|
Odynophagia
Odynophagia is pain when swallowing. The pain may be felt in the mouth or throat and can occur with or without difficulty swallowing. The pain may be described as an ache, burning sensation, or occasionally a stabbing pain that radiates to the back. Odynophagia often results in inadvertent weight loss. The term is from ''-'' 'pain' and ' 'to eat'. Causes Odynophagia may have environmental or behavioral causes, such as: * Very hot or cold food and drinks (termed cryodynophagia when associated with cold drinks, classically in the setting of cryoglobulinaemia). * Taking certain medications * Using drugs, tobacco, or alcohol * Trauma or injury to the mouth, throat, or tongue It can also be caused by certain medical conditions, such as: * Ulcers * Abscesses * Upper respiratory tract infections * Inflammation or infection of the mouth, tongue, or throat ( esophagitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils in the upper part of the throat. It can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysphagia
Dysphagia is difficulty in swallowing. Although classified under " symptoms and signs" in ICD-10, in some contexts it is classified as a condition in its own right. It may be a sensation that suggests difficulty in the passage of solids or liquids from the mouth to the stomach, a lack of pharyngeal sensation or various other inadequacies of the swallowing mechanism. Dysphagia is distinguished from other symptoms including odynophagia, which is defined as painful swallowing, and globus, which is the sensation of a lump in the throat. A person can have dysphagia without odynophagia (dysfunction without pain), odynophagia without dysphagia (pain without dysfunction) or both together. A psychogenic dysphagia is known as phagophobia. Classification Dysphagia is classified into the following major types: # Oropharyngeal dysphagia # Esophageal and obstructive dysphagia # Neuromuscular symptom complexes # Functional dysphagia is defined in some patients as having no organic caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parapharyngeal Abscess
A parapharyngeal abscess is a deep neck space abscess of the parapharyngeal space (or pharyngomaxillary space), which is lateral to the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle and medial to the masseter muscle. This space is divided by the styloid process into anterior and posterior compartments. The posterior compartment contains the carotid artery, internal jugular vein, and many nerves. Signs and symptoms Symptoms include fever, sore throat, painful swallowing, and swelling in the neck. An anterior space abscess can cause lockjaw (spasm of jaw muscle), and hard mass formation along the angle of the mandible, with medial bulging of the tonsil and lateral pharyngeal wall. A posterior space abscess causes swelling in the posterior pharyngeal wall, and lockjaw is minimal. Other structures within the carotid sheath may be involved, causing rigors, high fever, bacteremia, neurologic deficit, or a massive haemorrhage caused by carotid artery rupture. Cause Infection can occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
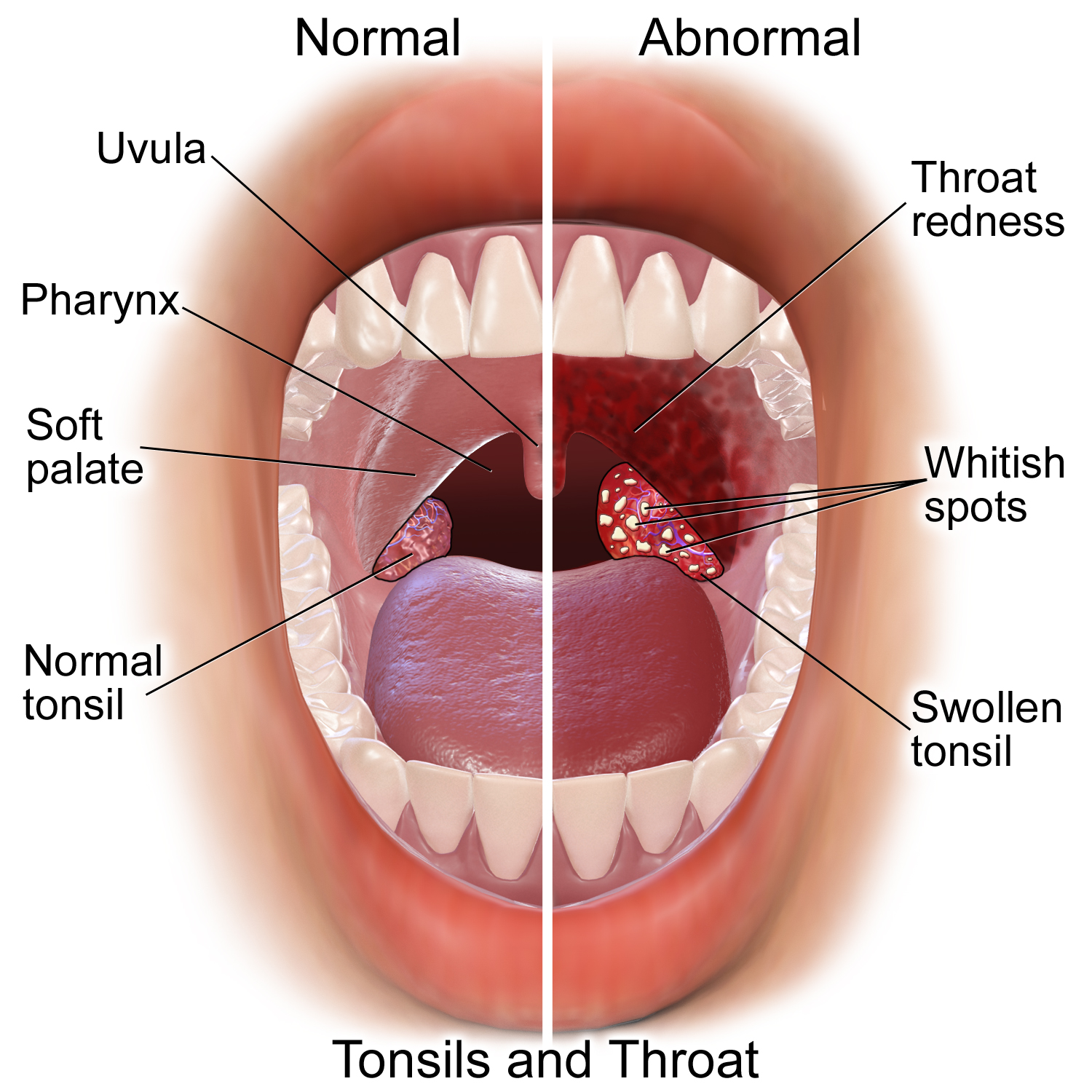
Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis is inflammation of the tonsils in the upper part of the throat. It can be acute or chronic. Acute tonsillitis typically has a rapid onset. Symptoms may include sore throat, fever, enlargement of the tonsils, trouble swallowing, and enlarged lymph nodes around the neck. Complications include peritonsillar abscess. Tonsillitis is most commonly caused by a viral infection and about 5% to 40% of cases are caused by a bacterial infection.Lang 2009p. 2083./ref> When caused by the bacterium group A streptococcus, it is classed as streptococcal tonsillitis also referred to as ''strep throat''. Rarely bacteria such as ''Neisseria gonorrhoeae'', ''Corynebacterium diphtheriae'', or '' Haemophilus influenzae'' may be the cause. Typically the infection is spread between people through the air. A scoring system, such as the Centor score, may help separate possible causes. Confirmation may be by a throat swab or rapid strep test. Treatment efforts involve improving sympt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology (from the Greek gastḗr- “belly”, -énteron “intestine”, and -logía "study of") is the branch of medicine focused on the digestive system and its disorders. The digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes referred to as the ''GI tract,'' which includes the esophagus, stomach, small intestine and large intestine as well as the accessory organs of digestion which includes the pancreas, gallbladder, and liver. The digestive system functions to move material through the GI tract via peristalsis, break down that material via digestion, absorb nutrients for use throughout the body, and remove waste from the body via defecation. Physicians who specialize in the medical specialty of gastroenterology are called gastroenterologists or sometimes ''GI doctors''. Some of the most common conditions managed by gastroenterologists include gastroesophageal reflux disease, gastrointestinal bleeding, irritable bowel syndrome, irritable bow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mouth Ulcer
A mouth ulcer (aphtha) is an ulcer that occurs on the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. Mouth ulcers are very common, occurring in association with many diseases and by many different mechanisms, but usually there is no serious underlying cause. Rarely, a mouth ulcer that does not heal may be a sign of oral cancer. These ulcers may form individually or multiple ulcers may appear at once (i.e., a "crop" of ulcers). Once formed, an ulcer may be maintained by inflammation and/or secondary infection. The two most common causes of oral ulceration are local trauma (e.g. rubbing from a sharp edge on a broken filling or braces, biting one's lip, etc.) and aphthous stomatitis ("canker sores"), a condition characterized by recurrent formation of oral ulcers for largely unknown reasons. Mouth ulcers often cause pain and discomfort and may alter the person's choice of food while healing occurs (e.g. avoiding acidic, sugary, salty or spicy foods and beverages). Definition An ulcer (; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
An upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) is an illness caused by an acute infection, which involves the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, sinuses, pharynx, larynx or trachea. This commonly includes nasal obstruction, sore throat, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, otitis media, and the common cold. Most infections are viral in nature, and in other instances, the cause is bacterial. URTIs can also be fungal or helminthic in origin, but these are less common. In 2015, 17.2 billion cases of URTIs are estimated to have occurred. As of 2014, they caused about 3,000 deaths, down from 4,000 in 1990. Signs and symptoms In uncomplicated colds, coughing and nasal discharge may persist for 14 days or more even after other symptoms have resolved. Acute URTIs include rhinitis, pharyngitis/tonsillitis, and laryngitis often referred to as a common cold, and their complications: sinusitis, ear infection, and sometimes bronchitis (though bronchi are generally c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esophagitis
Esophagitis, also spelled oesophagitis, is a disease characterized by inflammation of the esophagus. The esophagus is a tube composed of a mucosal lining, and longitudinal and circular smooth muscle fibers. It connects the pharynx to the stomach; swallowed food and liquids normally pass through it. Esophagitis can be asymptomatic; or can cause epigastric and/or substernal burning pain, especially when lying down or straining; and can make swallowing difficult (dysphagia). The most common cause of esophagitis is the reverse flow of acid from the stomach into the lower esophagus: gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). __TOC__ Signs and symptoms The symptoms of esophagitis include: * Heartburn – a burning sensation in the lower mid-chest * Nausea * Dysphagia – swallowing is painful, with difficulty passing or inability to pass food through the esophagus * Vomiting (emesis) * Abdominal pain * Cough Complications If the disease remains untreated, it can cause scarring and disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pharyngitis
Pharyngitis is inflammation of the back of the throat, known as the pharynx. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, difficulty swallowing, swollen lymph nodes, and a hoarse voice. Symptoms usually last 3–5 days, but can be longer depending on cause. Complications can include sinusitis and acute otitis media. Pharyngitis is a type of upper respiratory tract infection. Most cases are caused by a viral infection. Strep throat, a bacterial infection, is the cause in about 25% of children and 10% of adults. Uncommon causes include other bacteria such as ''gonococcus'', fungi, irritants such as smoke, allergies, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Specific testing is not recommended in people who have clear symptoms of a viral infection, such as a cold. Otherwise, a rapid antigen detection test or throat swab is recommended. PCR testing is becoming commonly used as it is as good as taking a throat swab bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epiglottitis
Epiglottitis is the inflammation of the epiglottis—the flap at the base of the tongue that prevents food entering the trachea (windpipe). Symptoms are usually rapid in onset and include trouble swallowing which can result in drooling, changes to the voice, fever, and an increased breathing rate. As the epiglottis is in the upper airway, swelling can interfere with breathing. People may lean forward in an effort to open the airway. As the condition worsens, stridor and bluish skin may occur. Epiglottitis was historically mostly caused by infection by '' H. influenzae type b'' (commonly referred to as "Hib"). With vaccination, it is now more often caused by other bacteria, most commonly ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', ''Streptococcus pyogenes'', or ''Staphylococcus aureus''. Predisposing factors include burns and trauma to the area. The most accurate way to make the diagnosis is to look directly at the epiglottis. X-rays of the neck from the side may show a "thumbprint sign" but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Disorder
An immune disorder is a dysfunction of the immune system. These disorders can be characterized in several different ways: * By the component(s) of the immune system affected * By whether the immune system is overactive or underactive * By whether the condition is congenital or acquired According to the International Union of Immunological Societies, more than 150 primary immunodeficiency diseases (PIDs) have been characterized. However, the number of acquired immunodeficiencies exceeds the number of PIDs. It has been suggested that most people have at least one primary immunodeficiency. Due to redundancies in the immune system, though, many of these are never detected. Autoimmune diseases An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a normal body part. There are at least 80 types of autoimmune diseases. Nearly any body part can be involved. Common symptoms include low-grade fever and feeling tired. Often symptoms come and go. List of some a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Cancer
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, is cancer of the lining of the lips, mouth, or upper throat. In the mouth, it most commonly starts as a painless white patch, that thickens, develops red patches, an ulcer, and continues to grow. When on the lips, it commonly looks like a persistent crusting ulcer that does not heal, and slowly grows. Other symptoms may include difficult or painful swallowing, new lumps or bumps in the neck, a swelling in the mouth, or a feeling of numbness in the mouth or lips. Risk factors include tobacco and alcohol use. Those who use both alcohol and tobacco have a 15 times greater risk of oral cancer than those who use neither. Other risk factors include HPV infection, chewing paan, and sun exposure on the lower lip. Oral cancer is a subgroup of head and neck cancers. Diagnosis is made by biopsy of the concerning area, followed by investigation with CT scan, MRI, PET scan, and examination to determine if it has spread to distant parts of the body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Throat Cancer
Head and neck cancer develops from tissues in the lip and oral cavity (mouth), larynx (throat), salivary glands, nose, sinuses or the skin of the face. The most common types of head and neck cancers occur in the lip, mouth, and larynx. Symptoms predominantly include a sore that does not heal or a change in the voice. Some may experience a sore throat that does not go away. In those with advanced disease, there may be unusual bleeding, facial pain, numbness or swelling, and visible lumps on the outside of the neck or oral cavity. Given the location of these cancers, trouble breathing may also be present. The majority of head and neck cancer is caused by the use of alcohol or tobacco, including smokeless tobacco, with increasing cases linked to the human papillomavirus (HPV). Other risk factors include Epstein-Barr virus, betel quid, radiation exposure, certain workplace exposures. About 90% are pathologically classified as squamous cell cancers. The diagnosis is confirmed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)


_squamous_cell_carcinoma_histopathology.jpg)