Worsley Boys' Club on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Worsley () is a village in the
 Worsley later fell under the control of the Anglo-Saxons, who controlled much of the area around Manchester and who also defeated the British at the Battle of Chester in AD 615. Edward the Elder rebuilt the fortifications at Manchester, and in AD 924 captured all the land between the rivers Mersey and Irwell, making it
Worsley later fell under the control of the Anglo-Saxons, who controlled much of the area around Manchester and who also defeated the British at the Battle of Chester in AD 615. Edward the Elder rebuilt the fortifications at Manchester, and in AD 924 captured all the land between the rivers Mersey and Irwell, making it
City of Salford
The City of Salford () is a metropolitan borough within Greater Manchester, England. The borough is named after its main settlement, Salford. The borough covers the towns of Eccles, Swinton,
Walkden and Pendlebury, as well as the villages ...
, Greater Manchester, England, which in 2014 had a population of 10,090. It lies along Worsley Brook, west of Manchester.
Within the boundaries of the historic county of Lancashire, there is evidence of Roman and Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
activity, including two Roman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
s. The completion in 1761 of the Bridgewater Canal allowed Worsley to expand from a small village of cottage industries
The putting-out system is a means of subcontracting work. Historically, it was also known as the workshop system and the domestic system. In putting-out, work is contracted by a central agent to subcontractors who complete the project via remote w ...
to an important town based upon cotton manufacture, iron-working, brick-making and extensive coal mining. Later expansion came after the First
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
and Second World Wars, when large urban estates were built.
Worsley Delph is a scheduled monument and a significant part of the town's historic centre is now a conservation area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural, ecological or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the ena ...
.
History
Toponymy
Worsley is first mentioned in a Pipe roll of 1195–96 as ''Werkesleia'', in the claim of a Hugh Putrell to a part of the fee of two knights in nearby Barton-upon-Irwell and Worsley. There are many variations on the name; Werkesleia, 1195; Wyrkedele, 1212; Whurkedeleye, c. 1220; Worketley, 1254; Worcotesley, Workedesle, 1276; Wrkesley, Wrkedeley, Workedeley, 1292; Wyrkeslegh, Workesley, 1301; Worsley, 1444; and "Workdisley alias Workesley alias Worseley", 1581. The spelling of the name in early documents, suggests aSaxon
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
origin. ''Ge-Weore'', the Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
form of the name, means "the cleared place which was cultivated or settled." The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle
The ''Anglo-Saxon Chronicle'' is a collection of annals in Old English, chronicling the history of the Anglo-Saxons. The original manuscript of the ''Chronicle'' was created late in the 9th century, probably in Wessex, during the reign of Alf ...
'' contain no references to Worsley.
Early history
TwoRoman road
Roman roads ( la, viae Romanae ; singular: ; meaning "Roman way") were physical infrastructure vital to the maintenance and development of the Roman state, and were built from about 300 BC through the expansion and consolidation of the Roman Re ...
s run through the area. Connecting Mamucium (Manchester) with Coccium (Wigan), one passes through Worsley near Drywood, and over Mosley Common. The present-day A6 road follows part of the course of another Roman road, which passes through the northern part of the area near Walkden and Little Hulton. In 1947 a hoard of 550 Roman coins was found near a quarry in Boothstown, dated to between AD 250 and 275, and in 1958 the head of a man was found on Worsley Moss. Named "Worsley man
Chat Moss is a large area of peat bog that makes up part of the City of Salford, Metropolitan Borough of Wigan and Trafford in Greater Manchester, England. It also makes up part of Metropolitan Borough of St Helens in Merseyside and Warrington ...
", and originally thought to be no more than 20 years old, upon the discovery of Lindow Man
Lindow Man, also known as Lindow II and (in jest) as Pete Marsh, is the preserved bog body of a man discovered in a peat bog at Lindow Moss near Wilmslow in Cheshire, North West England. The remains were found on 1 August 1984 by commer ...
it was re-examined and dated to approximately the 2nd century AD, in the Romano-British period.
 Worsley later fell under the control of the Anglo-Saxons, who controlled much of the area around Manchester and who also defeated the British at the Battle of Chester in AD 615. Edward the Elder rebuilt the fortifications at Manchester, and in AD 924 captured all the land between the rivers Mersey and Irwell, making it
Worsley later fell under the control of the Anglo-Saxons, who controlled much of the area around Manchester and who also defeated the British at the Battle of Chester in AD 615. Edward the Elder rebuilt the fortifications at Manchester, and in AD 924 captured all the land between the rivers Mersey and Irwell, making it demesne
A demesne ( ) or domain was all the land retained and managed by a lord of the manor under the feudal system for his own use, occupation, or support. This distinguished it from land sub-enfeoffed by him to others as sub-tenants. The concept or ...
in the Kingdom of Wessex. During the Middle Ages the area was covered with forests and marshlands. Thinly populated by craftsmen and serf
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which developed ...
s, Worsley grew as a settlement adjoining an ancient corn mill, close to the location of the present-day Worsley Road Bridge. Most farms throughout Lancashire were small with their tenants dependent upon secondary employment, however in 1719 a John Kay of Worsley had five stirks, two bulls, 17 cows, "young cattle upon the moors", and a "cow at hire", all valued at £97 5s. Marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, clays, and silt. When hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
Marl makes up the lower part o ...
was commonly used as a fertiliser, and is recorded in use in 1719. Wheeler's ''Manchester: Its Political, Social and Commercial History, Ancient and Modern'' (1836) states that about one-fifth of the land around Worsley, Astley and Tyldesley was in tillage, lower on average than the surrounding areas.
Bridgewater estates
Worsley was, originally, the largestmanor
Manor may refer to:
Land ownership
*Manorialism or "manor system", the method of land ownership (or "tenure") in parts of medieval Europe, notably England
*Lord of the manor, the owner of an agreed area of land (or "manor") under manorialism
*Man ...
of the seven ancient manors of the Bridgewater Estates. It was created by William I and held for him by the Barton family in thegnage, and for them by a Norman
Norman or Normans may refer to:
Ethnic and cultural identity
* The Normans, a people partly descended from Norse Vikings who settled in the territory of Normandy in France in the 10th and 11th centuries
** People or things connected with the Norm ...
knight named Elias, who fought in the crusades. On his death in Rhodes, the manor remained with Elias' son, whose family had by that time adopted the name of the village as its family name. On 23 June 1311 a substantial part of the Manor of Hulton was granted to the Worsleys. The family held both manors until the late 14th century, whereon they passed to the Massey family of Tatton, and then in the 16th century to the Brereton family of Malpas, Cheshire.. The Brereton family added the Manor of Bedford (a small area of land to the west of Worsley) to the estate. Richard Brereton later married Dorothy Egerton, and upon his death the estates passed into the Egerton family.
In 1617 John Egerton, son of Sir Thomas Egerton, became Earl of Bridgewater. The Egerton family was descended from Sir Richard Egerton of Ridley, Cheshire
Ridley is a civil parish in the unitary authority of Cheshire East and the ceremonial county of Cheshire, England, which lies to the north east of Malpas and to the west of Nantwich. The parish is largely rural with scattered farms and buildings ...
. His illegitimate son, Thomas Egerton, was a prominent lawyer who served as Master of the Rolls from 1594 to 1603, and Lord Keeper of the Great Seal from 1596 to 1617 and also as Lord High Chancellor of England
The lord chancellor, formally the lord high chancellor of Great Britain, is the highest-ranking traditional minister among the Great Officers of State in Scotland and England in the United Kingdom, nominally outranking the prime minister. Th ...
. John Egerton succeeded to Worsley in 1639, and died in 1649. He was succeeded by the second and third Earls of Bridgewater. The title of Duke of Bridgewater was first given to Scroop Egerton in 1720. He devised a navigation system for Worsley which was not carried out. His son, the third Duke of Bridgewater Francis Egerton, was to build the Bridgewater Canal.
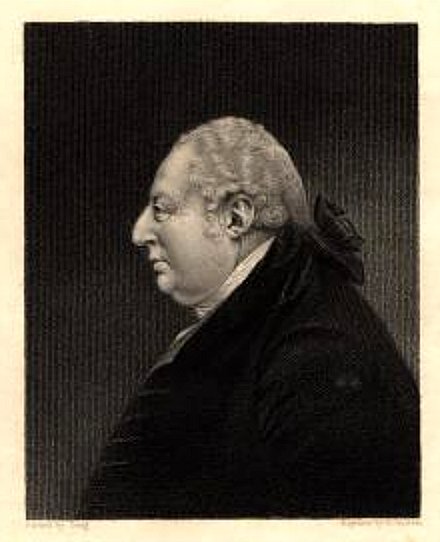
The Duke purchased the Manor of Pemberton (near Wigan) in 1758, the Manor of Hindley in 1765, and the Manor of Cadishead in 1776. Upon his death in 1803 he was succeeded by George Leveson-Gower, 1st Duke of Sutherland. In 1833 the estate was inherited by Gower's son, Francis Leveson-Gower who changed his surname to Egerton, and in 1846 became the Earl of Ellesmere. In 1836 he purchased the Manor of Tyldesley. He is recorded as saying that he found Worsley to be "a God-forsaken place, full of drunken, rude people with deplorable morals".
Worsley New Hall
Worsley New Hall is a former mansion and gardens by the Bridgewater Canal in Worsley, Greater Manchester, England, west of Manchester. The gardens were renovated by the Royal Horticultural Society and opened as RHS Garden Bridgewater in 2021.
...
, designed by Edward Blore
Edward Blore (13 September 1787 – 4 September 1879) was a 19th-century English landscape and architectural artist, architect and antiquary.
Early career
He was born in Derby, the son of the antiquarian writer Thomas Blore.
Blore's backg ...
, was built in 1846 for Francis Egerton the First Earl of Ellesmere. The plans are held at the Victoria and Albert Museum. Queen Victoria visited the hall in 1851 and 1857; Edward VII and Queen Alexandra visited when Edward was Prince of Wales in 1869, and on 6 July 1909. The hall was used as a hospital in World War I and in World War II housed Dunkirk
Dunkirk (french: Dunkerque ; vls, label=French Flemish, Duunkerke; nl, Duinkerke(n) ; , ;) is a commune in the department of Nord in northern France.Lancashire Fusiliers. In 1943 the hall was badly damaged by fire and demolished in 1949.
 Coal has been mined around Worsley from as long ago as 1376, originally in
Coal has been mined around Worsley from as long ago as 1376, originally in
 Under the
Under the

 From the 11th century, Worsley was a township in the Eccles parish of the
From the 11th century, Worsley was a township in the Eccles parish of the 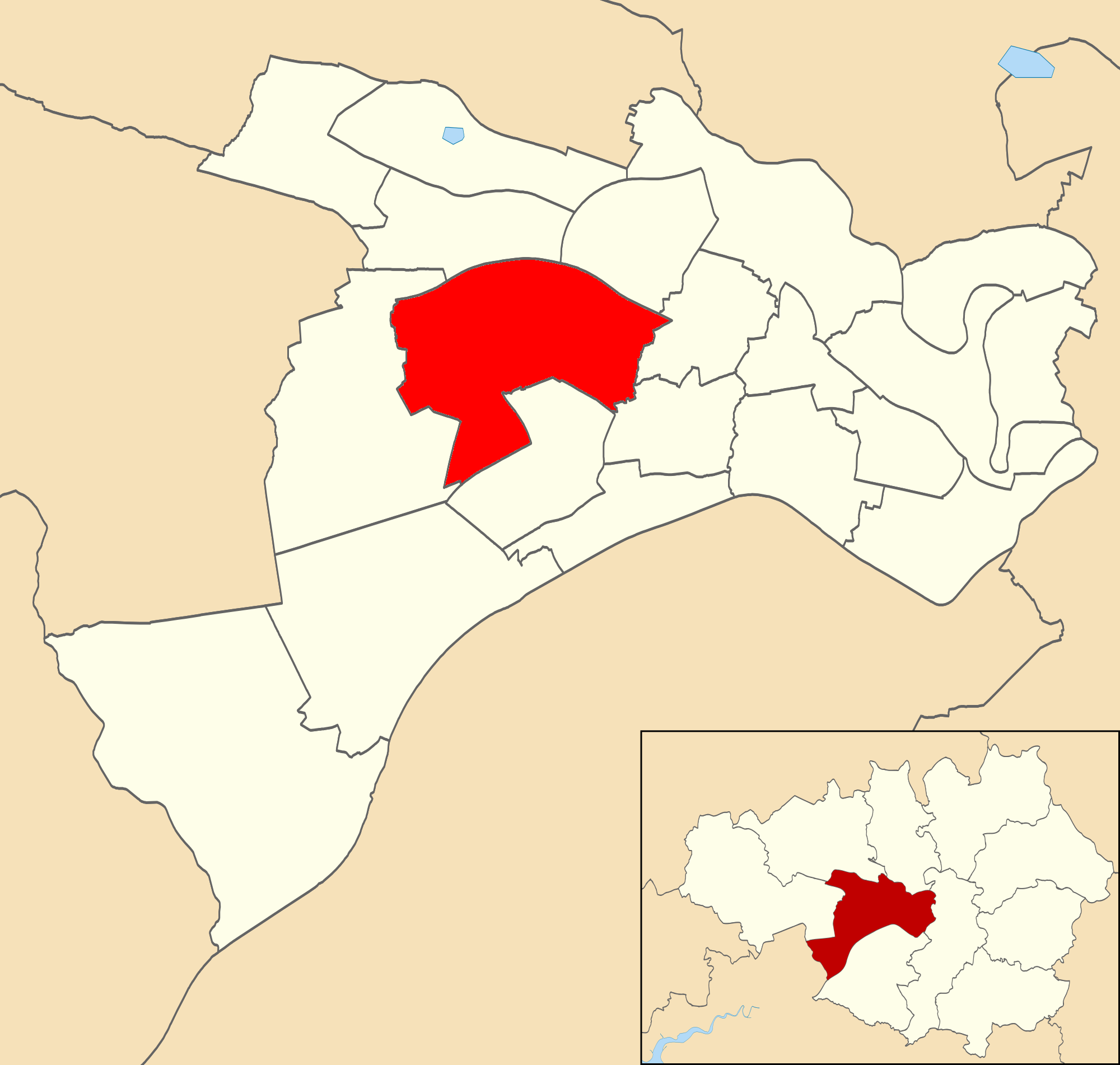 In 1955 Swinton and Pendlebury Borough gained a small part of Worsley Urban District, and under the
In 1955 Swinton and Pendlebury Borough gained a small part of Worsley Urban District, and under the
 Worsley Village was in 1969 designated as a
Worsley Village was in 1969 designated as a
 Following an Act of Parliament of 1861, in 1864 the Eccles, Tyldesley and Wigan branch line was opened by the
Following an Act of Parliament of 1861, in 1864 the Eccles, Tyldesley and Wigan branch line was opened by the
 Ellenbrook Chapel, the first church in Worsley was built in 1209 by the Worsley family. Methodism was first practised in the area in 1784, by the notable preacher Matthew Mayer. Later services were held in various locations around the area, and in 1801 a Methodist chapel was built along Barton Road. The foundation stone for
Ellenbrook Chapel, the first church in Worsley was built in 1209 by the Worsley family. Methodism was first practised in the area in 1784, by the notable preacher Matthew Mayer. Later services were held in various locations around the area, and in 1801 a Methodist chapel was built along Barton Road. The foundation stone for
Eccles Parish Townships 1800Duke of Bridgewater Archive from the University of Salford site History of Worsley
{{Good article Towns in Greater Manchester Unparished areas in Greater Manchester Irwell Valley Geography of Salford
Industrial Revolution
 Coal has been mined around Worsley from as long ago as 1376, originally in
Coal has been mined around Worsley from as long ago as 1376, originally in bell pit
A bell pit is a primitive method of mining coal, iron ore, or other minerals lying near the surface.
Operation
A shaft is sunk to reach the mineral which is excavated by miners, transported to the surface by a winch, and removed by means of a b ...
s. The coal seams in the area tend to be fairly thin, slanting downwards from north to south, and so deeper mining became necessary during the 17th century.
With the onset of the Industrial Revolution and the growing use of steam power
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
, there was a rapid increase in the demand for coal. The Duke's mines were among those supplying the surrounding districts but transport was both inefficient and expensive, and the mines also suffered from persistent flooding. His solution to these problems was to build a canal from Worsley to Salford, and an underground canal into the mines from Worsley Delph. The canal boats would carry at a time, – more than ten times the amount of cargo per horse that was possible with a cart. The Duke and his estate manager obtained an Act of Parliament empowering them to begin construction on a planned route directly to Salford, avoiding the River Irwell
The River Irwell ( ) is a tributary of the River Mersey in north west England. It rises at Irwell Springs on Deerplay Moor, approximately north of Bacup and flows southwards for to meet the Mersey near Irlam. The Irwell marks the boundary be ...
.
James Brindley was brought in for his technical expertise and suggested varying the route of the proposed canal away from Salford and across the Irwell into Manchester. A second Act was secured for this variance, which included an aqueduct to cross the Irwell. This was built relatively quickly for the time; work commenced in September 1760 and the first boat crossed on 17 July 1761. The canal opened in 1761 and along with the stone aqueduct at Barton-upon-Irwell, was considered a major engineering achievement. One writer said that when finished, it "will be the most extraordanary thing in the kingdom, if not in Europe. The boats in some places are to go underground, and in other places over a navigable river, without communicating with its waters ..."
Worsley Delph, now a scheduled monument, was the entrance to the Duke's underground mines. Two entrances, built years apart, allowed access to the Starvationer boats, the largest of which could carry of coal. The entrances allow access to of underground canal on four levels, linked by inclined planes.
The burgeoning village became a hub of commercial activity. The Duke employed craftsmen to service a wide range of industries including boat-making, plastering, blacksmithing and mining. A local quarry supplied limestone, for which a kiln was constructed at the junction of Barton Road (B5211) and Stableford Road. A quarry at the Delph supplied building materials for the region, including the stone used to construct Brindley's aqueduct. To accommodate the workers needed for these industries the Duke built extra housing and cottages. In a diary entry of 1773, Josiah Wedgwood wrote of the area "We next visited Worsley which has the appearance of a considerable Seaport Town. His Grace has built some hundreds of houses, & is every year adding considerably to their number." Worsley Green became a thriving centre of industry.
With the death of the Duke in 1803, his estates were inherited by his nephew, George Leveson-Gower
Sir George Granville Leveson-Gower Order of the British Empire, KBE (19 May 1858 – 18 July 1951), was a British civil servant and Liberal Party (UK), Liberal politician from the Leveson-Gower family. He held political office as Comptroller of ...
, who later became the Duke of Sutherland
Duke of Sutherland is a title in the Peerage of the United Kingdom which was created by William IV in 1833 for George Leveson-Gower, 2nd Marquess of Stafford. A series of marriages to heiresses by members of the Leveson-Gower family made th ...
. The canal and coal estates were placed under the control of the Bridgewater Trust, and in 1833 the rest of the estates were inherited by the Duke of Sutherland's son, Francis Leveson-Gower who changed his surname to Egerton, and in 1846 became the Earl of Ellesmere. The mines ceased production in 1887, and with the expiration of the Bridgewater Trust in 1903 the village began to change; the Duke's warehouse and the works on what is now Worsley Green were demolished. Worsley Brook was culverted, and a memorial fountain to the Duke was built from the bricks of the works' chimney.
Although much of the industry that dominated Worsley was in decline, in 1937 Sir Montague Maurice Burton opened the Burtonville Clothing Works along the East Lancashire Road
The A580 (officially the Liverpool–East Lancashire Road, colloquially the East Lancs Road) is the United Kingdom's first purpose-built inter-city highway. The road, which remains a primary A road, was officially opened by King George V on 18 ...
. Built in the Art Deco style, in 1938 the factory employed 3,000 people.
Modern history
 Under the
Under the Housing Act 1919
The Housing, Town Planning, &c. Act 1919 (c 35) was an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It was also known as the Addison Act after Minister of Health, Christopher Addison, who was Minister for Housing. The Act was passed to allow the ...
, large overspill estates were built by the council for veterans of the First World War, but a larger change to the area came after the end of the Second World War, when the City of Salford
The City of Salford () is a metropolitan borough within Greater Manchester, England. The borough is named after its main settlement, Salford. The borough covers the towns of Eccles, Swinton,
Walkden and Pendlebury, as well as the villages ...
was forced to rehouse many of its inhabitants. With little land left, 4,518 new houses were built in the urban district
Urban district may refer to:
* District
* Urban area
* Quarter (urban subdivision)
* Neighbourhood
Specific subdivisions in some countries:
* Urban districts of Denmark
* Urban districts of Germany
* Urban district (Great Britain and Ireland) (hist ...
by the Worsley Project. 18,000 people were rehoused under the scheme, which included new facilities, shops and schools. Another housing estate was built during the 1970s to the north of Worsley Green.
In 1944, during the Second World War, a flying bomb landed on a house near Worsley Dam. An Anti Aircraft Operations Room (AAOR) was built in the 1950s. Although unused the building still exists, in wooded land to the west of the town, on the site of the former Worsley New Hall.
Governance

 From the 11th century, Worsley was a township in the Eccles parish of the
From the 11th century, Worsley was a township in the Eccles parish of the hundred of Salford
The Salford Hundred (also known as Salfordshire) was one of the subdivisions of the historic county of Lancashire, in Northern England (see:Hundred (county division). Its name alludes to its judicial centre being the township of Salford (the s ...
, and county of Lancashire. Worsley was originally in Eccles ecclesiastical parish, and also in Barton-upon-Irwell Poor Law Union. The Swinton area of the township was in 1867 included in the Swinton Local Board of Health, which from 1869 became the Swinton and Pendlebury
Swinton may refer to:
Places England
* Swinton, Greater Manchester
* Swinton, Harrogate, near Masham, North Yorkshire
** Swinton Estate, including Swinton Park
* Swinton, Ryedale, near Malton, North Yorkshire
* Swinton, South Yorkshire
No ...
Local Board of Health. In 1892 a small part of the township of Worsley was included in the Borough of Eccles. In 1894, under the Local Government Act 1894, Worsley Urban District
Urban district may refer to:
* District
* Urban area
* Quarter (urban subdivision)
* Neighbourhood
Specific subdivisions in some countries:
* Urban districts of Denmark
* Urban districts of Germany
* Urban district (Great Britain and Ireland) (hist ...
was created. A part of the township then within the area of the Swinton and Pendlebury Local Board of Health was formed into Swinton township, becoming part of Swinton and Pendlebury Urban District
Urban district may refer to:
* District
* Urban area
* Quarter (urban subdivision)
* Neighbourhood
Specific subdivisions in some countries:
* Urban districts of Denmark
* Urban districts of Germany
* Urban district (Great Britain and Ireland) (hist ...
. In 1907 two small detached parts of Worsley civil parish, then inside Swinton civil parish, were added to Swinton civil parish. A town hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
was opened on 22 June 1911. Worsley Urban District gained of land from Barton-upon-Irwell Civil Parish in 1921, and in 1933 gained the area of Little Hulton Urban District. Parts were added to Eccles Borough and Irlam Urban District
Irlam is a suburb in the City of Salford, Greater Manchester, England. In 2011, it had a population of 19,933. It lies on flat ground on the south side of the M62 motorway and the north bank of the Manchester Ship Canal, southwest of Salfo ...
.  In 1955 Swinton and Pendlebury Borough gained a small part of Worsley Urban District, and under the
In 1955 Swinton and Pendlebury Borough gained a small part of Worsley Urban District, and under the Local Government Act 1972
The Local Government Act 1972 (c. 70) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed local government in England and Wales on 1 April 1974. It was one of the most significant Acts of Parliament to be passed by the Heath Gov ...
, in 1974 Worsley's Urban District status was abolished, becoming part of Salford Metropolitan District.
Following its 2006 review of parliamentary representation in Greater Manchester, the Boundary Commission for England recommended the creation of a modified Worsley constituency, incorporating a part of Eccles. The new constituency is called Worsley and Eccles South
Worsley and Eccles South is a county constituency represented in the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. The seat is currently held by Barbara Keeley MP of the Labour Party. It elects one Member of Parliament (MP) by the ...
. Until the 2010 general election, Worsley was represented in the House of Commons by Barbara Keeley
Barbara Mary Keeley (born 26 March 1952) is a British Labour Party politician who has served as the Member of Parliament (MP) for Worsley and Eccles South, previously Worsley, since 2005 United Kingdom general election, 2005. A member of the ...
, Labour Party member for the Worsley constituency. After the election, Keeley became the MP for Worsley and Eccles South.
Geography
At (53.5000°, −2.3833°), Worsley stands about above sea level. Sheltered at the foot of a middle coal measure running approximately northwest and southeast across the area, the village lies along the course of Worsley Brook, which cuts through the ridge. The ridge also forms part of the northern edge of the Irwell Valley. The area is bordered on the north by theEast Lancashire Road
The A580 (officially the Liverpool–East Lancashire Road, colloquially the East Lancs Road) is the United Kingdom's first purpose-built inter-city highway. The road, which remains a primary A road, was officially opened by King George V on 18 ...
, and on the south by the Liverpool and Manchester Railway and part of the Bridgewater Canal. The larger towns of Swinton and Eccles lie to the east and southeast respectively, and to the west the area is largely bordered by Chat Moss, open fields, and forest. The M60 and M62 motorways cut directly through the area.
The underlying measures of coal have proved important for the development of the area; it was around Worsley Delph that the settlement first began to grow. Parts of the area are within an indicated floodplain. Worsley's climate is generally temperate, like the rest of Greater Manchester. The mean highest and lowest temperatures ( and ) are slightly above the national average, while the annual rainfall () and average hours of sunshine (1394.5 hours) are respectively above and below the national averages.
Demography
According to the Office for National Statistics, at the time of the United Kingdom Census 2001, the ward of Worsley had a population of 9,833, of which 4,801 were male and 5,032 female. It is the fifth least populous ward in Salford, and the third least densely populated. The ward has a higher proportion of married couples with and without children than Salford as a whole. Of those over 16 years old, 1,929 were single (never married) and 4,267 married. Worsley's 4,102 households included 632 married couples without children, 818 with dependent children and 356 with non-dependent children. There were 249 lone-parent households with children. 642 households were occupied by pensioners living alone. Of those aged 16–74, 1,428 had no academic qualifications, 1,078 had attained a level one qualification, 183 children aged between 16–17 and 242 people aged 18–74 were in full-time education. Worsley ward has the lowest levels of unemployment in Salford, in April 2006 0.9% of the economically active population were unemployment benefit claimants, comparing well to Salford as a whole where the figure is 3.7%. The area is considered to be one of the more affluent parts of Salford. At 12.6 reported crimes per thousand population, the crime rate in Worsley is lower on average than Salford, which stands at 163.1 per thousand population.Economy
One of Worsley's early industries was weaving. Acottage industry
The putting-out system is a means of subcontracting work. Historically, it was also known as the workshop system and the domestic system. In putting-out, work is contracted by a central agent to subcontractors who complete the project via remote ...
, cotton would be spun on spinning wheels and hand-operated loom
A loom is a device used to weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but th ...
s in people's homes to produce cloth. Merchants would then purchase this cloth, selling it at the Bridgewater Hotel, then known as the Old Grapes Inn.
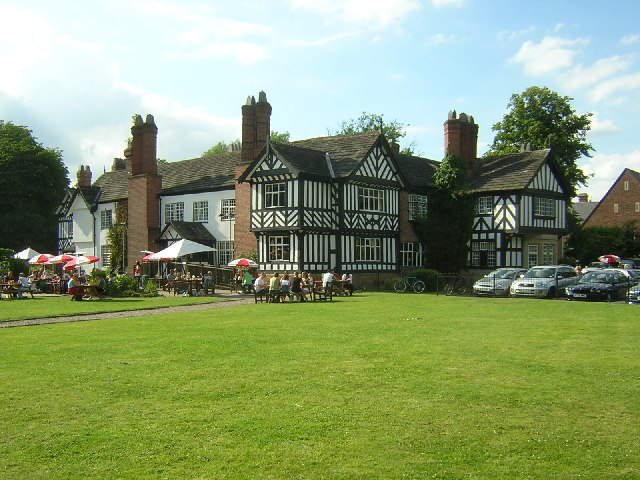
Worsley now has little industry, and is in the main a tourist destination and commuter town. The area has two large hotels; a Novotel and a Marriott. Worsley Old Hall is now a public house and restaurant in the Brunning and Price chain, part of the Restaurant Group.
Landmarks
 Worsley Village was in 1969 designated as a
Worsley Village was in 1969 designated as a conservation area
Protected areas or conservation areas are locations which receive protection because of their recognized natural, ecological or cultural values. There are several kinds of protected areas, which vary by level of protection depending on the ena ...
by the former Lancashire County Council. Bisected by the A572 Worsley Road, the area covered about of land and included 40 listed buildings, such as the Packet House, a telephone kiosk, and the Delph sluice gates, but this list has since increased to 48 listed buildings. Much of the area around the canal and Worsley Delph was restored and landscaped between 1966 and 1967 by the Worsley Civic Trust and the local council, ready for a visit by Elizabeth II on 17 May 1968. As the canal passes through Worsley, iron oxide
Iron oxides are chemical compounds composed of iron and oxygen. Several iron oxides are recognized. All are black magnetic solids. Often they are non-stoichiometric. Oxyhydroxides are a related class of compounds, perhaps the best known of whic ...
from the mines has, for many years, stained the water bright orange. The removal of this colouration is the subject of a £2.5 million remedial scheme, which was completed in 2004. This has not been successful and as of 2017 much of the canal centered on the Delph is still bright orange.
Wardley Hall Wardley may refer to:
Organisations
*Wardley (company), a fish food manufacturer
*Wardley, a former merchant banking division of The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation
The Hongkong and Shanghai Banking Corporation Limited (), commonl ...
is an early medieval manor house and a Grade I listed building in Wardley. The current hall dates from around 1500 but was extensively rebuilt in the 19th and 20th centuries. Worsley Old Hall
Worsley Old Hall is a public house and restaurant in Worsley, Greater Manchester, England. It is recorded in the National Heritage List for England as a designated Grade II listed building.
History
The present building on the site dates fr ...
is a Grade II listed building near Walkden Road. The Post Medieval
Post-medieval archaeology is a term used in Europe to describe the study of the material past over the last 500 years. The field is also referred to as historical archaeology, a term originating in North America, and common in countries impacted ...
building is said to have been moated, but no signs of the moat now remain.
Parts of Worsley are currently being considered as World Heritage Sites. The area includes Worsley Delph (itself a scheduled monument), parts of Worsley Green, and the Bridgewater Canal.
In 2015, the Royal Horticultural Society announced plans for a restoration of the garden at Worsley New Hall
Worsley New Hall is a former mansion and gardens by the Bridgewater Canal in Worsley, Greater Manchester, England, west of Manchester. The gardens were renovated by the Royal Horticultural Society and opened as RHS Garden Bridgewater in 2021.
...
, to open in 2019 under the name RHS Garden Bridgewater
RHS Garden Bridgewater is the Royal Horticultural Society's fifth public display garden. It is located in the village of Worsley in Salford, Greater Manchester, England.
Gardens
Bridgewater Gardens has been created in of the former Worsley Ne ...
.
Transport
 Following an Act of Parliament of 1861, in 1864 the Eccles, Tyldesley and Wigan branch line was opened by the
Following an Act of Parliament of 1861, in 1864 the Eccles, Tyldesley and Wigan branch line was opened by the London and North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the L&NWR was the largest joint stock company in the United Kingdom.
In 1923, it became a constituent of the Lo ...
, along with a station at Worsley which required the demolition of six cottages. The first sod had been cut by the Earl of Ellesmere. An additional branch line to Bolton was opened in 1870, branching from the Tyldesley Loopline
The Tyldesley Loopline was part of the London and North Western Railway's Manchester and Wigan Railway line from Eccles to the junction west of Tyldesley station and its continuance south west via Bedford Leigh to Kenyon Junction on the Liver ...
line at Roe Green. A railway station at Monton Green was opened in 1887 to cater mainly for commuters into Manchester. The lines were important thoroughfares for the transport of coal in the area, including Mosley Common Colliery
Mosley Common Colliery was a coal mine originally owned by the Bridgewater Trustees operating on the Manchester Coalfield after 1866 in Mosley Common, Greater Manchester, then in the historic county of Lancashire, England. The colliery eventual ...
. Both lines were closed under the Beeching Axe
The Beeching cuts (also Beeching Axe) was a plan to increase the efficiency of the nationalised railway system in Great Britain. The plan was outlined in two reports: ''The Reshaping of British Railways'' (1963) and ''The Development of the ...
in 1969, and have since been partially reclaimed by Salford City Council as recreational pathways.
Early public transport included the Farnworth horse-bus service, with a terminus at the nearby Stocks Hotel in 1885. An electric tram service was founded in 1903 by the South Lancashire Tramways
South Lancashire Tramways was a system of electric Tram, tramways in south Lancashire authorised by the South Lancashire Tramways Act of 1900. The ''South Lancashire Tramways Company'' was authorised by the act to build over of track to serve t ...
Company.
Education
One of the firstSunday school
A Sunday school is an educational institution, usually (but not always) Christian in character. Other religions including Buddhism, Islam, and Judaism have also organised Sunday schools in their temples and mosques, particularly in the West.
Su ...
s to be established in England may have been at Worsley. Built in the 1780s in a cottage close to the present-day courthouse, and founded by Thomas Bury (a colliery manager for the 3rd Duke) children were taught by a Luke Lowe, a cooper also in the Duke's employ. In 1785 a further three Sunday schools were established in the area, and by 1788 over 300 children were attending the four schools. Francis Egerton built a day school in 1838, which later became known as St Mark's School. This was demolished during construction of the M62 motorway, and replaced with a new school on Aviary Road, opened 19 October 1968.
The area of Worsley contains a number of primary schools, including (but not limited to) Christ the King RC Primary School, Hilton Lane Primary School and Mesne Lea Primary School. Secondary schools include Bridgewater School and The Lowry Academy.
Salford College
Pendleton Sixth Form College is a further education college in City of Salford, Salford, Greater Manchester. It offers A-levels and vocational courses. The college was established nearly half a century ago from Salford Grammar School for Boys, ...
has a campus in nearby Walkden (once within Worsley Urban District). The college's Worsley Campus, the Learning Resource and specialist Media Centre, caters for 16- to 18-year-olds, and provides access to 50 internet workstations, 15,000 books, and resources for e-learning. It also has a suite of hair and beauty salons, a performing arts theatre and a sports hall and fitness suite.
Religious sites
 Ellenbrook Chapel, the first church in Worsley was built in 1209 by the Worsley family. Methodism was first practised in the area in 1784, by the notable preacher Matthew Mayer. Later services were held in various locations around the area, and in 1801 a Methodist chapel was built along Barton Road. The foundation stone for
Ellenbrook Chapel, the first church in Worsley was built in 1209 by the Worsley family. Methodism was first practised in the area in 1784, by the notable preacher Matthew Mayer. Later services were held in various locations around the area, and in 1801 a Methodist chapel was built along Barton Road. The foundation stone for St Mark's Church St. Mark's Church, or variations such as St. Mark Church or with Saint spelled out, may mean:
Australia
* St Mark's Anglican Church, Warwick, Queensland
* St Mark's Church, Darling Point, New South Wales
* Old St Mark's Anglican Church, Slacks ...
was laid on 14 June 1844 by George Granville Francis Egerton, the son of Francis Egerton. Designed by the architect George Gilbert Scott
Sir George Gilbert Scott (13 July 1811 – 27 March 1878), known as Sir Gilbert Scott, was a prolific English Gothic Revival architect, chiefly associated with the design, building and renovation of churches and cathedrals, although he started ...
, the church was consecrated on 2 July 1846 by the Bishop of Chester, John Bird Sumner. The church tower is now home to the mechanism for the Bridgewater Clock from the Bridgewater workshops at Worsley Green. The clock strikes 13 times at 1 pm, originally so that workmen did not miss the end of their dinner break. Many gravestones in the churchyard were cut from rock sourced at Worsley Delph. Following a proposed hotel development in 1981 the area around the church and vicarage was designated a conservation area.
Sports
Worsley Golf Club was founded in 1894 on part of the Earl of Ellesmere's estate at Broadoak Park. The area has aclay pigeon shooting
Clay pigeon shooting, also known as clay target shooting, is a shooting sport involving shooting a firearm at special flying targets known as clay pigeons, or clay targets.
The terminology commonly used by clay shooters often relates to time ...
club, west of the M60. A racecourse development proposed on land near Boothstown was the subject of a public inquiry
A tribunal of inquiry is an official review of events or actions ordered by a government body. In many common law countries, such as the United Kingdom, Republic of Ireland, Ireland, Australia and Canada, such a public inquiry differs from a royal ...
and rejected by the local council after a sustained campaign by local councillors.
Public services
Home Office policing in Worsley is provided by the Greater Manchester Police. The nearest police station is at Little Hulton. Public transport is co-ordinated by Transport for Greater Manchester. Statutory emergency fire and rescue service is provided by the Greater Manchester Fire and Rescue Service.Notable people
Notable people from Worsley include the actress Helen Cherry, and television commentator Kenneth Wolstenholme. Statistician Harry Campion, who played a leading role in the development of official statistics after the Second World War, was born in Kearsley in May 1905 and brought up in Worsley. Arthur Thomas Doodson was a mathematician and oceanographer born in Boothstown in March 1890. FootballerRyan Giggs
Ryan Joseph Giggs (né Wilson; 29 November 1973) is a Welsh association football, football coach and former player. Regarded as one of the greatest players of his generation, Giggs played his List of one-club men in association football, entir ...
caused controversy in the mid-2000s when he bought a Victorian
Victorian or Victorians may refer to:
19th century
* Victorian era, British history during Queen Victoria's 19th-century reign
** Victorian architecture
** Victorian house
** Victorian decorative arts
** Victorian fashion
** Victorian literature ...
mansion on the outskirts of the village and demolished it to build a new house. The house was put on the market in 2019 with an asking price of £3.5m. Giggs' former team-mate David Beckham
David Robert Joseph Beckham (; born 2 May 1975) is an English former professional footballer, the current president and co-owner of Inter Miami CF and co-owner of Salford City. Known for his range of passing, crossing ability and bending fr ...
also owned a property in Worsley until 2014.
See also
*Listed buildings in Worsley
Worsley is a town in the City of Salford Metropolitan Borough, Greater Manchester, England. The town, together with the areas of Walkden and Little Hulton, contains 56 listed buildings that are recorded in the National Heritage List for Englan ...
* William Brereton (groom)
William Brereton (c. 1487 – 17 May 1536), the son of a Cheshire landowner, was a Groom of the Privy Chamber to Henry VIII. In May 1536, Brereton, the queen's brother George Boleyn, Viscount Rochford, Sir Henry Norris, Sir Francis West ...
References
Notes
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
Eccles Parish Townships 1800
{{Good article Towns in Greater Manchester Unparished areas in Greater Manchester Irwell Valley Geography of Salford