Renaissance Du Livre on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. It occurred after the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages and was associated with great social change. In addition to the standard periodization, proponents of a "long Renaissance" may put its beginning in the 14th century and its end in the 17th century.
The traditional view focuses more on the early modern aspects of the Renaissance and argues that it was a break from the past, but many historians today focus more on its medieval aspects and argue that it was an extension of the Middle Ages. However, the beginnings of the period – the early Renaissance of the 15th century and the Italian Proto-Renaissance from around 1250 or 1300 – overlap considerably with the Late Middle Ages, conventionally dated to , and the Middle Ages themselves were a long period filled with gradual changes, like the modern age; and as a transitional period between both, the Renaissance has close similarities to both, especially the late and early sub-periods of either.
The intellectual basis of the Renaissance was its version of humanism, derived from the concept of Roman '' humanitas'' and the rediscovery of classical Greek philosophy, such as that of
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. It occurred after the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages and was associated with great social change. In addition to the standard periodization, proponents of a "long Renaissance" may put its beginning in the 14th century and its end in the 17th century.
The traditional view focuses more on the early modern aspects of the Renaissance and argues that it was a break from the past, but many historians today focus more on its medieval aspects and argue that it was an extension of the Middle Ages. However, the beginnings of the period – the early Renaissance of the 15th century and the Italian Proto-Renaissance from around 1250 or 1300 – overlap considerably with the Late Middle Ages, conventionally dated to , and the Middle Ages themselves were a long period filled with gradual changes, like the modern age; and as a transitional period between both, the Renaissance has close similarities to both, especially the late and early sub-periods of either.
The intellectual basis of the Renaissance was its version of humanism, derived from the concept of Roman '' humanitas'' and the rediscovery of classical Greek philosophy, such as that of
Humanities in the Western Tradition
Ch. 13 Renaissance humanists such as Poggio Bracciolini sought out in Europe's monastic libraries the Latin literary, historical, and oratorical texts of
Looking at the Renaissance: Religious Context in the Renaissance
' (Retrieved May 10, 2007) In addition, many Greek Christian works, including the Greek New Testament, were brought back from
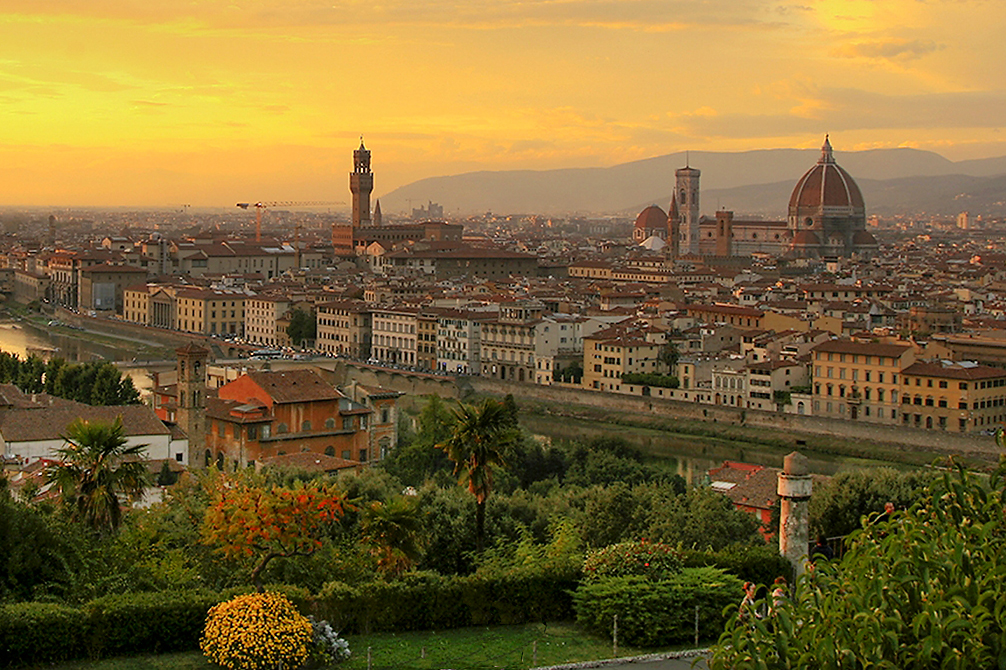 Many argue that the ideas characterizing the Renaissance had their origin in Florence at the turn of the 13th and 14th centuries, in particular with the writings of Dante Alighieri (1265–1321) and Petrarch (1304–1374), as well as the paintings of Giotto di Bondone (1267–1337). Some writers date the Renaissance quite precisely; one proposed starting point is 1401, when the rival geniuses Lorenzo Ghiberti and
Many argue that the ideas characterizing the Renaissance had their origin in Florence at the turn of the 13th and 14th centuries, in particular with the writings of Dante Alighieri (1265–1321) and Petrarch (1304–1374), as well as the paintings of Giotto di Bondone (1267–1337). Some writers date the Renaissance quite precisely; one proposed starting point is 1401, when the rival geniuses Lorenzo Ghiberti and
 In stark contrast to the High Middle Ages, when Latin scholars focused almost entirely on studying Greek and Arabic works of natural science, philosophy and mathematics, Renaissance scholars were most interested in recovering and studying Latin and Greek literary, historical, and oratorical texts. Broadly speaking, this began in the 14th century with a Latin phase, when Renaissance scholars such as Petrarch, Coluccio Salutati (1331–1406), Niccolò de' Niccoli (1364–1437), and Poggio Bracciolini (1380–1459) scoured the libraries of Europe in search of works by such Latin authors as Cicero, Lucretius, Livy, and Seneca. By the early 15th century, the bulk of the surviving such Latin literature had been recovered; the Greek phase of Renaissance humanism was under way, as Western European scholars turned to recovering ancient Greek literary, historical, oratorical and theological texts.
Unlike with Latin texts, which had been preserved and studied in Western Europe since late antiquity, the study of ancient Greek texts was very limited in medieval Western Europe. Ancient Greek works on science, mathematics, and philosophy had been studied since the High Middle Ages in Western Europe and in the Islamic Golden Age (normally in translation), but Greek literary, oratorical and historical works (such as Homer, the Greek dramatists, Demosthenes and Thucydides) were not studied in either the Latin or medieval
In stark contrast to the High Middle Ages, when Latin scholars focused almost entirely on studying Greek and Arabic works of natural science, philosophy and mathematics, Renaissance scholars were most interested in recovering and studying Latin and Greek literary, historical, and oratorical texts. Broadly speaking, this began in the 14th century with a Latin phase, when Renaissance scholars such as Petrarch, Coluccio Salutati (1331–1406), Niccolò de' Niccoli (1364–1437), and Poggio Bracciolini (1380–1459) scoured the libraries of Europe in search of works by such Latin authors as Cicero, Lucretius, Livy, and Seneca. By the early 15th century, the bulk of the surviving such Latin literature had been recovered; the Greek phase of Renaissance humanism was under way, as Western European scholars turned to recovering ancient Greek literary, historical, oratorical and theological texts.
Unlike with Latin texts, which had been preserved and studied in Western Europe since late antiquity, the study of ancient Greek texts was very limited in medieval Western Europe. Ancient Greek works on science, mathematics, and philosophy had been studied since the High Middle Ages in Western Europe and in the Islamic Golden Age (normally in translation), but Greek literary, oratorical and historical works (such as Homer, the Greek dramatists, Demosthenes and Thucydides) were not studied in either the Latin or medieval
Marvin Perry, Myrna Chase, Margaret C. Jacob, James R. Jacob, 2008, pp. 261–262. The movement to reintegrate the regular study of Greek literary, historical, oratorical and theological texts back into the Western European curriculum is usually dated to the 1396 invitation from Coluccio Salutati to the Byzantine diplomat and scholar Manuel Chrysoloras (c. 1355–1415) to teach Greek in Florence. This legacy was continued by a number of expatriate Greek scholars, from Basilios Bessarion to
 The unique political structures of Late Middle Ages Italy have led some to theorize that its unusual social climate allowed the emergence of a rare cultural efflorescence. Italy did not exist as a political entity in the early modern period. Instead, it was divided into smaller city-states and territories: the
The unique political structures of Late Middle Ages Italy have led some to theorize that its unusual social climate allowed the emergence of a rare cultural efflorescence. Italy did not exist as a political entity in the early modern period. Instead, it was divided into smaller city-states and territories: the
The Civilization of the Renaissance in Italy
'', translated by S.G.C. Middlemore, 1878. Likewise, the position of Italian cities such as Venice as great trading centres made them intellectual crossroads.
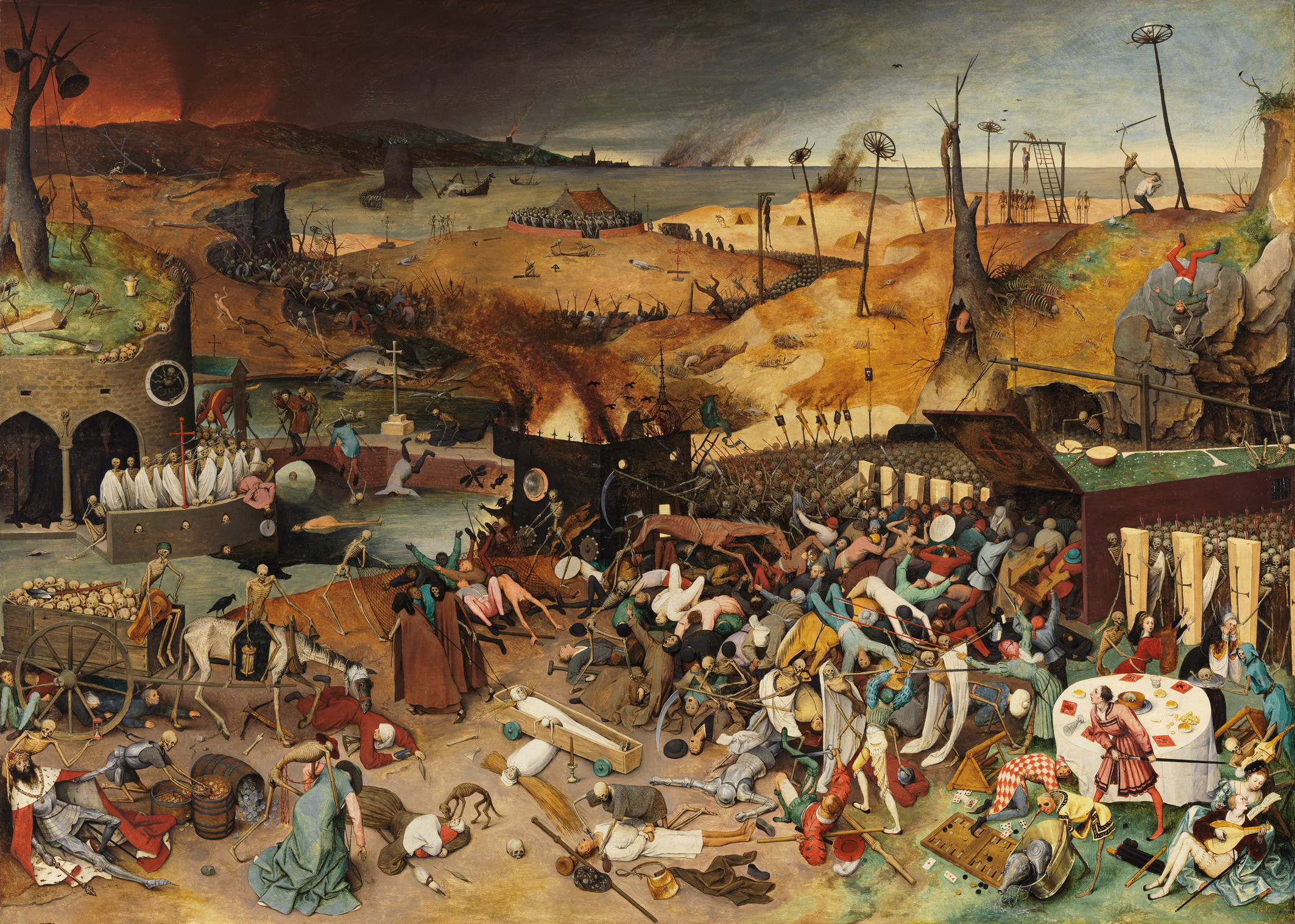 One theory that has been advanced is that the devastation in Florence caused by the
One theory that has been advanced is that the devastation in Florence caused by the
 It has long been a matter of debate why the Renaissance began in Florence, and not elsewhere in Italy. Scholars have noted several features unique to Florentine cultural life that may have caused such a cultural movement. Many have emphasized the role played by the Medici, a banking family and later ducal ruling house, in patronizing and stimulating the arts. Lorenzo de' Medici (1449–1492) was the catalyst for an enormous amount of arts patronage, encouraging his countrymen to commission works from the leading artists of Florence, including Leonardo da Vinci, Sandro Botticelli, and Michelangelo Buonarroti. Works by Neri di Bicci, Botticelli, da Vinci, and Filippino Lippi had been commissioned additionally by the Convent of San Donato in Scopeto in Florence.
The Renaissance was certainly underway before Lorenzo de' Medici came to power – indeed, before the Medici family itself achieved hegemony in Florentine society. Some historians have postulated that Florence was the birthplace of the Renaissance as a result of luck, i.e., because " Great Men" were born there by chance:Burckhardt, Jacob, ''The Development of the Individual'',
It has long been a matter of debate why the Renaissance began in Florence, and not elsewhere in Italy. Scholars have noted several features unique to Florentine cultural life that may have caused such a cultural movement. Many have emphasized the role played by the Medici, a banking family and later ducal ruling house, in patronizing and stimulating the arts. Lorenzo de' Medici (1449–1492) was the catalyst for an enormous amount of arts patronage, encouraging his countrymen to commission works from the leading artists of Florence, including Leonardo da Vinci, Sandro Botticelli, and Michelangelo Buonarroti. Works by Neri di Bicci, Botticelli, da Vinci, and Filippino Lippi had been commissioned additionally by the Convent of San Donato in Scopeto in Florence.
The Renaissance was certainly underway before Lorenzo de' Medici came to power – indeed, before the Medici family itself achieved hegemony in Florentine society. Some historians have postulated that Florence was the birthplace of the Renaissance as a result of luck, i.e., because " Great Men" were born there by chance:Burckhardt, Jacob, ''The Development of the Individual'',
The Civilization of the Renaissance in Italy
'', translated by S.G.C. Middlemore, 1878. Leonardo da Vinci, Botticelli and Michelangelo were all born in Tuscany. Arguing that such chance seems improbable, other historians have contended that these "Great Men" were only able to rise to prominence because of the prevailing cultural conditions at the time.
 Humanist scholars shaped the intellectual landscape throughout the early modern period. Political philosophers such as Niccolò Machiavelli and Thomas More revived the ideas of Greek and Roman thinkers and applied them in critiques of contemporary government, following the Islamic steps of
Humanist scholars shaped the intellectual landscape throughout the early modern period. Political philosophers such as Niccolò Machiavelli and Thomas More revived the ideas of Greek and Roman thinkers and applied them in critiques of contemporary government, following the Islamic steps of
 The development of perspective was part of a wider trend towards realism in the arts. Painters developed other techniques, studying light, shadow, and, famously in the case of Leonardo da Vinci,
The development of perspective was part of a wider trend towards realism in the arts. Painters developed other techniques, studying light, shadow, and, famously in the case of Leonardo da Vinci,

 Applied innovation extended to commerce. At the end of the 15th century,
Applied innovation extended to commerce. At the end of the 15th century,
 During the Renaissance, extending from 1450 to 1650, every continent was visited and mostly mapped by Europeans, except the south polar continent now known as Antarctica. This development is depicted in the large world map ''Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Tabula'' made by the Dutch cartographer Joan Blaeu in 1648 to commemorate the
During the Renaissance, extending from 1450 to 1650, every continent was visited and mostly mapped by Europeans, except the south polar continent now known as Antarctica. This development is depicted in the large world map ''Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Tabula'' made by the Dutch cartographer Joan Blaeu in 1648 to commemorate the
 The new ideals of humanism, although more secular in some aspects, developed against a Christian backdrop, especially in the Northern Renaissance. Much, if not most, of the new art was commissioned by or in dedication to the Church. However, the Renaissance had a profound effect on contemporary theology, particularly in the way people perceived the relationship between man and God. Many of the period's foremost theologians were followers of the humanist method, including Erasmus, Zwingli, Thomas More, Martin Luther, and
The new ideals of humanism, although more secular in some aspects, developed against a Christian backdrop, especially in the Northern Renaissance. Much, if not most, of the new art was commissioned by or in dedication to the Church. However, the Renaissance had a profound effect on contemporary theology, particularly in the way people perceived the relationship between man and God. Many of the period's foremost theologians were followers of the humanist method, including Erasmus, Zwingli, Thomas More, Martin Luther, and 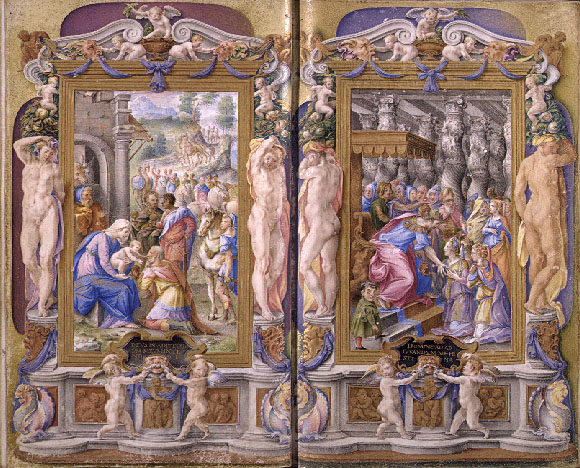 The Renaissance began in times of religious turmoil. The late Middle Ages was a period of political intrigue surrounding the
The Renaissance began in times of religious turmoil. The late Middle Ages was a period of political intrigue surrounding the
 By the 15th century, writers, artists, and architects in Italy were well aware of the transformations that were taking place and were using phrases such as ''modi antichi'' (in the antique manner) or ''alle romana et alla antica'' (in the manner of the Romans and the ancients) to describe their work. In the 1330s Petrarch referred to pre-Christian times as ''antiqua'' (ancient) and to the Christian period as ''nova'' (new). From Petrarch's Italian perspective, this new period (which included his own time) was an age of national eclipse.
Leonardo Bruni was the first to use tripartite periodization in his ''History of the Florentine People'' (1442).Leonardo Bruni, James Hankins, ''History of the Florentine people'', Volume 1, Books 1–4 (2001), p. xvii. Bruni's first two periods were based on those of Petrarch, but he added a third period because he believed that Italy was no longer in a state of decline. Flavio Biondo used a similar framework in ''Decades of History from the Deterioration of the Roman Empire'' (1439–1453).
Humanist historians argued that contemporary scholarship restored direct links to the classical period, thus bypassing the Medieval period, which they then named for the first time the "Middle Ages". The term first appears in Latin in 1469 as ''media tempestas'' (middle times).Albrow, Martin, ''The Global Age: state and society beyond modernity'' (1997), Stanford University Press
By the 15th century, writers, artists, and architects in Italy were well aware of the transformations that were taking place and were using phrases such as ''modi antichi'' (in the antique manner) or ''alle romana et alla antica'' (in the manner of the Romans and the ancients) to describe their work. In the 1330s Petrarch referred to pre-Christian times as ''antiqua'' (ancient) and to the Christian period as ''nova'' (new). From Petrarch's Italian perspective, this new period (which included his own time) was an age of national eclipse.
Leonardo Bruni was the first to use tripartite periodization in his ''History of the Florentine People'' (1442).Leonardo Bruni, James Hankins, ''History of the Florentine people'', Volume 1, Books 1–4 (2001), p. xvii. Bruni's first two periods were based on those of Petrarch, but he added a third period because he believed that Italy was no longer in a state of decline. Flavio Biondo used a similar framework in ''Decades of History from the Deterioration of the Roman Empire'' (1439–1453).
Humanist historians argued that contemporary scholarship restored direct links to the classical period, thus bypassing the Medieval period, which they then named for the first time the "Middle Ages". The term first appears in Latin in 1469 as ''media tempestas'' (middle times).Albrow, Martin, ''The Global Age: state and society beyond modernity'' (1997), Stanford University Press
p. 205
. The term ''rinascita'' (rebirth) first appeared, however, in its broad sense in Giorgio Vasari's '' Lives of the Artists'', 1550, revised 1568. Panofsky, Erwin. ''Renaissance and Renascences in Western Art'', New York: Harper and Row, 1960. Vasari divides the age into three phases: the first phase contains Cimabue, Giotto, and
 The word "Renaissance" is borrowed from the French language, where it means "re-birth". It was first used in the eighteenth century and was later popularized by French historian
The word "Renaissance" is borrowed from the French language, where it means "re-birth". It was first used in the eighteenth century and was later popularized by French historian
 In the second half of the 15th century, the Renaissance spirit spread to Germany and the Low Countries, where the development of the printing press (ca. 1450) and Renaissance artists such as
In the second half of the 15th century, the Renaissance spirit spread to Germany and the Low Countries, where the development of the printing press (ca. 1450) and Renaissance artists such as
The Renaissance in Hungary
(Retrieved May 10, 2007) The most important humanists living in Matthias' court were
 The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. It occurred after the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages and was associated with great social change. In addition to the standard periodization, proponents of a "long Renaissance" may put its beginning in the 14th century and its end in the 17th century.
The traditional view focuses more on the early modern aspects of the Renaissance and argues that it was a break from the past, but many historians today focus more on its medieval aspects and argue that it was an extension of the Middle Ages. However, the beginnings of the period – the early Renaissance of the 15th century and the Italian Proto-Renaissance from around 1250 or 1300 – overlap considerably with the Late Middle Ages, conventionally dated to , and the Middle Ages themselves were a long period filled with gradual changes, like the modern age; and as a transitional period between both, the Renaissance has close similarities to both, especially the late and early sub-periods of either.
The intellectual basis of the Renaissance was its version of humanism, derived from the concept of Roman '' humanitas'' and the rediscovery of classical Greek philosophy, such as that of
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. It occurred after the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages and was associated with great social change. In addition to the standard periodization, proponents of a "long Renaissance" may put its beginning in the 14th century and its end in the 17th century.
The traditional view focuses more on the early modern aspects of the Renaissance and argues that it was a break from the past, but many historians today focus more on its medieval aspects and argue that it was an extension of the Middle Ages. However, the beginnings of the period – the early Renaissance of the 15th century and the Italian Proto-Renaissance from around 1250 or 1300 – overlap considerably with the Late Middle Ages, conventionally dated to , and the Middle Ages themselves were a long period filled with gradual changes, like the modern age; and as a transitional period between both, the Renaissance has close similarities to both, especially the late and early sub-periods of either.
The intellectual basis of the Renaissance was its version of humanism, derived from the concept of Roman '' humanitas'' and the rediscovery of classical Greek philosophy, such as that of Protagoras
Protagoras (; el, Πρωταγόρας; )Guthrie, p. 262–263. was a pre-Socratic Greek philosopher and rhetorical theorist. He is numbered as one of the sophists by Plato. In his dialogue '' Protagoras'', Plato credits him with inventing the r ...
, who said that "man is the measure of all things". This new thinking became manifest in art, architecture, politics, science and literature. Early examples were the development of perspective in oil painting and the revived knowledge of how to make concrete. Although the invention of metal movable type
Movable type (US English; moveable type in British English) is the system and technology of printing and typography that uses movable components to reproduce the elements of a document (usually individual alphanumeric characters or punctuatio ...
sped the dissemination of ideas from the later 15th century, the changes of the Renaissance were not uniform across Europe: the first traces appear in Italy as early as the late 13th century, in particular with the writings of Dante and the paintings of Giotto.
As a cultural movement, the Renaissance encompassed innovative flowering of Latin and vernacular literatures, beginning with the 14th-century resurgence of learning based on classical sources, which contemporaries credited to Petrarch; the development of linear perspective and other techniques of rendering a more natural reality in painting; and gradual but widespread educational reform. In politics, the Renaissance contributed to the development of the customs and conventions of diplomacy, and in science to an increased reliance on observation and inductive reasoning
Inductive reasoning is a method of reasoning in which a general principle is derived from a body of observations. It consists of making broad generalizations based on specific observations. Inductive reasoning is distinct from ''deductive'' re ...
. Although the Renaissance saw revolutions in many intellectual and social scientific
Social science is one of the branches of science, devoted to the study of societies and the relationships among individuals within those societies. The term was formerly used to refer to the field of sociology, the original "science of soc ...
pursuits, as well as the introduction of modern banking and the field of accounting
Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the measurement, processing, and communication of financial and non financial information about economic entities such as businesses and corporations. Accounting, which has been called the "languag ...
, it is perhaps best known for its artistic developments and the contributions of such polymaths as Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was insp ...
, who inspired the term "Renaissance man".
The Renaissance began in the Republic of Florence, one of the many states of Italy. Various theories have been proposed to account for its origins and characteristics, focusing on a variety of factors including the social and civic peculiarities of Florence at the time: its political structure, the patronage of its dominant family, the Medici,Strathern, Paul ''The Medici: Godfathers of the Renaissance'' (2003) and the migration of Greek scholars and their texts to Italy following the Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city fell on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 53-day siege which had begun o ...
to the Ottoman Turks
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
.''Encyclopædia Britannica'', "Renaissance", 2008, O.Ed.Norwich, John Julius, ''A Short History of Byzantium'', 1997, Knopf, Other major centers were northern Italian city-states
The Italian city-states were numerous political and independent territorial entities that existed in the Italian Peninsula from the beginning of the Middle Ages until the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, which took place in 1861.
After the ...
such as Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, Genoa, Milan, Bologna, Rome during the Renaissance Papacy and Naples. From Italy, the Renaissance spread throughout Europe in Flanders, France, Britain, Ireland, Spain, Portugal, Germany, Poland, Hungary (with Beatrice of Naples) and elsewhere.
The Renaissance has a long and complex historiography, and, in line with general scepticism of discrete periodizations, there has been much debate among historians reacting to the 19th-century glorification of the "Renaissance" and individual cultural heroes as "Renaissance men", questioning the usefulness of ''Renaissance'' as a term and as a historical delineation. Some observers have called into question whether the Renaissance was a cultural "advance" from the Middle Ages, instead seeing it as a period of pessimism and nostalgia
Nostalgia is a sentimentality for the past, typically for a period or place with happy personal associations. The word ''nostalgia'' is a learned formation of a Greek language, Greek compound, consisting of (''nóstos''), meaning "homecoming", ...
for classical antiquity, Huizanga, Johan, ''The Waning of the Middle Ages
''The Autumn of the Middle Ages'', ''The Waning of the Middle Ages'', or ''Autumntide of the Middle Ages'' (published in 1919 as ''Herfsttij der Middeleeuwen'' and translated into English in 1924, German in 1924, and French in 1932), is the best ...
'' (1919, trans. 1924) while social and economic historians, especially of the '' longue durée'', have instead focused on the continuity between the two eras, which are linked, as Panofsky observed, "by a thousand ties".
The term ''rinascita'' ('rebirth') first appeared in Giorgio Vasari's '' Lives of the Artists'' (c. 1550), anglicized as the ''Renaissance'' in the 1830s. The word has also been extended to other historical and cultural movements, such as the Carolingian Renaissance
The Carolingian Renaissance was the first of three medieval renaissances, a period of cultural activity in the Carolingian Empire. It occurred from the late 8th century to the 9th century, taking inspiration from the State church of the Roman Emp ...
(8th and 9th centuries), Ottonian Renaissance
The Ottonian Renaissance was a renaissance of Byzantine and Late Antique art in Central and Southern Europe that accompanied the reigns of the first three Holy Roman Emperors of the Ottonian (or Saxon) dynasty: Otto I (936–973), Otto II (97 ...
(10th and 11th century), and the Renaissance of the 12th century
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
.
Overview
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that profoundly affected European intellectual life in the early modern period. Beginning in Italy, and spreading to the rest of Europe by the 16th century, its influence was felt in art, architecture,philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
, literature, music, science, technology, politics, religion, and other aspects of intellectual inquiry. Renaissance scholars employed the humanist method in study, and searched for realism and human emotion in art.Perry, MHumanities in the Western Tradition
Ch. 13 Renaissance humanists such as Poggio Bracciolini sought out in Europe's monastic libraries the Latin literary, historical, and oratorical texts of
antiquity
Antiquity or Antiquities may refer to:
Historical objects or periods Artifacts
*Antiquities, objects or artifacts surviving from ancient cultures
Eras
Any period before the European Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries) but still within the histo ...
, while the Fall of Constantinople
The Fall of Constantinople, also known as the Conquest of Constantinople, was the capture of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Empire. The city fell on 29 May 1453 as part of the culmination of a 53-day siege which had begun o ...
(1453) generated a wave of émigré Greek scholars bringing precious manuscripts in ancient Greek, many of which had fallen into obscurity in the West. It is in their new focus on literary and historical texts that Renaissance scholars differed so markedly from the medieval scholars of the Renaissance of the 12th century
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
, who had focused on studying Greek and Arabic works of natural sciences, philosophy, and mathematics, rather than on such cultural texts.
In the revival of neoplatonism Renaissance humanists did not reject Christianity; quite the contrary, many of the greatest works of the Renaissance were devoted to it, and the Church patronized many works of Renaissance art. However, a subtle shift took place in the way that intellectuals approached religion that was reflected in many other areas of cultural life.Open University, Looking at the Renaissance: Religious Context in the Renaissance
' (Retrieved May 10, 2007) In addition, many Greek Christian works, including the Greek New Testament, were brought back from
Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
to Western Europe and engaged Western scholars for the first time since late antiquity. This new engagement with Greek Christian works, and particularly the return to the original Greek of the New Testament promoted by humanists Lorenzo Valla and Erasmus, would help pave the way for the Reformation.
Well after the first artistic return to classicism had been exemplified in the sculpture of Nicola Pisano, Florentine painters led by Masaccio
Masaccio (, , ; December 21, 1401 – summer 1428), born Tommaso di Ser Giovanni di Simone, was a Florentine artist who is regarded as the first great Italian painter of the Quattrocento period of the Italian Renaissance. According to Vasari, ...
strove to portray the human form realistically, developing techniques to render perspective and light more naturally. Political philosophers, most famously Niccolò Machiavelli, sought to describe political life as it really was, that is to understand it rationally. A critical contribution to Italian Renaissance humanism, Giovanni Pico della Mirandola wrote the famous text '' De hominis dignitate'' (''Oration on the Dignity of Man'', 1486), which consists of a series of theses on philosophy, natural thought, faith, and magic defended against any opponent on the grounds of reason. In addition to studying classical Latin and Greek, Renaissance authors also began increasingly to use vernacular languages; combined with the introduction of the printing press, this would allow many more people access to books, especially the Bible.
In all, the Renaissance could be viewed as an attempt by intellectuals to study and improve the secular and worldly, both through the revival of ideas from antiquity, and through novel approaches to thought. Some scholars, such as Rodney Stark, play down the Renaissance in favor of the earlier innovations of the Italian city-states
The Italian city-states were numerous political and independent territorial entities that existed in the Italian Peninsula from the beginning of the Middle Ages until the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, which took place in 1861.
After the ...
in the High Middle Ages, which married responsive government, Christianity and the birth of capitalism. This analysis argues that, whereas the great European states (France and Spain) were absolute monarchies, and others were under direct Church control, the independent city-republics of Italy took over the principles of capitalism invented on monastic estates and set off a vast unprecedented Commercial Revolution that preceded and financed the Renaissance.
Origins
 Many argue that the ideas characterizing the Renaissance had their origin in Florence at the turn of the 13th and 14th centuries, in particular with the writings of Dante Alighieri (1265–1321) and Petrarch (1304–1374), as well as the paintings of Giotto di Bondone (1267–1337). Some writers date the Renaissance quite precisely; one proposed starting point is 1401, when the rival geniuses Lorenzo Ghiberti and
Many argue that the ideas characterizing the Renaissance had their origin in Florence at the turn of the 13th and 14th centuries, in particular with the writings of Dante Alighieri (1265–1321) and Petrarch (1304–1374), as well as the paintings of Giotto di Bondone (1267–1337). Some writers date the Renaissance quite precisely; one proposed starting point is 1401, when the rival geniuses Lorenzo Ghiberti and Filippo Brunelleschi
Filippo Brunelleschi ( , , also known as Pippo; 1377 – 15 April 1446), considered to be a founding father of Renaissance architecture, was an Italian architect, designer, and sculptor, and is now recognized to be the first modern engineer, p ...
competed for the contract to build the bronze doors for the Baptistery of the Florence Cathedral
Florence Cathedral, formally the (; in English Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Flower), is the cathedral of Florence, Italy ( it, Duomo di Firenze). It was begun in 1296 in the Gothic style to a design of Arnolfo di Cambio and was structurally c ...
(Ghiberti then won). Others see more general competition between artists and polymaths such as Brunelleschi, Ghiberti, Donatello, and Masaccio
Masaccio (, , ; December 21, 1401 – summer 1428), born Tommaso di Ser Giovanni di Simone, was a Florentine artist who is regarded as the first great Italian painter of the Quattrocento period of the Italian Renaissance. According to Vasari, ...
for artistic commissions as sparking the creativity of the Renaissance. Yet it remains much debated why the Renaissance began in Italy, and why it began when it did. Accordingly, several theories have been put forward to explain its origins.
During the Renaissance, money and art went hand in hand. Artists depended entirely on patrons while the patrons needed money to foster artistic talent. Wealth was brought to Italy in the 14th, 15th, and 16th centuries by expanding trade into Asia and Europe. Silver mining in Tyrol increased the flow of money. Luxuries from the Muslim world, brought home during the Crusades, increased the prosperity of Genoa and Venice.
Jules Michelet
Jules Michelet (; 21 August 1798 – 9 February 1874) was a French historian and an author on other topics whose major work was a history of France and its culture. His aphoristic style emphasized his anti-clerical republicanism.
In Michelet's ...
defined the 16th-century Renaissance in France as a period in Europe's cultural history that represented a break from the Middle Ages, creating a modern understanding of humanity and its place in the world.
Latin and Greek phases of Renaissance humanism
 In stark contrast to the High Middle Ages, when Latin scholars focused almost entirely on studying Greek and Arabic works of natural science, philosophy and mathematics, Renaissance scholars were most interested in recovering and studying Latin and Greek literary, historical, and oratorical texts. Broadly speaking, this began in the 14th century with a Latin phase, when Renaissance scholars such as Petrarch, Coluccio Salutati (1331–1406), Niccolò de' Niccoli (1364–1437), and Poggio Bracciolini (1380–1459) scoured the libraries of Europe in search of works by such Latin authors as Cicero, Lucretius, Livy, and Seneca. By the early 15th century, the bulk of the surviving such Latin literature had been recovered; the Greek phase of Renaissance humanism was under way, as Western European scholars turned to recovering ancient Greek literary, historical, oratorical and theological texts.
Unlike with Latin texts, which had been preserved and studied in Western Europe since late antiquity, the study of ancient Greek texts was very limited in medieval Western Europe. Ancient Greek works on science, mathematics, and philosophy had been studied since the High Middle Ages in Western Europe and in the Islamic Golden Age (normally in translation), but Greek literary, oratorical and historical works (such as Homer, the Greek dramatists, Demosthenes and Thucydides) were not studied in either the Latin or medieval
In stark contrast to the High Middle Ages, when Latin scholars focused almost entirely on studying Greek and Arabic works of natural science, philosophy and mathematics, Renaissance scholars were most interested in recovering and studying Latin and Greek literary, historical, and oratorical texts. Broadly speaking, this began in the 14th century with a Latin phase, when Renaissance scholars such as Petrarch, Coluccio Salutati (1331–1406), Niccolò de' Niccoli (1364–1437), and Poggio Bracciolini (1380–1459) scoured the libraries of Europe in search of works by such Latin authors as Cicero, Lucretius, Livy, and Seneca. By the early 15th century, the bulk of the surviving such Latin literature had been recovered; the Greek phase of Renaissance humanism was under way, as Western European scholars turned to recovering ancient Greek literary, historical, oratorical and theological texts.
Unlike with Latin texts, which had been preserved and studied in Western Europe since late antiquity, the study of ancient Greek texts was very limited in medieval Western Europe. Ancient Greek works on science, mathematics, and philosophy had been studied since the High Middle Ages in Western Europe and in the Islamic Golden Age (normally in translation), but Greek literary, oratorical and historical works (such as Homer, the Greek dramatists, Demosthenes and Thucydides) were not studied in either the Latin or medieval Islamic world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. In ...
s; in the Middle Ages these sorts of texts were only studied by Byzantine scholars. Some argue that the Timurid Renaissance in Samarkand
fa, سمرقند
, native_name_lang =
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from the top:Registan square, Shah-i-Zinda necropolis, Bibi-Khanym Mosque, view inside Shah-i-Zinda, ...
and Herat, whose magnificence toned with Florence as the center of a cultural rebirth, were linked to the Ottoman Empire, whose conquests led to the migration of Greek scholars to Italian cities. One of the greatest achievements of Renaissance scholars was to bring this entire class of Greek cultural works back into Western Europe for the first time since late antiquity.
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
logicians, most notably Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic G ...
and Averroes, had inherited Greek ideas after they had invaded and conquered Egypt and the Levant. Their translations and commentaries on these ideas worked their way through the Arab West into Iberia and Sicily, which became important centers for this transmission of ideas. From the 11th to the 13th century, many schools dedicated to the translation of philosophical and scientific works from Classical Arabic
Classical Arabic ( ar, links=no, ٱلْعَرَبِيَّةُ ٱلْفُصْحَىٰ, al-ʿarabīyah al-fuṣḥā) or Quranic Arabic is the standardized literary form of Arabic used from the 7th century and throughout the Middle Ages, most notab ...
to Medieval Latin were established in Iberia, most notably the Toledo School of Translators. This work of translation from Islamic culture, though largely unplanned and disorganized, constituted one of the greatest transmissions of ideas in history.''Western Civilization: Ideas, Politics, and Society''Marvin Perry, Myrna Chase, Margaret C. Jacob, James R. Jacob, 2008, pp. 261–262. The movement to reintegrate the regular study of Greek literary, historical, oratorical and theological texts back into the Western European curriculum is usually dated to the 1396 invitation from Coluccio Salutati to the Byzantine diplomat and scholar Manuel Chrysoloras (c. 1355–1415) to teach Greek in Florence. This legacy was continued by a number of expatriate Greek scholars, from Basilios Bessarion to
Leo Allatius
Leo Allatius (Greek: Λέων Αλλάτιος, ''Leon Allatios'', Λιωνής Αλάτζης, ''Lionis Allatzis''; Italian: ''Leone Allacci, Allacio''; Latin: ''Leo Allatius, Allacius''; c. 1586 – January 19, 1669) was a Greek scholar, theolog ...
.
Social and political structures in Italy
 The unique political structures of Late Middle Ages Italy have led some to theorize that its unusual social climate allowed the emergence of a rare cultural efflorescence. Italy did not exist as a political entity in the early modern period. Instead, it was divided into smaller city-states and territories: the
The unique political structures of Late Middle Ages Italy have led some to theorize that its unusual social climate allowed the emergence of a rare cultural efflorescence. Italy did not exist as a political entity in the early modern period. Instead, it was divided into smaller city-states and territories: the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
controlled the south, the Republic of Florence and the Papal States at the center, the Milanese and the Genoese
Genoese may refer to:
* a person from Genoa
* Genoese dialect, a dialect of the Ligurian language
* Republic of Genoa (–1805), a former state in Liguria
See also
* Genovese, a surname
* Genovesi, a surname
*
*
*
*
* Genova (disambiguati ...
to the north and west respectively, and the Venetians to the east. Fifteenth-century Italy was one of the most urbanized areas in Europe. Many of its cities stood among the ruins of ancient Roman buildings; it seems likely that the classical nature of the Renaissance was linked to its origin in the Roman Empire's heartland.
Historian and political philosopher Quentin Skinner
Quentin Robert Duthie Skinner (born 26 November 1940) is a British intellectual historian. He is regarded as one of the founders of the Cambridge School of the history of political thought. He has won numerous prizes for his work, including th ...
points out that Otto of Freising (c. 1114–1158), a German bishop visiting north Italy during the 12th century, noticed a widespread new form of political and social organization, observing that Italy appeared to have exited from feudalism so that its society was based on merchants and commerce. Linked to this was anti-monarchical thinking, represented in the famous early Renaissance fresco
Fresco (plural ''frescos'' or ''frescoes'') is a technique of mural painting executed upon freshly laid ("wet") lime plaster. Water is used as the vehicle for the dry-powder pigment to merge with the plaster, and with the setting of the plaste ...
cycle '' The Allegory of Good and Bad Government'' by Ambrogio Lorenzetti (painted 1338–1340), whose strong message is about the virtues of fairness, justice, republicanism and good administration. Holding both Church and Empire at bay, these city republics were devoted to notions of liberty. Skinner reports that there were many defences of liberty such as the Matteo Palmieri (1406–1475) celebration of Florentine genius not only in art, sculpture and architecture, but "the remarkable efflorescence of moral, social and political philosophy that occurred in Florence at the same time".Skinner, Quentin, ''The Foundations of Modern Political Thought'', vol I: ''The Renaissance''; vol II: ''The Age of Reformation'', Cambridge University Press, p. 69
Even cities and states beyond central Italy, such as the Republic of Florence at this time, were also notable for their merchant republics
The maritime republics ( it, repubbliche marinare), also called merchant republics ( it, repubbliche mercantili), were thalassocratic city-states of the Mediterranean Basin during the Middle Ages. Being a significant presence in Italy in the Mi ...
, especially the Republic of Venice. Although in practice these were oligarchical
Oligarchy (; ) is a conceptual form of power structure in which power rests with a small number of people. These people may or may not be distinguished by one or several characteristics, such as nobility, fame, wealth, education, or corporate, r ...
, and bore little resemblance to a modern democracy, they did have democratic features and were responsive states, with forms of participation in governance and belief in liberty. The relative political freedom they afforded was conducive to academic and artistic advancement.Burckhardt, Jacob, ''The Republics: Venice and Florence'', The Civilization of the Renaissance in Italy
'', translated by S.G.C. Middlemore, 1878. Likewise, the position of Italian cities such as Venice as great trading centres made them intellectual crossroads.
Merchant
A merchant is a person who trades in commodities produced by other people, especially one who trades with foreign countries. Historically, a merchant is anyone who is involved in business or trade. Merchants have operated for as long as indust ...
s brought with them ideas from far corners of the globe, particularly the Levant. Venice was Europe's gateway to trade with the East, and a producer of fine glass, while Florence was a capital of textiles. The wealth such business brought to Italy meant large public and private artistic projects could be commissioned and individuals had more leisure time for study.
Black Death
 One theory that has been advanced is that the devastation in Florence caused by the
One theory that has been advanced is that the devastation in Florence caused by the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
, which hit Europe between 1348 and 1350, resulted in a shift in the world view of people in 14th century Italy. Italy was particularly badly hit by the plague, and it has been speculated that the resulting familiarity with death caused thinkers to dwell more on their lives on Earth, rather than on spirituality
The meaning of ''spirituality'' has developed and expanded over time, and various meanings can be found alongside each other. Traditionally, spirituality referred to a religious process of re-formation which "aims to recover the original shape o ...
and the afterlife
The afterlife (also referred to as life after death) is a purported existence in which the essential part of an individual's identity or their stream of consciousness continues to live after the death of their physical body. The surviving ess ...
. It has also been argued that the Black Death prompted a new wave of piety, manifested in the sponsorship of religious works of art. However, this does not fully explain why the Renaissance occurred specifically in Italy in the 14th century. The Black Death was a pandemic
A pandemic () is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. A widespread endemic (epidemiology), endemic disease wi ...
that affected all of Europe in the ways described, not only Italy. The Renaissance's emergence in Italy was most likely the result of the complex interaction of the above factors.Brotton, J., ''The Renaissance: A Very Short Introduction'', OUP, 2006 .
The plague was carried by fleas on sailing vessels returning from the ports of Asia, spreading quickly due to lack of proper sanitation: the population of England, then about 4.2 million, lost 1.4 million people to the bubonic plague
Bubonic plague is one of three types of plague caused by the plague bacterium (''Yersinia pestis''). One to seven days after exposure to the bacteria, flu-like symptoms develop. These symptoms include fever, headaches, and vomiting, as well a ...
. Florence's population was nearly halved in the year 1347. As a result of the decimation in the populace the value of the working class increased, and commoners came to enjoy more freedom. To answer the increased need for labor, workers traveled in search of the most favorable position economically.
The demographic decline due to the plague had economic consequences: the prices of food dropped and land values declined by 30–40% in most parts of Europe between 1350 and 1400. Landholders faced a great loss, but for ordinary men and women it was a windfall. The survivors of the plague found not only that the prices of food were cheaper but also that lands were more abundant, and many of them inherited property from their dead relatives.
The spread of disease was significantly more rampant in areas of poverty. Epidemics ravaged cities, particularly children. Plagues were easily spread by lice, unsanitary drinking water, armies, or by poor sanitation. Children were hit the hardest because many diseases, such as typhus and congenital syphilis, target the immune system, leaving young children without a fighting chance. Children in city dwellings were more affected by the spread of disease than the children of the wealthy.
The Black Death caused greater upheaval to Florence's social and political structure than later epidemics. Despite a significant number of deaths among members of the ruling classes, the government of Florence continued to function during this period. Formal meetings of elected representatives were suspended during the height of the epidemic due to the chaotic conditions in the city, but a small group of officials was appointed to conduct the affairs of the city, which ensured continuity of government.
Cultural conditions in Florence
 It has long been a matter of debate why the Renaissance began in Florence, and not elsewhere in Italy. Scholars have noted several features unique to Florentine cultural life that may have caused such a cultural movement. Many have emphasized the role played by the Medici, a banking family and later ducal ruling house, in patronizing and stimulating the arts. Lorenzo de' Medici (1449–1492) was the catalyst for an enormous amount of arts patronage, encouraging his countrymen to commission works from the leading artists of Florence, including Leonardo da Vinci, Sandro Botticelli, and Michelangelo Buonarroti. Works by Neri di Bicci, Botticelli, da Vinci, and Filippino Lippi had been commissioned additionally by the Convent of San Donato in Scopeto in Florence.
The Renaissance was certainly underway before Lorenzo de' Medici came to power – indeed, before the Medici family itself achieved hegemony in Florentine society. Some historians have postulated that Florence was the birthplace of the Renaissance as a result of luck, i.e., because " Great Men" were born there by chance:Burckhardt, Jacob, ''The Development of the Individual'',
It has long been a matter of debate why the Renaissance began in Florence, and not elsewhere in Italy. Scholars have noted several features unique to Florentine cultural life that may have caused such a cultural movement. Many have emphasized the role played by the Medici, a banking family and later ducal ruling house, in patronizing and stimulating the arts. Lorenzo de' Medici (1449–1492) was the catalyst for an enormous amount of arts patronage, encouraging his countrymen to commission works from the leading artists of Florence, including Leonardo da Vinci, Sandro Botticelli, and Michelangelo Buonarroti. Works by Neri di Bicci, Botticelli, da Vinci, and Filippino Lippi had been commissioned additionally by the Convent of San Donato in Scopeto in Florence.
The Renaissance was certainly underway before Lorenzo de' Medici came to power – indeed, before the Medici family itself achieved hegemony in Florentine society. Some historians have postulated that Florence was the birthplace of the Renaissance as a result of luck, i.e., because " Great Men" were born there by chance:Burckhardt, Jacob, ''The Development of the Individual'', The Civilization of the Renaissance in Italy
'', translated by S.G.C. Middlemore, 1878. Leonardo da Vinci, Botticelli and Michelangelo were all born in Tuscany. Arguing that such chance seems improbable, other historians have contended that these "Great Men" were only able to rise to prominence because of the prevailing cultural conditions at the time.
Characteristics
Humanism
In some ways, Renaissance humanism was not a philosophy but a method of learning. In contrast to the medievalscholastic
Scholastic may refer to:
* a philosopher or theologian in the tradition of scholasticism
* ''Scholastic'' (Notre Dame publication)
* Scholastic Corporation, an American publishing company of educational materials
* Scholastic Building, in New Y ...
mode, which focused on resolving contradictions between authors, Renaissance humanists would study ancient texts in the original and appraise them through a combination of reasoning and empirical evidence. Humanist education was based on the programme of ''Studia Humanitatis'', the study of five humanities: poetry, grammar, history, moral philosophy
Ethics or moral philosophy is a branch of philosophy that "involves systematizing, defending, and recommending concepts of right and wrong behavior".''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' The field of ethics, along with aesthetics, concerns ma ...
, and rhetoric
Rhetoric () is the art of persuasion, which along with grammar and logic (or dialectic), is one of the three ancient arts of discourse. Rhetoric aims to study the techniques writers or speakers utilize to inform, persuade, or motivate parti ...
. Although historians have sometimes struggled to define humanism precisely, most have settled on "a middle of the road definition... the movement to recover, interpret, and assimilate the language, literature, learning and values of ancient Greece and Rome". Above all, humanists asserted "the genius of man ... the unique and extraordinary ability of the human mind".
 Humanist scholars shaped the intellectual landscape throughout the early modern period. Political philosophers such as Niccolò Machiavelli and Thomas More revived the ideas of Greek and Roman thinkers and applied them in critiques of contemporary government, following the Islamic steps of
Humanist scholars shaped the intellectual landscape throughout the early modern period. Political philosophers such as Niccolò Machiavelli and Thomas More revived the ideas of Greek and Roman thinkers and applied them in critiques of contemporary government, following the Islamic steps of Ibn Khaldun
Ibn Khaldun (; ar, أبو زيد عبد الرحمن بن محمد بن خلدون الحضرمي, ; 27 May 1332 – 17 March 1406, 732-808 AH) was an Arab
The Historical Muhammad', Irving M. Zeitlin, (Polity Press, 2007), p. 21; "It is, of ...
. Pico della Mirandola
Giovanni Pico della Mirandola (24 February 1463 – 17 November 1494) was an Italian Renaissance nobleman and philosopher. He is famed for the events of 1486, when, at the age of 23, he proposed to defend 900 theses on religion, philosophy, ...
wrote the "manifesto" of the Renaissance, the '' Oration on the Dignity of Man'', a vibrant defence of thinking. Matteo Palmieri (1406–1475), another humanist, is most known for his work ''Della vita civile'' ("On Civic Life"; printed 1528), which advocated civic humanism
Classical republicanism, also known as civic republicanism or civic humanism, is a form of republicanism developed in the Renaissance inspired by the governmental forms and writings of classical antiquity, especially such classical writers as Ar ...
, and for his influence in refining the Tuscan vernacular to the same level as Latin. Palmieri drew on Roman philosophers and theorists, especially Cicero, who, like Palmieri, lived an active public life as a citizen and official, as well as a theorist and philosopher and also Quintilian
Marcus Fabius Quintilianus (; 35 – 100 AD) was a Roman educator and rhetorician from Hispania, widely referred to in medieval schools of rhetoric and in Renaissance writing. In English translation, he is usually referred to as Quintilia ...
. Perhaps the most succinct expression of his perspective on humanism is in a 1465 poetic work ''La città di vita'', but an earlier work, ''Della vita civile'', is more wide-ranging. Composed as a series of dialogues set in a country house in the Mugello countryside outside Florence during the plague of 1430, Palmieri expounds on the qualities of the ideal citizen. The dialogues include ideas about how children develop mentally and physically, how citizens can conduct themselves morally, how citizens and states can ensure probity in public life, and an important debate on the difference between that which is pragmatically useful and that which is honest.
The humanists believed that it is important to transcend to the afterlife with a perfect mind and body, which could be attained with education. The purpose of humanism was to create a universal man whose person combined intellectual and physical excellence and who was capable of functioning honorably in virtually any situation. This ideology was referred to as the '' uomo universale'', an ancient Greco-Roman ideal. Education during the Renaissance was mainly composed of ancient literature and history as it was thought that the classics provided moral instruction and an intensive understanding of human behavior.
Humanism and libraries
A unique characteristic of some Renaissance libraries is that they were open to the public. These libraries were places where ideas were exchanged and where scholarship and reading were considered both pleasurable and beneficial to the mind and soul. As freethinking was a hallmark of the age, many libraries contained a wide range of writers. Classical texts could be found alongside humanist writings. These informal associations of intellectuals profoundly influenced Renaissance culture. Some of the richest "bibliophiles" built libraries as temples to books and knowledge. A number of libraries appeared as manifestations of immense wealth joined with a love of books. In some cases, cultivated library builders were also committed to offering others the opportunity to use their collections. Prominent aristocrats and princes of the Church created great libraries for the use of their courts, called "court libraries", and were housed in lavishly designed monumental buildings decorated with ornate woodwork, and the walls adorned with frescoes (Murray, Stuart A.P.).Art
Renaissance art marks a cultural rebirth at the close of the Middle Ages and rise of the Modern world. One of the distinguishing features of Renaissance art was its development of highly realistic linear perspective. Giotto di Bondone (1267–1337) is credited with first treating a painting as a window into space, but it was not until the demonstrations of architectFilippo Brunelleschi
Filippo Brunelleschi ( , , also known as Pippo; 1377 – 15 April 1446), considered to be a founding father of Renaissance architecture, was an Italian architect, designer, and sculptor, and is now recognized to be the first modern engineer, p ...
(1377–1446) and the subsequent writings of Leon Battista Alberti (1404–1472) that perspective was formalized as an artistic technique.
 The development of perspective was part of a wider trend towards realism in the arts. Painters developed other techniques, studying light, shadow, and, famously in the case of Leonardo da Vinci,
The development of perspective was part of a wider trend towards realism in the arts. Painters developed other techniques, studying light, shadow, and, famously in the case of Leonardo da Vinci, human anatomy
The human body is the structure of a human being. It is composed of many different types of cells that together create tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the viability of the human body.
It comprises a he ...
. Underlying these changes in artistic method was a renewed desire to depict the beauty of nature and to unravel the axioms of aesthetics, with the works of Leonardo, Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was insp ...
and Raphael representing artistic pinnacles that were much imitated by other artists. Other notable artists include Sandro Botticelli, working for the Medici in Florence, Donatello, another Florentine, and Titian in Venice, among others.
In the Netherlands, a particularly vibrant artistic culture developed. The work of Hugo van der Goes and Jan van Eyck
Jan van Eyck ( , ; – July 9, 1441) was a painter active in Bruges who was one of the early innovators of what became known as Early Netherlandish painting, and one of the most significant representatives of Early Northern Renaissance art. Ac ...
was particularly influential on the development of painting in Italy, both technically with the introduction of oil paint and canvas, and stylistically in terms of naturalism in representation. Later, the work of Pieter Brueghel the Elder would inspire artists to depict themes of everyday life.
In architecture, Filippo Brunelleschi was foremost in studying the remains of ancient classical buildings. With rediscovered knowledge from the 1st-century writer Vitruvius and the flourishing discipline of mathematics, Brunelleschi formulated the Renaissance style that emulated and improved on classical forms. His major feat of engineering was building the dome of the Florence Cathedral
Florence Cathedral, formally the (; in English Cathedral of Saint Mary of the Flower), is the cathedral of Florence, Italy ( it, Duomo di Firenze). It was begun in 1296 in the Gothic style to a design of Arnolfo di Cambio and was structurally c ...
. Another building demonstrating this style is the church of St. Andrew in Mantua, built by Alberti. The outstanding architectural work of the High Renaissance was the rebuilding of St. Peter's Basilica, combining the skills of Bramante, Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was insp ...
, Raphael, Sangallo and Maderno.
During the Renaissance, architects aimed to use columns, pilasters, and entablatures
An entablature (; nativization of Italian language, Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of molding (decorative), moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capital (architecture), capitals. E ...
as an integrated system. The Roman orders types of columns are used: Tuscan and Composite. These can either be structural, supporting an arcade or architrave, or purely decorative, set against a wall in the form of pilasters. One of the first buildings to use pilasters as an integrated system was in the Old Sacristy (1421–1440) by Brunelleschi. Arches, semi-circular or (in the Mannerist style) segmental, are often used in arcades, supported on piers or columns with capitals. There may be a section of entablature between the capital and the springing of the arch. Alberti was one of the first to use the arch on a monumental. Renaissance vaults do not have ribs; they are semi-circular or segmental and on a square plan, unlike the Gothic vault, which is frequently rectangular.
Renaissance artists were not pagans, although they admired antiquity and kept some ideas and symbols of the medieval past. Nicola Pisano (c. 1220 – c. 1278) imitated classical forms by portraying scenes from the Bible. His ''Annunciation'', from the Baptistry at Pisa, demonstrates that classical models influenced Italian art before the Renaissance took root as a literary movement.
Science

 Applied innovation extended to commerce. At the end of the 15th century,
Applied innovation extended to commerce. At the end of the 15th century, Luca Pacioli
Fra Luca Bartolomeo de Pacioli (sometimes ''Paccioli'' or ''Paciolo''; 1447 – 19 June 1517) was an Italian mathematician, Franciscan friar, collaborator with Leonardo da Vinci, and an early contributor to the field now known as accounting ...
published the first work on bookkeeping
Bookkeeping is the recording of financial transactions, and is part of the process of accounting in business and other organizations. It involves preparing source documents for all transactions, operations, and other events of a business. Tr ...
, making him the founder of accounting
Accounting, also known as accountancy, is the measurement, processing, and communication of financial and non financial information about economic entities such as businesses and corporations. Accounting, which has been called the "languag ...
.
The rediscovery of ancient texts and the invention of the printing press in about 1440 democratized learning and allowed a faster propagation of more widely distributed ideas. In the first period of the Italian Renaissance, humanists favored the study of humanities over natural philosophy or applied mathematics, and their reverence for classical sources further enshrined the Aristotelian and Ptolemaic views of the universe. Writing around 1450, Nicholas Cusanus
Nicholas of Cusa (1401 – 11 August 1464), also referred to as Nicholas of Kues and Nicolaus Cusanus (), was a German Catholic cardinal, philosopher, theologian, jurist, mathematician, and astronomer. One of the first German proponents of Renai ...
anticipated the heliocentric
Heliocentrism (also known as the Heliocentric model) is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around the Sun at the center of the universe. Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth at ...
worldview of Copernicus, but in a philosophical fashion.
Science and art were intermingled in the early Renaissance, with polymath artists such as Leonardo da Vinci making observational drawings of anatomy and nature. Da Vinci set up controlled experiments in water flow, medical dissection, and systematic study of movement and aerodynamics, and he devised principles of research method that led Fritjof Capra to classify him as the "father of modern science". Other examples of Da Vinci's contribution during this period include machines designed to saw marbles and lift monoliths, and new discoveries in acoustics, botany, geology, anatomy, and mechanics.
A suitable environment had developed to question classical scientific doctrine. The discovery in 1492 of the New World by Christopher Columbus challenged the classical worldview. The works of Ptolemy (in geography) and Galen (in medicine) were found to not always match everyday observations. As the Reformation and Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
clashed, the Northern Renaissance showed a decisive shift in focus from Aristotelean natural philosophy to chemistry and the biological sciences (botany, anatomy, and medicine). The willingness to question previously held truths and search for new answers resulted in a period of major scientific advancements.
Some view this as a " scientific revolution", heralding the beginning of the modern age, others as an acceleration of a continuous process stretching from the ancient world to the present day. Significant scientific advances were made during this time by Galileo Galilei, Tycho Brahe, and Johannes Kepler
Johannes Kepler (; ; 27 December 1571 – 15 November 1630) was a German astronomer, mathematician, astrologer, natural philosopher and writer on music. He is a key figure in the 17th-century Scientific Revolution, best known for his laws ...
. Copernicus, in '' De revolutionibus orbium coelestium'' (''On the Revolutions of the Heavenly Spheres''), posited that the Earth moved around the Sun. '' De humani corporis fabrica'' (''On the Workings of the Human Body'') by Andreas Vesalius, gave a new confidence to the role of dissection
Dissection (from Latin ' "to cut to pieces"; also called anatomization) is the dismembering of the body of a deceased animal or plant to study its anatomical structure. Autopsy is used in pathology and forensic medicine to determine the cause o ...
, observation, and the mechanistic view of anatomy.Brotton, J., "Science and Philosophy", ''The Renaissance: A Very Short Introduction'' Oxford University Press, 2006 .
Another important development was in the ''process'' for discovery, the scientific method, focusing on empirical evidence and the importance of mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, while discarding much of Aristotelian science. Early and influential proponents of these ideas included Copernicus, Galileo, and Francis Bacon. The new scientific method led to great contributions in the fields of astronomy, physics, biology, and anatomy.
Navigation and geography
 During the Renaissance, extending from 1450 to 1650, every continent was visited and mostly mapped by Europeans, except the south polar continent now known as Antarctica. This development is depicted in the large world map ''Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Tabula'' made by the Dutch cartographer Joan Blaeu in 1648 to commemorate the
During the Renaissance, extending from 1450 to 1650, every continent was visited and mostly mapped by Europeans, except the south polar continent now known as Antarctica. This development is depicted in the large world map ''Nova Totius Terrarum Orbis Tabula'' made by the Dutch cartographer Joan Blaeu in 1648 to commemorate the Peace of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
.
In 1492, Christopher Columbus sailed across the Atlantic Ocean from Spain seeking a direct route to India of the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206–1526).
. He accidentally stumbled upon the Americas, but believed he had reached the East Indies.
In 1606, the Dutch navigator Willem Janszoon sailed from the East Indies in the VOC ship Duyfken and landed in Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
. He charted about 300 km of the west coast of Cape York Peninsula in Queensland. More than thirty Dutch expeditions followed, mapping sections of the north, west, and south coasts. In 1642–1643, Abel Tasman circumnavigated the continent, proving that it was not joined to the imagined south polar continent.
By 1650, Dutch cartographers had mapped most of the coastline of the continent, which they named New Holland, except the east coast which was charted in 1770 by James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
.
The long-imagined south polar continent was eventually sighted in 1820. Throughout the Renaissance it had been known as Terra Australis, or 'Australia' for short. However, after that name was transferred to New Holland in the nineteenth century, the new name of 'Antarctica' was bestowed on the south polar continent.
Music
From this changing society emerged a common, unifying musical language, in particular thepolyphonic
Polyphony ( ) is a type of musical texture consisting of two or more simultaneous lines of independent melody, as opposed to a musical texture with just one voice, monophony, or a texture with one dominant melodic voice accompanied by chords, h ...
style of the Franco-Flemish school. The development of printing made distribution of music possible on a wide scale. Demand for music as entertainment and as an activity for educated amateurs increased with the emergence of a bourgeois class. Dissemination of chansons, motet
In Western classical music, a motet is mainly a vocal musical composition, of highly diverse form and style, from high medieval music to the present. The motet was one of the pre-eminent polyphonic forms of Renaissance music. According to Margar ...
s, and masses throughout Europe coincided with the unification of polyphonic practice into the fluid style that culminated in the second half of the sixteenth century in the work of composers such as Palestrina, Lassus, Victoria, and William Byrd.
Religion
 The new ideals of humanism, although more secular in some aspects, developed against a Christian backdrop, especially in the Northern Renaissance. Much, if not most, of the new art was commissioned by or in dedication to the Church. However, the Renaissance had a profound effect on contemporary theology, particularly in the way people perceived the relationship between man and God. Many of the period's foremost theologians were followers of the humanist method, including Erasmus, Zwingli, Thomas More, Martin Luther, and
The new ideals of humanism, although more secular in some aspects, developed against a Christian backdrop, especially in the Northern Renaissance. Much, if not most, of the new art was commissioned by or in dedication to the Church. However, the Renaissance had a profound effect on contemporary theology, particularly in the way people perceived the relationship between man and God. Many of the period's foremost theologians were followers of the humanist method, including Erasmus, Zwingli, Thomas More, Martin Luther, and John Calvin
John Calvin (; frm, Jehan Cauvin; french: link=no, Jean Calvin ; 10 July 150927 May 1564) was a French theologian, pastor and reformer in Geneva during the Protestant Reformation. He was a principal figure in the development of the system ...
.
 The Renaissance began in times of religious turmoil. The late Middle Ages was a period of political intrigue surrounding the
The Renaissance began in times of religious turmoil. The late Middle Ages was a period of political intrigue surrounding the Papacy
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
, culminating in the Western Schism, in which three men simultaneously claimed to be true Bishop of Rome. While the schism was resolved by the Council of Constance
The Council of Constance was a 15th-century ecumenical council recognized by the Catholic Church, held from 1414 to 1418 in the Bishopric of Constance in present-day Germany. The council ended the Western Schism by deposing or accepting the res ...
(1414), a resulting reform movement known as Conciliarism sought to limit the power of the pope. Although the papacy eventually emerged supreme in ecclesiastical matters by the Fifth Council of the Lateran (1511), it was dogged by continued accusations of corruption, most famously in the person of Pope Alexander VI
Pope Alexander VI ( it, Alessandro VI, va, Alexandre VI, es, Alejandro VI; born Rodrigo de Borja; ca-valencia, Roderic Llançol i de Borja ; es, Rodrigo Lanzol y de Borja, lang ; 1431 – 18 August 1503) was head of the Catholic Churc ...
, who was accused variously of simony
Simony () is the act of selling church offices and roles or sacred things. It is named after Simon Magus, who is described in the Acts of the Apostles as having offered two disciples of Jesus payment in exchange for their empowering him to imp ...
, nepotism
Nepotism is an advantage, privilege, or position that is granted to relatives and friends in an occupation or field. These fields may include but are not limited to, business, politics, academia, entertainment, sports, fitness, religion, an ...
, and fathering children (most of whom were married off, presumably for the consolidation of power) while a cardinal.
Churchmen such as Erasmus and Luther proposed reform to the Church, often based on humanist textual criticism of the New Testament. In October 1517 Luther published the ''Ninety-five Theses
The ''Ninety-five Theses'' or ''Disputation on the Power and Efficacy of Indulgences''-The title comes from the 1517 Basel pamphlet printing. The first printings of the ''Theses'' use an incipit rather than a title which summarizes the content ...
'', challenging papal authority and criticizing its perceived corruption, particularly with regard to instances of sold indulgences. The 95 Theses led to the Reformation, a break with the Roman Catholic Church that previously claimed hegemony in Western Europe. Humanism and the Renaissance therefore played a direct role in sparking the Reformation, as well as in many other contemporaneous religious debates and conflicts.
Pope Paul III
Pope Paul III ( la, Paulus III; it, Paolo III; 29 February 1468 – 10 November 1549), born Alessandro Farnese, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 13 October 1534 to his death in November 1549.
He came to ...
came to the papal throne (1534–1549) after the sack of Rome in 1527
The Sack of Rome, then part of the Papal States, followed the capture of the city on 6 May 1527 by the mutinous troops of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor during the War of the League of Cognac. Despite not being ordered to storm the city, wit ...
, with uncertainties prevalent in the Catholic Church following the Protestant Reformation. Nicolaus Copernicus dedicated '' De revolutionibus orbium coelestium'' (On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres) to Paul III, who became the grandfather of Alessandro Farnese, who had paintings by Titian, Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was insp ...
, and Raphael, as well as an important collection of drawings, and who commissioned the masterpiece of Giulio Clovio, arguably the last major illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared document where the text is often supplemented with flourishes such as borders and miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Church for prayers, liturgical services and psalms, the ...
, the '' Farnese Hours''.
Self-awareness
 By the 15th century, writers, artists, and architects in Italy were well aware of the transformations that were taking place and were using phrases such as ''modi antichi'' (in the antique manner) or ''alle romana et alla antica'' (in the manner of the Romans and the ancients) to describe their work. In the 1330s Petrarch referred to pre-Christian times as ''antiqua'' (ancient) and to the Christian period as ''nova'' (new). From Petrarch's Italian perspective, this new period (which included his own time) was an age of national eclipse.
Leonardo Bruni was the first to use tripartite periodization in his ''History of the Florentine People'' (1442).Leonardo Bruni, James Hankins, ''History of the Florentine people'', Volume 1, Books 1–4 (2001), p. xvii. Bruni's first two periods were based on those of Petrarch, but he added a third period because he believed that Italy was no longer in a state of decline. Flavio Biondo used a similar framework in ''Decades of History from the Deterioration of the Roman Empire'' (1439–1453).
Humanist historians argued that contemporary scholarship restored direct links to the classical period, thus bypassing the Medieval period, which they then named for the first time the "Middle Ages". The term first appears in Latin in 1469 as ''media tempestas'' (middle times).Albrow, Martin, ''The Global Age: state and society beyond modernity'' (1997), Stanford University Press
By the 15th century, writers, artists, and architects in Italy were well aware of the transformations that were taking place and were using phrases such as ''modi antichi'' (in the antique manner) or ''alle romana et alla antica'' (in the manner of the Romans and the ancients) to describe their work. In the 1330s Petrarch referred to pre-Christian times as ''antiqua'' (ancient) and to the Christian period as ''nova'' (new). From Petrarch's Italian perspective, this new period (which included his own time) was an age of national eclipse.
Leonardo Bruni was the first to use tripartite periodization in his ''History of the Florentine People'' (1442).Leonardo Bruni, James Hankins, ''History of the Florentine people'', Volume 1, Books 1–4 (2001), p. xvii. Bruni's first two periods were based on those of Petrarch, but he added a third period because he believed that Italy was no longer in a state of decline. Flavio Biondo used a similar framework in ''Decades of History from the Deterioration of the Roman Empire'' (1439–1453).
Humanist historians argued that contemporary scholarship restored direct links to the classical period, thus bypassing the Medieval period, which they then named for the first time the "Middle Ages". The term first appears in Latin in 1469 as ''media tempestas'' (middle times).Albrow, Martin, ''The Global Age: state and society beyond modernity'' (1997), Stanford University Pressp. 205
. The term ''rinascita'' (rebirth) first appeared, however, in its broad sense in Giorgio Vasari's '' Lives of the Artists'', 1550, revised 1568. Panofsky, Erwin. ''Renaissance and Renascences in Western Art'', New York: Harper and Row, 1960. Vasari divides the age into three phases: the first phase contains Cimabue, Giotto, and
Arnolfo di Cambio
Arnolfo di Cambio (c. 1240 – 1300/1310) was an Italian architect and sculptor. He designed Florence Cathedral and the sixth city wall around Florence (1284–1333), while his most important surviving work as a sculptor is the tomb of Cardin ...
; the second phase contains Masaccio
Masaccio (, , ; December 21, 1401 – summer 1428), born Tommaso di Ser Giovanni di Simone, was a Florentine artist who is regarded as the first great Italian painter of the Quattrocento period of the Italian Renaissance. According to Vasari, ...
, Brunelleschi, and Donatello; the third centers on Leonardo da Vinci and culminates with Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was insp ...
. It was not just the growing awareness of classical antiquity that drove this development, according to Vasari, but also the growing desire to study and imitate nature.
Spread
In the 15th century, the Renaissance spread rapidly from its birthplace in Florence to the rest of Italy and soon to the rest of Europe. The invention of the printing press by German printerJohannes Gutenberg
Johannes Gensfleisch zur Laden zum Gutenberg (; – 3 February 1468) was a German inventor and Artisan, craftsman who introduced letterpress printing to Europe with his movable type, movable-type printing press. Though not the first of its ki ...
allowed the rapid transmission of these new ideas. As it spread, its ideas diversified and changed, being adapted to local culture. In the 20th century, scholars began to break the Renaissance into regional and national movements.

England
In England, the sixteenth century marked the beginning of the English Renaissance with the work of writers William Shakespeare (1564 –1616),Christopher Marlowe
Christopher Marlowe, also known as Kit Marlowe (; baptised 26 February 156430 May 1593), was an English playwright, poet and translator of the Elizabethan era. Marlowe is among the most famous of the Elizabethan playwrights. Based upon the ...
(1564 – 1593), Edmund Spenser
Edmund Spenser (; 1552/1553 – 13 January 1599) was an English poet best known for ''The Faerie Queene'', an epic poem and fantastical allegory celebrating the Tudor dynasty and Elizabeth I. He is recognized as one of the premier craftsmen of ...
(1552/1553 – 1599), Sir Thomas More
Sir Thomas More (7 February 1478 – 6 July 1535), venerated in the Catholic Church as Saint Thomas More, was an English lawyer, judge, social philosopher, author, statesman, and noted Renaissance humanist. He also served Henry VIII as Lord ...
(1478 – 1535), Francis Bacon (1561 – 1626), Sir Philip Sidney (1554 – 1586), architects (such as Inigo Jones
Inigo Jones (; 15 July 1573 – 21 June 1652) was the first significant architect in England and Wales in the early modern period, and the first to employ Vitruvian rules of proportion and symmetry in his buildings.
As the most notable archit ...
(1573 – 1652), who introduced Italianate architecture to England), and composers such as Thomas Tallis (1505 – 1585), John Taverner (c. 1490 – 1545), and William Byrd (c.1539/40 or 1543 – 1623).
France
 The word "Renaissance" is borrowed from the French language, where it means "re-birth". It was first used in the eighteenth century and was later popularized by French historian
The word "Renaissance" is borrowed from the French language, where it means "re-birth". It was first used in the eighteenth century and was later popularized by French historian Jules Michelet
Jules Michelet (; 21 August 1798 – 9 February 1874) was a French historian and an author on other topics whose major work was a history of France and its culture. His aphoristic style emphasized his anti-clerical republicanism.
In Michelet's ...
(1798–1874) in his 1855 work, ''Histoire de France'' (History of France).Michelet, Jules. ''History of France'', trans. G.H. Smith (New York: D. Appleton, 1847)
In 1495 the Italian Renaissance arrived in France, imported by King Charles VIII after his invasion of Italy. A factor that promoted the spread of secularism was the inability of the Church to offer assistance against the Black Death
The Black Death (also known as the Pestilence, the Great Mortality or the Plague) was a bubonic plague pandemic occurring in Western Eurasia and North Africa from 1346 to 1353. It is the most fatal pandemic recorded in human history, causi ...
. Francis I imported Italian art and artists, including Leonardo da Vinci, and built ornate palaces at great expense. Writers such as François Rabelais
François Rabelais ( , , ; born between 1483 and 1494; died 1553) was a French Renaissance writer, physician, Renaissance humanist, monk and Greek scholar. He is primarily known as a writer of satire, of the grotesque, and of bawdy jokes and ...
, Pierre de Ronsard, Joachim du Bellay, and Michel de Montaigne
Michel Eyquem, Sieur de Montaigne ( ; ; 28 February 1533 – 13 September 1592), also known as the Lord of Montaigne, was one of the most significant philosophers of the French Renaissance. He is known for popularizing the essay as a liter ...
, painters such as Jean Clouet, and musicians such as Jean Mouton also borrowed from the spirit of the Renaissance.
In 1533, a fourteen-year-old Caterina de' Medici (1519–1589), born in Florence to Lorenzo de' Medici, Duke of Urbino and Madeleine de la Tour d'Auvergne, married Henry II of France, second son of King Francis I and Queen Claude. Though she became famous and infamous for her role in France's religious wars, she made a direct contribution in bringing arts, sciences, and music (including the origins of ballet) to the French court from her native Florence.
Germany
 In the second half of the 15th century, the Renaissance spirit spread to Germany and the Low Countries, where the development of the printing press (ca. 1450) and Renaissance artists such as
In the second half of the 15th century, the Renaissance spirit spread to Germany and the Low Countries, where the development of the printing press (ca. 1450) and Renaissance artists such as Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer (; ; hu, Ajtósi Adalbert; 21 May 1471 – 6 April 1528),Müller, Peter O. (1993) ''Substantiv-Derivation in Den Schriften Albrecht Dürers'', Walter de Gruyter. . sometimes spelled in English as Durer (without an umlaut) or Due ...
(1471–1528) predated the influence from Italy. In the early Protestant areas of the country humanism became closely linked to the turmoil of the Protestant Reformation, and the art and writing of the German Renaissance
The German Renaissance, part of the Northern Renaissance, was a cultural and artistic movement that spread among Germany, German thinkers in the 15th and 16th centuries, which developed from the Italian Renaissance. Many areas of the arts and ...
frequently reflected this dispute. However, the Gothic style and medieval scholastic philosophy remained exclusively until the turn of the 16th century. Emperor Maximilian I Maximilian I may refer to:
*Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor, reigned 1486/93–1519
*Maximilian I, Elector of Bavaria, reigned 1597–1651
*Maximilian I, Prince of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen (1636-1689)
*Maximilian I Joseph of Bavaria, reigned 1795� ...
of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
(ruling 1493–1519) was the first truly Renaissance monarch of the Holy Roman Empire.
Hungary
After Italy, Hungary was the first European country where the Renaissance appeared. The Renaissance style came directly from Italy during the Quattrocento to Hungary first in the Central European region, thanks to the development of early Hungarian-Italian relationships—not only in dynastic connections, but also in cultural, humanistic and commercial relations—growing in strength from the 14th century. The relationship between Hungarian and Italian Gothic styles was a second reason—exaggerated breakthrough of walls is avoided, preferring clean and light structures. Large-scale building schemes provided ample and long term work for the artists, for example, the building of the Friss (New) Castle in Buda, the castles of Visegrád, Tata, and Várpalota. In Sigismund's court there were patrons such as Pipo Spano, a descendant of the Scolari family of Florence, who invited Manetto Ammanatini and Masolino da Pannicale to Hungary. The new Italian trend combined with existing national traditions to create a particular local Renaissance art. Acceptance of Renaissance art was furthered by the continuous arrival of humanist thought in the country. Many young Hungarians studying at Italian universities came closer to the Florentine humanist center, so a direct connection with Florence evolved. The growing number of Italian traders moving to Hungary, specially toBuda
Buda (; german: Ofen, sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Budim, Будим, Czech and sk, Budín, tr, Budin) was the historic capital of the Kingdom of Hungary and since 1873 has been the western part of the Hungarian capital Budapest, on the ...
, helped this process. New thoughts were carried by the humanist prelates, among them Vitéz János, archbishop of Esztergom, one of the founders of Hungarian humanism. During the long reign of emperor Sigismund of Luxemburg the Royal Castle of Buda became probably the largest Gothic palace of the late Middle Ages. King Matthias Corvinus (r. 1458–1490) rebuilt the palace in early Renaissance style and further expanded it.
After the marriage in 1476 of King Matthias to Beatrice of Naples, Buda
Buda (; german: Ofen, sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Budim, Будим, Czech and sk, Budín, tr, Budin) was the historic capital of the Kingdom of Hungary and since 1873 has been the western part of the Hungarian capital Budapest, on the ...
became one of the most important artistic centers of the Renaissance north of the Alps.Czigány, Lóránt, ''A History of Hungarian Literature'',The Renaissance in Hungary
(Retrieved May 10, 2007) The most important humanists living in Matthias' court were
Antonio Bonfini
Antonio Bonfini (Latin variant: ''Antonius Bonfinius'') (1427‒1502) was an Italian humanist and poet who spent the last years of his career as a court historian in Hungary with King Matthias Corvinus
Matthias Corvinus, also called Matthias ...
and the famous Hungarian poet Janus Pannonius. András Hess
András Hess set up a printing press in Buda in 1472.
He printed the first book in Hungary on 5 June 1473 in his Buda press. Hess was probably of German origin. He dedicated the book, the Chronica Hungarorum or Buda Chronicle ( hu, Budai Krónika) ...
set up a printing press in Buda in 1472. Matthias Corvinus's library, the Bibliotheca Corviniana, was Europe's greatest collections of secular books: historical chronicles, philosophic and scientific works in the 15th century. His library was second only in size to the Vatican Library. (However, the Vatican Library mainly contained Bibles and religious materials.) In 1489, Bartolomeo della Fonte of Florence wrote that Lorenzo de' Medici founded his own Greek-Latin library encouraged by the example of the Hungarian king. Corvinus's library is part of UNESCO World Heritage.
Matthias started at least two major building projects. The works in Buda and Visegrád began in about 1479. Two new wings and a hanging garden
A hanging garden is a sustainable landscape architecture, an artistic garden or a small urban farm, attached to or built on a wall. They are mainly found in areas where land is scarce or where the farmer is mobile or not permanent.
History
The m ...
were built at the royal castle of Buda, and the palace at Visegrád was rebuilt in Renaissance style. Matthias appointed the Italian Chimenti Camicia and the Dalmatian Giovanni Dalmata to direct these projects. Matthias commissioned the leading Italian artists of his age to embellish his palaces: for instance, the sculptor Benedetto da Majano
Benedetto da Maiano (1442 – May 24, 1497) was an Italian Early Renaissance sculptor.
Biography
Born in the village of Maiano (now part of Fiesole), he started his career as companion of his brother, the architect Giuliano da Maiano. When h ...
and the painters Filippino Lippi and Andrea Mantegna worked for him. A copy of Mantegna's portrait of Matthias survived. Matthias also hired the Italian military engineer Aristotele Fioravanti to direct the rebuilding of the forts along the southern frontier. He had new monasteries built in Late Gothic
International Gothic is a period of Gothic art which began in Burgundy, France, and northern Italy in the late 14th and early 15th century. It then spread very widely across Western Europe, hence the name for the period, which was introduced by t ...
style for the Franciscans in Kolozsvár, Szeged and Hunyad, and for the Paulines in Fejéregyháza. In the spring of 1485, Leonardo da Vinci travelled to Hungary on behalf of Sforza to meet king Matthias Corvinus, and was commissioned by him to paint a Madonna
Madonna Louise Ciccone (; ; born August 16, 1958) is an American singer-songwriter and actress. Widely dubbed the " Queen of Pop", Madonna has been noted for her continual reinvention and versatility in music production, songwriting, a ...
.
Matthias enjoyed the company of Humanists and had lively discussions on various topics with them. The fame of his magnanimity encouraged many scholarsmostly Italianto settle in Buda. Antonio Bonfini, Pietro Ranzano, Bartolomeo Fonzio, and Francesco Bandini
Francesco Bandini Piccolomini (1505–1588) was a Roman Catholic prelate who served as Archbishop of Siena (1529–1588). ''(in Latin)''Neoplatonism to Hungary. Like all intellectuals of his age, Matthias was convinced that the movements and combinations of the stars and planets exercised influence on individuals' life and on the history of nations. Galeotto Marzio described him as "king and astrologer", and Antonio Bonfini said Matthias "never did anything without consulting the stars". Upon his request, the famous astronomers of the age, Johannes Regiomontanus and Marcin Bylica, set up an observatory in Buda and installed it with
 Culture in the Netherlands at the end of the 15th century was influenced by the Italian Renaissance through trade via Bruges, which made Flanders wealthy. Its nobles commissioned artists who became known across Europe. In science, the anatomist Andreas Vesalius led the way; in cartography,
Culture in the Netherlands at the end of the 15th century was influenced by the Italian Renaissance through trade via Bruges, which made Flanders wealthy. Its nobles commissioned artists who became known across Europe. In science, the anatomist Andreas Vesalius led the way; in cartography,
 Renaissance trends from Italy and Central Europe influenced Russia in many ways. Their influence was rather limited, however, due to the large distances between Russia and the main European cultural centers and the strong adherence of Russians to their Orthodox traditions and Byzantine legacy.
Prince Ivan III introduced Renaissance architecture to Russia by inviting a number of architects from Italy, who brought new construction techniques and some Renaissance style elements with them, while in general following the traditional designs of Russian architecture. In 1475 the Bolognese architect Aristotele Fioravanti came to rebuild the Cathedral of the Dormition in the
Renaissance trends from Italy and Central Europe influenced Russia in many ways. Their influence was rather limited, however, due to the large distances between Russia and the main European cultural centers and the strong adherence of Russians to their Orthodox traditions and Byzantine legacy.
Prince Ivan III introduced Renaissance architecture to Russia by inviting a number of architects from Italy, who brought new construction techniques and some Renaissance style elements with them, while in general following the traditional designs of Russian architecture. In 1475 the Bolognese architect Aristotele Fioravanti came to rebuild the Cathedral of the Dormition in the
 The Renaissance arrived in the Iberian peninsula through the Mediterranean possessions of the Crown of Aragon, Aragonese Crown and the city of Valencia (city in Spain), Valencia. Many early Spanish Renaissance writers come from the Kingdom of Aragon, including Ausiàs March and Joanot Martorell. In the Kingdom of Castile, the early Renaissance was heavily influenced by the Italian humanism, starting with writers and poets such as Íñigo López de Mendoza, marqués de Santillana, the Marquis of Santillana, who introduced the new Italian poetry to Spain in the early 15th century. Other writers, such as Jorge Manrique, Fernando de Rojas, Juan del Encina, Juan Boscán Almogáver, and Garcilaso de la Vega (poet), Garcilaso de la Vega, kept a close resemblance to the Italian canon. Miguel de Cervantes's masterpiece ''Don Quixote'' is credited as the first Western novel. Renaissance humanism flourished in the early 16th century, with influential writers such as philosopher Juan Luis Vives, grammarian Antonio de Nebrija and natural historian Pedro Mexía, Pedro de Mexía.
Later Spanish Renaissance tended towards religious themes and mysticism, with poets such as Luis de León, Teresa of Ávila, and John of the Cross, and treated issues related to the exploration of the New World, with chroniclers and writers such as Inca Garcilaso de la Vega and Bartolomé de las Casas, giving rise to a body of work, now known as Spanish Renaissance literature. The late Renaissance in Spain produced artists such as El Greco and composers such as Tomás Luis de Victoria and Antonio de Cabezón.
The Renaissance arrived in the Iberian peninsula through the Mediterranean possessions of the Crown of Aragon, Aragonese Crown and the city of Valencia (city in Spain), Valencia. Many early Spanish Renaissance writers come from the Kingdom of Aragon, including Ausiàs March and Joanot Martorell. In the Kingdom of Castile, the early Renaissance was heavily influenced by the Italian humanism, starting with writers and poets such as Íñigo López de Mendoza, marqués de Santillana, the Marquis of Santillana, who introduced the new Italian poetry to Spain in the early 15th century. Other writers, such as Jorge Manrique, Fernando de Rojas, Juan del Encina, Juan Boscán Almogáver, and Garcilaso de la Vega (poet), Garcilaso de la Vega, kept a close resemblance to the Italian canon. Miguel de Cervantes's masterpiece ''Don Quixote'' is credited as the first Western novel. Renaissance humanism flourished in the early 16th century, with influential writers such as philosopher Juan Luis Vives, grammarian Antonio de Nebrija and natural historian Pedro Mexía, Pedro de Mexía.
Later Spanish Renaissance tended towards religious themes and mysticism, with poets such as Luis de León, Teresa of Ávila, and John of the Cross, and treated issues related to the exploration of the New World, with chroniclers and writers such as Inca Garcilaso de la Vega and Bartolomé de las Casas, giving rise to a body of work, now known as Spanish Renaissance literature. The late Renaissance in Spain produced artists such as El Greco and composers such as Tomás Luis de Victoria and Antonio de Cabezón.
 The Italian artist and critic Giorgio Vasari (1511–1574) first used the term ''rinascita'' in his book ''Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects, The Lives of the Artists'' (published 1550). In the book Vasari attempted to define what he described as a break with the barbarities of Gothic art: the arts (he held) had fallen into decay with the collapse of the Roman Empire and only the Tuscany, Tuscan artists, beginning with Cimabue (1240–1301) and Giotto (1267–1337) began to reverse this decline in the arts. Vasari saw ancient art as central to the rebirth of Italian art.
However, only in the 19th century did the French word ''renaissance'' achieve popularity in describing the self-conscious cultural movement based on revival of Roman models that began in the late 13th century. French historian
The Italian artist and critic Giorgio Vasari (1511–1574) first used the term ''rinascita'' in his book ''Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects, The Lives of the Artists'' (published 1550). In the book Vasari attempted to define what he described as a break with the barbarities of Gothic art: the arts (he held) had fallen into decay with the collapse of the Roman Empire and only the Tuscany, Tuscan artists, beginning with Cimabue (1240–1301) and Giotto (1267–1337) began to reverse this decline in the arts. Vasari saw ancient art as central to the rebirth of Italian art.
However, only in the 19th century did the French word ''renaissance'' achieve popularity in describing the self-conscious cultural movement based on revival of Roman models that began in the late 13th century. French historian
 On the other hand, many historians now point out that most of the negative social factors popularly associated with the medieval period—poverty, warfare, religious and political persecution, for example—seem to have worsened in this era, which saw the rise of Machiavelli, Machiavellian politics, the French Wars of Religion, Wars of Religion, the corrupt Borgia List of popes from the Borgia family, Popes, and the intensified witch hunts of the 16th century. Many people who lived during the Renaissance did not view it as the "golden age" imagined by certain 19th-century authors, but were concerned by these social maladies. Significantly, though, the artists, writers, and patrons involved in the cultural movements in question believed they were living in a new era that was a clean break from the Middle Ages. Some Historical materialism, Marxist historians prefer to describe the Renaissance in material terms, holding the view that the changes in art, literature, and philosophy were part of a general economic trend from feudalism towards capitalism, resulting in a bourgeois class with leisure time to devote to the arts.
Johan Huizinga (1872–1945) acknowledged the existence of the Renaissance but questioned whether it was a positive change. In his book ''The Autumn of the Middle Ages'', he argued that the Renaissance was a period of decline from the High Middle Ages, destroying much that was important. The Latin, Latin language, for instance, had evolved greatly from the classical period and was still a living language used in the church and elsewhere. The Renaissance obsession with classical purity halted its further evolution and saw Latin revert to its classical form. Robert S. Lopez has contended that it was a period of deep economic recession. Meanwhile, George Sarton and Lynn Thorndike have both argued that Science, scientific progress was perhaps less original than has traditionally been supposed. Finally, Joan Kelly argued that the Renaissance led to greater gender dichotomy, lessening the agency women had had during the Middle Ages.
Some historians have begun to consider the word ''Renaissance'' to be unnecessarily loaded, implying an unambiguously positive rebirth from the supposedly more primitive "Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages", the Middle Ages. Most historians now prefer to use the term "Early Modern Europe, early modern" for this period, a more neutral designation that highlights the period as a transitional one between the Middle Ages and the modern era. Others such as Roger Osborne have come to consider the Italian Renaissance as a repository of the myths and ideals of western history in general, and instead of rebirth of ancient ideas as a period of great innovation.
The Art history, art historian Erwin Panofsky observed of this resistance to the concept of "Renaissance":
On the other hand, many historians now point out that most of the negative social factors popularly associated with the medieval period—poverty, warfare, religious and political persecution, for example—seem to have worsened in this era, which saw the rise of Machiavelli, Machiavellian politics, the French Wars of Religion, Wars of Religion, the corrupt Borgia List of popes from the Borgia family, Popes, and the intensified witch hunts of the 16th century. Many people who lived during the Renaissance did not view it as the "golden age" imagined by certain 19th-century authors, but were concerned by these social maladies. Significantly, though, the artists, writers, and patrons involved in the cultural movements in question believed they were living in a new era that was a clean break from the Middle Ages. Some Historical materialism, Marxist historians prefer to describe the Renaissance in material terms, holding the view that the changes in art, literature, and philosophy were part of a general economic trend from feudalism towards capitalism, resulting in a bourgeois class with leisure time to devote to the arts.
Johan Huizinga (1872–1945) acknowledged the existence of the Renaissance but questioned whether it was a positive change. In his book ''The Autumn of the Middle Ages'', he argued that the Renaissance was a period of decline from the High Middle Ages, destroying much that was important. The Latin, Latin language, for instance, had evolved greatly from the classical period and was still a living language used in the church and elsewhere. The Renaissance obsession with classical purity halted its further evolution and saw Latin revert to its classical form. Robert S. Lopez has contended that it was a period of deep economic recession. Meanwhile, George Sarton and Lynn Thorndike have both argued that Science, scientific progress was perhaps less original than has traditionally been supposed. Finally, Joan Kelly argued that the Renaissance led to greater gender dichotomy, lessening the agency women had had during the Middle Ages.
Some historians have begun to consider the word ''Renaissance'' to be unnecessarily loaded, implying an unambiguously positive rebirth from the supposedly more primitive "Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages", the Middle Ages. Most historians now prefer to use the term "Early Modern Europe, early modern" for this period, a more neutral designation that highlights the period as a transitional one between the Middle Ages and the modern era. Others such as Roger Osborne have come to consider the Italian Renaissance as a repository of the myths and ideals of western history in general, and instead of rebirth of ancient ideas as a period of great innovation.
The Art history, art historian Erwin Panofsky observed of this resistance to the concept of "Renaissance":
excerpt and text search 2007 edition
als
complete text online
* * * * * * * Reynolds, L. D. and Wilson, Nigel, ''Scribes and Scholars: A Guide to the Transmission of Greek and Latin Literature'', Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1974. *
excerpt and text search
* Hall, Bert S. ''Weapons and Warfare in Renaissance Europe: Gunpowder, Technology, and Tactics'' (2001)
excerpt and text search
* Hattaway, Michael, ed. ''A Companion to English Renaissance Literature and Culture''. (2000). 747 pp. * Jensen, De Lamar (1992), ''Renaissance Europe'', * Johnson, Paul. ''The Renaissance: A Short History''. (2000). 197 pp.
excerpt and text search
also
online free
* Keene, Bryan C. ''Gardens of the Renaissance''. (2013). * King, Margaret L. ''Women of the Renaissance'' (1991
excerpt and text search
* Kristeller, Paul Oskar, and Michael Mooney. '' Renaissance Thought and its Sources'' (1979)
excerpt and text search
* Nauert, Charles G. ''Historical Dictionary of the Renaissance''. (2004). 541 pp. * Patrick, James A., ed. ''Renaissance and Reformation'' (5 vol 2007), 1584 pages; comprehensive encyclopedia * Plumb, J.H. ''The Italian Renaissance'' (2001)
excerpt and text search
* Paoletti, John T. and Gary M. Radke. ''Art in Renaissance Italy'' (4th ed. 2011) * Potter, G.R. ed. ''The New Cambridge Modern History: Volume 1: The Renaissance, 1493–1520'' (1957
online
major essays by multiple scholars. Summarizes the viewpoint of 1950s. * Robin, Diana; Larsen, Anne R.; and Levin, Carole, eds. ''Encyclopedia of Women in the Renaissance: Italy, France, and England'' (2007) 459 pp. * A. L. Rowse, Rowse, A.L. ''The Elizabethan Renaissance: The Life of the Society'' (2000)
excerpt and text search
* Ruggiero, Guido. ''The Renaissance in Italy: A Social and Cultural History of the Rinascimento'' (Cambridge University Press, 2015). 648 pp
online review
* Rundle, David, ed. ''The Hutchinson Encyclopedia of the Renaissance''. (1999). 434 pp.; numerous brief article
online edition
* Turner, Richard N. ''Renaissance Florence'' (2005)
excerpt and text search
* Ward, A
older essays by scholars; emphasis on politics
in JSTOR
* Caferro, William. ''Contesting the Renaissance'' (2010)
excerpt and text search
* Ferguson, Wallace K. "The Interpretation of the Renaissance: Suggestions for a Synthesis." ''Journal of the History of Ideas'' (1951): 483–495. online in JSTOR * Ferguson, Wallace K. "Recent trends in the economic historiography of the Renaissance." ''Studies in the Renaissance'' (1960): 7–26. * Ferguson, Wallace Klippert. ''The Renaissance in historical thought'' (AMS Press, 1981) * Grendler, Paul F. "The Future of Sixteenth Century Studies: Renaissance and Reformation Scholarship in the Next Forty Years," ''Sixteenth Century Journal'' Spring 2009, Vol. 40 Issue 1, pp. 182+ * Murray, Stuart A.P. The Library: An Illustrated History. American Library Association, Chicago, 2012. * Ruggiero, Guido, ed. ''A Companion to the Worlds of the Renaissance''. (2002). 561 pp. * Starn, Randolph. "A Postmodern Renaissance?" ''Renaissance Quarterly'' 2007 60(1): 1–2
* Summit, Jennifer. "Renaissance Humanism and the Future of the Humanities". ''Literature Compass'' (2012) 9#10 pp: 665–678. * Trivellato, Francesca. "Renaissance Italy and the Muslim Mediterranean in Recent Historical Work", ''Journal of Modern History'' (March 2010), 82#1 pp: 127–155. * Woolfson, Jonathan, ed. ''Palgrave advances in Renaissance historiography'' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2005)
excerpt and text search
"The Renaissance"
''In Our Time'', BBC Radio 4 discussion with Francis Ames-Lewis, Peter Burke and Evelyn Welch (June 8, 2000).
*
Renaissance Philosophy
entry in the Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy Interactive resources
Florence: 3D Panoramas of Florentine Renaissance Sites(English/Italian)
Interactive Glossary of Terms Relating to the Renaissance
Multimedia Exploration of the Renaissance
RSS News Feed: Get an entry from Leonardo's Journal delivered each day
Exhibits Collection – Renaissance
Lectures and galleries
The Bagatti Valsecchi Museum
The Society for Renaissance Studies
{{good article Renaissance, 14th century in Europe 15th century in Europe 16th century in Europe 17th century in Europe Early Modern period Historical eras History of Europe by period Medieval philosophy Western culture
astrolabe
An astrolabe ( grc, ἀστρολάβος ; ar, ٱلأَسْطُرلاب ; persian, ستارهیاب ) is an ancient astronomical instrument that was a handheld model of the universe. Its various functions also make it an elaborate inclin ...
s and celestial globes. Regiomontanus dedicated his book on navigation that was used by Christopher Columbus to Matthias.
Other important figures of Hungarian Renaissance include Bálint Balassi (poet), Sebestyén Tinódi Lantos (poet), Bálint Bakfark (composer and lutenist), and Master MS (fresco painter).
Renaissance in the Low Countries
 Culture in the Netherlands at the end of the 15th century was influenced by the Italian Renaissance through trade via Bruges, which made Flanders wealthy. Its nobles commissioned artists who became known across Europe. In science, the anatomist Andreas Vesalius led the way; in cartography,
Culture in the Netherlands at the end of the 15th century was influenced by the Italian Renaissance through trade via Bruges, which made Flanders wealthy. Its nobles commissioned artists who became known across Europe. In science, the anatomist Andreas Vesalius led the way; in cartography, Gerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator (; 5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a 16th-century geographer, cosmographer and cartographer from the County of Flanders. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represented ...
's map assisted explorers and navigators. In art, Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting ranged from the strange work of Hieronymus Bosch to the everyday life depictions of Pieter Brueghel the Elder.
Northern Europe
The Renaissance in Northern Europe has been termed the "Northern Renaissance". While Renaissance ideas were moving north from Italy, there was a simultaneous southward spread of some areas of innovation, particularly in music. The music of the 15th-century Burgundian School defined the beginning of the Renaissance in music, and the polyphony of the Netherlanders, as it moved with the musicians themselves into Italy, formed the core of the first true international style in music since the standardization of Gregorian Chant in the 9th century. The culmination of the Netherlandish school was in the music of the Italiancomposer
A composer is a person who writes music. The term is especially used to indicate composers of Western classical music, or those who are composers by occupation. Many composers are, or were, also skilled performers of music.
Etymology and Defi ...
Palestrina. At the end of the 16th century Italy again became a center of musical innovation, with the development of the polychoral style of the Venetian School, which spread northward into Germany around 1600.
The paintings of the Italian Renaissance differed from those of the Northern Renaissance. Italian Renaissance artists were among the first to paint secular scenes, breaking away from the purely religious art of medieval painters. Northern Renaissance artists initially remained focused on religious subjects, such as the contemporary religious upheaval portrayed by Albrecht Dürer
Albrecht Dürer (; ; hu, Ajtósi Adalbert; 21 May 1471 – 6 April 1528),Müller, Peter O. (1993) ''Substantiv-Derivation in Den Schriften Albrecht Dürers'', Walter de Gruyter. . sometimes spelled in English as Durer (without an umlaut) or Due ...
. Later, the works of Pieter Bruegel influenced artists to paint scenes of daily life rather than religious or classical themes. It was also during the Northern Renaissance that Flemish brothers Hubert and Jan van Eyck
Jan van Eyck ( , ; – July 9, 1441) was a painter active in Bruges who was one of the early innovators of what became known as Early Netherlandish painting, and one of the most significant representatives of Early Northern Renaissance art. Ac ...
perfected the oil painting technique, which enabled artists to produce strong colors on a hard surface that could survive for centuries. A feature of the Northern Renaissance was its use of the vernacular in place of Latin or Greek, which allowed greater freedom of expression. This movement had started in Italy with the decisive influence of Dante Alighieri on the development of vernacular languages; in fact the focus on writing in Italian has neglected a major source of Florentine ideas expressed in Latin. The spread of the printing press technology boosted the Renaissance in Northern Europe as elsewhere, with Venice becoming a world center of printing.
Poland
An early Italian humanist who came to Poland in the mid-15th century was Filippo Buonaccorsi. Many Italian artists came to Poland withBona Sforza
Bona Sforza d'Aragona (2 February 1494 – 19 November 1557) was Queen of Poland and Grand Duchess of Lithuania as the second wife of Sigismund I the Old, and Duchess of Bari and Rossano by her own right. She was a surviving member of ...
of Milan, when she married King Sigismund I in 1518. This was supported by temporarily strengthened monarchies in both areas, as well as by newly established universities. The Polish Renaissance lasted from the late 15th to the late 16th century and was the Golden Age of Polish culture
The culture of Poland ( pl, Kultura Polski ) is the product of its geography and distinct historical evolution, which is closely connected to an intricate thousand-year history. Polish culture forms an important part of western civilization and ...
. Ruled by the Jagiellonian dynasty, the Kingdom of Poland (from 1569 known as the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth) actively participated in the broad European Renaissance. The multi-national Polish state experienced a substantial period of cultural growth thanks in part to a century without major wars – aside from conflicts in the sparsely populated eastern and southern borderlands. The Reformation spread peacefully throughout the country (giving rise to the Polish Brethren), while living conditions improved, cities grew, and exports of agricultural products enriched the population, especially the nobility (''szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in the ...
'') who gained dominance in the new political system of Golden Liberty. The Polish Renaissance architecture has three periods of development.
The greatest monument of this style in the territory of the former Duchy of Pomerania is the Ducal Castle in Szczecin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major s ...
.
Portugal
Although Italian Renaissance had a modest impact in Portuguese arts, Portugal was influential in broadening the European worldview, stimulating humanist inquiry. Renaissance arrived through the influence of wealthy Italian and Flemish merchants who invested in the profitable commerce overseas. As the pioneer headquarters of European exploration,Lisbon
Lisbon (; pt, Lisboa ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 544,851 within its administrative limits in an area of 100.05 km2. Grande Lisboa, Lisbon's urban area extends beyond the city's administr ...
flourished in the late 15th century, attracting experts who made several breakthroughs in mathematics, astronomy and naval technology, including Pedro Nunes
Pedro Nunes (; Latin: ''Petrus Nonius''; 1502 – 11 August 1578) was a Portuguese mathematician, cosmographer, and professor, from a New Christian (of Jewish origin) family.
Considered one of the greatest mathematicians of his time, Nunes ...
, João de Castro, Abraham Zacuto
Abraham Zacuto ( he, , translit=Avraham ben Shmuel Zacut, pt, Abraão ben Samuel Zacuto; 12 August 1452 – ) was a Castilian astronomer, astrologer, mathematician, rabbi and historian who served as Royal Astronomer to King John II of Portugal.
...
and Martin Behaim. Cartographers Pedro Reinel, Lopo Homem, Estêvão Gomes and Diogo Ribeiro made crucial advances in mapping the world. Apothecary Tomé Pires and physicians Garcia de Orta and Cristóvão da Costa collected and published works on plants and medicines, soon translated by Flemish pioneer botanist Carolus Clusius.
In architecture, the huge profits of the spice trade financed a sumptuous composite style in the first decades of the 16th century, the Manueline, incorporating maritime elements. The primary painters were Nuno Gonçalves, Gregório Lopes
Gregório Lopes (''c.'' 1490 – 1550) was one of the most important Renaissance painters from Portugal.
Gregório Lopes was educated in the workshop of Jorge Afonso, the court painter of King Manuel I. Later he himself became court painter f ...
and Vasco Fernandes. In music, Pedro de Escobar and Duarte Lobo produced four songbooks, including the Cancioneiro de Elvas
The ''Cancioneiro de Elvas'' (in English: ''Elvas Songbook'') is one of the four Renaissance songbooks of Portuguese music from the 16th century - along with the Lisbon Songbook, the Belém Songbook, and the Paris songbook. It is one important s ...
. In literature, Sá de Miranda introduced Italian forms of verse. Bernardim Ribeiro
Bernardim Ribeiro (1482October 1552) was a Renaissance Portuguese poet and writer.
Early life
Ribeiro was a native of Torrão in the Alentejo. His father, Damião Ribeiro, was implicated in a conspiracy against King John II in 1484, and had to f ...
developed pastoral romance
A pastoral lifestyle is that of shepherds herding livestock around open areas of land according to seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. It lends its name to a genre of literature, art, and music (pastorale) that depict ...
, plays by Gil Vicente fused it with popular culture, reporting the changing times, and Luís de Camões inscribed the Portuguese feats overseas in the epic poem '' Os Lusíadas''. Travel literature especially flourished: João de Barros
João de Barros () (1496 – 20 October 1570), called the ''Portuguese Livy'', is one of the first great Portuguese historians, most famous for his ''Décadas da Ásia'' ("Decades of Asia"), a history of the Portuguese in India, Asia, and southea ...
, Castanheda, António Galvão
António Galvão (c. 1490–1557), also known as Antonio Galvano, was a Portuguese soldier, chronicler and administrator in the Maluku islands, and a Renaissance historian who was the first person to present a comprehensive report of the leading v ...
, Gaspar Correia, Duarte Barbosa, and Fernão Mendes Pinto, among others, described new lands and were translated and spread with the new printing press. After joining the Portuguese exploration of Brazil in 1500, Amerigo Vespucci coined the term New World, in his letters to Lorenzo di Pierfrancesco de' Medici.
The intense international exchange produced several cosmopolitan humanist scholars, including Francisco de Holanda, André de Resende and Damião de Góis, a friend of Erasmus who wrote with rare independence on the reign of King Manuel I. Diogo and André de Gouveia made relevant teaching reforms via France. Foreign news and products in the Portuguese factory in Antwerp
Antwerp (; nl, Antwerpen ; french: Anvers ; es, Amberes) is the largest city in Belgium by area at and the capital of Antwerp Province in the Flemish Region. With a population of 520,504,
attracted the interest of Thomas More and Albrecht Dürer to the wider world. There, profits and know-how helped nurture the Dutch Renaissance and Golden Age, especially after the arrival of the wealthy cultured Jewish community expelled from Portugal.
Russia
There was no Renaissance in Russia in the original sense of the term.
 Renaissance trends from Italy and Central Europe influenced Russia in many ways. Their influence was rather limited, however, due to the large distances between Russia and the main European cultural centers and the strong adherence of Russians to their Orthodox traditions and Byzantine legacy.
Prince Ivan III introduced Renaissance architecture to Russia by inviting a number of architects from Italy, who brought new construction techniques and some Renaissance style elements with them, while in general following the traditional designs of Russian architecture. In 1475 the Bolognese architect Aristotele Fioravanti came to rebuild the Cathedral of the Dormition in the
Renaissance trends from Italy and Central Europe influenced Russia in many ways. Their influence was rather limited, however, due to the large distances between Russia and the main European cultural centers and the strong adherence of Russians to their Orthodox traditions and Byzantine legacy.
Prince Ivan III introduced Renaissance architecture to Russia by inviting a number of architects from Italy, who brought new construction techniques and some Renaissance style elements with them, while in general following the traditional designs of Russian architecture. In 1475 the Bolognese architect Aristotele Fioravanti came to rebuild the Cathedral of the Dormition in the Moscow Kremlin
The Kremlin ( rus, Московский Кремль, r=Moskovskiy Kreml', p=ˈmɐˈskofskʲɪj krʲemlʲ, t=Moscow Kremlin) is a fortified complex in the center of Moscow founded by the Rurik dynasty. It is the best known of the kremlins (R ...
, which had been damaged in an earthquake. Fioravanti was given the 12th-century Assumption Cathedral in Vladimir, Vladimir Cathedral as a model, and he produced a design combining traditional Russian style with a Renaissance sense of spaciousness, proportion and symmetry.
In 1485 Ivan III commissioned the building of the royal residence, Terem Palace, within the Kremlin, with Aloisio da Milano as the architect of the first three floors. He and other Italian architects also contributed to the construction of the Moscow Kremlin Wall, Kremlin walls and List of Moscow Kremlin towers, towers. The small banquet hall of the Russian Tsars, called the Palace of Facets because of its facetted upper story, is the work of two Italians, Marco Ruffo and Pietro Solario, and shows a more Italian style. In 1505, an Italian known in Russia as Aleviz Novyi or Aleviz Fryazin arrived in Moscow. He may have been the Venetian sculptor, Alevisio Lamberti da Montagne. He built twelve churches for Ivan III, including the Cathedral of the Archangel, a building remarkable for the successful blending of Russian tradition, Orthodox requirements and Renaissance style. It is believed that the Cathedral of the Metropolitan Peter in Vysokopetrovsky Monastery, another work of Aleviz Novyi, later served as an inspiration for the so-called ''octagon-on-tetragon'' architectural form in the Moscow Baroque of the late 17th century.
Between the early 16th and the late 17th centuries, an original tradition of stone tented roof architecture developed in Russia. It was quite unique and different from the contemporary Renaissance architecture elsewhere in Europe, though some research terms the style 'Russian Gothic' and compares it with the European Gothic architecture of the earlier period. The Italians, with their advanced technology, may have influenced the invention of the stone tented roof (the wooden tents were known in Russia and Europe long before). According to one hypothesis, an Italian architect called Petrok Maly may have been an author of the Ascension Church in Kolomenskoye, one of the earliest and most prominent tented roof churches.
By the 17th century the influence of Renaissance painting resulted in Russian icons becoming slightly more realistic, while still following most of the old icon painting Aesthetic canon, canons, as seen in the works of Bogdan Saltanov, Simon Ushakov, Gury Nikitin, Karp Zolotaryov, and other Russian artists of the era. Gradually the new type of secular portrait painting appeared, called ''parsúna'' (from "persona" – person), which was transitional style between abstract iconographics and real paintings.
In the mid 16th-century Russians adopted printing from Central Europe, with Ivan Fyodorov (printer), Ivan Fyodorov being the first known Russian printer. In the 17th century printing became widespread, and woodcuts became especially popular. That led to the development of a special form of folk art known as lubok printing, which persisted in Russia well into the 19th century.
A number of technologies from the European Renaissance period were adopted by Russia rather early and subsequently perfected to become a part of a strong domestic tradition. Mostly these were military technologies, such as cannon casting adopted by at least the 15th century. The Tsar Cannon, which is the List of largest cannon by caliber, world's largest bombard by caliber, is a masterpiece of Russian cannon making. It was cast in 1586 by Andrey Chokhov and is notable for its rich, decorative relief. Another technology, that according to one hypothesis originally was brought from Europe by the Italians, resulted in the development of vodka, the national beverage of Russia. As early as 1386 Genoese ambassadors brought the first aqua vitae ("water of life") to Moscow and presented it to Grand Duchy of Moscow, Grand Duke Dmitry Donskoy. The Genoese likely developed this beverage with the help of the alchemists of Provence, who used an Arab-invented distillation apparatus to convert grape must into ethanol, alcohol. A Moscovite monk called Isidore (inventor), Isidore used this technology to produce the first original Russian vodka c. 1430.
Spain
 The Renaissance arrived in the Iberian peninsula through the Mediterranean possessions of the Crown of Aragon, Aragonese Crown and the city of Valencia (city in Spain), Valencia. Many early Spanish Renaissance writers come from the Kingdom of Aragon, including Ausiàs March and Joanot Martorell. In the Kingdom of Castile, the early Renaissance was heavily influenced by the Italian humanism, starting with writers and poets such as Íñigo López de Mendoza, marqués de Santillana, the Marquis of Santillana, who introduced the new Italian poetry to Spain in the early 15th century. Other writers, such as Jorge Manrique, Fernando de Rojas, Juan del Encina, Juan Boscán Almogáver, and Garcilaso de la Vega (poet), Garcilaso de la Vega, kept a close resemblance to the Italian canon. Miguel de Cervantes's masterpiece ''Don Quixote'' is credited as the first Western novel. Renaissance humanism flourished in the early 16th century, with influential writers such as philosopher Juan Luis Vives, grammarian Antonio de Nebrija and natural historian Pedro Mexía, Pedro de Mexía.
Later Spanish Renaissance tended towards religious themes and mysticism, with poets such as Luis de León, Teresa of Ávila, and John of the Cross, and treated issues related to the exploration of the New World, with chroniclers and writers such as Inca Garcilaso de la Vega and Bartolomé de las Casas, giving rise to a body of work, now known as Spanish Renaissance literature. The late Renaissance in Spain produced artists such as El Greco and composers such as Tomás Luis de Victoria and Antonio de Cabezón.
The Renaissance arrived in the Iberian peninsula through the Mediterranean possessions of the Crown of Aragon, Aragonese Crown and the city of Valencia (city in Spain), Valencia. Many early Spanish Renaissance writers come from the Kingdom of Aragon, including Ausiàs March and Joanot Martorell. In the Kingdom of Castile, the early Renaissance was heavily influenced by the Italian humanism, starting with writers and poets such as Íñigo López de Mendoza, marqués de Santillana, the Marquis of Santillana, who introduced the new Italian poetry to Spain in the early 15th century. Other writers, such as Jorge Manrique, Fernando de Rojas, Juan del Encina, Juan Boscán Almogáver, and Garcilaso de la Vega (poet), Garcilaso de la Vega, kept a close resemblance to the Italian canon. Miguel de Cervantes's masterpiece ''Don Quixote'' is credited as the first Western novel. Renaissance humanism flourished in the early 16th century, with influential writers such as philosopher Juan Luis Vives, grammarian Antonio de Nebrija and natural historian Pedro Mexía, Pedro de Mexía.
Later Spanish Renaissance tended towards religious themes and mysticism, with poets such as Luis de León, Teresa of Ávila, and John of the Cross, and treated issues related to the exploration of the New World, with chroniclers and writers such as Inca Garcilaso de la Vega and Bartolomé de las Casas, giving rise to a body of work, now known as Spanish Renaissance literature. The late Renaissance in Spain produced artists such as El Greco and composers such as Tomás Luis de Victoria and Antonio de Cabezón.
Further countries
* Renaissance in Croatia * Renaissance in ScotlandHistoriography
Conception
 The Italian artist and critic Giorgio Vasari (1511–1574) first used the term ''rinascita'' in his book ''Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects, The Lives of the Artists'' (published 1550). In the book Vasari attempted to define what he described as a break with the barbarities of Gothic art: the arts (he held) had fallen into decay with the collapse of the Roman Empire and only the Tuscany, Tuscan artists, beginning with Cimabue (1240–1301) and Giotto (1267–1337) began to reverse this decline in the arts. Vasari saw ancient art as central to the rebirth of Italian art.
However, only in the 19th century did the French word ''renaissance'' achieve popularity in describing the self-conscious cultural movement based on revival of Roman models that began in the late 13th century. French historian
The Italian artist and critic Giorgio Vasari (1511–1574) first used the term ''rinascita'' in his book ''Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculptors, and Architects, The Lives of the Artists'' (published 1550). In the book Vasari attempted to define what he described as a break with the barbarities of Gothic art: the arts (he held) had fallen into decay with the collapse of the Roman Empire and only the Tuscany, Tuscan artists, beginning with Cimabue (1240–1301) and Giotto (1267–1337) began to reverse this decline in the arts. Vasari saw ancient art as central to the rebirth of Italian art.
However, only in the 19th century did the French word ''renaissance'' achieve popularity in describing the self-conscious cultural movement based on revival of Roman models that began in the late 13th century. French historian Jules Michelet
Jules Michelet (; 21 August 1798 – 9 February 1874) was a French historian and an author on other topics whose major work was a history of France and its culture. His aphoristic style emphasized his anti-clerical republicanism.
In Michelet's ...
(1798–1874) defined "The Renaissance" in his 1855 work ''Histoire de France'' as an entire historical period, whereas previously it had been used in a more limited sense.Murray, P. and Murray, L. (1963) ''The Art of the Renaissance''. London: Thames & Hudson (World of Art), p. 9. . "...in 1855 we find, for the first time, the word 'Renaissance' used – by the French historian Michelet – as an adjective to describe a whole period of history and not confined to the rebirth of Latin letters or a classically inspired style in the arts." For Michelet, the Renaissance was more a development in science than in art and culture. He asserted that it spanned the period from Christopher Columbus, Columbus to Copernicus to Galileo; that is, from the end of the 15th century to the middle of the 17th century. Moreover, Michelet distinguished between what he called, "the bizarre and monstrous" quality of the Middle Ages and the democracy, democratic values that he, as a vocal Republicanism, Republican, chose to see in its character. A French nationalist, Michelet also sought to claim the Renaissance as a French movement.
The Switzerland, Swiss historian Jacob Burckhardt (1818–1897) in his ''The Civilization of the Renaissance in Italy'' (1860), by contrast, defined the Renaissance as the period between Giotto and Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was insp ...
in Italy, that is, the 14th to mid-16th centuries. He saw in the Renaissance the emergence of the modern spirit of individualism, individuality, which the Middle Ages had stifled. His book was widely read and became influential in the development of the modern interpretation of the Italian Renaissance. However, Buckhardt has been accused of setting forth a linear Whig history, Whiggish view of history in seeing the Renaissance as the origin of the modern world.
More recently, some historians have been much less keen to define the Renaissance as a historical age, or even as a coherent cultural movement. The historian Randolph Starn, of the University of California Berkeley, stated in 1998:
Debates about progress
There is debate about the extent to which the Renaissance improved on the culture of the Middle Ages. Both Michelet and Burckhardt were keen to describe the progress made in the Renaissance towards the modern age. Burckhardt likened the change to a veil being removed from man's eyes, allowing him to see clearly. On the other hand, many historians now point out that most of the negative social factors popularly associated with the medieval period—poverty, warfare, religious and political persecution, for example—seem to have worsened in this era, which saw the rise of Machiavelli, Machiavellian politics, the French Wars of Religion, Wars of Religion, the corrupt Borgia List of popes from the Borgia family, Popes, and the intensified witch hunts of the 16th century. Many people who lived during the Renaissance did not view it as the "golden age" imagined by certain 19th-century authors, but were concerned by these social maladies. Significantly, though, the artists, writers, and patrons involved in the cultural movements in question believed they were living in a new era that was a clean break from the Middle Ages. Some Historical materialism, Marxist historians prefer to describe the Renaissance in material terms, holding the view that the changes in art, literature, and philosophy were part of a general economic trend from feudalism towards capitalism, resulting in a bourgeois class with leisure time to devote to the arts.
Johan Huizinga (1872–1945) acknowledged the existence of the Renaissance but questioned whether it was a positive change. In his book ''The Autumn of the Middle Ages'', he argued that the Renaissance was a period of decline from the High Middle Ages, destroying much that was important. The Latin, Latin language, for instance, had evolved greatly from the classical period and was still a living language used in the church and elsewhere. The Renaissance obsession with classical purity halted its further evolution and saw Latin revert to its classical form. Robert S. Lopez has contended that it was a period of deep economic recession. Meanwhile, George Sarton and Lynn Thorndike have both argued that Science, scientific progress was perhaps less original than has traditionally been supposed. Finally, Joan Kelly argued that the Renaissance led to greater gender dichotomy, lessening the agency women had had during the Middle Ages.
Some historians have begun to consider the word ''Renaissance'' to be unnecessarily loaded, implying an unambiguously positive rebirth from the supposedly more primitive "Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages", the Middle Ages. Most historians now prefer to use the term "Early Modern Europe, early modern" for this period, a more neutral designation that highlights the period as a transitional one between the Middle Ages and the modern era. Others such as Roger Osborne have come to consider the Italian Renaissance as a repository of the myths and ideals of western history in general, and instead of rebirth of ancient ideas as a period of great innovation.
The Art history, art historian Erwin Panofsky observed of this resistance to the concept of "Renaissance":
On the other hand, many historians now point out that most of the negative social factors popularly associated with the medieval period—poverty, warfare, religious and political persecution, for example—seem to have worsened in this era, which saw the rise of Machiavelli, Machiavellian politics, the French Wars of Religion, Wars of Religion, the corrupt Borgia List of popes from the Borgia family, Popes, and the intensified witch hunts of the 16th century. Many people who lived during the Renaissance did not view it as the "golden age" imagined by certain 19th-century authors, but were concerned by these social maladies. Significantly, though, the artists, writers, and patrons involved in the cultural movements in question believed they were living in a new era that was a clean break from the Middle Ages. Some Historical materialism, Marxist historians prefer to describe the Renaissance in material terms, holding the view that the changes in art, literature, and philosophy were part of a general economic trend from feudalism towards capitalism, resulting in a bourgeois class with leisure time to devote to the arts.
Johan Huizinga (1872–1945) acknowledged the existence of the Renaissance but questioned whether it was a positive change. In his book ''The Autumn of the Middle Ages'', he argued that the Renaissance was a period of decline from the High Middle Ages, destroying much that was important. The Latin, Latin language, for instance, had evolved greatly from the classical period and was still a living language used in the church and elsewhere. The Renaissance obsession with classical purity halted its further evolution and saw Latin revert to its classical form. Robert S. Lopez has contended that it was a period of deep economic recession. Meanwhile, George Sarton and Lynn Thorndike have both argued that Science, scientific progress was perhaps less original than has traditionally been supposed. Finally, Joan Kelly argued that the Renaissance led to greater gender dichotomy, lessening the agency women had had during the Middle Ages.
Some historians have begun to consider the word ''Renaissance'' to be unnecessarily loaded, implying an unambiguously positive rebirth from the supposedly more primitive "Dark Ages (historiography), Dark Ages", the Middle Ages. Most historians now prefer to use the term "Early Modern Europe, early modern" for this period, a more neutral designation that highlights the period as a transitional one between the Middle Ages and the modern era. Others such as Roger Osborne have come to consider the Italian Renaissance as a repository of the myths and ideals of western history in general, and instead of rebirth of ancient ideas as a period of great innovation.
The Art history, art historian Erwin Panofsky observed of this resistance to the concept of "Renaissance":
It is perhaps no accident that the factuality of the Italian Renaissance has been most vigorously questioned by those who are not obliged to take a professional interest in the aesthetic aspects of civilization – historians of economic and social developments, political and religious situations, and, most particularly, natural science – but only exceptionally by students of literature and hardly ever by historians of Art.
Other Renaissances
The term ''Renaissance'' has also been used to define periods outside of the 15th and 16th centuries. Charles H. Haskins (1870–1937), for example, made a case for aRenaissance of the 12th century
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
. Other historians have argued for a Carolingian Renaissance
The Carolingian Renaissance was the first of three medieval renaissances, a period of cultural activity in the Carolingian Empire. It occurred from the late 8th century to the 9th century, taking inspiration from the State church of the Roman Emp ...
in the 8th and 9th centuries, Ottonian Renaissance
The Ottonian Renaissance was a renaissance of Byzantine and Late Antique art in Central and Southern Europe that accompanied the reigns of the first three Holy Roman Emperors of the Ottonian (or Saxon) dynasty: Otto I (936–973), Otto II (97 ...
in the 10th century and for the Timurid Renaissance of the 14th century. The Islamic Golden Age has been also sometimes termed with the Islamic Renaissance.Hubert, Jean, ''L'Empire carolingien'' (English: ''The Carolingian Renaissance'', translated by James Emmons, New York: G. Braziller, 1970).
Other periods of cultural rebirth have also been termed "renaissances", such as the Bengal Renaissance, Tamil Renaissance, Nepal Bhasa renaissance, al-Nahda or the Harlem Renaissance. The term can also be used in cinema. In animation, the Disney Renaissance is a period that spanned the years from 1989 to 1999 which saw the studio return to the level of quality not witnessed since their Golden Age of Animation. The San Francisco Renaissance was a vibrant period of exploratory poetry and fiction writing in San Francisco, that city in the mid-20th century.
See also
* Index of Renaissance articles * Outline of the Renaissance * List of Renaissance figures * List of Renaissance structures * Roman Renaissance * Venetian Renaissance * Scientific Revolution * Age of EnlightenmentReferences
Explanatory notes
Citations
General sources
* Jacob Burckhardt, Burckhardt, Jacob, ''The Civilization of the Renaissance in Italy'' (1860), a famous classicexcerpt and text search 2007 edition
als
complete text online
* * * * * * * Reynolds, L. D. and Wilson, Nigel, ''Scribes and Scholars: A Guide to the Transmission of Greek and Latin Literature'', Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1974. *
Further reading
* Vincent Cronin, Cronin, Vincent (1969), ''The Flowering of the Renaissance'', * Vincent Cronin, Cronin, Vincent (1992), ''The Renaissance'', * Campbell, Gordon. ''The Oxford Dictionary of the Renaissance''. (2003). 862 pp. online at OUP * Davis, Robert C. ''Renaissance People: Lives that Shaped the Modern Age''. (2011). * Ergang, Robert (1967), ''The Renaissance'', * Ferguson, Wallace K. (1962), [''Europe in Transition, 1300–1500''], * Fisher, Celia. ''Flowers of the Renaissance''. (2011). * Fletcher, Stella. ''The Longman Companion to Renaissance Europe, 1390–1530''. (2000). 347 pp. * Grendler, Paul F., ed. ''The Renaissance: An Encyclopedia for Students''. (2003). 970 pp. * Hale, John. ''The Civilization of Europe in the Renaissance''. (1994). 648 pp.; a magistral survey, heavily illustratedexcerpt and text search
* Hall, Bert S. ''Weapons and Warfare in Renaissance Europe: Gunpowder, Technology, and Tactics'' (2001)
excerpt and text search
* Hattaway, Michael, ed. ''A Companion to English Renaissance Literature and Culture''. (2000). 747 pp. * Jensen, De Lamar (1992), ''Renaissance Europe'', * Johnson, Paul. ''The Renaissance: A Short History''. (2000). 197 pp.
excerpt and text search
also
online free
* Keene, Bryan C. ''Gardens of the Renaissance''. (2013). * King, Margaret L. ''Women of the Renaissance'' (1991
excerpt and text search
* Kristeller, Paul Oskar, and Michael Mooney. '' Renaissance Thought and its Sources'' (1979)
excerpt and text search
* Nauert, Charles G. ''Historical Dictionary of the Renaissance''. (2004). 541 pp. * Patrick, James A., ed. ''Renaissance and Reformation'' (5 vol 2007), 1584 pages; comprehensive encyclopedia * Plumb, J.H. ''The Italian Renaissance'' (2001)
excerpt and text search
* Paoletti, John T. and Gary M. Radke. ''Art in Renaissance Italy'' (4th ed. 2011) * Potter, G.R. ed. ''The New Cambridge Modern History: Volume 1: The Renaissance, 1493–1520'' (1957
online
major essays by multiple scholars. Summarizes the viewpoint of 1950s. * Robin, Diana; Larsen, Anne R.; and Levin, Carole, eds. ''Encyclopedia of Women in the Renaissance: Italy, France, and England'' (2007) 459 pp. * A. L. Rowse, Rowse, A.L. ''The Elizabethan Renaissance: The Life of the Society'' (2000)
excerpt and text search
* Ruggiero, Guido. ''The Renaissance in Italy: A Social and Cultural History of the Rinascimento'' (Cambridge University Press, 2015). 648 pp
online review
* Rundle, David, ed. ''The Hutchinson Encyclopedia of the Renaissance''. (1999). 434 pp.; numerous brief article
online edition
* Turner, Richard N. ''Renaissance Florence'' (2005)
excerpt and text search
* Ward, A
older essays by scholars; emphasis on politics
Historiography
* Bouwsma, William J. "The Renaissance and the drama of Western history." ''American Historical Review'' (1979): 1–15in JSTOR
* Caferro, William. ''Contesting the Renaissance'' (2010)
excerpt and text search
* Ferguson, Wallace K. "The Interpretation of the Renaissance: Suggestions for a Synthesis." ''Journal of the History of Ideas'' (1951): 483–495. online in JSTOR * Ferguson, Wallace K. "Recent trends in the economic historiography of the Renaissance." ''Studies in the Renaissance'' (1960): 7–26. * Ferguson, Wallace Klippert. ''The Renaissance in historical thought'' (AMS Press, 1981) * Grendler, Paul F. "The Future of Sixteenth Century Studies: Renaissance and Reformation Scholarship in the Next Forty Years," ''Sixteenth Century Journal'' Spring 2009, Vol. 40 Issue 1, pp. 182+ * Murray, Stuart A.P. The Library: An Illustrated History. American Library Association, Chicago, 2012. * Ruggiero, Guido, ed. ''A Companion to the Worlds of the Renaissance''. (2002). 561 pp. * Starn, Randolph. "A Postmodern Renaissance?" ''Renaissance Quarterly'' 2007 60(1): 1–2
* Summit, Jennifer. "Renaissance Humanism and the Future of the Humanities". ''Literature Compass'' (2012) 9#10 pp: 665–678. * Trivellato, Francesca. "Renaissance Italy and the Muslim Mediterranean in Recent Historical Work", ''Journal of Modern History'' (March 2010), 82#1 pp: 127–155. * Woolfson, Jonathan, ed. ''Palgrave advances in Renaissance historiography'' (Palgrave Macmillan, 2005)
Primary sources
* Bartlett, Kenneth, ed. ''The Civilization of the Italian Renaissance: A Sourcebook'' (2nd ed., 2011) * Ross, James Bruce, and Mary M. McLaughlin, eds. ''The Portable Renaissance Reader'' (1977)excerpt and text search
External links
"The Renaissance"
''In Our Time'', BBC Radio 4 discussion with Francis Ames-Lewis, Peter Burke and Evelyn Welch (June 8, 2000).
*
Renaissance Philosophy
entry in the Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy Interactive resources
Florence: 3D Panoramas of Florentine Renaissance Sites(English/Italian)
Interactive Glossary of Terms Relating to the Renaissance
Multimedia Exploration of the Renaissance
RSS News Feed: Get an entry from Leonardo's Journal delivered each day
Exhibits Collection – Renaissance
Lectures and galleries
The Bagatti Valsecchi Museum
The Society for Renaissance Studies
{{good article Renaissance, 14th century in Europe 15th century in Europe 16th century in Europe 17th century in Europe Early Modern period Historical eras History of Europe by period Medieval philosophy Western culture