|
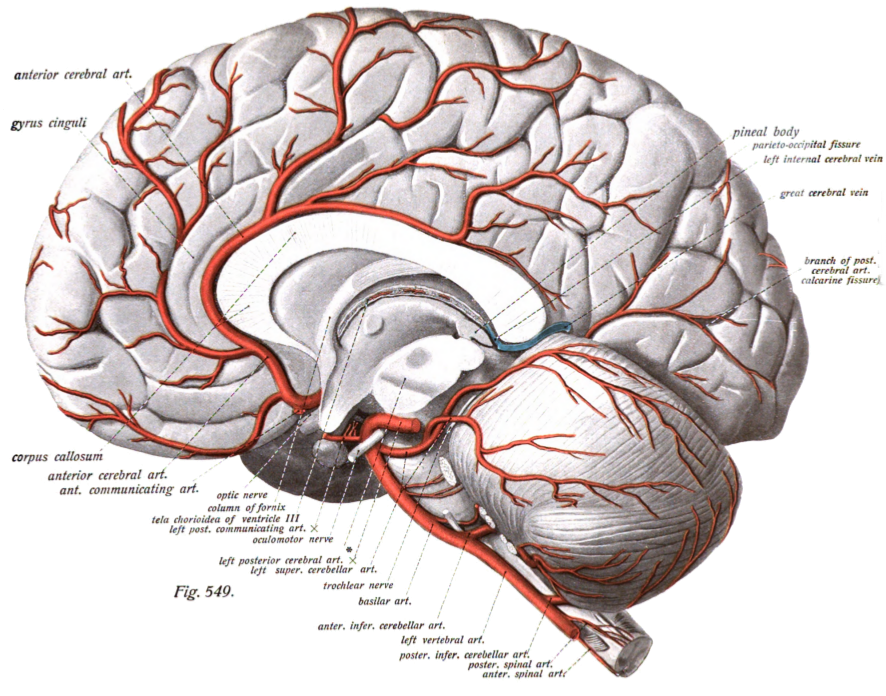
Recurrent Artery Of Heubner
The recurrent artery of Heubner, Heubner's artery or distal medial striate artery is an artery in the head. It is named after the German paediatrician Otto Heubner. It is a branch of the anterior cerebral artery. Its vascular territory is the anteromedial section of the caudate nucleus and the anterioinferior section of the internal capsule, as well as parts of the putamen and septal nuclei. Structure The recurrent artery of Heubner is a branch of the anterior cerebral artery. It has a mean diameter of 0.8 mm, and a mean length of 2.4 mm. It is also known together with the lenticulostriate arteries as a striate artery. The lenticulostriate arteries arise from the middle cerebral artery. Variation The recurrent artery of Heubner usually arises from the A1-A2 junction (between 44% and 62% of the time), but may arise from the proximal A2 segment (between 23% and 43%), or more rarely from the A1 segment (maybe up to 14% of the time). The recurrent artery of Heubner has a very ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Cerebral Artery
The anterior cerebral artery (ACA) is one of a pair of cerebral arteries that supplies oxygenated blood to most midline portions of the frontal lobes and superior medial parietal lobes of the brain. The two anterior cerebral arteries arise from the internal carotid artery and are part of the circle of Willis. The left and right anterior cerebral arteries are connected by the anterior communicating artery. Anterior cerebral artery syndrome refers to symptoms that follow a stroke occurring in the area normally supplied by one of the arteries. It is characterized by weakness and sensory loss in the lower leg and foot opposite to the lesion and behavioral changes. Structure The anterior cerebral artery is divided into 5 segments. Its smaller branches: the callosal (supracallosal) arteries are considered to be the A4 and A5 segments. *A1 originates from the internal carotid artery and extends to the ''anterior communicating artery'' (AComm). The ''anteromedial central'' (media ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mean
There are several kinds of mean in mathematics, especially in statistics. Each mean serves to summarize a given group of data, often to better understand the overall value ( magnitude and sign) of a given data set. For a data set, the '' arithmetic mean'', also known as "arithmetic average", is a measure of central tendency of a finite set of numbers: specifically, the sum of the values divided by the number of values. The arithmetic mean of a set of numbers ''x''1, ''x''2, ..., x''n'' is typically denoted using an overhead bar, \bar. If the data set were based on a series of observations obtained by sampling from a statistical population, the arithmetic mean is the '' sample mean'' (\bar) to distinguish it from the mean, or expected value, of the underlying distribution, the '' population mean'' (denoted \mu or \mu_x).Underhill, L.G.; Bradfield d. (1998) ''Introstat'', Juta and Company Ltd.p. 181/ref> Outside probability and statistics, a wide range of other notions of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontal Lobe Disorder
Frontal lobe disorder, also frontal lobe syndrome, is an impairment of the frontal lobe that occurs due to disease or frontal lobe injury. The frontal lobe of the brain plays a key role in executive functions such as motivation, planning, social behaviour, and speech production. Frontal lobe syndrome can be caused by a range of conditions including head trauma, tumours, neurodegenerative diseases, Neurodevelopmental disorders, neurosurgery and cerebrovascular disease. Frontal lobe impairment can be detected by recognition of typical signs and symptoms, use of simple screening tests, and specialist neurological testing. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of frontal lobe disorder can be indicated by dysexecutive syndrome which consists of a number of symptoms which tend to occur together. Broadly speaking, these symptoms fall into three main categories; cognitive (movement and speech), emotional or behavioral. Although many of these symptoms regularly co-occur, it is c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gait Apraxia
Bruns apraxia, or frontal ataxia, is a gait apraxia found in patients with bilateral frontal lobe disorders. It is characterised by an inability to initiate the process of walking, despite the power and coordination of the legs being normal when tested in the seated or lying position. The gait is broad-based with short steps with a tendency to fall backwards. It was originally described in patients with frontal lobe tumours, but is now more commonly seen in patients with cerebrovascular disease. It is named after Ludwig Bruns. Symptoms and signs Unlike ataxias of cerebellar origin, Bruns apraxia exhibits many frontal lobe ataxia characteristics, with some or all present. * Difficulty in initiating movement * Poor truncal mobility * Falls due to minor balance disturbances * Greatly hindered postural responses * Characteristic magnetic gait, the inability to raise one's foot off of the floor. * Wide base, poor balance control when in stance * Short stride * En bloc turns Often pati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled leakage of urine. It is a common and distressing problem, which may have a large impact on quality of life. It has been identified as an important issue in geriatric health care. The term enuresis is often used to refer to urinary incontinence primarily in children, such as nocturnal enuresis (bed wetting). UI is an example of a stigmatized medical condition, which creates barriers to successful management and makes the problem worse. People may be too embarrassed to seek medical help, and attempt to self-manage the symptom in secrecy from others. Pelvic surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, and menopause are major risk factors. Urinary incontinence is often a result of an underlying medical condition but is under-reported to medical practitioners. There are four main types of incontinence: * Urge incontinence due to an overactive bladder * Stress incontinence due to "a poorly functioning urethral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraparesis
Paraplegia, or paraparesis, is an impairment in motor or sensory function of the lower extremities. The word comes from Ionic Greek () "half-stricken". It is usually caused by spinal cord injury or a congenital condition that affects the neural (brain) elements of the spinal canal. The area of the spinal canal that is affected in paraplegia is either the thoracic, lumbar, or sacral regions. If four limbs are affected by paralysis, tetraplegia or quadriplegia is the correct term. If only one limb is affected, the correct term is monoplegia. Spastic paraplegia is a form of paraplegia defined by spasticity of the affected muscles, rather than flaccid paralysis. The American Spinal Injury Association classifies spinal cord injury severity in the following manner. ASIA A is the complete loss of sensory function and motor skills below the injury. ASIA B is having some sensory function below the injury, but no motor function. In ASIA C, there is some motor function below the level ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemiparesis
Hemiparesis, or unilateral paresis, is weakness of one entire side of the body ('' hemi-'' means "half"). Hemiplegia is, in its most severe form, complete paralysis of half of the body. Hemiparesis and hemiplegia can be caused by different medical conditions, including congenital causes, trauma, tumors, or stroke.Detailed article about hemiparesis at Disabled-World.com Signs and symptoms Depending on the type of hemiparesis diagnosed, different bodily functions can be affected. Some effects are expected (e.g., partial paralysis of a limb on the affected side). Other impairments, though, can at first seem completely non-related to the limb weakness but are, in fact, a direct result of the damage to the affected side of the brain. Loss of ...
|
Middle Cerebral Artery
The middle cerebral artery (MCA) is one of the three major paired cerebral arteries that supply blood to the cerebrum. The MCA arises from the internal carotid artery and continues into the lateral sulcus where it then branches and projects to many parts of the lateral cerebral cortex. It also supplies blood to the anterior temporal lobes and the insular cortices. The left and right MCAs rise from trifurcations of the internal carotid arteries and thus are connected to the anterior cerebral arteries and the posterior communicating arteries, which connect to the posterior cerebral arteries. The MCAs are not considered a part of the Circle of Willis. Structure The middle cerebral artery divides into four segments, named by the region they supply as opposed to order of branching as the latter can be somewhat variable: *M1: The ''sphenoidal'' segment (stem), receiving its name due to its course along the adjacent sphenoid bone. It is also referred to as the ''horizontal'' segment, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Striate Artery
The lenticulostriate arteries, anterolateral central arteries, or antero-lateral ganglionic branches are a group of small arteries arising from the initial part M1 of the middle cerebral artery that supply the basal ganglia. Structure The lenticulostriate arteries are also known as the lateral striate arteries that arise from the middle cerebral artery. The other striate artery is the medial striate artery known as the recurrent artery of Heubner that arises from the anterior cerebral artery. The lenticulostriate arteries originate from the initial segment ( M1) of the middle cerebral artery (MCA). They are small perforating arteries, which enter the underside of the brain at the anterior perforated substance to supply blood to part of the basal ganglia and posterior limb of the internal capsule. The lenticulostriate perforators are end arteries. The name of these arteries is derived from some of the structures they supply, namely the lentiform nucleus and the striatum. Clinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Anatomy
''Clinical Anatomy'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal that covers anatomy in all its aspects— gross, histologic, developmental, and neurologic—as applied to medical practice. It is the official publication of the American Association of Clinical Anatomists, the British Association of Clinical Anatomists, the Australian and New Zealand Association of Clinical Anatomists, and the Anatomical Society of Southern Africa. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 2.414. References External links * {{Official, http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/journal/10.1002/(ISSN)1098-2353 Australian and New Zealand Association of Clinical Anatomists Wiley-Liss academic journals Publications e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artery
An artery (plural arteries) () is a blood vessel in humans and most animals that takes blood away from the heart to one or more parts of the body (tissues, lungs, brain etc.). Most arteries carry oxygenated blood; the two exceptions are the pulmonary and the umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the organs that oxygenate it (lungs and placenta, respectively). The effective arterial blood volume is that extracellular fluid which fills the arterial system. The arteries are part of the circulatory system, that is responsible for the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all cells, as well as the removal of carbon dioxide and waste products, the maintenance of optimum blood pH, and the circulation of proteins and cells of the immune system. Arteries contrast with veins, which carry blood back towards the heart. Structure The anatomy of arteries can be separated into gross anatomy, at the macroscopic level, and microanatomy, which must be studied with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |