Schweizerischen Nordbahn on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Swiss Northeastern Railway (''Schweizerische Nordostbahn''; NOB) was an early railway company in Switzerland. It also operated shipping on
 The Swiss Northeast Railway was created on 1 July 1853 by the merger of the
The Swiss Northeast Railway was created on 1 July 1853 by the merger of the 
 The NOB started work on the Winterthur–Schaffhausen railway in 1856 and it was opened on 16 April 1857. The line of the former Northern Railway between Zürich and Baden was extended to the west. The section of the Baden–Aarau railway from Baden to Brugg with the bridge over the
The NOB started work on the Winterthur–Schaffhausen railway in 1856 and it was opened on 16 April 1857. The line of the former Northern Railway between Zürich and Baden was extended to the west. The section of the Baden–Aarau railway from Baden to Brugg with the bridge over the
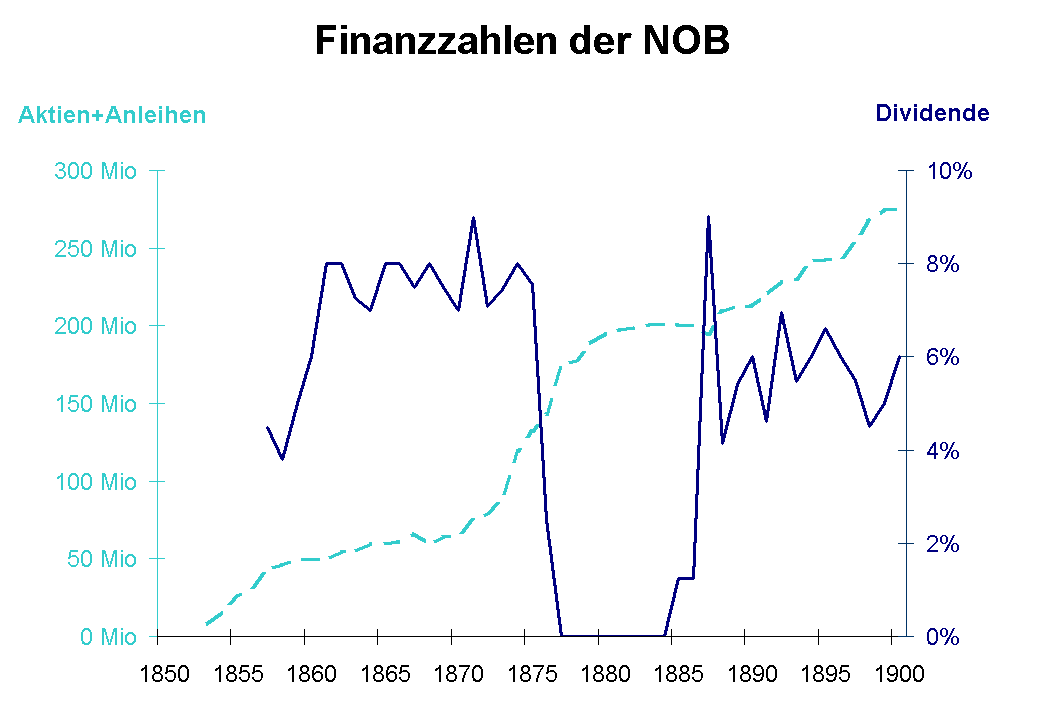
 The behavior of the Zürich railway barons led the Swiss National Railway (''Schweizerische Nationalbahn''; SNB) to attempt to build a second rail link between Lake Geneva and Lake Constance to compete with the existing railway companies from 1872. As a defense measure, the NOB and SCB extended their existing networks between 1873 and 1882. The two companies founded the Aargau Southern Railway (''Aargauische Südbahn'') and the Bötzberg Railway (german: Bötzbergbahn) with equal shareholdings. The former was built and opened between 1873 and 1882 the
The behavior of the Zürich railway barons led the Swiss National Railway (''Schweizerische Nationalbahn''; SNB) to attempt to build a second rail link between Lake Geneva and Lake Constance to compete with the existing railway companies from 1872. As a defense measure, the NOB and SCB extended their existing networks between 1873 and 1882. The two companies founded the Aargau Southern Railway (''Aargauische Südbahn'') and the Bötzberg Railway (german: Bötzbergbahn) with equal shareholdings. The former was built and opened between 1873 and 1882 the

 The situation of the NOB slowly improved again after 1880. Increasing traffic led to the extension of stations and the procurement of additional rolling stock. After Alfred Escher's death in 1882,
The situation of the NOB slowly improved again after 1880. Increasing traffic led to the extension of stations and the procurement of additional rolling stock. After Alfred Escher's death in 1882,  On 8 January 1885, a Winterthur– Zürich train ran into a train coming from after passing a stop signal. The train from Wettingen was pushed back from over the junction on the open track towards Zurich. The accident caused seven casualties and major property damage. An NOB passenger train hit a group of Central Railway
workers, which had been busy with track work, at the southern exit from Gütsch tunnel near Lucerne on 30 May 1898. Seven railway workers were killed immediately and four seriously injured. On 4 June 1899, the Zurich– night express of the NOB ran past a designated stopping point in Aarau and ran into two stationary Central Railway locomotives. The accident caused two deaths and three serious injuries.
Labour regulations and the wage demands of railway workers, which the other private railways acceded to in 1896, met with resistance from the profit-oriented NOB. This led to a labour dispute with NOB staff in 1897. In Zurich, masses of passengers wrote in the complaints book. At times, milk was scarce. The 5000 employees were able to enforce their claims after 41 hours of strikes. The industrial action at the NOB contributed to the holding of a referendum in 1898, which approved the nationalisation of the largest private railways.
The NOB with a route network of 853 km and the Swiss Lake Constance fleet passed into the possession of the
On 8 January 1885, a Winterthur– Zürich train ran into a train coming from after passing a stop signal. The train from Wettingen was pushed back from over the junction on the open track towards Zurich. The accident caused seven casualties and major property damage. An NOB passenger train hit a group of Central Railway
workers, which had been busy with track work, at the southern exit from Gütsch tunnel near Lucerne on 30 May 1898. Seven railway workers were killed immediately and four seriously injured. On 4 June 1899, the Zurich– night express of the NOB ran past a designated stopping point in Aarau and ran into two stationary Central Railway locomotives. The accident caused two deaths and three serious injuries.
Labour regulations and the wage demands of railway workers, which the other private railways acceded to in 1896, met with resistance from the profit-oriented NOB. This led to a labour dispute with NOB staff in 1897. In Zurich, masses of passengers wrote in the complaints book. At times, milk was scarce. The 5000 employees were able to enforce their claims after 41 hours of strikes. The industrial action at the NOB contributed to the holding of a referendum in 1898, which approved the nationalisation of the largest private railways.
The NOB with a route network of 853 km and the Swiss Lake Constance fleet passed into the possession of the
 The Lake Constance (''Bodensee'') route was the most important trade route for traffic between Switzerland and Germany. The Rhine only became navigable to Basel in 1904. The NOB started operating shipping services on Lake Constance with the ''Thurgau'' and the '' Stadt Zürich'' in 1855. The NOB merged with the ''Schweizerischen Dampfboot-Aktiengesellschaft für den Rhein und Bodensee'' (Swiss Steamboat Corporation for the Rhine and Lake Constance) on 1 January 1857. It was founded in 1850 in Schaffhausen as a cantonal enterprise and in the following four years put into service the steamships ''Stadt Schaffhausen'', ''Rhein'', ''Stadt St. Gallen'' and ''Bodan''. In 1863, shipping operations on
The Lake Constance (''Bodensee'') route was the most important trade route for traffic between Switzerland and Germany. The Rhine only became navigable to Basel in 1904. The NOB started operating shipping services on Lake Constance with the ''Thurgau'' and the '' Stadt Zürich'' in 1855. The NOB merged with the ''Schweizerischen Dampfboot-Aktiengesellschaft für den Rhein und Bodensee'' (Swiss Steamboat Corporation for the Rhine and Lake Constance) on 1 January 1857. It was founded in 1850 in Schaffhausen as a cantonal enterprise and in the following four years put into service the steamships ''Stadt Schaffhausen'', ''Rhein'', ''Stadt St. Gallen'' and ''Bodan''. In 1863, shipping operations on
GD Thurgau.jpg, Flat-deck steamer ''Thurgau''
GD Bodan.gif, Flat-deck steamer ''Bodan'' in about 1880 in Rorschach
SD Helvetia.jpg, Steam/sailing ship ''Helvetia'' in Romanshorn
Dampftrajekt I.jpg, Stean train ferry I in Romanshorn harbour
Dampftrajekt II.jpg, Stean train ferry II in the Romanshorn shipyard
SD Saentis.jpg, Steam/sailing ship ''Saentis''
SD St. Gotthard.jpg, Steam/sailing ship ''St. Gotthard''
Zürichsee Helvetia I.jpg, '' Helvetia'', commissioned in 1875
Zürichsee Concordia.jpg, ''Concordia'' (1864) operating to the Zürich theatre.
Zürichsee St.Gotthard Hinterschiff.jpg, Rear of the ''St. Gotthard'' (1865)
Zürichsee Lukmanier.jpg, ''Lukmanier'' (1865), sister ship of the ''St. Gotthard''
Zürichsee Schwalbe.jpg, ''Schwalbe'' (1865), the first screw steamer on Lake Zurich
Zürichsee Trajekt.jpg, Unnamed train ferry, commissioned in 1885


Lake Constance
Lake Constance (german: Bodensee, ) refers to three Body of water, bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, ca ...
(''Bodensee'') and Lake Zürich. Until the merger of the Western Swiss Railways
The Western Switzerland Railways (''Chemins de fer de la Suisse Occidentale'', shortened to ''Suisse-Occidentale''; SO or S-O), were initially a joint operation of three Swiss railway companies, but these companies merged on 1 January 1872. The co ...
into the Jura–Simplon Railway (JS) in 1890/91, it was the largest Swiss railway company.
History
 The Swiss Northeast Railway was created on 1 July 1853 by the merger of the
The Swiss Northeast Railway was created on 1 July 1853 by the merger of the Swiss Northern Railway
The Swiss Northern Railway (German: ''Schweizerische Nordbahn'', SNB), informally known as the ''Spanisch-Brötli-Bahn'', opened the first railway line within Switzerland in 1847, the Zürich–Baden line. This followed the extension of a Fre ...
(''Schweizerische Nordbahn''—SNB— informally known as the '' Spanisch-Brötli-Bahn''), and the Zürich-Lake Constance Railway
The Swiss Northeastern Railway (''Schweizerische Nordostbahn''; NOB) was an early railway company in Switzerland. It also operated shipping on Lake Constance (''Bodensee'') and Lake Zürich. Until the merger of the Western Swiss Railways into the ...
(''Zürich-Bodenseebahn''). The originally planned continuation of the Northern Railway from Baden to Basel initially failed due to the different interests of the cantons of Zürich, Aargau
Aargau, more formally the Canton of Aargau (german: Kanton Aargau; rm, Chantun Argovia; french: Canton d'Argovie; it, Canton Argovia), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capita ...
and Basel.
The main initiator of the merger was the Zürich-based businessman Alfred Escher, who previously headed the Zürich-Lake Constance Railway. He advocated the funding of the railways by private investors instead of public funds. He suggested the founding of Schweizerische Kreditanstalt to meet the large capital requirements of the railways.
The NOB endeavored to establish connections with foreign countries to generate freight traffic. It first opened a direct connection from Zürich to Lake Constance
Lake Constance (german: Bodensee, ) refers to three Body of water, bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, ca ...
. Thus it became a direct competitor of the United Swiss Railways
The United Swiss Railways (''Vereinigten Schweizerbahnen''; VSB or V.S.B.) was a former railway company in Switzerland. It was the smallest of the five main railways that were nationalised from 1902 to form the Swiss Federal Railways.
Foundatio ...
(''Vereinigte Schweizerbahnen''; VSB) based in St. Gallen. the NOB opened the line from Romanshorn to Winterthur on 16 May 1855. The Zürich–Winterthur extension was opened in two stages from Winterthur to Oerlikon on 27 December 1855 and to Zürich on 26 June 1856; this gave a connection to the former Northern Railway between Zürich and Baden. The arrival of the railway caused the peaceful village of Romanshorn to grow into one of the most important transport hubs in eastern Switzerland. The NOB started a shipping service on Lake Constance in 1855. The train ferry service between Romanshorn and Friedrichshafen (Germany) was established in 1869. This led the NOB to expand the railway facilities and to construct the largest of the ports on Lake Constance (measured by area), which required the shore to be raised.

 The NOB started work on the Winterthur–Schaffhausen railway in 1856 and it was opened on 16 April 1857. The line of the former Northern Railway between Zürich and Baden was extended to the west. The section of the Baden–Aarau railway from Baden to Brugg with the bridge over the
The NOB started work on the Winterthur–Schaffhausen railway in 1856 and it was opened on 16 April 1857. The line of the former Northern Railway between Zürich and Baden was extended to the west. The section of the Baden–Aarau railway from Baden to Brugg with the bridge over the Reuss Reuss may refer to:
*Reuss (surname)
*Reuss (river) in Switzerland
*Reuss (state) or Reuß, several former states or countries in present-day Germany, and the Republic of Reuss
*Reuss Elder Line and Reuss Younger Line (House of Reuss), members incl ...
was opened on 29 September 1856. The rest of the line to Aarau
Aarau (, ) is a List of towns in Switzerland, town, a Municipalities of Switzerland, municipality, and the capital of the northern Swiss Cantons of Switzerland, canton of Aargau. The List of towns in Switzerland, town is also the capital of the dis ...
was opened on 15 May 1858 where the network of NOB connected with the network of the Swiss Central Railway
The Swiss Central Railway (''Schweizerische Centralbahn''; SCB or S.C.B.) was one of the five major private railway companies of Switzerland. The SCB with a track length of 332 kilometres was integrated into the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB) in 19 ...
(''Schweizerische Centralbahn''; SCB) at Wöschnau on the Aargau
Aargau, more formally the Canton of Aargau (german: Kanton Aargau; rm, Chantun Argovia; french: Canton d'Argovie; it, Canton Argovia), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capita ...
- Solothurn canton border, meaning that Zürich was now connected with Basel.
On 18 August 1859, the NOB was able to complete a direct connection with a foreign country with the opening of the Turgi–Waldshut line. This completed the main network of Northeastern Railway. The most important northern gateway to Switzerland was Basel, but it was controlled by the SCB. Freight transport was NOB's most important business segment, which initially enjoyed good returns.
The NOB was involved with other railway companies. After the Schweizerische Ostwestbahn (Swiss East West Railway, OWB), which had been founded in 1861, had become bankrupt in an attempt to build a line from La Neuveville via Bern
german: Berner(in)french: Bernois(e) it, bernese
, neighboring_municipalities = Bremgarten bei Bern, Frauenkappelen, Ittigen, Kirchlindach, Köniz, Mühleberg, Muri bei Bern, Neuenegg, Ostermundigen, Wohlen bei Bern, Zollikofen
, website ...
and Lucerne
Lucerne ( , ; High Alemannic German, High Alemannic: ''Lozärn'') or Luzern ()Other languages: gsw, Lozärn, label=Lucerne German; it, Lucerna ; rm, Lucerna . is a city in central Switzerland, in the Languages of Switzerland, German-speaking po ...
to Zürich, the NOB together with the cantons of Zürich, Zug
, neighboring_municipalities = Cham, Baar, Walchwil, Steinhausen, Unterägeri
, twintowns = Fürstenfeld (Austria), Kalesija (Bosnia-Herzegowina)
Zug (Standard German: , Alemannic German: ; french: Zoug it, Zugo r ...
and Lucerne
Lucerne ( , ; High Alemannic German, High Alemannic: ''Lozärn'') or Luzern ()Other languages: gsw, Lozärn, label=Lucerne German; it, Lucerna ; rm, Lucerna . is a city in central Switzerland, in the Languages of Switzerland, German-speaking po ...
, took over part of its line and completed it as the Zürich–Zug–Lucerne Railway
The Zürich–Zug–Luzern Railway (Zürich-Zug-Luzern-Bahn) is a former railway company that built railway lines in the Swiss cantons of Zürich, Zug and Lucerne from the 1860s. It was absorbed by the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB) in 1902. Its l ...
(ZZL), which was finished on 1 June 1864.
The NOB—like other railway companies at the time—aimed at short-term profit maximisation for private bankers. The bankers took offices in management and the board of directors to secure their profits. The rights of the other shareholders was undermined by the use of common stock. They gained exemption from tax and subsidies through political influence. Alfred Escher was not only Chairman of the NOB and Chairman of Kreditanstalt, but also a member of the Executive Council of Zürich and, for 34 years, the National Council. Maintenance was neglected and the assets of the railway company were run down. This had already created a crisis in 1857, which was intensified in 1867.
Railway crisis
 The behavior of the Zürich railway barons led the Swiss National Railway (''Schweizerische Nationalbahn''; SNB) to attempt to build a second rail link between Lake Geneva and Lake Constance to compete with the existing railway companies from 1872. As a defense measure, the NOB and SCB extended their existing networks between 1873 and 1882. The two companies founded the Aargau Southern Railway (''Aargauische Südbahn'') and the Bötzberg Railway (german: Bötzbergbahn) with equal shareholdings. The former was built and opened between 1873 and 1882 the
The behavior of the Zürich railway barons led the Swiss National Railway (''Schweizerische Nationalbahn''; SNB) to attempt to build a second rail link between Lake Geneva and Lake Constance to compete with the existing railway companies from 1872. As a defense measure, the NOB and SCB extended their existing networks between 1873 and 1882. The two companies founded the Aargau Southern Railway (''Aargauische Südbahn'') and the Bötzberg Railway (german: Bötzbergbahn) with equal shareholdings. The former was built and opened between 1873 and 1882 the Rupperswil–Immensee railway line
The Rupperswil–Immensee railway line is a railway line in the cantons of Aargau and Zug, in Switzerland. It runs from to . The line runs north-south and interchanges with several other lines, including the Baden–Aarau, Heitersberg, Zofinge ...
with a branch line from Hendschiken to Brugg, connecting the network of the NOB and the SCB with the Gotthard Railway
The Gotthard railway (german: Gotthardbahn; it, Ferrovia del Gottardo) is the Swiss trans-alpine railway line from northern Switzerland to the canton of Ticino. The line forms a major part of an important international railway link between no ...
in 1882. The Bötzberg Railway, operated by the NOB, opened the Brugg–Pratteln railway in 1875, which together with the existing lines of the NOB and the SCB created a direct connection from Zurich to Basel.
In addition, the NOB under the new CEO Friedrich Peyer im Hof, tried to eliminate the competition in advance by an accelerated expansion of its own network. It secured concessions for various railway lines and entered into commitments with cantons and founding committees for the construction of these unprofitable lines. This forced the NOB to borrow money, which led to massive indebtedness. The financial difficulties brought the NOB to the brink of collapse. The construction of the Lake Zürich right-bank line, which it had begun in 1873, had to be discontinued because of the financial crisis. The important Lake Zürich left-bank railway
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ...
to Ziegelbrücke, however, was opened in 1875. The NOB could not pay dividends for years from 1877. The price of its shares collapsed from Swiss Francs (CHF) 670 in 1871 to CHF 53 in 1879. An investigation commissioned by the General Assembly found grave mistakes in corporate governance.
On 2 March 1877, the NOB requested that the Federal Council release it from its obligations to build railways. On 14 February 1878, the Federal Assembly confirmed an agreement that the construction obligations would be maintained, but would be deferred until the completion of the NOB's financial restructuring. The construction period for the so-called "moratorium lines" ( Thalwil–Zug, Etzwilen–Schaffhausen, Bülach–Schaffhausen, Koblenz–Stein, Dielsdorf–Niederweningen and the Lake Zurich right bank line) was extended. An agreement with the canton of Glarus
The canton of Glarus (german: Kanton Glarus rm, Chantun Glaruna; french: Canton de Glaris; it, Canton Glarona) is a canton in east central Switzerland. The capital is Glarus.
The population speaks a variety of Alemannic German.
The majority of ...
set the date for the completion of the Glarus–Linthal line at 1 May 1879. The payment of dividends was suspended from 1880 to 1883. On 25 October 1887, the Federal Council instructed the NOB to begin construction of the Lake Zurich right bank line. The deadlines for the remaining moratorium lines were set on 27 June 1888.
The ruinous competitive project of the National Railway ended in insolvency. The participating towns and municipalities had to suffer decades of debt. The NOB took over the network of its rival for a fraction of its construction cost on 1 October 1880. The Zofingen–Suhr section was resold to the SCB.
Recovery and nationalisation

 The situation of the NOB slowly improved again after 1880. Increasing traffic led to the extension of stations and the procurement of additional rolling stock. After Alfred Escher's death in 1882,
The situation of the NOB slowly improved again after 1880. Increasing traffic led to the extension of stations and the procurement of additional rolling stock. After Alfred Escher's death in 1882, Adolf Guyer-Zeller
Adolf Guyer-Zeller (1 May 1839 – 3 April 1899) was a Swiss entrepreneur.
Born in Bäretswil, Switzerland on 1 May 1839, Guyer-Zeller was the son of an owner of spinning mill and creator of a textile export trade in Zürich. After the death of ...
became head of the NOB.
The railway crisis had caused many domestic shareholders to sell their securities to major foreign shareholders. Railway shares played a major role in speculation
In finance, speculation is the purchase of an asset (a commodity, good (economics), goods, or real estate) with the hope that it will become more valuable shortly. (It can also refer to short sales in which the speculator hopes for a decline i ...
on the stock exchange
A stock exchange, securities exchange, or bourse is an exchange where stockbrokers and traders can buy and sell securities, such as shares of stock, bonds and other financial instruments. Stock exchanges may also provide facilities for th ...
. A financial group led by Adolf Guyer was able to secure a majority of votes at a general meeting of the company, allowing it to select the board of directors and replace it with people who would cooperate with its interests.
The vast majority of the shares were in foreign hands, the majority of the bonds belonged to Swiss owners. At the time, the interest rate was 4% for secure Swiss rail bonds. In order to increase the return of the shares, bonds were converted into shares with an interest rate of 3½%. This reduced the company's interest burden and increased profits.
 On 8 January 1885, a Winterthur– Zürich train ran into a train coming from after passing a stop signal. The train from Wettingen was pushed back from over the junction on the open track towards Zurich. The accident caused seven casualties and major property damage. An NOB passenger train hit a group of Central Railway
workers, which had been busy with track work, at the southern exit from Gütsch tunnel near Lucerne on 30 May 1898. Seven railway workers were killed immediately and four seriously injured. On 4 June 1899, the Zurich– night express of the NOB ran past a designated stopping point in Aarau and ran into two stationary Central Railway locomotives. The accident caused two deaths and three serious injuries.
Labour regulations and the wage demands of railway workers, which the other private railways acceded to in 1896, met with resistance from the profit-oriented NOB. This led to a labour dispute with NOB staff in 1897. In Zurich, masses of passengers wrote in the complaints book. At times, milk was scarce. The 5000 employees were able to enforce their claims after 41 hours of strikes. The industrial action at the NOB contributed to the holding of a referendum in 1898, which approved the nationalisation of the largest private railways.
The NOB with a route network of 853 km and the Swiss Lake Constance fleet passed into the possession of the
On 8 January 1885, a Winterthur– Zürich train ran into a train coming from after passing a stop signal. The train from Wettingen was pushed back from over the junction on the open track towards Zurich. The accident caused seven casualties and major property damage. An NOB passenger train hit a group of Central Railway
workers, which had been busy with track work, at the southern exit from Gütsch tunnel near Lucerne on 30 May 1898. Seven railway workers were killed immediately and four seriously injured. On 4 June 1899, the Zurich– night express of the NOB ran past a designated stopping point in Aarau and ran into two stationary Central Railway locomotives. The accident caused two deaths and three serious injuries.
Labour regulations and the wage demands of railway workers, which the other private railways acceded to in 1896, met with resistance from the profit-oriented NOB. This led to a labour dispute with NOB staff in 1897. In Zurich, masses of passengers wrote in the complaints book. At times, milk was scarce. The 5000 employees were able to enforce their claims after 41 hours of strikes. The industrial action at the NOB contributed to the holding of a referendum in 1898, which approved the nationalisation of the largest private railways.
The NOB with a route network of 853 km and the Swiss Lake Constance fleet passed into the possession of the Swiss Federal Railways
Swiss Federal Railways (german: link=no, Schweizerische Bundesbahnen, ''SBB''; french: link=no, Chemins de fer fédéraux suisses, ''CFF''; it, Ferrovie federali svizzere, ''FFS'') is the national railway company of Switzerland. It is usuall ...
(SBB) on 1 January 1902.
Shipping companies
Shipping was the natural continuation of the railway lines that ended at the lakes. The transport of the passengers was not difficult. The transport of goods, however, was much more complicated and expensive because the goods had to be reloaded twice.Lake Constance
 The Lake Constance (''Bodensee'') route was the most important trade route for traffic between Switzerland and Germany. The Rhine only became navigable to Basel in 1904. The NOB started operating shipping services on Lake Constance with the ''Thurgau'' and the '' Stadt Zürich'' in 1855. The NOB merged with the ''Schweizerischen Dampfboot-Aktiengesellschaft für den Rhein und Bodensee'' (Swiss Steamboat Corporation for the Rhine and Lake Constance) on 1 January 1857. It was founded in 1850 in Schaffhausen as a cantonal enterprise and in the following four years put into service the steamships ''Stadt Schaffhausen'', ''Rhein'', ''Stadt St. Gallen'' and ''Bodan''. In 1863, shipping operations on
The Lake Constance (''Bodensee'') route was the most important trade route for traffic between Switzerland and Germany. The Rhine only became navigable to Basel in 1904. The NOB started operating shipping services on Lake Constance with the ''Thurgau'' and the '' Stadt Zürich'' in 1855. The NOB merged with the ''Schweizerischen Dampfboot-Aktiengesellschaft für den Rhein und Bodensee'' (Swiss Steamboat Corporation for the Rhine and Lake Constance) on 1 January 1857. It was founded in 1850 in Schaffhausen as a cantonal enterprise and in the following four years put into service the steamships ''Stadt Schaffhausen'', ''Rhein'', ''Stadt St. Gallen'' and ''Bodan''. In 1863, shipping operations on the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, sou ...
were discontinued and the four steamships were relocated to Romanshorn.
On 11 March 1861 the steamer ''Stadt Zürich'' rammed and sank the Bavarian steamer ''Ludwig''. Three persons survived, 13 were killed. On 12 February 1864 the Bavarian steamer '' Jura'' was also rammed and sunk by the ''Stadt Zürich''.
In order to avoid the reloading of goods, the Bavarian and the Württemberg steamship administration together with the NOB decided in 1867 to transport railway wagons by train ferry. A steam ferry known as " steam ferry I" was used on the Friedrichshafen–Romanshorn route. This over 70 metre-long ferry was able to accommodate 18 freight wagons, but had a horrendous rate of coal consumption. It was retired in 1882 and subsequently scrapped. A second ferry known as "steam ferry II" started operating between Lindau and Romanshorn in 1874.
In 1884, the flat-deck steamer ''Stadt Zürich'' was converted into the semi-private steamer ''Zürich''. In 1887, the NOB put the newly built saloon steamer ''Helvetia III'' into service, which caused a sensation with its clipper bow and bowsprit. In 1892, the mixed steam/sailing ship ''Säntis'' replaced the ''Stadt Schaffhausen''. The mixed steam/sailing ship ''St. Gotthard'' was similarly replaced by the flat-deck steamer ''Stadt St. Gallen'' in 1897.
In 1902, with the nationalisation of the NOB the entire shipping company was transferred to the Swiss Federal Railways (SBB).
Lake Zürich
In 1864, the ''Dampfbootgesellschaft linkes Ufer'' (Left Bank Steamboat Company) was established in Horgen. In 1868, it merged with the older ''Zürichsee-Walensee-Gesellschaft AG'' (Lake Zürich-Walensee Company) to form the ''Dampfbootgesellschaft für den Zürichsee'' (Steamboat Company for Lake Zürich). Shortly before the commissioning of theLake Zürich left bank railway
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a Depression (geology), basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the World Ocean, oce ...
(''Linksufrige Zürichseebahn''), the NOB took over the entire shipping fleet in 1875. The NOB curtailed operations immediately so rival companies formed. When the Zürich–Meilen–Rapperswil railway started operation in 1894, the existing fleet of six ships: '' Helvetia'', ''Concordia'', ''Lukmanier'', ''St. Gotthard'', ''Taube'' and ''Schwalbe'' was reduced.
With the nationalisation of the NOB in 1903, shipping operations were outsourced. All public shipping services were taken over by the Zürichsee-Schifffahrtsgesellschaft (Lake Zürich Navigation Company; ZDG) in 1902. The paddle-wheel
A paddle wheel is a form of waterwheel or impeller in which a number of paddles are set around the periphery of the wheel. It has several uses, of which some are:
* Very low-lift water pumping, such as flooding paddy fields at no more than abo ...
and screw steamers taken over from the NOB were replaced by more modern ships, with the exception of the ''Helvetia''.
A train ferry operated on Lake Zurich only for a short time. The NOB put an unnamed train ferry built by Escher, Wyss & Cie. into operation in 1885. The traffic from the left bank transshipment port of Wollishofen to the right bank Uetikon
Uetikon am See is a municipality in the district of Meilen in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland.
History
Uetikon am See is first mentioned in 1150 as ''Uotinchova''. Until 1924 it was known as ''Uetikon''.
Geography
Uetikon am See has an ar ...
was used practically exclusively for traffic to/from the local ''CU Chemie Uetikon'' chemical factory. Operations were discontinued with the opening of the Zürich–Meilen–Rapperswil railway in the autumn of 1894.
Route network


Assumed lines
References
Notes
Footnotes
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * Jung, Joseph (2019) 022 ''The Laboratory of Progress: Switzerland in the Nineteenth Century'', Vol. 2, tr. Ashley Curtis. NY: Routledge. * Maw, W.H. and J. Dredge, eds. (1872). ''Engineering''. 19 April 1872. London. * Mieg, Harald, A and Heike Oevermann (2014). ''Industrial Heritage Sites in Transformation.'' London and NY: Routledge. {{Authority control Railway lines opened in 1853 Defunct railway companies of Switzerland Transport in Zürich Shipping companies of Switzerland Swiss companies established in 1853 Railway companies established in 1853