vein that derives from tributaries draining the lesser curvature of the stomach.
Structure
The left gastric vein runs from right to left along the lesser curvature of the stomach. It passes to the ...
. All these veins drain into the superior vena cava
The superior vena cava (SVC) is the superior of the two venae cavae, the great venous trunks that return deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation to the right atrium of the heart. It is a large-diameter (24 mm) short length vein th ...
, with the exception of the left gastric vein, which is a branch of the portal vein. Lymphatically, the upper third of the esophagus drains into the deep cervical lymph node
The deep cervical lymph nodes are a group of cervical lymph nodes found near the internal jugular vein in the neck.
Structure
The deep cervical lymph nodes can be divided into upper and lower groups, or superior and inferior groups.
Alternati ...
s, the middle into the superior and posterior mediastinal lymph nodes, and the lower esophagus into the gastric
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
and celiac lymph nodes
The celiac lymph nodes are associated with the branches of the celiac artery. Other lymph nodes in the abdomen are associated with the superior and inferior mesenteric arteries. The celiac lymph nodes are grouped into three sets: the gastric
...
. This is similar to the lymphatic drainage of the abdominal structures that arise from the foregut, which all drain into the celiac nodes.
;Position
The upper esophagus lies at the back of the mediastinum behind the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a Cartilage, cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends ...
, adjoining along the tracheoesophageal stripe The tracheoesophageal stripe is formed by the posterior wall of the trachea and the anterior wall of the esophagus
The esophagus ( American English) or oesophagus (British English; both ), non-technically known also as the food pipe or gullet ...
, and in front of the erector spinae muscle
The erector spinae ( ) or spinal erectors is a set of muscles that straighten and rotate the back. The spinal erectors work together with the glutes (gluteus maximus, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus) to maintain stable posture standing or s ...
s and the vertebral column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordata, ...
. The lower esophagus lies behind the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide t ...
and curves in front of the thoracic aorta
The descending thoracic aorta is a part of the aorta located in the thorax. It is a continuation of the aortic arch. It is located within the posterior mediastinal cavity, but frequently bulges into the left pleural cavity. The descending thoracic ...
. From the bifurcation of the trachea
In anatomy, the carina or tracheal bifurcation is a ridge of cartilage in the trachea that occurs between the division of the two main bronchi.
Structure
The carina occurs at the lower end of the trachea (usually at the level of the 4th to 5t ...
downwards, the esophagus passes behind the right pulmonary artery
A pulmonary artery is an artery in the pulmonary circulation that carries deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs. The largest pulmonary artery is the ''main pulmonary artery'' or ''pulmonary trunk'' from the heart, and ...
, left main bronchus
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronch ...
, and left atrium
The atrium ( la, ātrium, , entry hall) is one of two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular valves.
There are two at ...
. At this point, it passes through the diaphragm.
The thoracic duct
In human anatomy, the thoracic duct is the larger of the two lymph ducts of the lymphatic system. It is also known as the ''left lymphatic duct'', ''alimentary duct'', ''chyliferous duct'', and ''Van Hoorne's canal''. The other duct is the righ ...
, which drains the majority of the body's lymph
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to ...
, passes behind the esophagus, curving from lying behind the esophagus on the right in the lower part of the esophagus, to lying behind the esophagus on the left in the upper esophagus. The esophagus also lies in front of parts of the hemiazygos vein
The hemiazygos vein (vena azygos minor inferior) is a vein running superiorly in the lower thoracic region, just to the left side of the vertebral column.
Structure
The hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein, when taken together, essen ...
s and the intercostal vein
The intercostal veins are a group of veins which drain the area between the ribs ("costae"), called the intercostal space.
They can be divided as follows:
* Anterior intercostal veins
* Posterior intercostal veins
** Posterior intercost vein tha ...
s on the right side. The vagus nerve
The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract. It comprises two nerves—the left and right ...
divides and covers the esophagus in a plexus
In neuroanatomy, a plexus (from the Latin term for "braid") is a branching network of vessels or nerves. The vessels may be blood vessels (veins, capillaries) or lymphatic vessels. The nerves are typically axons outside the central nervous syste ...
.
;Constrictions
 The esophagus has four points of constriction. When a corrosive substance, or a solid object is swallowed, it is most likely to lodge and damage one of these four points. These constrictions arise from particular structures that compress the esophagus. These constrictions are:
* At the start of the esophagus, where the
The esophagus has four points of constriction. When a corrosive substance, or a solid object is swallowed, it is most likely to lodge and damage one of these four points. These constrictions arise from particular structures that compress the esophagus. These constrictions are:
* At the start of the esophagus, where the laryngopharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its struct ...
joins the esophagus, behind the cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
* Where it is crossed on the front by the aortic arch
The aortic arch, arch of the aorta, or transverse aortic arch () is the part of the aorta between the ascending and descending aorta. The arch travels backward, so that it ultimately runs to the left of the trachea.
Structure
The aorta begins ...
in the superior mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagu ...
* Where the esophagus is compressed by the left main bronchus
A bronchus is a passage or airway in the lower respiratory tract that conducts air into the lungs. The first or primary bronchi pronounced (BRAN-KAI) to branch from the trachea at the carina are the right main bronchus and the left main bronchus. ...
in the posterior mediastinum
* The esophageal hiatus
In human anatomy, the esophageal hiatus is an opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus and the vagus nerve pass.
Structure
It is located in the right crus, one of the two tendinous structures that connect the diaphragm to the spine ...
, where it passes through the diaphragm in the posterior mediastinum
Sphincters
The esophagus is surrounded at the top and bottom by two muscular rings, known respectively as the upper esophageal sphincter and the lower esophageal sphincter. Thesesphincter
A sphincter is a circular muscle that normally maintains constriction of a natural body passage or orifice and which relaxes as required by normal physiological functioning. Sphincters are found in many animals. There are over 60 types in the h ...
s act to close the esophagus when food is not being swallowed. The upper esophageal sphincter is an anatomical sphincter, which is formed by the lower portion of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor, also known as the cricopharyngeal sphincter due to its relation with cricoid cartilage
The cricoid cartilage , or simply cricoid (from the Greek ''krikoeides'' meaning "ring-shaped") or cricoid ring, is the only complete ring of cartilage around the trachea. It forms the back part of the voice box and functions as an attachment si ...
of the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
anteriorly. However, the lower esophageal sphincter is not an anatomical but rather a functional sphincter, meaning that it acts as a sphincter but does not have a distinct thickening like other sphincters.
The upper esophageal sphincter surrounds the upper part of the esophagus. It consists of skeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of muscl ...
but is not under voluntary control. Opening of the upper esophageal sphincter is triggered by the swallowing reflex. The primary muscle of the upper esophageal sphincter is the cricopharyngeal part of the inferior pharyngeal constrictor
The inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle is a skeletal muscle of the neck. It is the thickest of the three outer pharyngeal muscles. It arises from the sides of the cricoid cartilage and the thyroid cartilage. It is supplied by the vagus nerve ( ...
.
The lower esophageal sphincter, or gastroesophageal sphincter, surrounds the lower part of the esophagus at the junction between the esophagus and the stomach. It is also called the cardiac sphincter or cardioesophageal sphincter, named from the adjacent part of the stomach, the '' cardia''. Dysfunction of the gastroesophageal sphincter causes gastroesophageal reflux
Reflux is a technique involving the condensation of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. It is used in industrial and laboratory distillations. It is also used in chemistry to supply energy to reactions ...
, which causes heartburn
Heartburn, also known as pyrosis, cardialgia or acid indigestion, is a burning sensation in the central chest or upper central abdomen. Heartburn is usually due to regurgitation of gastric acid (gastric reflux) into the esophagus. It is the m ...
, and, if it happens often enough, can lead to gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the upper gastrointestinal chronic diseases where stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/ ...
, with damage of the esophageal mucosa.
Nerve supply
The esophagus is innervated by the vagus nerve and the cervical and thoracicsympathetic trunk
The sympathetic trunks (sympathetic chain, gangliated cord) are a paired bundle of nerve fibers that run from the base of the skull to the coccyx. They are a major component of the sympathetic nervous system.
Structure
The sympathetic trunk lies j ...
. The vagus nerve has a parasympathetic function, supplying the muscles of the esophagus and stimulating glandular contraction. Two sets of nerve fibers travel in the vagus nerve to supply the muscles. The upper striated muscle, and upper esophageal sphincter, are supplied by neurons with bodies in the nucleus ambiguus
The nucleus ambiguus ("ambiguous nucleus" in English) is a group of large motor neurons, situated deep in the medullary reticular formation named by Jacob Clarke. The nucleus ambiguus contains the cell bodies of neurons that innervate the muscle ...
, whereas fibers that supply the smooth muscle and lower esophageal sphincter have bodies situated in the dorsal motor nucleus. The vagus nerve plays the primary role in initiating peristalsis
Peristalsis ( , ) is a radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an anterograde direction. Peristalsis is progression of coordinated contraction of involuntary circular muscles, whic ...
. The sympathetic trunk has a sympathetic function. It may enhance the function of the vagus nerve, increasing peristalsis and glandular activity, and causing sphincter contraction. In addition, sympathetic activation may relax the muscle wall and cause blood vessel constriction. Sensation along the esophagus is supplied by both nerves, with gross sensation being passed in the vagus nerve and pain passed up the sympathetic trunk.
Gastro-esophageal junction
The gastro-esophageal junction (also known as the esophagogastric junction) is the junction between the esophagus and the stomach, at the lower end of the esophagus. The pink color of the esophageal mucosa contrasts to the deeper red of the gastric mucosa, and the mucosal transition can be seen as an irregular zig-zag line, which is often called the z-line. Histological examination reveals abrupt transition between the stratified squamous epithelium of the esophagus and thesimple columnar epithelium
Simple columnar epithelium is a single layer of columnar epithelial cells which are tall and slender with oval-shaped nuclei located in the basal region, attached to the basement membrane. In humans, simple columnar epithelium lines most organ ...
of the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
. Normally, the cardia of the stomach is immediately distal to the z-line and the z-line coincides with the upper limit of the gastric folds of the cardia; however, when the anatomy of the mucosa is distorted in Barrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet ce ...
the true gastro-eshophageal junction can be identified by the upper limit of the gastric folds rather than the mucosal transition. The functional location of the lower oesophageal sphincter is generally situated about below the z-line.
Microanatomy
The human esophagus has amucous membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It i ...
consisting of a tough stratified squamous epithelium without keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
, a smooth lamina propria
The lamina propria is a thin layer of connective tissue that forms part of the moist linings known as mucous membranes or mucosae, which line various tubes in the body, such as the respiratory tract, the gastrointestinal tract, and the urogenita ...
, and a muscularis mucosae
The lamina muscularis mucosae (or muscularis mucosae) is a thin layer (lamina) of muscle of the gastrointestinal tract, located outside the lamina propria, and separating it from the submucosa. It is present in a continuous fashion from the es ...
. The epithelium of the esophagus has a relatively rapid turnover and serves a protective function against the abrasive effects of food. In many animals, the epithelium contains a layer of keratin, representing a coarser diet. There are two types of glands, with mucus-secreting esophageal glands being found in the submucosa and esophageal cardiac glands, similar to cardiac glands of the stomach, located in the lamina propria and most frequent in the terminal part of the organ. The mucus
Mucus ( ) is a slippery aqueous secretion produced by, and covering, mucous membranes. It is typically produced from cells found in mucous glands, although it may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both serous and mucous cells. It ...
from the glands gives a good protection to the lining. The submucosa also contains the submucosal plexus
The submucosal plexus (Meissner's plexus, plexus of the submucosa, plexus submucosus) lies in the submucosa of the intestinal wall. The nerves of this plexus are derived from the myenteric plexus which itself is derived from the plexuses of parasy ...
, a network of nerve cells
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. ...
that is part of the enteric nervous system
The enteric nervous system (ENS) or intrinsic nervous system is one of the main divisions of the autonomic nervous system (ANS) and consists of a mesh-like system of neurons that governs the function of the gastrointestinal tract. It is capable of ...
.
The muscular layer
The muscular layer (muscular coat, muscular fibers, muscularis propria, muscularis externa) is a region of muscle in many organs in the vertebrate body, adjacent to the submucosa. It is responsible for gut movement such as peristalsis. The Latin, ...
of the esophagus has two types of muscle. The upper third of the esophagus contains striated muscle
Striations means a series of ridges, furrows or linear marks, and is used in several ways:
* Glacial striation
* Striation (fatigue), in material
* Striation (geology), a ''striation'' as a result of a geological fault
* Striation Valley, in An ...
, the lower third contains smooth muscle, and the middle third contains a mixture of both. Muscle is arranged in two layers: one in which the muscle fibers run longitudinal to the esophagus, and the other in which the fibers encircle the esophagus. These are separated by the myenteric plexus, a tangled network of nerve fibers involved in the secretion of mucus and in peristalsis of the smooth muscle of the esophagus. The outermost layer of the esophagus is the adventitia
The adventitia () is the outer layer of fibrous connective tissue surrounding an organ.
The outer layer of connective tissue that surrounds an artery, or vein – the tunica externa, is also called the ''tunica adventitia''.
To some degree, its ...
in most of its length, with the abdominal part being covered in serosa
The serous membrane (or serosa) is a smooth tissue membrane of mesothelium lining the contents and inner walls of body cavities, which secrete serous fluid to allow lubricated sliding movements between opposing surfaces. The serous membrane ...
. This makes it distinct from many other structures in the gastrointestinal tract that only have a serosa.
Development
In earlyembryogenesis
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm ...
, the esophagus develops from the endoderm
Endoderm is the innermost of the three primary germ layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the ectoderm (outside layer) and mesoderm (middle layer). Cells migrating inward along the archenteron form the inner layer of the gast ...
al primitive gut tube. The ventral part of the embryo abuts the yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac'' is ...
. During the second week of embryological development, as the embryo grows, it begins to surround parts of the sac. The enveloped portions form the basis for the adult gastrointestinal tract. The sac is surrounded by a network of vitelline arteries
The vitelline arteries are the arterial counterpart to the vitelline veins. Like the veins, they play an important role in the vitelline circulation of blood to and from the yolk sac of a fetus. They are a branch of the dorsal aorta.
They give ri ...
. Over time, these arteries consolidate into the three main arteries that supply the developing gastrointestinal tract: the celiac artery
The celiac () artery (also spelled ''coeliac''), also known as the celiac trunk or truncus coeliacus, is the first major branch of the abdominal aorta. It is about 1.25 cm in length. Branching from the aorta at thoracic vertebra 12 (T12) in ...
, superior mesenteric artery
In human anatomy, the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) is an artery which arises from the anterior surface of the abdominal aorta, just inferior to the origin of the celiac trunk, and supplies blood to the intestine from the lower part of the ...
, and inferior mesenteric artery. The areas supplied by these arteries are used to define the midgut
The midgut is the portion of the embryo from which most of the intestines develop. After it bends around the superior mesenteric artery, it is called the "midgut loop". It comprises the portion of the alimentary canal from the end of the foregut a ...
, hindgut and foregut.
The surrounded sac becomes the primitive gut. Sections of this gut begin to differentiate into the organs of the gastrointestinal tract, such as the esophagus, stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
, and intestines. The esophagus develops as part of the foregut tube. The innervation of the esophagus develops from the pharyngeal arch
The pharyngeal arches, also known as visceral arches'','' are structures seen in the embryonic development of vertebrates that are recognisable precursors for many structures. In fish, the arches are known as the branchial arches, or gill arche ...
es.
Function
Swallowing
Food isingested
Ingestion is the consumption of a substance by an organism. In animals, it normally is accomplished by taking in a substance through the mouth into the gastrointestinal tract, such as through eating or drinking. In single-celled organisms inges ...
through the mouth and when swallowed
Swallowing, sometimes called deglutition in scientific contexts, is the process in the human or animal body that allows for a substance to pass from the mouth, to the pharynx, and into the esophagus, while shutting the epiglottis. Swallowing ...
passes first into the pharynx
The pharynx (plural: pharynges) is the part of the throat behind the mouth and nasal cavity, and above the oesophagus and trachea (the tubes going down to the stomach and the lungs). It is found in vertebrates and invertebrates, though its st ...
and then into the esophagus. The esophagus is thus one of the first components of the digestive system and the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive syste ...
. After food passes through the esophagus, it enters the stomach. When food is being swallowed, the epiglottis
The epiglottis is a leaf-shaped flap in the throat that prevents food and water from entering the trachea and the lungs. It stays open during breathing, allowing air into the larynx. During swallowing, it closes to prevent aspiration of food in ...
moves backward to cover the larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
, preventing food from entering the trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a Cartilage, cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air-breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends ...
. At the same time, the upper esophageal sphincter relaxes, allowing a bolus of food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is inge ...
to enter. Peristaltic
Peristalsis ( , ) is a radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an anterograde direction. Peristalsis is progression of coordinated contraction of involuntary circular muscles, which ...
contractions of the esophageal muscle push the food down the esophagus. These rhythmic contractions occur both as a reflex response to food that is in the mouth, and also as a response to the sensation of food within the esophagus itself. Along with peristalsis, the lower esophageal sphincter relaxes.
Reducing gastric reflux
The stomach produces gastric acid, a stronglyacid
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
ic mixture consisting of hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
(HCl) and potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosphe ...
and sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable iso ...
salts to enable food digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intest ...
. Constriction of the upper and lower esophageal sphincters helps to prevent reflux (backflow) of gastric contents and acid into the esophagus, protecting the esophageal mucosa. The acute angle of His
The angle of His, also known as the esophagogastric angle, is the acute angle created between the cardia at the entrance to the stomach, and the esophagus. It helps to prevent acid reflux of stomach acid into the esophagus. It is commonly undevel ...
and the lower crura of the diaphragm
The crus of diaphragm (pl. crura), refers to one of two tendon, tendinous structures that extends below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm to the vertebral column. There is a right crus and a left crus, which together form a tether for muscular cont ...
also help this sphincteric action.
Gene and protein expression
About 20,000 protein-coding genes are expressed in human cells and nearly 70% of these genes are expressed in the normal esophagus. Some 250 of these genes are more specifically expressed in the esophagus with less than 50 genes being highly specific. The corresponding esophagus-specific proteins are mainly involved in squamous differentiation such askeratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up scales, hair, nails, feathers, ho ...
s KRT13, KRT4 and KRT6C. Other specific proteins that help lubricate the inner surface of esophagus are mucin
Mucins () are a family of high molecular weight, heavily glycosylated proteins (glycoconjugates) produced by epithelial tissues in most animals. Mucins' key characteristic is their ability to form gels; therefore they are a key component in most ...
s such as MUC21 and MUC22. Many genes with elevated expression are also shared with skin and other organs that are composed of squamous epithelia
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellu ...
.
Clinical significance
The main conditions affecting the esophagus are described here. For a more complete list, seeesophageal disease Esophageal can refer to:
* The esophagus
* Esophageal arteries
* Esophageal glands
The esophageal glands are glands that are part of the digestive system of various animals, including humans.
In humans
Esophageal glands in humans are a part of a ...
.
Inflammation
Inflammation of the esophagus is known asesophagitis
Esophagitis, also spelled oesophagitis, is a disease characterized by inflammation of the esophagus. The esophagus is a tube composed of a mucosal lining, and longitudinal and circular smooth muscle fibers. It connects the pharynx to the stomach; s ...
. Reflux
Reflux is a technique involving the condensation of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. It is used in industrial and laboratory distillations. It is also used in chemistry to supply energy to reactions ...
of gastric acids from the stomach, infection, substances ingested (for example, corrosives), some medications (such as bisphosphonate
Bisphosphonates are a class of drugs that prevent the loss of bone density, used to treat osteoporosis and similar diseases. They are the most commonly prescribed drugs used to treat osteoporosis. They are called bisphosphonates because they ...
s), and food allergies
A food allergy is an abnormal immune response to food. The symptoms of the allergic reaction may range from mild to severe. They may include itchiness, swelling of the tongue, vomiting, diarrhea, hives, trouble breathing, or low blood pressur ...
can all lead to esophagitis. Esophageal candidiasis
Esophageal candidiasis is an opportunistic infection of the esophagus by ''Candida albicans''. The disease usually occurs in patients in immunocompromised states, including post-chemotherapy and in AIDS. However, it can also occur in patients wi ...
is an infection of the yeast ''Candida albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usu ...
'' that may occur when a person is immunocompromised
Immunodeficiency, also known as immunocompromisation, is a state in which the immune system's ability to fight infectious diseases and cancer is compromised or entirely absent. Most cases are acquired ("secondary") due to extrinsic factors that a ...
. the causes of some forms of esophagitis, such as eosinophilic esophagitis
Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is an allergic inflammatory condition of the esophagus that involves eosinophils, a type of white blood cell. In healthy individuals, the esophagus is typically devoid of eosinophils. In EoE, eosinophils migrate ...
, are not well-characterized, but may include Th2-mediated atopies or genetic factors. There appear to be correlations between eosinophilic esophagitis, asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
(itself with an eosinophilic
Eosinophilic (Greek suffix -phil-, meaning ''loves eosin'') is the staining of tissues, cells, or organelles after they have been washed with eosin, a dye.
Eosin is an acidic dye for staining cell cytoplasm, collagen, and muscle fibers. ''E ...
component), eczema
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can ...
, and allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis, of which the seasonal type is called hay fever, is a type of inflammation in the nose that occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the air. Signs and symptoms include a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, red, i ...
, though it is not clear whether these conditions contribute to eosinophilic esophagitis or vice versa, or if they are symptoms of mutual underlying factors. Esophagitis can cause painful swallowing and is usually treated by managing the cause of the esophagitis - such as managing reflux or treating infection.
Barrett's esophagus
Prolonged esophagitis, particularly from gastric reflux, is one factor thought to play a role in the development ofBarrett's esophagus
Barrett's esophagus is a condition in which there is an abnormal (metaplastic) change in the mucosal cells lining the lower portion of the esophagus, from stratified squamous epithelium to simple columnar epithelium with interspersed goblet ce ...
. In this condition, there is metaplasia
Metaplasia ( gr, "change in form") is the transformation of one differentiated cell type to another differentiated cell type. The change from one type of cell to another may be part of a normal maturation process, or caused by some sort of abno ...
of the lining of the lower esophagus, which changes from stratified squamous epithelia to simple columnar epithelia
Simple columnar epithelium is a single layer of columnar epithelial cells which are tall and slender with oval-shaped nuclei located in the basal region, attached to the basement membrane. In humans, simple columnar epithelium lines most organs ...
. Barrett's esophagus is thought to be one of the main contributors to the development of esophageal cancer.
Cancer
There are two main types of cancer of the esophagus. Squamous cell carcinoma is a carcinoma that can occur in the squamous cells lining the esophagus. This type is much more common inChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
and Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. The other main type is an adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma (; plural adenocarcinomas or adenocarcinomata ) (AC) is a type of cancerous tumor that can occur in several parts of the body. It is defined as neoplasia of epithelial tissue that has glandular origin, glandular characteristics, or ...
that occurs in the glands or columnar tissue of the esophagus. This is most common in developed countries
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
in those with Barrett's esophagus, and occurs in the cuboidal cells.
In its early stages, esophageal cancer may not have any symptoms at all. When severe, esophageal cancer may eventually cause obstruction of the esophagus, making swallowing of any solid foods very difficult and causing weight loss. The progress of the cancer is staged using a system that measures how far into the esophageal wall the cancer has invaded, how many lymph node
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
s are affected, and whether there are any metastases
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spread from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then ...
in different parts of the body. Esophageal cancer is often managed with radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and may also be managed by partial surgical removal of the esophagus. Inserting a stent
In medicine, a stent is a metal or plastic tube inserted into the lumen of an anatomic vessel or duct to keep the passageway open, and stenting is the placement of a stent. A wide variety of stents are used for different purposes, from expandab ...
into the esophagus, or inserting a nasogastric tube
Nasogastric intubation is a medical process involving the insertion of a plastic tube (nasogastric tube or NG tube) through the nose, down the oesophagus, and down into the stomach. Orogastric intubation is a similar process involving the inserti ...
, may also be used to ensure that a person is able to digest enough food and water. , the prognosis for esophageal cancer is still poor, so palliative therapy may also be a focus of treatment.
Varices
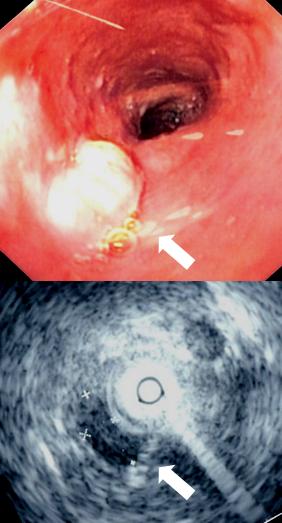
Esophageal varices
Esophageal varices are extremely dilated sub-mucosal veins in the lower third of the esophagus. They are most often a consequence of portal hypertension, commonly due to cirrhosis. People with esophageal varices have a strong tendency to develop ...
are swollen twisted branches of the azygous vein in the lower third of the esophagus. These blood vessels anastomose
An anastomosis (, plural anastomoses) is a connection or opening between two things (especially cavities or passages) that are normally diverging or branching, such as between blood vessels, leaf veins, or streams. Such a connection may be normal ...
(join up) with those of the portal vein when portal hypertension develops. These blood vessels are engorged more than normal, and in the worst cases may partially obstruct the esophagus. These blood vessels develop as part of a collateral circulation that occurs to drain blood from the abdomen
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the torso. ...
as a result of portal hypertension, usually as a result of liver disease
Liver disease, or hepatic disease, is any of many diseases of the liver. If long-lasting it is termed chronic liver disease. Although the diseases differ in detail, liver diseases often have features in common.
Signs and symptoms
Some of the si ...
s such as cirrhosis
Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is the impaired liver function caused by the formation of scar tissue known as fibrosis due to damage caused by liver disease. Damage causes tissue rep ...
. This collateral circulation occurs because the lower part of the esophagus drains into the left gastric vein, which is a branch of the portal vein. Because of the extensive venous plexus that exists between this vein and other veins, if portal hypertension occurs, the direction of blood drainage in this vein may reverse, with blood draining from the portal venous system, through the plexus. Veins in the plexus may engorge and lead to varices.
Esophageal varices often do not have symptoms until they rupture. A ruptured varix is considered a medical emergency because varices can bleed a lot. A bleeding varix may cause a person to vomit blood, or suffer shock
Shock may refer to:
Common uses Collective noun
*Shock, a historic commercial term for a group of 60, see English numerals#Special names
* Stook, or shock of grain, stacked sheaves
Healthcare
* Shock (circulatory), circulatory medical emergen ...
. To deal with a ruptured varix, a band may be placed around the bleeding blood vessel, or a small amount of a clotting agent may be injected near the bleed. A surgeon may also try to use a small inflatable balloon to apply pressure to stop the wound. IV fluids
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutri ...
and blood product
A blood product is any therapeutic substance prepared from human blood. This includes whole blood; blood components; and plasma derivatives. Whole blood is not commonly used in transfusion medicine. Blood components include: red blood cell concen ...
s may be given in order to prevent hypovolemia from excess blood loss.
Motility disorders
Several disorders affect the motility of food as it travels down the esophagus. This can cause difficult swallowing, calleddysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under "symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right.
It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liq ...
, or painful swallowing, called odynophagia
Odynophagia is pain when swallowing. The pain may be felt in the mouth or throat and can occur with or without difficulty swallowing. The pain may be described as an ache, burning sensation, or occasionally a stabbing pain that radiates to the b ...
. Achalasia
Esophageal achalasia, often referred to simply as achalasia, is a failure of smooth muscle fibers to relax, which can cause the lower esophageal sphincter to remain closed. Without a modifier, "achalasia" usually refers to achalasia of the esoph ...
refers to a failure of the lower esophageal sphincter to relax properly, and generally develops later in life. This leads to progressive enlargement of the esophagus, and possibly eventual megaesophagus
Megaesophagus, also known as esophageal dilatation, is a disorder of the esophagus in humans and other mammals, whereby the esophagus becomes abnormally enlarged. Megaesophagus may be caused by any disease which causes the muscles of the esophagus ...
. A nutcracker esophagus
Nutcracker esophagus, Jackhammer esophagus, or hypercontractile peristalsis, is a disorder of the movement of the esophagus characterized by contractions in the smooth muscle of the esophagus in a normal sequence but at an excessive amplitude or ...
refers to swallowing that can be extremely painful. Diffuse esophageal spasm
Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES), also known as distal esophageal spasm, is a condition characterized by uncoordinated contractions of the esophagus, which may cause difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) or regurgitation. In some cases, it may cause sym ...
is a spasm of the esophagus that can be one cause of chest pain. Such referred pain
Referred pain, also called reflective pain, is pain perceived at a location other than the site of the painful stimulus. An example is the case of angina pectoris brought on by a myocardial infarction (heart attack), where pain is often felt in ...
to the wall of the upper chest is quite common in esophageal conditions. Sclerosis of the esophagus, such as with systemic sclerosis
Systemic scleroderma, or systemic sclerosis, is an autoimmune rheumatic disease characterised by excessive production and accumulation of collagen, called fibrosis, in the skin and internal organs and by injuries to small arteries. There are two ...
or in CREST syndrome
CREST syndrome, also known as the limited cutaneous form of systemic sclerosis (lcSSc), is a multisystem connective tissue disorder. The acronym "CREST" refers to the five main features: calcinosis, Raynaud's phenomenon, esophageal dysmotility, ...
may cause hardening of the walls of the esophagus and interfere with peristalsis.
Malformations
Esophageal stricture
A benign esophageal stricture, or peptic stricture, is a narrowing or tightening of the esophagus that causes swallowing difficulties.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of esophageal strictures include heartburn, bitter or acid taste in the mouth, chok ...
s are usually benign and typically develop after a person has had reflux
Reflux is a technique involving the condensation of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. It is used in industrial and laboratory distillations. It is also used in chemistry to supply energy to reactions ...
for many years. Other strictures may include esophageal web
Esophageal webs are thin membranes occurring anywhere along the esophagus.
Presentation
Its main symptoms are pain and difficulty in swallowing (dysphagia).
Esophageal webs are thin membranes of normal esophageal tissue consisting of mucosa and ...
s (which can also be congenital) and damage to the esophagus by radiotherapy, corrosive ingestion, or eosinophilic esophagitis. A Schatzki ring
A Schatzki ring or Schatzki–Gary ring is a narrowing of the lower esophagus that can cause difficulty swallowing (dysphagia). The narrowing is caused by a ring of mucosal tissue (which lines the esophagus) or muscular tissue. A Schatzki ring is ...
is fibrosis at the gastro-esophageal junction. Strictures may also develop in chronic anemia
Anemia or anaemia (British English) is a blood disorder in which the blood has a reduced ability to carry oxygen due to a lower than normal number of red blood cells, or a reduction in the amount of hemoglobin. When anemia comes on slowly, th ...
, and Plummer-Vinson syndrome.
Two of the most common congenital
A birth defect, also known as a congenital disorder, is an abnormal condition that is present at birth regardless of its cause. Birth defects may result in disabilities that may be physical, intellectual, or developmental. The disabilities can ...
malformations affecting the esophagus are an esophageal atresia Esophageal can refer to:
* The esophagus
* Esophageal arteries
* Esophageal glands
* Esophageal cancer
Esophageal cancer is cancer arising from the esophagus—the food pipe that runs between the throat and the stomach. Symptoms often include ...
where the esophagus ends in a blind sac instead of connecting to the stomach; and an esophageal fistula – an abnormal connection between the esophagus and the trachea. Both of these conditions usually occur together. These are found in about 1 in 3500 births. Half of these cases may be part of a syndrome
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek language, Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a sy ...
where other abnormalities are also present, particularly of the heart
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide t ...
or limb
Limb may refer to:
Science and technology
*Limb (anatomy), an appendage of a human or animal
*Limb, a large or main branch of a tree
*Limb, in astronomy, the curved edge of the apparent disk of a celestial body, e.g. lunar limb
*Limb, in botany, ...
s. The other cases occur singly.
Imaging
 An
An X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
of swallowed barium may be used to reveal the size and shape of the esophagus, and the presence of any masses. The esophagus may also be imaged using a flexible camera inserted into the esophagus, in a procedure called an endoscopy
An endoscopy is a procedure used in medicine to look inside the body. The endoscopy procedure uses an endoscope to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike many other medical imaging techniques, endoscopes are insert ...
. If an endoscopy is used on the stomach, the camera will also have to pass through the esophagus. During an endoscopy, a biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiologist. The process involves extraction of sample cells or tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a dise ...
may be taken. If cancer of the esophagus is being investigated, other methods, including a CT scan, may also be used.
History
The word ''esophagus'' (British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
: ''oesophagus''), comes from the el, οἰσοφάγος () meaning ''gullet''. It derives from two roots ''(eosin)'' to carry and () to eat. The use of the word oesophagus, has been documented in anatomical literature since at least the time of Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of ...
, who noted that "the oesophagus ... receives the greatest amount of what we consume." Its existence in other animals and its relationship with the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
was documented by the Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
naturalist Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
(AD23–AD79), and the peristaltic
Peristalsis ( , ) is a radially symmetrical contraction and relaxation of muscles that propagate in a wave down a tube, in an anterograde direction. Peristalsis is progression of coordinated contraction of involuntary circular muscles, which ...
contractions of the esophagus have been documented since at least the time of Galen
Aelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus ( el, Κλαύδιος Γαληνός; September 129 – c. AD 216), often Anglicized as Galen () or Galen of Pergamon, was a Greek physician, surgeon and philosopher in the Roman Empire. Considered to be one of ...
.
The first attempt at surgery on the esophagus focused in the neck, and was conducted in dogs by Theodore Billroth
Christian Albert Theodor Billroth (26 April 18296 February 1894) was a German surgeon and amateur musician.
As a surgeon, he is generally regarded as the founding father of modern abdominal surgery. As a musician, he was a close friend and con ...
in 1871. In 1877 Czerny carried out surgery in people. By 1908, an operation had been performed by Voeckler to remove the esophagus, and in 1933 the first surgical removal of parts of the lower esophagus, (to control esophageal cancer), had been conducted.
The Nissen fundoplication
A Nissen fundoplication, or laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication when performed via laparoscopic surgery, is a surgical procedure to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and hiatal hernia. In GERD, it is usually performed when medical thera ...
, in which the stomach is wrapped around the lower esophageal sphincter to stimulate its function and control reflux
Reflux is a technique involving the condensation of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. It is used in industrial and laboratory distillations. It is also used in chemistry to supply energy to reactions ...
, was first conducted by Rudolph Nissen
Rudolph Nissen (sometimes spelled Rudolf Nissen) (September 5, 1896 – January 22, 1981) was a surgeon who chaired surgery departments in Turkey, the United States and Switzerland. The Nissen fundoplication, a surgical procedure for the treatment ...
in 1955.
Other animals
Vertebrates
Intetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct theraps ...
s, the pharynx is much shorter, and the esophagus correspondingly longer, than in fish. In the majority of vertebrates, the esophagus is simply a connecting tube, but in some birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweigh ...
, which regurgitate components to feed their young, it is extended towards the lower end to form a crop
A crop is a plant that can be grown and harvested extensively for profit or subsistence. When the plants of the same kind are cultivated at one place on a large scale, it is called a crop. Most crops are cultivated in agriculture or hydroponic ...
for storing food before it enters the true stomach. In ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are ungulate, hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally ...
s, animals with four stomachs, a groove called the ''sulcus reticuli'' is often found in the esophagus, allowing milk to drain directly into the hind stomach, the abomasum
The abomasum, also known as the maw,The Cham ...
. In the horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million y ...
the esophagus is about in length, and carries food to the stomach. A muscular ring, called the cardiac sphincter, connects the stomach to the esophagus. This sphincter is very well developed in horses. This and the oblique angle at which the esophagus connects to the stomach explains why horses cannot vomit
Vomiting (also known as emesis and throwing up) is the involuntary, forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose.
Vomiting can be the result of ailments like food poisoning, gastroenterit ...
. The esophagus is also the area of the digestive tract where horses may have the condition known as choke.
The esophagus of snake
Snakes are elongated, Limbless vertebrate, limbless, carnivore, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales. Ma ...
s is remarkable for the distension it undergoes when swallowing prey.
In most fish, the esophagus is extremely short, primarily due to the length of the pharynx (which is associated with the gill
A gill () is a respiratory organ that many aquatic organisms use to extract dissolved oxygen from water and to excrete carbon dioxide. The gills of some species, such as hermit crabs, have adapted to allow respiration on land provided they are ...
s). However, some fish, including lamprey
Lampreys (sometimes inaccurately called lamprey eels) are an ancient extant lineage of jawless fish of the order Petromyzontiformes , placed in the superclass Cyclostomata. The adult lamprey may be characterized by a toothed, funnel-like s ...
s, chimaeras, and lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, i ...
, have no true stomach, so that the esophagus effectively runs from the pharynx directly to the intestine, and is therefore somewhat longer.
In many vertebrates, the esophagus is lined by stratified squamous epithelium without glands. In fish, the esophagus is often lined with columnar epithelium, and in amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
s, shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachimo ...
s and rays
Ray may refer to:
Fish
* Ray (fish), any cartilaginous fish of the superorder Batoidea
* Ray (fish fin anatomy), a bony or horny spine on a fin
Science and mathematics
* Ray (geometry), half of a line proceeding from an initial point
* Ray (gra ...
, the esophageal epithelium is ciliated, helping to wash food along, in addition to the action of muscular peristalsis. In addition, in the bat
Bats are mammals of the order Chiroptera.''cheir'', "hand" and πτερόν''pteron'', "wing". With their forelimbs adapted as wings, they are the only mammals capable of true and sustained flight. Bats are more agile in flight than most ...
''Plecotus auritus
''Plecotus'' is a genus of vesper bat, commonly called long-eared bats. They are found throughout Eurasia and northern Africa. Many species in the genus have only been described and recognized in recent years.
Species
Genus ''Plecotus'' – lon ...
'', fish and some amphibians, glands secreting pepsinogen or hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
have been found.
The muscle of the esophagus in many mammals is initially striated but then becomes smooth muscle in the caudal third or so. In canines
Canine may refer to:
Zoology and anatomy
* a dog-like Canid animal in the subfamily Caninae
** ''Canis'', a genus including dogs, wolves, coyotes, and jackals
** Dog, the domestic dog
* Canine tooth, in mammalian oral anatomy
People with the surn ...
and ruminant
Ruminants (suborder Ruminantia) are ungulate, hoofed herbivorous grazing or browsing mammals that are able to acquire nutrients from plant-based food by Enteric fermentation, fermenting it in a specialized stomach prior to digestion, principally ...
s, however, it is entirely striated to allow regurgitation to feed young (canines) or regurgitation to chew cud (ruminants). It is entirely smooth muscle in amphibians, reptiles and birds.
Contrary to popular belief, an adult human body
The human body is the structure of a Human, human being. It is composed of many different types of Cell (biology), cells that together create Tissue (biology), tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the life, viabi ...
would not be able to pass through the esophagus of a whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully aquatic placental marine mammals. As an informal and colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea, i.e. all cetaceans apart from dolphins and ...
, which generally measures less than in diameter, although in larger baleen whales it may be up to when fully distended.
Invertebrates
A structure with the same name is often found in invertebrates, including molluscs andarthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arth ...
s, connecting the oral cavity with the stomach. In terms of the digestive system of snails and slugs, the mouth opens into an esophagus, which connects to the stomach. Because of torsion
Torsion may refer to:
Science
* Torsion (mechanics), the twisting of an object due to an applied torque
* Torsion of spacetime, the field used in Einstein–Cartan theory and
** Alternatives to general relativity
* Torsion angle, in chemistry
Bi ...
, which is the rotation of the main body of the animal during larval development, the esophagus usually passes around the stomach, and opens into its back, furthest from the mouth. In species that have undergone de-torsion, however, the esophagus may open into the anterior of the stomach, which is the reverse of the usual gastropod arrangement. There is an extensive rostrum
Rostrum may refer to:
* Any kind of a platform for a speaker:
**dais
**pulpit
* Rostrum (anatomy), a beak, or anatomical structure resembling a beak, as in the mouthparts of many sucking insects
* Rostrum (ship), a form of bow on naval ships
* Ros ...
at the front of the esophagus in all carnivorous snails and slugs. In the freshwater snail species ''Tarebia granifera
''Tarebia granifera'', common name (in the aquarium industry) the quilted melania, is a species of freshwater snail with an operculum, an aquatic gastropod mollusk in the family Thiaridae. MolluscaBase eds. (2020). MolluscaBase. Tarebia gr ...
'', the brood pouch is above the esophagus.Appleton C. C., Forbes A. T.& Demetriades N. T. (2009)"The occurrence, bionomics and potential impacts of the invasive freshwater snail ''Tarebia granifera'' (Lamarck, 1822) (Gastropoda: Thiaridae) in South Africa"
. ''Zoologische Mededelingen'' 83. In the
cephalopod
A cephalopod is any member of the molluscan class Cephalopoda (Greek plural , ; "head-feet") such as a squid, octopus, cuttlefish, or nautilus. These exclusively marine animals are characterized by bilateral body symmetry, a prominent head ...
s, the brain often surrounds the esophagus.
See also
References
External links
{{Authority control Digestive system Thorax (human anatomy) Organs (anatomy) Human head and neck Abdomen