|
Jejunum
The jejunum is the second part of the small intestine in humans and most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. Its lining is specialised for the absorption by enterocytes of small nutrient molecules which have been previously digested by enzymes in the duodenum. The jejunum lies between the duodenum and the ileum and is considered to start at the suspensory muscle of the duodenum, a location called the duodenojejunal flexure. The division between the jejunum and ileum is not anatomically distinct. In adult humans, the small intestine is usually long (post mortem), about two-fifths of which (about ) is the jejunum. Structure The interior surface of the jejunum—which is exposed to ingested food—is covered in finger–like projections of mucosa, called Intestinal villus, villi, which increase the surface area of tissue available to absorb nutrients from ingested foodstuffs. The epithelial cells which line these villi have Microvillus, microvilli. The tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
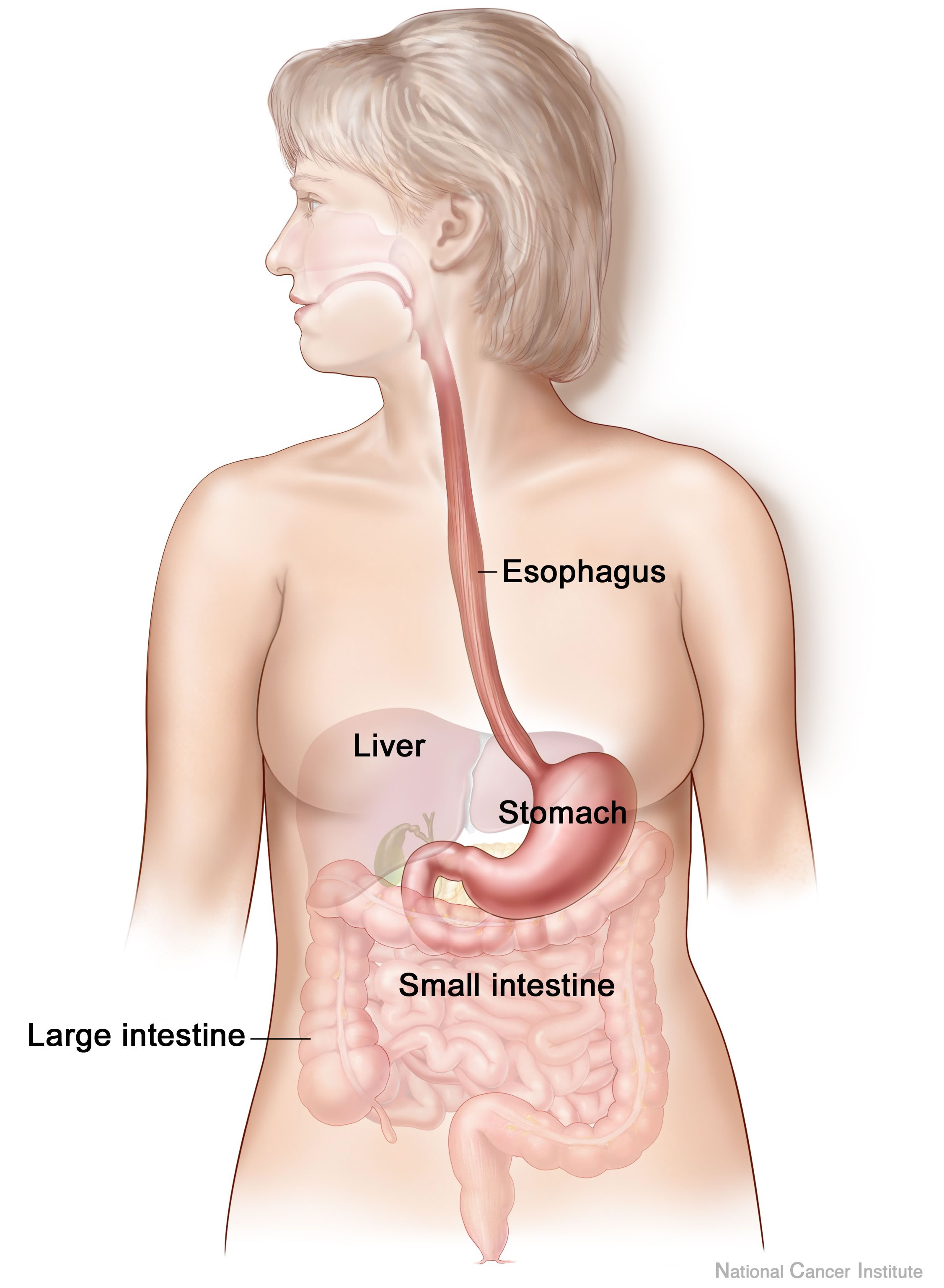
Small Intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the pancreatic duct to aid in digestion. The small intestine is about long and folds many times to fit in the abdomen. Although it is longer than the large intestine, it is called the small intestine because it is narrower in diameter. The small intestine has three distinct regions – the duodenum, jejunum, and ileum. The duodenum, the shortest, is where preparation for absorption through small finger-like protrusions called villi begins. The jejunum is specialized for the absorption through its lining by enterocytes: small nutrient particles which have been previously digested by enzymes in the duodenum. The main function of the ileum is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ileum
The ileum () is the final section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms posterior intestine or distal intestine may be used instead of ileum. Its main function is to absorb vitamin B12, bile salts, and whatever products of digestion that were not absorbed by the jejunum. The ileum follows the duodenum and jejunum and is separated from the cecum by the ileocecal valve (ICV). In humans, the ileum is about 2–4 m long, and the pH is usually between 7 and 8 (neutral or slightly basic). ''Ileum ''is derived from the Greek word ''eilein'', meaning "to twist up tightly". Structure The ileum is the third and final part of the small intestine. It follows the jejunum and ends at the ileocecal junction, where the terminal ileum communicates with the cecum of the large intestine through the ileocecal valve. The ileum, along with the jejunum, is sus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suspensory Muscle Of The Duodenum
The suspensory muscle of duodenum is a thin muscle connecting the junction between the duodenum, jejunum, and duodenojejunal flexure to connective tissue surrounding the superior mesenteric artery and coeliac artery. It is also known as the ligament of Treitz. The suspensory muscle most often connects to both the third and fourth parts of the duodenum, as well as the duodenojejunal flexure, although the attachment is quite variable. The suspensory muscle marks the formal division between the first and second parts of the small intestine, the duodenum and the jejunum. This division is used to mark the difference between the upper and lower gastrointestinal tracts, which is relevant in clinical medicine as it may determine the source of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract. The suspensory muscle is derived from mesoderm and plays a role in the embryological rotation of the gut, by offering a point of fixation for the rotating gut. It is also thought to help digestion by widenin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digestive System
The human digestive system consists of the gastrointestinal tract plus the accessory organs of digestion (the tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components, until they can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The process of digestion has three stages: the cephalic phase, the gastric phase, and the intestinal phase. The first stage, the cephalic phase of digestion, begins with secretions from gastric glands in response to the sight and smell of food. This stage includes the mechanical breakdown of food by chewing, and the chemical breakdown by digestive enzymes, that takes place in the mouth. Saliva contains the digestive enzymes amylase, and lingual lipase, secreted by the salivary and serous glands on the tongue. Chewing, in which the food is mixed with saliva, begins the mechanical process of digestion. This produces a bolus which is swallowed down the esophagus to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenojejunal Flexure
The duodenojejunal flexure or duodenojejunal junction is the border between the duodenum and the jejunum. Structure The ascending portion of the duodenum ascends on the left side of the aorta, as far as the level of the upper border of the second lumbar vertebra. At this point, it turns abruptly forward to merge with the jejunum, forming the duodenojejunal flexure. This forms the beginning of the jejunum. The duodenojejunal flexure is surrounded by the suspensory muscle of the duodenum. It is retroperitoneal, so is less mobile than the jejunum that comes after it, helping to stabilise the jejunum. The duodenojejunal flexure lies in front of the left psoas major muscle, the left renal artery, and the left renal vein. It is covered in front, and partly at the sides, by peritoneum continuous with the left portion of the mesentery. Clinical significance The ligament of Treitz, a peritoneal fold, from the right crus of diaphragm, is an identification point for the duodenojeju ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum. In mammals the duodenum may be the principal site for iron absorption. The duodenum precedes the jejunum and ileum and is the shortest part of the small intestine. In humans, the duodenum is a hollow jointed tube about 25–38 cm (10–15 inches) long connecting the stomach to the middle part of the small intestine. It begins with the duodenal bulb and ends at the suspensory muscle of duodenum. Duodenum can be divided into four parts: the first (superior), the second (descending), the third (horizontal) and the fourth (ascending) parts. Structure The duodenum is a C-shaped structure lying adjacent to the stomach. It is divided anatomically into four sections. The first part of the duodenu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestinal Villus
Intestinal villi (singular: villus) are small, finger-like projections that extend into the lumen of the small intestine. Each villus is approximately 0.5–1.6 mm in length (in humans), and has many microvilli projecting from the enterocytes of its epithelium which collectively form the striated or brush border. Each of these microvilli are about 1 µm in length, around 1000 times shorter than a single villus. The intestinal villi are much smaller than any of the circular folds in the intestine. Villi increase the internal surface area of the intestinal walls making available a greater surface area for absorption. An increased absorptive area is useful because digested nutrients (including monosaccharide and amino acids) pass into the semipermeable villi through diffusion, which is effective only at short distances. In other words, increased surface area (in contact with the fluid in the lumen) decreases the average distance travelled by nutrient molecules, so effecti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jejunal Arteries
The jejunal arteries are branches of the superior mesenteric artery which supply blood to the jejunum The jejunum is the second part of the small intestine in humans and most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. Its lining is specialised for the absorption by enterocytes of small nutrient molecules which have been previou .... External links Arteries of the abdomen {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
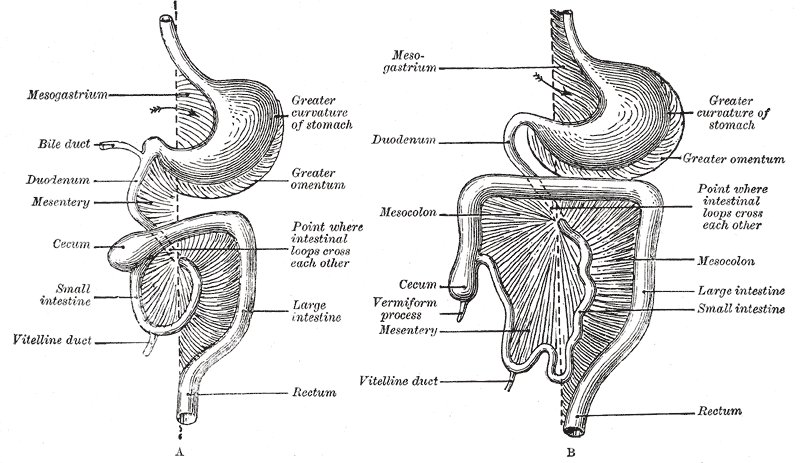
Mesentery
The mesentery is an organ that attaches the intestines to the posterior abdominal wall in humans and is formed by the double fold of peritoneum. It helps in storing fat and allowing blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves to supply the intestines, among other functions. The mesocolon was thought to be a fragmented structure, with all named parts—the ascending, transverse, descending, and sigmoid mesocolons, the mesoappendix, and the mesorectum—separately terminating their insertion into the posterior abdominal wall. However, in 2012, new microscopic and electron microscopic examinations showed the mesocolon to be a single structure derived from the duodenojejunal flexure and extending to the distal mesorectal layer. Thus, the mesentery is an internal organ. Structure The mesentery of the small intestine arises from the root of the mesentery (or mesenteric root) and is the part connected with the structures in front of the vertebral column. The root is narrow, about 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula . Glucose is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. Glucose is mainly made by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight, where it is used to make cellulose in cell walls, the most abundant carbohydrate in the world. In energy metabolism, glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms. Glucose for metabolism is stored as a polymer, in plants mainly as starch and amylopectin, and in animals as glycogen. Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. The naturally occurring form of glucose is -glucose, while -glucose is produced synthetically in comparatively small amounts and is less biologically active. Glucose is a monosaccharide containing six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group, and is therefore an aldohexose. The glucose molecule can exist in an open-chain (acyclic) as well as ring (cyclic) form. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microvillus
Microvilli (singular: microvillus) are microscopic cellular membrane protrusions that increase the surface area for diffusion and minimize any increase in volume, and are involved in a wide variety of functions, including absorption, secretion, cellular adhesion, and mechanotransduction. Structure Microvilli are covered in plasma membrane, which encloses cytoplasm and microfilaments. Though these are cellular extensions, there are little or no cellular organelles present in the microvilli. Each microvillus has a dense bundle of cross-linked actin filaments, which serves as its structural core. 20 to 30 tightly bundled actin filaments are cross-linked by bundling proteins fimbrin (or plastin-1), villin and espin to form the core of the microvilli. In the enterocyte microvillus, the structural core is attached to the plasma membrane along its length by lateral arms made of myosin 1a and Ca2+ binding protein calmodulin. Myosin 1a functions through a binding site for filamentous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |