|
Lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, including the presence of lobed fins with a well-developed internal skeleton. Lungfish represent the closest living relatives of the tetrapods. Today there are only six known species of lungfish, living in Africa, South America, and Australia. The fossil record shows that lungfish were abundant since the Triassic. While vicariance would suggest this represents an ancient distribution limited to the Mesozoic supercontinent Gondwana, the fossil record suggests advanced lungfish had a widespread freshwater distribution and the current distribution of modern lungfish species reflects extinction of many lineages subsequent to the breakup of Pangaea, Gondwana and Laurasia. Lungfish have historically been referred to as salamanderfish, but this t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
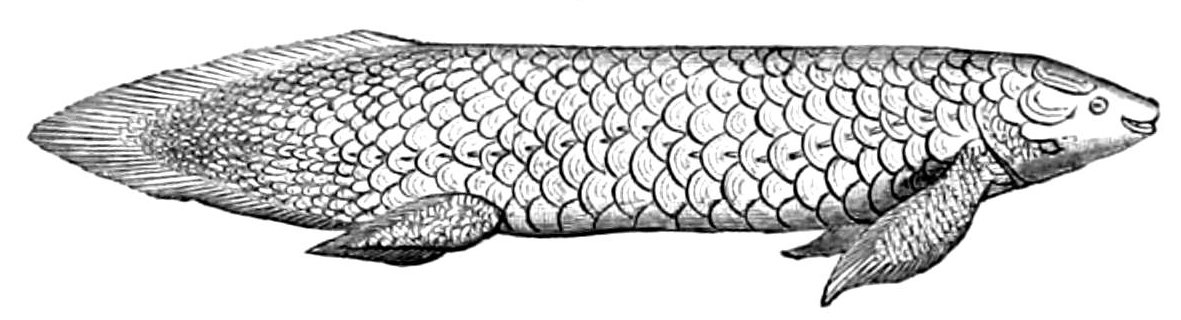
Queensland Lungfish
The Australian lungfish (''Neoceratodus forsteri''), also known as the Queensland lungfish, Burnett salmon and barramunda, is the only surviving member of the family Neoceratodontidae. It is one of only six extant lungfish species in the world. Endemic to Australia, the Neoceratodontidae are an ancient family belonging to the class Sarcopterygii, or lobe-finned fishes. Fossil records of this group date back 380 million years, around the time when the higher vertebrate classes were beginning to evolve. Fossils of lungfish almost identical to this species have been uncovered in northern New South Wales, indicating that ''Neoceratodus'' has remained virtually unchanged for well over 100 million years, making it a living fossil and one of the oldest living vertebrate genera on the planet. It is one of six extant representatives of the ancient air-breathing Dipnoi (lungfishes) that flourished during the Devonian period (about 413–365 million years ago) and is the outgroup to all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcopterygii
Sarcopterygii (; ) — sometimes considered synonymous with Crossopterygii () — is a taxon (traditionally a class or subclass) of the bony fishes known as the lobe-finned fishes. The group Tetrapoda, a mostly terrestrial superclass including amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (with mammals being the only extant group), evolved from certain sarcopterygians; under a cladistic view, tetrapods are themselves considered a subgroup within Sarcopterygii. The known extant non-tetrapod sarcopterygians include two species of coelacanths and six species of lungfishes. Characteristics Early lobe-finned fishes are bony fish with fleshy, lobed, paired fins, which are joined to the body by a single bone. The fins of lobe-finned fishes differ from those of all other fish in that each is borne on a fleshy, lobelike, scaly stalk extending from the body. The scales of sarcopterygians are true scaloids, consisting of lamellar bone sur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmine
Cosmine is a spongy, bony material that makes up the dentine-like layers in the scales of the lobe-finned fishes of the class Sarcopterygii. Fish scales that include layers of cosmine are known as cosmoid scales. Description As traditionally described, cosmine consists of a layer of dentine covered by a continuous sheet of enamel. Pulp cavities, which secrete dentine tubules, are surrounded by a complex polygonal network of 'pore cavities' which pierce the overlying enamel layer, giving cosmine its characteristic dotted appearance. The pulp cavities and pore chambers are connected by a complex, reticulated pore canal network which continues into a layer of vascular bone beneath the dentine. The exact configuration of the pore canal network and shape of the pore chambers differs between various taxa, although the general organization into a single layer of enamel over dentine with pore canals with vascular bone underneath remains consistent, at least within the Sarcopterygii. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoceratodontidae
Neoceratodontidae is a family of lungfish containing the extant Australian lungfish and several extinct genera. It and Lepidosirenidae represent the only lungfish families still extant. Fossils from this family are first known from Triassic-aged sediments in Kyrgyzstan, but phylogenetic evidence indicates that it first originated near the end of the Carboniferous period. Despite their name, they are in fact basal to the related genus ''Ceratodus ''Ceratodus'' (from el, κέρας , 'horn' and el, ὀδούς 'tooth') was a wide-ranging genus of extinct lungfish. Fossil evidence dates back to the Early Triassic. A wide range of fossil species from different time periods have been found ...'' (and thus diverged before ''Ceratodus'' did), rather than vice versa. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q10296196 Lungfish Extant Middle Triassic first appearances Fish families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteichthyes
Osteichthyes (), popularly referred to as the bony fish, is a diverse superclass of fish that have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. They can be contrasted with the Chondrichthyes, which have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. The vast majority of fish are members of Osteichthyes, which is an extremely diverse and abundant group consisting of 45 orders, and over 435 families and 28,000 species. It is the largest class of vertebrates in existence today. The group Osteichthyes is divided into the ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii) and lobe-finned fish (Sarcopterygii). The oldest known fossils of bony fish are about 425 million years old, which are also transitional fossils, showing a tooth pattern that is in between the tooth rows of sharks and bony fishes. Osteichthyes can be compared to Euteleostomi. In paleontology the terms are synonymous. In ichthyology the difference is that Euteleostomi presents a cladistic view which includes the terrestrial tetrap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct therapsids and all extant mammals). Tetrapods evolved from a clade of primitive semiaquatic animals known as the Tetrapodomorpha which, in turn, evolved from ancient lobe-finned fish (sarcopterygians) around 390 million years ago in the Middle Devonian period; their forms were transitional between lobe-finned fishes and true four-limbed tetrapods. Limbed vertebrates (tetrapods in the broad sense of the word) are first known from Middle Devonian trackways, and body fossils became common near the end of the Late Devonian but these were all aquatic. The first crown-tetrapods (last common ancestors of extant tetrapods capable of terrestrial locomotion) appeared by the very early Carboniferous, 350 million years ago. The specific aquatic ancestors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ray-finned Fish
Actinopterygii (; ), members of which are known as ray-finned fishes, is a class of bony fish. They comprise over 50% of living vertebrate species. The ray-finned fishes are so called because their fins are webs of skin supported by bony or horny spines (rays), as opposed to the fleshy, lobed fins that characterize the class Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish). These actinopterygian fin rays attach directly to the proximal or basal skeletal elements, the radials, which represent the link or connection between these fins and the internal skeleton (e.g., pelvic and pectoral girdles). By species count, actinopterygians dominate the vertebrates, and they constitute nearly 99% of the over 30,000 species of fish. They are ubiquitous throughout freshwater and marine environments from the deep sea to the highest mountain streams. Extant species can range in size from ''Paedocypris'', at , to the massive ocean sunfish, at , and the long-bodied oarfish, at . The vast majority of Actinoptery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidosirenidae
Lepidosirenidae is a family of lungfish containing the genera ''Lepidosiren'' (the South American lungfish) and ''Protopterus'' (the African lungfish). Both genera were formerly thought to represent the distinct families Lepidosirenidae and Protopteridae within the order Lepidosireniformes, but a 2017 study analyzing all post-Devonian lungfish taxa found them to be better classified as different genera in a single family. Taxonomy Their closest living relatives are of the family Neoceratodontidae, or the Australian lungfish, with both families being members of the suborder Ceratodontoidei. However, their closest relatives in general are of the extinct Gnathorhizidae, which forms a sister group to Lepidosirenidae. The clade containing both families forms a sister group to the extinct family Ptychoceratodontidae. The earliest fossils of the family come from the Late Cretaceous (Campanian-Maastrichtian) of Sudan, but phylogenetic evidence indicates the two genera split at the ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceratodontoidei
Ceratodontoidei is a suborder of lungfish that is defined as "the clade including all taxa more closely related to ''Lepidosiren'', '' Neoceratodus'' and '' Gnathorhiza'' than to '' Uronemus'', '' Conchopoma'' and ''Sagenodus''". Members of this suborder are known as ceratodontoids. The only presently extant lungfish in the families Neoceratodontidae and Lepidosirenidae belong to this suborder. Taxonomy The suborder was formerly defined as being within the order Ceratodontiformes and including the families Neoceratodontidae and Ceratodontidae, as they were formerly thought to be closely related to one another. However, phylogenetic analyses indicate that this classification is paraphyletic, as Ceratodontidae was found to be a sister group to a clade containing Lepidosirenidae, which was formerly classified as Lepidosireniformes, a distinct order from Ceratodontiformes. Due to this, Lepidosireniformes and Ceratodontiformes were redefined as families within the order Dipnoi, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order (taxonomic Rank)
Order ( la, ordo) is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pangaea, drifting farther north after the split and finally broke apart with the opening of the North Atlantic Ocean c. 56 Mya. The name is a portmanteau of Laurentia and Asia. Laurentia, Avalonia, Baltica, and a series of smaller terranes, collided in the Caledonian orogeny c. 400 Ma to form Laurussia (also known as Euramerica, or the Old Red Sandstone Continent). Laurussia then collided with Gondwana to form Pangaea. Kazakhstania and Siberia were then added to Pangaea 290–300 Ma to form Laurasia. Laurasia finally became an independent continental mass when Pangaea broke up into Gondwana and Laurasia. Terminology and origin of the concept Laurentia, the Palaeozoic core of North America and continental fragments that now make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homology (biology)
In biology, homology is similarity due to shared ancestry between a pair of structures or genes in different taxa. A common example of homologous structures is the forelimbs of vertebrates, where the wings of bats and birds, the arms of primates, the front flippers of whales and the forelegs of four-legged vertebrates like dogs and crocodiles are all derived from the same ancestral tetrapod structure. Evolutionary biology explains homologous structures adapted to different purposes as the result of descent with modification from a common ancestor. The term was first applied to biology in a non-evolutionary context by the anatomist Richard Owen in 1843. Homology was later explained by Charles Darwin's theory of evolution in 1859, but had been observed before this, from Aristotle onwards, and it was explicitly analysed by Pierre Belon in 1555. In developmental biology, organs that developed in the embryo in the same manner and from similar origins, such as from matching p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |