Shanghai City Animation Company on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Shanghai (; , ,
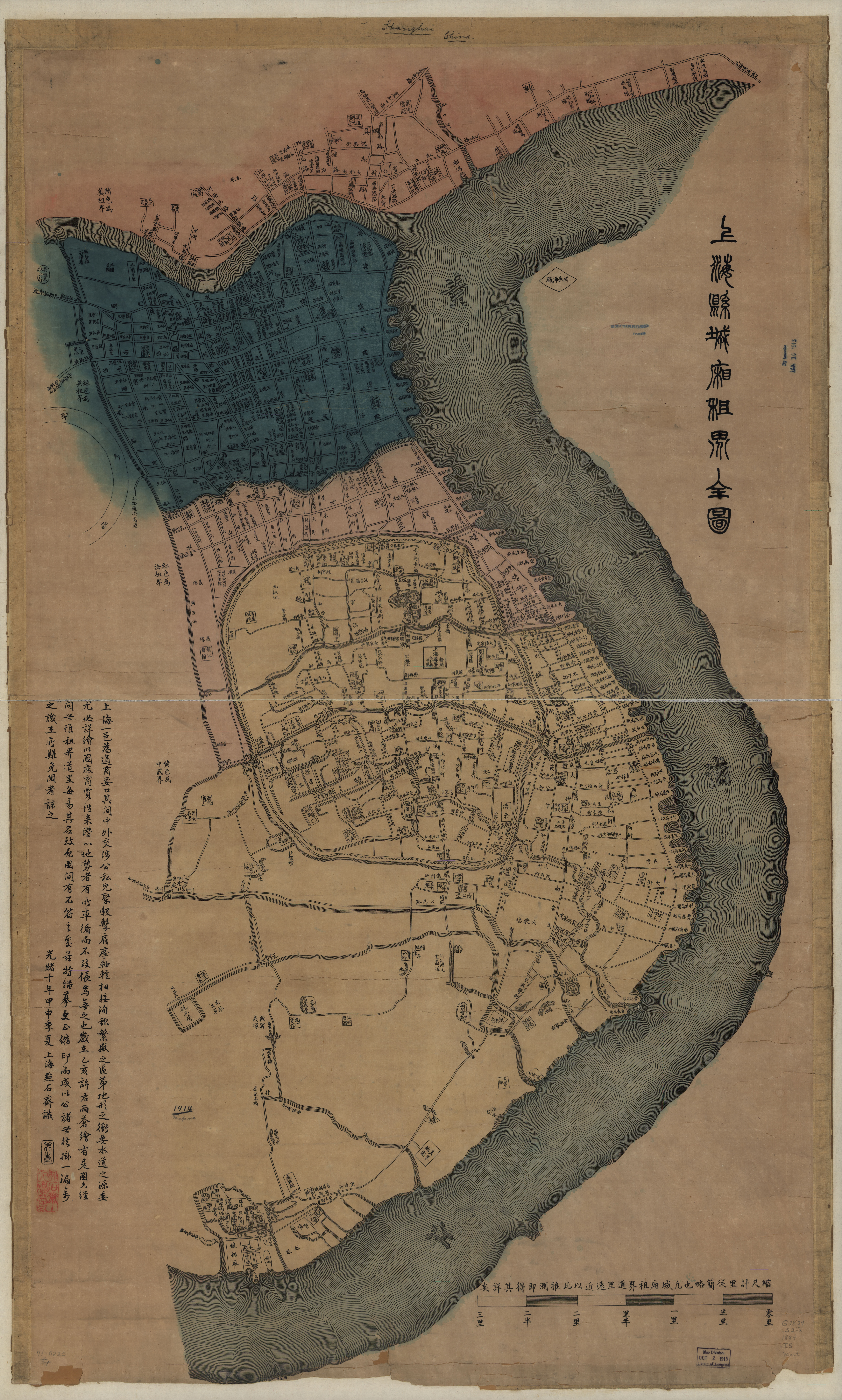
 By the end of the Song dynasty, the center of trading had moved downstream of the Wusong River to Shanghai. It was upgraded in status from a village to a market town in 1074, and in 1172, a second sea wall was built to stabilize the ocean coastline, supplementing an earlier dike. From the Yuan dynasty in 1292 until Shanghai officially became a municipality in 1927, central Shanghai was administered as a county under Songjiang Prefecture, which had its seat in the present-day Songjiang District.
By the end of the Song dynasty, the center of trading had moved downstream of the Wusong River to Shanghai. It was upgraded in status from a village to a market town in 1074, and in 1172, a second sea wall was built to stabilize the ocean coastline, supplementing an earlier dike. From the Yuan dynasty in 1292 until Shanghai officially became a municipality in 1927, central Shanghai was administered as a county under Songjiang Prefecture, which had its seat in the present-day Songjiang District.
 Two important events helped promote Shanghai's developments in the Ming dynasty. A city wall was built for the first time in 1554 to protect the town from raids by Wokou, Japanese pirates. It measured high and in circumference.Danielson, Eric N., Shanghai and the Yangzi Delta, 2004, p.10. A City God Temple was built in 1602 during the Wanli Emperor, Wanli reign. This honor was usually reserved for prefectural capitals and not normally given to a mere county seat such as Shanghai. Scholars have theorized that this likely reflected the town's economic importance, as opposed to its low political status.
Two important events helped promote Shanghai's developments in the Ming dynasty. A city wall was built for the first time in 1554 to protect the town from raids by Wokou, Japanese pirates. It measured high and in circumference.Danielson, Eric N., Shanghai and the Yangzi Delta, 2004, p.10. A City God Temple was built in 1602 during the Wanli Emperor, Wanli reign. This honor was usually reserved for prefectural capitals and not normally given to a mere county seat such as Shanghai. Scholars have theorized that this likely reflected the town's economic importance, as opposed to its low political status. During the Qing dynasty, Shanghai became one of the most important sea ports in the Yangtze Delta region as a result of two important central government policy changes: in 1684, the Kangxi Emperor reversed the Ming dynasty prohibition on oceangoing vessels—a ban that had been in force since 1525; and in 1732, the Qianlong Emperor moved the customs office for Jiangsu province (; see Customs House, Shanghai) from the prefectural capital of Songjiang to Shanghai, and gave Shanghai exclusive control over customs collections for Jiangsu's foreign trade. As a result of these two critical decisions, Shanghai became the major trade port for all of the lower Yangtze region by 1735, despite still being at the lowest administrative level in the political hierarchy.
During the Qing dynasty, Shanghai became one of the most important sea ports in the Yangtze Delta region as a result of two important central government policy changes: in 1684, the Kangxi Emperor reversed the Ming dynasty prohibition on oceangoing vessels—a ban that had been in force since 1525; and in 1732, the Qianlong Emperor moved the customs office for Jiangsu province (; see Customs House, Shanghai) from the prefectural capital of Songjiang to Shanghai, and gave Shanghai exclusive control over customs collections for Jiangsu's foreign trade. As a result of these two critical decisions, Shanghai became the major trade port for all of the lower Yangtze region by 1735, despite still being at the lowest administrative level in the political hierarchy.
 In the 19th century, international attention to Shanghai grew due to European recognition of its economic and trade potential at the Yangtze. During the
In the 19th century, international attention to Shanghai grew due to European recognition of its economic and trade potential at the Yangtze. During the
The Life and Campaigns of Hugh, First Viscount Gough, Field-Marshal
''. Volume 1. p. 267–268 The war ended in 1842 with the Treaty of Nanking, which opened Shanghai as one of the five treaty ports for international trade. The Treaty of the Bogue, the Treaty of Wanghia, and the Treaty of Whampoa (signed in 1843, 1844, and 1844, respectively) forced Chinese concession to European and American desires for visitation and trade on Chinese soil. Britain, France, and the United States all established a presence outside the walled city of Shanghai, which remained under the direct administration of the Chinese. The Chinese-held Old City of Shanghai fell to rebels from the Small Swords Society in 1853, but was recovered by the Qing government in February 1855. In 1854, the Shanghai Municipal Council was created to manage the foreign settlements. Between 1860 and 1862, the Taiping Rebellion, Taiping rebels Battle of Shanghai (1861), twice attacked Shanghai and destroyed the city's eastern and southern suburbs, but failed to take the city.Williams, S. Wells.
The Middle Kingdom: A Survey of the Geography, Government, Literature, Social Life, Arts, and History of the Chinese Empire and its Inhabitants
', Vol. 1, p. 107. Scribner (New York), 1904. In 1863, the British settlement to the south of Suzhou Creek (northern Huangpu District, Shanghai, Huangpu District) and the American settlement to the north (southern Hongkou District) joined in order to form the Shanghai International Settlement. The French opted out of the Shanghai Municipal Council and maintained Shanghai French Concession, its own concession to the south and southwest.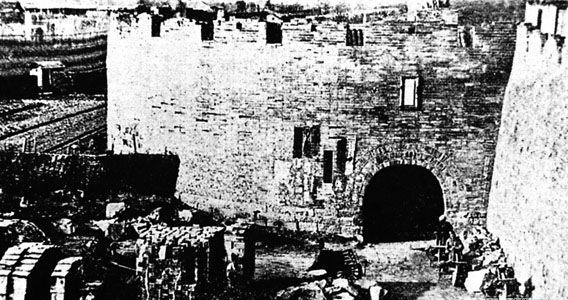 The First Sino-Japanese War concluded with the 1895 Treaty of Shimonoseki, which elevated Japan to become another foreign power in Shanghai. Japan built the first factories in Shanghai, which was soon copied by other foreign powers. All this international activity gave Shanghai the nickname "the Great Athens of China". In 1914, the Old City walls were dismantled because they blocked the city's expansion. In July 1921, the Chinese Communist Party was founded in the French Concession. On 30 May 1925, the May Thirtieth Movement broke out when a worker in a Japanese-owned cotton mill was shot and killed by a Japanese foreman.Ku, Hung-Ting [1979] (1979). Urban Mass Movement: The May Thirtieth Movement in Shanghai. Modern Asian Studies, Vol.13, No.2. pp.197–216 Workers in the city then launched general strikes against imperialism, which became nationwide protests that gave rise to Chinese nationalism.
The golden age of Shanghai began with its elevation to municipality after it was separated from Jiangsu on 7 July 1927. This new Chinese municipality covered an area of , including the modern-day districts of Baoshan District, Shanghai, Baoshan, Yangpu District, Yangpu, Zhabei, Nanshi District, Shanghai, Nanshi, and Pudong, but excluded the foreign concessions territories. Headed by a Chinese mayor and municipal council, the new city government's first task—the Greater Shanghai Plan—was to create a new city center in Jiangwan town of Yangpu district, outside the boundaries of the foreign concessions. The plan included a public museum, library, sports stadium, and city hall, which were partially constructed before being interrupted by the Japanese invasion. In the 1920s, ''shidaiqu'' became a new form of entertainment and was popularised in Shanghai.
The city flourished, becoming a primary commercial and financial hub of the Asia-Pacific region in the 1930s.
During the ensuing decades, citizens of many countries and all continents came to Shanghai to live and work; those who stayed for long periods—some for generations—called themselves "Shanghailanders". In the 1920s and 1930s, almost 20,000 White Movement, White Russians fled the newly established Soviet Union to reside in Shanghai. These Shanghai Russians constituted the second-largest foreign community. By 1932, Shanghai had become the world's fifth largest city and home to 70,000 foreigners. In the 1930s, some 30,000 Jewish refugees from Europe arrived in the city.
The First Sino-Japanese War concluded with the 1895 Treaty of Shimonoseki, which elevated Japan to become another foreign power in Shanghai. Japan built the first factories in Shanghai, which was soon copied by other foreign powers. All this international activity gave Shanghai the nickname "the Great Athens of China". In 1914, the Old City walls were dismantled because they blocked the city's expansion. In July 1921, the Chinese Communist Party was founded in the French Concession. On 30 May 1925, the May Thirtieth Movement broke out when a worker in a Japanese-owned cotton mill was shot and killed by a Japanese foreman.Ku, Hung-Ting [1979] (1979). Urban Mass Movement: The May Thirtieth Movement in Shanghai. Modern Asian Studies, Vol.13, No.2. pp.197–216 Workers in the city then launched general strikes against imperialism, which became nationwide protests that gave rise to Chinese nationalism.
The golden age of Shanghai began with its elevation to municipality after it was separated from Jiangsu on 7 July 1927. This new Chinese municipality covered an area of , including the modern-day districts of Baoshan District, Shanghai, Baoshan, Yangpu District, Yangpu, Zhabei, Nanshi District, Shanghai, Nanshi, and Pudong, but excluded the foreign concessions territories. Headed by a Chinese mayor and municipal council, the new city government's first task—the Greater Shanghai Plan—was to create a new city center in Jiangwan town of Yangpu district, outside the boundaries of the foreign concessions. The plan included a public museum, library, sports stadium, and city hall, which were partially constructed before being interrupted by the Japanese invasion. In the 1920s, ''shidaiqu'' became a new form of entertainment and was popularised in Shanghai.
The city flourished, becoming a primary commercial and financial hub of the Asia-Pacific region in the 1930s.
During the ensuing decades, citizens of many countries and all continents came to Shanghai to live and work; those who stayed for long periods—some for generations—called themselves "Shanghailanders". In the 1920s and 1930s, almost 20,000 White Movement, White Russians fled the newly established Soviet Union to reside in Shanghai. These Shanghai Russians constituted the second-largest foreign community. By 1932, Shanghai had become the world's fifth largest city and home to 70,000 foreigners. In the 1930s, some 30,000 Jewish refugees from Europe arrived in the city.
File:SkylineShanghaiPudongSeptember2021.jpg, Skyline of Shanghai Pudong at night, September 2021
File:1937 Shanghai, China VP8.webm, Shanghai filmed in 1937
File:Shanghai Bund seen from the French Concession.jpg, The Bund in the late 1920s seen from the French Concession
File:Shanghai tram, British section, 1920s, John Rossman's collection.jpg, Nanjing Road, Nanking Road (modern-day East Nanjing Road) in the 1930s
File:Shanghai Park Hotel 2007.jpg, alt=Shanghai Park Hotel was the tallest building in Asia for decades, Park Hotel Shanghai, Shanghai Park Hotel was the tallest building in Asia for decades.
File:Former Shanghai Library.jpg, Former Shanghai Library
File:The Hong Kong and Shanghai Bank, built in 1923 and The Customs House built in 1927.jpg, The HSBC Building, the Bund, HSBC Building built in 1923 and the Custom House, Shanghai, Customs House built in 1927
 On January 28 Incident, 28 January 1932, Japanese forces invaded Shanghai while the Chinese resisted. More than 10,000 shops and hundreds of factories and public buildings were destroyed, leaving Zhabei district ruined. About 18,000 civilians were either killed, injured, or declared missing. A ceasefire was brokered on 5 May. In 1937, the Battle of Shanghai resulted in the occupation of the Chinese-administered parts of Shanghai outside of the International Settlement and the French Concession. People who stayed in the occupied city suffered on a daily basis, experiencing hunger, oppression, or death. The foreign concessions were ultimately occupied by the Japanese on 8 December 1941 and remained occupied until Japan's surrender in 1945; multiple Japanese war crimes, war crimes were committed during that time.
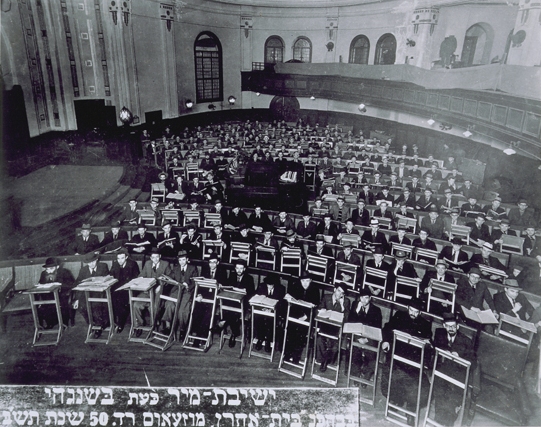
A side-effect of the Japanese invasion of Shanghai was the Shanghai Ghetto. Japanese consul to Kaunas, Lithuania, Chiune Sugihara issued thousands of visas to Jewish refugees who were escaping the Nazi's Final Solution to the Jewish Question. They traveled from Keidan, Lithuania across Russia by railroad to the Vladivostok from where they traveled by ship to Kobe, Japan. Their stay in Kobe was short as the Japanese government transferred them to Shanghai by November 1941. Other Jewish refugees found haven in Shanghai, not through Sugihara, but came on ships from Italy. The refugees from Europe were interned into a cramped ghetto in the Hongkou District, and after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, even the Iraqi Jews who had been living in Shanghai from before the outbreak of WWII were interned. Among the refugees in the Shanghai Ghetto was the Mir yeshiva (Belarus), Mirrer Yeshiva, including its students and faculty. On 3 September 1945, the Chinese Army liberated the Ghetto and most of the Jews left over the next few years. By 1957, there were only one hundred Jews remaining in Shanghai.
On 27 May 1949, the People's Liberation Army took control of Shanghai through the Shanghai Campaign. Under the new People's Republic of China (PRC), Shanghai was one of only three municipalities not merged into neighboring provinces (the others being Beijing and Tianjin). Most foreign firms moved their offices from Shanghai to Hong Kong, as part of a foreign divestment due to the PRC's victory.
On January 28 Incident, 28 January 1932, Japanese forces invaded Shanghai while the Chinese resisted. More than 10,000 shops and hundreds of factories and public buildings were destroyed, leaving Zhabei district ruined. About 18,000 civilians were either killed, injured, or declared missing. A ceasefire was brokered on 5 May. In 1937, the Battle of Shanghai resulted in the occupation of the Chinese-administered parts of Shanghai outside of the International Settlement and the French Concession. People who stayed in the occupied city suffered on a daily basis, experiencing hunger, oppression, or death. The foreign concessions were ultimately occupied by the Japanese on 8 December 1941 and remained occupied until Japan's surrender in 1945; multiple Japanese war crimes, war crimes were committed during that time.
A side-effect of the Japanese invasion of Shanghai was the Shanghai Ghetto. Japanese consul to Kaunas, Lithuania, Chiune Sugihara issued thousands of visas to Jewish refugees who were escaping the Nazi's Final Solution to the Jewish Question. They traveled from Keidan, Lithuania across Russia by railroad to the Vladivostok from where they traveled by ship to Kobe, Japan. Their stay in Kobe was short as the Japanese government transferred them to Shanghai by November 1941. Other Jewish refugees found haven in Shanghai, not through Sugihara, but came on ships from Italy. The refugees from Europe were interned into a cramped ghetto in the Hongkou District, and after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, even the Iraqi Jews who had been living in Shanghai from before the outbreak of WWII were interned. Among the refugees in the Shanghai Ghetto was the Mir yeshiva (Belarus), Mirrer Yeshiva, including its students and faculty. On 3 September 1945, the Chinese Army liberated the Ghetto and most of the Jews left over the next few years. By 1957, there were only one hundred Jews remaining in Shanghai.
On 27 May 1949, the People's Liberation Army took control of Shanghai through the Shanghai Campaign. Under the new People's Republic of China (PRC), Shanghai was one of only three municipalities not merged into neighboring provinces (the others being Beijing and Tianjin). Most foreign firms moved their offices from Shanghai to Hong Kong, as part of a foreign divestment due to the PRC's victory.
 Shanghai is located on the Yangtze Estuary of China's east coast, with the Yangtze River to the north and Hangzhou Bay to the south, with the East China Sea to the east. The land is formed by the Yangtze's natural deposition (geology), deposition and modern land reclamation projects. As such, it has Loam, sandy soil, and skyscrapers have to be built with deep concrete piles to avoid sinking into the soft ground. The provincial-level Municipality of Shanghai administers both the estuary and many of its islands of Shanghai, surrounding islands. It borders the provinces of Zhejiang to the south and Jiangsu to the west and north.
The municipality's northernmost point is on Chongming Island, which is the second-largest List of islands of China, island in mainland China after its expansion during the 20th century."Chongming Island" in the ''Encyclopedia of Shanghai'', p. 52.
Shanghai is located on the Yangtze Estuary of China's east coast, with the Yangtze River to the north and Hangzhou Bay to the south, with the East China Sea to the east. The land is formed by the Yangtze's natural deposition (geology), deposition and modern land reclamation projects. As such, it has Loam, sandy soil, and skyscrapers have to be built with deep concrete piles to avoid sinking into the soft ground. The provincial-level Municipality of Shanghai administers both the estuary and many of its islands of Shanghai, surrounding islands. It borders the provinces of Zhejiang to the south and Jiangsu to the west and north.
The municipality's northernmost point is on Chongming Island, which is the second-largest List of islands of China, island in mainland China after its expansion during the 20th century."Chongming Island" in the ''Encyclopedia of Shanghai'', p. 52.
Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers (Shanghai), 2010. Hosted by the Municipality of Shanghai. It does not administratively include an exclave of Jiangsu on northern Chongming or the two islands forming Shanghai's Yangshan Port, which are parts of Zhejiang's Shengsi County. Shanghai is roughly 1,100 km equidistant from Beijing to the north-west and 1400 km from Guangzhou to the south-east. Shanghai is located on an alluvial plain. As such, the vast majority of its land area is flat, with an average elevation of . Tidal flat ecosystems exist around the estuary, however, they have long been reclaimed for agricultural purposes. The city's few hills, such as Sheshan Hill, She Shan, lie to the southwest, and its highest point is the peak of Dajinshan Island () in Hangzhou Bay. Shanghai has many rivers, canals, streams, and lakes, and it is known for its rich water resources as part of the Lake Tai drainage basin. Downtown Shanghai is bisected by the Huangpu River, a man-made tributary of the Yangtze created by order of Lord Chunshen during the Warring States period. The historic center of the city was located on the west bank of the Huangpu (Puxi), near the mouth of Suzhou Creek, connecting it with Lake Tai and the Grand Canal of China, Grand Canal. The central financial district, Lujiazui, has been established on the east bank of the Huangpu (Pudong). Along Shanghai's eastern shore, the destruction of local wetlands due to the construction of Pudong International Airport has been partially offset by the protection and expansion of a nearby shoal, Jiuduansha, as a nature preserve."Fourth Island Wetland Emerging", pp. 1–2.
''Shanghai Daily''. 8 December 2009. Hosted at China.org.
 One distinctive cultural element is the shikumen (, "stone storage door") residence, typically two- or three-story gray brick houses with the front yard protected by a heavy wooden door in a stylistic stone arch. Each residence is connected and arranged in straight alleys, known as longtang (). The house is similar to western-style terrace houses or townhouses, but distinguishes by the tall, heavy brick wall and archway in front of each house.
The shikumen is a cultural blend of elements found in Western architecture with traditional Jiangnan Chinese architecture and social behavior. Like almost all traditional Chinese dwellings, it has a courtyard, which reduces outside noise. Vegetation can be grown in the courtyard, and it can also allow for sunlight and ventilation to the rooms.
One distinctive cultural element is the shikumen (, "stone storage door") residence, typically two- or three-story gray brick houses with the front yard protected by a heavy wooden door in a stylistic stone arch. Each residence is connected and arranged in straight alleys, known as longtang (). The house is similar to western-style terrace houses or townhouses, but distinguishes by the tall, heavy brick wall and archway in front of each house.
The shikumen is a cultural blend of elements found in Western architecture with traditional Jiangnan Chinese architecture and social behavior. Like almost all traditional Chinese dwellings, it has a courtyard, which reduces outside noise. Vegetation can be grown in the courtyard, and it can also allow for sunlight and ventilation to the rooms.
 Some of Shanghai's buildings feature Soviet Union, Soviet neoclassical architecture or Stalinist architecture, though the city has fewer such structures than Beijing. These buildings were mostly erected between the founding of the People's Republic of China, People's Republic in 1949 and the Sino-Soviet Split in the late 1960s. During this time period, large numbers of Soviet experts, including architects, poured into China to aid the country in the construction of a communist state. An example of Soviet neoclassical architecture in Shanghai is the modern-day Shanghai Exhibition Center.
Shanghai—Lujiazui in particular—has List of tallest buildings in Shanghai, numerous skyscrapers, making it the fifth List of cities with the most skyscrapers, city in the world with the most skyscrapers. Among the most prominent examples are the high Jin Mao Tower, the high Shanghai World Financial Center, and the high Shanghai Tower, which is the tallest building in China and the List of tallest buildings, second tallest in the world. Completed in 2015, the tower takes the form of nine twisted sections stacked atop each other, totaling 128 floors. It is featured in its double-skin facade design, which eliminates the need for either layer to be opaqued for reflectivity as the double-layer structure has already reduced the heat absorption. The futuristic-looking Oriental Pearl Tower, at , is located nearby at the northern tip of Lujiazui. Skyscrapers outside of Lujiazui include the White Magnolia Plaza in Hongkou, the Shimao International Plaza in Huangpu, and the Shanghai Wheelock Square in Jing'an District, Jing'an.
Some of Shanghai's buildings feature Soviet Union, Soviet neoclassical architecture or Stalinist architecture, though the city has fewer such structures than Beijing. These buildings were mostly erected between the founding of the People's Republic of China, People's Republic in 1949 and the Sino-Soviet Split in the late 1960s. During this time period, large numbers of Soviet experts, including architects, poured into China to aid the country in the construction of a communist state. An example of Soviet neoclassical architecture in Shanghai is the modern-day Shanghai Exhibition Center.
Shanghai—Lujiazui in particular—has List of tallest buildings in Shanghai, numerous skyscrapers, making it the fifth List of cities with the most skyscrapers, city in the world with the most skyscrapers. Among the most prominent examples are the high Jin Mao Tower, the high Shanghai World Financial Center, and the high Shanghai Tower, which is the tallest building in China and the List of tallest buildings, second tallest in the world. Completed in 2015, the tower takes the form of nine twisted sections stacked atop each other, totaling 128 floors. It is featured in its double-skin facade design, which eliminates the need for either layer to be opaqued for reflectivity as the double-layer structure has already reduced the heat absorption. The futuristic-looking Oriental Pearl Tower, at , is located nearby at the northern tip of Lujiazui. Skyscrapers outside of Lujiazui include the White Magnolia Plaza in Hongkou, the Shimao International Plaza in Huangpu, and the Shanghai Wheelock Square in Jing'an District, Jing'an.
File:·˙·ChinaUli2010·.· Shanghai - panoramio (231).jpg, The Shanghai Museum
File:Shanghaigrandtheatre.jpg, The Shanghai Grand Theater
File:The Sino-Soviet Friendship Mansion.JPG, The Shanghai Exhibition Center, an example of Stalinist architecture
File:The Oriental Pearl Radio & Television Tower at night.jpg, The Oriental Pearl Tower at night
File:Shanghai - Shanghai Tower - 0003.jpg, Shanghai Tower
File:Skyscrapers in Shanghai.jpg, Glass facades of two skyscrapers
 Like virtually all Politics of China, governing institutions in mainland China, Shanghai has a parallel party-government system, in which the Party Committee Secretary, officially termed the Communist Party of China Shanghai Municipal Committee Secretary, outranks the Mayor. The acts as the top policy-formulation body, and is typically composed of 12 members (including the secretary).
Political power in Shanghai has frequently been a stepping stone to higher positions in the central government. Since Jiang Zemin became the General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party in June 1989, all former Shanghai party secretaries but one were elevated to the Politburo Standing Committee of the Chinese Communist Party, Politburo Standing Committee, the ''de facto'' highest decision-making body in China, including Jiang himself (Party General Secretary), Zhu Rongji (Premier), Wu Bangguo (Chairman of the National People's Congress), Huang Ju (Vice Premier), Xi Jinping (current General Secretary), Yu Zhengsheng, Han Zheng, and Li Qiang. Zeng Qinghong, a former deputy party secretary of Shanghai, also rose to the Politburo Standing Committee and became the Vice President and an influential power broker. The only exception is Chen Liangyu, who was fired in 2006 and later convicted of Corruption in China, corruption.
Officials with ties to the Shanghai administration collectively form a powerful faction in the central government known as the Shanghai Clique, which has often been viewed to compete against the rival Youth League Faction over personnel appointments and policy decisions. However, Xi Jinping, successor to Hu Jintao as General Secretary and President of the People's Republic of China, President, was largely an independent leader and took Anti-corruption campaign under Xi Jinping, anti-corruption campaigns on both factions.
Like virtually all Politics of China, governing institutions in mainland China, Shanghai has a parallel party-government system, in which the Party Committee Secretary, officially termed the Communist Party of China Shanghai Municipal Committee Secretary, outranks the Mayor. The acts as the top policy-formulation body, and is typically composed of 12 members (including the secretary).
Political power in Shanghai has frequently been a stepping stone to higher positions in the central government. Since Jiang Zemin became the General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party in June 1989, all former Shanghai party secretaries but one were elevated to the Politburo Standing Committee of the Chinese Communist Party, Politburo Standing Committee, the ''de facto'' highest decision-making body in China, including Jiang himself (Party General Secretary), Zhu Rongji (Premier), Wu Bangguo (Chairman of the National People's Congress), Huang Ju (Vice Premier), Xi Jinping (current General Secretary), Yu Zhengsheng, Han Zheng, and Li Qiang. Zeng Qinghong, a former deputy party secretary of Shanghai, also rose to the Politburo Standing Committee and became the Vice President and an influential power broker. The only exception is Chen Liangyu, who was fired in 2006 and later convicted of Corruption in China, corruption.
Officials with ties to the Shanghai administration collectively form a powerful faction in the central government known as the Shanghai Clique, which has often been viewed to compete against the rival Youth League Faction over personnel appointments and policy decisions. However, Xi Jinping, successor to Hu Jintao as General Secretary and President of the People's Republic of China, President, was largely an independent leader and took Anti-corruption campaign under Xi Jinping, anti-corruption campaigns on both factions.
 Seven of the districts govern Puxi ( "The West Bank", or "West of the River Pu"), the older part of urban Shanghai on the west bank of the Huangpu River. These seven districts are collectively referred to as Shanghai Proper () or the core city (), which comprise Huangpu, Xuhui, Changning District, Changning, Jing'an, Putuo, Hongkou, and Yangpu.
Pudong ( "The East Bank", or "East of the River Pu"), the newer part of urban and suburban Shanghai on the east bank of the Huangpu River, is governed by Pudong New Area ().
Seven of the districts govern suburbs, satellite towns, and rural areas farther away from the urban core: Baoshan, Minhang District, Minhang, Jiading, Jinshan, Songjiang, Qingpu, and Fengxian.
Chongming District comprises the islands of Changxing and Hengsha and most—but not all—of Chongming Island.
The former district of Nanhui was absorbed into Pudong District in 2009. In 2011, Luwan District merged with Huangpu District. , these county-level divisions are further divided into the following 210 Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#Township level, township-level divisions: 109 town of China, towns, 2 Townships of the People's Republic of China, townships, and 99 Subdistricts of China, subdistricts. Those are in turn divided into the following Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#Village level, village-level divisions: 3,661 neighborhood committees and 1,704 village committees.
There is a sizable Korean community of Shanghai and Japanese community of Shanghai largely in the Minhang District.
Seven of the districts govern Puxi ( "The West Bank", or "West of the River Pu"), the older part of urban Shanghai on the west bank of the Huangpu River. These seven districts are collectively referred to as Shanghai Proper () or the core city (), which comprise Huangpu, Xuhui, Changning District, Changning, Jing'an, Putuo, Hongkou, and Yangpu.
Pudong ( "The East Bank", or "East of the River Pu"), the newer part of urban and suburban Shanghai on the east bank of the Huangpu River, is governed by Pudong New Area ().
Seven of the districts govern suburbs, satellite towns, and rural areas farther away from the urban core: Baoshan, Minhang District, Minhang, Jiading, Jinshan, Songjiang, Qingpu, and Fengxian.
Chongming District comprises the islands of Changxing and Hengsha and most—but not all—of Chongming Island.
The former district of Nanhui was absorbed into Pudong District in 2009. In 2011, Luwan District merged with Huangpu District. , these county-level divisions are further divided into the following 210 Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#Township level, township-level divisions: 109 town of China, towns, 2 Townships of the People's Republic of China, townships, and 99 Subdistricts of China, subdistricts. Those are in turn divided into the following Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#Village level, village-level divisions: 3,661 neighborhood committees and 1,704 village committees.
There is a sizable Korean community of Shanghai and Japanese community of Shanghai largely in the Minhang District.
 Shanghai has been described as the "showpiece" of the booming
Shanghai has been described as the "showpiece" of the booming
 Shanghai is a global financial center, ranking first in the whole of Asia & Oceania region and third globally (after New York and London) in the 28th edition of the Global Financial Centres Index, published in September 2020 by Z/Yen and China Development Institute. Shanghai is also a large hub of the Chinese and global technology industry and home to a large startup ecosystem. As of 2021, the city was ranked as the 2nd Fintech powerhouse in the world after New York City.
, the
Shanghai is a global financial center, ranking first in the whole of Asia & Oceania region and third globally (after New York and London) in the 28th edition of the Global Financial Centres Index, published in September 2020 by Z/Yen and China Development Institute. Shanghai is also a large hub of the Chinese and global technology industry and home to a large startup ecosystem. As of 2021, the city was ranked as the 2nd Fintech powerhouse in the world after New York City.
, the
 As one of the main industrial centers of China, Shanghai plays a key role in domestic manufacturing and heavy industry. Several industrial zones—including Shanghai Hongqiao Economic and Technological Development Zone, Jinqiao Export Economic Processing Zone, Minhang Economic and Technological Development Zone, and Shanghai Caohejing High-Tech Development Zone—are backbones of Shanghai's secondary sector. Shanghai is home to China's largest steelmaker Baosteel Group, China's largest shipbuilding base Hudong-Zhonghua Shipbuilding, Hudong-Zhonghua Shipbuilding Group, and one of China's oldest shipbuilders, the Jiangnan Shipyard. Auto manufacturing is another important industry. The Shanghai-based SAIC Motor is one of the three largest automotive corporations in China, and has strategic partnerships with Volkswagen and General Motors.
As one of the main industrial centers of China, Shanghai plays a key role in domestic manufacturing and heavy industry. Several industrial zones—including Shanghai Hongqiao Economic and Technological Development Zone, Jinqiao Export Economic Processing Zone, Minhang Economic and Technological Development Zone, and Shanghai Caohejing High-Tech Development Zone—are backbones of Shanghai's secondary sector. Shanghai is home to China's largest steelmaker Baosteel Group, China's largest shipbuilding base Hudong-Zhonghua Shipbuilding, Hudong-Zhonghua Shipbuilding Group, and one of China's oldest shipbuilders, the Jiangnan Shipyard. Auto manufacturing is another important industry. The Shanghai-based SAIC Motor is one of the three largest automotive corporations in China, and has strategic partnerships with Volkswagen and General Motors.
 Tourism is a major industry of Shanghai. In 2017, the number of domestic tourists increased by 7.5% to 318 million, while the number of overseas tourists increased by 2.2% to 8.73 million. In 2017, Shanghai was the highest earning tourist city in the world, which is expected to maintain until 2027. As of 2019, Shanghai had 71 five star hotel, five-star hotels, 61 four star hotels, 1,758 travel agencies, 113 Tourist Attraction Rating Categories of China, rated tourist attractions, and 34 Red tourism, red tourist attractions.
The conference and meeting sector is also growing. According to the International Congress and Convention Association, Shanghai hosted 82 international meetings in 2018, a 34% increase from 61 in 2017.
Tourism is a major industry of Shanghai. In 2017, the number of domestic tourists increased by 7.5% to 318 million, while the number of overseas tourists increased by 2.2% to 8.73 million. In 2017, Shanghai was the highest earning tourist city in the world, which is expected to maintain until 2027. As of 2019, Shanghai had 71 five star hotel, five-star hotels, 61 four star hotels, 1,758 travel agencies, 113 Tourist Attraction Rating Categories of China, rated tourist attractions, and 34 Red tourism, red tourist attractions.
The conference and meeting sector is also growing. According to the International Congress and Convention Association, Shanghai hosted 82 international meetings in 2018, a 34% increase from 61 in 2017.
 Due to its cosmopolitan history, Shanghai has a blend of religious heritage; religious buildings and institutions are scattered around the city. According to a 2012 survey, only 13.1% of the city's population belongs to organized religions, including Buddhists with 10.4%, Protestants with 1.9%, Catholics with 0.7%, and other faiths with 0.1% while the remaining 86.9% of the population could be either atheists or involved in Chinese folk religion, worship of nature deities and ancestors or Chinese salvationist religions, folk religious sects.
Buddhism, in its Chinese Buddhism, Chinese varieties, has had a presence in Shanghai since the Three Kingdoms period, during which the Longhua Temple—the largest temple in Shanghai—and the Jing'an Temple were founded. Another significant temple is the Jade Buddha Temple, which was named after a large statue of Gautama Buddha, Buddha carved out of jade in the temple. , Buddhism in Shanghai had 114 temples, 1,182 Clergy#Buddhism, clergical staff, and 453,300 registered followers. The religion also has its own college, the , and its own press, .
Due to its cosmopolitan history, Shanghai has a blend of religious heritage; religious buildings and institutions are scattered around the city. According to a 2012 survey, only 13.1% of the city's population belongs to organized religions, including Buddhists with 10.4%, Protestants with 1.9%, Catholics with 0.7%, and other faiths with 0.1% while the remaining 86.9% of the population could be either atheists or involved in Chinese folk religion, worship of nature deities and ancestors or Chinese salvationist religions, folk religious sects.
Buddhism, in its Chinese Buddhism, Chinese varieties, has had a presence in Shanghai since the Three Kingdoms period, during which the Longhua Temple—the largest temple in Shanghai—and the Jing'an Temple were founded. Another significant temple is the Jade Buddha Temple, which was named after a large statue of Gautama Buddha, Buddha carved out of jade in the temple. , Buddhism in Shanghai had 114 temples, 1,182 Clergy#Buddhism, clergical staff, and 453,300 registered followers. The religion also has its own college, the , and its own press, .
 Catholicism was brought into Shanghai in 1608 by Italian missionary Lazzaro Cattaneo. The Apostolic Vicariate of Shanghai was erected in 1933, and was further elevated to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Shanghai, Diocese of Shanghai in 1946. Notable Catholic sites include the St. Ignatius Cathedral in Xujiahui—the largest Catholic church in the city, the St. Francis Xavier Church (Shanghai), St. Francis Xavier Church, and the She Shan Basilica. Other forms of Christianity in Shanghai include Eastern Orthodox minorities and, since 1996, registered Christian Protestant churches.
Although currently making up a fraction of the religious population in Shanghai, Jewish people have played an influential role in the city's history. After the Treaty of Nanking ended the
Catholicism was brought into Shanghai in 1608 by Italian missionary Lazzaro Cattaneo. The Apostolic Vicariate of Shanghai was erected in 1933, and was further elevated to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Shanghai, Diocese of Shanghai in 1946. Notable Catholic sites include the St. Ignatius Cathedral in Xujiahui—the largest Catholic church in the city, the St. Francis Xavier Church (Shanghai), St. Francis Xavier Church, and the She Shan Basilica. Other forms of Christianity in Shanghai include Eastern Orthodox minorities and, since 1996, registered Christian Protestant churches.
Although currently making up a fraction of the religious population in Shanghai, Jewish people have played an influential role in the city's history. After the Treaty of Nanking ended the
 Shanghai is an international center of research and development and as of 2022, it was ranked List of cities by scientific output, 3rd globally and 2nd in the whole Asia & Oceania region (after Beijing) by scientific research outputs, as tracked by the Nature Index. It is also a major center of higher education in China. As of 2022, Shanghai had 64 universities and colleges, ranking first in East China region as a city with most higher education institutions. Shanghai has many highly ranked educational institutions, with 15 universities listed in Double First Class University Plan, 147 Double First-Class Universities ranking second nationwide among all cities in China (after Beijing). A number of Rankings of universities in China, China's most prestigious universities appearing in the global university rankings are based in Shanghai, including Fudan University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Tongji University, East China Normal University, Shanghai University, East China University of Science and Technology, Donghua University,
Shanghai is an international center of research and development and as of 2022, it was ranked List of cities by scientific output, 3rd globally and 2nd in the whole Asia & Oceania region (after Beijing) by scientific research outputs, as tracked by the Nature Index. It is also a major center of higher education in China. As of 2022, Shanghai had 64 universities and colleges, ranking first in East China region as a city with most higher education institutions. Shanghai has many highly ranked educational institutions, with 15 universities listed in Double First Class University Plan, 147 Double First-Class Universities ranking second nationwide among all cities in China (after Beijing). A number of Rankings of universities in China, China's most prestigious universities appearing in the global university rankings are based in Shanghai, including Fudan University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Tongji University, East China Normal University, Shanghai University, East China University of Science and Technology, Donghua University,  The city has many , such as the Shanghai University–University of Technology Sydney Business School since 1994, the University of Michigan–Shanghai Jiao Tong University Joint Institute since 2006, and New York University Shanghai—the first China–U.S. joint venture university—since 2012. In 2013, the Shanghai Municipality and the Chinese Academy of Sciences founded the ShanghaiTech University in the Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park in Pudong. Shanghai is also home to the cadre school China Executive Leadership Academy in Pudong and the China Europe International Business School. The city government's education agency is the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission.
The city is also a seat of the Shanghai Academy of Social Sciences, China, China's oldest think tank for the humanities and social sciences. It is the largest one outside the capital of Beijing after the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS).
By the end of 2019, the city also had 929 secondary schools, 698 primary schools, and 31 special schools. In Shanghai, the nine years of compulsory education—including five years of primary education and four years of Education in China#Junior secondary, junior secondary education—are free, with a gross enrollment ratio of over 99.9%. The city's compulsory education system is among the best in the world: in 2009 and 2012, 15-year-old students from Shanghai ranked first in every subject (math, reading, and science) in the Program for International Student Assessment, a worldwide study of academic performance conducted by the OECD. The consecutive three-year senior secondary education is priced and uses the Senior High School Entrance Examination (''Zhongkao'') as a selection process, with a gross enrollment ratio of 98%. Among all senior high schools, the four with the best teaching quality—Shanghai High School, No. 2 High School Attached to East China Normal University, High School Affiliated to Fudan University, and High School Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University—are termed "The Four Schools" () of Shanghai. , the city's National College Entrance Examination (''Gaokao'') is structured under the "3+3" system, in which all general senior high school students study three compulsory subjects (Chinese, English, and math) and three subjects chosen from six options (physics, chemistry, biology, history, geography, and politics).
The city has many , such as the Shanghai University–University of Technology Sydney Business School since 1994, the University of Michigan–Shanghai Jiao Tong University Joint Institute since 2006, and New York University Shanghai—the first China–U.S. joint venture university—since 2012. In 2013, the Shanghai Municipality and the Chinese Academy of Sciences founded the ShanghaiTech University in the Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park in Pudong. Shanghai is also home to the cadre school China Executive Leadership Academy in Pudong and the China Europe International Business School. The city government's education agency is the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission.
The city is also a seat of the Shanghai Academy of Social Sciences, China, China's oldest think tank for the humanities and social sciences. It is the largest one outside the capital of Beijing after the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS).
By the end of 2019, the city also had 929 secondary schools, 698 primary schools, and 31 special schools. In Shanghai, the nine years of compulsory education—including five years of primary education and four years of Education in China#Junior secondary, junior secondary education—are free, with a gross enrollment ratio of over 99.9%. The city's compulsory education system is among the best in the world: in 2009 and 2012, 15-year-old students from Shanghai ranked first in every subject (math, reading, and science) in the Program for International Student Assessment, a worldwide study of academic performance conducted by the OECD. The consecutive three-year senior secondary education is priced and uses the Senior High School Entrance Examination (''Zhongkao'') as a selection process, with a gross enrollment ratio of 98%. Among all senior high schools, the four with the best teaching quality—Shanghai High School, No. 2 High School Attached to East China Normal University, High School Affiliated to Fudan University, and High School Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University—are termed "The Four Schools" () of Shanghai. , the city's National College Entrance Examination (''Gaokao'') is structured under the "3+3" system, in which all general senior high school students study three compulsory subjects (Chinese, English, and math) and three subjects chosen from six options (physics, chemistry, biology, history, geography, and politics).

 Shanghai has an extensive public transportation system comprising metros, buses, ferries, and taxis, all of which can be accessed using a Shanghai Public Transport Card.
Shanghai's rapid transit system, the Shanghai Metro, incorporates both subway and light metro lines and extends to every core urban district as well as neighboring suburban districts. , there are 19 metro lines (excluding the Shanghai maglev train and Jinshan Railway), 515 List of Shanghai Metro stations, stations, and of lines in operation, making it the List of metro systems, longest network in the world. On 8 March 2019, it set the city's daily metro ridership record with 13.3 million. The average fare ranges from () to (), depending on the travel distance.
Opened in 2004, the Shanghai maglev train is the first and the fastest commercial high-speed maglev in the world, with a maximum operation speed of . The train can complete the journey between Longyang Road Station and Pudong International Airport in 7 minutes 20 seconds, comparing to 32 minutes by Line 2 (Shanghai Metro), Metro Line 2 and 30 minutes by car. A one-way ticket costs (), or () for those with airline tickets or public transportation cards. A round-trip ticket costs (), and VIP tickets cost double the standard fare.
With the first tram line been in service in 1908, trams were once popular Trams in Shanghai, in Shanghai in the early 20th century. By 1925, there were 328 tramcars and 14 routes operated by Chinese, French, and British companies collaboratively, all of which were nationalized after the PRC's victory in 1949. Since the 1960s, many tram lines were either dismantled or replaced by trolleybus or motorbus lines; the last tram line was demolished in 1975. Shanghai reintroduced trams in 2010, as a modern rubber-tire Translohr system in Zhangjiang area of East Shanghai as Zhangjiang Tram. In 2018, the steel wheeled Songjiang Tram started operating in Songjiang District. Additional tram lines are under planning in Hongqiao Subdistrict, Shanghai, Hongqiao Subdistrict and Jiading District .
Shanghai has an extensive public transportation system comprising metros, buses, ferries, and taxis, all of which can be accessed using a Shanghai Public Transport Card.
Shanghai's rapid transit system, the Shanghai Metro, incorporates both subway and light metro lines and extends to every core urban district as well as neighboring suburban districts. , there are 19 metro lines (excluding the Shanghai maglev train and Jinshan Railway), 515 List of Shanghai Metro stations, stations, and of lines in operation, making it the List of metro systems, longest network in the world. On 8 March 2019, it set the city's daily metro ridership record with 13.3 million. The average fare ranges from () to (), depending on the travel distance.
Opened in 2004, the Shanghai maglev train is the first and the fastest commercial high-speed maglev in the world, with a maximum operation speed of . The train can complete the journey between Longyang Road Station and Pudong International Airport in 7 minutes 20 seconds, comparing to 32 minutes by Line 2 (Shanghai Metro), Metro Line 2 and 30 minutes by car. A one-way ticket costs (), or () for those with airline tickets or public transportation cards. A round-trip ticket costs (), and VIP tickets cost double the standard fare.
With the first tram line been in service in 1908, trams were once popular Trams in Shanghai, in Shanghai in the early 20th century. By 1925, there were 328 tramcars and 14 routes operated by Chinese, French, and British companies collaboratively, all of which were nationalized after the PRC's victory in 1949. Since the 1960s, many tram lines were either dismantled or replaced by trolleybus or motorbus lines; the last tram line was demolished in 1975. Shanghai reintroduced trams in 2010, as a modern rubber-tire Translohr system in Zhangjiang area of East Shanghai as Zhangjiang Tram. In 2018, the steel wheeled Songjiang Tram started operating in Songjiang District. Additional tram lines are under planning in Hongqiao Subdistrict, Shanghai, Hongqiao Subdistrict and Jiading District .
 Shanghai also has the world's most extensive Buses in Shanghai, bus network, including the world's oldest continuously operating Trolleybuses in Shanghai, trolleybus system, with 1,575 lines covering a total length of by 2019. The system is operated by multiple companies. Bus fares generally cost ().
, a total of 40,000 taxis were in operation in Shanghai. The base fare for taxis is (), which covers the first and includes a () fuel surcharge. The base fare is () between 11:00 pm and 5:00 am. Each additional kilometer costs (), or () between 11:00 pm and 5:00 am. Taxicabs and DiDi play major roles in urban transportation and DiDi is often cheaper than taxis.
As of January 2021, Shanghai Metro has 459 stations and 772 km. The scale of operation is the first in the world. in 2017, the average daily passenger traffic of the Shanghai metro was 9.693 million, and the total passenger traffic reached 3.538 billion. It is one of the busiest metro cities in the world. The metro lines cover the central city densely and connect most districts and counties.
Shanghai also has the world's most extensive Buses in Shanghai, bus network, including the world's oldest continuously operating Trolleybuses in Shanghai, trolleybus system, with 1,575 lines covering a total length of by 2019. The system is operated by multiple companies. Bus fares generally cost ().
, a total of 40,000 taxis were in operation in Shanghai. The base fare for taxis is (), which covers the first and includes a () fuel surcharge. The base fare is () between 11:00 pm and 5:00 am. Each additional kilometer costs (), or () between 11:00 pm and 5:00 am. Taxicabs and DiDi play major roles in urban transportation and DiDi is often cheaper than taxis.
As of January 2021, Shanghai Metro has 459 stations and 772 km. The scale of operation is the first in the world. in 2017, the average daily passenger traffic of the Shanghai metro was 9.693 million, and the total passenger traffic reached 3.538 billion. It is one of the busiest metro cities in the world. The metro lines cover the central city densely and connect most districts and counties.
 Shanghai is a major hub of Expressways of China, China's expressway network. Many national expressways (prefixed with the letter G) pass through or end in Shanghai, including G2 Beijing–Shanghai Expressway, Jinghu Expressway (overlaps with G42 Shanghai–Chengdu Expressway, Hurong Expressway), G15 Shenyang–Haikou Expressway, Shenhai Expressway, G40 Shanghai–Xi'an Expressway, Hushaan Expressway, G50 Shanghai–Chongqing Expressway, Huyu Expressway, G60 Shanghai–Kunming Expressway, Hukun Expressway (overlaps with G92 Hangzhou Bay Ring Expressway, Hangzhou Bay Ring Expressway), and G1503 Shanghai Ring Expressway, Shanghai Ring Expressway. There are also numerous municipal expressways prefixed with the letter S. As of 2019, Shanghai has a total of 12 bridges and 14 tunnels crossing the Huangpu River. The Shanghai Yangtze River Bridge is the city's only Yangtze River bridges and tunnels, bridge–tunnel complex across Yangtze River.
The expressway network within the city center consists of North–South Elevated Road (Shanghai), North–South Elevated Road, Yan'an Elevated Road, and Inner Ring Road (Shanghai), Inner Ring Road. Other ring roads in Shanghai include Middle Ring Road (Shanghai), Middle Ring Road, Shanghai Outer Ring Expressway, Outer Ring Expressway, and Shanghai Ring Expressway.
Shanghai is a major hub of Expressways of China, China's expressway network. Many national expressways (prefixed with the letter G) pass through or end in Shanghai, including G2 Beijing–Shanghai Expressway, Jinghu Expressway (overlaps with G42 Shanghai–Chengdu Expressway, Hurong Expressway), G15 Shenyang–Haikou Expressway, Shenhai Expressway, G40 Shanghai–Xi'an Expressway, Hushaan Expressway, G50 Shanghai–Chongqing Expressway, Huyu Expressway, G60 Shanghai–Kunming Expressway, Hukun Expressway (overlaps with G92 Hangzhou Bay Ring Expressway, Hangzhou Bay Ring Expressway), and G1503 Shanghai Ring Expressway, Shanghai Ring Expressway. There are also numerous municipal expressways prefixed with the letter S. As of 2019, Shanghai has a total of 12 bridges and 14 tunnels crossing the Huangpu River. The Shanghai Yangtze River Bridge is the city's only Yangtze River bridges and tunnels, bridge–tunnel complex across Yangtze River.
The expressway network within the city center consists of North–South Elevated Road (Shanghai), North–South Elevated Road, Yan'an Elevated Road, and Inner Ring Road (Shanghai), Inner Ring Road. Other ring roads in Shanghai include Middle Ring Road (Shanghai), Middle Ring Road, Shanghai Outer Ring Expressway, Outer Ring Expressway, and Shanghai Ring Expressway.
 Bicycle lanes are common in Shanghai, separating non-motorized traffic from car traffic on most surface streets. However, on some main roads, including all expressways, bicycles and motorcycles are banned. In recent years, cycling has seen a resurgence in popularity due to the emergence of a large number of dockless app-based bicycle-sharing systems, such as Mobike, Bluegogo, and ofo (company), ofo. , bicycle-sharing systems had an average of 1.15 million daily riders within the city.
Private car ownership in Shanghai is rapidly increasing: in 2019, there were 3.40 million private cars in the city, a 12.5% increase from 2018. New private cars cannot be driven without a license plate, which are sold in monthly license plate auctions. Around 9,500 license plates are auctioned each month, and the average price is about () in 2019. According to the city's vehicle regulations introduced in June 2016, only locally registered residents and those who have paid social insurance or individual income taxes for over three years are eligible to be in the auction. The purpose of this policy is to limit the growth of automobile traffic and alleviate congestion.
Bicycle lanes are common in Shanghai, separating non-motorized traffic from car traffic on most surface streets. However, on some main roads, including all expressways, bicycles and motorcycles are banned. In recent years, cycling has seen a resurgence in popularity due to the emergence of a large number of dockless app-based bicycle-sharing systems, such as Mobike, Bluegogo, and ofo (company), ofo. , bicycle-sharing systems had an average of 1.15 million daily riders within the city.
Private car ownership in Shanghai is rapidly increasing: in 2019, there were 3.40 million private cars in the city, a 12.5% increase from 2018. New private cars cannot be driven without a license plate, which are sold in monthly license plate auctions. Around 9,500 license plates are auctioned each month, and the average price is about () in 2019. According to the city's vehicle regulations introduced in June 2016, only locally registered residents and those who have paid social insurance or individual income taxes for over three years are eligible to be in the auction. The purpose of this policy is to limit the growth of automobile traffic and alleviate congestion.
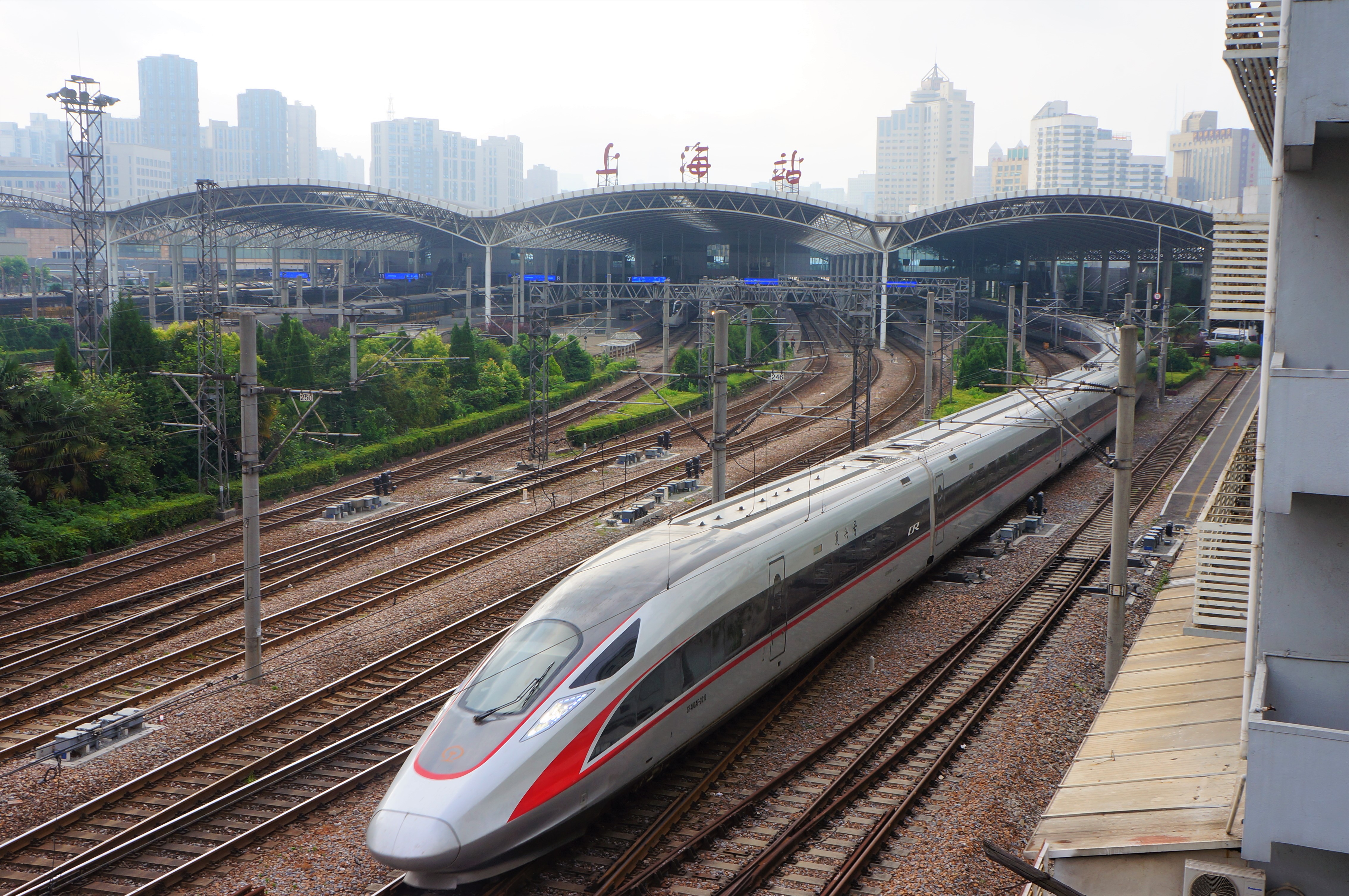 Shanghai has four major railway stations: Shanghai railway station, Shanghai South railway station, Shanghai West railway station, and Shanghai Hongqiao railway station. All are connected to the metro network and serve as hubs in the Rail transport in the People's Republic of China, railway network of China. And now Shanghai has around twenty railway lines running under this city, which largely facilitate people's life in Shanghai.
Built in 1876, the Woosung Road, Woosung railway was the first railway in Shanghai and the first railway in operation in China By 1909, Shanghai–Nanjing railway and Shanghai–Hangzhou railway were in service. , the two railways have been integrated into two main railways in China: Beijing–Shanghai railway and Shanghai–Kunming railway, respectively.
Shanghai has four high-speed railways (HSRs): Beijing–Shanghai high-speed railway, Beijing–Shanghai HSR (overlaps with Shanghai–Wuhan–Chengdu passenger railway), Shanghai–Nanjing intercity railway, Shanghai–Kunming high-speed railway, Shanghai–Kunming HSR, and Shanghai–Nantong railway. One HSR is under construction: Shanghai–Suzhou–Huzhou high-speed railway, Shanghai–Suzhou–Huzhou HSR.
Shanghai also has four Shanghai Metropolitan Area Intercity Railway, commuter railways: Pudong railway (passenger service is currently suspended) and Jinshan railway operated by China Railway, and Line 16 (Shanghai Metro), Line 16 and Line 17 (Shanghai Metro), Line 17 operated by Shanghai Metro. , four additional lines—Chongming line, Jiamin line, Airport Link line (Shanghai), Airport link line and Lianggang Express line—are under construction.
Shanghai has four major railway stations: Shanghai railway station, Shanghai South railway station, Shanghai West railway station, and Shanghai Hongqiao railway station. All are connected to the metro network and serve as hubs in the Rail transport in the People's Republic of China, railway network of China. And now Shanghai has around twenty railway lines running under this city, which largely facilitate people's life in Shanghai.
Built in 1876, the Woosung Road, Woosung railway was the first railway in Shanghai and the first railway in operation in China By 1909, Shanghai–Nanjing railway and Shanghai–Hangzhou railway were in service. , the two railways have been integrated into two main railways in China: Beijing–Shanghai railway and Shanghai–Kunming railway, respectively.
Shanghai has four high-speed railways (HSRs): Beijing–Shanghai high-speed railway, Beijing–Shanghai HSR (overlaps with Shanghai–Wuhan–Chengdu passenger railway), Shanghai–Nanjing intercity railway, Shanghai–Kunming high-speed railway, Shanghai–Kunming HSR, and Shanghai–Nantong railway. One HSR is under construction: Shanghai–Suzhou–Huzhou high-speed railway, Shanghai–Suzhou–Huzhou HSR.
Shanghai also has four Shanghai Metropolitan Area Intercity Railway, commuter railways: Pudong railway (passenger service is currently suspended) and Jinshan railway operated by China Railway, and Line 16 (Shanghai Metro), Line 16 and Line 17 (Shanghai Metro), Line 17 operated by Shanghai Metro. , four additional lines—Chongming line, Jiamin line, Airport Link line (Shanghai), Airport link line and Lianggang Express line—are under construction.
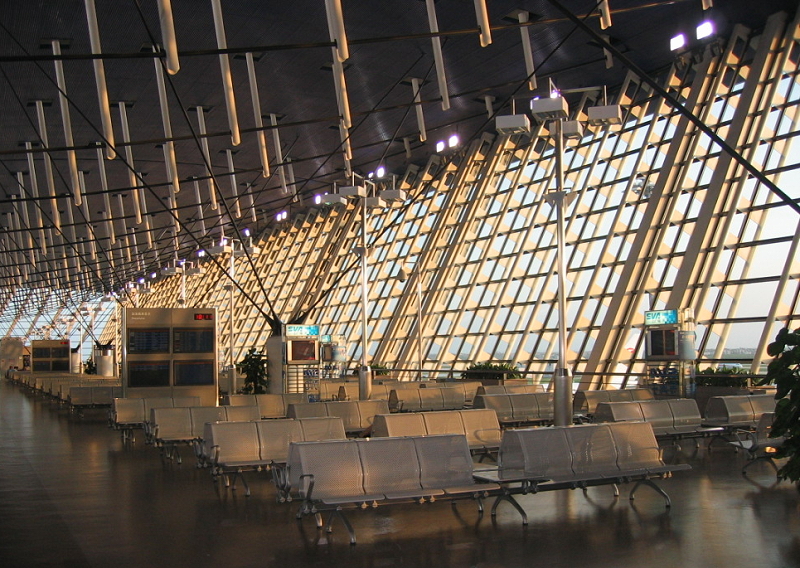 Shanghai is one of the largest air transportation hubs in Asia. The city has two commercial airports: Shanghai Pudong International Airport and Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport. Pudong International Airport is the primary international airport, while Hongqiao International Airport mainly operates domestic flights with limited short-haul international flights. In 2018, Pudong International Airport served 74.0 million passengers and handled 3.8 million tons of cargo, making it the ninth-busiest airport by passenger volume and third-busiest airport by cargo volume. The same year, Hongqiao International Airport served 43.6 million passengers, making it the 19th-busiest airport by passenger volume.
Shanghai is one of the largest air transportation hubs in Asia. The city has two commercial airports: Shanghai Pudong International Airport and Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport. Pudong International Airport is the primary international airport, while Hongqiao International Airport mainly operates domestic flights with limited short-haul international flights. In 2018, Pudong International Airport served 74.0 million passengers and handled 3.8 million tons of cargo, making it the ninth-busiest airport by passenger volume and third-busiest airport by cargo volume. The same year, Hongqiao International Airport served 43.6 million passengers, making it the 19th-busiest airport by passenger volume.
 Since its opening, the Port of Shanghai has rapidly grown to become the largest port in China. Yangshan Port was built in 2005 because the river was unsuitable for docking large container ships. The port is connected with the mainland through the long Donghai Bridge. Although the port is run by the Shanghai International Port Group under the government of Shanghai, it administratively belongs to Shengsi County, Zhejiang.
Overtaking the Port of Singapore in 2010, the Port of Shanghai has become List of world's busiest container ports, world's busiest container port with an annual twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEU transportation of 42 million in 2018.One Hundred Ports 2019
Since its opening, the Port of Shanghai has rapidly grown to become the largest port in China. Yangshan Port was built in 2005 because the river was unsuitable for docking large container ships. The port is connected with the mainland through the long Donghai Bridge. Although the port is run by the Shanghai International Port Group under the government of Shanghai, it administratively belongs to Shengsi County, Zhejiang.
Overtaking the Port of Singapore in 2010, the Port of Shanghai has become List of world's busiest container ports, world's busiest container port with an annual twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEU transportation of 42 million in 2018.One Hundred Ports 2019
Lloyd's List,2019 Besides cargo, the Port of Shanghai handled 259 cruises and 1.89 million passengers in 2019. Shanghai is part of the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road that runs from the Chinese coast to the south via the southern tip of India to Mombasa, from there to the Mediterranean, there to the Upper Adriatic region to the northern Italian hub of Trieste with its rail connections to Central Europe, Central and the Eastern Europe.
 The culture of Shanghai was formed by a combination of the nearby Wuyue culture and the "East Meets West" Haipai culture. Wuyue culture's influence is manifested in Shanghainese language—which comprises dialectal elements from nearby Jiaxing, Suzhou, and Ningbo—and Shanghai cuisine, which was influenced by Jiangsu cuisine and Zhejiang cuisine. Haipai culture emerged after Shanghai became a prosperous port in the early 20th century, with numerous foreigners from Europe, America, Japan, and India moving into the city. The culture fuses elements of Western cultures with the local Wuyue culture, and its influence extends to the city's literature, fashion, architecture, music, and cuisine. The term Haipai—originally referring to a painting school in Shanghai—was coined by a group of Beijing writers in 1920 to criticize some Shanghai scholars for admiring capitalism and Western culture. In the early 21st century, Shanghai has been recognized as a new influence and inspiration for cyberpunk culture. Futuristic structures, such as the Oriental Pearl Tower and the neon-illuminated Yan'an Elevated Road, are examples that have boosted Shanghai's cyberpunk image.
The culture of Shanghai was formed by a combination of the nearby Wuyue culture and the "East Meets West" Haipai culture. Wuyue culture's influence is manifested in Shanghainese language—which comprises dialectal elements from nearby Jiaxing, Suzhou, and Ningbo—and Shanghai cuisine, which was influenced by Jiangsu cuisine and Zhejiang cuisine. Haipai culture emerged after Shanghai became a prosperous port in the early 20th century, with numerous foreigners from Europe, America, Japan, and India moving into the city. The culture fuses elements of Western cultures with the local Wuyue culture, and its influence extends to the city's literature, fashion, architecture, music, and cuisine. The term Haipai—originally referring to a painting school in Shanghai—was coined by a group of Beijing writers in 1920 to criticize some Shanghai scholars for admiring capitalism and Western culture. In the early 21st century, Shanghai has been recognized as a new influence and inspiration for cyberpunk culture. Futuristic structures, such as the Oriental Pearl Tower and the neon-illuminated Yan'an Elevated Road, are examples that have boosted Shanghai's cyberpunk image.
 Cultural curation in Shanghai has seen significant growth since 2013, with several new museums having been opened in the city. This is in part due to the city's 2018 development plans, which aim to make Shanghai "an excellent global city". As such, Shanghai has several museums of regional and national importance. The Shanghai Museum has one of the largest collections of Chinese artifacts in the world, including a large collection of ancient Chinese bronzes and Chinese ceramics, ceramics. The China Art Museum, located in the former China Pavilion of Expo 2010, is one of the largest museums in Asia and displays an animated replica of the 12th century painting Along the River During the Qingming Festival. The Shanghai Natural History Museum and the Shanghai Science and Technology Museum are notable natural history and science museums. In addition, there are numerous smaller, specialist museums housed in important archeological and historical sites, such as the Songze culture, Songze Museum, the Museum of the First National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, the site of the former Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea, the Shanghai Jewish Refugees Museum, and the Shanghai Post Office Museum (located in the General Post Office Building, Shanghai, General Post Office Building).
Cultural curation in Shanghai has seen significant growth since 2013, with several new museums having been opened in the city. This is in part due to the city's 2018 development plans, which aim to make Shanghai "an excellent global city". As such, Shanghai has several museums of regional and national importance. The Shanghai Museum has one of the largest collections of Chinese artifacts in the world, including a large collection of ancient Chinese bronzes and Chinese ceramics, ceramics. The China Art Museum, located in the former China Pavilion of Expo 2010, is one of the largest museums in Asia and displays an animated replica of the 12th century painting Along the River During the Qingming Festival. The Shanghai Natural History Museum and the Shanghai Science and Technology Museum are notable natural history and science museums. In addition, there are numerous smaller, specialist museums housed in important archeological and historical sites, such as the Songze culture, Songze Museum, the Museum of the First National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, the site of the former Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea, the Shanghai Jewish Refugees Museum, and the Shanghai Post Office Museum (located in the General Post Office Building, Shanghai, General Post Office Building).
 The Songjiang School (), containing the Huating School () founded by Gu Zhengyi, was a small painting school in Shanghai during the Ming and Qing Dynasties. It was represented by Dong Qichang. The school was considered an expansion of the Wu School in Suzhou, the cultural center of the Jiangnan region at the time. In the mid 19th century, the Shanghai School movement commenced, focusing less on the symbolism emphasized by the Ink wash painting, Literati style but more on the visual content of painting through the use of bright colors. Secular objects like flowers and birds were often selected as themes. Western art was introduced to Shanghai in 1847 by Spanish missionary Joannes Ferrer (), and the city's first Western atelier was established in 1864 inside the . During the Republic of China, many famous artists including Zhang Daqian, Liu Haisu, Xu Beihong, Feng Zikai, and Yan Wenliang settled in Shanghai, allowing it to gradually become the art center of China. Various art forms—including photography, wood carving, sculpture, comics (Manhua), and Lianhuanhua—thrived. Sanmao (comics), Sanmao was created to dramatize the chaos created by the Second Sino-Japanese War. Today, the most comprehensive art and cultural facility in Shanghai is the China Art Museum. In addition, the Chinese Painting Academy features traditional Chinese painting, while the Power Station of Art displays contemporary art. The city also has many art galleries, many of which are located in the M50 Art District and Tianzifang. First held in 1996, the Shanghai Biennale has become an important place for Chinese and foreign arts to interact.
The Songjiang School (), containing the Huating School () founded by Gu Zhengyi, was a small painting school in Shanghai during the Ming and Qing Dynasties. It was represented by Dong Qichang. The school was considered an expansion of the Wu School in Suzhou, the cultural center of the Jiangnan region at the time. In the mid 19th century, the Shanghai School movement commenced, focusing less on the symbolism emphasized by the Ink wash painting, Literati style but more on the visual content of painting through the use of bright colors. Secular objects like flowers and birds were often selected as themes. Western art was introduced to Shanghai in 1847 by Spanish missionary Joannes Ferrer (), and the city's first Western atelier was established in 1864 inside the . During the Republic of China, many famous artists including Zhang Daqian, Liu Haisu, Xu Beihong, Feng Zikai, and Yan Wenliang settled in Shanghai, allowing it to gradually become the art center of China. Various art forms—including photography, wood carving, sculpture, comics (Manhua), and Lianhuanhua—thrived. Sanmao (comics), Sanmao was created to dramatize the chaos created by the Second Sino-Japanese War. Today, the most comprehensive art and cultural facility in Shanghai is the China Art Museum. In addition, the Chinese Painting Academy features traditional Chinese painting, while the Power Station of Art displays contemporary art. The city also has many art galleries, many of which are located in the M50 Art District and Tianzifang. First held in 1996, the Shanghai Biennale has become an important place for Chinese and foreign arts to interact. Traditional Chinese opera (Xiqu) became a popular source of public entertainment in the late 19th century. In the early 20th century, monologue and burlesque in Shanghainese appeared, absorbing elements from traditional dramas. The Great World opened in 1912 and was a significant stage at the time. In the 1920s, Suzhou Pingtan, Pingtan expanded from Suzhou to Shanghai. Pingtan art developed rapidly to 103 programs every day by the 1930s because of the abundant commercial radio stations in the city. Around the same time, a Shanghai-style Beijing Opera was formed. Led by Zhou Xinfang and , it attracted many Xiqu masters, like Mei Lanfang, to the city. A small troupe from Shengxian (now Shengzhou) also began to promote Yue opera on the Shanghainese stage. A unique style of opera, Shanghai opera, was formed when local folksongs were fused with modern operas. As of 2012, prominent troupes in Shanghai include Shanghai Jingju Theatre Company, , Shanghai Yue Opera House, and Shanghai Huju Opera House.
Drama appeared in Mission school, missionary schools in Shanghai in the late 19th century. At the time, it was mainly performed in English. ''Scandals in Officialdom'' (), staged in 1899, was one of the earliest-recorded plays. In 1907, ''Uncle Tom's Cabin; or, Life Among the Lowly'' () was performed at the . After the New Culture Movement, drama became a popular way for students and intellectuals to express their views. The city has several major institutes of theater training, including the Shanghai Conservatory of Music, the Shanghai Dramatic Arts Centre, the Shanghai Opera House, and the Shanghai Theatre Academy. Notable theaters in Shanghai include the Shanghai Grand Theatre, the Oriental Art Center, and the People's Theatre.
Traditional Chinese opera (Xiqu) became a popular source of public entertainment in the late 19th century. In the early 20th century, monologue and burlesque in Shanghainese appeared, absorbing elements from traditional dramas. The Great World opened in 1912 and was a significant stage at the time. In the 1920s, Suzhou Pingtan, Pingtan expanded from Suzhou to Shanghai. Pingtan art developed rapidly to 103 programs every day by the 1930s because of the abundant commercial radio stations in the city. Around the same time, a Shanghai-style Beijing Opera was formed. Led by Zhou Xinfang and , it attracted many Xiqu masters, like Mei Lanfang, to the city. A small troupe from Shengxian (now Shengzhou) also began to promote Yue opera on the Shanghainese stage. A unique style of opera, Shanghai opera, was formed when local folksongs were fused with modern operas. As of 2012, prominent troupes in Shanghai include Shanghai Jingju Theatre Company, , Shanghai Yue Opera House, and Shanghai Huju Opera House.
Drama appeared in Mission school, missionary schools in Shanghai in the late 19th century. At the time, it was mainly performed in English. ''Scandals in Officialdom'' (), staged in 1899, was one of the earliest-recorded plays. In 1907, ''Uncle Tom's Cabin; or, Life Among the Lowly'' () was performed at the . After the New Culture Movement, drama became a popular way for students and intellectuals to express their views. The city has several major institutes of theater training, including the Shanghai Conservatory of Music, the Shanghai Dramatic Arts Centre, the Shanghai Opera House, and the Shanghai Theatre Academy. Notable theaters in Shanghai include the Shanghai Grand Theatre, the Oriental Art Center, and the People's Theatre.
 Shanghai is considered to be the birthplace of Cinema of China, Chinese cinema. China's first short film, ''The Difficult Couple'' (1913), and the country's first fictional feature film, ''An Orphan Rescues His Grandfather'' (, 1923) were both produced in Shanghai. Shanghai's film industry grew during the early 1930s, generating stars such as Hu Die, Ruan Lingyu, Zhou Xuan, Jin Yan, and Zhao Dan. Another film star, Jiang Qing, went on to become Madame Mao Zedong. The exile of Shanghainese filmmakers and actors as a result of the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Communist revolution contributed enormously to the development of the Hong Kong film industry. The movie ''In the Mood for Love'' directed by Wong Kar-wai, a Shanghai native, depicts a slice of the displaced Shanghainese community in Hong Kong and the nostalgia for that era, featuring 1940s music by Zhou Xuan.
Shanghai's cultural festivals include Shanghai International Television Festival, Shanghai International Film Festival, Shanghai International Art Festival, Shanghai International Tourism Festival, Shanghai Spring International Music Festival, etc. Shanghai TV Festival is the earliest international TV festival founded in China. It was founded in 1986. The Shanghai International Film Festival was founded in 1993 and is one of the nine major international film festivals in the A category. The highest award is the "Golden Goblet Award"
Shanghai is considered to be the birthplace of Cinema of China, Chinese cinema. China's first short film, ''The Difficult Couple'' (1913), and the country's first fictional feature film, ''An Orphan Rescues His Grandfather'' (, 1923) were both produced in Shanghai. Shanghai's film industry grew during the early 1930s, generating stars such as Hu Die, Ruan Lingyu, Zhou Xuan, Jin Yan, and Zhao Dan. Another film star, Jiang Qing, went on to become Madame Mao Zedong. The exile of Shanghainese filmmakers and actors as a result of the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Communist revolution contributed enormously to the development of the Hong Kong film industry. The movie ''In the Mood for Love'' directed by Wong Kar-wai, a Shanghai native, depicts a slice of the displaced Shanghainese community in Hong Kong and the nostalgia for that era, featuring 1940s music by Zhou Xuan.
Shanghai's cultural festivals include Shanghai International Television Festival, Shanghai International Film Festival, Shanghai International Art Festival, Shanghai International Tourism Festival, Shanghai Spring International Music Festival, etc. Shanghai TV Festival is the earliest international TV festival founded in China. It was founded in 1986. The Shanghai International Film Festival was founded in 1993 and is one of the nine major international film festivals in the A category. The highest award is the "Golden Goblet Award"
 Shanghai is home to several Association football, football teams, including two in the Chinese Super League: Shanghai Shenhua Football Club, Shanghai Shenhua and Shanghai Port F.C., Shanghai Port. China's top-tier basketball team, the Shanghai Sharks of the Chinese Basketball Association, developed Yao Ming before he entered the National Basketball Association, NBA. Shanghai's baseball team, the Shanghai Golden Eagles, plays in the China Baseball League.
The Shanghai Cricket Club dates back to 1858 when the first recorded cricket match was played between a team of British Navy, British Naval officers and a Shanghai 11. Following a 45-year dormancy after the founding of the PRC in 1949, the club was re-established in 1994 by expatriates living in the city and has since grown to over 300 members. The Shanghai cricket team played various international matches between 1866 and 1948. With cricket in the rest of China almost non-existent, for that period they were the de facto China national cricket team.
Shanghai is home to several Association football, football teams, including two in the Chinese Super League: Shanghai Shenhua Football Club, Shanghai Shenhua and Shanghai Port F.C., Shanghai Port. China's top-tier basketball team, the Shanghai Sharks of the Chinese Basketball Association, developed Yao Ming before he entered the National Basketball Association, NBA. Shanghai's baseball team, the Shanghai Golden Eagles, plays in the China Baseball League.
The Shanghai Cricket Club dates back to 1858 when the first recorded cricket match was played between a team of British Navy, British Naval officers and a Shanghai 11. Following a 45-year dormancy after the founding of the PRC in 1949, the club was re-established in 1994 by expatriates living in the city and has since grown to over 300 members. The Shanghai cricket team played various international matches between 1866 and 1948. With cricket in the rest of China almost non-existent, for that period they were the de facto China national cricket team.
 Shanghai is home to many prominent Chinese professional athletes, such as basketball player Yao Ming, 110-meter hurdler Liu Xiang (hurdler), Liu Xiang, table tennis player Wang Liqin, and badminton player Wang Yihan.
Shanghai is home to many prominent Chinese professional athletes, such as basketball player Yao Ming, 110-meter hurdler Liu Xiang (hurdler), Liu Xiang, table tennis player Wang Liqin, and badminton player Wang Yihan.
 Shanghai is the host of several international sports events. Since 2004, it has hosted the Chinese Grand Prix, a round of the Formula One World Championship. The race is staged annually at the Shanghai International Circuit. It hosted the 2019 Chinese Grand Prix, 1000th Formula One race on 14 April 2019. In 2010, Shanghai became the host city of Deutsche Tourenwagen Masters, which raced in a street circuit in Pudong. In 2012, Shanghai began hosting 4 Hours of Shanghai as one round from the inaugural season of the FIA World Endurance Championship. The city also hosts the Shanghai Masters (tennis), Shanghai Masters tennis tournament, which is part of ATP World Tour Masters 1000, as well as golf tournaments including the BMW Masters and WGC-HSBC Champions.
On 21 September 2017, Shanghai hosted a National Hockey League (NHL) ice hockey exhibition game in an effort to increase fan interest for the 2017–18 NHL season.
Shanghai is the host of several international sports events. Since 2004, it has hosted the Chinese Grand Prix, a round of the Formula One World Championship. The race is staged annually at the Shanghai International Circuit. It hosted the 2019 Chinese Grand Prix, 1000th Formula One race on 14 April 2019. In 2010, Shanghai became the host city of Deutsche Tourenwagen Masters, which raced in a street circuit in Pudong. In 2012, Shanghai began hosting 4 Hours of Shanghai as one round from the inaugural season of the FIA World Endurance Championship. The city also hosts the Shanghai Masters (tennis), Shanghai Masters tennis tournament, which is part of ATP World Tour Masters 1000, as well as golf tournaments including the BMW Masters and WGC-HSBC Champions.
On 21 September 2017, Shanghai hosted a National Hockey League (NHL) ice hockey exhibition game in an effort to increase fan interest for the 2017–18 NHL season.
 The People's Square (Shanghai), People's Square park, located in the heart of downtown Shanghai, is especially well known for its proximity to other major landmarks in the city. Fuxing Park, located in the former French Concession, features formal French-style gardens and is surrounded by high-end bars and cafes.
Zhongshan Park (Shanghai), Zhongshan Park in western central Shanghai is famous for its monument of Frédéric Chopin, Chopin, the tallest statue dedicated to the composer in the world. Built in 1914 as Jessfield Park, it once contained the campus of Saint John's University, Shanghai, St. John's University, Shanghai's first international college; today, the park features sakura and peony gardens and a 150-year-old platanus, and it also serves as an interchange hub in the metro system.
One of Shanghai's newer parks is the Xujiahui Park, which was built in 1999, on the former grounds of the Great Chinese Rubber Works Factory and the EMI Recording Studio (now La Villa Rouge restaurant). The park has an artificial lake with a sky bridge running across the park. Shanghai Botanical Garden is located southwest of the city center and was established in 1978. In 2011, the largest botanical garden in Shanghai—Shanghai Chen Shan Botanical Garden—opened in Songjiang District.
The People's Square (Shanghai), People's Square park, located in the heart of downtown Shanghai, is especially well known for its proximity to other major landmarks in the city. Fuxing Park, located in the former French Concession, features formal French-style gardens and is surrounded by high-end bars and cafes.
Zhongshan Park (Shanghai), Zhongshan Park in western central Shanghai is famous for its monument of Frédéric Chopin, Chopin, the tallest statue dedicated to the composer in the world. Built in 1914 as Jessfield Park, it once contained the campus of Saint John's University, Shanghai, St. John's University, Shanghai's first international college; today, the park features sakura and peony gardens and a 150-year-old platanus, and it also serves as an interchange hub in the metro system.
One of Shanghai's newer parks is the Xujiahui Park, which was built in 1999, on the former grounds of the Great Chinese Rubber Works Factory and the EMI Recording Studio (now La Villa Rouge restaurant). The park has an artificial lake with a sky bridge running across the park. Shanghai Botanical Garden is located southwest of the city center and was established in 1978. In 2011, the largest botanical garden in Shanghai—Shanghai Chen Shan Botanical Garden—opened in Songjiang District.
 Other notable parks in Shanghai include Lu Xun Park (Shanghai), Lu Xun Park, Century Park (Shanghai), Century Park, , Gongqing Forest Park, and Jing'an Park.
The Shanghai Disney Resort Project was approved by the government on 4 November 2009
and opened in 2016.
The $4.4 billion theme park and resort in Pudong features a castle that is the biggest among Disney's resorts. More than 11 million people visited the resort in its first year of operation.
Other notable parks in Shanghai include Lu Xun Park (Shanghai), Lu Xun Park, Century Park (Shanghai), Century Park, , Gongqing Forest Park, and Jing'an Park.
The Shanghai Disney Resort Project was approved by the government on 4 November 2009
and opened in 2016.
The $4.4 billion theme park and resort in Pudong features a castle that is the biggest among Disney's resorts. More than 11 million people visited the resort in its first year of operation.
 Air pollution in Shanghai is not as severe as in many other Chinese cities, but is still considered substantial by world standards. During the December 2013 Eastern China smog, air pollution rates reached between 23 and 31 times the international standard. On 6 December 2013, levels of PM2.5 particulate matter in Shanghai rose above 600 micrograms per cubic meter and in the surrounding area, above 700 micrograms per cubic meter. Levels of PM2.5 in Putuo District reached 726 micrograms per cubic meter. As a result, the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission received orders to suspend students' outdoor activities. Authorities pulled nearly one-third of government vehicles from the roads, while much construction work was halted. Most inbound flights were canceled, and more than 50 flights at Pudong International Airport were diverted.
On 23 January 2014, Yang Xiong (politician), Yang Xiong, the mayor of Shanghai, announced that three main measures would be taken to manage the air pollution in Shanghai, along with surrounding Anhui, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang provinces. The measures involved implementing the 2013 air-cleaning program, establishing a linkage mechanism with the three surrounding provinces, and improving the city's early-warning systems. On 12 February 2014, China's cabinet announced that a () fund will be set up to help companies meet the new environmental standards. The effect of the policy was significant. From 2013 to 2018, more than 3,000 treatment facilities for industrial waste gases were installed, and the city's annual smoke, nitrogen oxide, and sulfur dioxide emission decreased by 65%, 54%, and 95%, respectively.
Air pollution in Shanghai is not as severe as in many other Chinese cities, but is still considered substantial by world standards. During the December 2013 Eastern China smog, air pollution rates reached between 23 and 31 times the international standard. On 6 December 2013, levels of PM2.5 particulate matter in Shanghai rose above 600 micrograms per cubic meter and in the surrounding area, above 700 micrograms per cubic meter. Levels of PM2.5 in Putuo District reached 726 micrograms per cubic meter. As a result, the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission received orders to suspend students' outdoor activities. Authorities pulled nearly one-third of government vehicles from the roads, while much construction work was halted. Most inbound flights were canceled, and more than 50 flights at Pudong International Airport were diverted.
On 23 January 2014, Yang Xiong (politician), Yang Xiong, the mayor of Shanghai, announced that three main measures would be taken to manage the air pollution in Shanghai, along with surrounding Anhui, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang provinces. The measures involved implementing the 2013 air-cleaning program, establishing a linkage mechanism with the three surrounding provinces, and improving the city's early-warning systems. On 12 February 2014, China's cabinet announced that a () fund will be set up to help companies meet the new environmental standards. The effect of the policy was significant. From 2013 to 2018, more than 3,000 treatment facilities for industrial waste gases were installed, and the city's annual smoke, nitrogen oxide, and sulfur dioxide emission decreased by 65%, 54%, and 95%, respectively.

online review
* * * * * Yan Jin. "Shanghai Studies: An evolving academic field" ''History Compass'' (October 2018) e12496 Historiography of recent scholarship
online
Official website
()
ShanghaiEye
an English news website of SMG *
WikiSatellite view of Shanghai at WikiMapia
* {{Authority control Shanghai, 10th-century establishments in China Articles containing video clips East China Jiangnan Metropolitan areas of China Municipalities of China Populated coastal places in China Populated places established in the 10th century Port cities and towns in China Province-level divisions of China Wu (region) Yangtze River Delta
Standard Mandarin
Standard Chinese ()—in linguistics Standard Northern Mandarin or Standard Beijing Mandarin, in common speech simply Mandarin, better qualified as Standard Mandarin, Modern Standard Mandarin or Standard Mandarin Chinese—is a modern standar ...
pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River
The Huangpu (), formerly romanized as Whangpoo, is a river flowing north through Shanghai. The Bund and Lujiazui are located along the Huangpu River.
The Huangpu is the biggest river in central Shanghai, with the Suzhou Creek being its maj ...
flowing through it. With a population of 24.89 million as of 2021, Shanghai is the most populous urban area in China with 39,300,000 inhabitants living in the Shanghai metropolitan area, the second most populous city proper in the world (after Chongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Romanization, alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a Direct-administered municipalities of China, municipality in Southwes ...
) and the only city in East Asia with a GDP greater than its corresponding capital. Shanghai ranks second
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
among the administrative divisions of Mainland China in human development index (after Beijing). As of 2018, the Greater Shanghai metropolitan area was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product ( nominal) of nearly 9.1 trillion RMB ($1.33 trillion), exceeding that of Mexico with GDP of $1.22 trillion, the 15th largest in the world. Shanghai is one of the world's major centers for finance
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of fina ...
, business and economics
Business economics is a field in applied economics which uses economic theory and quantitative methods to analyze business enterprises and the factors contributing to the diversity of organizational structures and the relationships of firms with ...
, research, education, science and technology
Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) is an umbrella term used to group together the distinct but related technical disciplines of science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. The term is typically used in the context of ...
, manufacturing, tourism, culture, dining, art, fashion
Fashion is a form of self-expression and autonomy at a particular period and place and in a specific context, of clothing, footwear, lifestyle, accessories, makeup, hairstyle, and body posture. The term implies a look defined by the fashion in ...
, sports, and transportation, and the Port of Shanghai
The Port of Shanghai (), located in the vicinity of Shanghai, comprises a deep-sea port and a river port.
The main port enterprise in Shanghai, the Shanghai International Port Group (SIPG), was established during the reconstitution of the S ...
is the world's busiest container port
This article lists the world's busiest container ports (ports with container terminals that specialize in handling goods transported in intermodal shipping containers), by total number of twenty-foot equivalent units (TEUs) transported through ...
. Shanghai is classified as a Large-Port Megacity, the largest type of port-city in the world . In 2019, the Shanghai Pudong International Airport was one of the world's 10 busiest airports by passenger traffic, and one of the two international airports serving the Shanghai metropolitan area, the other one being the Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport.
Originally a fishing village and market town, Shanghai grew in importance in the 19th century due to both domestic and foreign trade and its favorable port location. The city was one of five treaty ports forced to open to European trade after the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
. The Shanghai International Settlement and the French Concession were subsequently established. The city then flourished, becoming a primary commercial and financial hub of Asia in the 1930s. During the Second Sino-Japanese War, the city was the site of the major Battle of Shanghai. After the war, with the communists takeover of the mainland in 1949, trade was limited to other socialist countries and the city's global influence declined. Despite this, modern trade in the newly established PRC began in the late 1940s/early 1950s, and Shanghai officially became one of the biggest and most important cities among socialist states before the economic reform in 1978.
By the 1990s, economic reforms introduced by Deng Xiaoping a decade earlier resulted in an intense redevelopment of the city, especially the Pudong New Area, aiding the return of finance and foreign investment. The city has since re-emerged as a hub for international trade and finance; it is the home of the Shanghai Stock Exchange
The Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) is a stock exchange based in the city of Shanghai, China. It is one of the three stock exchanges operating independently in mainland China, the others being the Beijing Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Stock Exc ...
, one of the largest stock exchanges in the world by market capitalization and the Shanghai Free-Trade Zone, the first free-trade zone in mainland China. As of 2020, Shanghai was classified as an Alpha+ ( global first-tier) city by the GaWC and ranked as having the 3rd most competitive and largest financial center
A financial centre ( BE), financial center ( AE), or financial hub, is a location with a concentration of participants in banking, asset management, insurance or financial markets with venues and supporting services for these activities to t ...
in the world behind New York City and London. It has the largest metro network of any city in the world, the fifth-highest number of billionaires of any city in the world, the fifth-largest number of skyscrapers of any city in the world, the fifth-most Fortune Global 500 headquarters of any city in the world within its city limits, the third-largest scientific research output of any city in the world, and highly ranked Double First Class Universities including Fudan
Fudan University () is a national public research university in Shanghai, China. Fudan is a member of the C9 League, Project 985, Project 211, and the Double First Class University identified by the Ministry of Education of China. It is als ...
, Shanghai Jiao Tong, Tongji, East China Normal, Shanghai, Donghua, ShanghaiTech, Shanghai University of Finance and Economics
The Shanghai University of Finance and Economics (SUFE; ), founded in 1917, is a finance- and economics-oriented research university located in Shanghai, the People's Republic of China. The university is under the direct administration of the ...
, and East China University of Science and Technology.
Shanghai has been described as the "showpiece" of the booming economy of China
The China, People's Republic of China has an upper middle income Developing country, developing Mixed economy, mixed socialist market economy that incorporates economic planning through Industrial policy, industrial policies and strategic Five- ...
. Featuring several architectural styles such as Art Deco and shikumen, the city is renowned for its Lujiazui skyline, museums and historic buildings including the City God Temple, Yu Garden, the China Pavilion and buildings along the Bund, which includes Oriental Pearl TV Tower. Shanghai is also known for its sugary cuisine, distinctive local language and vibrant international flair. As an important international city, Shanghai is the seat of the New Development Bank, a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS states and the city hosts more than 75 foreign representatives, the second highest after Beijing and numerous national and international events every year, such as Shanghai Fashion Week, the Chinese Grand Prix and ChinaJoy. Shanghai is the highest earning tourist city in the world, with the seventh most five-star hotels in the world, and the third tallest building in the world, the Shanghai Tower. In 2018, Shanghai hosted the first China International Import Expo (CIIE), the world's first import-themed national-level expo. Shanghai joined the UNESCO Global Network of Learning Cities in 2019.
Etymology
The two Chinese characters in the city's name are (/''zan'', "upon") and (/''hae'', "sea"), together meaning "On the Sea". The earliest occurrence of this name dates from the 11th-century Song dynasty, when there was already a river confluence and a town with this name in the area. How the name should be understood has been disputed, but Chinese historians have concluded that during the Tang dynasty, the area of modern-day Shanghai was under the sea level, so the land appeared to be literally "on the sea".Danielson, Eric N., ''Shanghai and the Yangzi Delta'', 2004, pp. 8–9. Shanghai is officially abbreviated (/''Vu''2) in Chinese, a contraction of (/''Vu Doh'', " Harpoon Ditch"), a 4th- or Jin name for the mouth ofSuzhou Creek
Suzhou Creek (or Soochow Creek), also called the Wusong (Woosung) River, is a river that passes through the Shanghai city center. It is named after the neighboring city of Suzhou (Soochow), Jiangsu, the predominant settlement in this area prior ...
when it was the main conduit into the ocean. This character appears on all motor vehicle license plates issued in the municipality today.
Alternative names
(''Shēn'') or (''Shēnchéng'', "Shen City") was an early name originating fromLord Chunshen
Lord Chunshen (; died 238 BC), born Huang Xie (),was a Chinese military general and politician. He served as the Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Chu during the late Warring States period of ancient China. He was one of the Four Lords of the Wa ...
, a 3rd-century BC nobleman and prime minister of the state of Chu
Chu, or Ch'u in Wade–Giles romanization, (, Hanyu Pinyin: Chǔ, Old Chinese: ''*s-r̥aʔ'') was a Zhou dynasty vassal state. Their first ruler was King Wu of Chu in the early 8th century BCE. Chu was located in the south of the Zhou hea ...
, whose fief included modern Shanghai. Shanghai-based sports teams and newspapers often use Shen in their names, such as Shanghai Shenhua and '' Shen Bao''.
(''Huátíng'') was another early name for Shanghai. In AD 751 during the mid-Tang dynasty, Huating County was established by Zhao Juzhen
Zhao Juzhen was a Tang dynasty politician who served during the reign of Emperor Xuanzong of Tang. He was the founder of Huating County, the first county-level division in Shanghai.
Life
Zhao was born in Dingzhou. He was a member of the Zhao c ...
, the governor of Wu Commandery, at modern-day Songjiang, the first county-level administration within modern-day Shanghai. The first five-star hotel in the city was named after Huating.
(''Módū'', "Magical City"), a contemporary nickname for Shanghai, is widely known among the youth. The name was first mentioned in Shōfu Muramatsu
, the pen-name of Muramatsu Giichi, was a Japanese novelist active during the Shōwa period of Japan.
Early life
Muramatsu was born in what is now part of the town of Mori, Shizuoka, Mori, in Shizuoka prefecture, which was (and is) a rural distr ...
's 1924 novel ''Mato'', which portrayed Shanghai as a dichotomic city where both light and darkness existed.
The city has various nicknames in English, including "Pearl of the Orient" and "Paris of the East". This is similar to Ho Chi Minh City
, population_density_km2 = 4,292
, population_density_metro_km2 = 697.2
, population_demonym = Saigonese
, blank_name = GRP (Nominal)
, blank_info = 2019
, blank1_name = – Total
, blank1_ ...
(also known as Saigon), in Vietnam, which has also been nicknamed as "Paris of the Orient", due to Vietnam's historical French status.
History
Antiquity
The western part of modern-day Shanghai was inhabited 6000 years ago. During theSpring and Autumn period
The Spring and Autumn period was a period in Chinese history from approximately 770 to 476 BC (or according to some authorities until 403 BC) which corresponds roughly to the first half of the Eastern Zhou period. The period's name derives fr ...
(approximately 771 to 476 BC), it belonged to the Kingdom of Wu, which was conquered by the Yue (state), Kingdom of Yue, which in turn was conquered by the Kingdom of Chu. During the Warring States period (475 BC), Shanghai was part of the fief of Lord Chunshen
Lord Chunshen (; died 238 BC), born Huang Xie (),was a Chinese military general and politician. He served as the Prime Minister of the Kingdom of Chu during the late Warring States period of ancient China. He was one of the Four Lords of the Wa ...
of Chu, one of the Four Lords of the Warring States. He ordered the excavation of the Huangpu River
The Huangpu (), formerly romanized as Whangpoo, is a river flowing north through Shanghai. The Bund and Lujiazui are located along the Huangpu River.
The Huangpu is the biggest river in central Shanghai, with the Suzhou Creek being its maj ...
. Its former or poetic name, the Chunshen River, gave Shanghai its nickname of "Shēn". Fishermen living in the Shanghai area then created a fish tool called the ''hù'', which lent its name to the outlet of Suzhou Creek north of the Old City of Shanghai, Old City and became a common nickname and Chinese abbreviations, abbreviation for the city.
Imperialism
During the Tang and Song dynasties, Qinglong Town () in modern Qingpu District was a major trading port. Established in 746 (the fifth year of the Tang Tianbao era), it developed into what historically called a "giant town of the Southeast", with thirteen temples and seven pagodas. Mi Fu, a scholar and artist of the Song dynasty, served as its mayor. The port experienced thriving trade with provinces along the Yangtze and the Chinese coast, as well as with foreign countries such as Japan and Silla. During the Qing dynasty, Shanghai became one of the most important sea ports in the Yangtze Delta region as a result of two important central government policy changes: in 1684, the Kangxi Emperor reversed the Ming dynasty prohibition on oceangoing vessels—a ban that had been in force since 1525; and in 1732, the Qianlong Emperor moved the customs office for Jiangsu province (; see Customs House, Shanghai) from the prefectural capital of Songjiang to Shanghai, and gave Shanghai exclusive control over customs collections for Jiangsu's foreign trade. As a result of these two critical decisions, Shanghai became the major trade port for all of the lower Yangtze region by 1735, despite still being at the lowest administrative level in the political hierarchy.
During the Qing dynasty, Shanghai became one of the most important sea ports in the Yangtze Delta region as a result of two important central government policy changes: in 1684, the Kangxi Emperor reversed the Ming dynasty prohibition on oceangoing vessels—a ban that had been in force since 1525; and in 1732, the Qianlong Emperor moved the customs office for Jiangsu province (; see Customs House, Shanghai) from the prefectural capital of Songjiang to Shanghai, and gave Shanghai exclusive control over customs collections for Jiangsu's foreign trade. As a result of these two critical decisions, Shanghai became the major trade port for all of the lower Yangtze region by 1735, despite still being at the lowest administrative level in the political hierarchy.
Rise and golden age
 In the 19th century, international attention to Shanghai grew due to European recognition of its economic and trade potential at the Yangtze. During the
In the 19th century, international attention to Shanghai grew due to European recognition of its economic and trade potential at the Yangtze. During the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
(1839–1842), British forces occupied the city.Rait, Robert S. (1903). The Life and Campaigns of Hugh, First Viscount Gough, Field-Marshal
''. Volume 1. p. 267–268 The war ended in 1842 with the Treaty of Nanking, which opened Shanghai as one of the five treaty ports for international trade. The Treaty of the Bogue, the Treaty of Wanghia, and the Treaty of Whampoa (signed in 1843, 1844, and 1844, respectively) forced Chinese concession to European and American desires for visitation and trade on Chinese soil. Britain, France, and the United States all established a presence outside the walled city of Shanghai, which remained under the direct administration of the Chinese. The Chinese-held Old City of Shanghai fell to rebels from the Small Swords Society in 1853, but was recovered by the Qing government in February 1855. In 1854, the Shanghai Municipal Council was created to manage the foreign settlements. Between 1860 and 1862, the Taiping Rebellion, Taiping rebels Battle of Shanghai (1861), twice attacked Shanghai and destroyed the city's eastern and southern suburbs, but failed to take the city.Williams, S. Wells.
The Middle Kingdom: A Survey of the Geography, Government, Literature, Social Life, Arts, and History of the Chinese Empire and its Inhabitants
', Vol. 1, p. 107. Scribner (New York), 1904. In 1863, the British settlement to the south of Suzhou Creek (northern Huangpu District, Shanghai, Huangpu District) and the American settlement to the north (southern Hongkou District) joined in order to form the Shanghai International Settlement. The French opted out of the Shanghai Municipal Council and maintained Shanghai French Concession, its own concession to the south and southwest.
 The First Sino-Japanese War concluded with the 1895 Treaty of Shimonoseki, which elevated Japan to become another foreign power in Shanghai. Japan built the first factories in Shanghai, which was soon copied by other foreign powers. All this international activity gave Shanghai the nickname "the Great Athens of China". In 1914, the Old City walls were dismantled because they blocked the city's expansion. In July 1921, the Chinese Communist Party was founded in the French Concession. On 30 May 1925, the May Thirtieth Movement broke out when a worker in a Japanese-owned cotton mill was shot and killed by a Japanese foreman.Ku, Hung-Ting [1979] (1979). Urban Mass Movement: The May Thirtieth Movement in Shanghai. Modern Asian Studies, Vol.13, No.2. pp.197–216 Workers in the city then launched general strikes against imperialism, which became nationwide protests that gave rise to Chinese nationalism.
The golden age of Shanghai began with its elevation to municipality after it was separated from Jiangsu on 7 July 1927. This new Chinese municipality covered an area of , including the modern-day districts of Baoshan District, Shanghai, Baoshan, Yangpu District, Yangpu, Zhabei, Nanshi District, Shanghai, Nanshi, and Pudong, but excluded the foreign concessions territories. Headed by a Chinese mayor and municipal council, the new city government's first task—the Greater Shanghai Plan—was to create a new city center in Jiangwan town of Yangpu district, outside the boundaries of the foreign concessions. The plan included a public museum, library, sports stadium, and city hall, which were partially constructed before being interrupted by the Japanese invasion. In the 1920s, ''shidaiqu'' became a new form of entertainment and was popularised in Shanghai.
The city flourished, becoming a primary commercial and financial hub of the Asia-Pacific region in the 1930s.
During the ensuing decades, citizens of many countries and all continents came to Shanghai to live and work; those who stayed for long periods—some for generations—called themselves "Shanghailanders". In the 1920s and 1930s, almost 20,000 White Movement, White Russians fled the newly established Soviet Union to reside in Shanghai. These Shanghai Russians constituted the second-largest foreign community. By 1932, Shanghai had become the world's fifth largest city and home to 70,000 foreigners. In the 1930s, some 30,000 Jewish refugees from Europe arrived in the city.
The First Sino-Japanese War concluded with the 1895 Treaty of Shimonoseki, which elevated Japan to become another foreign power in Shanghai. Japan built the first factories in Shanghai, which was soon copied by other foreign powers. All this international activity gave Shanghai the nickname "the Great Athens of China". In 1914, the Old City walls were dismantled because they blocked the city's expansion. In July 1921, the Chinese Communist Party was founded in the French Concession. On 30 May 1925, the May Thirtieth Movement broke out when a worker in a Japanese-owned cotton mill was shot and killed by a Japanese foreman.Ku, Hung-Ting [1979] (1979). Urban Mass Movement: The May Thirtieth Movement in Shanghai. Modern Asian Studies, Vol.13, No.2. pp.197–216 Workers in the city then launched general strikes against imperialism, which became nationwide protests that gave rise to Chinese nationalism.
The golden age of Shanghai began with its elevation to municipality after it was separated from Jiangsu on 7 July 1927. This new Chinese municipality covered an area of , including the modern-day districts of Baoshan District, Shanghai, Baoshan, Yangpu District, Yangpu, Zhabei, Nanshi District, Shanghai, Nanshi, and Pudong, but excluded the foreign concessions territories. Headed by a Chinese mayor and municipal council, the new city government's first task—the Greater Shanghai Plan—was to create a new city center in Jiangwan town of Yangpu district, outside the boundaries of the foreign concessions. The plan included a public museum, library, sports stadium, and city hall, which were partially constructed before being interrupted by the Japanese invasion. In the 1920s, ''shidaiqu'' became a new form of entertainment and was popularised in Shanghai.
The city flourished, becoming a primary commercial and financial hub of the Asia-Pacific region in the 1930s.
During the ensuing decades, citizens of many countries and all continents came to Shanghai to live and work; those who stayed for long periods—some for generations—called themselves "Shanghailanders". In the 1920s and 1930s, almost 20,000 White Movement, White Russians fled the newly established Soviet Union to reside in Shanghai. These Shanghai Russians constituted the second-largest foreign community. By 1932, Shanghai had become the world's fifth largest city and home to 70,000 foreigners. In the 1930s, some 30,000 Jewish refugees from Europe arrived in the city.
Japanese invasion

 On January 28 Incident, 28 January 1932, Japanese forces invaded Shanghai while the Chinese resisted. More than 10,000 shops and hundreds of factories and public buildings were destroyed, leaving Zhabei district ruined. About 18,000 civilians were either killed, injured, or declared missing. A ceasefire was brokered on 5 May. In 1937, the Battle of Shanghai resulted in the occupation of the Chinese-administered parts of Shanghai outside of the International Settlement and the French Concession. People who stayed in the occupied city suffered on a daily basis, experiencing hunger, oppression, or death. The foreign concessions were ultimately occupied by the Japanese on 8 December 1941 and remained occupied until Japan's surrender in 1945; multiple Japanese war crimes, war crimes were committed during that time.
A side-effect of the Japanese invasion of Shanghai was the Shanghai Ghetto. Japanese consul to Kaunas, Lithuania, Chiune Sugihara issued thousands of visas to Jewish refugees who were escaping the Nazi's Final Solution to the Jewish Question. They traveled from Keidan, Lithuania across Russia by railroad to the Vladivostok from where they traveled by ship to Kobe, Japan. Their stay in Kobe was short as the Japanese government transferred them to Shanghai by November 1941. Other Jewish refugees found haven in Shanghai, not through Sugihara, but came on ships from Italy. The refugees from Europe were interned into a cramped ghetto in the Hongkou District, and after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, even the Iraqi Jews who had been living in Shanghai from before the outbreak of WWII were interned. Among the refugees in the Shanghai Ghetto was the Mir yeshiva (Belarus), Mirrer Yeshiva, including its students and faculty. On 3 September 1945, the Chinese Army liberated the Ghetto and most of the Jews left over the next few years. By 1957, there were only one hundred Jews remaining in Shanghai.
On 27 May 1949, the People's Liberation Army took control of Shanghai through the Shanghai Campaign. Under the new People's Republic of China (PRC), Shanghai was one of only three municipalities not merged into neighboring provinces (the others being Beijing and Tianjin). Most foreign firms moved their offices from Shanghai to Hong Kong, as part of a foreign divestment due to the PRC's victory.
On January 28 Incident, 28 January 1932, Japanese forces invaded Shanghai while the Chinese resisted. More than 10,000 shops and hundreds of factories and public buildings were destroyed, leaving Zhabei district ruined. About 18,000 civilians were either killed, injured, or declared missing. A ceasefire was brokered on 5 May. In 1937, the Battle of Shanghai resulted in the occupation of the Chinese-administered parts of Shanghai outside of the International Settlement and the French Concession. People who stayed in the occupied city suffered on a daily basis, experiencing hunger, oppression, or death. The foreign concessions were ultimately occupied by the Japanese on 8 December 1941 and remained occupied until Japan's surrender in 1945; multiple Japanese war crimes, war crimes were committed during that time.
A side-effect of the Japanese invasion of Shanghai was the Shanghai Ghetto. Japanese consul to Kaunas, Lithuania, Chiune Sugihara issued thousands of visas to Jewish refugees who were escaping the Nazi's Final Solution to the Jewish Question. They traveled from Keidan, Lithuania across Russia by railroad to the Vladivostok from where they traveled by ship to Kobe, Japan. Their stay in Kobe was short as the Japanese government transferred them to Shanghai by November 1941. Other Jewish refugees found haven in Shanghai, not through Sugihara, but came on ships from Italy. The refugees from Europe were interned into a cramped ghetto in the Hongkou District, and after the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor, even the Iraqi Jews who had been living in Shanghai from before the outbreak of WWII were interned. Among the refugees in the Shanghai Ghetto was the Mir yeshiva (Belarus), Mirrer Yeshiva, including its students and faculty. On 3 September 1945, the Chinese Army liberated the Ghetto and most of the Jews left over the next few years. By 1957, there were only one hundred Jews remaining in Shanghai.
On 27 May 1949, the People's Liberation Army took control of Shanghai through the Shanghai Campaign. Under the new People's Republic of China (PRC), Shanghai was one of only three municipalities not merged into neighboring provinces (the others being Beijing and Tianjin). Most foreign firms moved their offices from Shanghai to Hong Kong, as part of a foreign divestment due to the PRC's victory.
Modernity
After the war, Shanghai's economy was restored—from 1949 to 1952, the city's agricultural and industrial output increased by 51.5% and 94.2%, respectively. There were 20 urban districts and 10 suburbs at the time. On 17 January 1958, Jiading District, Jiading, Baoshan, and Shanghai County in Jiangsu became part of Shanghai Municipality, which expanded to . The following December, the land area of Shanghai was further expanded to after more surrounding suburban areas in Jiangsu were added: Chongming District, Chongming, Jinshan District, Jinshan, Qingpu, Fengxian District, Fengxian, Chuansha County, Chuansha, and Nanhui County, Nanhui. In 1964, the city's administrative divisions were rearranged to 10 urban districts and 10 counties. As the industrial center of China with the most skilled industrial workers, Shanghai became a center for radical Left-wing politics, leftism during the 1950s and 1960s. The radical leftist Jiang Qing and her three allies, together the Gang of Four, were based in the city. During the Cultural Revolution (1966–1976), Shanghai's society was severely damaged, with 310,000 wrongful convictions involving more than 1 million people. About 11,500 people were unjustly persecuted to death. Despite this, Shanghai maintained economic production with a positive annual growth rate. The Shanghai People's Commune was established in the city during the January Storm of 1967. Since 1949, Shanghai has been a comparatively heavy contributor of tax revenue to the central government; in 1983, the city's contribution in tax revenue was greater than investment received in the past 33 years combined. Its importance to the fiscal well-being of the central government also denied it from Chinese economic reform, economic liberalizations begun in 1978. In 1990, Deng Xiaoping finally permitted Shanghai to initiate economic reforms, which reintroduced foreign capital to the city and developed the Pudong district, resulting in the birth of Lujiazui. As of 2020, Shanghai is classified as an Alpha+ city by the Globalization and World Cities Research Network, making it one of the world's Top 10 major cities. In early 2022, Shanghai experienced a large outbreak of COVID-19 cases. After localized lockdowns failed to stem the rise in cases, the 2022 Shanghai COVID-19 outbreak, Chinese government locked down the entire city on April 5. This resulted in widespread food shortages across the city emerged as food-supply chains were severely disrupted by the government's lockdown measures, which was not lifted until June 1.Geography
 Shanghai is located on the Yangtze Estuary of China's east coast, with the Yangtze River to the north and Hangzhou Bay to the south, with the East China Sea to the east. The land is formed by the Yangtze's natural deposition (geology), deposition and modern land reclamation projects. As such, it has Loam, sandy soil, and skyscrapers have to be built with deep concrete piles to avoid sinking into the soft ground. The provincial-level Municipality of Shanghai administers both the estuary and many of its islands of Shanghai, surrounding islands. It borders the provinces of Zhejiang to the south and Jiangsu to the west and north.
The municipality's northernmost point is on Chongming Island, which is the second-largest List of islands of China, island in mainland China after its expansion during the 20th century."Chongming Island" in the ''Encyclopedia of Shanghai'', p. 52.
Shanghai is located on the Yangtze Estuary of China's east coast, with the Yangtze River to the north and Hangzhou Bay to the south, with the East China Sea to the east. The land is formed by the Yangtze's natural deposition (geology), deposition and modern land reclamation projects. As such, it has Loam, sandy soil, and skyscrapers have to be built with deep concrete piles to avoid sinking into the soft ground. The provincial-level Municipality of Shanghai administers both the estuary and many of its islands of Shanghai, surrounding islands. It borders the provinces of Zhejiang to the south and Jiangsu to the west and north.
The municipality's northernmost point is on Chongming Island, which is the second-largest List of islands of China, island in mainland China after its expansion during the 20th century."Chongming Island" in the ''Encyclopedia of Shanghai'', p. 52.Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers (Shanghai), 2010. Hosted by the Municipality of Shanghai. It does not administratively include an exclave of Jiangsu on northern Chongming or the two islands forming Shanghai's Yangshan Port, which are parts of Zhejiang's Shengsi County. Shanghai is roughly 1,100 km equidistant from Beijing to the north-west and 1400 km from Guangzhou to the south-east. Shanghai is located on an alluvial plain. As such, the vast majority of its land area is flat, with an average elevation of . Tidal flat ecosystems exist around the estuary, however, they have long been reclaimed for agricultural purposes. The city's few hills, such as Sheshan Hill, She Shan, lie to the southwest, and its highest point is the peak of Dajinshan Island () in Hangzhou Bay. Shanghai has many rivers, canals, streams, and lakes, and it is known for its rich water resources as part of the Lake Tai drainage basin. Downtown Shanghai is bisected by the Huangpu River, a man-made tributary of the Yangtze created by order of Lord Chunshen during the Warring States period. The historic center of the city was located on the west bank of the Huangpu (Puxi), near the mouth of Suzhou Creek, connecting it with Lake Tai and the Grand Canal of China, Grand Canal. The central financial district, Lujiazui, has been established on the east bank of the Huangpu (Pudong). Along Shanghai's eastern shore, the destruction of local wetlands due to the construction of Pudong International Airport has been partially offset by the protection and expansion of a nearby shoal, Jiuduansha, as a nature preserve."Fourth Island Wetland Emerging", pp. 1–2.
''Shanghai Daily''. 8 December 2009. Hosted at China.org.
Climate
Shanghai has a humid subtropical climate (Köppen climate classification, Cfa), with an average annual temperature of for urban districts and for suburbs. The city experiences four distinct seasons. Winters are temperate to cold and damp—northwesterly winds from Siberia can cause nighttime temperatures to drop below freezing. Each year, there are an average of 6.2 days with snowfall and 2.8 days with snow cover. Summers are hot and humid, and occasional downpours or freak thunderstorms can be expected. On average, 8.7 days exceed annually. In summer and the beginning of autumn, the city is susceptible to typhoons. The most pleasant seasons are generally spring, although changeable and often rainy, and autumn, which is usually sunny and dry. With monthly percent possible sunshine ranging from 34% in March to 54% in August, the city receives 1,895 hours of bright sunshine annually. Extremes since 1951 have ranged from on 31 January 1977 (unofficial record of was set on 19 January 1893) to on 13 July 2022 at a weather station in Xujiahui.Cityscape
The Bund, located by the bank of the Huangpu River, is home to a row of early 20th-century architecture, ranging in style from the neoclassical architecture, neoclassical HSBC Building, Shanghai, HSBC Building to the Art Deco Sassoon House (now part of the Peace Hotel). Many areas in the former foreign concessions are also well-preserved, the most notable being the French Concession. Shanghai is also home to many architecturally distinctive and even eccentric buildings, including the Shanghai Museum, the Shanghai Grand Theatre, the Shanghai Oriental Art Center, and the Oriental Pearl Tower. Despite rampant redevelopment, the Old City still retains some traditional architecture and designs, such as the Yu Garden, an elaborate Jiangnan style garden. As a result of its construction boom during the 1920s and 1930s, Shanghai has among the most Art Deco buildings in the world. One of the most famous architects working in Shanghai was László Hudec, a Hungarians in Slovakia, Hungarian-Slovak who lived in the city between 1918 and 1947. His most notable Art Deco buildings include the Park Hotel Shanghai, Park Hotel, the Grand Cinema (Shanghai), Grand Cinema, and the Paramount (Shanghai), Paramount. Other prominent architects who contributed to the Art Deco style are P&T Group, Clement Palmer and Arthur Turner, who together designed the Peace Hotel, the Metropole Hotel (Shanghai), Metropole Hotel, and the Broadway Mansions; and Austrian architect C. H. Gonda, C.H. Gonda, who designed the Capitol Theater (Shanghai), Capitol Theatre. The Bund has been revitalized several times. The first was in 1986, with a new Esplanade, promenade by the Dutch architect Paulus Snoeren. The second was before the Expo 2010, 2010 Expo, which includes restoration of the century-old Waibaidu Bridge and reconfiguration of traffic flow. One distinctive cultural element is the shikumen (, "stone storage door") residence, typically two- or three-story gray brick houses with the front yard protected by a heavy wooden door in a stylistic stone arch. Each residence is connected and arranged in straight alleys, known as longtang (). The house is similar to western-style terrace houses or townhouses, but distinguishes by the tall, heavy brick wall and archway in front of each house.
The shikumen is a cultural blend of elements found in Western architecture with traditional Jiangnan Chinese architecture and social behavior. Like almost all traditional Chinese dwellings, it has a courtyard, which reduces outside noise. Vegetation can be grown in the courtyard, and it can also allow for sunlight and ventilation to the rooms.
One distinctive cultural element is the shikumen (, "stone storage door") residence, typically two- or three-story gray brick houses with the front yard protected by a heavy wooden door in a stylistic stone arch. Each residence is connected and arranged in straight alleys, known as longtang (). The house is similar to western-style terrace houses or townhouses, but distinguishes by the tall, heavy brick wall and archway in front of each house.
The shikumen is a cultural blend of elements found in Western architecture with traditional Jiangnan Chinese architecture and social behavior. Like almost all traditional Chinese dwellings, it has a courtyard, which reduces outside noise. Vegetation can be grown in the courtyard, and it can also allow for sunlight and ventilation to the rooms.
 Some of Shanghai's buildings feature Soviet Union, Soviet neoclassical architecture or Stalinist architecture, though the city has fewer such structures than Beijing. These buildings were mostly erected between the founding of the People's Republic of China, People's Republic in 1949 and the Sino-Soviet Split in the late 1960s. During this time period, large numbers of Soviet experts, including architects, poured into China to aid the country in the construction of a communist state. An example of Soviet neoclassical architecture in Shanghai is the modern-day Shanghai Exhibition Center.
Shanghai—Lujiazui in particular—has List of tallest buildings in Shanghai, numerous skyscrapers, making it the fifth List of cities with the most skyscrapers, city in the world with the most skyscrapers. Among the most prominent examples are the high Jin Mao Tower, the high Shanghai World Financial Center, and the high Shanghai Tower, which is the tallest building in China and the List of tallest buildings, second tallest in the world. Completed in 2015, the tower takes the form of nine twisted sections stacked atop each other, totaling 128 floors. It is featured in its double-skin facade design, which eliminates the need for either layer to be opaqued for reflectivity as the double-layer structure has already reduced the heat absorption. The futuristic-looking Oriental Pearl Tower, at , is located nearby at the northern tip of Lujiazui. Skyscrapers outside of Lujiazui include the White Magnolia Plaza in Hongkou, the Shimao International Plaza in Huangpu, and the Shanghai Wheelock Square in Jing'an District, Jing'an.
Some of Shanghai's buildings feature Soviet Union, Soviet neoclassical architecture or Stalinist architecture, though the city has fewer such structures than Beijing. These buildings were mostly erected between the founding of the People's Republic of China, People's Republic in 1949 and the Sino-Soviet Split in the late 1960s. During this time period, large numbers of Soviet experts, including architects, poured into China to aid the country in the construction of a communist state. An example of Soviet neoclassical architecture in Shanghai is the modern-day Shanghai Exhibition Center.
Shanghai—Lujiazui in particular—has List of tallest buildings in Shanghai, numerous skyscrapers, making it the fifth List of cities with the most skyscrapers, city in the world with the most skyscrapers. Among the most prominent examples are the high Jin Mao Tower, the high Shanghai World Financial Center, and the high Shanghai Tower, which is the tallest building in China and the List of tallest buildings, second tallest in the world. Completed in 2015, the tower takes the form of nine twisted sections stacked atop each other, totaling 128 floors. It is featured in its double-skin facade design, which eliminates the need for either layer to be opaqued for reflectivity as the double-layer structure has already reduced the heat absorption. The futuristic-looking Oriental Pearl Tower, at , is located nearby at the northern tip of Lujiazui. Skyscrapers outside of Lujiazui include the White Magnolia Plaza in Hongkou, the Shimao International Plaza in Huangpu, and the Shanghai Wheelock Square in Jing'an District, Jing'an.
Politics
Structure
 Like virtually all Politics of China, governing institutions in mainland China, Shanghai has a parallel party-government system, in which the Party Committee Secretary, officially termed the Communist Party of China Shanghai Municipal Committee Secretary, outranks the Mayor. The acts as the top policy-formulation body, and is typically composed of 12 members (including the secretary).
Political power in Shanghai has frequently been a stepping stone to higher positions in the central government. Since Jiang Zemin became the General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party in June 1989, all former Shanghai party secretaries but one were elevated to the Politburo Standing Committee of the Chinese Communist Party, Politburo Standing Committee, the ''de facto'' highest decision-making body in China, including Jiang himself (Party General Secretary), Zhu Rongji (Premier), Wu Bangguo (Chairman of the National People's Congress), Huang Ju (Vice Premier), Xi Jinping (current General Secretary), Yu Zhengsheng, Han Zheng, and Li Qiang. Zeng Qinghong, a former deputy party secretary of Shanghai, also rose to the Politburo Standing Committee and became the Vice President and an influential power broker. The only exception is Chen Liangyu, who was fired in 2006 and later convicted of Corruption in China, corruption.
Officials with ties to the Shanghai administration collectively form a powerful faction in the central government known as the Shanghai Clique, which has often been viewed to compete against the rival Youth League Faction over personnel appointments and policy decisions. However, Xi Jinping, successor to Hu Jintao as General Secretary and President of the People's Republic of China, President, was largely an independent leader and took Anti-corruption campaign under Xi Jinping, anti-corruption campaigns on both factions.
Like virtually all Politics of China, governing institutions in mainland China, Shanghai has a parallel party-government system, in which the Party Committee Secretary, officially termed the Communist Party of China Shanghai Municipal Committee Secretary, outranks the Mayor. The acts as the top policy-formulation body, and is typically composed of 12 members (including the secretary).
Political power in Shanghai has frequently been a stepping stone to higher positions in the central government. Since Jiang Zemin became the General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party in June 1989, all former Shanghai party secretaries but one were elevated to the Politburo Standing Committee of the Chinese Communist Party, Politburo Standing Committee, the ''de facto'' highest decision-making body in China, including Jiang himself (Party General Secretary), Zhu Rongji (Premier), Wu Bangguo (Chairman of the National People's Congress), Huang Ju (Vice Premier), Xi Jinping (current General Secretary), Yu Zhengsheng, Han Zheng, and Li Qiang. Zeng Qinghong, a former deputy party secretary of Shanghai, also rose to the Politburo Standing Committee and became the Vice President and an influential power broker. The only exception is Chen Liangyu, who was fired in 2006 and later convicted of Corruption in China, corruption.
Officials with ties to the Shanghai administration collectively form a powerful faction in the central government known as the Shanghai Clique, which has often been viewed to compete against the rival Youth League Faction over personnel appointments and policy decisions. However, Xi Jinping, successor to Hu Jintao as General Secretary and President of the People's Republic of China, President, was largely an independent leader and took Anti-corruption campaign under Xi Jinping, anti-corruption campaigns on both factions.
Administrative divisions
Shanghai is one of the four Direct-administered municipalities of China, municipalities under the direct administration of the Government of the People's Republic of China, and is divided into 16 county-level division, county-level district of China, districts. Although every district has its own urban core, the city hall and major administrative units are located in Huangpu District, which also serves as a commercial area, including the famous Nanjing Road (Shanghai), Nanjing Road. Other major commercial areas include Xintiandi and Huaihai Road in Huangpu District, and Xujiahui in Xuhui District. Many List of universities and colleges in Shanghai, universities in Shanghai are located in residential areas in Yangpu District and Putuo District, Shanghai, Putuo District.Economy
 Shanghai has been described as the "showpiece" of the booming
Shanghai has been described as the "showpiece" of the booming economy of China
The China, People's Republic of China has an upper middle income Developing country, developing Mixed economy, mixed socialist market economy that incorporates economic planning through Industrial policy, industrial policies and strategic Five- ...
. The city is a global center for finance and Science and technology in China, innovation, and a national center for commerce, trade, and transportation, with the world's busiest container port—the Port of Shanghai
The Port of Shanghai (), located in the vicinity of Shanghai, comprises a deep-sea port and a river port.
The main port enterprise in Shanghai, the Shanghai International Port Group (SIPG), was established during the reconstitution of the S ...
. , Shanghai had a Gross Domestic Product, GDP of () that makes up 3.85% of China's GDP, and a GDP per capita of (). As of 2018, the Greater Shanghai metropolitan area, which includes Suzhou, Wuxi, Nantong, Ningbo, Jiaxing, Zhoushan, and Huzhou, was estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product ( nominal) of nearly 9.1 trillion RMB ($1.33 trillion), exceeding that of Mexico with GDP of $1.22 trillion, the 15th largest in the world. As of 2020, the economy of Shanghai was estimated to be $1 trillion (Purchasing power parity, PPP), ranking the most productive metro area of China and among the top ten List of cities by GDP, largest metropolitan economies in the world. Shanghai's six largest industries—retail, finance, IT, real estate, machine industry, machine manufacturing, and automotive manufacturing—comprise about half the city's GDP. In 2021, the average annual disposable income of Shanghai's residents was () per capita, making it one of the wealthiest cities in China, but also the most expensive city in mainland China to live in according to a 2017 study by the Economist Intelligence Unit.
In 2021, Shanghai was the most expensive city in the world. Shanghai was the 5th wealthiest city in the world, with a total wealth amounts to $1.8 trillion, and Shanghai was ranked List of cities by number of billionaires, fifth-highest in the number of billionaires by Forbes. Shanghai's nominal GDP was projected to reach US$1.3 trillion in 2035 (ranking first in China), making it one of the world's Top 5 major cities in terms of Gross regional product, GRP according to a study by Oxford Economics. As of August 2022, Shanghai ranked 5th in the world and 2nd in China (after Beijing) by the largest number of the Fortune Global 500#Fortune Global 500 of 2021, ''Fortune'' Global 500 companies in the world.
Shanghai was the largest and most prosperous city in East Asia during the 1930s, and its rapid redevelopment began in the 1990s. In the last two decades, Shanghai has been one of the fastest-developing cities in the world; it has recorded double-digit GDP growth in almost every year between 1992 and 2008, before the financial crisis of 2007–08.
Finance
Shanghai Stock Exchange
The Shanghai Stock Exchange (SSE) is a stock exchange based in the city of Shanghai, China. It is one of the three stock exchanges operating independently in mainland China, the others being the Beijing Stock Exchange and the Shenzhen Stock Exc ...
had a market capitalization of , making it the largest stock exchange in China and the List of stock exchanges, fourth-largest stock exchange in the world. In 2009, the trading volume of six key commodities—including rubber, copper, and zinc—on the Shanghai Futures Exchange all ranked first globally. By the end of 2017, Shanghai had 1,491 financial institutions, of which 251 were foreign-invested.
In September 2013 with the backing of Chinese Premier Li Keqiang, the city launched the China (Shanghai) Pilot Free-Trade Zone—the first free-trade zone in mainland China. The zone introduced a number of pilot reforms designed to incentivize foreign investment. In April 2014, ''The Banker'' reported that Shanghai "has attracted the highest volumes of financial sector foreign direct investment in the Asia-Pacific region in the 12 months to the end of January 2014". In August 2014, ''fDi magazine'' named Shanghai the "Chinese Province of the Future 2014/15" due to "particularly impressive performances in the Business Friendliness and Connectivity categories, as well as placing second in the Economic Potential and Human Capital and Lifestyle categories".
Manufacturing
Tourism
 Tourism is a major industry of Shanghai. In 2017, the number of domestic tourists increased by 7.5% to 318 million, while the number of overseas tourists increased by 2.2% to 8.73 million. In 2017, Shanghai was the highest earning tourist city in the world, which is expected to maintain until 2027. As of 2019, Shanghai had 71 five star hotel, five-star hotels, 61 four star hotels, 1,758 travel agencies, 113 Tourist Attraction Rating Categories of China, rated tourist attractions, and 34 Red tourism, red tourist attractions.
The conference and meeting sector is also growing. According to the International Congress and Convention Association, Shanghai hosted 82 international meetings in 2018, a 34% increase from 61 in 2017.
Tourism is a major industry of Shanghai. In 2017, the number of domestic tourists increased by 7.5% to 318 million, while the number of overseas tourists increased by 2.2% to 8.73 million. In 2017, Shanghai was the highest earning tourist city in the world, which is expected to maintain until 2027. As of 2019, Shanghai had 71 five star hotel, five-star hotels, 61 four star hotels, 1,758 travel agencies, 113 Tourist Attraction Rating Categories of China, rated tourist attractions, and 34 Red tourism, red tourist attractions.
The conference and meeting sector is also growing. According to the International Congress and Convention Association, Shanghai hosted 82 international meetings in 2018, a 34% increase from 61 in 2017.
Free-trade zone
Shanghai is home to China (Shanghai) Pilot Free-Trade Zone, the first free-trade zone in mainland China. , it is also the second largest free-trade zone in mainland China in terms of land area (behind , which covers the whole Hainan province) by covering an area of and integrating four existing bonded zones—Waigaoqiao Free Trade Zone, Waigaoqiao Free Trade Logistics Park, Yangshan Free Trade Port Area, and Pudong Airport Comprehensive Free Trade Zone. Several preferential policies have been implemented to attract foreign investment in various industries to the zone. Because the zone is not technically considered Chinese territory for tax purposes, commodities entering the zone are exempt from duty and customs clearance.Demographics
, Shanghai had a total population of 24,281,400, including 14,504,300 (59.7%) Hukou system, hukou holders (registered locally). According to the Sixth National Population Census of the People's Republic of China, 2010 national census, 89.3% of Shanghai's population live in urban areas, and 10.7% live in rural areas. Based on the population of its total administrative area, Shanghai is the second largest of the four municipalities of China, behindChongqing
Chongqing ( or ; ; Sichuanese dialects, Sichuanese pronunciation: , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ), Postal Romanization, alternately romanized as Chungking (), is a Direct-administered municipalities of China, municipality in Southwes ...
, but is generally considered the largest Chinese city because the urban population of Chongqing is much smaller. p. 395 According to the OECD, Shanghai's metropolitan area has an estimated population of 34 million.
According to the Shanghai Municipal Statistics Bureau, about 157,900 residents in Shanghai are foreigners, including 28,900 Japanese, 21,900 Americans and, 20,800 Koreans. The actual number of foreign citizens in the city is probably much higher. Shanghai is also a domestic immigration city—40.3% (9.8 million) of the city's residents are from other regions of China.
Shanghai has a life expectancy of 83.6 years for the city's registered population, the highest life expectancy of List of cities in China by life expectancy, all cities in mainland China. This has also caused the city to Aging of China, experience population aging—in 2017, 33.1% (4.8 million) of the city's registered population was aged 60 or above. In 2017, the Chinese government implemented population controls for Shanghai, resulting in a population decline of 10,000 people by the end of the year.
Religion
 Due to its cosmopolitan history, Shanghai has a blend of religious heritage; religious buildings and institutions are scattered around the city. According to a 2012 survey, only 13.1% of the city's population belongs to organized religions, including Buddhists with 10.4%, Protestants with 1.9%, Catholics with 0.7%, and other faiths with 0.1% while the remaining 86.9% of the population could be either atheists or involved in Chinese folk religion, worship of nature deities and ancestors or Chinese salvationist religions, folk religious sects.
Buddhism, in its Chinese Buddhism, Chinese varieties, has had a presence in Shanghai since the Three Kingdoms period, during which the Longhua Temple—the largest temple in Shanghai—and the Jing'an Temple were founded. Another significant temple is the Jade Buddha Temple, which was named after a large statue of Gautama Buddha, Buddha carved out of jade in the temple. , Buddhism in Shanghai had 114 temples, 1,182 Clergy#Buddhism, clergical staff, and 453,300 registered followers. The religion also has its own college, the , and its own press, .
Due to its cosmopolitan history, Shanghai has a blend of religious heritage; religious buildings and institutions are scattered around the city. According to a 2012 survey, only 13.1% of the city's population belongs to organized religions, including Buddhists with 10.4%, Protestants with 1.9%, Catholics with 0.7%, and other faiths with 0.1% while the remaining 86.9% of the population could be either atheists or involved in Chinese folk religion, worship of nature deities and ancestors or Chinese salvationist religions, folk religious sects.
Buddhism, in its Chinese Buddhism, Chinese varieties, has had a presence in Shanghai since the Three Kingdoms period, during which the Longhua Temple—the largest temple in Shanghai—and the Jing'an Temple were founded. Another significant temple is the Jade Buddha Temple, which was named after a large statue of Gautama Buddha, Buddha carved out of jade in the temple. , Buddhism in Shanghai had 114 temples, 1,182 Clergy#Buddhism, clergical staff, and 453,300 registered followers. The religion also has its own college, the , and its own press, .
 Catholicism was brought into Shanghai in 1608 by Italian missionary Lazzaro Cattaneo. The Apostolic Vicariate of Shanghai was erected in 1933, and was further elevated to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Shanghai, Diocese of Shanghai in 1946. Notable Catholic sites include the St. Ignatius Cathedral in Xujiahui—the largest Catholic church in the city, the St. Francis Xavier Church (Shanghai), St. Francis Xavier Church, and the She Shan Basilica. Other forms of Christianity in Shanghai include Eastern Orthodox minorities and, since 1996, registered Christian Protestant churches.
Although currently making up a fraction of the religious population in Shanghai, Jewish people have played an influential role in the city's history. After the Treaty of Nanking ended the
Catholicism was brought into Shanghai in 1608 by Italian missionary Lazzaro Cattaneo. The Apostolic Vicariate of Shanghai was erected in 1933, and was further elevated to the Roman Catholic Diocese of Shanghai, Diocese of Shanghai in 1946. Notable Catholic sites include the St. Ignatius Cathedral in Xujiahui—the largest Catholic church in the city, the St. Francis Xavier Church (Shanghai), St. Francis Xavier Church, and the She Shan Basilica. Other forms of Christianity in Shanghai include Eastern Orthodox minorities and, since 1996, registered Christian Protestant churches.
Although currently making up a fraction of the religious population in Shanghai, Jewish people have played an influential role in the city's history. After the Treaty of Nanking ended the First Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
in 1842, the city was opened up to western populations and merchants traveled to Shanghai for its rich business potential, including many prominent Jewish families. The Sassoon family, Sassoons amassed great wealth in the opium and textile trades, cementing their status by funding many of the buildings that have become iconic in Shanghai's skyline, such as the Cathay Hotel in 1929. The Hardoons were another prominent Baghdadi Jewish family that used their business success to define Shanghai in the 20th century. The head of the family, Silas Hardoon, one of the richest people in the world during the 1800s, financed Nanjing Road, which then housed departmental stores in the International Settlement, that is now one of the busiest shopping centers in the world.
During World War II, thousands of Jews emigrated to Shanghai in an effort to flee Nazi Germany. They lived in a designated area called the Shanghai Ghetto and formed a community centered on the Ohel Moishe Synagogue, which is now the Shanghai Jewish Refugees Museum. In 1939, Horace Kadoorie, the head of the powerful philanthropic Sephardic Jewish family in Shanghai, founded the Shanghai Jewish Youth Association to support Jewish refugees through English education so they would be prepared to emigrate from Shanghai when the time came.
Islam came into Shanghai during the Yuan dynasty. The city's first mosque, Songjiang Mosque, was built during the Zhizheng () era under Toghon Temür, Emperor Huizong. Shanghai's Muslim population increased in the 19th and early 20th centuries (when the city was a treaty port), during which time many mosques—including the Xiaotaoyuan Mosque, the Huxi Mosque, and the Pudong Mosque—were built. The Shanghai Islamic Association is located in the Xiaotaoyuan Mosque in Huangpu.
Shanghai has several folk religious temples, including the City God Temple at the heart of the Old City, the Dajing Ge Pavilion dedicated to the Three Kingdoms general Guan Yu, the Confucian Temple of Shanghai, and a major Taoist center where the Shanghai Taoist Association locates.
Language
The vernacular language spoken in the city is Shanghainese, a dialect of the Taihu Wu subgroup of the Wu Chinese family. This is different from the official Chinese dialect, Standard Chinese, Mandarin, which is mutually unintelligible with Wu Chinese. Modern Shanghainese is based on other dialects of Taihu Wu: Suzhou dialect, Suzhounese, Ningbo dialect, Ningbonese, and the local dialect of Songjiang Prefecture. Prior to its expansion, the language spoken in Shanghai was subordinate to those spoken around Jiaxing and later Suzhou, and was known as "the local tongue" (), which is now being used in suburbs only. In the late 19th century, downtown Shanghainese () appeared, undergoing rapid changes and quickly replacing Suzhounese as the prestige dialect of the Yangtze River Delta region. At the time, most of the city's residents were immigrants from the two adjacent provinces, Jiangsu and Zhejiang, so Shanghainese was mostly a hybrid between Southern Jiangsu and Ningbo dialects. After 1949, Putonghua (Standard Mandarin) has also had a great impact on Shanghainese as a result of being rigorously promoted by the government. Since the 1990s, many migrants outside of the Wu-speaking region have come to Shanghai for education and jobs. They often cannot speak the local language and therefore use Putonghua as a lingua franca. Because Putonghua and English were more favored, Shanghainese began to decline, and fluency among young speakers weakened. In recent years, there have been movements within the city to promote the local language and protect it from fading out. Notable people: * Xu Guangqi (徐光启):(ad 1562-ad 1633) Christian, high-ranking official and scientist of the Ming dynasty. * Desmond Shum (沈桐):entrepreneur, author of the book: ''Red Roulette'' * Tingyu Fang: Chinese professor of English.Education and research
 Shanghai is an international center of research and development and as of 2022, it was ranked List of cities by scientific output, 3rd globally and 2nd in the whole Asia & Oceania region (after Beijing) by scientific research outputs, as tracked by the Nature Index. It is also a major center of higher education in China. As of 2022, Shanghai had 64 universities and colleges, ranking first in East China region as a city with most higher education institutions. Shanghai has many highly ranked educational institutions, with 15 universities listed in Double First Class University Plan, 147 Double First-Class Universities ranking second nationwide among all cities in China (after Beijing). A number of Rankings of universities in China, China's most prestigious universities appearing in the global university rankings are based in Shanghai, including Fudan University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Tongji University, East China Normal University, Shanghai University, East China University of Science and Technology, Donghua University,
Shanghai is an international center of research and development and as of 2022, it was ranked List of cities by scientific output, 3rd globally and 2nd in the whole Asia & Oceania region (after Beijing) by scientific research outputs, as tracked by the Nature Index. It is also a major center of higher education in China. As of 2022, Shanghai had 64 universities and colleges, ranking first in East China region as a city with most higher education institutions. Shanghai has many highly ranked educational institutions, with 15 universities listed in Double First Class University Plan, 147 Double First-Class Universities ranking second nationwide among all cities in China (after Beijing). A number of Rankings of universities in China, China's most prestigious universities appearing in the global university rankings are based in Shanghai, including Fudan University, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Tongji University, East China Normal University, Shanghai University, East China University of Science and Technology, Donghua University, Shanghai University of Finance and Economics
The Shanghai University of Finance and Economics (SUFE; ), founded in 1917, is a finance- and economics-oriented research university located in Shanghai, the People's Republic of China. The university is under the direct administration of the ...
, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai International Studies University, University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, Shanghai University of Electric Power, Shanghai Normal University, Shanghai Maritime University, Second Military Medical University, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai Ocean University, Shanghai University of Engineering Science, Shanghai Institute of Technology, Shanghai Conservatory of Music and Shanghai University of Sport. Some of these universities were selected as "Project 985, 985 universities" or "Project 211, 211 universities" since the 90s by the Chinese government in order to build world-class universities.
Shanghai is a seat of two members (Fudan University and Shanghai Jiao Tong University) of the C9 League, an alliance of elite Chinese universities offering comprehensive and leading education, and these two universities are ranked in the global top 100 Research university, research comprehensive universities according to the most influential university rankings in the world such as QS Rankings, Shanghai rankings, Shanghai Rankings, and Times Higher Education World University Rankings, Times Higher Education Rankings. The other two members of the "Project 985", Tongji University and East China Normal University, are also based in Shanghai and internationally; they are regarded as one of the most reputable Chinese universities by the ''Times Higher Education World Reputation Rankings'' where they ranked 150-175th globally.
Fudan University established a joint Executive MBA, EMBA program with Washington University in St. Louis in 2002 which has since consistently been ranked as one of the best in the world.
 The city has many , such as the Shanghai University–University of Technology Sydney Business School since 1994, the University of Michigan–Shanghai Jiao Tong University Joint Institute since 2006, and New York University Shanghai—the first China–U.S. joint venture university—since 2012. In 2013, the Shanghai Municipality and the Chinese Academy of Sciences founded the ShanghaiTech University in the Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park in Pudong. Shanghai is also home to the cadre school China Executive Leadership Academy in Pudong and the China Europe International Business School. The city government's education agency is the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission.
The city is also a seat of the Shanghai Academy of Social Sciences, China, China's oldest think tank for the humanities and social sciences. It is the largest one outside the capital of Beijing after the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS).
By the end of 2019, the city also had 929 secondary schools, 698 primary schools, and 31 special schools. In Shanghai, the nine years of compulsory education—including five years of primary education and four years of Education in China#Junior secondary, junior secondary education—are free, with a gross enrollment ratio of over 99.9%. The city's compulsory education system is among the best in the world: in 2009 and 2012, 15-year-old students from Shanghai ranked first in every subject (math, reading, and science) in the Program for International Student Assessment, a worldwide study of academic performance conducted by the OECD. The consecutive three-year senior secondary education is priced and uses the Senior High School Entrance Examination (''Zhongkao'') as a selection process, with a gross enrollment ratio of 98%. Among all senior high schools, the four with the best teaching quality—Shanghai High School, No. 2 High School Attached to East China Normal University, High School Affiliated to Fudan University, and High School Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University—are termed "The Four Schools" () of Shanghai. , the city's National College Entrance Examination (''Gaokao'') is structured under the "3+3" system, in which all general senior high school students study three compulsory subjects (Chinese, English, and math) and three subjects chosen from six options (physics, chemistry, biology, history, geography, and politics).
The city has many , such as the Shanghai University–University of Technology Sydney Business School since 1994, the University of Michigan–Shanghai Jiao Tong University Joint Institute since 2006, and New York University Shanghai—the first China–U.S. joint venture university—since 2012. In 2013, the Shanghai Municipality and the Chinese Academy of Sciences founded the ShanghaiTech University in the Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park in Pudong. Shanghai is also home to the cadre school China Executive Leadership Academy in Pudong and the China Europe International Business School. The city government's education agency is the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission.
The city is also a seat of the Shanghai Academy of Social Sciences, China, China's oldest think tank for the humanities and social sciences. It is the largest one outside the capital of Beijing after the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS).
By the end of 2019, the city also had 929 secondary schools, 698 primary schools, and 31 special schools. In Shanghai, the nine years of compulsory education—including five years of primary education and four years of Education in China#Junior secondary, junior secondary education—are free, with a gross enrollment ratio of over 99.9%. The city's compulsory education system is among the best in the world: in 2009 and 2012, 15-year-old students from Shanghai ranked first in every subject (math, reading, and science) in the Program for International Student Assessment, a worldwide study of academic performance conducted by the OECD. The consecutive three-year senior secondary education is priced and uses the Senior High School Entrance Examination (''Zhongkao'') as a selection process, with a gross enrollment ratio of 98%. Among all senior high schools, the four with the best teaching quality—Shanghai High School, No. 2 High School Attached to East China Normal University, High School Affiliated to Fudan University, and High School Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University—are termed "The Four Schools" () of Shanghai. , the city's National College Entrance Examination (''Gaokao'') is structured under the "3+3" system, in which all general senior high school students study three compulsory subjects (Chinese, English, and math) and three subjects chosen from six options (physics, chemistry, biology, history, geography, and politics).
Transportation
Public

 Shanghai has an extensive public transportation system comprising metros, buses, ferries, and taxis, all of which can be accessed using a Shanghai Public Transport Card.
Shanghai's rapid transit system, the Shanghai Metro, incorporates both subway and light metro lines and extends to every core urban district as well as neighboring suburban districts. , there are 19 metro lines (excluding the Shanghai maglev train and Jinshan Railway), 515 List of Shanghai Metro stations, stations, and of lines in operation, making it the List of metro systems, longest network in the world. On 8 March 2019, it set the city's daily metro ridership record with 13.3 million. The average fare ranges from () to (), depending on the travel distance.
Opened in 2004, the Shanghai maglev train is the first and the fastest commercial high-speed maglev in the world, with a maximum operation speed of . The train can complete the journey between Longyang Road Station and Pudong International Airport in 7 minutes 20 seconds, comparing to 32 minutes by Line 2 (Shanghai Metro), Metro Line 2 and 30 minutes by car. A one-way ticket costs (), or () for those with airline tickets or public transportation cards. A round-trip ticket costs (), and VIP tickets cost double the standard fare.
With the first tram line been in service in 1908, trams were once popular Trams in Shanghai, in Shanghai in the early 20th century. By 1925, there were 328 tramcars and 14 routes operated by Chinese, French, and British companies collaboratively, all of which were nationalized after the PRC's victory in 1949. Since the 1960s, many tram lines were either dismantled or replaced by trolleybus or motorbus lines; the last tram line was demolished in 1975. Shanghai reintroduced trams in 2010, as a modern rubber-tire Translohr system in Zhangjiang area of East Shanghai as Zhangjiang Tram. In 2018, the steel wheeled Songjiang Tram started operating in Songjiang District. Additional tram lines are under planning in Hongqiao Subdistrict, Shanghai, Hongqiao Subdistrict and Jiading District .
Shanghai has an extensive public transportation system comprising metros, buses, ferries, and taxis, all of which can be accessed using a Shanghai Public Transport Card.
Shanghai's rapid transit system, the Shanghai Metro, incorporates both subway and light metro lines and extends to every core urban district as well as neighboring suburban districts. , there are 19 metro lines (excluding the Shanghai maglev train and Jinshan Railway), 515 List of Shanghai Metro stations, stations, and of lines in operation, making it the List of metro systems, longest network in the world. On 8 March 2019, it set the city's daily metro ridership record with 13.3 million. The average fare ranges from () to (), depending on the travel distance.
Opened in 2004, the Shanghai maglev train is the first and the fastest commercial high-speed maglev in the world, with a maximum operation speed of . The train can complete the journey between Longyang Road Station and Pudong International Airport in 7 minutes 20 seconds, comparing to 32 minutes by Line 2 (Shanghai Metro), Metro Line 2 and 30 minutes by car. A one-way ticket costs (), or () for those with airline tickets or public transportation cards. A round-trip ticket costs (), and VIP tickets cost double the standard fare.
With the first tram line been in service in 1908, trams were once popular Trams in Shanghai, in Shanghai in the early 20th century. By 1925, there were 328 tramcars and 14 routes operated by Chinese, French, and British companies collaboratively, all of which were nationalized after the PRC's victory in 1949. Since the 1960s, many tram lines were either dismantled or replaced by trolleybus or motorbus lines; the last tram line was demolished in 1975. Shanghai reintroduced trams in 2010, as a modern rubber-tire Translohr system in Zhangjiang area of East Shanghai as Zhangjiang Tram. In 2018, the steel wheeled Songjiang Tram started operating in Songjiang District. Additional tram lines are under planning in Hongqiao Subdistrict, Shanghai, Hongqiao Subdistrict and Jiading District .
 Shanghai also has the world's most extensive Buses in Shanghai, bus network, including the world's oldest continuously operating Trolleybuses in Shanghai, trolleybus system, with 1,575 lines covering a total length of by 2019. The system is operated by multiple companies. Bus fares generally cost ().
, a total of 40,000 taxis were in operation in Shanghai. The base fare for taxis is (), which covers the first and includes a () fuel surcharge. The base fare is () between 11:00 pm and 5:00 am. Each additional kilometer costs (), or () between 11:00 pm and 5:00 am. Taxicabs and DiDi play major roles in urban transportation and DiDi is often cheaper than taxis.
As of January 2021, Shanghai Metro has 459 stations and 772 km. The scale of operation is the first in the world. in 2017, the average daily passenger traffic of the Shanghai metro was 9.693 million, and the total passenger traffic reached 3.538 billion. It is one of the busiest metro cities in the world. The metro lines cover the central city densely and connect most districts and counties.
Shanghai also has the world's most extensive Buses in Shanghai, bus network, including the world's oldest continuously operating Trolleybuses in Shanghai, trolleybus system, with 1,575 lines covering a total length of by 2019. The system is operated by multiple companies. Bus fares generally cost ().
, a total of 40,000 taxis were in operation in Shanghai. The base fare for taxis is (), which covers the first and includes a () fuel surcharge. The base fare is () between 11:00 pm and 5:00 am. Each additional kilometer costs (), or () between 11:00 pm and 5:00 am. Taxicabs and DiDi play major roles in urban transportation and DiDi is often cheaper than taxis.
As of January 2021, Shanghai Metro has 459 stations and 772 km. The scale of operation is the first in the world. in 2017, the average daily passenger traffic of the Shanghai metro was 9.693 million, and the total passenger traffic reached 3.538 billion. It is one of the busiest metro cities in the world. The metro lines cover the central city densely and connect most districts and counties.
Roads and expressways
 Shanghai is a major hub of Expressways of China, China's expressway network. Many national expressways (prefixed with the letter G) pass through or end in Shanghai, including G2 Beijing–Shanghai Expressway, Jinghu Expressway (overlaps with G42 Shanghai–Chengdu Expressway, Hurong Expressway), G15 Shenyang–Haikou Expressway, Shenhai Expressway, G40 Shanghai–Xi'an Expressway, Hushaan Expressway, G50 Shanghai–Chongqing Expressway, Huyu Expressway, G60 Shanghai–Kunming Expressway, Hukun Expressway (overlaps with G92 Hangzhou Bay Ring Expressway, Hangzhou Bay Ring Expressway), and G1503 Shanghai Ring Expressway, Shanghai Ring Expressway. There are also numerous municipal expressways prefixed with the letter S. As of 2019, Shanghai has a total of 12 bridges and 14 tunnels crossing the Huangpu River. The Shanghai Yangtze River Bridge is the city's only Yangtze River bridges and tunnels, bridge–tunnel complex across Yangtze River.
The expressway network within the city center consists of North–South Elevated Road (Shanghai), North–South Elevated Road, Yan'an Elevated Road, and Inner Ring Road (Shanghai), Inner Ring Road. Other ring roads in Shanghai include Middle Ring Road (Shanghai), Middle Ring Road, Shanghai Outer Ring Expressway, Outer Ring Expressway, and Shanghai Ring Expressway.
Shanghai is a major hub of Expressways of China, China's expressway network. Many national expressways (prefixed with the letter G) pass through or end in Shanghai, including G2 Beijing–Shanghai Expressway, Jinghu Expressway (overlaps with G42 Shanghai–Chengdu Expressway, Hurong Expressway), G15 Shenyang–Haikou Expressway, Shenhai Expressway, G40 Shanghai–Xi'an Expressway, Hushaan Expressway, G50 Shanghai–Chongqing Expressway, Huyu Expressway, G60 Shanghai–Kunming Expressway, Hukun Expressway (overlaps with G92 Hangzhou Bay Ring Expressway, Hangzhou Bay Ring Expressway), and G1503 Shanghai Ring Expressway, Shanghai Ring Expressway. There are also numerous municipal expressways prefixed with the letter S. As of 2019, Shanghai has a total of 12 bridges and 14 tunnels crossing the Huangpu River. The Shanghai Yangtze River Bridge is the city's only Yangtze River bridges and tunnels, bridge–tunnel complex across Yangtze River.
The expressway network within the city center consists of North–South Elevated Road (Shanghai), North–South Elevated Road, Yan'an Elevated Road, and Inner Ring Road (Shanghai), Inner Ring Road. Other ring roads in Shanghai include Middle Ring Road (Shanghai), Middle Ring Road, Shanghai Outer Ring Expressway, Outer Ring Expressway, and Shanghai Ring Expressway.
 Bicycle lanes are common in Shanghai, separating non-motorized traffic from car traffic on most surface streets. However, on some main roads, including all expressways, bicycles and motorcycles are banned. In recent years, cycling has seen a resurgence in popularity due to the emergence of a large number of dockless app-based bicycle-sharing systems, such as Mobike, Bluegogo, and ofo (company), ofo. , bicycle-sharing systems had an average of 1.15 million daily riders within the city.
Private car ownership in Shanghai is rapidly increasing: in 2019, there were 3.40 million private cars in the city, a 12.5% increase from 2018. New private cars cannot be driven without a license plate, which are sold in monthly license plate auctions. Around 9,500 license plates are auctioned each month, and the average price is about () in 2019. According to the city's vehicle regulations introduced in June 2016, only locally registered residents and those who have paid social insurance or individual income taxes for over three years are eligible to be in the auction. The purpose of this policy is to limit the growth of automobile traffic and alleviate congestion.
Bicycle lanes are common in Shanghai, separating non-motorized traffic from car traffic on most surface streets. However, on some main roads, including all expressways, bicycles and motorcycles are banned. In recent years, cycling has seen a resurgence in popularity due to the emergence of a large number of dockless app-based bicycle-sharing systems, such as Mobike, Bluegogo, and ofo (company), ofo. , bicycle-sharing systems had an average of 1.15 million daily riders within the city.
Private car ownership in Shanghai is rapidly increasing: in 2019, there were 3.40 million private cars in the city, a 12.5% increase from 2018. New private cars cannot be driven without a license plate, which are sold in monthly license plate auctions. Around 9,500 license plates are auctioned each month, and the average price is about () in 2019. According to the city's vehicle regulations introduced in June 2016, only locally registered residents and those who have paid social insurance or individual income taxes for over three years are eligible to be in the auction. The purpose of this policy is to limit the growth of automobile traffic and alleviate congestion.
Railways
 Shanghai has four major railway stations: Shanghai railway station, Shanghai South railway station, Shanghai West railway station, and Shanghai Hongqiao railway station. All are connected to the metro network and serve as hubs in the Rail transport in the People's Republic of China, railway network of China. And now Shanghai has around twenty railway lines running under this city, which largely facilitate people's life in Shanghai.
Built in 1876, the Woosung Road, Woosung railway was the first railway in Shanghai and the first railway in operation in China By 1909, Shanghai–Nanjing railway and Shanghai–Hangzhou railway were in service. , the two railways have been integrated into two main railways in China: Beijing–Shanghai railway and Shanghai–Kunming railway, respectively.
Shanghai has four high-speed railways (HSRs): Beijing–Shanghai high-speed railway, Beijing–Shanghai HSR (overlaps with Shanghai–Wuhan–Chengdu passenger railway), Shanghai–Nanjing intercity railway, Shanghai–Kunming high-speed railway, Shanghai–Kunming HSR, and Shanghai–Nantong railway. One HSR is under construction: Shanghai–Suzhou–Huzhou high-speed railway, Shanghai–Suzhou–Huzhou HSR.
Shanghai also has four Shanghai Metropolitan Area Intercity Railway, commuter railways: Pudong railway (passenger service is currently suspended) and Jinshan railway operated by China Railway, and Line 16 (Shanghai Metro), Line 16 and Line 17 (Shanghai Metro), Line 17 operated by Shanghai Metro. , four additional lines—Chongming line, Jiamin line, Airport Link line (Shanghai), Airport link line and Lianggang Express line—are under construction.
Shanghai has four major railway stations: Shanghai railway station, Shanghai South railway station, Shanghai West railway station, and Shanghai Hongqiao railway station. All are connected to the metro network and serve as hubs in the Rail transport in the People's Republic of China, railway network of China. And now Shanghai has around twenty railway lines running under this city, which largely facilitate people's life in Shanghai.
Built in 1876, the Woosung Road, Woosung railway was the first railway in Shanghai and the first railway in operation in China By 1909, Shanghai–Nanjing railway and Shanghai–Hangzhou railway were in service. , the two railways have been integrated into two main railways in China: Beijing–Shanghai railway and Shanghai–Kunming railway, respectively.
Shanghai has four high-speed railways (HSRs): Beijing–Shanghai high-speed railway, Beijing–Shanghai HSR (overlaps with Shanghai–Wuhan–Chengdu passenger railway), Shanghai–Nanjing intercity railway, Shanghai–Kunming high-speed railway, Shanghai–Kunming HSR, and Shanghai–Nantong railway. One HSR is under construction: Shanghai–Suzhou–Huzhou high-speed railway, Shanghai–Suzhou–Huzhou HSR.
Shanghai also has four Shanghai Metropolitan Area Intercity Railway, commuter railways: Pudong railway (passenger service is currently suspended) and Jinshan railway operated by China Railway, and Line 16 (Shanghai Metro), Line 16 and Line 17 (Shanghai Metro), Line 17 operated by Shanghai Metro. , four additional lines—Chongming line, Jiamin line, Airport Link line (Shanghai), Airport link line and Lianggang Express line—are under construction.
Air and sea
 Shanghai is one of the largest air transportation hubs in Asia. The city has two commercial airports: Shanghai Pudong International Airport and Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport. Pudong International Airport is the primary international airport, while Hongqiao International Airport mainly operates domestic flights with limited short-haul international flights. In 2018, Pudong International Airport served 74.0 million passengers and handled 3.8 million tons of cargo, making it the ninth-busiest airport by passenger volume and third-busiest airport by cargo volume. The same year, Hongqiao International Airport served 43.6 million passengers, making it the 19th-busiest airport by passenger volume.
Shanghai is one of the largest air transportation hubs in Asia. The city has two commercial airports: Shanghai Pudong International Airport and Shanghai Hongqiao International Airport. Pudong International Airport is the primary international airport, while Hongqiao International Airport mainly operates domestic flights with limited short-haul international flights. In 2018, Pudong International Airport served 74.0 million passengers and handled 3.8 million tons of cargo, making it the ninth-busiest airport by passenger volume and third-busiest airport by cargo volume. The same year, Hongqiao International Airport served 43.6 million passengers, making it the 19th-busiest airport by passenger volume.
 Since its opening, the Port of Shanghai has rapidly grown to become the largest port in China. Yangshan Port was built in 2005 because the river was unsuitable for docking large container ships. The port is connected with the mainland through the long Donghai Bridge. Although the port is run by the Shanghai International Port Group under the government of Shanghai, it administratively belongs to Shengsi County, Zhejiang.
Overtaking the Port of Singapore in 2010, the Port of Shanghai has become List of world's busiest container ports, world's busiest container port with an annual twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEU transportation of 42 million in 2018.One Hundred Ports 2019
Since its opening, the Port of Shanghai has rapidly grown to become the largest port in China. Yangshan Port was built in 2005 because the river was unsuitable for docking large container ships. The port is connected with the mainland through the long Donghai Bridge. Although the port is run by the Shanghai International Port Group under the government of Shanghai, it administratively belongs to Shengsi County, Zhejiang.
Overtaking the Port of Singapore in 2010, the Port of Shanghai has become List of world's busiest container ports, world's busiest container port with an annual twenty-foot equivalent unit, TEU transportation of 42 million in 2018.One Hundred Ports 2019Lloyd's List,2019 Besides cargo, the Port of Shanghai handled 259 cruises and 1.89 million passengers in 2019. Shanghai is part of the 21st Century Maritime Silk Road that runs from the Chinese coast to the south via the southern tip of India to Mombasa, from there to the Mediterranean, there to the Upper Adriatic region to the northern Italian hub of Trieste with its rail connections to Central Europe, Central and the Eastern Europe.
Culture
 The culture of Shanghai was formed by a combination of the nearby Wuyue culture and the "East Meets West" Haipai culture. Wuyue culture's influence is manifested in Shanghainese language—which comprises dialectal elements from nearby Jiaxing, Suzhou, and Ningbo—and Shanghai cuisine, which was influenced by Jiangsu cuisine and Zhejiang cuisine. Haipai culture emerged after Shanghai became a prosperous port in the early 20th century, with numerous foreigners from Europe, America, Japan, and India moving into the city. The culture fuses elements of Western cultures with the local Wuyue culture, and its influence extends to the city's literature, fashion, architecture, music, and cuisine. The term Haipai—originally referring to a painting school in Shanghai—was coined by a group of Beijing writers in 1920 to criticize some Shanghai scholars for admiring capitalism and Western culture. In the early 21st century, Shanghai has been recognized as a new influence and inspiration for cyberpunk culture. Futuristic structures, such as the Oriental Pearl Tower and the neon-illuminated Yan'an Elevated Road, are examples that have boosted Shanghai's cyberpunk image.
The culture of Shanghai was formed by a combination of the nearby Wuyue culture and the "East Meets West" Haipai culture. Wuyue culture's influence is manifested in Shanghainese language—which comprises dialectal elements from nearby Jiaxing, Suzhou, and Ningbo—and Shanghai cuisine, which was influenced by Jiangsu cuisine and Zhejiang cuisine. Haipai culture emerged after Shanghai became a prosperous port in the early 20th century, with numerous foreigners from Europe, America, Japan, and India moving into the city. The culture fuses elements of Western cultures with the local Wuyue culture, and its influence extends to the city's literature, fashion, architecture, music, and cuisine. The term Haipai—originally referring to a painting school in Shanghai—was coined by a group of Beijing writers in 1920 to criticize some Shanghai scholars for admiring capitalism and Western culture. In the early 21st century, Shanghai has been recognized as a new influence and inspiration for cyberpunk culture. Futuristic structures, such as the Oriental Pearl Tower and the neon-illuminated Yan'an Elevated Road, are examples that have boosted Shanghai's cyberpunk image.
Museums
 Cultural curation in Shanghai has seen significant growth since 2013, with several new museums having been opened in the city. This is in part due to the city's 2018 development plans, which aim to make Shanghai "an excellent global city". As such, Shanghai has several museums of regional and national importance. The Shanghai Museum has one of the largest collections of Chinese artifacts in the world, including a large collection of ancient Chinese bronzes and Chinese ceramics, ceramics. The China Art Museum, located in the former China Pavilion of Expo 2010, is one of the largest museums in Asia and displays an animated replica of the 12th century painting Along the River During the Qingming Festival. The Shanghai Natural History Museum and the Shanghai Science and Technology Museum are notable natural history and science museums. In addition, there are numerous smaller, specialist museums housed in important archeological and historical sites, such as the Songze culture, Songze Museum, the Museum of the First National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, the site of the former Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea, the Shanghai Jewish Refugees Museum, and the Shanghai Post Office Museum (located in the General Post Office Building, Shanghai, General Post Office Building).
Cultural curation in Shanghai has seen significant growth since 2013, with several new museums having been opened in the city. This is in part due to the city's 2018 development plans, which aim to make Shanghai "an excellent global city". As such, Shanghai has several museums of regional and national importance. The Shanghai Museum has one of the largest collections of Chinese artifacts in the world, including a large collection of ancient Chinese bronzes and Chinese ceramics, ceramics. The China Art Museum, located in the former China Pavilion of Expo 2010, is one of the largest museums in Asia and displays an animated replica of the 12th century painting Along the River During the Qingming Festival. The Shanghai Natural History Museum and the Shanghai Science and Technology Museum are notable natural history and science museums. In addition, there are numerous smaller, specialist museums housed in important archeological and historical sites, such as the Songze culture, Songze Museum, the Museum of the First National Congress of the Chinese Communist Party, the site of the former Provisional Government of the Republic of Korea, the Shanghai Jewish Refugees Museum, and the Shanghai Post Office Museum (located in the General Post Office Building, Shanghai, General Post Office Building).
Cuisine
Benbang cuisine () is cooking style that originated in the 1600s, with influences from surrounding provinces. It emphasizes the use of condiments while retaining the original flavors of the raw ingredients. Sugar is an important ingredient in Benbang cuisine, especially when used in combination with soy sauce. Signature dishes of Benbang cuisine include Xiaolongbao, Red braised pork belly, and Chinese mitten crab, Shanghai hairy crab. Haipai cuisine, on the other hand, is a Western-influenced cooking style that originated in Shanghai. It absorbed elements from French, British, Russian, German, and Italian cuisines and adapted them to suit the local taste according to the features of local ingredients. Famous dishes of Haipai cuisine include Shanghai-style borscht (, "Russian soup"), crispy pork cutlets, and Shanghai salad derived from Olivier salad. Both Benbang and Haipai cuisine make use of a variety of seafood, including freshwater fish, shrimps, and crabs.Arts
 The Songjiang School (), containing the Huating School () founded by Gu Zhengyi, was a small painting school in Shanghai during the Ming and Qing Dynasties. It was represented by Dong Qichang. The school was considered an expansion of the Wu School in Suzhou, the cultural center of the Jiangnan region at the time. In the mid 19th century, the Shanghai School movement commenced, focusing less on the symbolism emphasized by the Ink wash painting, Literati style but more on the visual content of painting through the use of bright colors. Secular objects like flowers and birds were often selected as themes. Western art was introduced to Shanghai in 1847 by Spanish missionary Joannes Ferrer (), and the city's first Western atelier was established in 1864 inside the . During the Republic of China, many famous artists including Zhang Daqian, Liu Haisu, Xu Beihong, Feng Zikai, and Yan Wenliang settled in Shanghai, allowing it to gradually become the art center of China. Various art forms—including photography, wood carving, sculpture, comics (Manhua), and Lianhuanhua—thrived. Sanmao (comics), Sanmao was created to dramatize the chaos created by the Second Sino-Japanese War. Today, the most comprehensive art and cultural facility in Shanghai is the China Art Museum. In addition, the Chinese Painting Academy features traditional Chinese painting, while the Power Station of Art displays contemporary art. The city also has many art galleries, many of which are located in the M50 Art District and Tianzifang. First held in 1996, the Shanghai Biennale has become an important place for Chinese and foreign arts to interact.
The Songjiang School (), containing the Huating School () founded by Gu Zhengyi, was a small painting school in Shanghai during the Ming and Qing Dynasties. It was represented by Dong Qichang. The school was considered an expansion of the Wu School in Suzhou, the cultural center of the Jiangnan region at the time. In the mid 19th century, the Shanghai School movement commenced, focusing less on the symbolism emphasized by the Ink wash painting, Literati style but more on the visual content of painting through the use of bright colors. Secular objects like flowers and birds were often selected as themes. Western art was introduced to Shanghai in 1847 by Spanish missionary Joannes Ferrer (), and the city's first Western atelier was established in 1864 inside the . During the Republic of China, many famous artists including Zhang Daqian, Liu Haisu, Xu Beihong, Feng Zikai, and Yan Wenliang settled in Shanghai, allowing it to gradually become the art center of China. Various art forms—including photography, wood carving, sculpture, comics (Manhua), and Lianhuanhua—thrived. Sanmao (comics), Sanmao was created to dramatize the chaos created by the Second Sino-Japanese War. Today, the most comprehensive art and cultural facility in Shanghai is the China Art Museum. In addition, the Chinese Painting Academy features traditional Chinese painting, while the Power Station of Art displays contemporary art. The city also has many art galleries, many of which are located in the M50 Art District and Tianzifang. First held in 1996, the Shanghai Biennale has become an important place for Chinese and foreign arts to interact. Traditional Chinese opera (Xiqu) became a popular source of public entertainment in the late 19th century. In the early 20th century, monologue and burlesque in Shanghainese appeared, absorbing elements from traditional dramas. The Great World opened in 1912 and was a significant stage at the time. In the 1920s, Suzhou Pingtan, Pingtan expanded from Suzhou to Shanghai. Pingtan art developed rapidly to 103 programs every day by the 1930s because of the abundant commercial radio stations in the city. Around the same time, a Shanghai-style Beijing Opera was formed. Led by Zhou Xinfang and , it attracted many Xiqu masters, like Mei Lanfang, to the city. A small troupe from Shengxian (now Shengzhou) also began to promote Yue opera on the Shanghainese stage. A unique style of opera, Shanghai opera, was formed when local folksongs were fused with modern operas. As of 2012, prominent troupes in Shanghai include Shanghai Jingju Theatre Company, , Shanghai Yue Opera House, and Shanghai Huju Opera House.
Drama appeared in Mission school, missionary schools in Shanghai in the late 19th century. At the time, it was mainly performed in English. ''Scandals in Officialdom'' (), staged in 1899, was one of the earliest-recorded plays. In 1907, ''Uncle Tom's Cabin; or, Life Among the Lowly'' () was performed at the . After the New Culture Movement, drama became a popular way for students and intellectuals to express their views. The city has several major institutes of theater training, including the Shanghai Conservatory of Music, the Shanghai Dramatic Arts Centre, the Shanghai Opera House, and the Shanghai Theatre Academy. Notable theaters in Shanghai include the Shanghai Grand Theatre, the Oriental Art Center, and the People's Theatre.
Traditional Chinese opera (Xiqu) became a popular source of public entertainment in the late 19th century. In the early 20th century, monologue and burlesque in Shanghainese appeared, absorbing elements from traditional dramas. The Great World opened in 1912 and was a significant stage at the time. In the 1920s, Suzhou Pingtan, Pingtan expanded from Suzhou to Shanghai. Pingtan art developed rapidly to 103 programs every day by the 1930s because of the abundant commercial radio stations in the city. Around the same time, a Shanghai-style Beijing Opera was formed. Led by Zhou Xinfang and , it attracted many Xiqu masters, like Mei Lanfang, to the city. A small troupe from Shengxian (now Shengzhou) also began to promote Yue opera on the Shanghainese stage. A unique style of opera, Shanghai opera, was formed when local folksongs were fused with modern operas. As of 2012, prominent troupes in Shanghai include Shanghai Jingju Theatre Company, , Shanghai Yue Opera House, and Shanghai Huju Opera House.
Drama appeared in Mission school, missionary schools in Shanghai in the late 19th century. At the time, it was mainly performed in English. ''Scandals in Officialdom'' (), staged in 1899, was one of the earliest-recorded plays. In 1907, ''Uncle Tom's Cabin; or, Life Among the Lowly'' () was performed at the . After the New Culture Movement, drama became a popular way for students and intellectuals to express their views. The city has several major institutes of theater training, including the Shanghai Conservatory of Music, the Shanghai Dramatic Arts Centre, the Shanghai Opera House, and the Shanghai Theatre Academy. Notable theaters in Shanghai include the Shanghai Grand Theatre, the Oriental Art Center, and the People's Theatre.
 Shanghai is considered to be the birthplace of Cinema of China, Chinese cinema. China's first short film, ''The Difficult Couple'' (1913), and the country's first fictional feature film, ''An Orphan Rescues His Grandfather'' (, 1923) were both produced in Shanghai. Shanghai's film industry grew during the early 1930s, generating stars such as Hu Die, Ruan Lingyu, Zhou Xuan, Jin Yan, and Zhao Dan. Another film star, Jiang Qing, went on to become Madame Mao Zedong. The exile of Shanghainese filmmakers and actors as a result of the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Communist revolution contributed enormously to the development of the Hong Kong film industry. The movie ''In the Mood for Love'' directed by Wong Kar-wai, a Shanghai native, depicts a slice of the displaced Shanghainese community in Hong Kong and the nostalgia for that era, featuring 1940s music by Zhou Xuan.
Shanghai's cultural festivals include Shanghai International Television Festival, Shanghai International Film Festival, Shanghai International Art Festival, Shanghai International Tourism Festival, Shanghai Spring International Music Festival, etc. Shanghai TV Festival is the earliest international TV festival founded in China. It was founded in 1986. The Shanghai International Film Festival was founded in 1993 and is one of the nine major international film festivals in the A category. The highest award is the "Golden Goblet Award"
Shanghai is considered to be the birthplace of Cinema of China, Chinese cinema. China's first short film, ''The Difficult Couple'' (1913), and the country's first fictional feature film, ''An Orphan Rescues His Grandfather'' (, 1923) were both produced in Shanghai. Shanghai's film industry grew during the early 1930s, generating stars such as Hu Die, Ruan Lingyu, Zhou Xuan, Jin Yan, and Zhao Dan. Another film star, Jiang Qing, went on to become Madame Mao Zedong. The exile of Shanghainese filmmakers and actors as a result of the Second Sino-Japanese War and the Communist revolution contributed enormously to the development of the Hong Kong film industry. The movie ''In the Mood for Love'' directed by Wong Kar-wai, a Shanghai native, depicts a slice of the displaced Shanghainese community in Hong Kong and the nostalgia for that era, featuring 1940s music by Zhou Xuan.
Shanghai's cultural festivals include Shanghai International Television Festival, Shanghai International Film Festival, Shanghai International Art Festival, Shanghai International Tourism Festival, Shanghai Spring International Music Festival, etc. Shanghai TV Festival is the earliest international TV festival founded in China. It was founded in 1986. The Shanghai International Film Festival was founded in 1993 and is one of the nine major international film festivals in the A category. The highest award is the "Golden Goblet Award"
Fashion
Since 2001, Shanghai has held its own fashion week called Shanghai Fashion Week twice every year in April and October. The main venue is in Fuxing Park, and the opening and closing ceremonies are held in the Shanghai Fashion Center. The April session is also part of the one-month Shanghai International Fashion Culture Festival. Shanghai Fashion Week is considered to be an event of national significance featuring both international and Chinese designers. The international presence has included many promising young British fashion designers. The event is hosted by the Shanghai Municipal Government and supported by the People's Republic Ministry of Commerce.Sports
 Shanghai is home to several Association football, football teams, including two in the Chinese Super League: Shanghai Shenhua Football Club, Shanghai Shenhua and Shanghai Port F.C., Shanghai Port. China's top-tier basketball team, the Shanghai Sharks of the Chinese Basketball Association, developed Yao Ming before he entered the National Basketball Association, NBA. Shanghai's baseball team, the Shanghai Golden Eagles, plays in the China Baseball League.
The Shanghai Cricket Club dates back to 1858 when the first recorded cricket match was played between a team of British Navy, British Naval officers and a Shanghai 11. Following a 45-year dormancy after the founding of the PRC in 1949, the club was re-established in 1994 by expatriates living in the city and has since grown to over 300 members. The Shanghai cricket team played various international matches between 1866 and 1948. With cricket in the rest of China almost non-existent, for that period they were the de facto China national cricket team.
Shanghai is home to several Association football, football teams, including two in the Chinese Super League: Shanghai Shenhua Football Club, Shanghai Shenhua and Shanghai Port F.C., Shanghai Port. China's top-tier basketball team, the Shanghai Sharks of the Chinese Basketball Association, developed Yao Ming before he entered the National Basketball Association, NBA. Shanghai's baseball team, the Shanghai Golden Eagles, plays in the China Baseball League.
The Shanghai Cricket Club dates back to 1858 when the first recorded cricket match was played between a team of British Navy, British Naval officers and a Shanghai 11. Following a 45-year dormancy after the founding of the PRC in 1949, the club was re-established in 1994 by expatriates living in the city and has since grown to over 300 members. The Shanghai cricket team played various international matches between 1866 and 1948. With cricket in the rest of China almost non-existent, for that period they were the de facto China national cricket team.
 Shanghai is home to many prominent Chinese professional athletes, such as basketball player Yao Ming, 110-meter hurdler Liu Xiang (hurdler), Liu Xiang, table tennis player Wang Liqin, and badminton player Wang Yihan.
Shanghai is home to many prominent Chinese professional athletes, such as basketball player Yao Ming, 110-meter hurdler Liu Xiang (hurdler), Liu Xiang, table tennis player Wang Liqin, and badminton player Wang Yihan.
 Shanghai is the host of several international sports events. Since 2004, it has hosted the Chinese Grand Prix, a round of the Formula One World Championship. The race is staged annually at the Shanghai International Circuit. It hosted the 2019 Chinese Grand Prix, 1000th Formula One race on 14 April 2019. In 2010, Shanghai became the host city of Deutsche Tourenwagen Masters, which raced in a street circuit in Pudong. In 2012, Shanghai began hosting 4 Hours of Shanghai as one round from the inaugural season of the FIA World Endurance Championship. The city also hosts the Shanghai Masters (tennis), Shanghai Masters tennis tournament, which is part of ATP World Tour Masters 1000, as well as golf tournaments including the BMW Masters and WGC-HSBC Champions.
On 21 September 2017, Shanghai hosted a National Hockey League (NHL) ice hockey exhibition game in an effort to increase fan interest for the 2017–18 NHL season.
Shanghai is the host of several international sports events. Since 2004, it has hosted the Chinese Grand Prix, a round of the Formula One World Championship. The race is staged annually at the Shanghai International Circuit. It hosted the 2019 Chinese Grand Prix, 1000th Formula One race on 14 April 2019. In 2010, Shanghai became the host city of Deutsche Tourenwagen Masters, which raced in a street circuit in Pudong. In 2012, Shanghai began hosting 4 Hours of Shanghai as one round from the inaugural season of the FIA World Endurance Championship. The city also hosts the Shanghai Masters (tennis), Shanghai Masters tennis tournament, which is part of ATP World Tour Masters 1000, as well as golf tournaments including the BMW Masters and WGC-HSBC Champions.
On 21 September 2017, Shanghai hosted a National Hockey League (NHL) ice hockey exhibition game in an effort to increase fan interest for the 2017–18 NHL season.
Environment
Parks and resorts
Shanghai has an extensive public park system; by 2018, the city had 300 parks, of which 281 had free admission, and the per capita park area was . Some of the parks also have become popular tourist attractions due to their unique location, history, or architecture. The People's Square (Shanghai), People's Square park, located in the heart of downtown Shanghai, is especially well known for its proximity to other major landmarks in the city. Fuxing Park, located in the former French Concession, features formal French-style gardens and is surrounded by high-end bars and cafes.
Zhongshan Park (Shanghai), Zhongshan Park in western central Shanghai is famous for its monument of Frédéric Chopin, Chopin, the tallest statue dedicated to the composer in the world. Built in 1914 as Jessfield Park, it once contained the campus of Saint John's University, Shanghai, St. John's University, Shanghai's first international college; today, the park features sakura and peony gardens and a 150-year-old platanus, and it also serves as an interchange hub in the metro system.
One of Shanghai's newer parks is the Xujiahui Park, which was built in 1999, on the former grounds of the Great Chinese Rubber Works Factory and the EMI Recording Studio (now La Villa Rouge restaurant). The park has an artificial lake with a sky bridge running across the park. Shanghai Botanical Garden is located southwest of the city center and was established in 1978. In 2011, the largest botanical garden in Shanghai—Shanghai Chen Shan Botanical Garden—opened in Songjiang District.
The People's Square (Shanghai), People's Square park, located in the heart of downtown Shanghai, is especially well known for its proximity to other major landmarks in the city. Fuxing Park, located in the former French Concession, features formal French-style gardens and is surrounded by high-end bars and cafes.
Zhongshan Park (Shanghai), Zhongshan Park in western central Shanghai is famous for its monument of Frédéric Chopin, Chopin, the tallest statue dedicated to the composer in the world. Built in 1914 as Jessfield Park, it once contained the campus of Saint John's University, Shanghai, St. John's University, Shanghai's first international college; today, the park features sakura and peony gardens and a 150-year-old platanus, and it also serves as an interchange hub in the metro system.
One of Shanghai's newer parks is the Xujiahui Park, which was built in 1999, on the former grounds of the Great Chinese Rubber Works Factory and the EMI Recording Studio (now La Villa Rouge restaurant). The park has an artificial lake with a sky bridge running across the park. Shanghai Botanical Garden is located southwest of the city center and was established in 1978. In 2011, the largest botanical garden in Shanghai—Shanghai Chen Shan Botanical Garden—opened in Songjiang District.
 Other notable parks in Shanghai include Lu Xun Park (Shanghai), Lu Xun Park, Century Park (Shanghai), Century Park, , Gongqing Forest Park, and Jing'an Park.
The Shanghai Disney Resort Project was approved by the government on 4 November 2009
and opened in 2016.
The $4.4 billion theme park and resort in Pudong features a castle that is the biggest among Disney's resorts. More than 11 million people visited the resort in its first year of operation.
Other notable parks in Shanghai include Lu Xun Park (Shanghai), Lu Xun Park, Century Park (Shanghai), Century Park, , Gongqing Forest Park, and Jing'an Park.
The Shanghai Disney Resort Project was approved by the government on 4 November 2009
and opened in 2016.
The $4.4 billion theme park and resort in Pudong features a castle that is the biggest among Disney's resorts. More than 11 million people visited the resort in its first year of operation.
Air pollution
 Air pollution in Shanghai is not as severe as in many other Chinese cities, but is still considered substantial by world standards. During the December 2013 Eastern China smog, air pollution rates reached between 23 and 31 times the international standard. On 6 December 2013, levels of PM2.5 particulate matter in Shanghai rose above 600 micrograms per cubic meter and in the surrounding area, above 700 micrograms per cubic meter. Levels of PM2.5 in Putuo District reached 726 micrograms per cubic meter. As a result, the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission received orders to suspend students' outdoor activities. Authorities pulled nearly one-third of government vehicles from the roads, while much construction work was halted. Most inbound flights were canceled, and more than 50 flights at Pudong International Airport were diverted.
On 23 January 2014, Yang Xiong (politician), Yang Xiong, the mayor of Shanghai, announced that three main measures would be taken to manage the air pollution in Shanghai, along with surrounding Anhui, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang provinces. The measures involved implementing the 2013 air-cleaning program, establishing a linkage mechanism with the three surrounding provinces, and improving the city's early-warning systems. On 12 February 2014, China's cabinet announced that a () fund will be set up to help companies meet the new environmental standards. The effect of the policy was significant. From 2013 to 2018, more than 3,000 treatment facilities for industrial waste gases were installed, and the city's annual smoke, nitrogen oxide, and sulfur dioxide emission decreased by 65%, 54%, and 95%, respectively.
Air pollution in Shanghai is not as severe as in many other Chinese cities, but is still considered substantial by world standards. During the December 2013 Eastern China smog, air pollution rates reached between 23 and 31 times the international standard. On 6 December 2013, levels of PM2.5 particulate matter in Shanghai rose above 600 micrograms per cubic meter and in the surrounding area, above 700 micrograms per cubic meter. Levels of PM2.5 in Putuo District reached 726 micrograms per cubic meter. As a result, the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission received orders to suspend students' outdoor activities. Authorities pulled nearly one-third of government vehicles from the roads, while much construction work was halted. Most inbound flights were canceled, and more than 50 flights at Pudong International Airport were diverted.
On 23 January 2014, Yang Xiong (politician), Yang Xiong, the mayor of Shanghai, announced that three main measures would be taken to manage the air pollution in Shanghai, along with surrounding Anhui, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang provinces. The measures involved implementing the 2013 air-cleaning program, establishing a linkage mechanism with the three surrounding provinces, and improving the city's early-warning systems. On 12 February 2014, China's cabinet announced that a () fund will be set up to help companies meet the new environmental standards. The effect of the policy was significant. From 2013 to 2018, more than 3,000 treatment facilities for industrial waste gases were installed, and the city's annual smoke, nitrogen oxide, and sulfur dioxide emission decreased by 65%, 54%, and 95%, respectively.
Environmental protection
Public awareness of the environment is growing, and the city is investing in a number of environmental protection projects. A 16-year rehabilitation of Suzhou Creek, which runs through the city, was finished in 2012, clearing the creek of barges and factories and removing 1.3 million cubic meters of sludge. Additionally, the government has moved almost all the factories within the city center to either the outskirts or other provinces, and provided incentives for transportation companies to invest in liquefied petroleum gas, LPG buses and taxis. On 1 July 2019, Shanghai adopted a new garbage-classification system that sorts out waste into residual waste, kitchen waste, recyclable waste, and hazardous waste. The wastes are collected by separate vehicles and sent to incineration plants, landfills, recycling centers, and hazardous-waste-disposal facilities, respectively.Media
covers newspapers, publisher, broadcast, television, and Internet, with some media having influence over the country. In regard to foreign publications in Shanghai, Hartmut Walravens of the International Federation of Library Associations and Institutions, IFLA Newspapers Section said that when the Japanese controlled Shanghai in the 1940s "it was very difficult to publish good papers – one either had to concentrate on emigration problems, or cooperate like the ''Shanghai Jewish Chronicle, Chronicle''". , newspapers publishing in Shanghai include: * ''Jiefang Daily'' * ''Oriental Sports Daily'' * ''Shanghai Review of Books'' * ''Shanghai Daily'' * ''Shanghai Star'' * ''Xinmin Evening News'' * ''Wen Hui Bao'' * ''Wenhui Book Review'' Newspapers formerly published in Shanghai include: * ''Der Ostasiatische Lloyd'' * ''Deutsche Shanghai Zeitung'' * ''Gelbe Post'' * ''North China Daily News'' * ''Shanghai Evening Post & Mercury'' * ''The Shanghai Gazette'' * ''Shanghai Jewish Chronicle'' * ''Shanghai Herald'' * ''The Shanghai Mercury'' * ''The Shanghai Post (German-language newspaper), The Shanghai Post'' * ' * '' Shen Bao'' * ''Israel's Messenger'' The city's main broadcaster is Shanghai Media Group.International relations
The city is the home of the New Development Bank, a multilateral development bank established by the BRICS states.Twin towns – sister cities
Shanghai is Sister city, twinned with:Consulates and consulates general
As of September 2020, Shanghai hosts 71 consulates general and 5 consulates, excluding Hong Kong and Macao trade office.
See also
* List of economic and technological development zones in Shanghai * List of fiction set in Shanghai * List of films set in Shanghai * List of people from Shanghai * Shanghai Detention Center * Shanghai International Football Tournament * Shanghai Scientific and Technical Publishers * Shuping Scholarship * Urban planning in ShanghaiNotes
References
Further reading
* * * * * Haarmann, Anke. ''Shanghai (Urban Public) Space'' (Berlin: Jovis, 2009). 192 pponline review
* * * * * Yan Jin. "Shanghai Studies: An evolving academic field" ''History Compass'' (October 2018) e12496 Historiography of recent scholarship
online
External links
*Official website
()
ShanghaiEye
an English news website of SMG *
WikiSatellite view of Shanghai at WikiMapia
* {{Authority control Shanghai, 10th-century establishments in China Articles containing video clips East China Jiangnan Metropolitan areas of China Municipalities of China Populated coastal places in China Populated places established in the 10th century Port cities and towns in China Province-level divisions of China Wu (region) Yangtze River Delta