|
Isoleucine
Isoleucine (symbol Ile or I) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO form under biological conditions), and a hydrocarbon side chain with a branch (a central carbon atom bound to three other carbon atoms). It is classified as a non-polar, uncharged (at physiological pH), branched-chain, aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it, and must be ingested in our diet. Isoleucine is synthesized from pyruvate employing leucine biosynthesis enzymes in other organisms such as bacteria. It is encoded by the codons AUU, AUC, and AUA. Metabolism Biosynthesis As an essential nutrient, it is not synthesized in the body, hence it must be ingested, usually as a component of proteins. In plants and microorganisms, it is synthesized via several steps, startin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Essential Amino Acid
An essential amino acid, or indispensable amino acid, is an amino acid that cannot be synthesized from scratch by the organism fast enough to supply its demand, and must therefore come from the diet. Of the 21 amino acids common to all life forms, the nine amino acids humans cannot synthesize are phenylalanine, valine, threonine, tryptophan, methionine, leucine, isoleucine, lysine, and histidine. Six other amino acids are considered conditionally essential in the human diet, meaning their synthesis can be limited under special pathophysiological conditions, such as prematurity in the infant or individuals in severe catabolic distress. These six are arginine, cysteine, glycine, glutamine, proline, and tyrosine. Six amino acids are non-essential (dispensable) in humans, meaning they can be synthesized in sufficient quantities in the body. These six are alanine, aspartic acid, asparagine, glutamic acid, serine, and selenocysteine (considered the 21st amino acid). Pyrrolysine (consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha amino acids appear in the genetic code. Amino acids can be classified according to the locations of the core structural functional groups, as Alpha and beta carbon, alpha- , beta- , gamma- or delta- amino acids; other categories relate to Chemical polarity, polarity, ionization, and side chain group type (aliphatic, Open-chain compound, acyclic, aromatic, containing hydroxyl or sulfur, etc.). In the form of proteins, amino acid '' residues'' form the second-largest component (water being the largest) of human muscles and other tissues. Beyond their role as residues in proteins, amino acids participate in a number of processes such as neurotransmitter transport and biosynthesis. It is thought that they played a key role in enabling life ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branched-chain Amino Acid
A branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) is an amino acid having an aliphatic side-chain with a branch (a central carbon atom bound to three or more carbon atoms). Among the proteinogenic amino acids, there are three BCAAs: leucine, isoleucine, and valine. Non-proteinogenic BCAAs include 2-aminoisobutyric acid. The three proteinogenic BCAAs are among the nine essential amino acids for humans, accounting for 35% of the essential amino acids in muscle proteins and 40% of the preformed amino acids required by mammals. Synthesis for BCAAs occurs in all locations of plants, within the plastids of the cell, as determined by presence of mRNAs which encode for enzymes in the metabolic pathway. BCAAs fill several metabolic and physiologic roles. Metabolically, BCAAs promote protein synthesis and turnover, signaling pathways, and metabolism of glucose. Oxidation of BCAAs may increase fatty acid oxidation and play a role in obesity. Physiologically, BCAAs take on roles in the immune system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeletal Formula
The skeletal formula, or line-angle formula or shorthand formula, of an organic compound is a type of molecular structural formula that serves as a shorthand representation of a molecule's bonding and some details of its molecular geometry. A skeletal formula shows the skeletal structure or skeleton of a molecule, which is composed of the skeletal atoms that make up the molecule. It is represented in two dimensions, as on a piece of paper. It employs certain conventions to represent carbon and hydrogen atoms, which are the most common in organic chemistry. An early form of this representation was first developed by organic chemist August Kekulé, while the modern form is closely related to and influenced by the Lewis structure of molecules and their valence electrons. Hence they are sometimes termed Kekulé structures or Lewis–Kekulé structures. Skeletal formulae have become ubiquitous in organic chemistry, partly because they are relatively quick and simple to draw, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dihydroxyacid Dehydratase
The enzyme dihydroxy-acid dehydratase () catalyzes the chemical reaction :2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate \rightleftharpoons 3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate + H2O This enzyme participates in valine, leucine and isoleucine biosynthesis and pantothenate and coenzyme A (CoA) biosynthesis. Nomenclature This enzyme belongs to the family of lyases, specifically the hydro-lyases, which cleave carbon-oxygen bonds. The systematic name A systematic name is a name given in a systematic way to one unique group, organism, object or chemical substance, out of a specific population or collection. Systematic names are usually part of a nomenclature. A semisystematic name or semitrivial ... of this enzyme class is 2,3-dihydroxy-3-methylbutanoate hydro-lyase (3-methyl-2-oxobutanoate-forming). Other names in common use include * acetohydroxyacid dehydratase, * α,β-dihydroxyacid dehydratase, * 2,3-dihydroxyisovalerate dehydratase, * α,β-dihydroxyisovalerate dehydratase, * dihydroxy acid dehydrase, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
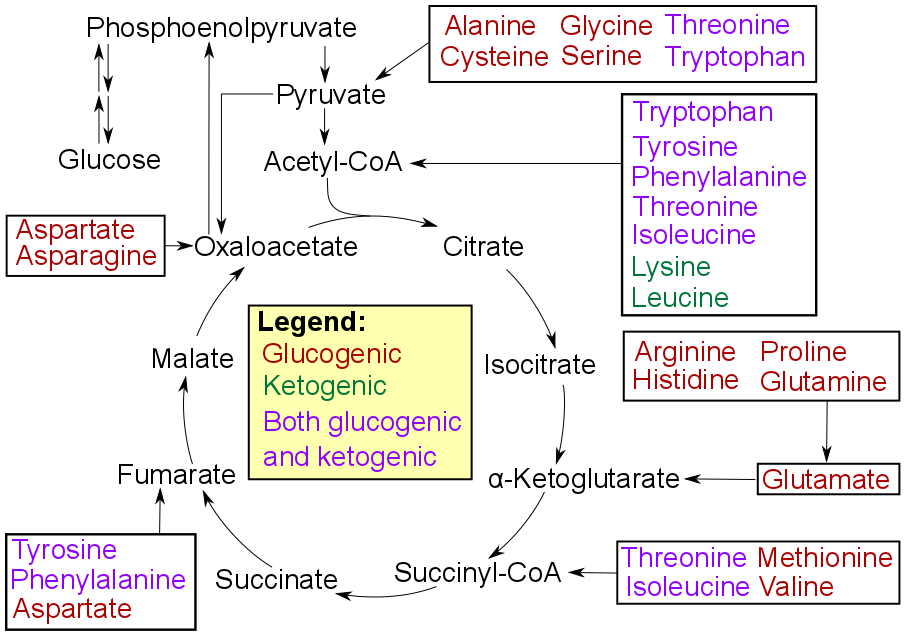
Glucogenic
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. It is one of two primary mechanisms – the other being degradation of glycogen ( glycogenolysis) – used by humans and many other animals to maintain blood sugar levels, avoiding low levels (hypoglycemia). In ruminants, because dietary carbohydrates tend to be metabolized by rumen organisms, gluconeogenesis occurs regardless of fasting, low-carbohydrate diets, exercise, etc. In many other animals, the process occurs during periods of fasting, starvation, low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise. In humans, substrates for gluconeogenesis may come from any non-carbohydrate sources that can be converted to pyruvate or intermediates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketogenic
Ketogenesis is the biochemical process through which organisms produce ketone bodies by breaking down fatty acids and ketogenic amino acids. The process supplies energy to certain organs, particularly the brain, heart and skeletal muscle, under specific scenarios including fasting, caloric restriction, sleep, or others. (In rare metabolic diseases, insufficient gluconeogenesis can cause excessive ketogenesis and hypoglycemia, which may lead to the life-threatening condition known as non-diabetic ketoacidosis.) Ketone bodies are not obligately produced from fatty acids; rather a meaningful amount of them is synthesized only in a situation of carbohydrate and protein insufficiency, where only fatty acids are readily available as fuel for their production. Production Ketone bodies are produced mainly in the mitochondria of liver cells, and synthesis can occur in response to an unavailability of blood glucose, such as during fasting. Other cells, e.g. human astrocytes, are capable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propionyl-CoA
Propionyl-CoA is a coenzyme A derivative of propionic acid. It is composed of a 24 total carbon chain (without the coenzyme, it is a 3 carbon structure) and its production and metabolic fate depend on which organism it is present in. Several different pathways can lead to its production, such as through the catabolism of specific amino acids or the oxidation of odd-chain fatty acids. It later can be broken down by propionyl-CoA carboxylase or through the methylcitrate cycle. In different organisms, however, propionyl-CoA can be sequestered into controlled regions, to alleviate its potential toxicity through accumulation. Genetic deficiencies regarding the production and breakdown of propionyl-CoA also have great clinical and human significance. Production There are several different pathways through which propionyl-CoA can be produced: * Propionyl-CoA, a three-carbon structure, is considered to be a minor species of propionic acid. Therefore, odd-number chains of fatty acids are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |