Striatal Necrosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the striate nucleus), is a
 The striatum is the largest structure of the basal ganglia. The striatum is divided into a ventral and a dorsal subdivision, based upon function and connections.
The ventral striatum is composed of the nucleus accumbens and the
The striatum is the largest structure of the basal ganglia. The striatum is divided into a ventral and a dorsal subdivision, based upon function and connections.
The ventral striatum is composed of the nucleus accumbens and the
 Types of cells in the striatum include:
*
Types of cells in the striatum include:
*
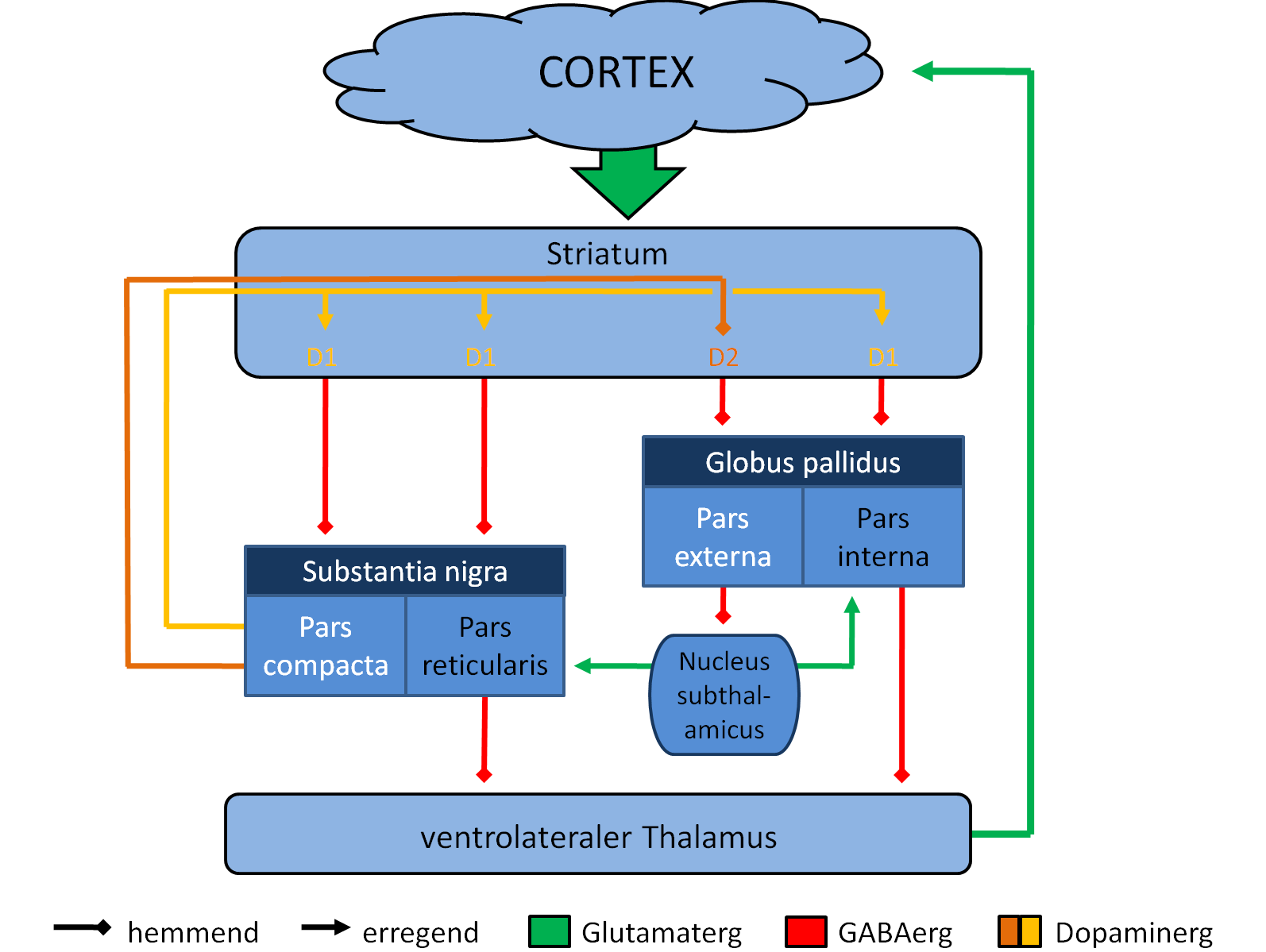
 The largest connection is from the cortex, in terms of cell axons. Many parts of the
The largest connection is from the cortex, in terms of cell axons. Many parts of the
Table 1
/ref>
File:Striatum coronal sections.gif, Striatum highlighted in green on coronal T1 MRI images
File:Striatum sagittal sections.gif, Striatum highlighted in green on sagittal T1 MRI images
File:Striatum transversal sections.gif, Striatum highlighted in green on transversal T1 MRI images
nucleus
Nucleus ( : nuclei) is a Latin word for the seed inside a fruit. It most often refers to:
*Atomic nucleus, the very dense central region of an atom
*Cell nucleus, a central organelle of a eukaryotic cell, containing most of the cell's DNA
Nucle ...
(a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting of ...
basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward
Reward may refer to:
Places
* Reward (Shelltown, Maryland), a historic home in Shelltown Maryland
* Reward, California (disambiguation)
* Reward-Tilden's Farm, a historic home in Chestertown Maryland
Arts, entertainment, and media
* "Rewa ...
systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic
Dopaminergic means "related to dopamine" (literally, "working on dopamine"), dopamine being a common neurotransmitter. Dopaminergic substances or actions increase dopamine-related activity in the brain. Dopaminergic brain pathways facilitate d ...
inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia.
Functionally, the striatum coordinates multiple aspects of cognition
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
, including both motor and action planning
Planning is the process of thinking regarding the activities required to achieve a desired goal. Planning is based on foresight, the fundamental capacity for mental time travel. The evolution of forethought, the capacity to think ahead, is consi ...
, decision-making
In psychology, decision-making (also spelled decision making and decisionmaking) is regarded as the Cognition, cognitive process resulting in the selection of a belief or a course of action among several possible alternative options. It could be ...
, motivation
Motivation is the reason for which humans and other animals initiate, continue, or terminate a behavior at a given time. Motivational states are commonly understood as forces acting within the agent that create a disposition to engage in goal-dire ...
, reinforcement, and reward
Reward may refer to:
Places
* Reward (Shelltown, Maryland), a historic home in Shelltown Maryland
* Reward, California (disambiguation)
* Reward-Tilden's Farm, a historic home in Chestertown Maryland
Arts, entertainment, and media
* "Rewa ...
perception. The striatum is made up of the caudate nucleus and the lentiform nucleus. The lentiform nucleus is made up of the larger putamen, and the smaller globus pallidus
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rod ...
. Strictly speaking the globus pallidus is part of the striatum. It is common practice, however, to implicitly exclude the globus pallidus when referring to striatal structures.
In primates, the striatum is divided into a ventral striatum, and a dorsal striatum, subdivisions that are based upon function and connections. The ventral striatum consists of the nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle
The olfactory tubercle (OT), also known as the tuberculum olfactorium, is a multi-sensory processing center that is contained within the olfactory cortex and ventral striatum and plays a role in reward cognition. The OT has also been shown to ...
. The dorsal striatum consists of the caudate nucleus and the putamen. A white matter, nerve tract
A nerve tract is a bundle of nerve fibers (axons) connecting nuclei of the central nervous system. In the peripheral nervous system this is known as a nerve, and has associated connective tissue. The main nerve tracts in the central nervous syste ...
(the internal capsule) in the dorsal striatum separates the caudate nucleus and the putamen. Anatomically, the term ''striatum'' describes its striped (striated) appearance of grey-and-white matter.
Structure
 The striatum is the largest structure of the basal ganglia. The striatum is divided into a ventral and a dorsal subdivision, based upon function and connections.
The ventral striatum is composed of the nucleus accumbens and the
The striatum is the largest structure of the basal ganglia. The striatum is divided into a ventral and a dorsal subdivision, based upon function and connections.
The ventral striatum is composed of the nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle
The olfactory tubercle (OT), also known as the tuberculum olfactorium, is a multi-sensory processing center that is contained within the olfactory cortex and ventral striatum and plays a role in reward cognition. The OT has also been shown to ...
. The nucleus accumbens is made up of the nucleus accumbens core
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for "nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypotha ...
and the nucleus accumbens shell
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for "nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypotha ...
, which differ by neural populations. The olfactory tubercle receives input from the olfactory bulb but has not been shown to play a role in processing smell. In non-primate species, the islands of Calleja
The islands of Calleja (; IC, ISC, or IClj) are a group of neural granule cells located within the ventral striatum in the brains of most animals. This region of the brain is part of the limbic system, where it aids in the reinforcing effects of ...
are included. The ventral striatum is associated with the limbic system and has been implicated as a vital part of the circuitry for decision making and reward-related behavior.
The dorsal striatum is composed of the caudate nucleus and the putamen.
Staining
Staining is a technique used to enhance contrast in samples, generally at the microscopic level. Stains and dyes are frequently used in histology (microscopic study of biological tissues), in cytology (microscopic study of cells), and in the ...
can differentiate the striatum into two distinct compartments of striosome
The striosomes (also referred to as ''patches'') are one of two complementary chemical compartments within the striatum (the other compartment is known as the matrix) that can be visualized by staining for immunocytochemical markers such as acetyl ...
s or ''patches'', and a surrounding matrix
Matrix most commonly refers to:
* ''The Matrix'' (franchise), an American media franchise
** ''The Matrix'', a 1999 science-fiction action film
** "The Matrix", a fictional setting, a virtual reality environment, within ''The Matrix'' (franchis ...
; this is particularly evident on the components of acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that a ...
and calbindin. More studies have been carried out on the dorsal striatum but the compartments have also been identified in the ventral striatum. In the dorsal striatum striosomes make up 10-15 per cent of the striatal volume.
Cell types
 Types of cells in the striatum include:
*
Types of cells in the striatum include:
* Medium spiny neurons
Medium spiny neurons (MSNs), also known as spiny projection neurons (SPNs), are a special type of GABAergic inhibitory cell representing 95% of neurons within the human striatum, a basal ganglia structure. Medium spiny neurons have two primary ...
(MSNs), which are the principal neurons of the striatum. They are GABAergic
In molecular biology and physiology, something is GABAergic or GABAnergic if it pertains to or affects the neurotransmitter GABA. For example, a synapse is GABAergic if it uses GABA as its neurotransmitter, and a GABAergic neuron produces GABA. A ...
and, thus, are classified as inhibitory neurons. Medium spiny projection neurons comprise 95% of the total neuronal population of the human striatum. Medium spiny neurons have two characteristic types: D1-type
The D1-like receptors are a subfamily of dopamine receptors that bind the endogenous neurotransmitter dopamine. The D1-like subfamily consists of two G protein–coupled receptors that are coupled to Gs and mediate excitatory neurotransmission
...
MSNs and D2-type MSNs. A subpopulation of MSNs contain both D1-type and D2-type receptors, with approximately 40% of striatal MSNs expressing both DRD1
Dopamine receptor D1, also known as DRD1. It is one of the two types of D1-like receptor family - receptors D1 and D5. It is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DRD1 gene.
Tissue distribution
D1 receptors are the most abundant kind of do ...
and DRD2
Dopamine receptor D2, also known as D2R, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''DRD2'' gene. After work from Paul Greengard's lab had suggested that dopamine receptors were the site of action of antipsychotic drugs, several groups, in ...
mRNA.
* Cholinergic interneurons release acetylcholine, which has a variety of important effects in the striatum. In humans, other primates, and rodents, these interneurons respond to salient environmental stimuli with stereotyped responses that are temporally aligned with the responses of dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. ''Substantia nigra'' is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra app ...
. The large aspiny cholinergic interneurons themselves are affected by dopamine through D5 dopamine receptors. Dopamine also directly controls communication between cholinergic interneurons.
* There are many types of GABAergic interneurons. The best known are parvalbumin expressing interneurons, also known as fast-spiking interneurons, which participate in powerful feedforward
Feedforward is the provision of context of what one wants to communicate prior to that communication. In purposeful activity, feedforward creates an expectation which the actor anticipates. When expected experience occurs, this provides confirmato ...
inhibition of principal neurons. Also, there are GABAergic interneurons that express tyrosine hydroxylase, somatostatin
Somatostatin, also known as growth hormone-inhibiting hormone (GHIH) or by several other names, is a peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system and affects neurotransmission and cell proliferation via interaction with G protein-couple ...
, nitric oxide synthase and neuropeptide-y. Recently, two types of neuropeptide-y expressing GABAergic interneurons have been described in detail, one of which translates synchronous activity of cholinergic interneurons into inhibition of principal neurons. These neurons of the striatum are not distributed evenly.
There are two regions of neurogenesis
Neurogenesis is the process by which nervous system cells, the neurons, are produced by neural stem cells (NSCs). It occurs in all species of animals except the porifera (sponges) and placozoans. Types of NSCs include neuroepithelial cells (NECs) ...
in the brain – the subventricular zone in the lateral ventricles, and the dentate gyrus in the hippocampal formation. Neuroblast
In vertebrates, a neuroblast or primitive nerve cell is a postmitotic cell that does not divide further, and which will develop into a neuron after a migration phase. In invertebrates such as ''Drosophila,'' neuroblasts are neural progenitor cells ...
s that form in the lateral ventricle adjacent to the striatum, integrate in the striatum. This has been noted in the human striatum following an ischemic stroke. Injury caused to the striatum stimulates the migration of neuroblasts from the subventricular zone, to the striatum, where they differentiate into adult neurons. The normal passage of SVZ neuroblasts is to the olfactory bulb but this traffic is diverted to the striatum after an ischemic stroke. However, few of the new developed neurons survive.
Inputs

neocortex
The neocortex, also called the neopallium, isocortex, or the six-layered cortex, is a set of layers of the mammalian cerebral cortex involved in higher-order brain functions such as sensory perception, cognition, generation of motor commands, sp ...
innervate
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons) in the peripheral nervous system.
A nerve transmits electrical impulses. It is the basic unit of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the e ...
the dorsal striatum. The cortical pyramidal neurons projecting to the striatum are located in layers II-VI, with the most dense projections come from layer V. They end mainly on the dendritic spines of the spiny neurons. They are glutamatergic, exciting striatal neurons.
The striatum is seen as having its own internal microcircuitry. The ventral striatum receives direct input from multiple regions in the cerebral cortex and limbic structures such as the amygdala, thalamus, and hippocampus, as well as the entorhinal cortex and the inferior temporal gyrus. Its primary input is to the basal ganglia system. Additionally, the mesolimbic pathway projects from the ventral tegmental area to the nucleus accumbens of the ventral striatum.
Another well-known afferent is the nigrostriatal The nigrostriatal pathway is a bilateral dopaminergic pathway in the brain that connects the substantia nigra pars compacta (SNc) in the midbrain with the dorsal striatum (i.e., the caudate nucleus and putamen) in the forebrain. It is one of the fo ...
connection arising from the neurons of the substantia nigra
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. ''Substantia nigra'' is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra app ...
pars compacta. While cortical axons synapse mainly on spine heads of spiny neurons, nigral axons synapse mainly on spine shafts.
In primates, the thalamostriatal afferent comes from the central median-parafascicular complex of the thalamus (see primate basal ganglia system
The basal ganglia form a major brain system in all species of vertebrates, but in primates (including humans) there are special features that justify a separate consideration. As in other vertebrates, the primate basal ganglia can be divided into ...
). This afferent is glutamatergic. The participation of truly intralaminar neurons is much more limited.
The striatum also receives afferents from other elements of the basal ganglia such as the subthalamic nucleus
The subthalamic nucleus (STN) is a small lens-shaped nucleus in the brain where it is, from a functional point of view, part of the basal ganglia system. In terms of anatomy, it is the major part of the subthalamus. As suggested by its name, the ...
(glutamatergic) or the external globus pallidus
The external globus pallidus (GPe or lateral globus pallidus) combines with the internal globus pallidus (GPi) to form the globus pallidus, an anatomical subset of the basal ganglia. Globus pallidus means "pale globe" in Latin, indicating its appea ...
(GABAergic
In molecular biology and physiology, something is GABAergic or GABAnergic if it pertains to or affects the neurotransmitter GABA. For example, a synapse is GABAergic if it uses GABA as its neurotransmitter, and a GABAergic neuron produces GABA. A ...
).
Targets
The primary outputs of the ventral striatum project to the ventral pallidum, then the medial dorsal nucleus of the thalamus, which is part of the frontostriatal circuit. Additionally, the ventral striatum projects to theglobus pallidus
The globus pallidus (GP), also known as paleostriatum or dorsal pallidum, is a subcortical structure of the brain. It consists of two adjacent segments, one external, known in rodents simply as the globus pallidus, and one internal, known in rod ...
, and substantia nigra pars reticulata. Some of its other outputs include projections to the extended amygdala, lateral hypothalamus, and pedunculopontine nucleus
The pedunculopontine nucleus (PPN) or pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus (PPT or PPTg) is a collection of neurons located in the upper pons in the brainstem. It lies caudal to the substantia nigra and adjacent to the superior cerebellar peduncle. ...
.
Striatal outputs from both the dorsal and ventral components are primarily composed of medium spiny neuron
Medium spiny neurons (MSNs), also known as spiny projection neurons (SPNs), are a special type of GABAergic inhibitory cell representing 95% of neurons within the human striatum, a basal ganglia structure. Medium spiny neurons have two primary ...
s (MSNs), a type of projection neuron
The projection fibers consist of efferent and afferent fibers uniting the cortex with the lower parts of the brain and with the spinal cord. In human neuroanatomy, bundles of axons (nerve fibers) called tracts, within the brain, can be catego ...
, which have two primary phenotypes: "indirect" MSNs that express D2-like receptors and "direct" MSNs that express D1-like receptors.
The main nucleus of the basal ganglia is the striatum which projects directly to the globus pallidus via a pathway of striatopallidal fibers
The striatopallidal fibres, also Wilson's pencils, pencil fibres of Wilson, and pencils of Wilson, are prominent myelinated fibres that connect the striatum to the globus pallidus.
Their distinctive appearance allows the putamen to be identified ...
. The striato-pallidal pathway has a whitish appearance due to the myelinated fibers. This projection comprises successively the external globus pallidus (GPe), the internal globus pallidus (GPi), the pars compacta of the substantia nigra
The substantia nigra (SN) is a basal ganglia structure located in the midbrain that plays an important role in reward and movement. ''Substantia nigra'' is Latin for "black substance", reflecting the fact that parts of the substantia nigra app ...
(SNc), and the pars reticulata of substantia nigra (SNr). The neurons of this projection are inhibited by GABAergic synapses from the dorsal striatum. Among these targets, the GPe does not send axons outside the system. Others send axons to the superior colliculus
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the homologous structure is known as the optic tectum, or optic lobe. The adjective form ''tectal'' is commonly ...
. Two others comprise the output to the thalamus, forming two separate channels: one through the internal segment of the globus pallidus to the ventral oralis nuclei of the thalamus and from there to the cortical supplementary motor area and another through the substantia nigra to the ventral anterior nuclei of the thalamus and from there to the frontal cortex
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove betwe ...
and the occulomotor cortex.
Blood supply
Deep penetratingstriate arteries The lenticulostriate arteries, anterolateral central arteries, or antero-lateral ganglionic branches are a group of small arteries arising from the initial part M1 of the middle cerebral artery that supply the basal ganglia.
Structure
The lenticul ...
supply blood to the striatum. These arteries include the recurrent artery of Heubner
The recurrent artery of Heubner, Heubner's artery or distal medial striate artery is an artery in the head. It is named after the German paediatrician Otto Heubner. It is a branch of the anterior cerebral artery. Its vascular territory is the ant ...
arising from the anterior cerebral artery
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from t ...
, and the lenticulostriate arteries The lenticulostriate arteries, anterolateral central arteries, or antero-lateral ganglionic branches are a group of small arteries arising from the initial part M1 of the middle cerebral artery that supply the basal ganglia.
Structure
The lenticul ...
arising from the middle cerebral artery.
Function
The ventral striatum, and the nucleus accumbens in particular, primarily mediatesreward
Reward may refer to:
Places
* Reward (Shelltown, Maryland), a historic home in Shelltown Maryland
* Reward, California (disambiguation)
* Reward-Tilden's Farm, a historic home in Chestertown Maryland
Arts, entertainment, and media
* "Rewa ...
, cognition, reinforcement, and motivational salience
Motivational salience is a cognitive process and a form of attention that ''motivates'' or propels an individual's behavior towards or away from a particular object, perceived event or outcome. Motivational salience regulates the intensity of be ...
, whereas the dorsal striatum primarily mediates cognition involving motor function, certain executive functions (e.g., inhibitory control and impulsivity
In psychology, impulsivity (or impulsiveness) is a tendency to act on a whim, displaying behavior characterized by little or no forethought, reflection, or consideration of the consequences. Impulsive actions are typically "poorly conceived, prema ...
), and stimulus-response learning; there is a small degree of overlap, as the dorsal striatum is also a component of the reward system
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and class ...
that, along with the nucleus accumbens core
The nucleus accumbens (NAc or NAcc; also known as the accumbens nucleus, or formerly as the ''nucleus accumbens septi'', Latin for "nucleus adjacent to the septum") is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypotha ...
, mediates the encoding of new motor programs associated with future reward acquisition (e.g., the conditioned motor response to a reward cue).
Metabotropic dopamine receptors are present both on spiny neurons and on cortical axon terminals. Second messenger
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form or cell signaling, encompassing both first me ...
cascades triggered by activation of these dopamine receptors can modulate pre- and postsynaptic function, both in the short term and in the long term. In humans, the striatum is activated by stimuli associated with reward, but also by aversive
In psychology, aversives are unpleasant stimuli that induce changes in behavior via negative reinforcement or positive punishment. By applying an aversive immediately before or after a behavior the likelihood of the target behavior occurring in ...
, novel
A novel is a relatively long work of narrative fiction, typically written in prose and published as a book. The present English word for a long work of prose fiction derives from the for "new", "news", or "short story of something new", itsel ...
, unexpected
Unexpected may refer to:
Film and television
* ''Unexpected'' (2005 film), an Italian documentary directed by Domenico Distilo
* ''Unexpected'' (2015 film), an American film directed by Kris Swanberg
* ''The Unexpected'' (TV series), a 1950s TV ...
, or intense stimuli, and cues associated with such events. fMRI evidence suggests that the common property linking these stimuli, to which the striatum is reacting, is salience under the conditions of presentation. A number of other brain areas and circuits are also related to reward, such as frontal areas. Functional maps of the striatum reveal interactions with widely distributed regions of the cerebral cortex important to a diverse range of functions.
The interplay between the striatum and the prefrontal cortex is relevant for behavior, particularly adolescent development as proposed by the dual systems model
The dual systems model, also known as the maturational imbalance model, is a theory arising from developmental cognitive neuroscience which posits that increased risk-taking during adolescence is a result of a combination of heightened reward sensi ...
.
Clinical significance
Parkinson's disease and other movement disorders
Parkinson's disease results in loss of dopaminergic innervation to the dorsal striatum (and other basal ganglia) and a cascade of consequences.Atrophy
Atrophy is the partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Causes of atrophy include mutations (which can destroy the gene to build up the organ), poor nourishment, poor circulation, loss of hormonal support, loss of nerve supply t ...
of the striatum is also involved in Huntington's disease, and movement disorders such as chorea, choreoathetosis, and dyskinesias
Dyskinesia refers to a category of movement disorders that are characterized by involuntary muscle movements, including movements similar to tics or chorea and diminished voluntary movements. Dyskinesia can be anything from a slight tremor of t ...
. These have also been described as ''circuit disorders'' of the basal ganglia.
Addiction
Addiction, a disorder of the brain'sreward system
The reward system (the mesocorticolimbic circuit) is a group of neural structures responsible for incentive salience (i.e., "wanting"; desire or craving for a reward and motivation), associative learning (primarily positive reinforcement and class ...
, arises through the overexpression of DeltaFosB (ΔFosB), a transcription factor, in the D1-type
The D1-like receptors are a subfamily of dopamine receptors that bind the endogenous neurotransmitter dopamine. The D1-like subfamily consists of two G protein–coupled receptors that are coupled to Gs and mediate excitatory neurotransmission
...
medium spiny neuron
Medium spiny neurons (MSNs), also known as spiny projection neurons (SPNs), are a special type of GABAergic inhibitory cell representing 95% of neurons within the human striatum, a basal ganglia structure. Medium spiny neurons have two primary ...
s of the ventral striatum. ΔFosB is an inducible gene which is increasingly expressed in the nucleus accumbens as a result of repeatedly overdosing
A drug overdose (overdose or OD) is the ingestion or application of a drug or other substance in quantities much greater than are recommended.
on an addictive drug or overexposure to other addictive stimuli.Table 1
/ref>
Bipolar disorder
An association has been observed between striatal expression of variants of the PDE10A gene and somebipolar I disorder
Bipolar I disorder (BD-I; pronounced "type one bipolar disorder") is a type of bipolar spectrum disorder characterized by the occurrence of at least one manic episode, with or without mixed or psychotic features. Most people also, at other time ...
patients. Variants of other genes, DISC1 and GNAS, have been associated with bipolar II disorder.
Autism spectrum disorder
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is characterized by cognitive inflexibility and poor understanding of social systems. This inflexible behavior originates in defects in the pre-frontal cortex as well as the striatal circuits. The defects in the striatum seem to specifically contribute to the motor, social and communication impairments seen in ASD patients. In mice which have an ASD-like phenotype induced via the overexpression of the eukaryotic initiation of translation factor 4E, it has been shown that these defects seem to stem from the reduced ability to store and process information in the striatum, which leads to the difficulty seen in forming new motor patterns, as well as disengaging from existing ones.Dysfunction
Dysfunction in the ventral striatum can lead to a variety of disorders, most notably, depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Because of its involvement in reward pathways, the ventral striatum has also been implicated in playing a critical role in addiction. It has been well established that the ventral striatum is strongly involved in mediating the reinforcing effects of drugs, especially stimulants, through dopaminergic stimulation.History
In the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries, the term "corpus striatum" was used to designate many distinct, deep, infracortical elements of the hemisphere. Etymologically it is derived from (Latin) "striatus" = "grooved, striated" and the English "striated" = having parallel lines or grooves on the surface. In 1876 David Ferrier contributed decades of research to the subject; concluding that the corpus striatum was vital in the "organization and generation of voluntary movement". In 1941, Cécile and Oskar Vogt simplified the nomenclature by proposing the term ''striatum'' for all elements in the basal ganglia built with striatal elements: the caudate nucleus, the putamen, and the fundus striati, which is the ventral part linking the two preceding together ventrally to the inferior part of the internal capsule. The term ''neostriatum'' was forged by comparative anatomists comparing the subcortical structures between vertebrates, because it was thought to be a phylogenetically newer section of the corpus striatum. The term is still used by some sources, includingMedical Subject Headings
Medical Subject Headings (MeSH) is a comprehensive controlled vocabulary for the purpose of indexing journal articles and books in the life sciences. It serves as a thesaurus that facilitates searching. Created and updated by the United States N ...
.
Other animals
In birds the term used was the ''paleostriatum augmentatum'', and in the new avian terminology listing (as of 2002) for ''neostriatum'' this has been changed to the ''nidopallium
The nidopallium, meaning nested pallium, is the region of the avian brain that is used mostly for some types of executive functions but also for other higher cognitive tasks. The region was renamed nidopallium in 2002 during the Avian Brain Nomen ...
''.
In non-primate species, the islands of Calleja
The islands of Calleja (; IC, ISC, or IClj) are a group of neural granule cells located within the ventral striatum in the brains of most animals. This region of the brain is part of the limbic system, where it aids in the reinforcing effects of ...
are included in the ventral striatum.
See also
* Cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop *List of regions in the human brain
The human brain anatomical regions are ordered following standard neuroanatomy hierarchies. Functional, connective, and developmental regions are listed in parentheses where appropriate.
Hindbrain (rhombencephalon)
Myelencephalon
* Med ...
* Striatopallidal fibres
The striatopallidal fibres, also Wilson's pencils, pencil fibres of Wilson, and pencils of Wilson, are prominent myelinated fibres that connect the striatum to the globus pallidus.
Their distinctive appearance allows the putamen to be identified o ...
Additional images
References
External links
* * * * https://web.archive.org/web/20131029195257/http://www.nimh.nih.gov/images/news-items/r1_braindorsal1.jpg * https://web.archive.org/web/20090914200329/http://www.hnl.bcm.tmc.edu/fmri.html {{Authority control Cerebrum Basal ganglia Addiction