Protein (nutrient) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Proteins are essential
Proteins are essential
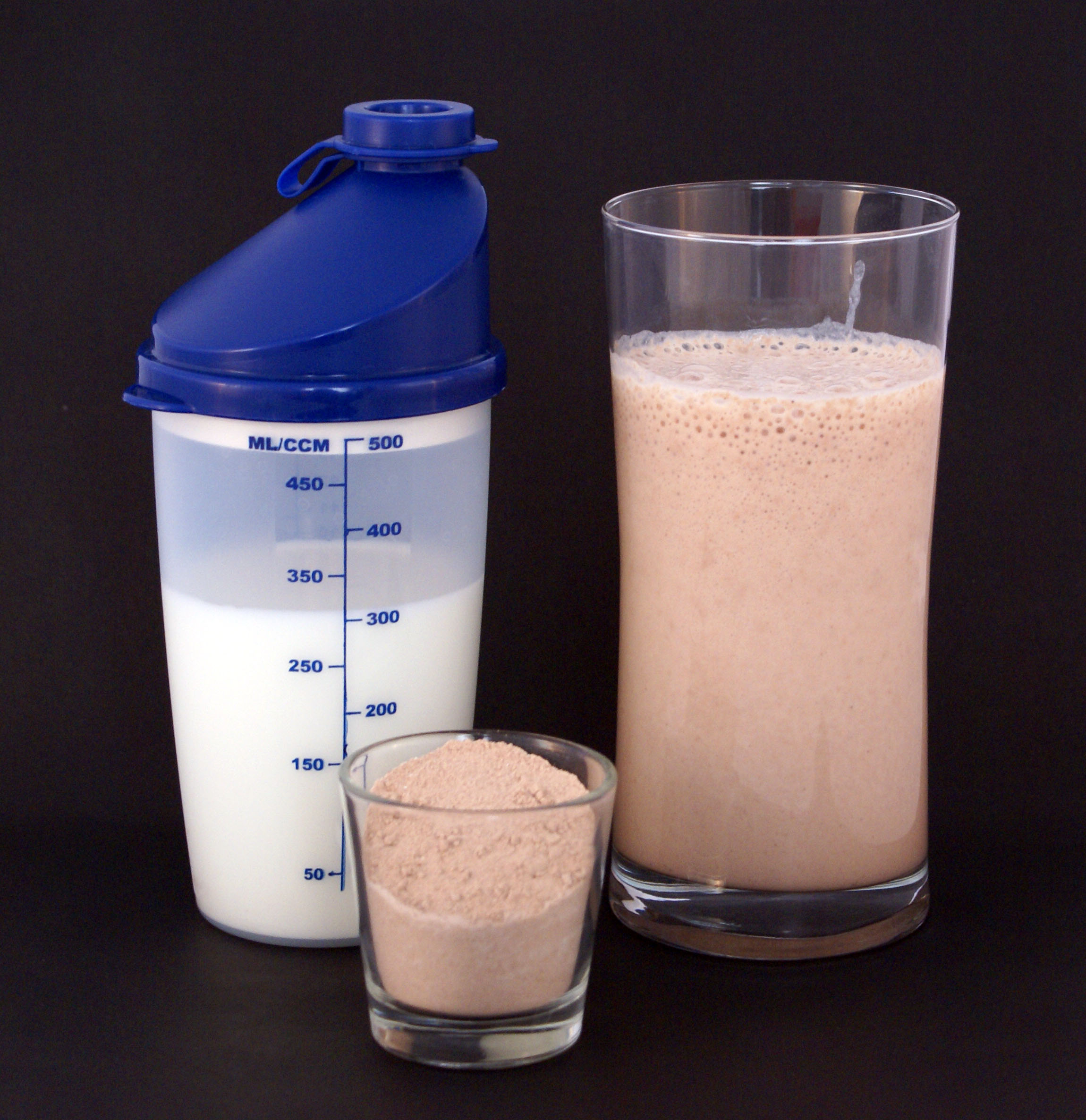 Protein powders – such as
Protein powders – such as
/ref> In 2013 FAO proposed changing to
/ref> Digestion typically begins in the stomach when pepsinogen is converted to
Nutrition Working Group of the Medical and Scientific Commission of the International Olympic Committee, Revised and Updated in June 2016.
 Protein deficiency and malnutrition (PEM) can lead to variety of ailments including
Protein deficiency and malnutrition (PEM) can lead to variety of ailments including
 Proteins are essential
Proteins are essential nutrient
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excret ...
s for the human body
The human body is the structure of a Human, human being. It is composed of many different types of Cell (biology), cells that together create Tissue (biology), tissues and subsequently organ systems. They ensure homeostasis and the life, viabi ...
. They are one of the building blocks of body tissue and can also serve as a fuel source. As a fuel, proteins provide as much energy density
In physics, energy density is the amount of energy stored in a given system or region of space per unit volume. It is sometimes confused with energy per unit mass which is properly called specific energy or .
Often only the ''useful'' or extract ...
as carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ma ...
s: 4 kcal
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of o ...
(17 kJ) per gram; in contrast, lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
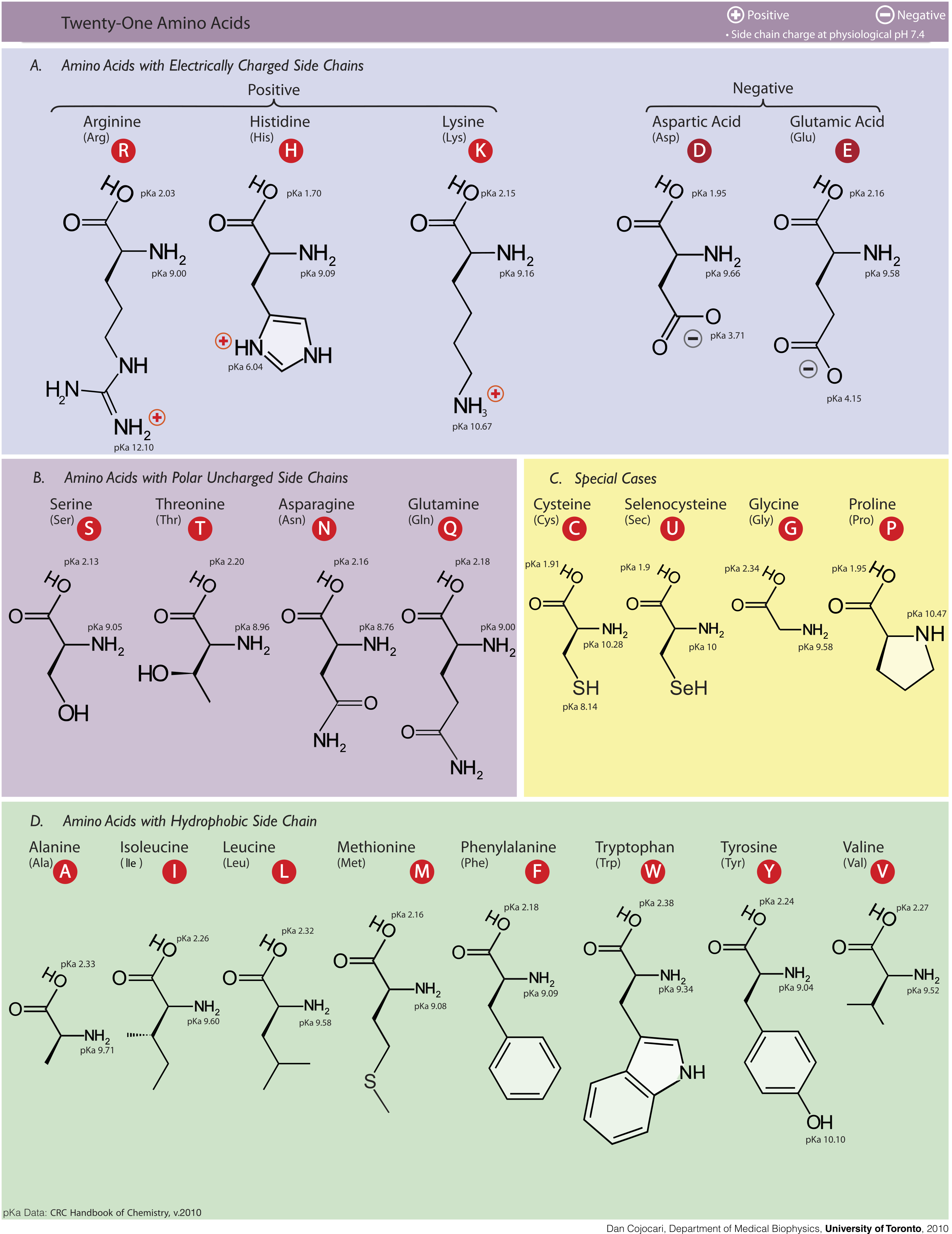
s provide 9 kcal (37 kJ) per gram. The most important aspect and defining characteristic of protein from a nutritional standpoint is its amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
composition.
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
s are polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
chains made of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds
In organic chemistry, a peptide bond is an amide type of covalent chemical bond linking two consecutive alpha-amino acids from C1 (carbon number one) of one alpha-amino acid and N2 (nitrogen number two) of another, along a peptide or protein cha ...
. During human digestion
Digestion is the breakdown of large insoluble food molecules into small water-soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the watery blood plasma. In certain organisms, these smaller substances are absorbed through the small intest ...
, proteins are broken down in the stomach to smaller polypeptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A p ...
chains via hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
and protease
A protease (also called a peptidase, proteinase, or proteolytic enzyme) is an enzyme that catalyzes (increases reaction rate or "speeds up") proteolysis, breaking down proteins into smaller polypeptides or single amino acids, and spurring the ...
actions. This is crucial for the absorption of the essential amino acid
An essential amino acid, or indispensable amino acid, is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its demand, and must therefore come from the diet. Of the 21 amino acids common to all life form ...
s that cannot be biosynthesized
Biosynthesis is a multi-step, enzyme- catalyzed process where substrates are converted into more complex products in living organisms. In biosynthesis, simple compounds are modified, converted into other compounds, or joined to form macromolecules ...
by the body.
There are nine essential amino acids which humans must obtain from their diet in order to prevent protein–energy malnutrition
Protein–energy malnutrition (PEM), sometimes called protein-energy undernutrition (PEU), is a form of malnutrition that is defined as a range of conditions arising from coincident lack of dietary protein and/or energy (calories) in varying propo ...
and resulting death. They are phenylalanine
Phenylalanine (symbol Phe or F) is an essential α-amino acid with the formula . It can be viewed as a benzyl group substituted for the methyl group of alanine, or a phenyl group in place of a terminal hydrogen of alanine. This essential amino a ...
, valine
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonat ...
, threonine
Threonine (symbol Thr or T) is an amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated −COO� ...
, tryptophan
Tryptophan (symbol Trp or W)
is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Tryptophan contains an α-amino group, an α- carboxylic acid group, and a side chain indole, making it a polar molecule with a non-polar aromatic ...
, methionine
Methionine (symbol Met or M) () is an essential amino acid in humans. As the precursor of other amino acids such as cysteine and taurine, versatile compounds such as SAM-e, and the important antioxidant glutathione, methionine plays a critical ro ...
, leucine
Leucine (symbol Leu or L) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Leucine is an α-amino acid, meaning it contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- ca ...
, isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprot ...
, lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −C ...
, and histidine
Histidine (symbol His or H) is an essential amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated –NH3+ form under biological conditions), a carboxylic acid group (which is in the de ...
. There has been debate as to whether there are 8 or 9 essential amino acids. The consensus seems to lean towards 9 since histidine is not synthesized in adults. There are five amino acids which humans are able to synthesize in the body. These five are alanine
Alanine (symbol Ala or A), or α-alanine, is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an amine group and a carboxylic acid group, both attached to the central carbon atom which also carries a methyl group side c ...
, aspartic acid
Aspartic acid (symbol Asp or D; the ionic form is known as aspartate), is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Like all other amino acids, it contains an amino group and a carboxylic acid. Its α-amino group is in the pro ...
, asparagine
Asparagine (symbol Asn or N) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the depro ...
, glutamic acid
Glutamic acid (symbol Glu or E; the ionic form is known as glutamate) is an α-amino acid that is used by almost all living beings in the biosynthesis of proteins. It is a non-essential nutrient for humans, meaning that the human body can synt ...
and serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form un ...
. There are six conditionally essential amino acids whose synthesis can be limited under special pathophysiological conditions, such as prematurity in the infant or individuals in severe catabolic distress. These six are arginine
Arginine is the amino acid with the formula (H2N)(HN)CN(H)(CH2)3CH(NH2)CO2H. The molecule features a guanidino group appended to a standard amino acid framework. At physiological pH, the carboxylic acid is deprotonated (−CO2−) and both the am ...
, cysteine
Cysteine (symbol Cys or C; ) is a semiessential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula . The thiol side chain in cysteine often participates in enzymatic reactions as a nucleophile.
When present as a deprotonated catalytic residue, sometime ...
, glycine
Glycine (symbol Gly or G; ) is an amino acid that has a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. It is the simplest stable amino acid (carbamic acid is unstable), with the chemical formula NH2‐ CH2‐ COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogeni ...
, glutamine
Glutamine (symbol Gln or Q) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. Its side chain is similar to that of glutamic acid, except the carboxylic acid group is replaced by an amide. It is classified as a charge-neutral, ...
, proline
Proline (symbol Pro or P) is an organic acid classed as a proteinogenic amino acid (used in the biosynthesis of proteins), although it does not contain the amino group but is rather a secondary amine. The secondary amine nitrogen is in the prot ...
and tyrosine
-Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Gr ...
. Dietary sources of protein include grain
A grain is a small, hard, dry fruit (caryopsis) – with or without an attached hull layer – harvested for human or animal consumption. A grain crop is a grain-producing plant. The two main types of commercial grain crops are cereals and legum ...
s, legume
A legume () is a plant in the family Fabaceae (or Leguminosae), or the fruit or seed of such a plant. When used as a dry grain, the seed is also called a pulse. Legumes are grown agriculturally, primarily for human consumption, for livestock f ...
s, nuts, seeds, beans, meats, dairy products, fish, eggs, edible insects
Insects as food or edible insects are insect species used for human consumption. More than 2,000 insects species worldwide are considered edible. However, a much smaller number is discussed for industrialized mass production and partly regiona ...
, and seaweeds.
Protein functions in human body
Protein is a nutrient needed by the human body for growth and maintenance. Aside from water, proteins are the most abundant kind of molecules in the body. Protein can be found in all cells of the body and is the major structural component of all cells in the body, especially muscle. This also includes body organs, hair and skin. Proteins are also used in membranes, such asglycoprotein
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos ...
s. When broken down into amino acids, they are used as precursors to nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
, co-enzymes, hormones, immune response, cellular repair, and other molecules essential for life. Additionally, protein is needed to form blood cells.
Sources
Protein occurs in a wide range of food. On a worldwide basis, plant protein foods contribute over 60% of the per capita supply of protein. In North America, animal-derived foods contribute about 70% of protein sources. Insects are a source of protein in many parts of the world. In parts of Africa, up to 50% of dietary protein derives from insects. It is estimated that more than 2 billion people eat insects daily. Meat, dairy, eggs,soy
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu and ...
, fish, whole grain
A whole grain is a grain of any cereal and pseudocereal that contains the endosperm, germ, and bran, in contrast to refined grains, which retain only the endosperm.
As part of a general healthy diet, consumption of whole grains is associated w ...
s, and cereal
A cereal is any Poaceae, grass cultivated for the edible components of its grain (botanically, a type of fruit called a caryopsis), composed of the endosperm, Cereal germ, germ, and bran. Cereal Grain, grain crops are grown in greater quantit ...
s are sources of protein. Examples of food staple
A staple food, food staple, or simply a staple, is a food that is eaten often and in such quantities that it constitutes a dominant portion of a standard diet for a given person or group of people, supplying a large fraction of energy needs an ...
s and cereal sources of protein, each with a concentration greater than 7%, are (in no particular order) buckwheat, oats, rye, millet, maize (corn), rice, wheat, sorghum, amaranth, and quinoa. Some research highlights game meat
Game or quarry is any wild animal hunted for animal products (primarily meat), for recreation (" sporting"), or for trophies. The species of animals hunted as game varies in different parts of the world and by different local jurisdictions, th ...
as a protein source.
Vegan sources of proteins include legumes, nuts, seeds and fruits. Vegan foods with protein concentrations greater than 7% include soybeans, lentils, kidney beans, white beans, mung beans, chickpeas, cowpeas, lima beans, pigeon peas, lupines, wing beans, almonds, Brazil nuts, cashews, pecans, walnuts, cotton seeds, pumpkin seeds, hemp seeds, sesame seeds, and sunflower seeds.
Photovoltaic-driven microbial protein production uses electricity from solar panels and carbon dioxide from the air to create fuel for microbes, which are grown in bioreactor vats and then processed into dry protein powders. The process makes highly efficient use of land, water and fertiliser.
People eating a balanced diet do not need protein supplements.
The table below presents food group
A food group is a collection of foods that share similar nutritional properties or biological classifications. List of nutrition guides typically divide foods into food groups and Recommended Dietary Allowance recommend daily servings of each gr ...
s as protein sources.
Colour key:
: Protein source with highest density of respective amino acid.
: Protein source with lowest density of respective amino acid.
 Protein powders – such as
Protein powders – such as casein
Casein ( , from Latin ''caseus'' "cheese") is a family of related phosphoproteins (CSN1S1, αS1, aS2, CSN2, β, K-casein, κ) that are commonly found in mammalian milk, comprising about 80% of the proteins in cow's milk and between 20% and 60% of ...
, whey
Whey is the liquid remaining after milk has been curdled and strained. It is a byproduct of the manufacturing of cheese or casein and has several commercial uses. Sweet whey is a byproduct resulting from the manufacture of rennet types of hard ...
, egg
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the a ...
, rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima
''Oryza glaberrima'', commonly known as African rice, is one of the two domesticated rice species. It was first domesticated and grown i ...
, soy
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu and ...
and cricket flour
Cricket flour (or cricket powder) is a protein-rich powder made from Cricket (insect), crickets, using various processes. Cricket flour differs from true flours made from grains by being composed mainly of protein rather than starches and dietary f ...
– are processed and manufactured sources of protein.
Testing in foods
The classicassays
An assay is an investigative (analytic) procedure in laboratory medicine, mining, pharmacology, environmental biology and molecular biology for qualitatively assessing or quantitatively measuring the presence, amount, or functional activity of a ...
for protein concentration in food are the Kjeldahl method
The Kjeldahl method or Kjeldahl digestion () in analytical chemistry is a method for the quantitative determination of nitrogen contained in organic substances plus the nitrogen contained in the inorganic compounds ammonia and ammonium (NH3/NH4+) ...
and the Dumas method
The Dumas method in analytical chemistry is a method for the quantitative determination of nitrogen in chemical substances based on a method first described by Jean-Baptiste Dumas in 1826.
The Dumas technique has been automated and instrumentaliz ...
. These tests determine the total nitrogen in a sample. The only major component of most food which contains nitrogen is protein (fat, carbohydrate and dietary fiber do not contain nitrogen). If the amount of nitrogen is multiplied by a factor depending on the kinds of protein expected in the food the total protein can be determined. This value is known as the "''crude protein''" content. On food labels the protein is given by the nitrogen multiplied by 6.25, because the average nitrogen content of proteins is about 16%. The Kjeldahl test is typically used because it is the method the AOAC International has adopted and is therefore used by many food standards agencies around the world, though the Dumas method is also approved by some standards organizations.
Accidental contamination
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that spoils, corrupts, infects, makes unfit, or makes inferior a material, physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc.
Types of contamination
W ...
and intentional adulteration of protein meals with non-protein nitrogen
Non-protein nitrogen (or NPN) is a term used in animal nutrition to refer collectively to components such as urea, biuret, and ammonia, which are not proteins but can be converted into proteins by microbes in the ruminant stomach. Due to their lowe ...
sources that inflate crude protein content measurements have been known to occur in the food industry
The food industry is a complex, global network of diverse businesses that supplies most of the food consumed by the world's population. The food industry today has become highly diversified, with manufacturing ranging from small, traditiona ...
for decades. To ensure food quality
Food quality is a concept often based on the organoleptic characteristics (e.g., taste, aroma, appearance) and nutritional value of food. Producers reducing potential pathogens and other hazards through food safety practices is another important fa ...
, purchasers of protein meals routinely conduct quality control
Quality control (QC) is a process by which entities review the quality of all factors involved in production. ISO 9000 defines quality control as "a part of quality management focused on fulfilling quality requirements".
This approach places ...
tests designed to detect the most common non-protein nitrogen contaminants, such as urea
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula . This amide has two amino groups (–) joined by a carbonyl functional group (–C(=O)–). It is thus the simplest amide of carbamic acid.
Urea serves an important r ...
and ammonium nitrate
Ammonium nitrate is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is a white crystalline salt consisting of ions of ammonium and nitrate. It is highly soluble in water and hygroscopic as a solid, although it does not form hydrates. It is ...
.
In at least one segment of the food industry, the dairy industry, some countries (at least the U.S., Australia, France and Hungary) have adopted "''true protein''" measurement, as opposed to crude protein measurement, as the standard for payment and testing: "True protein is a measure of only the proteins in milk, whereas crude protein is a measure of all sources of nitrogen and includes nonprotein nitrogen, such as urea, which has no food value to humans. ... Current milk-testing equipment measures peptide bonds, a direct measure of true protein." Measuring peptide bonds in grains has also been put into practice in several countries including Canada, the UK, Australia, Russia and Argentina where near-infrared reflectance (NIR) technology, a type of infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or function ...
is used. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an intern ...
(FAO) recommends that only amino acid analysis be used to determine protein in, ''inter alia'', foods used as the sole source of nourishment, such as infant formula, but also provides: "When data on amino acids analyses are not available, determination of protein based on total N content by Kjeldahl (AOAC, 2000) or similar method ... is considered acceptable."
The testing method for protein in beef cattle feed has grown into a science over the post-war years. The standard text in the United States, ''Nutrient Requirements of Beef Cattle'', has been through eight editions over at least seventy years. The 1996 sixth edition substituted for the fifth edition's ''crude protein'' the concept of "'' metabolizeable protein''", which was defined around the year 2000 as "the ''true protein'' absorbed by the intestine, supplied by microbial protein and undegraded intake protein".
The limitations of the Kjeldahl method were at the heart of the Chinese protein export contamination
In China, the adulteration and contamination of several food and feed ingredients with inexpensive melamine and other compounds, such as cyanuric acid, ammeline and ammelide, are common practice. These adulterants can be used to inflate the ap ...
in 2007 and the 2008 China milk scandal in which the industrial chemical melamine
Melamine is an organic compound with the formula C3H6N6. This white solid is a trimer of cyanamide, with a 1,3,5-triazine skeleton. Like cyanamide, it contains 67% nitrogen by mass, and its derivatives have fire retardant properties due t ...
was added to the milk or glutens to increase the measured "protein".
Protein quality
The most important aspect and defining characteristic of protein from a nutritional standpoint is itsamino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha am ...
composition. There are multiple systems which rate proteins by their usefulness to an organism based on their relative percentage of amino acids and, in some systems, the digestibility of the protein source. They include biological value, net protein utilization The net protein utilization, or NPU, is the ratio of amino acid mass converted to proteins to the mass of amino acids supplied. This figure is somewhat affected by the salvage of essential amino acids within the body, but is profoundly affected by t ...
, and PDCAAS Protein digestibility-corrected amino acid score (PDCAAS) is a method of evaluating the quality of a protein based on both the amino acid requirements of humans and their ability to digest it.
The PDCAAS rating was adopted by the US FDA and the Fo ...
(Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acids Score) which was developed by the FDA as a modification of the Protein efficiency ratio Protein efficiency ratio (PER) is based on the weight gain of a test subject divided by its intake of a particular food protein during the test period.
From 1919 until very recently, the PER had been a widely used method for evaluating the quality ...
(PER) method. The PDCAAS rating was adopted by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations/World Health Organization
The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for international public health. The WHO Constitution states its main objective as "the attainment by all peoples of the highest possible level of h ...
(FAO/WHO) in 1993 as "the preferred 'best'" method to determine protein quality. These organizations have suggested that other methods for evaluating the quality of protein are inferior.Boutrif, E., Food Quality and Consumer Protection Group, Food Policy and Nutrition Division, FAO, Rome: "Recent Developments in Protein Quality Evaluation" ''Food, Nutrition and Agriculture'', Issue 2/3, 1991/ref> In 2013 FAO proposed changing to
Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score Digestible Indispensable Amino Acid Score (DIAAS) is a protein quality method proposed in March 2013 by the Food and Agriculture Organization to replace the current protein ranking standard, the Protein Digestibility Corrected Amino Acid Score (PDC ...
.
Digestion
Most proteins are decomposed to single amino acids by digestion in the gastro-intestinal tract.Digestion of Dietary Proteins in the Gastro-Intestinal Tract/ref> Digestion typically begins in the stomach when pepsinogen is converted to
pepsin
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, w ...
by the action of hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid
Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbol ...
, and continued by trypsin
Trypsin is an enzyme in the first section of the small intestine that starts the digestion of protein molecules by cutting these long chains of amino acids into smaller pieces. It is a serine protease from the PA clan superfamily, found in the dig ...
and chymotrypsin in the small intestine.
Before the absorption in the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
, most proteins are already reduced to single amino acid or peptides of several amino acids. Most peptides longer than four amino acids are not absorbed. Absorption into the intestinal absorptive cells is not the end. There, most of the peptides are broken into single amino acids.
Absorption of the amino acids and their derivatives
The derivative of a function is the rate of change of the function's output relative to its input value.
Derivative may also refer to:
In mathematics and economics
* Brzozowski derivative in the theory of formal languages
* Formal derivative, an ...
into which dietary protein is degraded is done by the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organ (biology), organs of the digestive syste ...
. The absorption rates of individual amino acids are highly dependent on the protein source; for example, the digestibilities of many amino acids in humans, the difference between soy
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu and ...
and milk proteins and between individual milk proteins, beta-lactoglobulin
β-Lactoglobulin (BLG) is the major whey protein of cow and sheep's milk (~3 g/L), and is also present in many other mammalian species; a notable exception being humans. Its structure, properties and biological role have been reviewed many time ...
and casein. For milk proteins, about 50% of the ingested protein is absorbed between the stomach and the jejunum
The jejunum is the second part of the small intestine in humans and most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. Its lining is specialised for the absorption by enterocytes of small nutrient molecules which have been previou ...
and 90% is absorbed by the time the digested food reaches the ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine ma ...
. Biological value (BV) is a measure of the proportion of absorbed protein from a food which becomes incorporated into the proteins of the organism's body.
Newborn
Newborns
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used t ...
of mammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
are exceptional in protein digestion and assimilation in that they can absorb intact proteins at the small intestine. This enables passive immunity Passive immunity is the transfer of active humoral immunity of ready-made antibodies. Passive immunity can occur naturally, when maternal antibodies are transferred to the fetus through the placenta, and it can also be induced artificially, when hi ...
, i.e., transfer of immunoglobulins from the mother to the newborn, via milk.
Dietary requirements
Considerable debate has taken place regarding issues surrounding protein intake requirements. The amount of protein required in a person's diet is determined in large part by overall energy intake, the body's need for nitrogen and essential amino acids, body weight and composition, rate of growth in the individual, physical activity level, the individual's energy and carbohydrate intake, and the presence of illness or injury. Physical activity and exertion as well as enhanced muscular mass increase the need for protein. Requirements are also greater during childhood for growth and development, during pregnancy, or when breastfeeding in order to nourish a baby or when the body needs to recover from malnutrition or trauma or after an operation.Dietary recommendations
According to US & CanadianDietary Reference Intake
The Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) is a system of nutrition recommendations from the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) of the National Academies (United States). It was introduced in 1997 in order to broaden the existing guidelines known as Reco ...
guidelines, women aged 19–70 need to consume 46 grams of protein per day while men aged 19–70 need to consume 56 grams of protein per day to minimize risk of deficiency. These Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs) were calculated based on 0.8 grams protein per kilogram body weight and average body weights of 57 kg (126 pounds) and 70 kg (154 pounds), respectively. However, this recommendation is based on structural requirements but disregards use of protein for energy metabolism
Bioenergetics is a field in biochemistry and cell biology that concerns energy flow through living systems. This is an active area of biological research that includes the study of the transformation of energy in living organisms and the study of ...
. This requirement is for a normal sedentary person. In the United States, average protein consumption is higher than the RDA. According to results of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES 2013–2014), average protein consumption for women ages 20 and older was 69.8 grams and for men 98.3 grams/day.
Active people
Several studies have concluded that active people and athletes may require elevated protein intake (compared to 0.8 g/kg) due to increase in muscle mass and sweat losses, as well as need for body repair and energy source. Suggested amounts vary from 1.2 to 1.4 g/kg for those doing endurance exercise to as much as 1.6-1.8 g/kg for strength exercise, while a proposed ''maximum'' daily protein intake would be approximately 25% of energy requirements i.e. approximately 2 to 2.5 g/kg. However, many questions still remain to be resolved. In addition, some have suggested that athletes using restricted-calorie diets for weight loss should further increase their protein consumption, possibly to 1.8–2.0 g/kg, in order to avoid loss of lean muscle mass.Aerobic exercise protein needs
Endurance athletes differ from strength-building athletes in that endurance athletes do not build as much muscle mass from training as strength-building athletes do. Research suggests that individuals performing endurance activity require more protein intake than sedentary individuals so that muscles broken down during endurance workouts can be repaired. Although the protein requirement for athletes still remains controversial (for instance see Lamont, Nutrition Research Reviews, pages 142 - 149, 2012), research does show that endurance athletes can benefit from increasing protein intake because the type of exercise endurance athletes participate in still alters the protein metabolism pathway. The overall protein requirement increases because of amino acid oxidation in endurance-trained athletes. Endurance athletes who exercise over a long period (2–5 hours per training session) use protein as a source of 5–10% of their total energy expended. Therefore, a slight increase in protein intake may be beneficial to endurance athletes by replacing the protein lost in energy expenditure and protein lost in repairing muscles. One review concluded that endurance athletes may increase daily protein intake to a maximum of 1.2–1.4 g per kg body weight.Anaerobic exercise protein needs
Research also indicates that individuals performingstrength training
Strength training or resistance training involves the performance of physical exercises that are designed to improve strength and endurance. It is often associated with the lifting of weights. It can also incorporate a variety of training te ...
activity require more protein than sedentary individuals. Strength-training athletes may increase their daily protein intake to a maximum of 1.4–1.8 g per kg body weight to enhance muscle protein synthesis, or to make up for the loss of amino acid oxidation during exercise. Many athletes maintain a high-protein diet
A high-protein diet is a diet in which 20% or more of the total daily calories comes from protein.Longe, Jacqueline L. (2008). ''High-protein diet''. In ''The Gale Encyclopedia of Diets: A Guide to Health and Nutrition''. Gale. pp. 524-526. Most ...
as part of their training. In fact, some athletes who specialize in anaerobic sports (e.g., weightlifting) believe a very high level of protein intake is necessary, and so consume high protein meals and also protein supplements.Nutrition for Athletes, International Olympic CommitteeNutrition Working Group of the Medical and Scientific Commission of the International Olympic Committee, Revised and Updated in June 2016.
Special populations
Protein allergies
A food allergy is an abnormalimmune response
An immune response is a reaction which occurs within an organism for the purpose of defending against foreign invaders. These invaders include a wide variety of different microorganisms including viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi which could ...
to proteins in food. The signs and symptoms may range from mild to severe. They may include itchiness
Itch (also known as pruritus) is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant ...
, swelling of the tongue, vomiting, diarrhea, hives, trouble breathing, or low blood pressure. These symptoms typically occurs within minutes to one hour after exposure. When the symptoms are severe, it is known as anaphylaxis
Anaphylaxis is a serious, potentially fatal allergic reaction and medical emergency that is rapid in onset and requires immediate medical attention regardless of use of emergency medication on site. It typically causes more than one of the follow ...
. The following eight foods are responsible for about 90% of allergic reactions: cow's milk
Milk is a white liquid food produced by the mammary glands of mammals. It is the primary source of nutrition for young mammals (including breastfed human infants) before they are able to digest solid food. Immune factors and immune-modulati ...
, eggs
Humans and human ancestors have scavenged and eaten animal eggs for millions of years. Humans in Southeast Asia had domesticated chickens and harvested their eggs for food by 1,500 BCE. The most widely consumed eggs are those of fowl, especial ...
, wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, shellfish
Shellfish is a colloquial and fisheries term for exoskeleton-bearing aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms. Although most kinds of shellfish are harvested from saltwater envir ...
, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
, peanut
The peanut (''Arachis hypogaea''), also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible Seed, seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small ...
s, tree nuts
A nut is a fruit consisting of a hard or tough nutshell protecting a kernel which is usually edible. In general usage and in a culinary sense, a wide variety of dry seeds are called nuts, but in a botanical context "nut" implies that the shell ...
and soy
The soybean, soy bean, or soya bean (''Glycine max'') is a species of legume native to East Asia, widely grown for its edible bean, which has numerous uses.
Traditional unfermented food uses of soybeans include soy milk, from which tofu and ...
.
Chronic kidney disease
While there is no conclusive evidence that a high protein diet can causechronic kidney disease
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a type of kidney disease in which a gradual loss of kidney function occurs over a period of months to years. Initially generally no symptoms are seen, but later symptoms may include leg swelling, feeling tired, vo ...
, there is a consensus that people with this disease should decrease consumption of protein. According to one 2009 review updated in 2018, people with chronic kidney disease who reduce protein consumption have less likelihood of progressing to end stage kidney disease. Moreover, people with this disease while using a low protein diet (0.6 g/kg/d - 0.8 g/kg/d) may develop metabolic compensations that preserve kidney function, although in some people, malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
may occur.
Phenylketonuria
Individuals withphenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated PKU can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, behavioral problems, and mental disorders. It may also re ...
(PKU) must keep their intake of phenylalaninean essential amino acidextremely low to prevent a mental disability and other metabolic complications. Phenylalanine is a component of the artificial sweetener aspartame, so people with PKU need to avoid low calorie beverages and foods with this ingredient.
Excess consumption
The U.S. and Canadian Dietary Reference Intake review for protein concluded that there was not sufficient evidence to establish aTolerable upper intake level
The Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) is a system of nutrition recommendations from the National Academy of Medicine (NAM) of the National Academies (United States). It was introduced in 1997 in order to broaden the existing guidelines known as Re ...
, i.e., an upper limit for how much protein can be safely consumed.
When amino acids are in excess of needs, the liver takes up the amino acids and deaminates them, a process converting the nitrogen from the amino acids into ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . A stable binary hydride, and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinct pungent smell. Biologically, it is a common nitrogenous was ...
, further processed in the liver into urea via the urea cycle
The urea cycle (also known as the ornithine cycle) is a cycle of Biochemistry, biochemical reactions that produces urea (NH2)2CO from ammonia (NH3). Animals that use this cycle, mainly amphibians and mammals, are called ureotelic.
The urea cycle ...
. Excretion of urea occurs via the kidneys. Other parts of the amino acid molecules can be converted into glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using ...
and used for fuel. When food protein intake is periodically high or low, the body tries to keep protein levels at an equilibrium by using the "labile protein reserve" to compensate for daily variations in protein intake. However, unlike body fat as a reserve for future caloric needs, there is no protein storage for future needs.
Excessive protein intake may increase calcium excretion in urine, occurring to compensate for the pH imbalance from oxidation of sulfur amino acids. This may lead to a higher risk of kidney stone formation from calcium in the renal circulatory system. One meta-analysis reported no adverse effect
An adverse effect is an undesired harmful effect resulting from a medication or other intervention, such as surgery. An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. The term complica ...
s of higher protein intakes on bone density. Another meta-analysis reported a small decrease in systolic and diastolic blood pressure with diets higher in protein, with no differences between animal and plant protein.
High protein diets have been shown to lead to an additional 1.21 kg of weight loss over a period of 3 months versus a baseline protein diet in a meta-analysis. Benefits of decreased body mass index
Body mass index (BMI) is a value derived from the mass (weight) and height of a person. The BMI is defined as the body mass divided by the square of the body height, and is expressed in units of kg/m2, resulting from mass in kilograms and he ...
as well as HDL cholesterol
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules (lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are t ...
were more strongly observed in studies with only a slight increase in protein intake rather where high protein intake was classified as 45% of total energy intake. Detrimental effects to cardiovascular activity were not observed in short-term diets of 6 months or less. There is little consensus on the potentially detrimental effects to healthy individuals of a long-term high protein diet, leading to caution advisories about using high protein intake as a form of weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health, or physical fitness, refers to a reduction of the total body mass, by a mean loss of fluid, body fat (adipose tissue), or lean mass (namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon, and other conn ...
.
The ''2015–2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans'' (DGA) recommends that men and teenage boys increase their consumption of fruits, vegetables and other under-consumed foods, and that a means of accomplishing this would be to reduce overall intake of protein foods. The 2015 - 2020 DGA report does not set a recommended limit for the intake of red and processed meat. While the report acknowledges research showing that lower intake of red and processed meat is correlated with reduced risk of cardiovascular diseases
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack). Other CVDs include stroke, ...
in adults, it also notes the value of nutrients provided from these meats. The recommendation is not to limit intake of meats or protein, but rather to monitor and keep within daily limits the sodium (< 2300 mg), saturated fat
A saturated fat is a type of fat in which the fatty acid chains have all single bonds. A fat known as a glyceride is made of two kinds of smaller molecules: a short glycerol backbone and fatty acids that each contain a long linear or branched c ...
s (less than 10% of total calories per day), and added sugars (less than 10% of total calories per day) that may be increased as a result of consumption of certain meats and proteins. While the 2015 DGA report does advise for a reduced level of consumption of red and processed meats, the 2015-2020 DGA key recommendations recommend that a variety of protein foods be consumed, including both vegetarian and non-vegetarian sources of protein.
Protein deficiency
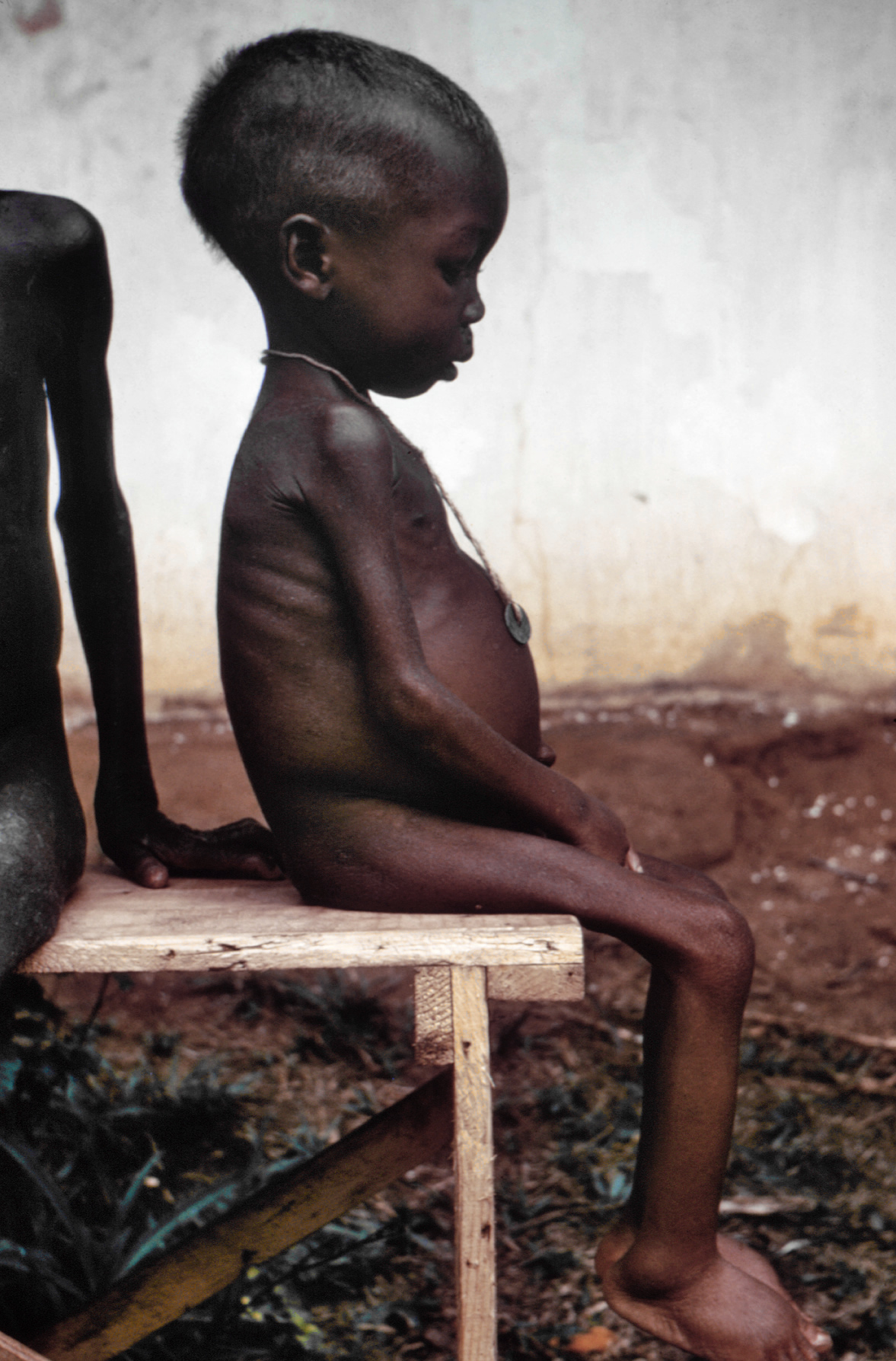
 Protein deficiency and malnutrition (PEM) can lead to variety of ailments including
Protein deficiency and malnutrition (PEM) can lead to variety of ailments including Intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation,Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signifi ...
and kwashiorkor. Symptoms of kwashiorkor include apathy, diarrhea, inactivity, failure to grow, flaky skin, fatty liver, and edema of the belly and legs. This edema is explained by the action of lipoxygenase on arachidonic acid to form leukotrienes and the normal functioning of proteins in fluid balance and lipoprotein transport.
PEM is fairly common worldwide in both children and adults and accounts for 6 million deaths annually. In the industrialized world, PEM is predominantly seen in hospitals, is associated with disease, or is often found in the elderly.
See also
*Azotorrhea Azotorrhea is the excessive discharge of nitrogenous substances in the feces or urine. As in when people eat a diet high in protein they may suffer from increased amount of amino acid byproduct (nitrogen) being broken and excreted through defecatio ...
* Biological value
*Bodybuilding supplement
Bodybuilding supplements are dietary supplements commonly used by those involved in bodybuilding, weightlifting, mixed martial arts, and athletics for the purpose of facilitating an increase in lean body mass. Bodybuilding supplements may contain ...
*Leaf protein concentrate
Leaf protein concentrate (LPC) is a concentration, concentrated form of the proteins found in the leaf, leaves of plants. It has been examined as a human or animal food source, because it is potentially the cheapest, most abundant source of availa ...
* Low-protein diet
*Protein bar
Protein bars are nutrition bars that contain a high proportion of protein to carbohydrates/ fats.
Dietary purpose
Protein bars are targeted to people who primarily want a convenient source of protein that does not require preparation (unless ...
* Single-cell protein
References
{{ReflistProteins
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
Nutrition