|
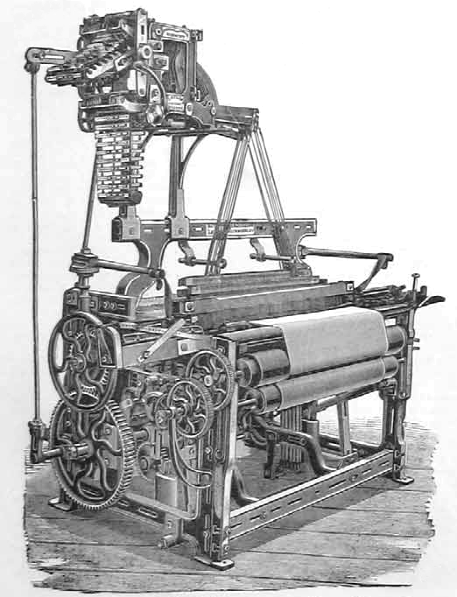
Loom
A loom is a device used to weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but the basic function is the same. Etymology and usage The word "loom" derives from the Old English ''geloma'', formed from ''ge-'' (perfective prefix) and ''loma'', a root of unknown origin; the whole word ''geloma'' meant a utensil, tool, or machine of any kind. In 1404 "lome" was used to mean a machine to enable weaving thread into cloth. By 1838 "loom" had gained the additional meaning of a machine for interlacing thread. Weaving Weaving is done by intersecting the longitudinal threads, the warp, i.e. "that which is thrown across", with the transverse threads, the weft, i.e. "that which is woven". The major components of the loom are the warp beam, heddles, harnesses or shafts (as few as two, four is common, sixteen not unheard of), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaving Shuttles
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. (''Weft'' is an Old English word meaning "that which is woven"; compare ''leave'' and ''left''.) The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth (warp threads with a weft thread winding between) can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms. The way the warp and filling threads interlace with each other is called the weave. The majority of woven products a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. (''Weft'' is an Old English word meaning "that which is woven"; compare ''leave'' and ''left''.) The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth (warp threads with a weft thread winding between) can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms. The way the warp and filling threads interlace with each other is called the weave. The majority of woven pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weaving Demonstrated On A Historic Loom In Leiden
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. (''Weft'' is an Old English word meaning "that which is woven"; compare ''leave'' and ''left''.) The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth (warp threads with a weft thread winding between) can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms. The way the warp and filling threads interlace with each other is called the weave. The majority of woven products ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
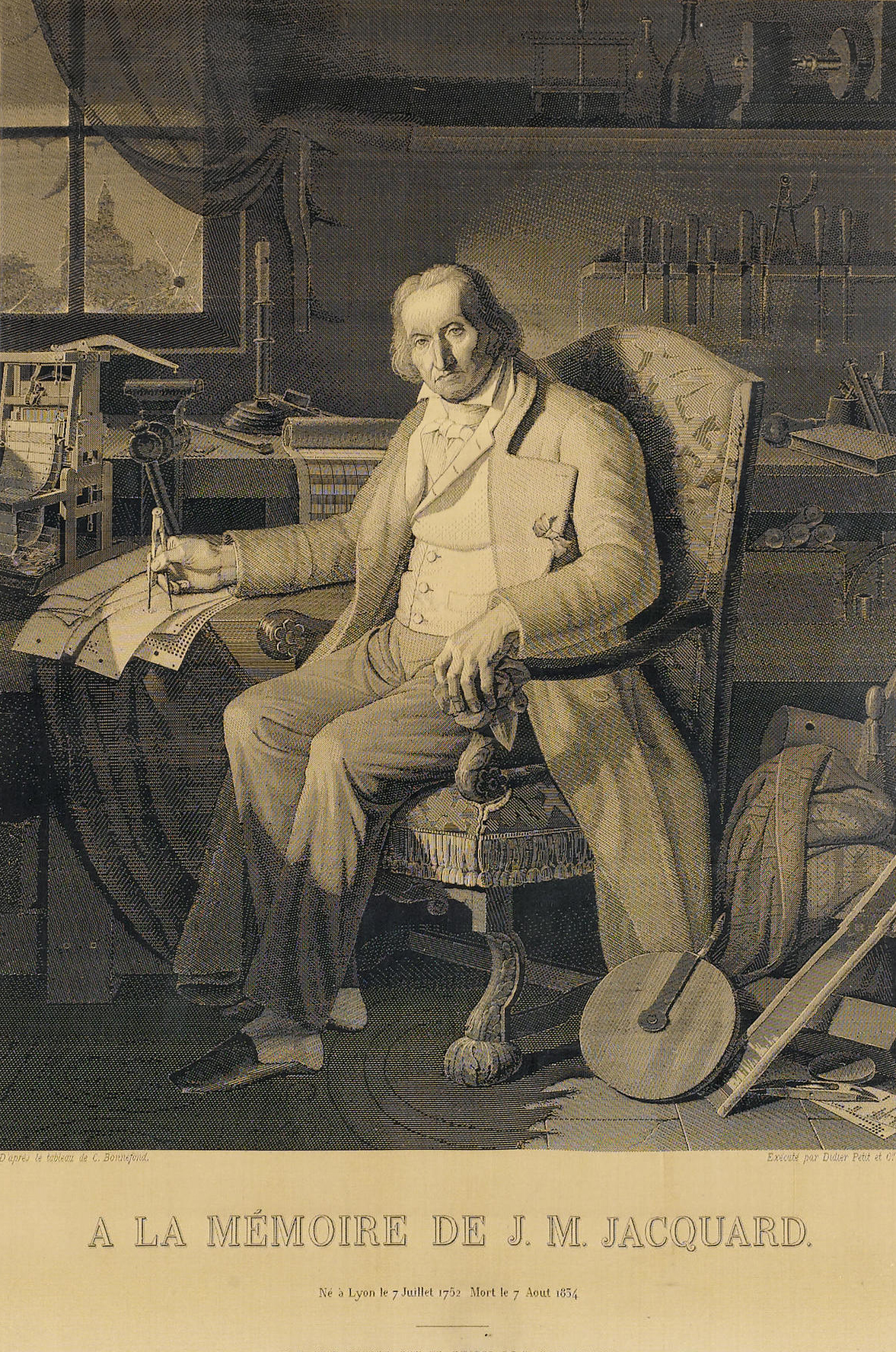
Jacquard Loom
The Jacquard machine () is a device fitted to a loom that simplifies the process of manufacturing textiles with such complex patterns as brocade, damask and matelassé. The resulting ensemble of the loom and Jacquard machine is then called a Jacquard loom. The machine was patented by Joseph Marie Jacquard in 1804, based on earlier inventions by the Frenchmen Basile Bouchon (1725), Jean Baptiste Falcon (1728), and Jacques Vaucanson (1740). The machine was controlled by a "chain of cards"; a number of punched cards laced together into a continuous sequence. Multiple rows of holes were punched on each card, with one complete card corresponding to one row of the design. Both the Jacquard process and the necessary loom attachment are named after their inventor. This mechanism is probably one of the most important weaving innovations as Jacquard shedding made possible the automatic production of unlimited varieties of complex pattern weaving. The term "Jacquard" is not specific or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dobby Loom
A dobby loom, or dobbie loom, is a type of floor loom that controls all the warp threads using a device called a dobby. Dobbies can produce more complex fabric designs than tappet looms but are limited in comparison to Jacquard looms. Dobby looms first appeared around 1843, roughly 40 years after Joseph Marie Jacquard invented the Jacquard device that can be mounted atop a loom to lift the individual heddles and warp threads. The word ''dobby'' is a corruption of "draw boy," which refers to the weaver's helpers who used to control the warp thread by pulling on draw threads. A dobby loom is an alternative to a treadle loom. Both are floor looms in which every warp thread on the loom is attached to a single shaft using a device called a heddle. A shaft is sometimes known as a harness. Each shaft controls a set of threads. Raising or lowering several shafts at the same time gives a huge variety of possible sheds (gaps) through which the shuttle containing the weft thread can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
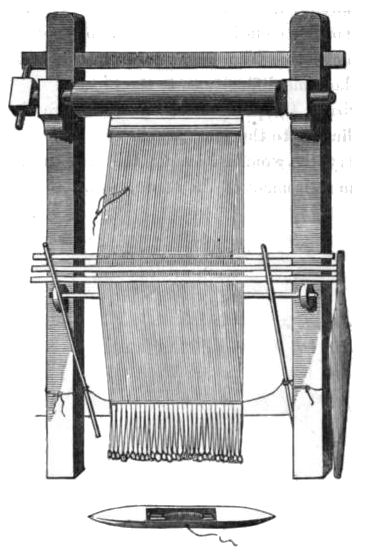
Warp-weighted Loom
The warp-weighted loom is a simple and ancient form of loom in which the warp yarns hang freely from a bar supported by upright poles which can be placed at a convenient slant against a wall. Bundles of warp threads are tied to hanging weights called loom weights which keep the threads taut. Evidence of the warp-weighted loom appears in the Neolithic period in central Europe. It is depicted in artifacts of Bronze Age Greece and was common throughout Europe, remaining in use in Scandinavia into modern times. Loom weights from the Bronze Age were excavated in Miletos, a Greek city in Anatolia. History The warp-weighted loom may have originated in the Neolithic period. The earliest evidence of warp-weighted looms comes from sites belonging to the Starčevo culture in modern Serbia and Hungary from late Neolithic sites in Switzerland. This loom was used in Ancient Greece, and spread north and west throughout Europe thereafter. It was extensively used in the north among Scandina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heddle
A heddle is an integral part of a loom. Each thread in the warp passes through a heddle,"Weaving." ''The Encyclopædia Britannica''. 11th ed. 1911. which is used to separate the warp threads for the passage of the weft."Heddle." ''The Oxford English Dictionary''. 2nd ed. 1989. The typical heddle is made of cord or wire and is suspended on a shaft of a loom. Each heddle has an eye in the center where the warp is threaded through. As there is one heddle for each thread of the warp, there can be near a thousand heddles used for fine or wide warps. A handwoven tea-towel will generally have between 300 and 400 warp threads and thus use that many heddles. In weaving, the warp threads are moved up or down by the shaft. This is achieved because each thread of the warp goes through a heddle on a shaft. When the shaft is raised the heddles are too, and thus the warp threads threaded through the heddles are raised. Heddles can be either equally or unequally distributed on the shafts, de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shed (weaving)
In weaving, the shed is the temporary separation between upper and lower warp yarns through which the weft is woven. The shed is created to make it easy to interlace the weft into the warp and thus create woven fabric. Most types of looms have some sort of device which separates some of the warp threads from the others. This separation is called the shed, and allows for a shuttle carrying the weft thread to move through the shed perpendicular to the warp threads. Which threads are raised and which are lowered are changed after each pass of the shuttle. The process of weaving can be simplified to a series of four steps: the shed is raised, the shuttle is passed through, the shed is closed, and the weft thread is beaten into place. These steps are then repeated, with a different set of threads being raised so as to interlace the warp and weft. The term ''shedding'' refers to the action of creating a shed. A ''shedding device'' is the device used to raise or open the shed. Creating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selvage
A selvage (US English) or selvedge (British English) is a "self-finished" edge of a piece of fabric which keeps it from unraveling and fraying. The term "self-finished" means that the edge does not require additional finishing work, such as hem or bias tape, to prevent fraying. In woven fabric, selvages are the edges that run parallel to the warp (the longitudinal threads that run the entire length of the fabric), and are created by the weft thread looping back at the end of each row. In knitted fabrics, selvages are the unfinished yet structurally sound edges that were neither cast on nor bound off. Historically, the term selvage applied only to loom woven fabric, though now can be applied to flat- knitted fabric. The terms ''selvage'' and ''selvedge'' are a corruption of "self-edge", and have been in use since the 16th century. In textiles Definition According to Hollen, Saddler & Langford, "A selvage is the self-edge of a fabric formed by the filling yarn when it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reed (weaving)
A reed is part of a weaving loom, and resembles a comb. It is used to separate and space the warp threads, to guide the shuttle's motion across the loom, and to push the weft threads into place."Reed." ''The Oxford English Dictionary''. 2nd ed. 1989.1911 Encyclopædia Britannica The reed is securely held by the beater, and consists of a frame with many vertical slits. Floor looms and mechanized looms both use a beater with a reed, whereas Inkle weaving and tablet weaving do not use reeds. History Modern reeds are made by placing flattened strips of wire (made of carbon or stainless steel) between two half round ribs of wood, and binding the whole together with tarred string. Historically, reeds were made of reed or split cane. The split cane was then bound between ribs of wood in the same manner as wire is now. In 1738, John Kay replaced split cane with flattened iron or brass wire, and the change was quickly adopted. To make a reed, wire is flattened to a uniform thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shuttle (weaving)
A shuttle is a tool designed to neatly and compactly store a holder that carries the thread of the weft yarn while weaving with a loom. Shuttles are thrown or passed back and forth through the shed, between the yarn threads of the warp in order to weave in the weft. The simplest shuttles, known as "stick shuttles", are made from a flat, narrow piece of wood with notches on the ends to hold the weft yarn. More complicated shuttles incorporate bobbins or pirns. In the United States, shuttles are often made of wood from the flowering dogwood, because it is hard, resists splintering, and can be polished to a very smooth finish. In the United Kingdom shuttles were usually made of boxwood, cornel, or persimmon. Flying shuttle Shuttles were originally passed back and forth by hand. However, John Kay invented a loom in 1733 that incorporated a flying shuttle. This shuttle could be thrown through the warp, which allowed much wider cloth to be woven much more quickly and made the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)
