Wales Administrative 1974 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the


 Wales has been inhabited by
Wales has been inhabited by
 The 400-year period following the collapse of Roman rule is the most difficult to interpret in the history of Wales. After the Roman departure in AD 410, much of the lowlands of Britain to the east and south-east was overrun by various Germanic peoples, commonly known as Anglo-Saxons. Some have theorized that the cultural dominance of the Anglo-Saxons was due to apartheid-like social conditions in which the Britons were at a disadvantage.
By AD 500 the land that would become Wales had divided into a number of kingdoms free from Anglo-Saxon rule. The kingdoms of
The 400-year period following the collapse of Roman rule is the most difficult to interpret in the history of Wales. After the Roman departure in AD 410, much of the lowlands of Britain to the east and south-east was overrun by various Germanic peoples, commonly known as Anglo-Saxons. Some have theorized that the cultural dominance of the Anglo-Saxons was due to apartheid-like social conditions in which the Britons were at a disadvantage.
By AD 500 the land that would become Wales had divided into a number of kingdoms free from Anglo-Saxon rule. The kingdoms of 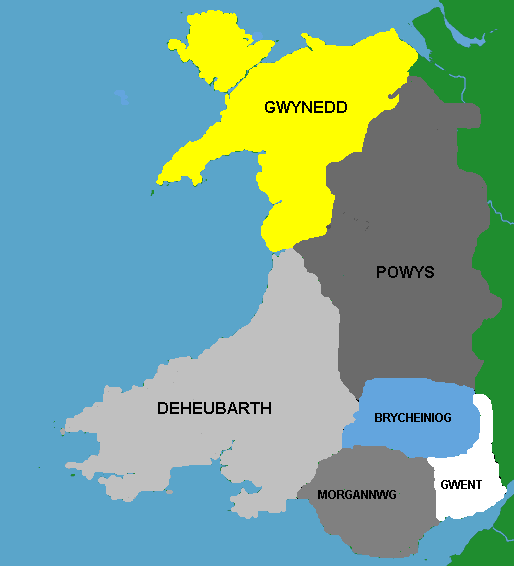
 The southern and eastern parts of Great Britain lost to English settlement became known in Welsh as (Modern Welsh ), which may have referred to the kingdom of Mercia originally and which came to refer to England as a whole. The Germanic tribes who now dominated these lands were invariably called , meaning " Saxons". The Anglo-Saxons called the Romano-British , meaning 'Romanised foreigner' or 'stranger'.Davies (1994) p. 2 The Welsh continued to call themselves (Brythons or Britons) well into the Middle Ages, though the first written evidence of the use of and is found in a praise poem to (, by ) . In , believed to be written around 930–942, the words and are used as often as 15 times. However, from the Anglo-Saxon settlement onwards, the people gradually begin to adopt the name over .Davies (2008) p. 186
From 800 onwards, a series of dynastic marriages led to 's ( 844–77) inheritance of and . His sons founded the three dynasties of ( for , for and for ). 's grandson (r. 900–50) founded out of his maternal and paternal inheritances of and in 930, ousted the dynasty from and and then codified Welsh law in the 940s. (r. 986–99) of , ('s grandson), temporarily ousted the line from control of and . 's great-grandson (through his daughter Princess ) (r. 1039–63) conquered his cousins' realms from his base in , and extended his authority into England.
The southern and eastern parts of Great Britain lost to English settlement became known in Welsh as (Modern Welsh ), which may have referred to the kingdom of Mercia originally and which came to refer to England as a whole. The Germanic tribes who now dominated these lands were invariably called , meaning " Saxons". The Anglo-Saxons called the Romano-British , meaning 'Romanised foreigner' or 'stranger'.Davies (1994) p. 2 The Welsh continued to call themselves (Brythons or Britons) well into the Middle Ages, though the first written evidence of the use of and is found in a praise poem to (, by ) . In , believed to be written around 930–942, the words and are used as often as 15 times. However, from the Anglo-Saxon settlement onwards, the people gradually begin to adopt the name over .Davies (2008) p. 186
From 800 onwards, a series of dynastic marriages led to 's ( 844–77) inheritance of and . His sons founded the three dynasties of ( for , for and for ). 's grandson (r. 900–50) founded out of his maternal and paternal inheritances of and in 930, ousted the dynasty from and and then codified Welsh law in the 940s. (r. 986–99) of , ('s grandson), temporarily ousted the line from control of and . 's great-grandson (through his daughter Princess ) (r. 1039–63) conquered his cousins' realms from his base in , and extended his authority into England.
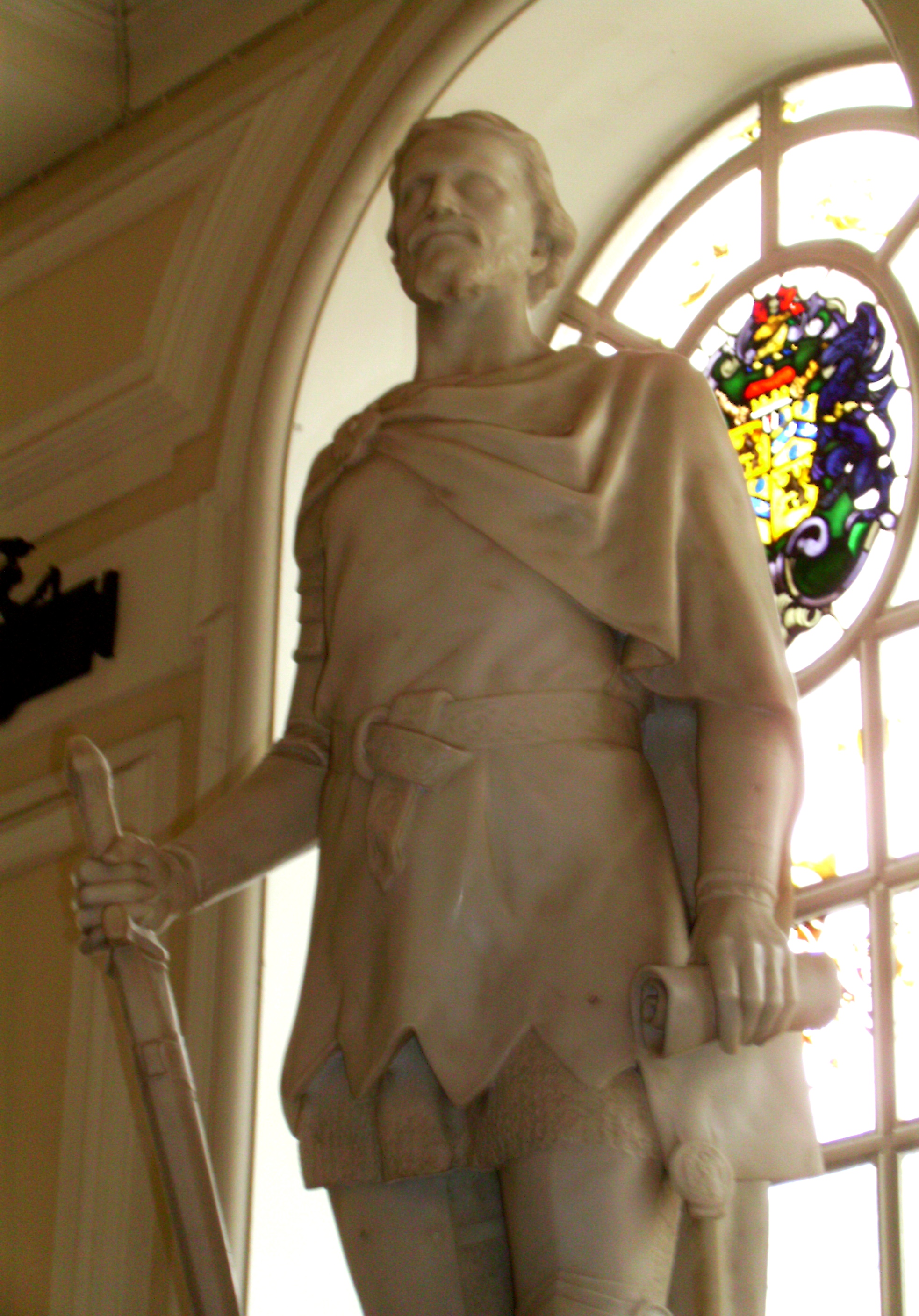 After the failed revolt in 1294–95 of – who styled himself Prince of Wales in the Penmachno Document – and the rising of (1316), the last uprising was led by , against
After the failed revolt in 1294–95 of – who styled himself Prince of Wales in the Penmachno Document – and the rising of (1316), the last uprising was led by , against
 In 1536 Wales had around 278,000 inhabitants, which increased to around 360,000 by 1620. This was primarily due to rural settlement, where animal farming was central to the Welsh economy. Increase in trade and increased economic stability occurred due to the increased diversity of the Welsh economy. Population growth however outpaced economic growth and the standard of living dropped.
Prior to the Industrial Revolution in Wales, there were small-scale industries scattered throughout Wales.Davies (2008) p. 392 These ranged from those connected to agriculture, such as milling and the manufacture of woollen textiles, through to mining and quarrying. Agriculture remained the dominant source of wealth. The emerging industrial period saw the development of copper smelting in the
In 1536 Wales had around 278,000 inhabitants, which increased to around 360,000 by 1620. This was primarily due to rural settlement, where animal farming was central to the Welsh economy. Increase in trade and increased economic stability occurred due to the increased diversity of the Welsh economy. Population growth however outpaced economic growth and the standard of living dropped.
Prior to the Industrial Revolution in Wales, there were small-scale industries scattered throughout Wales.Davies (2008) p. 392 These ranged from those connected to agriculture, such as milling and the manufacture of woollen textiles, through to mining and quarrying. Agriculture remained the dominant source of wealth. The emerging industrial period saw the development of copper smelting in the
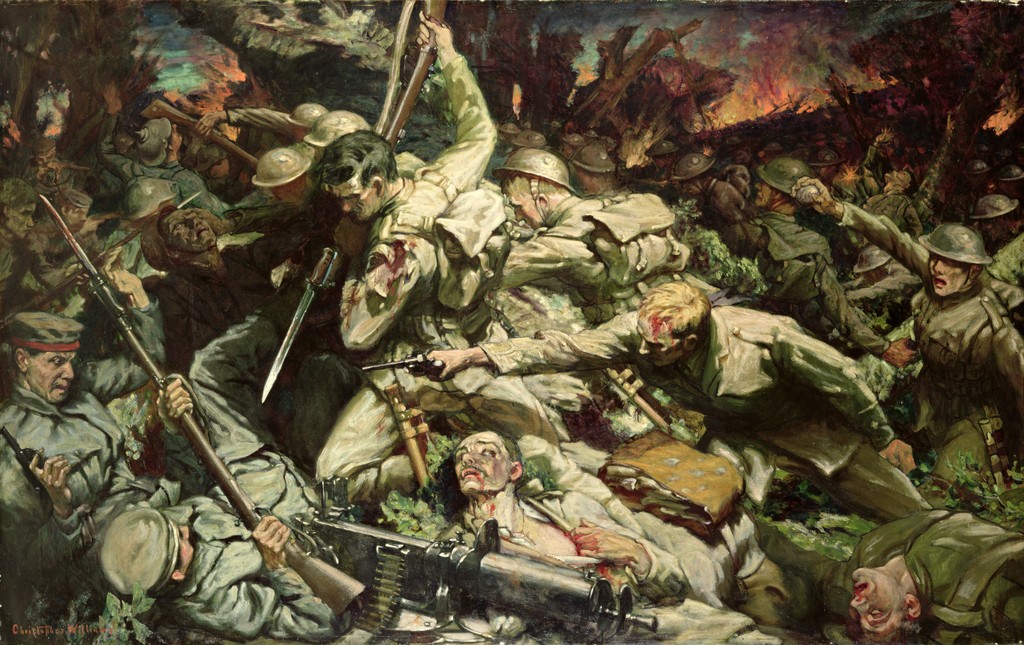

 Historian Kenneth Morgan described Wales on the eve of the First World War as a "relatively placid, self-confident and successful nation". The output from the coalfields continued to increase, with the Rhondda Valley recording a peak of 9.6 million tons of coal extracted in 1913. The First World War (1914–1918) saw a total of 272,924 Welshmen under arms, representing 21.5 per cent of the male population. Of these, roughly 35,000 were killed,Davies (2008) p. 284 with particularly heavy losses of Welsh forces at
Historian Kenneth Morgan described Wales on the eve of the First World War as a "relatively placid, self-confident and successful nation". The output from the coalfields continued to increase, with the Rhondda Valley recording a peak of 9.6 million tons of coal extracted in 1913. The First World War (1914–1918) saw a total of 272,924 Welshmen under arms, representing 21.5 per cent of the male population. Of these, roughly 35,000 were killed,Davies (2008) p. 284 with particularly heavy losses of Welsh forces at  By the end of the 1960s, the policy of bringing businesses into disadvantaged areas of Wales through financial incentives had proven very successful in diversifying the industrial economy.Davies (2008) p. 236 This policy, begun in 1934, was enhanced by the construction of industrial estates and improvements in transport communications, most notably the
By the end of the 1960s, the policy of bringing businesses into disadvantaged areas of Wales through financial incentives had proven very successful in diversifying the industrial economy.Davies (2008) p. 236 This policy, begun in 1934, was enhanced by the construction of industrial estates and improvements in transport communications, most notably the
 In a referendum in 1979, Wales voted against the creation of a Welsh assembly with an 80 per cent majority. In 1997, a second referendum on the same issue secured a very narrow majority (50.3 per cent). The National Assembly for Wales (''Cynulliad Cenedlaethol Cymru'') was set up in 1999 (under the Government of Wales Act 1998) with the power to determine how Wales' central government budget is spent and administered, although the UK Parliament reserved the right to set limits on its powers. The governments of the United Kingdom and of Wales almost invariably define Wales as a country.; The Welsh Government says: "Wales is not a Principality. Although we are joined with England by land, and we are part of Great Britain, Wales is a country in its own right."
The Government of Wales Act 2006 (c 32) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed the National Assembly for Wales and allows further powers to be granted to it more easily. The Act creates a system of government with a separate executive drawn from and accountable to the legislature. Following a successful referendum in 2011 on extending the law making powers of the National Assembly it is now able to make laws, known as Acts of the Assembly, on all matters in devolved subject areas, without needing the UK Parliament's agreement.
In the 2016 referendum, Wales voted in support of leaving the European Union, although demographic differences became evident. According to Danny Dorling, professor of geography at the Oxford University, “If you look at the more genuinely Welsh areas, especially the Welsh-speaking ones, they did not want to leave the EU,”
After the Senedd and Elections (Wales) Act 2020, the National Assembly was renamed "Senedd Cymru" (in Welsh) and the "Welsh Parliament" (in English) (also collectively referred to as the "
In a referendum in 1979, Wales voted against the creation of a Welsh assembly with an 80 per cent majority. In 1997, a second referendum on the same issue secured a very narrow majority (50.3 per cent). The National Assembly for Wales (''Cynulliad Cenedlaethol Cymru'') was set up in 1999 (under the Government of Wales Act 1998) with the power to determine how Wales' central government budget is spent and administered, although the UK Parliament reserved the right to set limits on its powers. The governments of the United Kingdom and of Wales almost invariably define Wales as a country.; The Welsh Government says: "Wales is not a Principality. Although we are joined with England by land, and we are part of Great Britain, Wales is a country in its own right."
The Government of Wales Act 2006 (c 32) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed the National Assembly for Wales and allows further powers to be granted to it more easily. The Act creates a system of government with a separate executive drawn from and accountable to the legislature. Following a successful referendum in 2011 on extending the law making powers of the National Assembly it is now able to make laws, known as Acts of the Assembly, on all matters in devolved subject areas, without needing the UK Parliament's agreement.
In the 2016 referendum, Wales voted in support of leaving the European Union, although demographic differences became evident. According to Danny Dorling, professor of geography at the Oxford University, “If you look at the more genuinely Welsh areas, especially the Welsh-speaking ones, they did not want to leave the EU,”
After the Senedd and Elections (Wales) Act 2020, the National Assembly was renamed "Senedd Cymru" (in Welsh) and the "Welsh Parliament" (in English) (also collectively referred to as the "
 The Welsh language ( cy, Cymraeg) is an
The Welsh language ( cy, Cymraeg) is an
 Wales is a country that is part of the sovereign state of the United Kingdom. Constitutionally, the UK is a '' de jure'' unitary state, with a parliament and government in Westminster. Wales has a devolved, unicameral legislature known as the
Wales is a country that is part of the sovereign state of the United Kingdom. Constitutionally, the UK is a '' de jure'' unitary state, with a parliament and government in Westminster. Wales has a devolved, unicameral legislature known as the
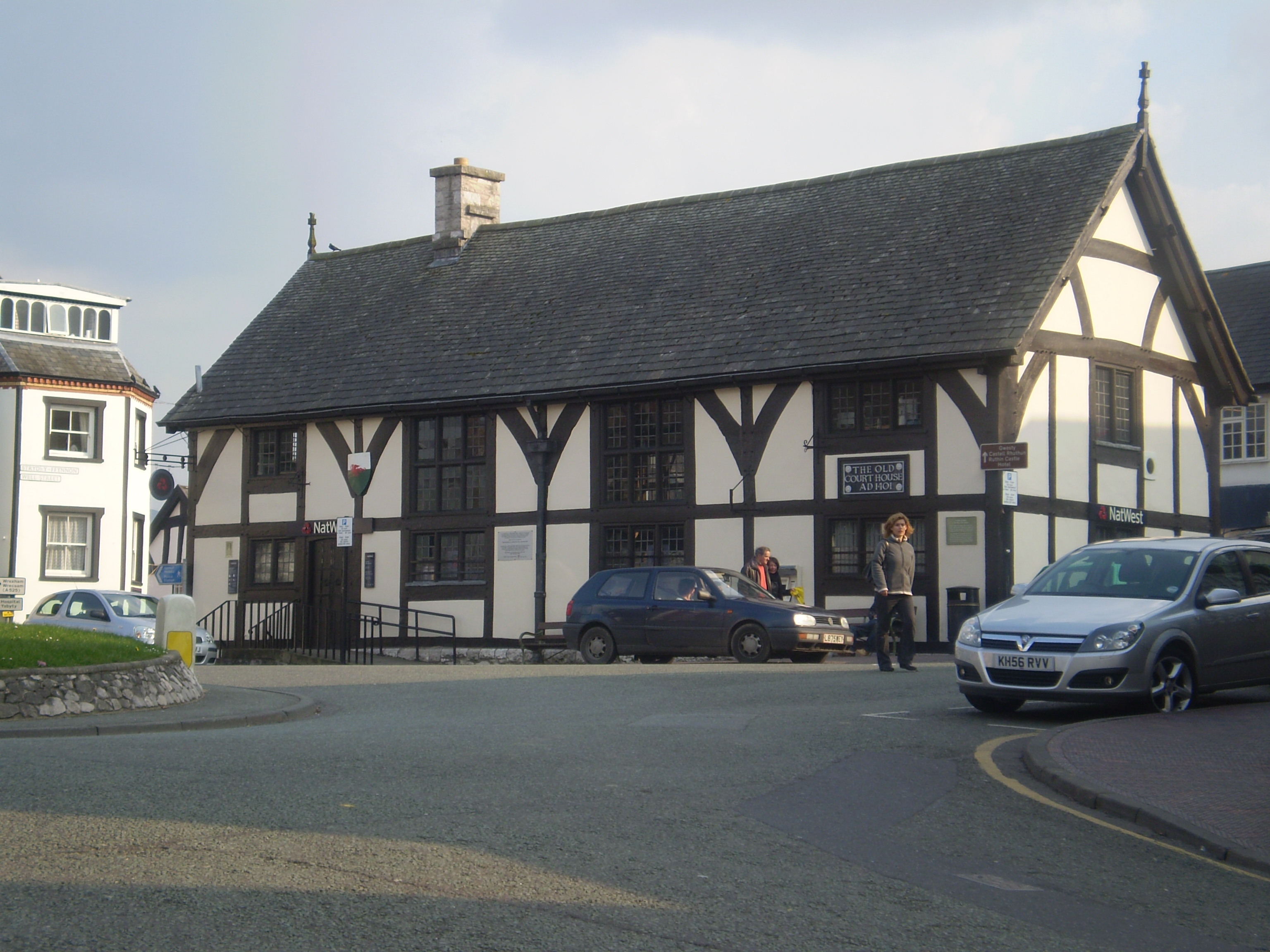 By tradition, Welsh Law was compiled during an assembly held at Whitland around 930 by Hywel Dda, king of most of Wales between 942 and his death in 950. The ' law of Hywel Dda' ( cy, Cyfraith Hywel), as it became known, codified the previously existing folk laws and legal customs that had evolved in Wales over centuries. Welsh Law emphasised the payment of compensation for a crime to the victim, or the victim's kin, rather than punishment by the ruler. Other than in the Marches, where
By tradition, Welsh Law was compiled during an assembly held at Whitland around 930 by Hywel Dda, king of most of Wales between 942 and his death in 950. The ' law of Hywel Dda' ( cy, Cyfraith Hywel), as it became known, codified the previously existing folk laws and legal customs that had evolved in Wales over centuries. Welsh Law emphasised the payment of compensation for a crime to the victim, or the victim's kin, rather than punishment by the ruler. Other than in the Marches, where
 Wales is a generally mountainous country on the western side of central southern Great Britain. It is about north to south. The oft-quoted ' size of Wales' is about . Wales is bordered by England to the east and by sea in all other directions: the Irish Sea to the north and west,
Wales is a generally mountainous country on the western side of central southern Great Britain. It is about north to south. The oft-quoted ' size of Wales' is about . Wales is bordered by England to the east and by sea in all other directions: the Irish Sea to the north and west,  Wales has three national parks: Snowdonia, Brecon Beacons and Pembrokeshire Coast. It has five Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty; Anglesey, the Clwydian Range and Dee Valley, the Gower Peninsula, the Llŷn Peninsula, and the Wye Valley. The Gower Peninsula was the first area in the United Kingdom to be designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, in 1956. As of 2019, the
Wales has three national parks: Snowdonia, Brecon Beacons and Pembrokeshire Coast. It has five Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty; Anglesey, the Clwydian Range and Dee Valley, the Gower Peninsula, the Llŷn Peninsula, and the Wye Valley. The Gower Peninsula was the first area in the United Kingdom to be designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, in 1956. As of 2019, the
 Wales lies within the north temperate zone. It has a changeable, maritime climate and is one of the wettest countries in Europe.Davies (2008) pp. 148–150 Welsh weather is often cloudy, wet and windy, with warm summers and mild winters.
* Highest maximum temperature: at Hawarden, Flintshire on 18 July 2022.
* Lowest minimum temperature: at Rhayader,
Wales lies within the north temperate zone. It has a changeable, maritime climate and is one of the wettest countries in Europe.Davies (2008) pp. 148–150 Welsh weather is often cloudy, wet and windy, with warm summers and mild winters.
* Highest maximum temperature: at Hawarden, Flintshire on 18 July 2022.
* Lowest minimum temperature: at Rhayader,
Bristol Channel
The Bristol Channel ( cy, Môr Hafren, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales from Devon and Somerset in South West England. It extends from the lower estuary of the River Seve ...
to the south. It had a population in 2021 of 3,107,500 and has a total area of . Wales has over of coastline and is largely mountainous with its higher peaks in the north and central areas, including Snowdon
Snowdon () or (), is the highest mountain in Wales, at an elevation of above sea level, and the highest point in the British Isles outside the Scottish Highlands. It is located in Snowdonia National Park (') in Gwynedd (historic ...
(), its highest summit. The country lies within the north temperate zone and has a changeable, maritime climate. The capital and largest city is Cardiff.
Welsh national identity emerged among the Celtic Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point th ...
after the Roman withdrawal from Britain in the 5th century, and Wales was formed as a kingdom under Gruffydd ap Llywelyn in 1055. Wales is regarded as one of the Celtic nations. The conquest of Wales by Edward I of England was completed by 1283, though Owain Glyndŵr
Owain ap Gruffydd (), commonly known as Owain Glyndŵr or Glyn Dŵr (, anglicised as Owen Glendower), was a Welsh leader, soldier and military commander who led a 15 year long Welsh War of Independence with the aim of ending English rule in Wa ...
led the Welsh Revolt against English rule In the field of law and economics, the English rule is a rule controlling assessment of lawyers' fees arising out of litigation. The English rule provides that the party that loses in court pays the other party's legal costs. The English rule cont ...
in the early 15th century, and briefly re-established an independent Welsh state with its own national parliament (). The whole of Wales was annexed by England and incorporated within the English legal system under the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. Distinctive Welsh politics
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
developed in the 19th century. Welsh Liberalism, exemplified in the early 20th century by David Lloyd George, was displaced by the growth of socialism and the Labour Party. Welsh national feeling grew over the century; a nationalist party, was formed in 1925, and the Welsh Language Society in 1962. A governing system of Welsh devolution is employed in Wales, of which the most major step was the formation of the (Welsh Parliament, formerly the National Assembly for Wales) in 1998, responsible for a range of devolved policy matters.
At the dawn of the Industrial Revolution, development of the mining and metallurgical industries transformed the country from an agricultural society into an industrial one; the South Wales Coalfield's exploitation caused a rapid expansion of Wales' population. Two-thirds of the population live in South Wales
South Wales ( cy, De Cymru) is a loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards ...
, including Cardiff, Swansea
Swansea (; cy, Abertawe ) is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Swansea ( cy, links=no, Dinas a Sir Abertawe).
The city is the twenty-fifth largest in ...
, Newport
Newport most commonly refers to:
*Newport, Wales
*Newport, Rhode Island, US
Newport or New Port may also refer to:
Places Asia
*Newport City, Metro Manila, a Philippine district in Pasay
Europe
Ireland
*Newport, County Mayo, a town on the ...
and the nearby valleys. The eastern region Eastern Region or East Region may refer to:
* Eastern Region (Abu Dhabi): Al Ain
*Eastern Region, Ghana
*Eastern Region (Iceland)
*Eastern Region, Nepal
*Eastern Region, Nigeria
* Eastern Region, Serbia
* Eastern Region, Uganda
* Eastern Region of ...
of North Wales has about a sixth of the overall population, with Wrexham being the largest northern city. The remaining parts of Wales are sparsely populated. Now that the country's traditional extractive and heavy industries have gone or are in decline, the economy is based on the public sector, light and service industries, and tourism. Agriculture in Wales is largely livestock based, making Wales a net exporter of animal produce, contributing towards national agricultural self-sufficiency
Autarky is the characteristic of self-sufficiency, usually applied to societies, communities, states, and their economic systems.
Autarky as an ideal or method has been embraced by a wide range of political ideologies and movements, especially ...
.
The country has a distinct national and cultural identity
Cultural identity is a part of a person's identity, or their self-conception and self-perception, and is related to nationality, ethnicity, religion, social class, generation, locality or any kind of social group that has its own distinct cultur ...
and from the late 19th century onwards Wales acquired its popular image as the "land of song", in part due to the '' eisteddfod'' tradition. Both Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
and English are official languages. A majority of the population in most areas speaks English whilst a majority of the population in parts of the north and west speak Welsh, with a total of 538,300 Welsh speakers across the whole country.
Etymology
The English words "Wales" and "Welsh" derive from the sameOld English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
root (singular , plural ), a descendant of Proto-Germanic , which was itself derived from the name of the Gauls known to the Romans as Volcae. This term was later used to refer indiscriminately to inhabitants of the Western Roman Empire. Anglo-Saxons came to use the term to refer to the Britons in particular; the plural form evolved into the name for their territory, Wales.Davies (1994) p. 71 Historically in Britain, the words were not restricted to modern Wales or to the Welsh but were used to refer to anything that Anglo-Saxons associated with Britons, including other non-Germanic territories in Britain (e.g. Cornwall) and places in Anglo-Saxon territory associated with Britons (e.g. Walworth in County Durham
County Durham ( ), officially simply Durham,UK General Acts 1997 c. 23Lieutenancies Act 1997 Schedule 1(3). From legislation.gov.uk, retrieved 6 April 2022. is a ceremonial county in North East England.North East Assembly �About North East E ...
and Walton in West Yorkshire).
The modern Welsh name for themselves is , and is the Welsh name for Wales. These words (both of which are pronounced ) are descended from the Brythonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
word ''combrogi'', meaning "fellow-countrymen",Davies (1994) p. 69 and probably came into use before the 7th century. In literature, they could be spelt or , regardless of whether it referred to the people or their homeland. The Latinised forms of these names, ''Cambrian'', ''Cambric'' and '' Cambria'', survive as names such as the Cambrian Mountains
The Cambrian Mountains ( cy, Mynyddoedd Cambria, in a narrower sense: ''Elenydd'') are a series of mountain ranges in Wales.
The term ''Cambrian Mountains'' used to apply to most of the upland of Wales. Since the 1950s, its application has becom ...
and the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
geological period
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronol ...
.
History
Prehistoric origins


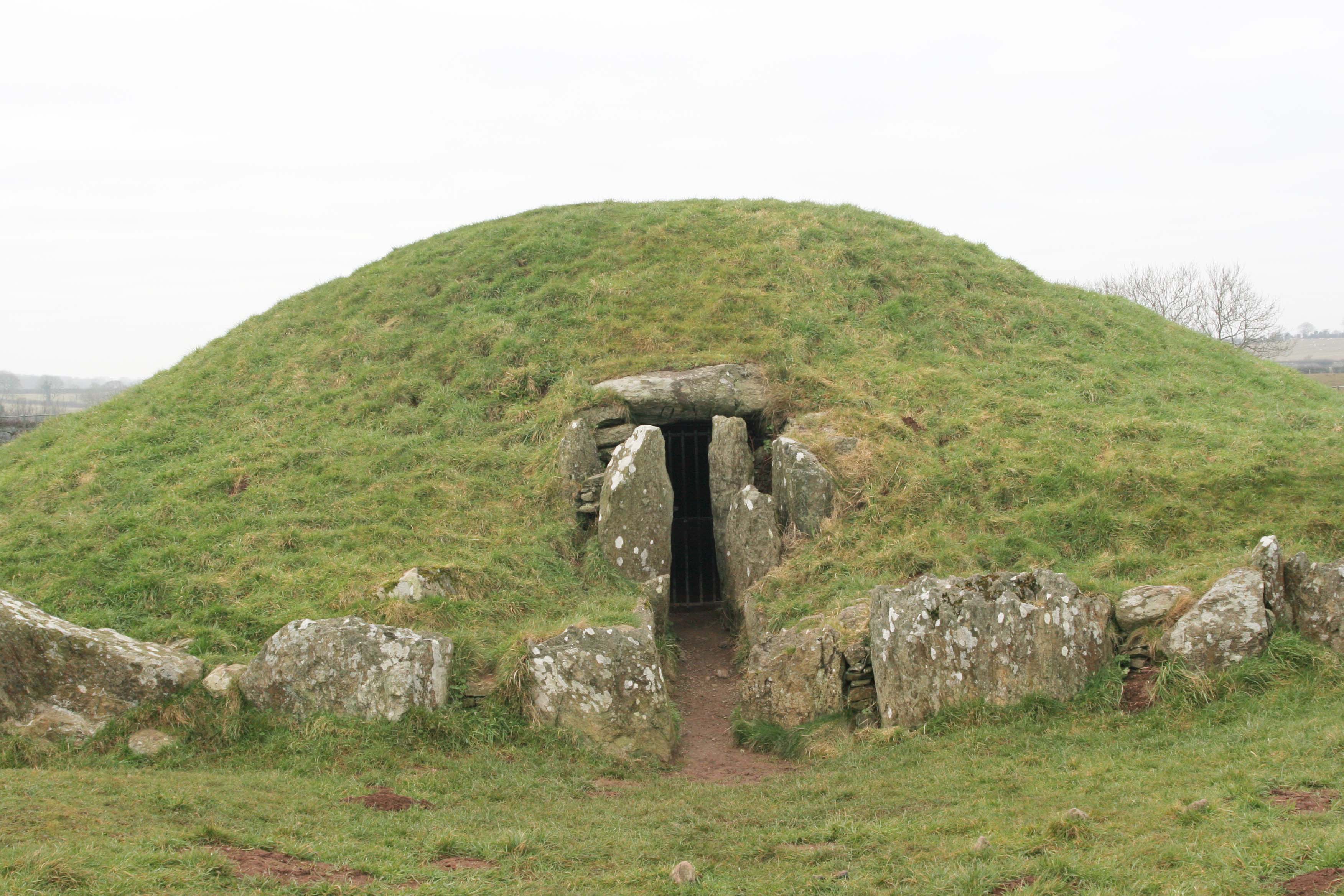
 Wales has been inhabited by
Wales has been inhabited by modern humans
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, an ...
for at least 29,000 years: ''see'' Red Lady of Paviland Continuous human habitation dates from the end of the last ice age, between 12,000 and 10,000 years before present (BP), when Mesolithic
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymous ...
hunter-gatherers from Central Europe began to migrate to Great Britain. At that time, sea levels were much lower than today. Wales was free of glaciers
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as ...
by about 10,250 BP, the warmer climate allowing the area to become heavily wooded. The post-glacial rise in sea level separated Wales and Ireland, forming the Irish Sea. By 8,000 BP the British Peninsula had become an island.; Davies (2008) pp. 647–648 By the beginning of the Neolithic () sea levels in the Bristol Channel
The Bristol Channel ( cy, Môr Hafren, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales from Devon and Somerset in South West England. It extends from the lower estuary of the River Seve ...
were still about lower than today. ; Davies (1994) p. 17; The historian John Davies theorised that the story of Cantre'r Gwaelod's drowning and tales in the ''Mabinogion
The ''Mabinogion'' () are the earliest Welsh prose stories, and belong to the Matter of Britain. The stories were compiled in Middle Welsh in the 12th–13th centuries from earlier oral traditions. There are two main source manuscripts, create ...
'', of the waters between Wales and Ireland being narrower and shallower, may be distant folk memories of this time.Davies (1994) pp. 4–6
Neolithic colonists integrated with the indigenous people, gradually changing their lifestyles from a nomadic life of hunting and gathering, to become settled farmers about 6,000 BP – the Neolithic Revolution
The Neolithic Revolution, or the (First) Agricultural Revolution, was the wide-scale transition of many human cultures during the Neolithic period from a lifestyle of hunting and gathering to one of agriculture and settlement, making an incre ...
. They cleared the forests to establish pasture and to cultivate the land, developed new technologies such as ceramics and textile production, and built cromlechs such as Pentre Ifan, Bryn Celli Ddu, and Parc Cwm long cairn between about 5,800 BP and 5,500 BP.; Over the following centuries they assimilated immigrants and adopted ideas from Bronze Age and Iron Age Celtic cultures. Some historians, such as John T. Koch
John T. Koch is an American academic, historian and linguist who specializes in Celtic studies, especially prehistory and the early Middle Ages. He is the editor of the five-volume ''Celtic Culture. A Historical Encyclopedia'' (2006, ABC Clio). He ...
, consider Wales in the Late Bronze Age as part of a maritime trading-networked culture that included other Celtic nations.; ; This "Atlantic-Celtic" view is opposed by others who hold that the Celtic languages derive their origins from the more easterly Hallstatt culture
The Hallstatt culture was the predominant Western Europe, Western and Central European Archaeological culture, culture of Late Bronze Age Europe, Bronze Age (Hallstatt A, Hallstatt B) from the 12th to 8th centuries BC and Early Iron Age Europe ...
. By the time of the Roman invasion of Britain the area of modern Wales had been divided among the tribes of the Deceangli (north-east), Ordovices
The Ordovīcēs (Common Brittonic: *''Ordowīcī'') were one of the Celtic tribes living in Great Britain before the Roman invasion. Their tribal lands were located in present-day North Wales and England, between the Silures to the south and the D ...
(north-west), Demetae (south-west), Silures
The Silures ( , ) were a powerful and warlike tribe or tribal confederation of ancient Britain, occupying what is now south east Wales and perhaps some adjoining areas. They were bordered to the north by the Ordovices; to the east by the Dobunn ...
(south-east) and Cornovii (east), centuries.
Leader of the Ordovices, Caractacus or ''Caradog'', was successful in resisting Roman invasions of north Wales for a period. He was eventually defeated and taken to Rome where, following a famous speech to the Roman senate, his life was spared and he was allowed to live peacefully in Rome.
Roman era
The Roman conquest of Wales began in AD 48 and took 30 years to complete; the occupation lasted over 300 years. The campaigns of conquest were opposed by two native tribes: theSilures
The Silures ( , ) were a powerful and warlike tribe or tribal confederation of ancient Britain, occupying what is now south east Wales and perhaps some adjoining areas. They were bordered to the north by the Ordovices; to the east by the Dobunn ...
and the Ordovices
The Ordovīcēs (Common Brittonic: *''Ordowīcī'') were one of the Celtic tribes living in Great Britain before the Roman invasion. Their tribal lands were located in present-day North Wales and England, between the Silures to the south and the D ...
. Roman rule in Wales was a military occupation, save for the southern coastal region of south Wales
South Wales ( cy, De Cymru) is a loosely defined region of Wales bordered by England to the east and mid Wales to the north. Generally considered to include the historic counties of Glamorgan and Monmouthshire, south Wales extends westwards ...
, where there is a legacy of Romanisation. The only town in Wales founded by the Romans, Caerwent, is in south east Wales. Both Caerwent and Carmarthen, also in southern Wales, became Roman ''civitates
In Ancient Rome, the Latin term (; plural ), according to Cicero in the time of the late Roman Republic, was the social body of the , or citizens, united by law (). It is the law that binds them together, giving them responsibilities () on th ...
''. Wales had a rich mineral wealth. The Romans used their engineering technology to extract large amounts of gold, copper and lead, as well as lesser amounts of zinc and silver. No significant industries were located in Wales in this time; this was largely a matter of circumstance as Wales had none of the necessary materials in suitable combination, and the forested, mountainous countryside was not amenable to industrialisation. Latin became the official language of Wales, though the people continued to speak in Brythonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
. While Romanisation was far from complete, the upper classes came to consider themselves Roman, particularly after the ruling of 212 that granted Roman citizenship to all free men throughout the Empire.Davies (2008) p. 915 Further Roman influence came through the spread of Christianity, which gained many followers when Christians were allowed to worship freely; state persecution ceased in the 4th century, as a result of Constantine I
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterranea ...
issuing an edict of toleration in 313.
Early historians, including the 6th-century cleric Gildas, have noted 383 as a significant point in Welsh history.Davies (2008) p. 531 In that year, the Roman general Magnus Maximus, or Macsen Wledig, stripped Britain of troops to launch a successful bid for imperial power, continuing to rule Britain from Gaul as emperor, and transferring power to local leaders. The earliest Welsh genealogies cite Maximus as the founder of several royal dynasties, and as the father of the Welsh Nation. He is given as the ancestor of a Welsh king on the Pillar of Eliseg, erected nearly 500 years after he left Britain, and he figures in lists of the Fifteen Tribes of Wales.Rachel Bromwich, editor and translator. Trioedd Ynys Prydein: The Welsh Triads. Cardiff: University of Wales Press, 3rd Edition, (2006) p. 441–444
Post-Roman era
 The 400-year period following the collapse of Roman rule is the most difficult to interpret in the history of Wales. After the Roman departure in AD 410, much of the lowlands of Britain to the east and south-east was overrun by various Germanic peoples, commonly known as Anglo-Saxons. Some have theorized that the cultural dominance of the Anglo-Saxons was due to apartheid-like social conditions in which the Britons were at a disadvantage.
By AD 500 the land that would become Wales had divided into a number of kingdoms free from Anglo-Saxon rule. The kingdoms of
The 400-year period following the collapse of Roman rule is the most difficult to interpret in the history of Wales. After the Roman departure in AD 410, much of the lowlands of Britain to the east and south-east was overrun by various Germanic peoples, commonly known as Anglo-Saxons. Some have theorized that the cultural dominance of the Anglo-Saxons was due to apartheid-like social conditions in which the Britons were at a disadvantage.
By AD 500 the land that would become Wales had divided into a number of kingdoms free from Anglo-Saxon rule. The kingdoms of Gwynedd
Gwynedd (; ) is a county and preserved county (latter with differing boundaries; includes the Isle of Anglesey) in the north-west of Wales. It shares borders with Powys, Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Anglesey over the Menai Strait, and C ...
, Powys, Dyfed, Caredigion , Morgannwg, the Ystrad Tywi, and Gwent emerged as independent Welsh successor states. Archaeological evidence, in the Low Countries and what was to become England, shows early Anglo-Saxon migration to Great Britain reversed between 500 and 550, which concurs with Frankish chronicles.Davies (1994) pp. 56 John Davies notes this as consistent with a victory for the Celtic Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point th ...
at Badon Hill
The Battle of Badon /ˈbeɪdən/ also known as the Battle of Mons Badonicus ( la, obsessio isBadonici montis, "Blockade/Siege of the Badonic Hill"; ''Bellum in monte Badonis'', "Battle on Badon Hill"; ''Bellum Badonis'', "Battle of Badon"; Ol ...
against the Saxons, which was attributed to Arthur by Nennius
Nennius – or Nemnius or Nemnivus – was a Welsh monk of the 9th century. He has traditionally been attributed with the authorship of the ''Historia Brittonum'', based on the prologue affixed to that work. This attribution is widely considered ...
.
Having lost much of what is now the West Midlands to Mercia in the 6th and early 7th centuries, a resurgent late-7th-century Powys checked Mercian advances. Aethelbald of Mercia, looking to defend recently acquired lands, had built Wat's Dyke. According to Davies, this had been with the agreement of king Elisedd ap Gwylog of Powys, as this boundary, extending north from the valley of the River Severn to the Dee estuary, gave him Oswestry
Oswestry ( ; ) is a market town, civil parish and historic railway town in Shropshire, England, close to the Welsh border. It is at the junction of the A5, A483 and A495 roads.
The town was the administrative headquarters of the Borough of ...
.Davies (1994) pp. 65–66 Another theory, after carbon dating placed the dyke's existence 300 years earlier, is that it was built by the post-Roman rulers of Wroxeter. King Offa of Mercia
Offa (died 29 July 796 AD) was List of monarchs of Mercia, King of Mercia, a kingdom of History of Anglo-Saxon England, Anglo-Saxon England, from 757 until his death. The son of Thingfrith and a descendant of Eowa of Mercia, Eowa, Offa came to ...
seems to have continued this initiative when he created a larger earthwork, now known as Offa's Dyke (). Davies wrote of Cyril Fox's study of Offa's Dyke: "In the planning of it, there was a degree of consultation with the kings of Powys and Gwent. On the Long Mountain near Trelystan
Trelystan is a remote parish and Townships in Montgomeryshire, township on the border of the historic county of Montgomeryshire with Shropshire. Trelystan now forms part of the community of Forden, Leighton and Trelystan in Powys. Trelystan was a c ...
, the dyke veers to the east, leaving the fertile slopes in the hands of the Welsh; near Rhiwabon
Ruabon ( cy, Rhiwabon ) is a village and community in Wrexham County Borough, Wales. The name comes from ''Rhiw Fabon'', ''rhiw'' being the Welsh word for "slope" or "hillside" and ''Fabon'' being a mutation from St Mabon, the original chu ...
, it was designed to ensure that Cadell ap Brochwel retained possession of the Fortress of Penygadden." And, for Gwent, Offa had the dyke built "on the eastern crest of the gorge, clearly with the intention of recognizing that the River Wye
The River Wye (; cy, Afon Gwy ) is the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, fourth-longest river in the UK, stretching some from its source on Plynlimon in mid Wales to the Severn estuary. For much of its length the river forms part of Wal ...
and its traffic belonged to the kingdom of Gwent." However, Fox's interpretations of both the length and purpose of the Dyke have been questioned by more recent research.
In 853, the Vikings raided Anglesey, but in 856, Rhodri Mawr defeated and killed their leader, Gorm. The Celtic Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point th ...
of Wales made peace with the Vikings and Anarawd ap Rhodri allied with the Norsemen occupying Northumbria to conquer the north. This alliance later broke down and Anarawd came to an agreement with Alfred, king of Wessex, with whom he fought against the west Welsh. According to , in 894, "Anarawd came with the Angles and laid waste Ceredigion and Ystrad Tywi." The southern and eastern parts of Great Britain lost to English settlement became known in Welsh as (Modern Welsh ), which may have referred to the kingdom of Mercia originally and which came to refer to England as a whole. The Germanic tribes who now dominated these lands were invariably called , meaning " Saxons". The Anglo-Saxons called the Romano-British , meaning 'Romanised foreigner' or 'stranger'.Davies (1994) p. 2 The Welsh continued to call themselves (Brythons or Britons) well into the Middle Ages, though the first written evidence of the use of and is found in a praise poem to (, by ) . In , believed to be written around 930–942, the words and are used as often as 15 times. However, from the Anglo-Saxon settlement onwards, the people gradually begin to adopt the name over .Davies (2008) p. 186
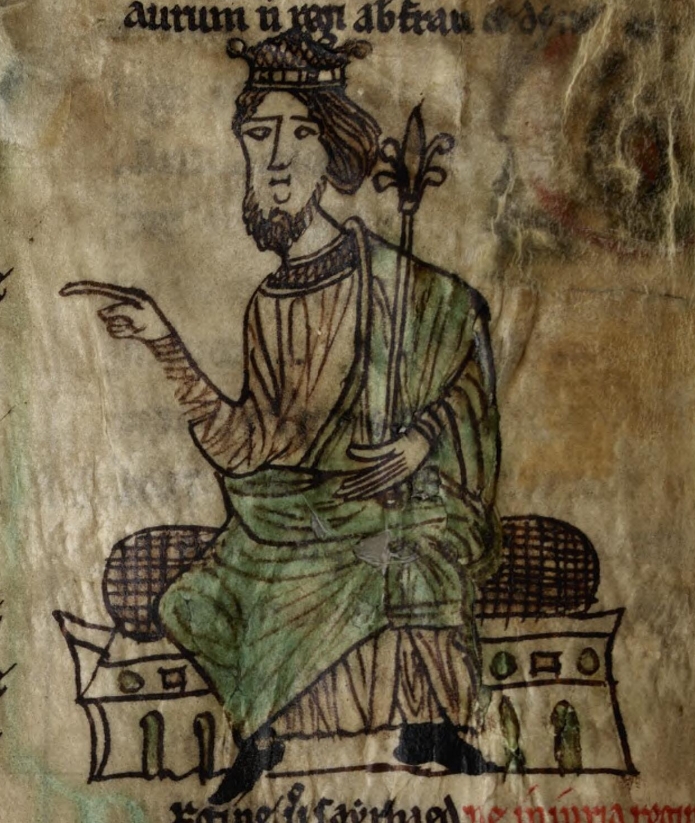
From 800 onwards, a series of dynastic marriages led to 's ( 844–77) inheritance of and . His sons founded the three dynasties of ( for , for and for ). 's grandson (r. 900–50) founded out of his maternal and paternal inheritances of and in 930, ousted the dynasty from and and then codified Welsh law in the 940s. (r. 986–99) of , ('s grandson), temporarily ousted the line from control of and . 's great-grandson (through his daughter Princess ) (r. 1039–63) conquered his cousins' realms from his base in , and extended his authority into England.
The southern and eastern parts of Great Britain lost to English settlement became known in Welsh as (Modern Welsh ), which may have referred to the kingdom of Mercia originally and which came to refer to England as a whole. The Germanic tribes who now dominated these lands were invariably called , meaning " Saxons". The Anglo-Saxons called the Romano-British , meaning 'Romanised foreigner' or 'stranger'.Davies (1994) p. 2 The Welsh continued to call themselves (Brythons or Britons) well into the Middle Ages, though the first written evidence of the use of and is found in a praise poem to (, by ) . In , believed to be written around 930–942, the words and are used as often as 15 times. However, from the Anglo-Saxon settlement onwards, the people gradually begin to adopt the name over .Davies (2008) p. 186
From 800 onwards, a series of dynastic marriages led to 's ( 844–77) inheritance of and . His sons founded the three dynasties of ( for , for and for ). 's grandson (r. 900–50) founded out of his maternal and paternal inheritances of and in 930, ousted the dynasty from and and then codified Welsh law in the 940s. (r. 986–99) of , ('s grandson), temporarily ousted the line from control of and . 's great-grandson (through his daughter Princess ) (r. 1039–63) conquered his cousins' realms from his base in , and extended his authority into England.
High to late middle ages
Gruffydd ap Llywelyn was the only ruler to unite all of Wales under his rule, becoming king of Wales. In 1055 Gruffydd ap Llywelyn killed his rival Gruffydd ap Rhydderch in battle and recaptured . Originally king of Gwynedd, by 1057 he was ruler of Wales and had annexed parts of England around the border. He ruled Wales with no internal battles. His territories were again divided into the traditional kingdoms. John Davies states that was "the only Welsh king ever to rule over the entire territory of Wales... Thus, from about 1057 until his death in 1063, the whole of Wales recognised the kingship of . For about seven brief years, Wales was one, under one ruler, a feat with neither precedent nor successor."Davies (1994) p. 100 Owain Gwynedd (1100–70) of the Aberffraw line was the first Welsh ruler to use the title (prince of the Welsh), a title of substance given his victory on theBerwyn Mountains
The Berwyn range (Welsh: ''Y Berwyn'' or ''Mynydd y Berwyn'') is an isolated and sparsely populated area of moorland in the northeast of Wales, roughly bounded by Llangollen in the northeast, Corwen in the northwest, Bala in the southwest, and ...
, according to Davies.Davies (1994) p. 128 During this time, between 1053 and 1063, Wales lacked any internal strife and was at peace.
Within four years of the Battle of Hastings (1066), England had been completely subjugated by the Normans. William I of England established a series of lordships, allocated to his most powerful warriors, along the Welsh border, their boundaries fixed only to the east (where they met other feudal properties inside England). Starting in the 1070s, these lords began conquering land in southern and eastern Wales, west of the River Wye
The River Wye (; cy, Afon Gwy ) is the Longest rivers of the United Kingdom, fourth-longest river in the UK, stretching some from its source on Plynlimon in mid Wales to the Severn estuary. For much of its length the river forms part of Wal ...
. The frontier region, and any English-held lordships in Wales, became known as , the Welsh Marches
The Welsh Marches ( cy, Y Mers) is an imprecisely defined area along the border between England and Wales in the United Kingdom. The precise meaning of the term has varied at different periods.
The English term Welsh March (in Medieval Latin ...
, in which the Marcher lords were subject to neither English nor Welsh law. The extent of the March varied as the fortunes of the Marcher lords and the Welsh princes ebbed and flowed.
's grandson (the Great, 1173–1240), received the fealty
An oath of fealty, from the Latin ''fidelitas'' (faithfulness), is a pledge of allegiance of one person to another.
Definition
In medieval Europe, the swearing of fealty took the form of an oath made by a vassal, or subordinate, to his lord. "Fea ...
of other Welsh lords in 1216 at the council at , becoming in effect the first prince of Wales. His grandson secured the recognition of the title ''Prince of Wales'' from Henry III with the Treaty of Montgomery in 1267. Subsequent disputes, including the imprisonment of 's wife Eleanor, culminated in the first invasion by King Edward I of England.Davies (1994) pp. 151–152 As a result of military defeat, the Treaty of Aberconwy exacted 's fealty to England in 1277. Peace was short-lived, and, with the 1282 Edwardian conquest, the rule of the Welsh princes permanently ended. With 's death and his brother prince 's execution, the few remaining Welsh lords did homage
Homage (Old English) or Hommage (French) may refer to:
History
*Homage (feudal) /ˈhɒmɪdʒ/, the medieval oath of allegiance
*Commendation ceremony, medieval homage ceremony Arts
*Homage (arts) /oʊˈmɑʒ/, an allusion or imitation by one arti ...
to Edward I
Edward I (17/18 June 1239 – 7 July 1307), also known as Edward Longshanks and the Hammer of the Scots, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1272 to 1307. Concurrently, he ruled the duchies of Aquitaine and Gascony as a vassal o ...
. The Statute of Rhuddlan in 1284 provided the constitutional basis for a post-conquest government of the Principality of North Wales from 1284 until 1535/36. It defined Wales as "annexed and united" to the English Crown, separate from England but under the same monarch. The king ruled directly in two areas: the Statute divided the north and delegated administrative duties to the Justice of Chester and Justiciar of North Wales, and further south in western Wales the King's authority was delegated to the Justiciar of South Wales. The existing royal lordships of Montgomery and remained unchanged. To maintain his dominance, Edward constructed a series of castles: Beaumaris, , Harlech and . His son, the future Edward II
Edward II (25 April 1284 – 21 September 1327), also called Edward of Caernarfon, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 1307 until he was deposed in January 1327. The fourth son of Edward I, Edward became the heir apparent to t ...
, was born at in 1284. He became the first English prince of Wales in 1301, which at the time provided an income from northwest Wales known as the Principality of Wales.  After the failed revolt in 1294–95 of – who styled himself Prince of Wales in the Penmachno Document – and the rising of (1316), the last uprising was led by , against
After the failed revolt in 1294–95 of – who styled himself Prince of Wales in the Penmachno Document – and the rising of (1316), the last uprising was led by , against Henry IV of England
Henry IV ( April 1367 – 20 March 1413), also known as Henry Bolingbroke, was King of England from 1399 to 1413. He asserted the claim of his grandfather King Edward III, a maternal grandson of Philip IV of France, to the Kingdom of F ...
. In 1404, was crowned prince of Wales in the presence of emissaries from France, Spain (Castille) and Scotland.Davies (1994) p. 194 went on to hold parliamentary assemblies at several Welsh towns, including a Welsh parliament () at . The rebellion was eventually defeated by 1412. Having failed went into hiding and nothing was known of him after 1413.
Henry Tudor (born in Wales in 1457) seized the throne of England from Richard III
Richard III (2 October 145222 August 1485) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from 26 June 1483 until his death in 1485. He was the last king of the House of York and the last of the Plantagenet dynasty. His defeat and death at the Battl ...
in 1485, uniting England and Wales under one royal house. The last remnants of Celtic-tradition Welsh law were abolished and replaced by English law by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542 during the reign of Henry VII's son, Henry VIII
Henry VIII (28 June 149128 January 1547) was King of England from 22 April 1509 until his death in 1547. Henry is best known for his six marriages, and for his efforts to have his first marriage (to Catherine of Aragon) annulled. His disa ...
. In the legal jurisdiction of England and Wales, Wales became unified with the kingdom of England; the " Principality of Wales" began to refer to the whole country, though it remained a "principality" only in a ceremonial sense. The Marcher lordships were abolished, and Wales began electing members of the Westminster parliament.
Early modern period
 In 1536 Wales had around 278,000 inhabitants, which increased to around 360,000 by 1620. This was primarily due to rural settlement, where animal farming was central to the Welsh economy. Increase in trade and increased economic stability occurred due to the increased diversity of the Welsh economy. Population growth however outpaced economic growth and the standard of living dropped.
Prior to the Industrial Revolution in Wales, there were small-scale industries scattered throughout Wales.Davies (2008) p. 392 These ranged from those connected to agriculture, such as milling and the manufacture of woollen textiles, through to mining and quarrying. Agriculture remained the dominant source of wealth. The emerging industrial period saw the development of copper smelting in the
In 1536 Wales had around 278,000 inhabitants, which increased to around 360,000 by 1620. This was primarily due to rural settlement, where animal farming was central to the Welsh economy. Increase in trade and increased economic stability occurred due to the increased diversity of the Welsh economy. Population growth however outpaced economic growth and the standard of living dropped.
Prior to the Industrial Revolution in Wales, there were small-scale industries scattered throughout Wales.Davies (2008) p. 392 These ranged from those connected to agriculture, such as milling and the manufacture of woollen textiles, through to mining and quarrying. Agriculture remained the dominant source of wealth. The emerging industrial period saw the development of copper smelting in the Swansea
Swansea (; cy, Abertawe ) is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Swansea ( cy, links=no, Dinas a Sir Abertawe).
The city is the twenty-fifth largest in ...
area. With access to local coal deposits and a harbour that connected it with Cornwall's copper mines in the south and the large copper deposits at Parys Mountain on Anglesey, Swansea developed into the world's major centre for non-ferrous metal smelting in the 19th century. The second metal industry to expand in Wales was iron smelting, and iron manufacturing became prevalent in both the north and the south of the country.Davies (2008) p. 393 In the north, John Wilkinson's Ironworks at Bersham was a major centre, while in the south, at Merthyr Tydfil
Merthyr Tydfil (; cy, Merthyr Tudful ) is the main town in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Wales, administered by Merthyr Tydfil County Borough Council. It is about north of Cardiff. Often called just Merthyr, it is said to be named after Tydf ...
, the ironworks of Dowlais, Cyfarthfa
Cyfarthfa is a community and electoral ward in the west of the town of Merthyr Tydfil in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Wales.
Community
Cyfarthfa mainly consists of the settlements of Gellideg and Heolgerrig and Rhyd-y-car area just west of Mer ...
, Plymouth and Penydarren became the most significant hub of iron manufacture in Wales. By the 1820s, south Wales produced 40 per cent of all Britain's pig iron
Pig iron, also known as crude iron, is an intermediate product of the iron industry in the production of steel which is obtained by smelting iron ore in a blast furnace. Pig iron has a high carbon content, typically 3.8–4.7%, along with silic ...
.
By the 18th century, lawyers, doctors, estate agents and government officials formed a bourgeoisie
The bourgeoisie ( , ) is a social class, equivalent to the middle or upper middle class. They are distinguished from, and traditionally contrasted with, the proletariat by their affluence, and their great cultural and financial capital. They ...
with sizeable houses. In the late 18th century, slate quarrying began to expand rapidly, most notably in North Wales. The Penrhyn Quarry, opened in 1770 by Richard Pennant
Richard Pennant, 1st Baron Penrhyn (1737 – 21 January 1808), was a Welsh politician and nobleman who served as an MP in the British Parliament, representing Petersfield and Liverpool for 29 years between 1761 and 1790. He was the owner of Penr ...
, was employing 15,000 men by the late 19th century,Davies (2008) p. 818 and along with Dinorwic Quarry, it dominated the Welsh slate trade. Although slate quarrying has been described as "the most Welsh of Welsh industries",Attributed to historian A. H. Dodd: Davies (2008) p. 819 it is coal mining which became the industry synonymous with Wales and its people. Initially, coal seams were exploited to provide energy for local metal industries but, with the opening of canal systems and later the railways, Welsh coal mining saw an explosion in demand. As the South Wales coalfield was exploited, Cardiff, Swansea, Penarth
Penarth (, ) is a town and Community (Wales), community in the Vale of Glamorgan ( cy, Bro Morgannwg), Wales, exactly south of Cardiff city centre on the west shore of the Severn Estuary at the southern end of Cardiff Bay.
Penarth is a weal ...
and Barry Barry may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Barry (name), including lists of people with the given name, nickname or surname, as well as fictional characters with the given name
* Dancing Barry, stage name of Barry Richards (born c. 195 ...
grew as world exporters of coal. By its height in 1913, Wales was producing almost 61 million tons of coal.
Modern period

 Historian Kenneth Morgan described Wales on the eve of the First World War as a "relatively placid, self-confident and successful nation". The output from the coalfields continued to increase, with the Rhondda Valley recording a peak of 9.6 million tons of coal extracted in 1913. The First World War (1914–1918) saw a total of 272,924 Welshmen under arms, representing 21.5 per cent of the male population. Of these, roughly 35,000 were killed,Davies (2008) p. 284 with particularly heavy losses of Welsh forces at
Historian Kenneth Morgan described Wales on the eve of the First World War as a "relatively placid, self-confident and successful nation". The output from the coalfields continued to increase, with the Rhondda Valley recording a peak of 9.6 million tons of coal extracted in 1913. The First World War (1914–1918) saw a total of 272,924 Welshmen under arms, representing 21.5 per cent of the male population. Of these, roughly 35,000 were killed,Davies (2008) p. 284 with particularly heavy losses of Welsh forces at Mametz Wood
The Mametz Wood Memorial commemorates an engagement of the 38th (Welsh) Division of the British Army during the First Battle of the Somme in France in 1916.
The memorial
The memorial, erected in 1987 by Welsh sculptor David Petersen, is a ...
on the Somme and the Battle of Passchendaele
The Third Battle of Ypres (german: link=no, Dritte Flandernschlacht; french: link=no, Troisième Bataille des Flandres; nl, Derde Slag om Ieper), also known as the Battle of Passchendaele (), was a campaign of the First World War, fought by t ...
. The first quarter of the 20th century also saw a shift in the political landscape of Wales. Since 1865, the Liberal Party had held a parliamentary majority in Wales and, following the general election of 1906, only one non-Liberal Member of Parliament, Keir Hardie of Merthyr Tydfil
Merthyr Tydfil (; cy, Merthyr Tudful ) is the main town in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Wales, administered by Merthyr Tydfil County Borough Council. It is about north of Cardiff. Often called just Merthyr, it is said to be named after Tydf ...
, represented a Welsh constituency at Westminster. Yet by 1906, industrial dissension and political militancy had begun to undermine Liberal consensus in the southern coalfields.Davies (2008) p. 461 In 1916, David Lloyd George became the first Welshman to become Prime Minister of Britain. In December 1918, Lloyd George was re-elected at the head of a Conservative-dominated coalition government, and his poor handling of the 1919 coal miners' strike was a key factor in destroying support for the Liberal party in south Wales.Davies (2008) p. 515 The industrial workers of Wales began shifting towards the Labour Party. When in 1908 the Miners' Federation of Great Britain became affiliated to the Labour Party, the four Labour candidates sponsored by miners were all elected as MPs. By 1922, half the Welsh seats at Westminster were held by Labour politicians—the start of a Labour dominance of Welsh politics that continued into the 21st century.Davies (2008) p. 439
After economic growth in the first two decades of the 20th century, Wales' staple industries endured a prolonged slump from the early 1920s to the late 1930s, leading to widespread unemployment and poverty. For the first time in centuries, the population of Wales went into decline; unemployment reduced only with the production demands of the Second World War. The war saw Welsh servicemen and women fight in all major theatres, with some 15,000 of them killed. Bombing raids brought high loss of life as the German Air Force
The German Air Force (german: Luftwaffe, lit=air weapon or air arm, ) is the aerial warfare branch of the , the armed forces of Germany. The German Air Force (as part of the ''Bundeswehr'') was founded in 1956 during the era of the Cold War a ...
targeted the docks at Swansea
Swansea (; cy, Abertawe ) is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Swansea ( cy, links=no, Dinas a Sir Abertawe).
The city is the twenty-fifth largest in ...
, Cardiff and Pembroke. After 1943, 10 per cent of Welsh conscripts aged 18 were sent to work in the coal mines, where there were labour shortages; they became known as Bevin Boys
Bevin Boys were young British men conscripted to work in coal mines between December 1943 and March 1948, to increase the rate of coal production, which had declined through the early years of World War II. The programme was named after Erne ...
. Pacifist
Pacifism is the opposition or resistance to war, militarism (including conscription and mandatory military service) or violence. Pacifists generally reject theories of Just War. The word ''pacifism'' was coined by the French peace campaign ...
numbers during both World Wars were fairly low, especially in the Second World War, which was seen as a fight against fascism.Davies (2008) p. 807
Plaid Cymru was formed in 1925, seeking greater autonomy or independence from the rest of the UK. The term " England and Wales" became common for describing the area to which English law applied, and in 1955 Cardiff was proclaimed as Wales' capital. '' Cymdeithas yr Iaith Gymraeg'' (The Welsh Language Society) was formed in 1962, in response to fears that the language might soon die out. Nationalist sentiment grew following the flooding of the Tryweryn valley in 1965 to create a reservoir to supply water to the English city of Liverpool. Although 35 of the 36 Welsh MPs voted against the bill (one abstained), Parliament passed the bill and the village of Capel Celyn was submerged, highlighting Wales' powerlessness in her own affairs in the face of the numerical superiority of English MPs in Parliament. Separatist groupings, such as the Free Wales Army and '' Mudiad Amddiffyn Cymru'' were formed, conducting campaigns from 1963. Prior to the investiture of Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
in 1969, these groups were responsible for a number of bomb attacks on infrastructure. At a by-election in 1966, Gwynfor Evans won the parliamentary seat of Carmarthen, Plaid Cymru's first Parliamentary seat.
 By the end of the 1960s, the policy of bringing businesses into disadvantaged areas of Wales through financial incentives had proven very successful in diversifying the industrial economy.Davies (2008) p. 236 This policy, begun in 1934, was enhanced by the construction of industrial estates and improvements in transport communications, most notably the
By the end of the 1960s, the policy of bringing businesses into disadvantaged areas of Wales through financial incentives had proven very successful in diversifying the industrial economy.Davies (2008) p. 236 This policy, begun in 1934, was enhanced by the construction of industrial estates and improvements in transport communications, most notably the M4 motorway
The M4, originally the London-South Wales Motorway, is a motorway in the United Kingdom running from west London to southwest Wales. The English section to the Severn Bridge was constructed between 1961 and 1971; the Welsh element was largely ...
linking south Wales directly to London. It was believed that the foundations for stable economic growth had been firmly established in Wales during this period, but this was shown to be optimistic after the recession of the early 1980s saw the collapse of much of the manufacturing base that had been built over the preceding forty years.Davies (2008) p. 237
Devolution
The Welsh Language Act 1967 repealed a section of the Wales and Berwick Act and thus "Wales" was no longer part of the legal definition of England. This essentially defined Wales as a separate entity legally (but within the UK), for the first time since before the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542 which defined Wales as a part of the Kingdom of England. The Welsh Language Act 1967 also expanded areas where use of Welsh was permitted, including in some legal situations. In a referendum in 1979, Wales voted against the creation of a Welsh assembly with an 80 per cent majority. In 1997, a second referendum on the same issue secured a very narrow majority (50.3 per cent). The National Assembly for Wales (''Cynulliad Cenedlaethol Cymru'') was set up in 1999 (under the Government of Wales Act 1998) with the power to determine how Wales' central government budget is spent and administered, although the UK Parliament reserved the right to set limits on its powers. The governments of the United Kingdom and of Wales almost invariably define Wales as a country.; The Welsh Government says: "Wales is not a Principality. Although we are joined with England by land, and we are part of Great Britain, Wales is a country in its own right."
The Government of Wales Act 2006 (c 32) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed the National Assembly for Wales and allows further powers to be granted to it more easily. The Act creates a system of government with a separate executive drawn from and accountable to the legislature. Following a successful referendum in 2011 on extending the law making powers of the National Assembly it is now able to make laws, known as Acts of the Assembly, on all matters in devolved subject areas, without needing the UK Parliament's agreement.
In the 2016 referendum, Wales voted in support of leaving the European Union, although demographic differences became evident. According to Danny Dorling, professor of geography at the Oxford University, “If you look at the more genuinely Welsh areas, especially the Welsh-speaking ones, they did not want to leave the EU,”
After the Senedd and Elections (Wales) Act 2020, the National Assembly was renamed "Senedd Cymru" (in Welsh) and the "Welsh Parliament" (in English) (also collectively referred to as the "
In a referendum in 1979, Wales voted against the creation of a Welsh assembly with an 80 per cent majority. In 1997, a second referendum on the same issue secured a very narrow majority (50.3 per cent). The National Assembly for Wales (''Cynulliad Cenedlaethol Cymru'') was set up in 1999 (under the Government of Wales Act 1998) with the power to determine how Wales' central government budget is spent and administered, although the UK Parliament reserved the right to set limits on its powers. The governments of the United Kingdom and of Wales almost invariably define Wales as a country.; The Welsh Government says: "Wales is not a Principality. Although we are joined with England by land, and we are part of Great Britain, Wales is a country in its own right."
The Government of Wales Act 2006 (c 32) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that reformed the National Assembly for Wales and allows further powers to be granted to it more easily. The Act creates a system of government with a separate executive drawn from and accountable to the legislature. Following a successful referendum in 2011 on extending the law making powers of the National Assembly it is now able to make laws, known as Acts of the Assembly, on all matters in devolved subject areas, without needing the UK Parliament's agreement.
In the 2016 referendum, Wales voted in support of leaving the European Union, although demographic differences became evident. According to Danny Dorling, professor of geography at the Oxford University, “If you look at the more genuinely Welsh areas, especially the Welsh-speaking ones, they did not want to leave the EU,”
After the Senedd and Elections (Wales) Act 2020, the National Assembly was renamed "Senedd Cymru" (in Welsh) and the "Welsh Parliament" (in English) (also collectively referred to as the "Senedd
The Senedd (; ), officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and () in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, it makes laws for Wales, agrees certain taxes and scrutinises the Welsh Gove ...
"), which was seen as a better reflection of the body's expanded legislative powers.
In 2016, YesCymru
YesCymru is a non party-political campaign for an independent Wales. The organisation was formed in the Summer of 2014 and officially launched on 20 February 2016 in Cardiff. In 2022 it became a private company limited by guarantee without sha ...
was launched. A non party-political campaign for an independent Wales which held its first rally in Cardiff in 2019. An opinion poll in March 2021 showed a record 39 per cent support for Welsh independence when excluding don't knows.
Welsh language
 The Welsh language ( cy, Cymraeg) is an
The Welsh language ( cy, Cymraeg) is an Indo-European language
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the overwhelming majority of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and the northern Indian subcontinent. Some European languages of this family, English, French, Portuguese, Russian, Dutch ...
of the Celtic family; the most closely related languages are Cornish and Breton. Most linguists believe that the Celtic languages arrived in Britain around 600 BCE. The Brythonic languages ceased to be spoken in England and were replaced by the English language, which arrived in Wales around the end of the eighth century due to the defeat of the Kingdom of Powys.
The Bible translations into Welsh
Parts of the Bible have been translated into Welsh since at least the 15th century, but the most widely used translation of the Bible into Welsh for several centuries was the 1588 translation by William Morgan, '' Y Beibl cyssegr-lan sef Yr Hen ...
and the Protestant Reformation, which encouraged use of the vernacular in religious services, helped the language survive after Welsh elites abandoned it in favour of English in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries.
Successive Welsh Language Acts, in 1942, 1967
Events
January
* January 1 – Canada begins a year-long celebration of the 100th anniversary of Confederation, featuring the Expo 67 World's Fair.
* January 5
** Spain and Romania sign an agreement in Paris, establishing full consular and ...
and 1993
File:1993 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The Oslo I Accord is signed in an attempt to resolve the Israeli–Palestinian conflict; The Russian White House is shelled during the 1993 Russian constitutional crisis; Czechoslovakia is peace ...
, improved the legal status of Welsh. The Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011 modernised the 1993 Welsh Language Act and gave Welsh an official status in Wales for the first time, a major landmark for the language. The Measure also created the post of Welsh Language Commissioner, replacing the Welsh Language Board. Following the referendum in 2011, the Official Languages Act became the first Welsh law to be created in 600 years, according to the First Minister at the time, Carwyn Jones. This law was passed by Welsh Assembly members (AMs) only and made Welsh an official language of the National Assembly.
Starting in the 1960s, many road signs have been replaced by bilingual versions. Various public and private sector bodies have adopted bilingualism to a varying degree and (since 2011) Welsh is the only official (''de jure'') language in any part of the United Kingdom.
Government and politics
 Wales is a country that is part of the sovereign state of the United Kingdom. Constitutionally, the UK is a '' de jure'' unitary state, with a parliament and government in Westminster. Wales has a devolved, unicameral legislature known as the
Wales is a country that is part of the sovereign state of the United Kingdom. Constitutionally, the UK is a '' de jure'' unitary state, with a parliament and government in Westminster. Wales has a devolved, unicameral legislature known as the Senedd
The Senedd (; ), officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and () in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, it makes laws for Wales, agrees certain taxes and scrutinises the Welsh Gove ...
(Senedd Cymru - Welsh Parliament) which holds devolved powers from the UK Parliament via a reserved powers model. For the purposes of local government, Wales has been divided into 22 council areas since 1996. These "principal areas" are responsible for the provision of all local government services.
In the House of Commons – the 650-member lower house
A lower house is one of two Debate chamber, chambers of a Bicameralism, bicameral legislature, the other chamber being the upper house. Despite its official position "below" the upper house, in many legislatures worldwide, the lower house has co ...
of the UK Parliament – there are 40 members of Parliament (MPs) who represent Welsh constituencies. At the 2019 general election, 22 Labour and Labour Co-op
Labour and Co-operative Party (often abbreviated Labour Co-op; cy, Llafur a'r Blaid Gydweithredol) is a description used by candidates in United Kingdom elections who stand on behalf of both the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party and the Co-operativ ...
MPs were elected, along with 14 Conservative MPs and 4 Plaid Cymru MPs from Wales. The Wales Office is a department of the UK government responsible for Wales, whose minister the Secretary of State for Wales sits in the UK cabinet
The Cabinet of the United Kingdom is the senior decision-making body of His Majesty's Government. A committee of the Privy Council of the United Kingdom, Privy Council, it is chaired by the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, prime minister a ...
.
Senedd
Followingdevolution
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories h ...
in 1997, the Government of Wales Act 1998 created a Welsh devolved assembly now known as the Senedd
The Senedd (; ), officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and () in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, it makes laws for Wales, agrees certain taxes and scrutinises the Welsh Gove ...
(formally "" or "the Welsh Parliament", and formerly the "National Assembly for Wales" until 2020). Powers of the Secretary of State for Wales were transferred to the devolved government on 1 July 1999, granting the assembly the power to decide how the Westminster government's budget for devolved areas is spent and administered. The 1998 Act was amended by the Government of Wales Act 2006, which enhanced the institution's powers, giving it legislative powers akin to those of the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyro ...
and Northern Ireland Assembly
sco-ulster, Norlin Airlan Assemblie
, legislature = 7th Northern Ireland Assembly, Seventh Assembly
, coa_pic = File:NI_Assembly.svg
, coa_res = 250px
, house_type = Unicameralism, Unicameral
, hou ...
. The 60 members of the Senedd (MSs) are elected to five-year terms (four-year terms before 2011) under an additional member system. There are 40 single-member constituencies, with MSs directly elected using the first-past-the-post system. The remaining 20 MSs represent five electoral regions, each including between seven and nine constituencies, using proportional representation. The Senedd must elect a first minister (), who in turn selects ministers to form the Welsh Government.
The twenty areas of responsibility devolved to the Welsh Government, known as "subjects", include agriculture, economic development, education, health, housing, local government, social services, tourism, transport and the Welsh language. On its creation in 1999, the National Assembly for Wales had no primary legislative powers. In 2007, following passage of the Government of Wales Act 2006 (GoWA 2006), the assembly developed powers to pass primary legislation
Primary legislation and secondary legislation (the latter also called delegated legislation or subordinate legislation) are two forms of law, created respectively by the legislature, legislative and executive (government), executive branches of ...
known at the time as Assembly Measures on some specific matters within the areas of devolved responsibility. Further matters have been added subsequently, either directly by the UK Parliament or by the UK Parliament approving a Legislative Competence Order
In Wales, a Legislative Competence Order (LCO; pronounced 'elco') was a piece of constitutional legislation in the form of an Order in Council. It transferred legislative authority from the Parliament of the United Kingdom to the National Assembly ...
(LCO, a request from the assembly for additional powers). The GoWA 2006 allows for the Senedd to gain primary lawmaking powers on a more extensive range of matters within the same devolved areas if approved in a referendum. A referendum on extending the law-making powers of the then National Assembly was held on 3 March 2011 and secured a majority for extension. Consequently, the assembly became empowered to make laws, now known as Acts of Senedd Cymru, on all matters in the subject areas, without needing the UK Parliament's agreement.
The Senedd also promotes Welsh interests abroad. It has its own envoy to America, primarily to promote Wales-specific business interests. The primary Welsh Government Office is based in the Washington British Embassy, with satellites in New York City, Chicago, San Francisco, and Atlanta. The United States has also established a caucus to build direct relations with Wales. In the United States Congress, legislators with Welsh heritage and interests in Wales have established the Friends of Wales Caucus
The Friends of Wales Caucus is a congressional caucus consisting of Welsh and Welsh heritage congresspeople in the United States Government, Senate and House of Representatives.
The group was founded by Rep. Morgan Griffith of Virginia and joined ...
.
Law
 By tradition, Welsh Law was compiled during an assembly held at Whitland around 930 by Hywel Dda, king of most of Wales between 942 and his death in 950. The ' law of Hywel Dda' ( cy, Cyfraith Hywel), as it became known, codified the previously existing folk laws and legal customs that had evolved in Wales over centuries. Welsh Law emphasised the payment of compensation for a crime to the victim, or the victim's kin, rather than punishment by the ruler. Other than in the Marches, where
By tradition, Welsh Law was compiled during an assembly held at Whitland around 930 by Hywel Dda, king of most of Wales between 942 and his death in 950. The ' law of Hywel Dda' ( cy, Cyfraith Hywel), as it became known, codified the previously existing folk laws and legal customs that had evolved in Wales over centuries. Welsh Law emphasised the payment of compensation for a crime to the victim, or the victim's kin, rather than punishment by the ruler. Other than in the Marches, where March law March law or marcher law is a system of legal compromises formerly in use in the border regions of England. Specifically, it may refer to:
*March law (Anglo-Irish border)
*March law (Anglo-Scottish border)
*March law (Anglo-Welsh border)
See also ...
was imposed by the Marcher Lords, Welsh Law remained in force in Wales until the Statute of Rhuddlan in 1284. Edward I of England annexed the Principality of Wales following the death of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd, and Welsh Law was replaced for criminal cases under the Statute. Marcher Law and Welsh Law (for civil cases) remained in force until Henry VIII of England annexed the whole of Wales under the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542 (often referred to as the Acts of Union of 1536 and 1543), after which English law applied to the whole of Wales. The Wales and Berwick Act 1746 provided that all laws that applied to England would automatically apply to Wales (and the Anglo-Scottish border town of Berwick) unless the law explicitly stated otherwise; this Act was repealed with regard to Wales in 1967. English law has been the legal system of England and Wales since 1536.Davies (1994) p. 263
English law is regarded as a common law system, with no major codification of the law and legal precedents are binding as opposed to persuasive. The court system is headed by the Supreme Court of the United Kingdom
The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (initialism: UKSC or the acronym: SCOTUK) is the final court of appeal in the United Kingdom for all civil cases, and for criminal cases originating in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. As the Unite ...
which is the highest court of appeal in the land for criminal and civil cases. The Senior Courts of England and Wales is the highest court of first instance as well as an appellate court. The three divisions are the Court of Appeal
A court of appeals, also called a court of appeal, appellate court, appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to hear an appeal of a trial court or other lower tribunal. In much of t ...
; the High Court of Justice and the Crown Court
The Crown Court is the court of first instance of England and Wales responsible for hearing all Indictable offence, indictable offences, some Hybrid offence, either way offences and appeals lied to it by the Magistrates' court, magistrates' court ...
. Minor cases are heard by magistrates' courts or the County Court
A county court is a court based in or with a jurisdiction covering one or more counties, which are administrative divisions (subnational entities) within a country, not to be confused with the medieval system of ''county courts'' held by the high ...
. In 2007 the Wales and Cheshire Region (known as the Wales and Cheshire Circuit before 2005) came to an end when Cheshire was attached to the North-Western England Region. From that point, Wales became a legal unit in its own right, although it remains part of the single jurisdiction of England and Wales.
The Senedd
The Senedd (; ), officially known as the Welsh Parliament in English and () in Welsh, is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Wales. A democratically elected body, it makes laws for Wales, agrees certain taxes and scrutinises the Welsh Gove ...
has the authority to draft and approve laws outside of the UK Parliamentary system to meet the specific needs of Wales. Under powers approved by a referendum held in March 2011, it is empowered to pass primary legislation, at the time referred to as an Act of the National Assembly for Wales but now known as an Act of Senedd Cymru in relation to twenty subjects listed in the Government of Wales Act 2006 such as health and education. Through this primary legislation, the Welsh Government can then also enact more specific subordinate legislation.
Wales is served by four regional police forces, Dyfed-Powys Police, Gwent Police, North Wales Police and South Wales Police. There are five prisons in Wales
The prisons in Wales are run by His Majesty's Prison Service, which is in turn a part of HM Prison and Probation Service (HMPPS) which is an executive agency of the Ministry of Justice responsible for the correctional services in England and Wale ...
; four in the southern half of the country and one
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. I ...
in Wrexham. Wales has no women's prisons; female inmates are imprisoned in England.
Geography and natural history
 Wales is a generally mountainous country on the western side of central southern Great Britain. It is about north to south. The oft-quoted ' size of Wales' is about . Wales is bordered by England to the east and by sea in all other directions: the Irish Sea to the north and west,
Wales is a generally mountainous country on the western side of central southern Great Britain. It is about north to south. The oft-quoted ' size of Wales' is about . Wales is bordered by England to the east and by sea in all other directions: the Irish Sea to the north and west, St George's Channel
St George's Channel ( cy, Sianel San Siôr, ga, Muir Bhreatan) is a sea channel connecting the Irish Sea to the north and the Celtic Sea to the southwest.
Historically, the name "St George's Channel" was used interchangeably with "Irish Sea" ...
and the Celtic Sea to the southwest and the Bristol Channel
The Bristol Channel ( cy, Môr Hafren, literal translation: "Severn Sea") is a major inlet in the island of Great Britain, separating South Wales from Devon and Somerset in South West England. It extends from the lower estuary of the River Seve ...
to the south. Wales has about of coastline (along the mean high water mark), including the mainland, Anglesey and Holyhead. Over 50 islands lie off the Welsh mainland; the largest being Anglesey, in the north-west.
Much of Wales' diverse landscape is mountainous, particularly in the north and central regions. The mountains were shaped during the last ice age, the Devensian glaciation. The highest mountains in Wales are in Snowdonia (), of which five are over . The highest of these is Snowdon
Snowdon () or (), is the highest mountain in Wales, at an elevation of above sea level, and the highest point in the British Isles outside the Scottish Highlands. It is located in Snowdonia National Park (') in Gwynedd (historic ...
(), at . The 14 Welsh mountains, or 15 if including Carnedd Gwenllian
, List of Furths, Furth
Carnedd Gwenllian (named Y Garnedd Uchaf before 2009) is a minor summit of the Carneddau range in Snowdonia, Wales, and included in the Welsh 3000s. From the summit, distant views to the north can extend as far as Irel ...
often discounted because of its low topographic prominenceover high are known collectively as the Welsh 3000s and are located in a small area in the north-west. The highest outside the 3000s is Aran Fawddwy
Aran Fawddwy is a mountain in southern Snowdonia, Wales, United Kingdom. It is the highest point (county top) of the historic county of Merionethshire (for local government purposes, it lies within the current council area of Gwynedd). ...
, at , in the south of Snowdonia. The Brecon Beacons
The Brecon Beacons ( cy, Bannau Brycheiniog, ) are a mountain range in South Wales. In a narrow sense, the name refers to the range of Old Red Sandstone peaks which lie to the south of Brecon. Sometimes referred to as "the central Beacons" t ...
() are in the south (highest point Pen y Fan, at ), and are joined by the Cambrian Mountains
The Cambrian Mountains ( cy, Mynyddoedd Cambria, in a narrower sense: ''Elenydd'') are a series of mountain ranges in Wales.
The term ''Cambrian Mountains'' used to apply to most of the upland of Wales. Since the 1950s, its application has becom ...
in Mid Wales
Mid Wales ( cy, Canolbarth Cymru or simply ''Y Canolbarth'', meaning "the midlands") or Central Wales refers to a region of Wales, encompassing its midlands, in-between North Wales and South Wales. The Mid Wales Regional Committee of the Senedd ...
(highest point Pumlumon
Pumlumon (historically anglicised in various ways including ''Plynlimon,'' Plinlimon and Plinlimmon) is the highest point of the Cambrian Mountains in Wales (taking a restricted definition of the Cambrian Mountains, excluding Snowdonia, ...
, at ).
coastline of Wales
The coastline of Wales extends from the Wales-England border, English border at Chepstow westwards to Pembrokeshire then north to Anglesey and back eastwards to the English border once again near Flint, Flintshire, Flint. Its character is determi ...
had 40 Blue Flag beach
The Blue Flag is a certification by the Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE) that a beach, marina, or sustainable boating tourism operator meets its standards.
The Blue Flag is a trademark owned by FEE, which is a not-for-profit non-gov ...
es, three Blue Flag marinas and one Blue Flag boat operator. Despite its heritage and award-winning beaches; the south and west coasts of Wales, along with the Irish and Cornish coasts, are frequently blasted by Atlantic westerlies/south westerlies that, over the years, have sunk and wrecked many vessels. In 1859 over 110 ships were destroyed off the coast of Wales in a hurricane that saw more than 800 lives lost across Britain. The greatest single loss occurred with the sinking of the '' Royal Charter'' off Anglesey in which 459 people died. The 19th century saw over 100 vessels lost with an average loss of 78 sailors per year.Davies (2008) p.814 Wartime action caused losses near Holyhead, Milford Haven
Milford Haven ( cy, Aberdaugleddau, meaning "mouth of the two Rivers Cleddau") is both a town and a community in Pembrokeshire, Wales. It is situated on the north side of the Milford Haven Waterway, an estuary forming a natural harbour that has ...
and Swansea. Because of offshore rocks and unlit islands, Anglesey and Pembrokeshire are still notorious for shipwrecks, most notably the ''Sea Empress'' oil spill in 1996.
The first border between Wales and England was zonal, apart from around the River Wye, which was the first accepted boundary.Davies (2008) p. 75 Offa's Dyke was supposed to form an early distinct line but this was thwarted by Gruffudd ap Llewellyn, who reclaimed swathes of land beyond the dyke. The Act of Union of 1536 formed a linear border stretching from the mouth of the Dee to the mouth of the Wye. Even after the Act of Union, many of the borders remained vague and moveable until the Welsh Sunday Closing act of 1881, which forced local businesses to decide which country they fell within to accept either the Welsh or English law.
Geology
The earliest geological period of thePalaeozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and '' ...
era, the Cambrian
The Cambrian Period ( ; sometimes symbolized C with bar, Ꞓ) was the first geological period of the Paleozoic Era, and of the Phanerozoic Eon. The Cambrian lasted 53.4 million years from the end of the preceding Ediacaran Period 538.8 million ...
, takes its name from the Cambrian Mountains
The Cambrian Mountains ( cy, Mynyddoedd Cambria, in a narrower sense: ''Elenydd'') are a series of mountain ranges in Wales.
The term ''Cambrian Mountains'' used to apply to most of the upland of Wales. Since the 1950s, its application has becom ...
, where geologists first identified Cambrian remnants. In the mid-19th century, Roderick Murchison
Sir Roderick Impey Murchison, 1st Baronet, (19 February 1792 – 22 October 1871) was a Scotland, Scottish geologist who served as director-general of the British Geological Survey from 1855 until his death in 1871. He is noted for investigat ...
and Adam Sedgwick
Adam Sedgwick (; 22 March 1785 – 27 January 1873) was a British geologist and Anglican priest, one of the founders of modern geology. He proposed the Cambrian and Devonian period of the geological timescale. Based on work which he did on W ...
used their studies of Welsh geology to establish certain principles of stratigraphy
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock (geology), rock layers (Stratum, strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary rock, sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks.
Stratigrap ...
and palaeontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
. The next two periods of the Palaeozoic era, the Ordovician and Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozo ...
, were named after ancient Celtic tribes from this area.
Climate
 Wales lies within the north temperate zone. It has a changeable, maritime climate and is one of the wettest countries in Europe.Davies (2008) pp. 148–150 Welsh weather is often cloudy, wet and windy, with warm summers and mild winters.
* Highest maximum temperature: at Hawarden, Flintshire on 18 July 2022.
* Lowest minimum temperature: at Rhayader,
Wales lies within the north temperate zone. It has a changeable, maritime climate and is one of the wettest countries in Europe.Davies (2008) pp. 148–150 Welsh weather is often cloudy, wet and windy, with warm summers and mild winters.
* Highest maximum temperature: at Hawarden, Flintshire on 18 July 2022.
* Lowest minimum temperature: at Rhayader, Radnorshire
, HQ = Presteigne
, Government = Radnorshire County Council (1889–1974) Radnorshire District Council (1974–1996)
, Origin =
, Status = historic county, administrative county
, Start ...
(now Powys) on 21 January 1940.
* Maximum number of hours of sunshine in a month: 354.3 hours at Dale Fort, Pembrokeshire in July 1955.
* Minimum number of hours of sunshine in a month: 2.7 hours at Llwynon, Brecknockshire
, image_flag=
, HQ= Brecon
, Government= Brecknockshire County Council (1889-1974)
, Origin= Brycheiniog
, Status=
, Start= 1535
, End= ...
in January 1962.
* Maximum rainfall in a day (0900 UTC − 0900 UTC): at Rhondda, Glamorgan, on 11 November 1929.
* Wettest spot – an average of rain a year at Crib Goch
Crib Goch is described as a "knife-edged" arête in the Snowdonia National Park in Gwynedd, Wales. The name means "red ridge" in the Welsh language.
The highest point on the arête is above sea level. All routes which tackle Crib Goch are co ...
in Snowdonia, Gwynedd (making it also the wettest spot in the United Kingdom).
Flora and fauna
Wales' wildlife is typical of Britain with several distinctions. Because of its long coastline, Wales hosts a variety of seabirds. The coasts and surrounding islands are home to colonies of gannets,Manx shearwater
The Manx shearwater (''Puffinus puffinus'') is a medium-sized shearwater in the seabird family Procellariidae. The scientific name of this species records a name shift: Manx shearwaters were called Manks puffins in the 17th century. Puffin is an ...
, puffin
Puffins are any of three species of small alcids (auks) in the bird genus ''Fratercula''. These are pelagic seabirds that feed primarily by diving in the water. They breed in large colonies on coastal cliffs or offshore islands, nesting in crev ...
s, kittiwakes
The kittiwakes (genus ''Rissa'') are two closely related seabird species in the gull family Laridae, the black-legged kittiwake (''Rissa tridactyla'') and the red-legged kittiwake (''Rissa brevirostris''). The epithets "black-legged" and "red- ...
, shags and razorbills. In comparison, with 60 per cent of Wales above the 150m contour, the country also supports a variety of upland habitat birds, including raven
A raven is any of several larger-bodied bird species of the genus ''Corvus''. These species do not form a single taxonomic group within the genus. There is no consistent distinction between "crows" and "ravens", common names which are assigned t ...
and ring ouzel. Birds of prey include the merlin
Merlin ( cy, Myrddin, kw, Marzhin, br, Merzhin) is a mythical figure prominently featured in the legend of King Arthur and best known as a mage, with several other main roles. His usual depiction, based on an amalgamation of historic and le ...
, hen harrier and the red kite, a national symbol of Welsh wildlife. In total, more than 200 different species of bird have been seen at the RSPB
The Royal Society for the Protection of Birds (RSPB) is a Charitable_organization#United_Kingdom, charitable organisation registered in Charity Commission for England and Wales, England and Wales and in Office of the Scottish Charity Regulator, ...
reserve at Conwy, including seasonal visitors. Larger mammals, including brown bears, wolves and wildcats, died out during the Norman period. Today, mammals include shrews, voles, badgers, otters, stoats, weasels, hedgehogs and fifteen species of bat. Two species of small rodent, the yellow-necked mouse and the dormouse, are of special Welsh note being found at the historically undisturbed border area.Davies (2008) p. 533 The pine marten, which has been sighted occasionally, has been reintroduced in parts of Wales since 2015, having previously not been officially recorded since the 1950s. The polecat was nearly driven to extinction in Britain, but hung on in Wales and is now rapidly spreading. Feral goats can be found in Snowdonia. In March 2021, Natural Resources Wales (NRW) granted a licence to release up to six beaver
Beavers are large, semiaquatic rodents in the genus ''Castor'' native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. There are two extant species: the North American beaver (''Castor canadensis'') and the Eurasian beaver (''C. fiber''). Beavers ar ...
s in the Dyfi Valley, the first official beaver release in Wales.
The waters of south-west Wales of Gower, Pembrokeshire and Cardigan Bay attract marine animals, including basking sharks
The basking shark (''Cetorhinus maximus'') is the second-largest living shark and fish, after the whale shark, and one of three plankton-eating shark species, along with the whale shark and megamouth shark. Adults typically reach in length. ...
, Atlantic grey seals, leatherback turtles, dolphins, porpoises
Porpoises are a group of fully aquatic marine mammals, all of which are classified under the family Phocoenidae, parvorder Odontoceti (toothed whales). Although similar in appearance to dolphins, they are more closely related to narwhals an ...
, jellyfish, crabs and lobsters. Pembrokeshire and Ceredigion, in particular, are recognised as an area of international importance for bottlenose dolphin
Bottlenose dolphins are aquatic mammals in the genus ''Tursiops.'' They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus definitively contains two species: the common ...
s, and New Quay has the only summer residence of bottlenose dolphins in the whole of the UK. River fish of note include char
Char may refer to:
People
*Char Fontane, American actress
*Char Margolis, American spiritualist
* René Char (1907–1988), French poet
*The Char family of Colombia:
** Fuad Char, Colombian senator
** Alejandro Char Chaljub, mayor of Barranquilla ...
, eel, salmon, shad
The Alosinae, or the shads,Alosinae
, sparling and Arctic char, whilst the
 Over the last 250 years, Wales has been transformed from a predominantly agricultural country to an industrial, and then to a post-industrial economy. In the 1950s Wales' GDP was twice as big as Ireland’s; by the 2020s Ireland's economy was four times that of Wales. Since the Second World War, the
Over the last 250 years, Wales has been transformed from a predominantly agricultural country to an industrial, and then to a post-industrial economy. In the 1950s Wales' GDP was twice as big as Ireland’s; by the 2020s Ireland's economy was four times that of Wales. Since the Second World War, the
 The
The
 A distinct education system has developed in Wales.Davies (2008) p. 238 Formal education before the 18th century was the preserve of the elite. The first grammar schools were established in Welsh towns such as Ruthin, Brecon and Cowbridge. One of the first successful schooling systems was started by Griffith Jones, who introduced the circulating schools in the 1730s; these are believed to have taught half the country's population to read.Davies (2008) p. 239 In the 19th century, with increasing state involvement in education, Wales was forced to adopt an education system that was English in ethos even though the country was predominantly Non-conformist, Welsh-speaking and demographically uneven because of the economic expansion in the south. In some schools, to ensure Welsh children spoke English at school, the Welsh Not was employed as corrective punishment; this was much resented, although the extent of its use is difficult to determine. State and local governmental edicts resulted in schooling in the English language which, following the 1847 Inquiry into the State of Education in Wales – an event subsequently referred to as the Treachery of the Blue Books () – was seen as more academic and worthwhile for children.
The University College of Wales opened in Aberystwyth in 1872. Cardiff and Bangor followed, and the three colleges came together in 1893 to form the University of Wales. The Welsh Intermediate Education Act of 1889 created 95 secondary schools. The Welsh Department for the Board of Education followed in 1907, which gave Wales its first significant educational devolution. A resurgence in Welsh-language schools in the latter half of the 20th century at nursery and primary level saw attitudes shift towards teaching in the medium of Welsh.Davies (2008) p. 240 Welsh is a compulsory subject in all of Wales' state schools for pupils aged 5–16 years old. While there has never been an exclusively Welsh-language college, Welsh-medium higher education is delivered through the individual universities and has since 2011 been supported by the Coleg Cymraeg Cenedlaethol (Welsh National College) as a delocalised federal institution. In 2021–2022, there were 1,470 maintained schools in Wales. In 2021–22, the country had 471,131 pupils taught by 25,210 full-time equivalent teachers.
A distinct education system has developed in Wales.Davies (2008) p. 238 Formal education before the 18th century was the preserve of the elite. The first grammar schools were established in Welsh towns such as Ruthin, Brecon and Cowbridge. One of the first successful schooling systems was started by Griffith Jones, who introduced the circulating schools in the 1730s; these are believed to have taught half the country's population to read.Davies (2008) p. 239 In the 19th century, with increasing state involvement in education, Wales was forced to adopt an education system that was English in ethos even though the country was predominantly Non-conformist, Welsh-speaking and demographically uneven because of the economic expansion in the south. In some schools, to ensure Welsh children spoke English at school, the Welsh Not was employed as corrective punishment; this was much resented, although the extent of its use is difficult to determine. State and local governmental edicts resulted in schooling in the English language which, following the 1847 Inquiry into the State of Education in Wales – an event subsequently referred to as the Treachery of the Blue Books () – was seen as more academic and worthwhile for children.
The University College of Wales opened in Aberystwyth in 1872. Cardiff and Bangor followed, and the three colleges came together in 1893 to form the University of Wales. The Welsh Intermediate Education Act of 1889 created 95 secondary schools. The Welsh Department for the Board of Education followed in 1907, which gave Wales its first significant educational devolution. A resurgence in Welsh-language schools in the latter half of the 20th century at nursery and primary level saw attitudes shift towards teaching in the medium of Welsh.Davies (2008) p. 240 Welsh is a compulsory subject in all of Wales' state schools for pupils aged 5–16 years old. While there has never been an exclusively Welsh-language college, Welsh-medium higher education is delivered through the individual universities and has since 2011 been supported by the Coleg Cymraeg Cenedlaethol (Welsh National College) as a delocalised federal institution. In 2021–2022, there were 1,470 maintained schools in Wales. In 2021–22, the country had 471,131 pupils taught by 25,210 full-time equivalent teachers.
 Public healthcare in Wales is provided by NHS Wales (), through seven local health boards and three all-Wales trusts. It was originally formed as part of the NHS structure for England and Wales by the
Public healthcare in Wales is provided by NHS Wales (), through seven local health boards and three all-Wales trusts. It was originally formed as part of the NHS structure for England and Wales by the
 Welsh is an official language in Wales as legislated by the Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011. Both Welsh and English are also official languages of the Senedd. The proportion of the Welsh population able to speak the Welsh language fell from just under 50 per cent in 1901 to 43.5 per cent in 1911, and continued to fall to a low of 18.9 per cent in 1981.Results of the 2001 Census: Country of birth (www.statistics.gov.uk)
Welsh is an official language in Wales as legislated by the Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011. Both Welsh and English are also official languages of the Senedd. The proportion of the Welsh population able to speak the Welsh language fell from just under 50 per cent in 1901 to 43.5 per cent in 1911, and continued to fall to a low of 18.9 per cent in 1981.Results of the 2001 Census: Country of birth (www.statistics.gov.uk)
/ref> The results of the 2001 Census showed an increase in the number of Welsh speakers to 21 per cent of the population aged 3 and older, compared with 18.7 per cent in 1991 and 19 per cent in 1981. This compares with a pattern of steady decline indicated by census results during the 20th century. In the 2011 census it was recorded that the proportion of people able to speak Welsh had dropped from 20.8 per cent to 19 per cent (still higher than 1991). Despite an increase in the overall size of the Welsh population this still meant that the number of Welsh speakers in Wales dropped from 582,000 in 2001 to 562,000 in 2011. However this figure was still much higher than 508,000 or 18.7 per cent of people who said they could speak Welsh in the 1991 census. According to the 2021 census, the Welsh-speaking population of Wales aged three or older was 17.8 per cent (538,300 people) and nearly three quarters of the population in Wales said they had no Welsh language skills. Other estimates suggest that 29.7 per cent (899,500) of people aged three or older in Wales could speak Welsh in June 2022. English is spoken by almost all people in Wales and is the main language in most of the country. Code-switching is common in all parts of Wales and is known by various terms, though none is recognised by professional linguists.Davies (2008) p. 262 "
 The 2021 census recorded 46.5 per cent had “No religion”, more than any single religious affiliation and up from 32.1 per cent in 2011. The largest religion in Wales is Christianity, with 43.6 per cent of the population describing themselves as Christian in the 2021 census.
The Church in Wales with 56,000 adherents has the largest attendance of the denominations. It is a province of the Anglican Communion, and was part of the Church of England until disestablishment in 1920 under the Welsh Church Act 1914. The first
The 2021 census recorded 46.5 per cent had “No religion”, more than any single religious affiliation and up from 32.1 per cent in 2011. The largest religion in Wales is Christianity, with 43.6 per cent of the population describing themselves as Christian in the 2021 census.
The Church in Wales with 56,000 adherents has the largest attendance of the denominations. It is a province of the Anglican Communion, and was part of the Church of England until disestablishment in 1920 under the Welsh Church Act 1914. The first
 Wales has one of the oldest unbroken literary traditions in EuropeDavies (2008) p. 464 going back to the sixth century and including Geoffrey of Monmouth and Gerald of Wales, regarded as among the finest Latin authors of the Middle Ages. The earliest body of Welsh verse, by poets Taliesin and Aneirin, survive not in their original form, but in much-changed, medieval versions. Welsh poetry and native lore and learning survived the Dark Ages, through the era of the
Wales has one of the oldest unbroken literary traditions in EuropeDavies (2008) p. 464 going back to the sixth century and including Geoffrey of Monmouth and Gerald of Wales, regarded as among the finest Latin authors of the Middle Ages. The earliest body of Welsh verse, by poets Taliesin and Aneirin, survive not in their original form, but in much-changed, medieval versions. Welsh poetry and native lore and learning survived the Dark Ages, through the era of the

 An Act of Parliament in 1857 provided for the establishment of a number of art schools throughout the United Kingdom and the
An Act of Parliament in 1857 provided for the establishment of a number of art schools throughout the United Kingdom and the
 Today, Wales is widely regarded as a modern Celtic nations, Celtic nation which contributes to Wales' national identity. Welsh artists are also regularly invited to List of Celtic festivals, Celtic festivals.
The Welsh Dragon, red dragon is an important symbol of national identity and pride in Wales and is said to personify the fearlessness of the Welsh nation. The dragon is first referenced in literature as a symbol of the people in the Historia Brittonum. Vortigern () King of the Britons, King of the Celtic Britons is interrupted whilst attempting to build a fort at Dinas Emrys. He is told by Ambrosius. Embreis Guletic is probably Emrys Gwledig. to dig up two dragons beneath the castle. He discovers a red dragon representing the
Today, Wales is widely regarded as a modern Celtic nations, Celtic nation which contributes to Wales' national identity. Welsh artists are also regularly invited to List of Celtic festivals, Celtic festivals.
The Welsh Dragon, red dragon is an important symbol of national identity and pride in Wales and is said to personify the fearlessness of the Welsh nation. The dragon is first referenced in literature as a symbol of the people in the Historia Brittonum. Vortigern () King of the Britons, King of the Celtic Britons is interrupted whilst attempting to build a fort at Dinas Emrys. He is told by Ambrosius. Embreis Guletic is probably Emrys Gwledig. to dig up two dragons beneath the castle. He discovers a red dragon representing the
 More than 50 Governing bodies of sports in Wales, national governing bodies regulate and organise their sports in Wales. Most of those involved in competitive sports select, organise and manage individuals or teams to represent their country at international events or fixtures against other countries. Wales is represented at major world sporting events such as the FIFA World Cup, Rugby World Cup, Rugby League World Cup and the Commonwealth Games. At the Olympic Games, Welsh athletes compete alongside those of Scotland, England and Northern Ireland as part of a Great Britain at the Olympics, Great Britain team. Wales has hosted several international sporting events. These include the 1958 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, 1958 Commonwealth Games, the 1999 Rugby World Cup, the 2010 Ryder Cup and the 2017 UEFA Champions League Final.
Although football has traditionally been the more popular sport in North Wales, rugby union in Wales, rugby union is seen as a symbol of Welsh national identity, Welsh identity and an expression of national consciousness. The Wales national rugby union team takes part in the annual Six Nations Championship and has also competed in every Rugby World Cup, hosting the tournament in 1999 Rugby World Cup, 1999. The five professional sides that replaced the traditional club sides in major competitions in 2003 were replaced in 2004 by the four regions: Cardiff Blues, Dragons (rugby union), Dragons, Ospreys (rugby union), Ospreys and Scarlets. The Welsh regional teams play in the United Rugby Championship, the Heineken Champions Cup if they qualify and the European Rugby Challenge Cup, again dependent on qualification. Rugby league in Wales dates back to 1907. A professional Welsh League existed from 1908 to 1910.
Wales has had football in Wales, its own football league, the Welsh Premier League, since 1992. For historical reasons, five Welsh clubs play in the English football league system; Cardiff City F.C., Cardiff City, Swansea City A.F.C., Swansea City, Newport County A.F.C, Newport County, Wrexham A.F.C., Wrexham, and Merthyr Town F.C. (2010), Merthyr Town. Famous Welsh players over the years include John Charles, John Toshack, Gary Speed, Ian Rush, Ryan Giggs, Gareth Bale, Aaron Ramsey, and Daniel James (footballer), Daniel James. At UEFA Euro 2016, the Wales national football team, Wales national team achieved their best ever finish, reaching the semi-finals where they were beaten by eventual champions Portugal.
In international cricket, Wales and England field a single representative team, administered by the England and Wales Cricket Board (ECB), called the England cricket team, or simply 'England'. Occasionally, a separate Wales cricket team, Wales team play limited-overs competitions. Glamorgan County Cricket Club is the only Welsh participant in the England and Wales County Championship. Wales has produced several notable participants of individual and team sports including snooker players Ray Reardon, Terry Griffiths, Mark Williams (snooker player), Mark Williams and Matthew Stevens. Track athletes who have made a mark on the world stage include hurdler Colin Jackson and Paralympian Tanni Grey-Thompson. Champion cyclists include Nicole Cooke and Geraint Thomas. Wales has a tradition of producing world-class boxers. Joe Calzaghe was WBO world super-middleweight champion and then won the WBA, WBC and Ring Magazine super middleweight and Ring Magazine light-heavyweight titles. Other former boxing world champions include Enzo Maccarinelli, Freddie Welsh, Howard Winstone, Percy Jones (boxer), Percy Jones, Jimmy Wilde, Steve Robinson (boxer), Steve Robinson and Robbie Regan. Tommy Farr, the "Tonypandy Terror", came close to defeating world heavyweight champion Joe Louis at the height of his fame in 1937.
More than 50 Governing bodies of sports in Wales, national governing bodies regulate and organise their sports in Wales. Most of those involved in competitive sports select, organise and manage individuals or teams to represent their country at international events or fixtures against other countries. Wales is represented at major world sporting events such as the FIFA World Cup, Rugby World Cup, Rugby League World Cup and the Commonwealth Games. At the Olympic Games, Welsh athletes compete alongside those of Scotland, England and Northern Ireland as part of a Great Britain at the Olympics, Great Britain team. Wales has hosted several international sporting events. These include the 1958 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, 1958 Commonwealth Games, the 1999 Rugby World Cup, the 2010 Ryder Cup and the 2017 UEFA Champions League Final.
Although football has traditionally been the more popular sport in North Wales, rugby union in Wales, rugby union is seen as a symbol of Welsh national identity, Welsh identity and an expression of national consciousness. The Wales national rugby union team takes part in the annual Six Nations Championship and has also competed in every Rugby World Cup, hosting the tournament in 1999 Rugby World Cup, 1999. The five professional sides that replaced the traditional club sides in major competitions in 2003 were replaced in 2004 by the four regions: Cardiff Blues, Dragons (rugby union), Dragons, Ospreys (rugby union), Ospreys and Scarlets. The Welsh regional teams play in the United Rugby Championship, the Heineken Champions Cup if they qualify and the European Rugby Challenge Cup, again dependent on qualification. Rugby league in Wales dates back to 1907. A professional Welsh League existed from 1908 to 1910.
Wales has had football in Wales, its own football league, the Welsh Premier League, since 1992. For historical reasons, five Welsh clubs play in the English football league system; Cardiff City F.C., Cardiff City, Swansea City A.F.C., Swansea City, Newport County A.F.C, Newport County, Wrexham A.F.C., Wrexham, and Merthyr Town F.C. (2010), Merthyr Town. Famous Welsh players over the years include John Charles, John Toshack, Gary Speed, Ian Rush, Ryan Giggs, Gareth Bale, Aaron Ramsey, and Daniel James (footballer), Daniel James. At UEFA Euro 2016, the Wales national football team, Wales national team achieved their best ever finish, reaching the semi-finals where they were beaten by eventual champions Portugal.
In international cricket, Wales and England field a single representative team, administered by the England and Wales Cricket Board (ECB), called the England cricket team, or simply 'England'. Occasionally, a separate Wales cricket team, Wales team play limited-overs competitions. Glamorgan County Cricket Club is the only Welsh participant in the England and Wales County Championship. Wales has produced several notable participants of individual and team sports including snooker players Ray Reardon, Terry Griffiths, Mark Williams (snooker player), Mark Williams and Matthew Stevens. Track athletes who have made a mark on the world stage include hurdler Colin Jackson and Paralympian Tanni Grey-Thompson. Champion cyclists include Nicole Cooke and Geraint Thomas. Wales has a tradition of producing world-class boxers. Joe Calzaghe was WBO world super-middleweight champion and then won the WBA, WBC and Ring Magazine super middleweight and Ring Magazine light-heavyweight titles. Other former boxing world champions include Enzo Maccarinelli, Freddie Welsh, Howard Winstone, Percy Jones (boxer), Percy Jones, Jimmy Wilde, Steve Robinson (boxer), Steve Robinson and Robbie Regan. Tommy Farr, the "Tonypandy Terror", came close to defeating world heavyweight champion Joe Louis at the height of his fame in 1937.
 Wales became the UK's first digital television nation. BBC Cymru Wales is the national broadcaster, producing both television and radio programmes in Welsh and English from its base in Central Square, Cardiff, Central Square, Cardiff. The broadcaster also produces programmes such as ''Life on Mars (British TV series), Life on Mars'', ''Doctor Who'' and ''Torchwood'' for BBC's network audience across the United Kingdom. ITV (TV network), ITV, the UK's main commercial broadcaster, has a Welsh-oriented service branded as ITV Cymru Wales, whose studios are in Cardiff Bay. S4C, based in Carmarthen, first broadcast on 1 November 1982. Its output was mostly in Welsh at peak hours but shared English-language content with Channel 4 at other times. Since the digital television transition, digital switchover in April 2010, the channel has broadcast exclusively in Welsh. BBC Radio Cymru is the BBC's Welsh-language radio service, which broadcasts throughout Wales. A number of independent radio stations broadcast in the Welsh regions, predominantly in English. In 2006, several regional radio stations broadcast in Welsh: output ranged from two two-minute news bulletins each weekday (Radio Maldwyn) to over 14 hours of Welsh-language programmes weekly (Swansea Sound) to essentially bilingual stations such as Heart Cymru and Radio Ceredigion.
Most of the newspapers sold and read in Wales are national newspapers available throughout Britain. The ''Western Mail (Wales), Western Mail'' is Wales's only print national daily newspaper, but a new online and occasional print national newspaper, ''The National'', launched on Saint David's Day in 2021. Wales-based regional daily newspapers include the ''Daily Post (North Wales), Daily Post'' (which covers North Wales), the ''South Wales Evening Post'' (Swansea), the ''South Wales Echo'' (Cardiff), and the ''South Wales Argus'' (Newport). ''Y Cymro'' is a Welsh-language newspaper, published weekly. ''Wales on Sunday'' is the only Welsh Sunday newspaper that covers the whole of Wales. The Books Council of Wales (BCW, previously known as the Welsh Books Council) is the Welsh-Government-funded body tasked with promoting Welsh literature in Welsh and English. The BCW provides publishing grants for qualifying English- and Welsh-language publications. Around 600–650 books are published each year, by some of the dozens of Welsh publishers. Wales' main publishing houses include Gomer Press, Gwasg Carreg Gwalch, Honno (press), Honno, the University of Wales Press and Y Lolfa. ''Cambria'', a Welsh affairs magazine published bi-monthly in English, has subscribers internationally. Titles published quarterly in English include ''Planet'' and ''Poetry Wales''. Welsh-language magazines include the current affairs titles ''Golwg'' ("View"), published weekly, and ''Barn (Welsh magazine), Barn'' ("Opinion"), published monthly. Among the specialist magazines, ''Y Wawr'' ("The Dawn") is published quarterly by ''Merched y Wawr'', the national organisation for women. ''Y Traethodydd'' ("The Essayist"), a quarterly publication by the Presbyterian Church of Wales, first appeared in 1845 and is the oldest Welsh publication still in print.
Wales became the UK's first digital television nation. BBC Cymru Wales is the national broadcaster, producing both television and radio programmes in Welsh and English from its base in Central Square, Cardiff, Central Square, Cardiff. The broadcaster also produces programmes such as ''Life on Mars (British TV series), Life on Mars'', ''Doctor Who'' and ''Torchwood'' for BBC's network audience across the United Kingdom. ITV (TV network), ITV, the UK's main commercial broadcaster, has a Welsh-oriented service branded as ITV Cymru Wales, whose studios are in Cardiff Bay. S4C, based in Carmarthen, first broadcast on 1 November 1982. Its output was mostly in Welsh at peak hours but shared English-language content with Channel 4 at other times. Since the digital television transition, digital switchover in April 2010, the channel has broadcast exclusively in Welsh. BBC Radio Cymru is the BBC's Welsh-language radio service, which broadcasts throughout Wales. A number of independent radio stations broadcast in the Welsh regions, predominantly in English. In 2006, several regional radio stations broadcast in Welsh: output ranged from two two-minute news bulletins each weekday (Radio Maldwyn) to over 14 hours of Welsh-language programmes weekly (Swansea Sound) to essentially bilingual stations such as Heart Cymru and Radio Ceredigion.
Most of the newspapers sold and read in Wales are national newspapers available throughout Britain. The ''Western Mail (Wales), Western Mail'' is Wales's only print national daily newspaper, but a new online and occasional print national newspaper, ''The National'', launched on Saint David's Day in 2021. Wales-based regional daily newspapers include the ''Daily Post (North Wales), Daily Post'' (which covers North Wales), the ''South Wales Evening Post'' (Swansea), the ''South Wales Echo'' (Cardiff), and the ''South Wales Argus'' (Newport). ''Y Cymro'' is a Welsh-language newspaper, published weekly. ''Wales on Sunday'' is the only Welsh Sunday newspaper that covers the whole of Wales. The Books Council of Wales (BCW, previously known as the Welsh Books Council) is the Welsh-Government-funded body tasked with promoting Welsh literature in Welsh and English. The BCW provides publishing grants for qualifying English- and Welsh-language publications. Around 600–650 books are published each year, by some of the dozens of Welsh publishers. Wales' main publishing houses include Gomer Press, Gwasg Carreg Gwalch, Honno (press), Honno, the University of Wales Press and Y Lolfa. ''Cambria'', a Welsh affairs magazine published bi-monthly in English, has subscribers internationally. Titles published quarterly in English include ''Planet'' and ''Poetry Wales''. Welsh-language magazines include the current affairs titles ''Golwg'' ("View"), published weekly, and ''Barn (Welsh magazine), Barn'' ("Opinion"), published monthly. Among the specialist magazines, ''Y Wawr'' ("The Dawn") is published quarterly by ''Merched y Wawr'', the national organisation for women. ''Y Traethodydd'' ("The Essayist"), a quarterly publication by the Presbyterian Church of Wales, first appeared in 1845 and is the oldest Welsh publication still in print.
 Traditional Welsh dishes include laverbread (made from ''Porphyra umbilicalis'', an edible seaweed); bara brith (fruit bread); cawl (a lamb stew); cawl cennin (leek soup); and Welsh cakes. Cockle (bivalve), Cockles are sometimes served as a traditional breakfast with bacon and laverbread. Although Wales has its own traditional food and has absorbed much of the cuisine of England, Welsh diets now owe more to the countries of Indian cuisine, India, Chinese cuisine, China and the Cuisine of the United States, United States. Chicken tikka masala is the country's favourite dish while hamburgers and Chinese food outsell fish and chips as takeaways.Davies (2008) p.293
Traditional Welsh dishes include laverbread (made from ''Porphyra umbilicalis'', an edible seaweed); bara brith (fruit bread); cawl (a lamb stew); cawl cennin (leek soup); and Welsh cakes. Cockle (bivalve), Cockles are sometimes served as a traditional breakfast with bacon and laverbread. Although Wales has its own traditional food and has absorbed much of the cuisine of England, Welsh diets now owe more to the countries of Indian cuisine, India, Chinese cuisine, China and the Cuisine of the United States, United States. Chicken tikka masala is the country's favourite dish while hamburgers and Chinese food outsell fish and chips as takeaways.Davies (2008) p.293
 The BBC National Orchestra of Wales performs in Wales and internationally. The Welsh National Opera is based at the Wales Millennium Centre in Cardiff Bay, while the National Youth Orchestra of Wales was the first of its type in the world. Wales has a tradition of producing notable singers, including Geraint Evans, Gwyneth Jones (soprano), Gwyneth Jones, Anne Evans (soprano), Anne Evans, Margaret Price, Tom Jones (singer), Tom Jones, Bonnie Tyler, Bryn Terfel, Mary Hopkin, Charlotte Church, Donna Lewis, Katherine Jenkins, and Shirley Bassey. Popular bands that emerged from Wales include Badfinger, the Manic Street Preachers, the Stereophonics and Feeder (band), Feeder, the Super Furry Animals and Catatonia (band), Catatonia. The Welsh traditional and folk music scene is in resurgence with performers such as Sian James (musician), Siân James
The BBC National Orchestra of Wales performs in Wales and internationally. The Welsh National Opera is based at the Wales Millennium Centre in Cardiff Bay, while the National Youth Orchestra of Wales was the first of its type in the world. Wales has a tradition of producing notable singers, including Geraint Evans, Gwyneth Jones (soprano), Gwyneth Jones, Anne Evans (soprano), Anne Evans, Margaret Price, Tom Jones (singer), Tom Jones, Bonnie Tyler, Bryn Terfel, Mary Hopkin, Charlotte Church, Donna Lewis, Katherine Jenkins, and Shirley Bassey. Popular bands that emerged from Wales include Badfinger, the Manic Street Preachers, the Stereophonics and Feeder (band), Feeder, the Super Furry Animals and Catatonia (band), Catatonia. The Welsh traditional and folk music scene is in resurgence with performers such as Sian James (musician), Siân James
 The earliest surviving Welsh plays are two medieval miracle plays, ''Y Tri Brenin o Gwlen'' ("The three Kings from Cologne") and ''Y Dioddefaint a'r Atgyfodiad'' ("The Passion and the Resurrection"). A recognised Welsh tradition of theatre emerged during the 18th century, in the form of an Play (theatre), interlude, a metrical play performed at fairs and markets. Drama in the early 20th century thrived, but the country established neither a Welsh National Theatre nor a national ballet company. After the Second World War the substantial number of amateur companies that had existed before the outbreak of hostilities reduced by two-thirds.Davies (2008) p. 224 Competition from television in the mid-20th century led to greater professionalism in the theatre. Plays by Emlyn Williams and Alun Owen and others were staged, while Welsh actors, including Richard Burton and Stanley Baker, were establishing themselves as artistic talents. Anthony Hopkins is an alumnus of the Royal Welsh College of Music & Drama, and other notable Welsh actors include Michael Sheen and Catherine Zeta-Jones. Wales has also produced well known comedians including Rob Brydon, Tommy Cooper, Terry Jones, and Harry Secombe.
Traditional dances include Welsh Welsh dance, folk dancing and Welsh stepdance, clog dancing. The first mention of dancing in Wales is in a 12th-century account by Gerald of Wales, Giraldus Cambrensis, but by the 19th century traditional dance had all but died out due to religious opposition.Davies (2008) p. 192 In the 20th century a revival was led by Lois Blake (1890–1974). Clog dancing was preserved and developed by Hywel Wood (1882–1967) and others who perpetuated the art on local and national stages.Davies (2008) p. 193 The Welsh Folk Dance Society was founded in 1949; it supports a network of national amateur dance teams and publishes support material. Contemporary dance grew out of Cardiff in the 1970s; one of the earliest companies, ''Moving Being'', came from London to Cardiff in 1973. ''Diversions'' was formed in 1983, eventually becoming the National Dance Company Wales, now the resident company at the Wales Millennium Centre.
The earliest surviving Welsh plays are two medieval miracle plays, ''Y Tri Brenin o Gwlen'' ("The three Kings from Cologne") and ''Y Dioddefaint a'r Atgyfodiad'' ("The Passion and the Resurrection"). A recognised Welsh tradition of theatre emerged during the 18th century, in the form of an Play (theatre), interlude, a metrical play performed at fairs and markets. Drama in the early 20th century thrived, but the country established neither a Welsh National Theatre nor a national ballet company. After the Second World War the substantial number of amateur companies that had existed before the outbreak of hostilities reduced by two-thirds.Davies (2008) p. 224 Competition from television in the mid-20th century led to greater professionalism in the theatre. Plays by Emlyn Williams and Alun Owen and others were staged, while Welsh actors, including Richard Burton and Stanley Baker, were establishing themselves as artistic talents. Anthony Hopkins is an alumnus of the Royal Welsh College of Music & Drama, and other notable Welsh actors include Michael Sheen and Catherine Zeta-Jones. Wales has also produced well known comedians including Rob Brydon, Tommy Cooper, Terry Jones, and Harry Secombe.
Traditional dances include Welsh Welsh dance, folk dancing and Welsh stepdance, clog dancing. The first mention of dancing in Wales is in a 12th-century account by Gerald of Wales, Giraldus Cambrensis, but by the 19th century traditional dance had all but died out due to religious opposition.Davies (2008) p. 192 In the 20th century a revival was led by Lois Blake (1890–1974). Clog dancing was preserved and developed by Hywel Wood (1882–1967) and others who perpetuated the art on local and national stages.Davies (2008) p. 193 The Welsh Folk Dance Society was founded in 1949; it supports a network of national amateur dance teams and publishes support material. Contemporary dance grew out of Cardiff in the 1970s; one of the earliest companies, ''Moving Being'', came from London to Cardiff in 1973. ''Diversions'' was formed in 1983, eventually becoming the National Dance Company Wales, now the resident company at the Wales Millennium Centre.
''200 Years of the Census in ... Wales'' (2001)
* *
Senedd Cymru – Welsh Parliament
BBC Wales
*
VisitWales.com
The official international guide to places to stay and things to do in Wales.
Wales – Official Gateway to Wales
Gathering the Jewels – Welsh Heritage and Culture
Photographs of Wales
on Geograph Britain and Ireland
Further historical information and sources at GENUKI
{{Authority control Wales, Celtic nations Articles containing video clips Great Britain English-speaking countries and territories Island countries NUTS 1 statistical regions of the United Kingdom United Kingdom by country Countries of Europe with multiple official languages
, sparling and Arctic char, whilst the
gwyniad
The gwyniad (''Coregonus pennantii'') is a freshwater whitefish native to Bala Lake ( cy, Llyn Tegid) in northern Wales.
The population is threatened by deteriorating water quality and by the ruffe, a fish introduced to the lake in the 1980s and ...
is unique to Wales, found only in Bala Lake. Wales is known for its shellfish, including cockles, limpet
Limpets are a group of aquatic snails that exhibit a conical shell shape (patelliform) and a strong, muscular foot. Limpets are members of the class Gastropoda, but are polyphyletic, meaning the various groups called "limpets" descended indep ...
, mussel
Mussel () is the common name used for members of several families of bivalve molluscs, from saltwater and Freshwater bivalve, freshwater habitats. These groups have in common a shell whose outline is elongated and asymmetrical compared with other ...
s and periwinkles. Herring
Herring are forage fish, mostly belonging to the family of Clupeidae.
Herring often move in large schools around fishing banks and near the coast, found particularly in shallow, temperate waters of the North Pacific and North Atlantic Oceans, i ...
, mackerel
Mackerel is a common name applied to a number of different species of pelagic fish, mostly from the family Scombridae. They are found in both temperate and tropical seas, mostly living along the coast or offshore in the oceanic environment.
...
and hake are the more common of the country's marine fish.Davies (1994) pp. 286–288 The north facing high grounds of Snowdonia support a relict pre-glacial flora including the iconic Snowdon lily – '' Gagea serotina'' – and other alpine species such as ''Saxifraga cespitosa
''Saxifraga cespitosa'', the tufted alpine saxifrage or tufted saxifrage, is a flower common to many arctic heights. It appears further south in mountainous areas of the Alps, Norway, Scotland, Wales, Iceland, Siberia, western North America and ...
'', '' Saxifraga oppositifolia'' and '' Silene acaulis''. Wales has a number of plant species not found elsewhere in the UK, including the spotted rock-rose '' Tuberaria guttata'' on Anglesey and ''Draba aizoides
''Draba aizoides'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Brassicaceae, known as yellow whitlow-grass. It is native to Europe where it is found on limestone rocks and walls. In the British Isles it is found only on the Gower Peninsula i ...
'' on the Gower.
Economy
 Over the last 250 years, Wales has been transformed from a predominantly agricultural country to an industrial, and then to a post-industrial economy. In the 1950s Wales' GDP was twice as big as Ireland’s; by the 2020s Ireland's economy was four times that of Wales. Since the Second World War, the
Over the last 250 years, Wales has been transformed from a predominantly agricultural country to an industrial, and then to a post-industrial economy. In the 1950s Wales' GDP was twice as big as Ireland’s; by the 2020s Ireland's economy was four times that of Wales. Since the Second World War, the service sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector (raw materials) and the second ...
has come to account for the majority of jobs, a feature typifying most advanced economies. in 2018, according to OECD and Eurostat data, gross domestic product (GDP) in Wales was £75 billion, an increase of 3.3 per cent from 2017. GDP per head in Wales in 2018 was £23,866, an increase of 2.9 per cent on 2017. This compares to Italy’s GDP/capita of £25,000, Spain £22,000, Slovenia £20,000 and New Zealand £30,000. In the three months to December 2017, 72.7 per cent of working-age adults were employed, compared to 75.2 per cent across the UK as a whole. For the 2018–19 fiscal year, the Welsh fiscal deficit accounts for 19.4 percent of Wales' estimated GDP.
In 2019 Wales was the world’s 5th largest exporter of electricity (22.7 TWh). In 2021, the Welsh government said that more than half the country's energy needs were being met by renewable sources, 2 percent of which was from 363 hydropower projects.
By UK law, Wales contributes to items that do not directly benefit Wales e.g. over £5 billion for HS2 "which will damage the Welsh economy by £200m pa", according to the UK and Welsh Government's transport adviser Mark Barry. Wales also pays more in military costs than most similar-sized countries e.g. Wales pays twice the amount Ireland spends on the military. The UK government spends £1.75bn per year on the military in Wales, which is almost as much as Wales spends on education every year (£1.8 billion in 2018/19) and five times as much as the total amount spent on the police in Wales (£365 million).
From the middle of the 19th century until the post-war era, the mining and export of coal was the dominant industry. At its peak of production in 1913, nearly 233,000 men and women were employed in the South Wales coalfield, mining 56 million tons of coal. Cardiff was once the largest coal-exporting port in the world and, for a few years before the First World War, handled a greater tonnage of cargo than either London or Liverpool. In the 1920s, over 40 per cent of the male Welsh population worked in heavy industry. According to Phil Williams, the Great Depression
The Great Depression (19291939) was an economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. It was a period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. The economic contagio ...
"devastated Wales", north and south, because of its "overwhelming dependence on coal and steel". From the mid-1970s, the Welsh economy faced massive restructuring with large numbers of jobs in heavy industry disappearing and being replaced eventually by new ones in light industry and in services. In the late 1970s and early 1980s, Wales was successful in attracting an above average share of foreign direct investment
A foreign direct investment (FDI) is an investment in the form of a controlling ownership in a business in one country by an entity based in another country. It is thus distinguished from a foreign portfolio investment by a notion of direct co ...
in the UK. Much of the new industry was essentially of a "branch (or "screwdriver") factory" type where a manufacturing plant or call centre is in Wales but the most highly-paid jobs in the company are elsewhere.
Poor-quality soil in much of Wales is unsuitable for crop-growing, so livestock farming has been the focus of farming. About 78 per cent of the land surface is used for agriculture. The Welsh landscape, with its three national parks and Blue Flag beach
The Blue Flag is a certification by the Foundation for Environmental Education (FEE) that a beach, marina, or sustainable boating tourism operator meets its standards.
The Blue Flag is a trademark owned by FEE, which is a not-for-profit non-gov ...
es, attracts large numbers of tourists, who bolster the economy of rural areas. Wales, like Northern Ireland, has relatively few high value-added employment in sectors such as finance and research and development, attributable in part to a comparative lack of "economic mass" (i.e. population) – Wales lacks a large metropolitan centre. The lack of high value-added employment is reflected in lower economic output per head relative to other regions of the UK: in 2002 it stood at 90 per cent of the EU25 average and around 80 per cent of the UK average. In June 2008, Wales made history by becoming the first nation to be awarded Fairtrade status.
The pound sterling
Sterling (abbreviation: stg; Other spelling styles, such as STG and Stg, are also seen. ISO code: GBP) is the currency of the United Kingdom and nine of its associated territories. The pound ( sign: £) is the main unit of sterling, and t ...
is the currency used in Wales. Numerous Welsh banks issued their own banknotes in the 19th century. The last bank to do so closed in 1908; since then the Bank of England
The Bank of England is the central bank of the United Kingdom and the model on which most modern central banks have been based. Established in 1694 to act as the English Government's banker, and still one of the bankers for the Government of ...
has a monopoly on the issue of banknotes in Wales. The Commercial Bank of Wales, established in Cardiff by Sir Julian Hodge
''Sir'' is a formal honorific address in English for men, derived from Sire in the High Middle Ages. Both are derived from the old French "Sieur" (Lord), brought to England by the French-speaking Normans, and which now exist in French only ...
in 1971, was taken over by the Bank of Scotland in 1988 and absorbed into its parent company in 2002. The Royal Mint
The Royal Mint is the United Kingdom's oldest company and the official maker of British coins.
Operating under the legal name The Royal Mint Limited, it is a limited company that is wholly owned by His Majesty's Treasury and is under an exclus ...
, which issues the coinage circulating through the whole of the UK, has been based at a single site in Llantrisant
Llantrisant (; "Parish of the Three Saints") is a town in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf, within the historic county boundaries of Glamorgan, Wales, lying on the River Ely and the Afon Clun. The three saints of the town's name are SS ...
since 1980. Since decimalisation
Decimalisation or decimalization (see spelling differences) is the conversion of a system of currency or of weights and measures to units related by powers of 10.
Most countries have decimalised their currencies, converting them from non-decimal ...
, in 1971, at least one of the coins in circulation emphasises Wales such as the 1995 and 2000 one pound coin (above). As at 2012, the last designs devoted to Wales saw production in 2008.
During 2020, and well into 2021, the restrictions and lockdowns necessitated by the COVID-19 pandemic affected all sectors of the economy and "tourism and hospitality suffered notable losses from the pandemic" across the UK. As of 6 April 2021, visitors from "red list" countries were still not allowed to enter unless they were UK residents. Restrictions will "likely be in place until the summer", one report predicted, with June being the most likely time for tourism from other countries to begin a rebound. On 12 April 2021, many tourist facilities were still closed in Wales but non-essential travel between Wales and England was finally permitted. Wales also allowed non-essential retail stores to open.
Transport
M4 motorway
The M4, originally the London-South Wales Motorway, is a motorway in the United Kingdom running from west London to southwest Wales. The English section to the Severn Bridge was constructed between 1961 and 1971; the Welsh element was largely ...
running from West London to South Wales links Newport
Newport most commonly refers to:
*Newport, Wales
*Newport, Rhode Island, US
Newport or New Port may also refer to:
Places Asia
*Newport City, Metro Manila, a Philippine district in Pasay
Europe
Ireland
*Newport, County Mayo, a town on the ...
, Cardiff and Swansea
Swansea (; cy, Abertawe ) is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Swansea ( cy, links=no, Dinas a Sir Abertawe).
The city is the twenty-fifth largest in ...
. Responsibility for the section of the motorway within Wales, from the Second Severn Crossing to Pont Abraham services, sits with the Welsh Government.
The A55 expressway has a similar role along the North Wales coast, connecting Holyhead
Holyhead (,; cy, Caergybi , "Cybi's fort") is the largest town and a community in the county of Isle of Anglesey, Wales, with a population of 13,659 at the 2011 census. Holyhead is on Holy Island, bounded by the Irish Sea to the north, and is ...
and Bangor with Wrexham and Flintshire. It also links to northwest England, principally Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
. The main north-south Wales link is the A470, which runs from Cardiff to Llandudno
Llandudno (, ) is a seaside resort, town and community in Conwy County Borough, Wales, located on the Creuddyn peninsula, which protrudes into the Irish Sea. In the 2011 UK census, the community – which includes Gogarth, Penrhyn Bay, Craigsi ...
. The Welsh Government manages those parts of the British railway network within Wales, through the Transport for Wales Rail train operating company. The Cardiff region has its own urban rail network. Beeching cuts in the 1960s mean that most of the remaining network is geared toward east-west travel connecting with the Irish Sea ports for ferries to Ireland. Services between north and south Wales operate through the English cities of Chester
Chester is a cathedral city and the county town of Cheshire, England. It is located on the River Dee, close to the English–Welsh border. With a population of 79,645 in 2011,"2011 Census results: People and Population Profile: Chester Loca ...
and Hereford
Hereford () is a cathedral city, civil parish and the county town of Herefordshire, England. It lies on the River Wye, approximately east of the border with Wales, south-west of Worcester and north-west of Gloucester. With a population ...
and towns of Shrewsbury
Shrewsbury ( , also ) is a market town, civil parish, and the county town of Shropshire, England, on the River Severn, north-west of London; at the 2021 census, it had a population of 76,782. The town's name can be pronounced as either 'Sh ...
, Gobowen for Oswestry and along the Welsh Marches Line, with trains on the Heart of Wales Line from Swansea
Swansea (; cy, Abertawe ) is a coastal city and the second-largest city of Wales. It forms a principal area, officially known as the City and County of Swansea ( cy, links=no, Dinas a Sir Abertawe).
The city is the twenty-fifth largest in ...
to Llandovery, Llandrindod
Llandrindod Wells (, ; cy, Llandrindod, /ɬanˈdɾindɔd/ "Trinity Parish"), sometimes known colloquially as Llandod, is a town and community in Powys, within the historic boundaries of Radnorshire, Wales. It serves as the seat of Powy ...
and Knighton connecting the Welsh March Line in Craven Arms. Trains in Wales are mainly diesel-powered but the South Wales Main Line branch of the Great Western Main Line
The Great Western Main Line (GWML) is a main line railway in England that runs westwards from London Paddington to . It connects to other main lines such as those from Reading to Penzance and Swindon to Swansea. Opened in 1841, it was the or ...
used by services from London Paddington to Cardiff is undergoing electrification, although the programme has experienced significant delays and costs-overruns.
Cardiff Airport is the international airport of Wales. Providing links to European, African and North American destinations, it is about southwest of Cardiff city centre, in the Vale of Glamorgan. Intra-Wales flights used to run between Anglesey (Valley) and Cardiff, and were operated since 2017 by Eastern Airways., those flights are no longer, as of 2022, available. Other internal flights operate to northern England, Scotland and Northern Ireland. Wales has four commercial ferry
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water taxi ...
ports. Regular ferry services to Ireland operate from Holyhead
Holyhead (,; cy, Caergybi , "Cybi's fort") is the largest town and a community in the county of Isle of Anglesey, Wales, with a population of 13,659 at the 2011 census. Holyhead is on Holy Island, bounded by the Irish Sea to the north, and is ...
, Pembroke Dock
Pembroke Dock ( cy, Doc Penfro) is a town and a community in Pembrokeshire, South West Wales, northwest of Pembroke on the banks of the River Cleddau. Originally Paterchurch, a small fishing village, Pembroke Dock town expanded rapidly following ...
and Fishguard. The Swansea to Cork service was cancelled in 2006, reinstated in March 2010, and withdrawn again in 2012.
Education
 A distinct education system has developed in Wales.Davies (2008) p. 238 Formal education before the 18th century was the preserve of the elite. The first grammar schools were established in Welsh towns such as Ruthin, Brecon and Cowbridge. One of the first successful schooling systems was started by Griffith Jones, who introduced the circulating schools in the 1730s; these are believed to have taught half the country's population to read.Davies (2008) p. 239 In the 19th century, with increasing state involvement in education, Wales was forced to adopt an education system that was English in ethos even though the country was predominantly Non-conformist, Welsh-speaking and demographically uneven because of the economic expansion in the south. In some schools, to ensure Welsh children spoke English at school, the Welsh Not was employed as corrective punishment; this was much resented, although the extent of its use is difficult to determine. State and local governmental edicts resulted in schooling in the English language which, following the 1847 Inquiry into the State of Education in Wales – an event subsequently referred to as the Treachery of the Blue Books () – was seen as more academic and worthwhile for children.
The University College of Wales opened in Aberystwyth in 1872. Cardiff and Bangor followed, and the three colleges came together in 1893 to form the University of Wales. The Welsh Intermediate Education Act of 1889 created 95 secondary schools. The Welsh Department for the Board of Education followed in 1907, which gave Wales its first significant educational devolution. A resurgence in Welsh-language schools in the latter half of the 20th century at nursery and primary level saw attitudes shift towards teaching in the medium of Welsh.Davies (2008) p. 240 Welsh is a compulsory subject in all of Wales' state schools for pupils aged 5–16 years old. While there has never been an exclusively Welsh-language college, Welsh-medium higher education is delivered through the individual universities and has since 2011 been supported by the Coleg Cymraeg Cenedlaethol (Welsh National College) as a delocalised federal institution. In 2021–2022, there were 1,470 maintained schools in Wales. In 2021–22, the country had 471,131 pupils taught by 25,210 full-time equivalent teachers.
A distinct education system has developed in Wales.Davies (2008) p. 238 Formal education before the 18th century was the preserve of the elite. The first grammar schools were established in Welsh towns such as Ruthin, Brecon and Cowbridge. One of the first successful schooling systems was started by Griffith Jones, who introduced the circulating schools in the 1730s; these are believed to have taught half the country's population to read.Davies (2008) p. 239 In the 19th century, with increasing state involvement in education, Wales was forced to adopt an education system that was English in ethos even though the country was predominantly Non-conformist, Welsh-speaking and demographically uneven because of the economic expansion in the south. In some schools, to ensure Welsh children spoke English at school, the Welsh Not was employed as corrective punishment; this was much resented, although the extent of its use is difficult to determine. State and local governmental edicts resulted in schooling in the English language which, following the 1847 Inquiry into the State of Education in Wales – an event subsequently referred to as the Treachery of the Blue Books () – was seen as more academic and worthwhile for children.
The University College of Wales opened in Aberystwyth in 1872. Cardiff and Bangor followed, and the three colleges came together in 1893 to form the University of Wales. The Welsh Intermediate Education Act of 1889 created 95 secondary schools. The Welsh Department for the Board of Education followed in 1907, which gave Wales its first significant educational devolution. A resurgence in Welsh-language schools in the latter half of the 20th century at nursery and primary level saw attitudes shift towards teaching in the medium of Welsh.Davies (2008) p. 240 Welsh is a compulsory subject in all of Wales' state schools for pupils aged 5–16 years old. While there has never been an exclusively Welsh-language college, Welsh-medium higher education is delivered through the individual universities and has since 2011 been supported by the Coleg Cymraeg Cenedlaethol (Welsh National College) as a delocalised federal institution. In 2021–2022, there were 1,470 maintained schools in Wales. In 2021–22, the country had 471,131 pupils taught by 25,210 full-time equivalent teachers.
Healthcare
 Public healthcare in Wales is provided by NHS Wales (), through seven local health boards and three all-Wales trusts. It was originally formed as part of the NHS structure for England and Wales by the
Public healthcare in Wales is provided by NHS Wales (), through seven local health boards and three all-Wales trusts. It was originally formed as part of the NHS structure for England and Wales by the National Health Service Act 1946
The National Health Service Act 1946c 81 came into effect on 5 July 1948 and created the National Health Service in England and Wales thus being the first implementation of the Beveridge model. Though the title 'National Health Service' implies a ...
, but with powers over the NHS in Wales coming under the Secretary of State for Wales in 1969. Responsibility for NHS Wales passed to the Welsh Assembly under devolution in 1999, and is now the responsibility of the Minister for Health and Social Services. Historically, Wales was served by smaller 'cottage' hospitals, built as voluntary institutions.Davies (2008), p.361 As newer, more expensive, diagnostic techniques and treatments became available, clinical work has been concentrated in newer, larger district hospitals. In 2006, there were seventeen district hospitals in Wales. NHS Wales directly employs over 90,000 staff, making it Wales' biggest employer. A 2009 Welsh health survey reported that 51 per cent of adults reported their health good or excellent, while 21 per cent described their health as fair or poor. The survey recorded that 27 per cent of Welsh adults had a long-term chronic illness, such as arthritis, asthma, diabetes or heart disease. The 2018 National Survey of Wales, which enquired into health-related lifestyle choices, reported that 19 per cent of the adult population were smokers, 18 per cent admitted drinking alcohol above weekly recommended guidelines, while 53 per cent undertook the recommended 150 minutes of physical activity each week.
Demography
Population history
The population of Wales doubled from 587,000 in 1801 to 1,163,000 in 1851 and had reached 2,421,000 by 1911. Most of the increase came in the coal mining districts, especially Glamorganshire, which grew from 71,000 in 1801 to 232,000 in 1851 and 1,122,000 in 1911. Part of this increase can be attributed to the demographic transition seen in most industrialising countries during the Industrial Revolution, as death rates dropped and birth rates remained steady. However, there was also large-scale migration into Wales during the Industrial Revolution. The English were the most numerous group, but there were also considerable numbers of Irish and smaller numbers of other ethnic groups, including Italians, who migrated to South Wales. Wales also received immigration from various parts of the British Commonwealth of Nations in the 20th century, andAfrican-Caribbean
Afro-Caribbean people or African Caribbean are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern African-Caribbeans descend from Africans taken as slaves to colonial Caribbean via the ...
and Asian communities add to the ethnocultural mix, particularly in urban Wales. Many of these self-identify as Welsh.
The population in 1972 stood at 2.74 million and remained broadly static for the rest of the decade. However, in the early 1980s, the population fell due to net migration out of Wales. Since the 1980s, net migration has generally been inward, and has contributed more to population growth
Population growth is the increase in the number of people in a population or dispersed group. Actual global human population growth amounts to around 83 million annually, or 1.1% per year. The global population has grown from 1 billion in 1800 to ...
than natural change. The resident population of Wales in 2021 according to the census was 3,107,500 (1,586,600 female and 1,521,000 male), an increase of 1.4 per cent over 2011. A decreased change from the 5 per cent increase between 2001 and 2011. Wales accounted for 5.2 per cent of the population of England and Wales in 2021. Wales has seven cities, those being Cardiff, Newport, Swansea, and Wrexham, with the communities of Bangor, St Asaph and St Davids
St Davids or St David's ( cy, Tyddewi, , "David's house”) is a city and a community (named St Davids and the Cathedral Close) with a cathedral in Pembrokeshire, Wales, lying on the River Alun. It is the resting place of Saint David, W ...
also having city status in the United Kingdom. Wrexham, north Wales' largest settlement, became Wales' newest and seventh city in September 2022
File:2022 collage V1.png, Clockwise, from top left: Road junction at Yamato-Saidaiji Station several hours after the assassination of Shinzo Abe; 2022 Sri Lankan protests, Anti-government protest in Sri Lanka in front of the Presidential Secretari ...
.
Language
 Welsh is an official language in Wales as legislated by the Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011. Both Welsh and English are also official languages of the Senedd. The proportion of the Welsh population able to speak the Welsh language fell from just under 50 per cent in 1901 to 43.5 per cent in 1911, and continued to fall to a low of 18.9 per cent in 1981.Results of the 2001 Census: Country of birth (www.statistics.gov.uk)
Welsh is an official language in Wales as legislated by the Welsh Language (Wales) Measure 2011. Both Welsh and English are also official languages of the Senedd. The proportion of the Welsh population able to speak the Welsh language fell from just under 50 per cent in 1901 to 43.5 per cent in 1911, and continued to fall to a low of 18.9 per cent in 1981.Results of the 2001 Census: Country of birth (www.statistics.gov.uk)/ref> The results of the 2001 Census showed an increase in the number of Welsh speakers to 21 per cent of the population aged 3 and older, compared with 18.7 per cent in 1991 and 19 per cent in 1981. This compares with a pattern of steady decline indicated by census results during the 20th century. In the 2011 census it was recorded that the proportion of people able to speak Welsh had dropped from 20.8 per cent to 19 per cent (still higher than 1991). Despite an increase in the overall size of the Welsh population this still meant that the number of Welsh speakers in Wales dropped from 582,000 in 2001 to 562,000 in 2011. However this figure was still much higher than 508,000 or 18.7 per cent of people who said they could speak Welsh in the 1991 census. According to the 2021 census, the Welsh-speaking population of Wales aged three or older was 17.8 per cent (538,300 people) and nearly three quarters of the population in Wales said they had no Welsh language skills. Other estimates suggest that 29.7 per cent (899,500) of people aged three or older in Wales could speak Welsh in June 2022. English is spoken by almost all people in Wales and is the main language in most of the country. Code-switching is common in all parts of Wales and is known by various terms, though none is recognised by professional linguists.Davies (2008) p. 262 "
Wenglish
Welsh English ( cy, Saesneg Gymreig) comprises the dialects of English spoken by Welsh people. The dialects are significantly influenced by Welsh grammar and often include words derived from Welsh. In addition to the distinctive words and gr ...
" is the Welsh English language dialect. It has been influenced significantly by Welsh grammar and includes words derived from Welsh. Northern and western Wales retain many areas where Welsh is spoken as a first language by the majority of the population, and English learnt as a second language. Although monoglotism in young children continues, life-long monoglotism in Welsh no longer occurs.
Since Poland joined the European Union, Wales has seen a significant increase in Polish immigrants. This has made Polish the third most spoken language in Wales, used as a main language by 0.6 percent of the population.
Religion
Independent Church Independent church may refer to:
* A self-governed church
* National church, especially in Lutheranism, Anglicanism and Orthodox Christianity, the organisation of that denomination within a given nation, which acts independently of the churches of ...
in Wales was founded at Llanvaches in 1638 by William Wroth. The Presbyterian Church of Wales was born out of the Welsh Methodist revival in the 18th century and seceded from the Church of England in 1811. The second largest attending faith in Wales is Roman Catholic, with an estimated 43,000 adherents.
The patron saint of Wales is Saint David
Saint David ( cy, Dewi Sant; la, Davidus; ) was a Welsh bishop of Mynyw (now St Davids) during the 6th century. He is the patron saint of Wales. David was a native of Wales, and tradition has preserved a relatively large amount of detail ab ...
(), with Saint David's Day () celebrated annually on 1 March. In 1904, there was a religious revival (known by some as the 1904–1905 Welsh Revival
Nineteen or 19 may refer to:
* 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20
* one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019
Films
* ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film
* ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film
Music ...
, or simply The 1904 Revival) which started through the evangelism of Evan Roberts and saw large numbers of people converting to non-Anglican Christianity, sometimes whole communities. Roberts' style of preaching became the blueprint for new religious bodies such as Pentecostalism and the Apostolic Church.
Non-Christian religions are small in Wales, making up approximately 2.7 per cent of the population. Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
is the largest, with 24,000 (0.8 per cent) reported Muslims in the 2011 census. There are also communities of Hindus and Sikhs
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism (Sikhi), a monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term ...
, mainly in the south Wales cities of Newport, Cardiff and Swansea, while the largest concentration of Buddhists
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
is in the western rural county of Ceredigion. Judaism was the first non-Christian faith to be established in Wales since Roman times, though by 2001 the community had declined to approximately 2,000 and as of 2019 only numbers in the hundreds.
Ethnicity
The 2021 census showed that 93.8 per cent of the population of Wales identified as "White", compared to 95.6 per cent in 2011. 90.6 per cent of the population identified as “White: Welsh, English, Scottish, Northern Irish or British” in 2021. The second most populous ethnicity in 2021 was “Asian, Asian Welsh or Asian British” at 2.9 per cent of the population, compared to 2.3 per cent in 2011. 1.6 per cent of the population identified as “Mixed or multiple ethnic groups” compared to 1.0 per cent in 2011. 0.9 per cent of the population identified as “Black, Black Welsh, Black British, Caribbean or African” compared to 0.6 per cent in 2011 and 0.9 per cent identified as "Other ethnic group" compared to 0.5 per cent in 2011. The local authorities with the highest proportions of "high-level" ethnic groups other than “White” were mainly urban areas including Cardiff, Newport and Swansea. 5.3 per cent of households in Wales were multiple ethnic group households, up from 4.2 per cent in 2011.National identity
The 2021 census showed that 55.2 per cent identified as "Welsh only", 8.1 per cent identified as "Welsh and British" and a combined proportion of people identifying as Welsh at 63.3 per cent. The Welsh Annual Population Survey showed that the proportion of people who identified as Welsh versus another identity was 62.3 per cent in 2022 compared to 69.2 per cent in 2001. A 2022 YouGov poll found that 21 per cent consider themselves Welsh not British, 15 per cent more Welsh than British, 24 per cent equally Welsh and British, 7 per cent more British than Welsh and 20 per cent British and not Welsh and 8 per cent other. A total of 67 per cent considered themselves Welsh to some degree.Culture
Wales has a distinctive culture including its own language, customs, holidays and music. There are four UNESCO World Heritage Sites in Wales: The Castles and Town Walls of King Edward I in Gwynedd; Pontcysyllte Aqueduct and Canal; the Blaenavon Industrial Landscape and The Slate Landscape of Northwest Wales.Mythology
Remnants of native Celtic mythology of the pre-Christian Britons was passed down orally by the ''cynfeirdd'' (the early poets). Some of their work survives in later medieval Welsh manuscripts: theBlack Book of Carmarthen
The Black Book of Carmarthen ( cy, Llyfr Du Caerfyrddin) is thought to be the earliest surviving manuscript written solely in Welsh. The book dates from the mid-13th century; its name comes from its association with the Priory of St. John the Ev ...
and the Book of Aneirin (both 13th-century); the Book of Taliesin
The Book of Taliesin ( cy, Llyfr Taliesin) is one of the most famous of Middle Welsh manuscripts, dating from the first half of the 14th century though many of the fifty-six poems it preserves are taken to originate in the 10th century or before ...
and the White Book of Rhydderch (both 14th-century); and the Red Book of Hergest (c. 1400). The prose stories from the White and Red Books are known as the ''Mabinogion
The ''Mabinogion'' () are the earliest Welsh prose stories, and belong to the Matter of Britain. The stories were compiled in Middle Welsh in the 12th–13th centuries from earlier oral traditions. There are two main source manuscripts, create ...
''. Poems such as '' Cad Goddeu'' (The Battle of the Trees) and mnemonic list-texts like the '' Welsh Triads'' and the '' Thirteen Treasures of the Island of Britain'', also contain mythological material. These texts include the earliest forms of the Arthurian legend and the traditional history of post- Roman Britain. Other sources of Welsh folklore include the 9th-century Latin historical compilation '' Historia Britonum'' (the History of the Britons) and Geoffrey of Monmouth's 12th-century Latin chronicle
A chronicle ( la, chronica, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and lo ...
'' Historia Regum Britanniae'' (the History of the Kings of Britain), and later folklore, such as ''The Welsh Fairy Book'' by W. Jenkyn Thomas.
Literature
 Wales has one of the oldest unbroken literary traditions in EuropeDavies (2008) p. 464 going back to the sixth century and including Geoffrey of Monmouth and Gerald of Wales, regarded as among the finest Latin authors of the Middle Ages. The earliest body of Welsh verse, by poets Taliesin and Aneirin, survive not in their original form, but in much-changed, medieval versions. Welsh poetry and native lore and learning survived the Dark Ages, through the era of the
Wales has one of the oldest unbroken literary traditions in EuropeDavies (2008) p. 464 going back to the sixth century and including Geoffrey of Monmouth and Gerald of Wales, regarded as among the finest Latin authors of the Middle Ages. The earliest body of Welsh verse, by poets Taliesin and Aneirin, survive not in their original form, but in much-changed, medieval versions. Welsh poetry and native lore and learning survived the Dark Ages, through the era of the Poets of the Princes
Medieval Welsh literature is the literature written in the Welsh language during the Middle Ages. This includes material starting from the 5th century AD, when Welsh was in the process of becoming distinct from Common Brittonic, and continuing ...
(c. 1100 – 1280) and then the Poets of the Gentry (c. 1350 – 1650). The former were professional poets who composed eulogies and elegies to their patrons while the latter favoured the cywydd metre.Davies (2008) pp. 688–689 The period produced one of Wales' greatest poets, Dafydd ap Gwilym. After the Anglicisation of the gentry the tradition declined.
Despite the extinction of the professional poet, the integration of the native elite into a wider cultural world did bring other literary benefits.Davies (2008) p. 465 Renaissance scholars such as William Salesbury and John Davies brought humanist ideals from English universities. In 1588 William Morgan became the first person to translate the Bible into Welsh. From the 16th century the proliferation of the 'free-metre' verse became the most important development in Welsh poetry, but from the middle of the 17th century a host of imported accentual metres from England became very popular. By the 19th century the creation of a Welsh epic, fuelled by the eisteddfod, became an obsession with Welsh-language writers.Davies (2008) p. 466 The output of this period was prolific in quantity but unequal in quality. Initially excluded, religious denominations came to dominate the competitions, with bardic themes becoming scriptural and didactic.
Developments in 19th-century Welsh literature include Lady Charlotte Guest's translation into English of the Mabinogion, one of the most important medieval Welsh prose works of Celtic mythology. 1885 saw the publication of '' Rhys Lewis'' by Daniel Owen, credited as the first novel written in the Welsh language. The 20th century saw a move from the verbose Victorian Welsh style, with works such as Thomas Gwynn Jones's '' Ymadawiad Arthur''. The First World War had a profound effect on Welsh literature with a more pessimistic style championed by T. H. Parry-Williams and R. Williams Parry. The industrialisation of south Wales saw a further shift with the likes of Rhydwen Williams who used the poetry and metre of a bygone rural Wales but in the context of an industrial landscape. The inter-war period is dominated by Saunders Lewis, for his political and reactionary views as much as his plays, poetry and criticism.
The careers of some 1930s writers continued after World War Two, including those of Gwyn Thomas, Vernon Watkins, and Dylan Thomas
Dylan Marlais Thomas (27 October 1914 – 9 November 1953) was a Welsh poet and writer whose works include the poems "Do not go gentle into that good night" and "And death shall have no dominion", as well as the "play for voices" ''Under ...
, whose most famous work '' Under Milk Wood'' was first broadcast in 1954. Thomas was one of the most notable and popular Welsh writers of the 20th century and one of the most innovative poets of his time. The attitude of the post-war generation of Welsh writers in English towards Wales differs from the previous generation, with greater sympathy for Welsh nationalism and the Welsh language. The change is linked to the nationalism of Saunders Lewis and the burning of the Bombing School on the Llŷn Peninsula in 1936. In poetry R. S. Thomas (1913–2000) was the most important figure throughout the second half of the twentieth century. He "did not learn the Welsh language until he was 30 and wrote all his poems in English". Major writers in the second half of the twentieth century include Emyr Humphreys (born 1919), who during his long writing career published over twenty novels, and Raymond Williams (1921–1988).
Museums and libraries

Amgueddfa Cymru – National Museum Wales
Amgueddfa Cymru – Museum Wales, branded as simply Amgueddfa Cymru (formerly the National Museums and Galleries of Wales and legally National Museum of Wales), is a Welsh Government sponsored body that comprises seven museums in Wales:
* N ...
was founded by royal charter in 1907 and is now a Welsh Government sponsored body. The National Museum is made up of seven sites across the country, including the National Museum Cardiff, St Fagans National History Museum
St Fagans National Museum of History ( ; cy, Sain Ffagan: Amgueddfa Werin Cymru, links=no), commonly referred to as St Fagans
St Fagans ( ; cy, Sain Ffagan) is a village and community in the west of the city of Cardiff, capital of Wales. I ...
and Big Pit National Coal Museum
Big Pit National Coal Museum ( cy, Pwll Mawr Amgueddfa Lofaol Cymru) is an industrial heritage museum in Blaenavon, Torfaen, Wales. A working coal mine from 1880 to 1980, it was opened to the public in 1983 as a charitable trust called the Big ...
. In April 2001, the attractions attached to the National Museum were granted free entry by the Assembly, and this action saw the visitor numbers to the sites increase during 2001–2002 by 87.8 per cent to 1,430,428. Aberystwyth is home to the National Library of Wales
The National Library of Wales ( cy, Llyfrgell Genedlaethol Cymru), Aberystwyth, is the national legal deposit library of Wales and is one of the Welsh Government sponsored bodies. It is the biggest library in Wales, holding over 6.5 million boo ...
, which houses some of the most important collections in Wales, including the Sir John Williams Collection and the Shirburn Castle collection.Davies (2008) p. 594 As well as its printed collection the Library holds important Welsh art collections including portraits and photographs, ephemera such as postcards, posters and Ordnance Survey maps.
Visual arts
Works of Celtic art have been found in Wales. In the Early Medieval period, theCeltic Christianity
Celtic Christianity ( kw, Kristoneth; cy, Cristnogaeth; gd, Crìosdaidheachd; gv, Credjue Creestee/Creestiaght; ga, Críostaíocht/Críostúlacht; br, Kristeniezh; gl, Cristianismo celta) is a form of Christianity that was common, or held ...
of Wales was part of the Insular art
Insular art, also known as Hiberno-Saxon art, was produced in the post-Roman era of Great Britain and Ireland. The term derives from ''insula'', the Latin term for "island"; in this period Britain and Ireland shared a largely common style dif ...
of the British Isles. A number of illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared document where the text is often supplemented with flourishes such as borders and miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Church for prayers, liturgical services and psalms, the ...
s from Wales survive, including the 8th-century Hereford Gospels
The Hereford Gospels (Hereford, Hereford Cathedral Library, MS P. I. 2) is an 8th-century illuminated manuscript gospel book in insular script (minuscule), with large illuminated initials in the Insular style. This is a very late Anglo-Saxon go ...
and Lichfield Gospels. The 11th-century Ricemarch Psalter
The Ricemarch Psalter is an 11th-century Welsh illuminated psalter, in a late Insular style, that has been described as "Hiberno-Danish", instead of the usual "Hiberno-Saxon", as it reflects Viking influence. Its 159 pages are vellum, and includ ...
(now in Dublin) is certainly Welsh, made in St David's, and shows a late Insular style with unusual Viking influence.
Some Welsh artists of the 16th–18th centuries tended to leave the country to work, moving to London or Italy. Richard Wilson (1714–1782) is arguably the first major British landscapist. Although more notable for his Italian scenes, he painted several Welsh scenes on visits from London. By the late 18th century, the popularity of landscape art grew and clients were found in the larger Welsh towns, allowing more Welsh artists to stay in their homeland. Artists from outside Wales were also drawn to paint Welsh scenery, at first because of the Celtic Revival.
 An Act of Parliament in 1857 provided for the establishment of a number of art schools throughout the United Kingdom and the
An Act of Parliament in 1857 provided for the establishment of a number of art schools throughout the United Kingdom and the Cardiff School of Art
Cardiff School of Art & Design (CSAD) is one of the five schools that comprise Cardiff Metropolitan University. It originated as the Cardiff School of Art in 1865.
History
Cardiff School of Art & Design opened in 1865 as the Cardiff School of S ...
opened in 1865. Graduates still very often had to leave Wales to work, but Betws-y-Coed became a popular centre for artists and its artists' colony helped form the Royal Cambrian Academy of Art in 1881. The sculptor Sir William Goscombe John made works for Welsh commissions, although he had settled in London. Christopher Williams, whose subjects were mostly resolutely Welsh, was also based in London. Thomas E. Stephens Thomas, Tom Stevens or Thomas, Tom Stephens may refer to:
Military
*Thomas Holdup Stevens (1795–1841), American naval commander in the War of 1812
* Thomas H. Stevens Jr. (1819–1896), admiral of the United States Navy who fought in the America ...
and Andrew Vicari had very successful careers as portraitists based respectively in the United States and France.
Welsh painters gravitated towards the art capitals of Europe. Augustus John and his sister Gwen John lived mostly in London and Paris. However, the landscapists Sir Kyffin Williams and Peter Prendergast lived in Wales for most of their lives, while remaining in touch with the wider art world. Ceri Richards was very engaged in the Welsh art scene as a teacher in Cardiff and even after moving to London. He was a figurative painter in international styles including Surrealism
Surrealism is a cultural movement that developed in Europe in the aftermath of World War I in which artists depicted unnerving, illogical scenes and developed techniques to allow the unconscious mind to express itself. Its aim was, according to l ...
. Various artists have moved to Wales, including Eric Gill, the London-Welshman David Jones and the sculptor Jonah Jones. The Kardomah Gang was an intellectual circle centred on the poet Dylan Thomas
Dylan Marlais Thomas (27 October 1914 – 9 November 1953) was a Welsh poet and writer whose works include the poems "Do not go gentle into that good night" and "And death shall have no dominion", as well as the "play for voices" ''Under ...
and poet and artist Vernon Watkins in Swansea, which also included the painter Alfred Janes.
South Wales had several notable potteries, one of the first important sites being the Ewenny Pottery in Bridgend, which began producing earthenware in the 17th century.Davies (2008) pp. 701–702 In the 18th and 19th centuries, with more scientific methods becoming available more refined ceramics were produced led by the Cambrian Pottery (1764–1870, also known as "Swansea pottery") and later Nantgarw Pottery
The Nantgarw China Works was a porcelain factory, later making other types of pottery, located in Nantgarw on the eastern bank of the Glamorganshire Canal, north of Cardiff in the River Taff valley, Glamorganshire, Wales.
The factory mad ...
near Cardiff, which was in operation from 1813 to 1822 making fine porcelain and then utilitarian pottery until 1920. Portmeirion Pottery, founded in 1960 by Susan Williams-Ellis
Susan Williams-Ellis (6 June 1918 – 26 November 2007) was a British pottery designer, who was best known for co-founding Portmeirion Pottery. She was the eldest daughter of Sir Clough Williams-Ellis.
Background
Williams-Ellis was born in Gui ...
, daughter of Clough Williams-Ellis, creator of the Italianate village of Portmeirion, Gwynedd
Gwynedd (; ) is a county and preserved county (latter with differing boundaries; includes the Isle of Anglesey) in the north-west of Wales. It shares borders with Powys, Conwy County Borough, Denbighshire, Anglesey over the Menai Strait, and C ...
, is based in Stoke-on-Trent
Stoke-on-Trent (often abbreviated to Stoke) is a city and Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area in Staffordshire, England, with an area of . In 2019, the city had an estimated population of 256,375. It is the largest settlement ...
, England.
National symbols and identity
Celtic Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point th ...
and a white dragon representing Anglo-Saxons. Ambrosius prophecies that the Celtic Britons will reclaim the island and push the Anglo-Saxons back to the sea.''wikisource:History of the Britons, Historia Brittonum'' by Nennius (translated by J.A.Giles) As an emblem, the red dragon of Wales has been used since the reign of Cadwaladr, List of rulers of Wales, King of Gwynedd from around 655AD and is present on the national flag of Wales, which became an official flag in 1959.
On 1 March, Welsh people celebrate Saint David's Day, St David's day, who is an icon of Welsh identity. There has been multiple calls and majority support in Wales to make St David's day a bank holiday in Wales, despite UK government refusal. The day is celebrated by schools and cultural societies across Wales and customs include wearing of a leek or a daffodil which are two national emblems of Wales. Children also wear the national costume. The origins of the leek can be traced to the 16th century, while the daffodil became popular in the 19th century, encouraged by David Lloyd George.Davies (2008) p. 189 This is attributed to confusion (or association) between the Welsh for leek, ''cenhinen'', and that for daffodil, ''cenhinen Bedr'' or St. Peter's leek. A report in 1916 gave preference to the leek, which has appeared on British pound coins.
The banner of Owain Glyndŵr
Owain ap Gruffydd (), commonly known as Owain Glyndŵr or Glyn Dŵr (, anglicised as Owen Glendower), was a Welsh leader, soldier and military commander who led a 15 year long Welsh War of Independence with the aim of ending English rule in Wa ...
is associated with Welsh nationhood. It was carried into battle by Welsh forces during Glyndŵr Rising, Glyndŵr's battles against the English, includes four lions on red and gold. The standard is similar to the arms of Llywelyn ap Gruffudd (Llywelyn the Last), the last Prince of Wales before the conquest of Wales by Edward I of England. The design may also be influenced by the arms of Glyndwr's parents, both of whom had lions in their arms. Owain Glyndŵr Day is celebrated on 16 September in Wales and there have been calls to make it a national bank holiday.
''"Hen Wlad Fy Nhadau" ( eng, Land of My Fathers)'' is the National Anthem of Wales, and is played at events such as football or rugby matches involving the Wales national team as well as the opening of the Senedd and other official occasions.
"" ("Wales forever") is a popular Welsh motto. Another Welsh motto "Y Welsh Dragon, Ddraig Goch Ddyry Cychwyn" ("the Welsh Dragon, red dragon inspires action") has been used on the Royal Badge of Wales when it was created in 1953.
British symbols
On its creation the Union Jack incorporated the flags of the kingdoms of Scotland, of Ireland and the Saint George's Cross, Cross of St. George which then represented the Kingdom of England and Wales. Wales by 1543 had been Annexation, annexed and incorporated by the crown of England. Present day media have explained why Wales is not represented on the flag. The heraldic badge of the Duke of Cornwall, or Heir Apparent of the British monarchy (commonly known as the Prince of Wales's feathers) is also used in Wales. It consists of three white feathers emerging from a gold coronet and the German language, German motto ''Ich dien'' (I serve). Several Welsh representative teams, including the Welsh rugby union, and Welsh regiments in the British Army (the Royal Welsh, for example) use the badge or a stylised version of it. There have been attempts made to curtail the use of the emblem for commercial purposes and restrict its use to those authorised by the Prince of Wales.Sport
 More than 50 Governing bodies of sports in Wales, national governing bodies regulate and organise their sports in Wales. Most of those involved in competitive sports select, organise and manage individuals or teams to represent their country at international events or fixtures against other countries. Wales is represented at major world sporting events such as the FIFA World Cup, Rugby World Cup, Rugby League World Cup and the Commonwealth Games. At the Olympic Games, Welsh athletes compete alongside those of Scotland, England and Northern Ireland as part of a Great Britain at the Olympics, Great Britain team. Wales has hosted several international sporting events. These include the 1958 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, 1958 Commonwealth Games, the 1999 Rugby World Cup, the 2010 Ryder Cup and the 2017 UEFA Champions League Final.
Although football has traditionally been the more popular sport in North Wales, rugby union in Wales, rugby union is seen as a symbol of Welsh national identity, Welsh identity and an expression of national consciousness. The Wales national rugby union team takes part in the annual Six Nations Championship and has also competed in every Rugby World Cup, hosting the tournament in 1999 Rugby World Cup, 1999. The five professional sides that replaced the traditional club sides in major competitions in 2003 were replaced in 2004 by the four regions: Cardiff Blues, Dragons (rugby union), Dragons, Ospreys (rugby union), Ospreys and Scarlets. The Welsh regional teams play in the United Rugby Championship, the Heineken Champions Cup if they qualify and the European Rugby Challenge Cup, again dependent on qualification. Rugby league in Wales dates back to 1907. A professional Welsh League existed from 1908 to 1910.
Wales has had football in Wales, its own football league, the Welsh Premier League, since 1992. For historical reasons, five Welsh clubs play in the English football league system; Cardiff City F.C., Cardiff City, Swansea City A.F.C., Swansea City, Newport County A.F.C, Newport County, Wrexham A.F.C., Wrexham, and Merthyr Town F.C. (2010), Merthyr Town. Famous Welsh players over the years include John Charles, John Toshack, Gary Speed, Ian Rush, Ryan Giggs, Gareth Bale, Aaron Ramsey, and Daniel James (footballer), Daniel James. At UEFA Euro 2016, the Wales national football team, Wales national team achieved their best ever finish, reaching the semi-finals where they were beaten by eventual champions Portugal.
In international cricket, Wales and England field a single representative team, administered by the England and Wales Cricket Board (ECB), called the England cricket team, or simply 'England'. Occasionally, a separate Wales cricket team, Wales team play limited-overs competitions. Glamorgan County Cricket Club is the only Welsh participant in the England and Wales County Championship. Wales has produced several notable participants of individual and team sports including snooker players Ray Reardon, Terry Griffiths, Mark Williams (snooker player), Mark Williams and Matthew Stevens. Track athletes who have made a mark on the world stage include hurdler Colin Jackson and Paralympian Tanni Grey-Thompson. Champion cyclists include Nicole Cooke and Geraint Thomas. Wales has a tradition of producing world-class boxers. Joe Calzaghe was WBO world super-middleweight champion and then won the WBA, WBC and Ring Magazine super middleweight and Ring Magazine light-heavyweight titles. Other former boxing world champions include Enzo Maccarinelli, Freddie Welsh, Howard Winstone, Percy Jones (boxer), Percy Jones, Jimmy Wilde, Steve Robinson (boxer), Steve Robinson and Robbie Regan. Tommy Farr, the "Tonypandy Terror", came close to defeating world heavyweight champion Joe Louis at the height of his fame in 1937.
More than 50 Governing bodies of sports in Wales, national governing bodies regulate and organise their sports in Wales. Most of those involved in competitive sports select, organise and manage individuals or teams to represent their country at international events or fixtures against other countries. Wales is represented at major world sporting events such as the FIFA World Cup, Rugby World Cup, Rugby League World Cup and the Commonwealth Games. At the Olympic Games, Welsh athletes compete alongside those of Scotland, England and Northern Ireland as part of a Great Britain at the Olympics, Great Britain team. Wales has hosted several international sporting events. These include the 1958 British Empire and Commonwealth Games, 1958 Commonwealth Games, the 1999 Rugby World Cup, the 2010 Ryder Cup and the 2017 UEFA Champions League Final.
Although football has traditionally been the more popular sport in North Wales, rugby union in Wales, rugby union is seen as a symbol of Welsh national identity, Welsh identity and an expression of national consciousness. The Wales national rugby union team takes part in the annual Six Nations Championship and has also competed in every Rugby World Cup, hosting the tournament in 1999 Rugby World Cup, 1999. The five professional sides that replaced the traditional club sides in major competitions in 2003 were replaced in 2004 by the four regions: Cardiff Blues, Dragons (rugby union), Dragons, Ospreys (rugby union), Ospreys and Scarlets. The Welsh regional teams play in the United Rugby Championship, the Heineken Champions Cup if they qualify and the European Rugby Challenge Cup, again dependent on qualification. Rugby league in Wales dates back to 1907. A professional Welsh League existed from 1908 to 1910.
Wales has had football in Wales, its own football league, the Welsh Premier League, since 1992. For historical reasons, five Welsh clubs play in the English football league system; Cardiff City F.C., Cardiff City, Swansea City A.F.C., Swansea City, Newport County A.F.C, Newport County, Wrexham A.F.C., Wrexham, and Merthyr Town F.C. (2010), Merthyr Town. Famous Welsh players over the years include John Charles, John Toshack, Gary Speed, Ian Rush, Ryan Giggs, Gareth Bale, Aaron Ramsey, and Daniel James (footballer), Daniel James. At UEFA Euro 2016, the Wales national football team, Wales national team achieved their best ever finish, reaching the semi-finals where they were beaten by eventual champions Portugal.
In international cricket, Wales and England field a single representative team, administered by the England and Wales Cricket Board (ECB), called the England cricket team, or simply 'England'. Occasionally, a separate Wales cricket team, Wales team play limited-overs competitions. Glamorgan County Cricket Club is the only Welsh participant in the England and Wales County Championship. Wales has produced several notable participants of individual and team sports including snooker players Ray Reardon, Terry Griffiths, Mark Williams (snooker player), Mark Williams and Matthew Stevens. Track athletes who have made a mark on the world stage include hurdler Colin Jackson and Paralympian Tanni Grey-Thompson. Champion cyclists include Nicole Cooke and Geraint Thomas. Wales has a tradition of producing world-class boxers. Joe Calzaghe was WBO world super-middleweight champion and then won the WBA, WBC and Ring Magazine super middleweight and Ring Magazine light-heavyweight titles. Other former boxing world champions include Enzo Maccarinelli, Freddie Welsh, Howard Winstone, Percy Jones (boxer), Percy Jones, Jimmy Wilde, Steve Robinson (boxer), Steve Robinson and Robbie Regan. Tommy Farr, the "Tonypandy Terror", came close to defeating world heavyweight champion Joe Louis at the height of his fame in 1937.
Media
 Wales became the UK's first digital television nation. BBC Cymru Wales is the national broadcaster, producing both television and radio programmes in Welsh and English from its base in Central Square, Cardiff, Central Square, Cardiff. The broadcaster also produces programmes such as ''Life on Mars (British TV series), Life on Mars'', ''Doctor Who'' and ''Torchwood'' for BBC's network audience across the United Kingdom. ITV (TV network), ITV, the UK's main commercial broadcaster, has a Welsh-oriented service branded as ITV Cymru Wales, whose studios are in Cardiff Bay. S4C, based in Carmarthen, first broadcast on 1 November 1982. Its output was mostly in Welsh at peak hours but shared English-language content with Channel 4 at other times. Since the digital television transition, digital switchover in April 2010, the channel has broadcast exclusively in Welsh. BBC Radio Cymru is the BBC's Welsh-language radio service, which broadcasts throughout Wales. A number of independent radio stations broadcast in the Welsh regions, predominantly in English. In 2006, several regional radio stations broadcast in Welsh: output ranged from two two-minute news bulletins each weekday (Radio Maldwyn) to over 14 hours of Welsh-language programmes weekly (Swansea Sound) to essentially bilingual stations such as Heart Cymru and Radio Ceredigion.
Most of the newspapers sold and read in Wales are national newspapers available throughout Britain. The ''Western Mail (Wales), Western Mail'' is Wales's only print national daily newspaper, but a new online and occasional print national newspaper, ''The National'', launched on Saint David's Day in 2021. Wales-based regional daily newspapers include the ''Daily Post (North Wales), Daily Post'' (which covers North Wales), the ''South Wales Evening Post'' (Swansea), the ''South Wales Echo'' (Cardiff), and the ''South Wales Argus'' (Newport). ''Y Cymro'' is a Welsh-language newspaper, published weekly. ''Wales on Sunday'' is the only Welsh Sunday newspaper that covers the whole of Wales. The Books Council of Wales (BCW, previously known as the Welsh Books Council) is the Welsh-Government-funded body tasked with promoting Welsh literature in Welsh and English. The BCW provides publishing grants for qualifying English- and Welsh-language publications. Around 600–650 books are published each year, by some of the dozens of Welsh publishers. Wales' main publishing houses include Gomer Press, Gwasg Carreg Gwalch, Honno (press), Honno, the University of Wales Press and Y Lolfa. ''Cambria'', a Welsh affairs magazine published bi-monthly in English, has subscribers internationally. Titles published quarterly in English include ''Planet'' and ''Poetry Wales''. Welsh-language magazines include the current affairs titles ''Golwg'' ("View"), published weekly, and ''Barn (Welsh magazine), Barn'' ("Opinion"), published monthly. Among the specialist magazines, ''Y Wawr'' ("The Dawn") is published quarterly by ''Merched y Wawr'', the national organisation for women. ''Y Traethodydd'' ("The Essayist"), a quarterly publication by the Presbyterian Church of Wales, first appeared in 1845 and is the oldest Welsh publication still in print.
Wales became the UK's first digital television nation. BBC Cymru Wales is the national broadcaster, producing both television and radio programmes in Welsh and English from its base in Central Square, Cardiff, Central Square, Cardiff. The broadcaster also produces programmes such as ''Life on Mars (British TV series), Life on Mars'', ''Doctor Who'' and ''Torchwood'' for BBC's network audience across the United Kingdom. ITV (TV network), ITV, the UK's main commercial broadcaster, has a Welsh-oriented service branded as ITV Cymru Wales, whose studios are in Cardiff Bay. S4C, based in Carmarthen, first broadcast on 1 November 1982. Its output was mostly in Welsh at peak hours but shared English-language content with Channel 4 at other times. Since the digital television transition, digital switchover in April 2010, the channel has broadcast exclusively in Welsh. BBC Radio Cymru is the BBC's Welsh-language radio service, which broadcasts throughout Wales. A number of independent radio stations broadcast in the Welsh regions, predominantly in English. In 2006, several regional radio stations broadcast in Welsh: output ranged from two two-minute news bulletins each weekday (Radio Maldwyn) to over 14 hours of Welsh-language programmes weekly (Swansea Sound) to essentially bilingual stations such as Heart Cymru and Radio Ceredigion.
Most of the newspapers sold and read in Wales are national newspapers available throughout Britain. The ''Western Mail (Wales), Western Mail'' is Wales's only print national daily newspaper, but a new online and occasional print national newspaper, ''The National'', launched on Saint David's Day in 2021. Wales-based regional daily newspapers include the ''Daily Post (North Wales), Daily Post'' (which covers North Wales), the ''South Wales Evening Post'' (Swansea), the ''South Wales Echo'' (Cardiff), and the ''South Wales Argus'' (Newport). ''Y Cymro'' is a Welsh-language newspaper, published weekly. ''Wales on Sunday'' is the only Welsh Sunday newspaper that covers the whole of Wales. The Books Council of Wales (BCW, previously known as the Welsh Books Council) is the Welsh-Government-funded body tasked with promoting Welsh literature in Welsh and English. The BCW provides publishing grants for qualifying English- and Welsh-language publications. Around 600–650 books are published each year, by some of the dozens of Welsh publishers. Wales' main publishing houses include Gomer Press, Gwasg Carreg Gwalch, Honno (press), Honno, the University of Wales Press and Y Lolfa. ''Cambria'', a Welsh affairs magazine published bi-monthly in English, has subscribers internationally. Titles published quarterly in English include ''Planet'' and ''Poetry Wales''. Welsh-language magazines include the current affairs titles ''Golwg'' ("View"), published weekly, and ''Barn (Welsh magazine), Barn'' ("Opinion"), published monthly. Among the specialist magazines, ''Y Wawr'' ("The Dawn") is published quarterly by ''Merched y Wawr'', the national organisation for women. ''Y Traethodydd'' ("The Essayist"), a quarterly publication by the Presbyterian Church of Wales, first appeared in 1845 and is the oldest Welsh publication still in print.
Cuisine
 Traditional Welsh dishes include laverbread (made from ''Porphyra umbilicalis'', an edible seaweed); bara brith (fruit bread); cawl (a lamb stew); cawl cennin (leek soup); and Welsh cakes. Cockle (bivalve), Cockles are sometimes served as a traditional breakfast with bacon and laverbread. Although Wales has its own traditional food and has absorbed much of the cuisine of England, Welsh diets now owe more to the countries of Indian cuisine, India, Chinese cuisine, China and the Cuisine of the United States, United States. Chicken tikka masala is the country's favourite dish while hamburgers and Chinese food outsell fish and chips as takeaways.Davies (2008) p.293
Traditional Welsh dishes include laverbread (made from ''Porphyra umbilicalis'', an edible seaweed); bara brith (fruit bread); cawl (a lamb stew); cawl cennin (leek soup); and Welsh cakes. Cockle (bivalve), Cockles are sometimes served as a traditional breakfast with bacon and laverbread. Although Wales has its own traditional food and has absorbed much of the cuisine of England, Welsh diets now owe more to the countries of Indian cuisine, India, Chinese cuisine, China and the Cuisine of the United States, United States. Chicken tikka masala is the country's favourite dish while hamburgers and Chinese food outsell fish and chips as takeaways.Davies (2008) p.293
Performing arts
Music and festivals
Wales is often referred to as "the land of song", notable for its harpists, male choirs, and solo artists. The main festival of music and poetry is the annual ''National Eisteddfod''. The ''Llangollen International Eisteddfod'' provides an opportunity for the singers and musicians of the world to perform. The Welsh Folk Song Society has published a number of collections of songs and tunes. Traditional instruments of Wales include ''telyn deires'' (triple harp), fiddle, ''crwth'' (bowed lyre), ''pibgorn'' (hornpipe) and other instruments. Male voice choirs emerged in the 19th century, formed as the tenor and bass sections of chapel choirs, and embraced the popular secular hymns of the day.Davies (2008), p. 532. Many of the historic choirs survive in modern Wales, singing a mixture of traditional and popular songs. The BBC National Orchestra of Wales performs in Wales and internationally. The Welsh National Opera is based at the Wales Millennium Centre in Cardiff Bay, while the National Youth Orchestra of Wales was the first of its type in the world. Wales has a tradition of producing notable singers, including Geraint Evans, Gwyneth Jones (soprano), Gwyneth Jones, Anne Evans (soprano), Anne Evans, Margaret Price, Tom Jones (singer), Tom Jones, Bonnie Tyler, Bryn Terfel, Mary Hopkin, Charlotte Church, Donna Lewis, Katherine Jenkins, and Shirley Bassey. Popular bands that emerged from Wales include Badfinger, the Manic Street Preachers, the Stereophonics and Feeder (band), Feeder, the Super Furry Animals and Catatonia (band), Catatonia. The Welsh traditional and folk music scene is in resurgence with performers such as Sian James (musician), Siân James
The BBC National Orchestra of Wales performs in Wales and internationally. The Welsh National Opera is based at the Wales Millennium Centre in Cardiff Bay, while the National Youth Orchestra of Wales was the first of its type in the world. Wales has a tradition of producing notable singers, including Geraint Evans, Gwyneth Jones (soprano), Gwyneth Jones, Anne Evans (soprano), Anne Evans, Margaret Price, Tom Jones (singer), Tom Jones, Bonnie Tyler, Bryn Terfel, Mary Hopkin, Charlotte Church, Donna Lewis, Katherine Jenkins, and Shirley Bassey. Popular bands that emerged from Wales include Badfinger, the Manic Street Preachers, the Stereophonics and Feeder (band), Feeder, the Super Furry Animals and Catatonia (band), Catatonia. The Welsh traditional and folk music scene is in resurgence with performers such as Sian James (musician), Siân James
Drama and dance
 The earliest surviving Welsh plays are two medieval miracle plays, ''Y Tri Brenin o Gwlen'' ("The three Kings from Cologne") and ''Y Dioddefaint a'r Atgyfodiad'' ("The Passion and the Resurrection"). A recognised Welsh tradition of theatre emerged during the 18th century, in the form of an Play (theatre), interlude, a metrical play performed at fairs and markets. Drama in the early 20th century thrived, but the country established neither a Welsh National Theatre nor a national ballet company. After the Second World War the substantial number of amateur companies that had existed before the outbreak of hostilities reduced by two-thirds.Davies (2008) p. 224 Competition from television in the mid-20th century led to greater professionalism in the theatre. Plays by Emlyn Williams and Alun Owen and others were staged, while Welsh actors, including Richard Burton and Stanley Baker, were establishing themselves as artistic talents. Anthony Hopkins is an alumnus of the Royal Welsh College of Music & Drama, and other notable Welsh actors include Michael Sheen and Catherine Zeta-Jones. Wales has also produced well known comedians including Rob Brydon, Tommy Cooper, Terry Jones, and Harry Secombe.
Traditional dances include Welsh Welsh dance, folk dancing and Welsh stepdance, clog dancing. The first mention of dancing in Wales is in a 12th-century account by Gerald of Wales, Giraldus Cambrensis, but by the 19th century traditional dance had all but died out due to religious opposition.Davies (2008) p. 192 In the 20th century a revival was led by Lois Blake (1890–1974). Clog dancing was preserved and developed by Hywel Wood (1882–1967) and others who perpetuated the art on local and national stages.Davies (2008) p. 193 The Welsh Folk Dance Society was founded in 1949; it supports a network of national amateur dance teams and publishes support material. Contemporary dance grew out of Cardiff in the 1970s; one of the earliest companies, ''Moving Being'', came from London to Cardiff in 1973. ''Diversions'' was formed in 1983, eventually becoming the National Dance Company Wales, now the resident company at the Wales Millennium Centre.
The earliest surviving Welsh plays are two medieval miracle plays, ''Y Tri Brenin o Gwlen'' ("The three Kings from Cologne") and ''Y Dioddefaint a'r Atgyfodiad'' ("The Passion and the Resurrection"). A recognised Welsh tradition of theatre emerged during the 18th century, in the form of an Play (theatre), interlude, a metrical play performed at fairs and markets. Drama in the early 20th century thrived, but the country established neither a Welsh National Theatre nor a national ballet company. After the Second World War the substantial number of amateur companies that had existed before the outbreak of hostilities reduced by two-thirds.Davies (2008) p. 224 Competition from television in the mid-20th century led to greater professionalism in the theatre. Plays by Emlyn Williams and Alun Owen and others were staged, while Welsh actors, including Richard Burton and Stanley Baker, were establishing themselves as artistic talents. Anthony Hopkins is an alumnus of the Royal Welsh College of Music & Drama, and other notable Welsh actors include Michael Sheen and Catherine Zeta-Jones. Wales has also produced well known comedians including Rob Brydon, Tommy Cooper, Terry Jones, and Harry Secombe.
Traditional dances include Welsh Welsh dance, folk dancing and Welsh stepdance, clog dancing. The first mention of dancing in Wales is in a 12th-century account by Gerald of Wales, Giraldus Cambrensis, but by the 19th century traditional dance had all but died out due to religious opposition.Davies (2008) p. 192 In the 20th century a revival was led by Lois Blake (1890–1974). Clog dancing was preserved and developed by Hywel Wood (1882–1967) and others who perpetuated the art on local and national stages.Davies (2008) p. 193 The Welsh Folk Dance Society was founded in 1949; it supports a network of national amateur dance teams and publishes support material. Contemporary dance grew out of Cardiff in the 1970s; one of the earliest companies, ''Moving Being'', came from London to Cardiff in 1973. ''Diversions'' was formed in 1983, eventually becoming the National Dance Company Wales, now the resident company at the Wales Millennium Centre.
Holidays
Wales has some unique celebratory days. An early festivity was Gŵyl Mabsant, Mabsant when local parishes would celebrate the patron saint of their local church. Wales's national day isSaint David
Saint David ( cy, Dewi Sant; la, Davidus; ) was a Welsh bishop of Mynyw (now St Davids) during the 6th century. He is the patron saint of Wales. David was a native of Wales, and tradition has preserved a relatively large amount of detail ab ...
's Day, marked on 1 March, believed to be the date of David's death in the year 589. Dydd Santes Dwynwen (St Dwynwen's Day) commemorates the local patron saint of friendship and love. It is celebrated on 25 January in a similar way to St Valentine's Day. Calan Gaeaf (in Celtic tradition, the first day of winter), associated with the supernatural and the dead, is observed on 1 November (All Saints Day). It has largely been replaced by Hallowe'en. Other festivities include Calan Mai (May Day), celebrating the beginning of summer; Calan Awst (Lammas Day); and Gŵyl Fair y Canhwyllau (Candlemas Day).
See also
* List of movements in Wales * Outline of Wales * Y Wladfa: Welsh settlement in ArgentinaNotes
Citations
General sources
* Census 2001''200 Years of the Census in ... Wales'' (2001)
* *
External links
Senedd Cymru – Welsh Parliament
BBC Wales
*
VisitWales.com
The official international guide to places to stay and things to do in Wales.
Wales – Official Gateway to Wales
Gathering the Jewels – Welsh Heritage and Culture
Photographs of Wales
on Geograph Britain and Ireland
Further historical information and sources at GENUKI
{{Authority control Wales, Celtic nations Articles containing video clips Great Britain English-speaking countries and territories Island countries NUTS 1 statistical regions of the United Kingdom United Kingdom by country Countries of Europe with multiple official languages