Polish PeopleŌĆÖs Republic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Polish People's Republic ( pl, Polska
 In the summer of 1944 the
In the summer of 1944 the  The official results of the election showed the Democratic Bloc with 80.1 percent of the vote. The Democratic Bloc was awarded 394 seats to only 28 for the PSL. Mikołajczyk immediately resigned to protest this so-called 'implausible result' and fled to the United Kingdom in April rather than face arrest. Later, some historians announced that the official results were only obtained through massive fraud. Government officials didn't even count the real votes in many areas and simply filled in the relevant documents in accordance with instructions from the communists. In other areas, the ballot boxes were either destroyed or replaced with boxes containing prefilled ballots.
The 1947 election marked the beginning of undisguised communist rule in Poland, though it was not officially transformed into the Polish People's Republic until the adoption of the 1952 Constitution. However, Gomułka never supported Stalin's control over the Polish communists and was soon replaced as party leader by the more pliable Bierut. In 1948, the communists consolidated their power, merging with Cyrankiewicz' faction of the PPS to form the Polish United Workers' Party (known in Poland as 'the Party'), which would monopolise political power in Poland until 1989. In 1949, Polish-born Soviet Marshal Konstantin Rokossovsky became the Minister of National Defence, with the additional title Marshal of Poland, and in 1952 he became Deputy Chairman of the Council of Ministers (deputy premier).
Over the coming years, private industry was
The official results of the election showed the Democratic Bloc with 80.1 percent of the vote. The Democratic Bloc was awarded 394 seats to only 28 for the PSL. Mikołajczyk immediately resigned to protest this so-called 'implausible result' and fled to the United Kingdom in April rather than face arrest. Later, some historians announced that the official results were only obtained through massive fraud. Government officials didn't even count the real votes in many areas and simply filled in the relevant documents in accordance with instructions from the communists. In other areas, the ballot boxes were either destroyed or replaced with boxes containing prefilled ballots.
The 1947 election marked the beginning of undisguised communist rule in Poland, though it was not officially transformed into the Polish People's Republic until the adoption of the 1952 Constitution. However, Gomułka never supported Stalin's control over the Polish communists and was soon replaced as party leader by the more pliable Bierut. In 1948, the communists consolidated their power, merging with Cyrankiewicz' faction of the PPS to form the Polish United Workers' Party (known in Poland as 'the Party'), which would monopolise political power in Poland until 1989. In 1949, Polish-born Soviet Marshal Konstantin Rokossovsky became the Minister of National Defence, with the additional title Marshal of Poland, and in 1952 he became Deputy Chairman of the Council of Ministers (deputy premier).
Over the coming years, private industry was
Stefan Wyszy┼äski, (1901ŌĆō1981).
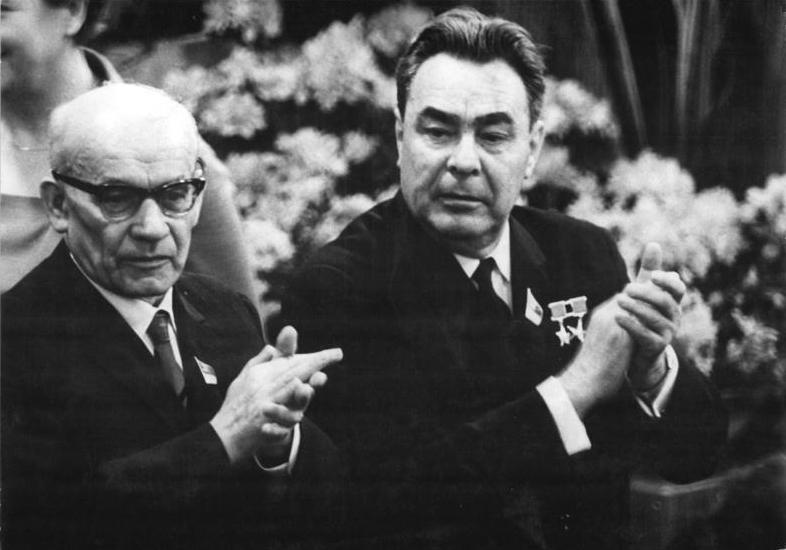
 In 1970, Gomułka's government had decided to adopt massive increases in the prices of basic goods, including food. The resulting widespread violent protests in December that same year resulted in a number of deaths. They also forced another major change in the government, as Gomułka was replaced by Edward Gierek as the new First Secretary. Gierek's plan for recovery was centered on massive borrowing, mainly from the United States and
In 1970, Gomułka's government had decided to adopt massive increases in the prices of basic goods, including food. The resulting widespread violent protests in December that same year resulted in a number of deaths. They also forced another major change in the government, as Gomułka was replaced by Edward Gierek as the new First Secretary. Gierek's plan for recovery was centered on massive borrowing, mainly from the United States and  On 16 October 1978, the Archbishop of Kraków,
On 16 October 1978, the Archbishop of Krak├│w,  On 13 December 1981, Jaruzelski proclaimed martial law, suspended Solidarity, and temporarily imprisoned most of its leaders. This sudden crackdown on Solidarity was reportedly out of fear of Soviet intervention (see
On 13 December 1981, Jaruzelski proclaimed martial law, suspended Solidarity, and temporarily imprisoned most of its leaders. This sudden crackdown on Solidarity was reportedly out of fear of Soviet intervention (see
 The government and politics of the Polish People's Republic were governed by the Polish United Workers' Party (''Polska Zjednoczona Partia Robotnicza, PZPR''). Despite the presence of two minor parties, the United People's Party and the
The government and politics of the Polish People's Republic were governed by the Polish United Workers' Party (''Polska Zjednoczona Partia Robotnicza, PZPR''). Despite the presence of two minor parties, the United People's Party and the
 During its existence, the Polish People's Republic maintained relations not only with the
During its existence, the Polish People's Republic maintained relations not only with the
 Poland suffered tremendous economic losses during World War II. In 1939, Poland had 35.1 million inhabitants, but the census of 14 February 1946 showed only 23.9 million inhabitants. The difference was partially the result of the border revision. Losses in national resources and infrastructure amounted to approximately 38%. The implementation of the immense tasks involved with the reconstruction of the country was intertwined with the struggle of the new government for the stabilisation of power, made even more difficult by the fact that a considerable part of society was mistrustful of the communist government. The occupation of Poland by the Red Army and the support the Soviet Union had shown for the Polish communists was decisive in the communists gaining the upper hand in the new Polish government.
As control of the Polish territories passed from occupying forces of
Poland suffered tremendous economic losses during World War II. In 1939, Poland had 35.1 million inhabitants, but the census of 14 February 1946 showed only 23.9 million inhabitants. The difference was partially the result of the border revision. Losses in national resources and infrastructure amounted to approximately 38%. The implementation of the immense tasks involved with the reconstruction of the country was intertwined with the struggle of the new government for the stabilisation of power, made even more difficult by the fact that a considerable part of society was mistrustful of the communist government. The occupation of Poland by the Red Army and the support the Soviet Union had shown for the Polish communists was decisive in the communists gaining the upper hand in the new Polish government.
As control of the Polish territories passed from occupying forces of
Reforma Rolna
Encyklopedia.PWN.pl (Internet Archive)
Nacjonalizacja w Polsce
Encyklopedia.PWN.pl (Internet Archive) The Allied punishment of Germany for the war of destruction was intended to include large-scale reparations to Poland. However, those were truncated into insignificance by the break-up of Germany into East and West and the onset of the Cold War. Poland was then relegated to receive her share from the Soviet-controlled
 During the Gierek era, Poland borrowed large sums from Western creditors in exchange for promise of social and economic reforms. None of these have been delivered due to resistance from the hardline communist leadership as any true reforms would require effectively abandoning the Marxian economy with central planning, state-owned enterprises and state-controlled prices and trade. After the West refused to grant Poland further loans, the living standards began to sharply fall again as the supply of imported goods dried up, and as Poland was forced to export everything it could, particularly food and coal, to service its massive debt, which would reach US$23 billion by 1980.
In 1981, Poland notified
During the Gierek era, Poland borrowed large sums from Western creditors in exchange for promise of social and economic reforms. None of these have been delivered due to resistance from the hardline communist leadership as any true reforms would require effectively abandoning the Marxian economy with central planning, state-owned enterprises and state-controlled prices and trade. After the West refused to grant Poland further loans, the living standards began to sharply fall again as the supply of imported goods dried up, and as Poland was forced to export everything it could, particularly food and coal, to service its massive debt, which would reach US$23 billion by 1980.
In 1981, Poland notified  In response to this situation, the government, which controlled all official foreign trade, continued to maintain a highly artificial
In response to this situation, the government, which controlled all official foreign trade, continued to maintain a highly artificial  In this desperate situation, all development and growth in the Polish economy slowed to a crawl. Most visibly, work on most of the major investment projects that had begun in the 1970s was stopped. As a result, most Polish cities acquired at least one infamous example of a large unfinished building languishing in a state of limbo. While some of these were eventually finished decades later, most, such as the Szkieletor
In this desperate situation, all development and growth in the Polish economy slowed to a crawl. Most visibly, work on most of the major investment projects that had begun in the 1970s was stopped. As a result, most Polish cities acquired at least one infamous example of a large unfinished building languishing in a state of limbo. While some of these were eventually finished decades later, most, such as the Szkieletor  After several years of the situation continuing to worsen, during which time the socialist government unsuccessfully tried various expedients to improve the performance of the economyŌĆöat one point resorting to placing military
After several years of the situation continuing to worsen, during which time the socialist government unsuccessfully tried various expedients to improve the performance of the economyŌĆöat one point resorting to placing military
 Being produced in a then-socialist country, the shows did contain a socialist agenda, but with a more informal and comical tone; they concentrated on everyday life which was appealing to ordinary people. These include '' Czterdziestolatek'' (1975ŌĆō1978), '' Alternatywy 4'' (1986ŌĆō1987) and '' Zmiennicy'' (1987ŌĆō1988). The wide range of topics covered featured petty disputes in the block of flats, work issues, human behaviour and interaction as well as comedy, sarcasm, drama and
Being produced in a then-socialist country, the shows did contain a socialist agenda, but with a more informal and comical tone; they concentrated on everyday life which was appealing to ordinary people. These include '' Czterdziestolatek'' (1975ŌĆō1978), '' Alternatywy 4'' (1986ŌĆō1987) and '' Zmiennicy'' (1987ŌĆō1988). The wide range of topics covered featured petty disputes in the block of flats, work issues, human behaviour and interaction as well as comedy, sarcasm, drama and
 The change in political climate in the 1950s gave rise to the
The change in political climate in the 1950s gave rise to the  ;Movies
*''
;Movies
*''
 The architecture in Poland under the Polish People's Republic had three major phases ŌĆō short-lived
The architecture in Poland under the Polish People's Republic had three major phases ŌĆō short-lived  Following the Polish October in 1956, the concept of socialist realism was condemned. It was then that modernist architecture was promoted globally, with simplistic designs made of glass, steel and concrete. Due to previous extravagances, the idea of functionalism (serving for a purpose) was encouraged by W┼éadys┼éaw Gomu┼éka.
Following the Polish October in 1956, the concept of socialist realism was condemned. It was then that modernist architecture was promoted globally, with simplistic designs made of glass, steel and concrete. Due to previous extravagances, the idea of functionalism (serving for a purpose) was encouraged by Władysław Gomułka.
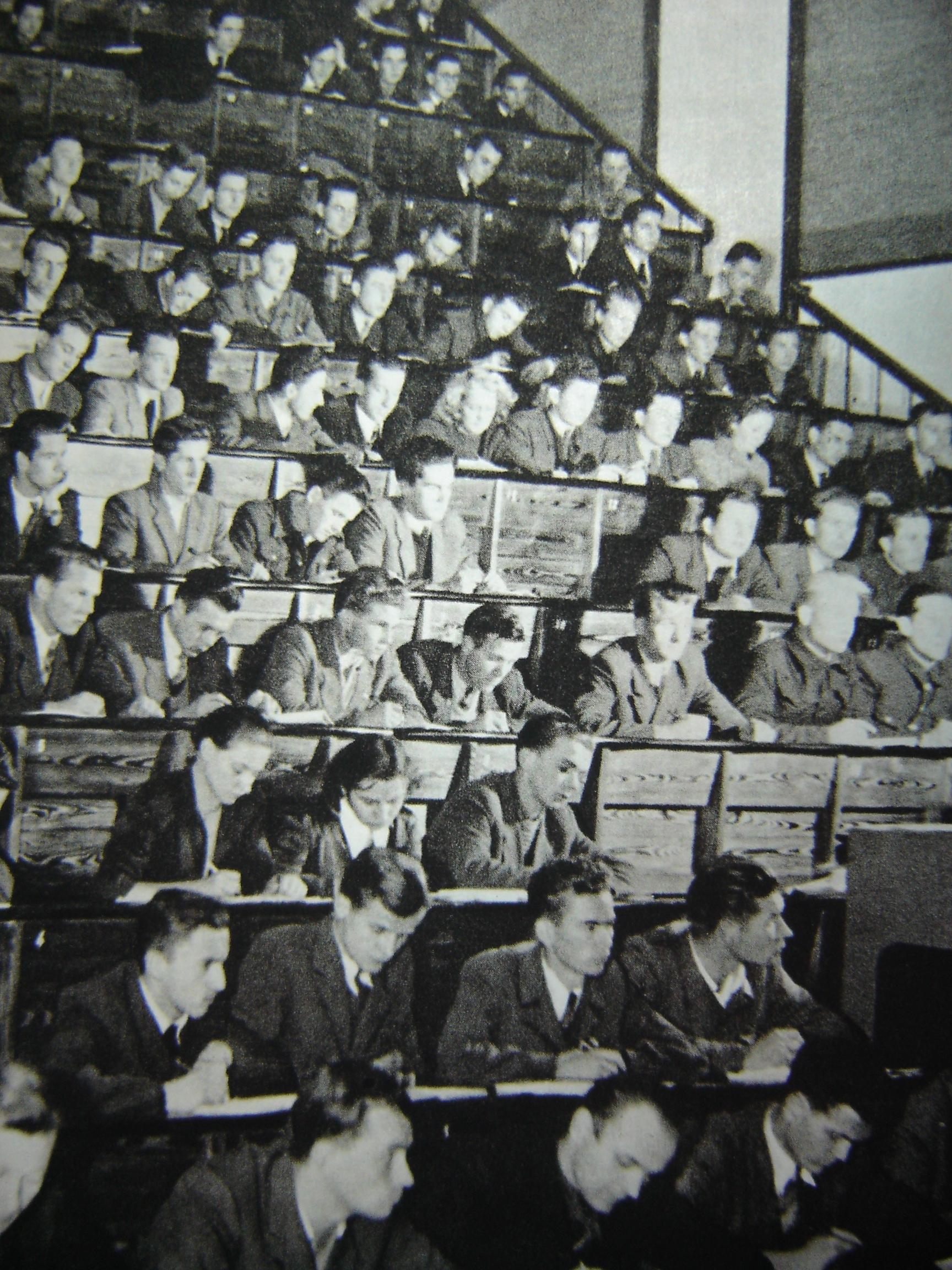 Communist authorities placed an emphasis on education since they considered it vital to create a new
Communist authorities placed an emphasis on education since they considered it vital to create a new
 The experiences in and after
The experiences in and after
 Before
Before  The population of Jews in Poland, which formed the largest Jewish community in pre-war Europe at about 3.3 million people, was all but destroyed by 1945. Approximately 3 million Jews died of starvation in
The population of Jews in Poland, which formed the largest Jewish community in pre-war Europe at about 3.3 million people, was all but destroyed by 1945. Approximately 3 million Jews died of starvation in
, YIVO Institute for Jewish Research, ''The YIVO Encyclopedia of Jews in Eastern Europe'', Yale University Press, 2005 According to the national census, which took place on 14 February 1946, population of Poland was 23.9 million, out of which 32% lived in cities and towns, and 68% lived in the countryside. The 1950 census (3 December 1950) showed the population rise to 25 million, and the 1960 census (6 December 1960) placed the population of Poland at 29.7 million. tatistical Yearbook of Poland, Warsaw, 1965/ref> In 1950, Warsaw was again the biggest city, with the population of 804,000 inhabitants. Second was Łódź (pop. 620,000), then Kraków (pop. 344,000), Poznań (pop. 321,000), and Wrocław (pop. 309,000). Females were in the majority in the country. In 1931, there were 105.6 women for 100 men. In 1946, the difference grew to 118.5/100, but in subsequent years, number of males grew, and in 1960, the ratio was 106.7/100. Most Germans were expelled from Poland and the annexed east German territories at the end of the war, while many
 The Polish People's Army (LWP) was initially formed during
The Polish People's Army (LWP) was initially formed during
 Geographically, the Polish People's Republic bordered the
Geographically, the Polish People's Republic bordered the
PRL
at Czas-PRL.pl
Internetowe Muzeum Polski Ludowej
at PolskaLudowa.com
Muzeum PRL
at MuzeumPRL.com
at Komunizm.eu
Propaganda komunistyczna
PRL Tube, a categorized collection of videos from the Polish Communist period
{{DEFAULTSORT:Poland, People's Republic Of Polish People's Republic, Eastern Bloc Former socialist republics Communist states Communism in Poland Soviet satellite states 1947 establishments in Poland 1989 disestablishments in Poland States and territories established in 1947 States and territories disestablished in 1989
Rzeczpospolita
() is the official name of Poland and a traditional name for some of its predecessor states. It is a compound of "thing, matter" and "common", a calque of Latin ''r├®s p├║blica'' ( "thing" + "public, common"), i.e. ''republic'', in Engli ...
Ludowa, PRL) was a country in Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618ŌĆō1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area' ...
that existed from 1947 to 1989 as the predecessor of the modern Republic of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
. With a population of approximately 37.9 million near the end of its existence, it was the second-most populous communist
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a s ...
and Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
country in Europe. It was also one of the main signatories of the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republic ...
alliance. The largest city and official capital since 1947 was Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
, followed by the industrial city of Łódź
Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of canti ...
and cultural city of Krak├│w
Krak├│w (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Krak├│w was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
. The country was bordered by the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53┬░N to 66┬░N latitude and from ...
to the north, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
to the east, Czechoslovakia
, rue, ą¦ąĄčüčīą║ąŠčüą╗ąŠą▓ąĄąĮčīčüą║ąŠ, , yi, ūśū®ūóūøūÉūĪū£ūÉūĢūĢūÉū¦ūÖūÖ,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918ŌĆō19391945ŌĆō1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
to the south, and East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
to the west.
The Polish People's Republic was a socialist
Socialism is a left-wing economic philosophy and movement encompassing a range of economic systems characterized by the dominance of social ownership of the means of production as opposed to private ownership. As a term, it describes the e ...
one-party state
A one-party state, single-party state, one-party system, or single-party system is a type of sovereign state in which only one political party has the right to form the government, usually based on the existing constitution. All other parties ...
, with a unitary
Unitary may refer to:
Mathematics
* Unitary divisor
* Unitary element
* Unitary group
* Unitary matrix
* Unitary morphism
* Unitary operator
* Unitary transformation
* Unitary representation
* Unitarity (physics)
* ''E''-unitary inverse semigroup ...
MarxistŌĆōLeninist
Marxism is a left-wing to far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand class relations and social conflict and a dialect ...
government headed by the Polish United Workers' Party (PZPR). The country's official name was the "Republic of Poland" (') between 1947 and 1952 in accordance with the transitional Small Constitution of 1947
The Small Constitution of 1947 ( pl, Mała Konstytucja z 1947) was a temporary constitution issued by the communist-dominated Sejm (Polish parliament) on 19 February 1947. It confirmed the practice of separation of powers and strengthened the Sejm ...
. The name "People's Republic" was introduced and defined by the Constitution of 1952. Like other Eastern Bloc countries (East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
, Czechoslovakia
, rue, ą¦ąĄčüčīą║ąŠčüą╗ąŠą▓ąĄąĮčīčüą║ąŠ, , yi, ūśū®ūóūøūÉūĪū£ūÉūĢūĢūÉū¦ūÖūÖ,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918ŌĆō19391945ŌĆō1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarorsz├Īg ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia a ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, ąæčŖą╗ą│ą░čĆąĖčÅ, BŪÄlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
and Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
), Poland was regarded as a satellite state in the Soviet sphere of interest, but it was never a constituent republic of the Soviet Union.Rao, B. V. (2006), ''History of Modern Europe Ad 1789ŌĆō2002: A.D. 1789ŌĆō2002'', Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd.
Despite this, some major achievements were established during the period of the Polish People's Republic, such as improved living conditions, rapid industrialization, urbanization
Urbanization (or urbanisation) refers to the population shift from rural to urban areas, the corresponding decrease in the proportion of people living in rural areas, and the ways in which societies adapt to this change. It is predominantly t ...
, access to universal health care
Universal health care (also called universal health coverage, universal coverage, or universal care) is a health care system in which all residents of a particular country or region are assured access to health care. It is generally organized ar ...
, and free education. The Polish People's Republic also implemented policies that eliminated homelessness
Homelessness or houselessness ŌĆō also known as a state of being unhoused or unsheltered ŌĆō is the condition of lacking stable, safe, and adequate housing. People can be categorized as homeless if they are:
* living on the streets, also kn ...
and established a job guarantee
A job guarantee is an economic policy proposal that aims to provide a sustainable solution to inflation and unemployment. Its aim is to create full employment and price stability by having the state promise to hire unemployed workers as an emplo ...
. As a result Poland's population almost doubled between 1947 and 1989.
The Polish People's Republic maintained a large standing army
A standing army is a permanent, often professional, army. It is composed of full-time soldiers who may be either career soldiers or conscripts. It differs from army reserves, who are enrolled for the long term, but activated only during wars or n ...
. It also hosted Soviet troops in its territory.Rao, B. V. (2006), ''History of Modern Europe Ad 1789ŌĆō2002: A.D. 1789ŌĆō2002'', Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd. Its chief intelligence agencies was the UB, which was succeeded by the SB. The official police organization, Citizens' Militia (MO), was also responsible for peacekeeping.
History
1945ŌĆō1956
 In the summer of 1944 the
In the summer of 1944 the Polish Committee of National Liberation
The Polish Committee of National Liberation (Polish: ''Polski Komitet Wyzwolenia Narodowego'', ''PKWN''), also known as the Lublin Committee, was an executive governing authority established by the Soviet-backed communists in Poland at the lat ...
was established by Soviet-backed Polish communists to control territory retaken from Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
. On 1 January 1945 the committee was replaced by the Provisional Government of the Republic of Poland
The Provisional Government of the Republic of Poland ( pl, Rz─ģd Tymczasowy Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej, RTRP) was created by the State National Council () on the night of 31 December 1944. Davies, Norman, 1982 and several reprints. ''God's Playgr ...
, all the key posts of which were held by members of the communist Polish Workers' Party.
At the Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference (codenamed Argonaut), also known as the Crimea Conference, held 4ŌĆō11 February 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union to discuss the post ...
in February 1945, Stalin was able to present his western allies, Franklin Roosevelt
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (; ; January 30, 1882April 12, 1945), often referred to by his initials FDR, was an American politician and attorney who served as the 32nd president of the United States from 1933 until his death in 1945. As the ...
and Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
, with a ''fait accompli
Many words in the English vocabulary are of French origin, most coming from the Anglo-Norman spoken by the upper classes in England for several hundred years after the Norman Conquest, before the language settled into what became Modern Engli ...
'' in Poland. His armed forces were in occupation of the country, and the communists were in control of its administration. The Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
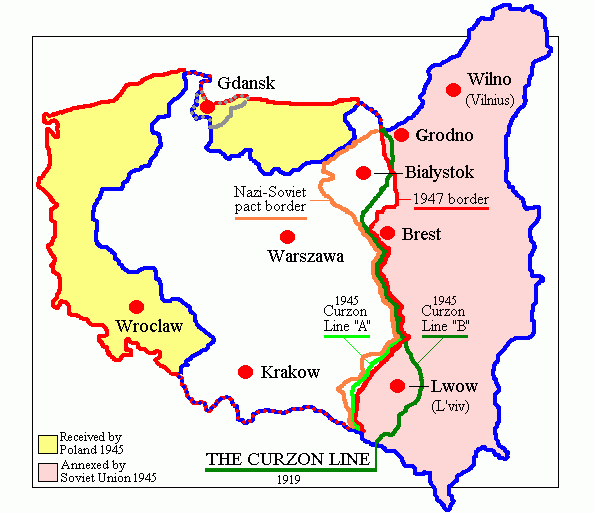
was in the process of reincorporating the lands to the east of the Curzon Line
The Curzon Line was a proposed demarcation line between the Second Polish Republic and the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Soviet Union, two new states emerging after World War I. It was first proposed by George Curzon, 1st Marque ...
, which it had invaded and occupied between 1939 and 1941.
In compensation, Poland was granted German-populated territories in Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''P├▓m├▓rsk├┤''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
, Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split ...
, and Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a states of Germany, state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an ar ...
east of the OderŌĆōNeisse line, including the southern half of East Prussia
East Prussia ; german: Ostprei├¤en, label=Low Prussian; pl, Prusy Wschodnie; lt, Ryt┼│ Pr┼½sija was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and again from 1878 (with the Kingdom itself being part of the German Empire from 187 ...
. These were confirmed, pending a final peace conference with Germany, at the Tripartite Conference of Berlin, otherwise known as the Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference (german: Potsdamer Konferenz) was held at Potsdam in the Soviet occupation zone from July 17 to August 2, 1945, to allow the three leading Allies to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistakes of the Paris Pe ...
in August 1945 after the end of the war in Europe. The Potsdam Agreement
The Potsdam Agreement (german: Potsdamer Abkommen) was the agreement between three of the Allies of World War II: the United Kingdom, the United States, and the Soviet Union on 1 August 1945. A product of the Potsdam Conference, it concerned th ...
also sanctioned the transfer of German population out of the acquired territories. Stalin was determined that Poland's new communist government would become his tool towards making Poland a satellite state like other countries in Central and Eastern Europe. He had severed relations with the Polish government-in-exile
The Polish government-in-exile, officially known as the Government of the Republic of Poland in exile ( pl, Rz─ģd Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej na uchod┼║stwie), was the government in exile of Poland formed in the aftermath of the Invasion of Pola ...
in London in 1943, but to appease Roosevelt and Churchill he agreed at Yalta that a coalition government would be formed. The Provisional Government of National Unity was established in June 1946 with the communists holding a majority of key posts, and with Soviet support they soon gained almost total control of the country.
In June 1946, the "Three Times Yes
The people's referendum ( pl, referendum ludowe) of 1946, also known as the Three Times Yes referendum (''Trzy razy tak'', often abbreviated as 3├ŚTAK), was a referendum held in Poland on 30 June 1946 on the authority of the State National Council ...
" referendum was held on a number of issuesŌĆöabolition of the Senate of Poland
The Senate ( pl, Senat) is the upper house of the Parliament of Poland, Polish parliament, the lower house being the Sejm of the Republic of Poland, Sejm. The history of the Polish Senate stretches back over 500 years; it was one of the first co ...
, land reform, and making the OderŌĆōNeisse line Poland's western border. The communist-controlled Interior Ministry issued results showing that all three questions passed overwhelmingly. Years later, however, evidence was uncovered showing that the referendum had been tainted by large-scale fraud, and only the third question actually passed. W┼éadys┼éaw Gomu┼éka then took advantage of a split in the Polish Socialist Party. One faction, which included Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
Edward Osóbka-Morawski, wanted to join forces with the Peasant Party and form a united front against the communists. Another faction, led by Józef Cyrankiewicz, argued that the socialists should support the communists in carrying through a socialist program while opposing the imposition of one-party rule. Pre-war political hostilities continued to influence events, and Stanisław Mikołajczyk would not agree to form a united front with the socialists. The communists played on these divisions by dismissing Osóbka-Morawski and making Cyrankiewicz Prime Minister.
Between the referendum and the January 1947 general elections, the opposition was subjected to persecution. Only the candidates of the pro-government "Democratic Bloc" (the PPR, Cyrankiewicz' faction of the PPS, and the Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
) were allowed to campaign completely unmolested. Meanwhile, several opposition candidates were prevented from campaigning at all. Mikołajczyk's Polish People's Party (PSL) in particular suffered persecution; it had opposed the abolition of the Senate as a test of strength against the government. Although it supported the other two questions, the Communist-dominated government branded the PSL "traitors". This massive oppression was overseen by Gomułka and the provisional president, Bolesław Bierut.
 The official results of the election showed the Democratic Bloc with 80.1 percent of the vote. The Democratic Bloc was awarded 394 seats to only 28 for the PSL. Mikołajczyk immediately resigned to protest this so-called 'implausible result' and fled to the United Kingdom in April rather than face arrest. Later, some historians announced that the official results were only obtained through massive fraud. Government officials didn't even count the real votes in many areas and simply filled in the relevant documents in accordance with instructions from the communists. In other areas, the ballot boxes were either destroyed or replaced with boxes containing prefilled ballots.
The 1947 election marked the beginning of undisguised communist rule in Poland, though it was not officially transformed into the Polish People's Republic until the adoption of the 1952 Constitution. However, Gomułka never supported Stalin's control over the Polish communists and was soon replaced as party leader by the more pliable Bierut. In 1948, the communists consolidated their power, merging with Cyrankiewicz' faction of the PPS to form the Polish United Workers' Party (known in Poland as 'the Party'), which would monopolise political power in Poland until 1989. In 1949, Polish-born Soviet Marshal Konstantin Rokossovsky became the Minister of National Defence, with the additional title Marshal of Poland, and in 1952 he became Deputy Chairman of the Council of Ministers (deputy premier).
Over the coming years, private industry was
The official results of the election showed the Democratic Bloc with 80.1 percent of the vote. The Democratic Bloc was awarded 394 seats to only 28 for the PSL. Mikołajczyk immediately resigned to protest this so-called 'implausible result' and fled to the United Kingdom in April rather than face arrest. Later, some historians announced that the official results were only obtained through massive fraud. Government officials didn't even count the real votes in many areas and simply filled in the relevant documents in accordance with instructions from the communists. In other areas, the ballot boxes were either destroyed or replaced with boxes containing prefilled ballots.
The 1947 election marked the beginning of undisguised communist rule in Poland, though it was not officially transformed into the Polish People's Republic until the adoption of the 1952 Constitution. However, Gomułka never supported Stalin's control over the Polish communists and was soon replaced as party leader by the more pliable Bierut. In 1948, the communists consolidated their power, merging with Cyrankiewicz' faction of the PPS to form the Polish United Workers' Party (known in Poland as 'the Party'), which would monopolise political power in Poland until 1989. In 1949, Polish-born Soviet Marshal Konstantin Rokossovsky became the Minister of National Defence, with the additional title Marshal of Poland, and in 1952 he became Deputy Chairman of the Council of Ministers (deputy premier).
Over the coming years, private industry was nationalised
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to pri ...
, the land seized from the pre-war landowners and redistributed to the lower-class farmers, and millions of Poles were transferred from the lost eastern territories to the lands acquired from Germany. Poland was now to be brought into line with the Soviet model of a "people's democracy" and a centrally planned socialist economy. The government also embarked on the collectivisation of agriculture, although the pace was slower than in other satellites: Poland remained the only Eastern Bloc country where individual farmers dominated agriculture.
Through a careful balance of agreement, compromise and resistance ŌĆö and having signed an agreement of coexistence with the communist regime ŌĆö cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**''Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, the ...
primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including huma ...
Stefan Wyszyński maintained and even strengthened the Polish church through a series of failed government leaders. He was put under house arrest
In justice and law, house arrest (also called home confinement, home detention, or, in modern times, electronic monitoring) is a measure by which a person is confined by the authorities to their residence. Travel is usually restricted, if all ...
from 1953 to 1956 for failing to punish priests who participated in anti-government activity.Britannica (10 April 2013)Stefan Wyszy┼äski, (1901ŌĆō1981).
Encyclop├”dia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclop├”dia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclop├”dia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various time ...
.
Bierut died in March 1956, and was replaced with Edward Ochab
Edward Ochab (; 16 August 1906 ŌĆō 1 May 1989) was a Polish Communism, communist politician and top leader of Poland between March and October 1956.
As a member of the Communist Party of Poland from 1929, he was repeatedly imprisoned for his ac ...
, who held the position for seven months. In June, workers in the industrial city of Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John ...
went on strike, in what became known as 1956 Poznań protests
The 1956 Poznań protests, also known as Poznań June ( pl, Poznański Czerwiec), were the first of several massive protests against the communist government of the Polish People's Republic. Demonstrations by workers demanding better working con ...
. Voices began to be raised in the Party and among the intellectuals calling for wider reforms of the Stalinist system. Eventually, power shifted towards Gomułka, who replaced Ochab as party leader. Hardline Stalinists were removed from power and many Soviet officers serving in the Polish Army were dismissed. This marked the end of the Stalinist era.
1970s and 1980s
 In 1970, Gomułka's government had decided to adopt massive increases in the prices of basic goods, including food. The resulting widespread violent protests in December that same year resulted in a number of deaths. They also forced another major change in the government, as Gomułka was replaced by Edward Gierek as the new First Secretary. Gierek's plan for recovery was centered on massive borrowing, mainly from the United States and
In 1970, Gomułka's government had decided to adopt massive increases in the prices of basic goods, including food. The resulting widespread violent protests in December that same year resulted in a number of deaths. They also forced another major change in the government, as Gomułka was replaced by Edward Gierek as the new First Secretary. Gierek's plan for recovery was centered on massive borrowing, mainly from the United States and West Germany
West Germany is the colloquial term used to indicate the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG; german: Bundesrepublik Deutschland , BRD) between its formation on 23 May 1949 and the German reunification through the accession of East Germany on 3 O ...
, to re-equip and modernize Polish industry, and to import consumer goods to give the workers some incentive to work. While it boosted the Polish economy, and is still remembered as the "Golden Age" of socialist Poland, it left the country vulnerable to global economic fluctuations and western undermining, and the repercussions in the form of massive debt is still felt in Poland even today. This Golden Age came to an end after the 1973 energy crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supp ...
. The failure of the Gierek government, both economically and politically, soon led to the creation of opposition in the form of trade union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ( ...
s, student groups, clandestine newspapers and publishers, imported books and newspapers, and even a "flying university."
 On 16 October 1978, the Archbishop of Krak├│w,
On 16 October 1978, the Archbishop of Krak├│w, Cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**''Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, the ...
Karol Wojtyła, was elected Pope, taking the name John Paul II
Pope John Paul II ( la, Ioannes Paulus II; it, Giovanni Paolo II; pl, Jan Paweł II; born Karol Józef Wojtyła ; 18 May 19202 April 2005) was the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 1978 until his ...
. The election of a Polish Pope had an electrifying effect on what had been, even under communist rule, one of the most devoutly Catholic nations in Europe. Gierek is alleged to have said to his cabinet, "O God, what are we going to do now?" or, as occasionally reported, "Jesus and Mary, this is the end". When John Paul II made his first papal tour of Poland in June 1979, half a million people heard him speak in Warsaw; he did not call for rebellion, but instead encouraged the creation of an "alternative Poland" of social institutions independent of the government, so that when the next economic crisis came, the nation would present a united front.
A new wave of labour strikes undermined Gierek's government, and in September Gierek, who was in poor health, was finally removed from office and replaced as Party leader by Stanisław Kania
Stanis┼éaw Kania (; 8 March 1927 ŌĆō 3 March 2020) was a Polish communist politician.
Life and career
Kania joined the Polish Workers' Party in April 1945 when the Germans were driven out by the Red Army and Polish Communists began to take contr ...
. However, Kania was unable to find an answer for the fast-eroding support of communism in Poland. Labour turmoil led to the formation of the independent trade union
A trade union (labor union in American English), often simply referred to as a union, is an organization of workers intent on "maintaining or improving the conditions of their employment", ch. I such as attaining better wages and benefits ( ...
Solidarity
''Solidarity'' is an awareness of shared interests, objectives, standards, and sympathies creating a psychological sense of unity of groups or classes. It is based on class collaboration.''Merriam Webster'', http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictio ...
(''Solidarno┼ø─ć'') in September 1980, originally led by Lech Wa┼é─Ösa. In fact, Solidarity became a broad anti-communist
Anti-communism is Political movement, political and Ideology, ideological opposition to communism. Organized anti-communism developed after the 1917 October Revolution in the Russian Empire, and it reached global dimensions during the Cold War, w ...
social movement ranging from people associated with the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, to members of the anti-Stalinist left. By the end of 1981, Solidarity had nine million membersŌĆöa quarter of Poland's population and three times as many as the PUWP had. Kania resigned under Soviet pressure in October and was succeeded by Wojciech Jaruzelski, who had been Defence minister since 1968 and Premier since February.
 On 13 December 1981, Jaruzelski proclaimed martial law, suspended Solidarity, and temporarily imprisoned most of its leaders. This sudden crackdown on Solidarity was reportedly out of fear of Soviet intervention (see
On 13 December 1981, Jaruzelski proclaimed martial law, suspended Solidarity, and temporarily imprisoned most of its leaders. This sudden crackdown on Solidarity was reportedly out of fear of Soviet intervention (see Soviet reaction to the Polish crisis of 1980ŌĆō1981
The Polish crisis of 1980ŌĆō1981, associated with the emergence of the Solidarity mass movement in the Polish People's Republic, challenged the rule of the Polish United Workers' Party and Poland's alignment with the Soviet Union.
For the first t ...
). The government then disallowed Solidarity on 8 October 1982. Martial law was formally lifted in July 1983, though many heightened controls on civil liberties and political life, as well as food rationing, remained in place through the mid-to-late-1980s. Jaruzelski stepped down as prime minister in 1985 and became president (chairman of the Council of State).
This did not prevent Solidarity from gaining more support and power. Eventually it eroded the dominance of the PUWP, which in 1981 lost approximately 85,000 of its 3 million members. Throughout the mid-1980s, Solidarity persisted solely as an underground organization, but by the late 1980s was sufficiently strong to frustrate Jaruzelski's attempts at reform, and nationwide strikes in 1988 were one of the factors that forced the government to open a dialogue with Solidarity.
From 6 February to 15 April 1989, talks of 13 working group
A working group, or working party, is a group of experts working together to achieve specified goals. The groups are domain-specific and focus on discussion or activity around a specific subject area. The term can sometimes refer to an interdis ...
s in 94 sessions, which became known as the " Roundtable Talks" (''Rozmowy Okr─ģg┼éego Sto┼éu'') saw the PUWP abandon power and radically altered the shape of the country. In June, shortly after the Tiananmen Square protests
The Tiananmen Square protests, known in Chinese as the June Fourth Incident (), were student-led demonstrations held in Tiananmen Square, Beijing during 1989. In what is known as the Tiananmen Square Massacre, or in Chinese the June Fourth ...
in China, the 1989 Polish legislative election
Parliamentary elections were held in Poland in 1989 to elect members of the Sejm and the recreated Senate. The first round took place on 4 June, with a second round on 18 June. They were the first elections in the country since the Communist Polis ...
took place. Much to its own surprise, Solidarity took all contested (35%) seats in the Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland (Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of t ...
, the Parliament's lower house, and all but one seat in the elected Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
.
Solidarity persuaded the communists' longtime allied parties, the United People's Party and Democratic Party, to throw their support to Solidarity. This all but forced Jaruzelski, who had been named president in July, to appoint a Solidarity member as prime minister. Finally, he appointed a Solidarity-led coalition government with Tadeusz Mazowiecki as the country's first non-communist prime minister since 1948.
On 10 December 1989, the statue
A statue is a free-standing sculpture in which the realistic, full-length figures of persons or animals are carved or cast in a durable material such as wood, metal or stone. Typical statues are life-sized or close to life-size; a sculpture t ...
of Vladimir Lenin
Vladimir Ilyich Ulyanov. ( 1870 ŌĆō 21 January 1924), better known as Vladimir Lenin,. was a Russian revolutionary, politician, and political theorist. He served as the first and founding head of government of Soviet Russia from 1917 to 19 ...
was removed in Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
by the PRL authorities.
The Parliament amended the Constitution on 29 December 1989 to formally rescind the PUWP's constitutionally-guaranteed power and restore democracy and civil liberties. This began the Third Polish Republic
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1Ōüä60 of a ''second'', or 1Ōüä3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (disambiguation)
* Third Avenue (disambiguation)
* Hig ...
, and served as a prelude to the democratic elections of 1991
File:1991 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: Boris Yeltsin, elected as Russia's first president, waves the new flag of Russia after the 1991 Soviet coup d'├®tat attempt, orchestrated by Soviet hardliners; Mount Pinatubo erupts in the Phil ...
ŌĆö the fourth ever held in Poland.
The PZPR was disbanded on 30 January 1990, but Wałęsa could be elected as president only eleven months later. The Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republic ...
was dissolved on 1 July 1991 and the Soviet Union ceased to exist in December 1991. On 27 October 1991, the 1991 Polish parliamentary election
Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 27 October 1991 to elect deputies to both houses of the National Assembly.Dieter Nohlen & Philip St├Čver (2010) ''Elections in Europe: A data handbook'', p1491 The 1991 election was notable on severa ...
, the first democratic election since the 1920s. This completed Poland's transition from a communist party rule to a Western-style liberal democratic political system. The last post-Soviet troops left Poland on 18 September 1993. After ten years of democratic consolidation Democratic consolidation is the process by which a new democracy matures, in a way that it becomes unlikely to revert to authoritarianism without an external shock, and is regarded as the only available system of government within a country. This is ...
, Poland joined OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coop├®ration et de d├®veloppement ├®conomiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
in 1996, NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du trait├® de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states ŌĆō 28 European and two No ...
in 1999 and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
in 2004.
Government and politics
Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
, the country was generally reckoned by western nations as a ''de facto'' one-party state
A one-party state, single-party state, one-party system, or single-party system is a type of sovereign state in which only one political party has the right to form the government, usually based on the existing constitution. All other parties ...
because these two parties were supposedly completely subservient to the Communists and had to accept the PZPR's "leading role" as a condition of their existence. It was politically influenced by the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
to the extent of being its satellite country, along with East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
, Czechoslovakia
, rue, ą¦ąĄčüčīą║ąŠčüą╗ąŠą▓ąĄąĮčīčüą║ąŠ, , yi, ūśū®ūóūøūÉūĪū£ūÉūĢūĢūÉū¦ūÖūÖ,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918ŌĆō19391945ŌĆō1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
and other Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
members.
From 1952, the highest law was the Constitution of the Polish People's Republic, and the Polish Council of State replaced the presidency of Poland. Elections were held on the single lists of the Front of National Unity. Despite these changes, Poland was one of the most liberal communist nations and was the only communist country in the world which did not have any communist symbols (red star
A red star, five-pointed and filled, is a symbol that has often historically been associated with communist ideology, particularly in combination with the hammer and sickle, but is also used as a purely socialist symbol in the 21st century. I ...
, stars, ears of wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, or hammer and sickle
The hammer and sickle (Unicode: "ŌśŁ") zh, s=ķöżÕŁÉÕÆīķĢ░ÕłĆ, p=Chu├Łzi h├® li├Īnd─üo or zh, s=ķĢ░ÕłĆķöżÕŁÉ, p=Li├Īnd─üo chu├Łzi, labels=no is a symbol meant to represent proletarian solidarity, a union between agricultural and industri ...
) on its flag
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design empl ...
and coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldry, heraldic communication design, visual design on an escutcheon (heraldry), escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central ele ...
. The White Eagle White Eagle(s) may refer to:
History and politics
* Coat of arms of Poland, a white eagle
* Crusade of Romanianism, or White Eagles, a 1930s far-right movement in Romania
* Task Force White Eagle, a Polish military unit during the War in Afghanist ...
founded by Polish monarchs in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
remained as Poland's national emblem; the only feature removed by the communists from the pre-war design was the crown, which was seen as imperialistic
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
and monarchist
Monarchism is the advocacy of the system of monarchy or monarchical rule. A monarchist is an individual who supports this form of government independently of any specific monarch, whereas one who supports a particular monarch is a royalist. ...
.
The Polish People's Republic maintained a large standing army and hosted Soviet troops in its territory, as Poland was a Warsaw Pact signatory.Rao, B. V. (2006), ''History of Modern Europe Ad 1789ŌĆō2002: A.D. 1789ŌĆō2002'', Sterling Publishers Pvt. Ltd. The UB and succeeding SB were the chief intelligence agencies that acted as secret police. The official police organization, which was also responsible for peacekeeping and suppression of protests, was renamed Citizens' Militia (MO). The Militia's elite ZOMO
The Motorized Reserves of the Citizens' Militia ( pl, Zmotoryzowane Odwody Milicji Obywatelskiej), commonly known as ZOMO, were paramilitary-police formations during the communist era in Poland. These elite units of Citizens' Militia (MO) were ...
squads committed various serious crimes to maintain the communists in power, including the harsh treatment of protesters, arrest of opposition leaders and in some cases, murder. According to Rudolph J. Rummel, at least 22,000 people killed by the regime during its rule. As a result, Poland had a high imprisonment rate but one of the lowest crime rates in the world.
Foreign relations
 During its existence, the Polish People's Republic maintained relations not only with the
During its existence, the Polish People's Republic maintained relations not only with the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, but several communist states around the world. It also had friendly relations with the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
, and the Western Bloc as well as the People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
. At the height of the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, Poland attempted to remain neutral to the conflict between the Soviets and the Americans. In particular, Edward Gierek sought to establish Poland as a mediator between the two powers in the 1970s. Both the U.S. presidents
The president of the United States is the head of state and head of government of the United States, indirectly elected to a four-year term
Term may refer to:
* Terminology, or term, a noun or compound word used in a specific context, in pa ...
and the Soviet general secretaries
Secretary is a title often used in organizations to indicate a person having a certain amount of authority, Power (social and political), power, or importance in the organization. Secretaries announce important events and communicate to the orga ...
or leaders visited communist Poland.
Under pressure from the USSR, Poland participated in the invasion of Czechoslovakia
The Warsaw Pact invasion of Czechoslovakia refers to the events of 20ŌĆō21 August 1968, when the Czechoslovak Socialist Republic was jointly invaded by four Warsaw Pact countries: the Soviet Union, the Polish People's Republic, the People's Rep ...
in 1968.
Poland's relations
Relation or relations may refer to:
General uses
*International relations, the study of interconnection of politics, economics, and law on a global level
*Interpersonal relationship, association or acquaintance between two or more people
*Public ...
with Israel
Israel (; he, ūÖų┤ū®ų░ūéū©ųĖūÉųĄū£, ; ar, žź┘Éž│┘Æž▒┘Äž¦ž”┘É┘Ŗ┘ä, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, ū×ų░ūōų┤ūÖūĀųĘū¬ ūÖų┤ū®ų░ūéū©ųĖūÉųĄū£, label=none, translit=Med─½nat Y─½sr─ü╩Š─ōl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
were on a fair level following the aftermath of the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
. In 1947, the PRL voted in favour of the United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine
The United Nations Partition Plan for Palestine was a proposal by the United Nations, which recommended a partition of Mandatory Palestine at the end of the British Mandate. On 29 November 1947, the UN General Assembly adopted the Plan as Re ...
, which led to Israel's recognition by the PRL on 19 May 1948. However, by the Six-Day War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, ž¦┘ä┘å┘āž│ž®, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 ArabŌĆōIsraeli War or Third ArabŌĆōIsraeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab world, Arab states (primarily United Arab Republic, Egypt, S ...
, it severed diplomatic relations with Israel in June 1967 and supported the Palestine Liberation Organization
The Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO; ar, ┘ģ┘åžĖ┘ģž® ž¦┘䞬žŁž▒┘Ŗž▒ ž¦┘ä┘ü┘äž│žĘ┘Ŗ┘å┘Ŗž®, ') is a Palestinian nationalism, Palestinian nationalist political and militant organization founded in 1964 with the initial purpose of establ ...
which recognized the State of Palestine
Palestine ( ar, ┘ü┘äž│žĘ┘Ŗ┘å, Filasß╣Ł─½n), Legal status of the State of Palestine, officially the State of Palestine ( ar, ž»┘ł┘äž® ┘ü┘äž│žĘ┘Ŗ┘å, Dawlat Filasß╣Ł─½n, label=none), is a state (polity), state located in Western Asia. Officiall ...
on 14 December 1988. In 1989, PRL restored relations with Israel.
The PRL participated as a member of the UN, the World Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and e ...
, the Warsaw Pact
The Warsaw Pact (WP) or Treaty of Warsaw, formally the Treaty of Friendship, Cooperation and Mutual Assistance, was a collective defense treaty signed in Warsaw, Poland, between the Soviet Union and seven other Eastern Bloc socialist republic ...
, Comecon, International Energy Agency
The International Energy Agency (IEA) is a Paris-based autonomous intergovernmental organisation, established in 1974, that provides policy recommendations, analysis and data on the entire global energy sector, with a recent focus on curbing carb ...
, Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold European Convention on Human Rights, human rights, democracy and the Law in Europe, rule of law in Europe. ...
, Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe, International Atomic Energy Agency
The International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) is an intergovernmental organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. It was established in 1957 ...
, and Interkosmos.
Economy
Early years
 Poland suffered tremendous economic losses during World War II. In 1939, Poland had 35.1 million inhabitants, but the census of 14 February 1946 showed only 23.9 million inhabitants. The difference was partially the result of the border revision. Losses in national resources and infrastructure amounted to approximately 38%. The implementation of the immense tasks involved with the reconstruction of the country was intertwined with the struggle of the new government for the stabilisation of power, made even more difficult by the fact that a considerable part of society was mistrustful of the communist government. The occupation of Poland by the Red Army and the support the Soviet Union had shown for the Polish communists was decisive in the communists gaining the upper hand in the new Polish government.
As control of the Polish territories passed from occupying forces of
Poland suffered tremendous economic losses during World War II. In 1939, Poland had 35.1 million inhabitants, but the census of 14 February 1946 showed only 23.9 million inhabitants. The difference was partially the result of the border revision. Losses in national resources and infrastructure amounted to approximately 38%. The implementation of the immense tasks involved with the reconstruction of the country was intertwined with the struggle of the new government for the stabilisation of power, made even more difficult by the fact that a considerable part of society was mistrustful of the communist government. The occupation of Poland by the Red Army and the support the Soviet Union had shown for the Polish communists was decisive in the communists gaining the upper hand in the new Polish government.
As control of the Polish territories passed from occupying forces of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
to the subsequent occupying forces of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
, and from the Soviet Union to the Soviet-imposed puppet satellite government, Poland's new economic system
An economic system, or economic order, is a system of Production (economics), production, resource allocation and Distribution (economics), distribution of goods and services within a society or a given geographic area. It includes the combinati ...
was forcibly imposed and began moving towards a radical, communist centrally planned economy. One of the first major steps in that direction involved the agricultural reform
Land reform is a form of agrarian reform involving the changing of laws, regulations, or customs regarding land ownership. Land reform may consist of a government-initiated or government-backed property redistribution, generally of agricultural ...
issued by the Polish Committee of National Liberation
The Polish Committee of National Liberation (Polish: ''Polski Komitet Wyzwolenia Narodowego'', ''PKWN''), also known as the Lublin Committee, was an executive governing authority established by the Soviet-backed communists in Poland at the lat ...
government on 6 September 1944. All estates over 0.5 km2 in pre-war Polish territories and all over 1 km2 in former German territories were nationalised without compensation. In total, 31,000 km2 of land were nationalised in Poland and 5 million in the former German territories, out of which 12,000 km2 were redistributed to farmers and the rest remained in the hands of the government (Most of this was eventually used in the collectivization and creation of sovkhoz-like State Agricultural Farms "PGR"). However, the collectivization of Polish farming never reached the same extent as it did in the Soviet Union or other countries of the Eastern Bloc.Wojciech RoszkowskiReforma Rolna
Encyklopedia.PWN.pl (Internet Archive)

Nationalisation
Nationalization (nationalisation in British English) is the process of transforming privately-owned assets into public assets by bringing them under the public ownership of a national government or state. Nationalization usually refers to pri ...
began in 1944, with the pro-Soviet government taking over industries in the newly acquired territories along with the rest of the country. As nationalization was unpopular, the communists delayed the nationalization reform until 1946, when after the 3xTAK
The people's referendum ( pl, referendum ludowe) of 1946, also known as the Three Times Yes referendum (''Trzy razy tak'', often abbreviated as 3├ŚTAK), was a referendum held in Poland on 30 June 1946 on the authority of the State National Council ...
referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
s they were fairly certain they had total control of the state and could deal a heavy blow to eventual public protests. Some semi-official nationalisation of various private enterprises had begun also in 1944. In 1946, all enterprises with over 50 employees were nationalised, with no compensation to Polish owners.Zbigniew LandauNacjonalizacja w Polsce
Encyklopedia.PWN.pl (Internet Archive) The Allied punishment of Germany for the war of destruction was intended to include large-scale reparations to Poland. However, those were truncated into insignificance by the break-up of Germany into East and West and the onset of the Cold War. Poland was then relegated to receive her share from the Soviet-controlled
East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
. However, even this was attenuated, as the Soviets pressured the Polish Government to cease receiving the reparations far ahead of schedule as a sign of 'friendship' between the two new communist neighbors and, therefore, now friends. Thus, without the reparations and without the massive Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred over $13 billion (equivalent of about $ in ) in economic re ...
implemented in the West at that time, Poland's postwar recovery was much harder than it could have been.
Later years
 During the Gierek era, Poland borrowed large sums from Western creditors in exchange for promise of social and economic reforms. None of these have been delivered due to resistance from the hardline communist leadership as any true reforms would require effectively abandoning the Marxian economy with central planning, state-owned enterprises and state-controlled prices and trade. After the West refused to grant Poland further loans, the living standards began to sharply fall again as the supply of imported goods dried up, and as Poland was forced to export everything it could, particularly food and coal, to service its massive debt, which would reach US$23 billion by 1980.
In 1981, Poland notified
During the Gierek era, Poland borrowed large sums from Western creditors in exchange for promise of social and economic reforms. None of these have been delivered due to resistance from the hardline communist leadership as any true reforms would require effectively abandoning the Marxian economy with central planning, state-owned enterprises and state-controlled prices and trade. After the West refused to grant Poland further loans, the living standards began to sharply fall again as the supply of imported goods dried up, and as Poland was forced to export everything it could, particularly food and coal, to service its massive debt, which would reach US$23 billion by 1980.
In 1981, Poland notified Club de Paris
The Paris Club (french: Club de Paris) is a group of officials from major creditor countries whose role is to find co-ordinated and sustainable solutions to the payment difficulties experienced by debtor countries. As debtor countries undertake ...
(a group of Western-European central banks) about its insolvency and a number of negotiations of repaying its foreign debt were completed between 1989 and 1991.
The party was forced to raise prices, which led to further large-scale social unrest and formation of the Solidarity
''Solidarity'' is an awareness of shared interests, objectives, standards, and sympathies creating a psychological sense of unity of groups or classes. It is based on class collaboration.''Merriam Webster'', http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictio ...
movement. During the Solidarity
''Solidarity'' is an awareness of shared interests, objectives, standards, and sympathies creating a psychological sense of unity of groups or classes. It is based on class collaboration.''Merriam Webster'', http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictio ...
years and the imposition of martial law
Martial law is the imposition of direct military control of normal civil functions or suspension of civil law by a government, especially in response to an emergency where civil forces are overwhelmed, or in an occupied territory.
Use
Marti ...
, Poland entered a decade of economic crisis, officially acknowledged as such even by the regime. Rationing and queuing became a way of life, with ration card
Rationing is the controlled distribution of scarce resources, goods, services, or an artificial restriction of demand. Rationing controls the size of the ration, which is one's allowed portion of the resources being distributed on a particular ...
s (''Kartki'') necessary to buy even such basic consumer staples as milk and sugar. Access to Western luxury goods became even more restricted, as Western governments applied economic sanction
Economic sanctions are commercial and financial penalties applied by one or more countries against a targeted self-governing state, group, or individual. Economic sanctions are not necessarily imposed because of economic circumstancesŌĆöthey may ...
s to express their dissatisfaction with the government repression of the opposition, while at the same time the government had to use most of the foreign currency it could obtain to pay the crushing rates on its foreign debt.
 In response to this situation, the government, which controlled all official foreign trade, continued to maintain a highly artificial
In response to this situation, the government, which controlled all official foreign trade, continued to maintain a highly artificial exchange rate
In finance, an exchange rate is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another currency. Currencies are most commonly national currencies, but may be sub-national as in the case of Hong Kong or supra-national as in the case of ...
with Western currencies. The exchange rate worsened distortions in the economy at all levels, resulting in a growing black market
A black market, underground economy, or shadow economy is a clandestine market or series of transactions that has some aspect of illegality or is characterized by noncompliance with an institutional set of rules. If the rule defines the se ...
and the development of a shortage economy
"Shortage economy" ( pl, gospodarka niedoboru, hu, hi├Īnygazdas├Īg) is a term coined by Hungarian economist J├Īnos Kornai, who used this term to criticize the old centrally-planned economies of the communist states of the Eastern Bloc.
In his mo ...
. The only way for an individual to buy most Western goods was to use Western currencies, notably the U.S. dollar
The United States dollar ( symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the officia ...
, which in effect became a parallel currency. However, it could not simply be exchanged at the official banks for zlotys, since the government exchange rate undervalued the dollar and placed heavy restrictions on the amount that could be exchanged, and so the only practical way to obtain it was from remittances
A remittance is a non-commercial transfer of money by a foreign worker, a member of a diaspora community, or a citizen with familial ties abroad, for household income in their home country or homeland. Money sent home by migrants competes with ...
or work outside the country. An entire illegal industry of street-corner money changers emerged as a result. The so-called ''Cinkciarze'' gave clients far better than official exchange rate and became wealthy from their opportunism albeit at the risk of punishment, usually diminished by the wide scale bribery of the Militia.
As Western currency came into the country from emigrant families and foreign workers, the government in turn attempted to gather it up by various means, most visibly by establishing a chain of state-run '' Pewex'' and ''Baltona'' stores in all Polish cities, where goods could only be bought with hard currency. It even introduced its own ''ersatz
An ersatz good () is a substitute good, especially one that is considered inferior to the good it replaces. It has particular connotations of wartime usage.
Etymology
''Ersatz'' is a German word literally meaning ''substitute'' or ''replacement ...
'' U.S. currency (''bony PeKaO'' in Polish). This paralleled the financial practices in East Germany running its own ration stamps at the same time. The trend led to an unhealthy state of affairs where the chief determinant of economic status was access to hard currency. This situation was incompatible with any remaining ideals of socialism, which were soon completely abandoned at the community level.
skyscraper
A skyscraper is a tall continuously habitable building having multiple floors. Modern sources currently define skyscrapers as being at least or in height, though there is no universally accepted definition. Skyscrapers are very tall high-ris ...
in Krak├│w, were never finished at all, wasting the considerable resources devoted to their construction. Polish investment in economic infrastructure and technological development fell rapidly, ensuring that the country lost whatever ground it had gained relative to Western European economies in the 1970s. To escape the constant economic and political pressures during these years, and the general sense of hopelessness, many family income providers traveled for work in Western Europe, particularly West Germany (''Wyjazd na saksy''). During the era, hundreds of thousands of Poles left the country permanently and settled in the West, few of them returning to Poland even after the end of socialism in Poland. Tens of thousands of others went to work in countries that could offer them salaries in hard currency, notably Libya
Libya (; ar, ┘ä┘Ŗž©┘Ŗž¦, L─½biy─ü), officially the State of Libya ( ar, ž»┘ł┘äž® ┘ä┘Ŗž©┘Ŗž¦, Dawlat L─½biy─ü), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to EgyptŌĆōLibya bo ...
and Iraq
Iraq,; ku, ž╣█Äž▒ž¦┘é, translit=├Ŗraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, ┌®█å┘ģž¦ž▒█ī ž╣█Äž▒ž¦┘é, translit=Komar├« ├Ŗraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to IraqŌĆōTurkey border, the north, Iran to IranŌĆōIraq ...
.
 After several years of the situation continuing to worsen, during which time the socialist government unsuccessfully tried various expedients to improve the performance of the economyŌĆöat one point resorting to placing military
After several years of the situation continuing to worsen, during which time the socialist government unsuccessfully tried various expedients to improve the performance of the economyŌĆöat one point resorting to placing military commissar
Commissar (or sometimes ''Kommissar'') is an English transliteration of the Russian (''komissar''), which means 'commissary'. In English, the transliteration ''commissar'' often refers specifically to the political commissars of Soviet and Eas ...
s to direct work in the factories ŌĆö it grudgingly accepted pressures to liberalize the economy. The government introduced a series of small-scale reforms, such as allowing more small-scale private enterprises to function. However, the government also realized that it lacked the legitimacy to carry out any large-scale reforms, which would inevitably cause large-scale social dislocation and economic difficulties for most of the population, accustomed to the extensive social safety net that the socialist system had provided. For example, when the government proposed to close the Gda┼äsk Shipyard
The Gdańsk Shipyard ( pl, Stocznia Gdańska, formerly Lenin Shipyard) is a large Polish shipyard, located in the city of Gdańsk. The yard gained international fame when Solidarity () was founded there in September 1980. It is situated on the w ...
, a decision in some ways justifiable from an economic point of view but also largely political, there was a wave of public outrage and the government was forced to back down.
The only way to carry out such changes without social upheaval would be to acquire at least some support from the opposition side. The government accepted the idea that some kind of a deal with the opposition would be necessary, and repeatedly attempted to find common ground throughout the 1980s. However, at this point the communists generally still believed that they should retain the reins of power for the near future, and only allowed the opposition limited, advisory participation in the running of the country. They believed that this would be essential to pacifying the Soviet Union, which they felt was not yet ready to accept a non-Communist Poland.
Culture
Television and media
The origins of Polish television date back to the late 1930s, however, the beginning ofWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposin ...
interrupted further progress at establishing a regularly televised program. The first prime state television corporation, Telewizja Polska
Telewizja Polska S.A. (; "Polish Television"; TVP), also known in English as the public Polish Television is a Polish state media corporation. It is the largest Polish television network, although viewership has been declining in the 2010s.
Sinc ...
, was founded after the war in 1952 and was hailed as a great success by the communist authorities. The foundation date corresponds to the time of the very first regularly televised broadcast which occurred at 07:00 p.m CET
CET or cet may refer to:
Places
* Cet, Albania
* Cet, standard astronomical abbreviation for the constellation Cetus
* Colchester Town railway station (National Rail code CET), in Colchester, England
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Comcast Ente ...
on 25 October 1952. Initially, the auditions were broadcast to a limited number of viewers and at set dates, often a month apart. On 23 January 1953 regular shows began to appear on the first and only channel, TVP1
TVP1 (TVP Jeden, ''Program I Telewizji Polskiej'', ''"Jedynka"'') is the main public television channel of TVP (Telewizja Polska S.A.), Poland's national television broadcaster. It was the first Polish channel to be broadcast and remains one ...
. The second channel, TVP2
TVP 2 (TVP Dwa, ''Program II Telewizji Polskiej'', ''"Dw├│jka"'') is a Polish public mainstream TV channel operated by TVP. Launched in October 1970, its varied line-up contains a variety of programming (documentary, history, talk-shows, game-sh ...
, was launched in 1970 and coloured television was introduced in 1971. Most reliable sources of information in the 1950s were newspapers, most notably '' Trybuna Ludu'' (People's Tribune).
The chief newscast
News broadcasting is the medium of broadcasting various news events and other information via television, radio, or the internet in the field of broadcast journalism. The content is usually either produced locally in a radio studio or televis ...
under the Polish People's Republic for over 31 years was ''Dziennik Telewizyjny
''Dziennik Telewizyjny'' ( en, Television Journal; DT), commonly simplified to ''Dziennik'' (lit. Journal), was the chief news program of Telewizja Polska between 1958 and 1989, in the Polish People's Republic. It was Poland's second regularly te ...
'' (Television Journal). Commonly known to the viewers as ''Dziennik'', aired in the years 1958ŌĆō1989 and was utilized by the Polish United Workers' Party as a propaganda tool to control the masses. Transmitted daily at 07:30 p.m CET
CET or cet may refer to:
Places
* Cet, Albania
* Cet, standard astronomical abbreviation for the constellation Cetus
* Colchester Town railway station (National Rail code CET), in Colchester, England
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Comcast Ente ...
since 1965, it was infamous for its manipulative techniques and emotive language as well as the controversial content. For instance, the ''Dziennik'' provided more information on world news, particularly bad events, war, corruption or scandals in the West. This method was intentionally used to minimize the effects of the issues that were occurring in communist Poland at the time. With its format, the show shared many similarities with the East German
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
''Aktuelle Kamera
Aktuelle Kamera (''"Current Camera")'' was the flagship television newscast of Deutscher Fernsehfunk, the state broadcaster of the German Democratic Republic (known as ''Fernsehen der DDR'' from 11 February 1972 to 11 March 1990). On air from 21 ...
''. Throughout the 1970s, ''Dziennik Telewizyjny'' was regularly watched by over 11 million viewers, approximately in every third household in the Polish People's Republic. The long legacy of communist television continues to this day; the older generation in contemporary Poland refers to every televised news program as "Dziennik" and the term also became synonymous with authoritarianism, propaganda, manipulation, lies, deception and disinformation.
Under martial law in Poland, from December 1981 ''Dziennik'' was presented by officers of the Polish Armed Forces
The Armed Forces of the Republic of Poland ( pl, Si┼éy Zbrojne Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej, abbreviated ''SZ RP''; popularly called ''Wojsko Polskie'' in Poland, abbreviated ''WP''ŌĆöroughly, the "Polish Military") are the national armed forces of ...
or newsreaders in military uniforms and broadcast 24-hours a day. The running time has also been extended to 60 minutes. The program returned to its original form in 1983. The audience viewed this move as an attempt to militarize the country under a military junta. As a result, several newsreaders had difficulty in finding employment after the fall of communism in 1989.
Despite the political agenda of Telewizja Polska, the authorities did emphasize the need to provide entertainment for younger viewers without exposing the children to inappropriate content. Initially created in the 1950s, an evening cartoon block called ''Dobranocka'', which was targeted at young children, is still broadcast today under a different format. Among the most well-known animations of the 1970s and 1980s in Poland were ''Reksio
Reksio is a Polish cartoon character who is the protagonist of the children's animated adventure-comedy Polish TV series of the same name. Reksio was created by Polish director Lechosław Marszałek. Its 65 episodes were designed and produced fro ...
'', ''Bolek and Lolek
''Bolek and Lolek'' are two Polish cartoon characters from the children's animated comedy television series by the same name. They were created by Władysław Nehrebecki the author, scriptwriter and main director and partially designed by Wła ...
'', ''Krtek
Mole ( Czech: ''Krtek'', ''Krte─Źek'') is an animated character in a series of cartoons created by Czech animator Zden─øk Miler. The premiere of the first short film with Mole took place at the Venice Film Festival in 1957. Since its inception, ...
'' (Polish: Krecik) and ''The Moomins
The Moomins ( sv, Mumintroll) are the central characters in a series of novels, short stories, and a comic strip by Finnish writer and illustrator Tove Jansson, originally published in Swedish by Schildts in Finland. They are a family of white ...
''.
Countless shows were made relating to Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposin ...
history such as ''Four Tank-Men and a Dog
''Four Tank-Men and a Dog'' (Polish: ''Czterej pancerni i pies'', ) was a Polish black and white TV series based on the book by Janusz Przymanowski. Made between 1966 and 1970, the series is composed of 21 episodes of 55 minutes each, divided ...
'' (1966ŌĆō1970) and '' Stakes Larger Than Life'' with Kapitan Kloss (1967ŌĆō1968), but were purely fictional and not based on real events. The horrors of war, Soviet invasion and the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
were taboo topics, avoided and downplayed when possible. In most cases, producers and directors were encouraged to portray the Soviet Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: ąĀą░ą▒ąŠ╠üč湥-ą║čĆąĄčüčéčīčÅ╠üąĮčüą║ą░čÅ ąÜčĆą░╠üčüąĮą░čÅ ą░čĆą╝ąĖčÅ),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
as a friendly and victorious force which entirely liberated Poland from Nazi
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in ...
sm, Imperialism
Imperialism is the state policy, practice, or advocacy of extending power and dominion, especially by direct territorial acquisition or by gaining political and economic control of other areas, often through employing hard power (economic and ...
or Capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for Profit (economics), profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, pric ...
. The goal was to strengthen the artificial Polish-Soviet friendship and eliminate any knowledge of the crimes or acts of terror committed by the Soviets during World War II, such as the Katyn massacre
The Katyn massacre, "Katy┼ä crime"; russian: link=yes, ąÜą░čéčŗąĮčüą║ą░čÅ čĆąĄąĘąĮčÅ ''Katynskaya reznya'', "Katyn massacre", or russian: link=no, ąÜą░čéčŗąĮčüą║ąĖą╣ čĆą░čüčüčéčĆąĄą╗, ''Katynsky rasstrel'', "Katyn execution" was a series of m ...
. Hence, the Polish audience were more lenient towards a TV series exclusively featuring Polish history from the times of the Kingdom of Poland or the PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth
The PolishŌĆōLithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
.
 Being produced in a then-socialist country, the shows did contain a socialist agenda, but with a more informal and comical tone; they concentrated on everyday life which was appealing to ordinary people. These include '' Czterdziestolatek'' (1975ŌĆō1978), '' Alternatywy 4'' (1986ŌĆō1987) and '' Zmiennicy'' (1987ŌĆō1988). The wide range of topics covered featured petty disputes in the block of flats, work issues, human behaviour and interaction as well as comedy, sarcasm, drama and
Being produced in a then-socialist country, the shows did contain a socialist agenda, but with a more informal and comical tone; they concentrated on everyday life which was appealing to ordinary people. These include '' Czterdziestolatek'' (1975ŌĆō1978), '' Alternatywy 4'' (1986ŌĆō1987) and '' Zmiennicy'' (1987ŌĆō1988). The wide range of topics covered featured petty disputes in the block of flats, work issues, human behaviour and interaction as well as comedy, sarcasm, drama and satire
Satire is a genre of the visual, literary, and performing arts, usually in the form of fiction and less frequently non-fiction, in which vices, follies, abuses, and shortcomings are held up to ridicule, often with the intent of shaming ...
. Every televised show was censored
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governments ...
if necessary and political content was erased. Ridiculing the communist government was illegal, though Poland remained the most liberal of the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
members and censorship
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governments ...
eventually lost its authority by the mid-1980s. The majority of the TV shows and serials made during the Polish People's Republic earned a cult
In modern English, ''cult'' is usually a pejorative term for a social group that is defined by its unusual religious, spiritual, or philosophical beliefs and rituals, or its common interest in a particular personality, object, or goal. This ...
status in Poland today, particularly due to their symbolism of a bygone era.
Cinema
In November 1945 the newly formed communist government founded the film production and distribution corporation Film Polski, and placed the well-known Polish filmmaker of Jewish descentAleksander Ford
Aleksander Ford (born Mosze Lifszyc; 24 November 1908 in Kiev, Russian Empire ŌĆō 4 April 1980 in Naples, Florida, United States, U.S.) was a Polish film director; and head of the Polish People's Army of Poland, People's Army Film Crew in the Sov ...
in charge. The Film Polski output was limited; only thirteen features were released between 1947 and its dissolution in 1952, concentrating on Polish suffering at the hands of the Nazis during World War II for propaganda purposes. In 1947, Ford's contribution to film was crucial in establishing the new National Film School in Łódź
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality ŌĆō a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, ce ...
, where he taught for 20 years. The first film produced in Poland following the war was '' Forbidden Songs'' (1946), which was seen by 10.8 million people in its initial theatrical screening, almost half of the population at the time. Ford's biggest success was ''Knights of the Teutonic Order
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
'' from 1960, one of the most celebrated and attended Polish films in history.
 The change in political climate in the 1950s gave rise to the
The change in political climate in the 1950s gave rise to the Polish Film School
Polish Film School ( pl, Polska Szkoła Filmowa) refers to an informal group of Polish film directors and screenplay writers active between 1956 and approximately 1963. Among the most prominent representatives of the school are Andrzej Wajda, And ...
movement, a training ground for some of the icons of the world cinematography. It was then that independent Polish filmmakers such as Andrzej Wajda
Andrzej Witold Wajda (; 6 March 1926 ŌĆō 9 October 2016) was a Polish film and theatre director. Recipient of an Honorary Oscar, the Palme d'Or, as well as Honorary Golden Lion and Honorary Golden Bear Awards, he was a prominent member of the ...
, Roman Polanski
Raymond Roman Thierry Pola┼äski , group=lower-alpha, name=note_a (n├® Liebling; 18 August 1933) is a French-Polish film director, producer, screenwriter, and actor. He is the recipient of numerous accolades, including an Academy Award, two ...
, Wojciech Has, Kie┼ølowski, Zanussi
Zanussi () is an Italian producer of home appliances that was bought by Electrolux in 1984. Zanussi has been exporting products from Italy since 1946.
History
The Zanussi Company began as the small workshop of Antonio Zanussi in 1916. The 26 ...
, Bareja and Andrzej Munk
Andrzej Munk (16 October 1921 ŌĆō 20 September 1961) was a Polish film director, screen writer and documentalist. He was one of the most influential artists of the post-Stalinist period in the People's Republic of Poland. His feature films '' Ma ...
often directed films which were a political satire aimed at stultifying the communist authorities in the most gentle manner as possible. However, due to censorship, some films were not screened in cinemas until 1989 when communism ended in Central and Eastern Europe. The Hourglass Sanatorium
''The Hourglass Sanatorium'' ( pl, Sanatorium pod klepsydr─ģ) is a 1973 Polish surrealist film directed by Wojciech Jerzy Has, starring Jan Nowicki, Tadeusz Kondrat, Mieczys┼éaw Voit, Halina Kowalska and Gustaw Holoubek. It is also known as ''The ...
(1973) was so controversial, the communist government forbade Wojciech Has to direct for a period of ten years. The authorities also hired or bribed film critics and literary scholars to poorly review the film. The reviewers, however, were so ineffective that in turn the film was applauded in the West and won the Jury Prize at the 1973 Cannes Film Festival
The 26th Cannes Film Festival was held from 10 to 25 May 1973. The Grand Prix du Festival International du Film went to ''Scarecrow'' by Jerry Schatzberg and ''The Hireling'' by Alan Bridges. At this festival two new non-competitive sections were ...
.
The first nominated Polish film at the Academy Awards was Knife in the Water
''Knife in the Water'' ( pl, N├│┼╝ w wodzie) is a 1962 Polish psychological thriller film co-written and directed by Roman Polanski in his feature debut, and starring Leon Niemczyk, Jolanta Umecka, and Zygmunt Malanowicz. Its plot follows a husband ...
by Polanski in 1963. Between 1974 and 1981, Polish films were nominated five times and three consecutively from 1974 to 1976.
 ;Movies
*''
;Movies
*''A Generation
''A Generation'' ( pl, Pokolenie) is a 1955 Polish film directed by Andrzej Wajda. It is based on the novel ''Pokolenie'' by Bohdan Czeszko, who also wrote the script. It was Wajda's first film and the opening installment of what became his Thr ...
''
*''Ashes and Diamonds
''Ashes and Diamonds'' ( Polish original: ''Popiół i diament'', literally: ''Ash and Diamond'') is a 1948 novel by the Polish writer Jerzy Andrzejewski. The story takes place during the last few days of World War II in Europe, and describes th ...
''
*'' Nights and Days''
*''The Deluge
The Genesis flood narrative (chapters 6ŌĆō9 of the Book of Genesis) is the Hebrew version of the universal flood myth. It tells of God's decision to return the universe to its pre- creation state of watery chaos and remake it through the microc ...
''
*''Knights of the Teutonic Order
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
''
*''The Quack
The Quack ( pl, Znachor) is a 1982 Polish drama film directed by Jerzy Hoffman. The screenplay was written based on the novel by Tadeusz Dołęga-Mostowicz written in 1937. The first adaptation of the book was filmed the same year the book was w ...
''
*'' The Doll''
*'' Countess Cosel'' ŌĆō Anna Constantia von Brockdorff
Anna Constantia von Brockdorff (17 October 1680 ŌĆō 31 March 1765), later the Countess of Cosel, was a German lady-in-waiting and noblewoman, and mistress of Augustus the Strong, King of Poland and Elector of Saxony, in 1706ŌĆō1713. Eventual ...
*'' Salt of the Black Earth''
*'' Westerplatte'' ŌĆō Battle of Westerplatte
The Battle of Westerplatte was the first battle of the German invasion of Poland, marking the start of World War II in Europe. It occurred on the Westerplatte peninsula in the harbour of the Free City of Danzig (now Gdańsk, Poland).
In the mi ...
*'' Death of a President'' ŌĆō Assassination of Gabriel Narutowicz
*''The Coup d'Etat''
*'' The Cruise''
*''Sexmission
''Sexmission'' ( pl, Seksmisja) is a 1984 Polish cult comedy science fiction action film. It also contains a hidden political satire layer specific to the time and place of its production (the socialist-feminist system as proposed by the Communi ...
''
*''Teddy Bear
A teddy bear is a stuffed toy in the form of a bear. Developed apparently simultaneously by toymakers Morris Michtom in the U.S. and Richard Steiff under his aunt Margarete Steiff's company in Germany in the early 20th century, the teddy bear, ...
''
*''How I Unleashed World War II
''How I Unleashed World War II'' ( pl, Jak rozp─Öta┼éem drug─ģ wojn─Ö ┼øwiatow─ģ) is a Polish feature film made in 1969, based on Kazimierz S┼éawi┼äski's novel "''Przygody kanoniera Dolasa''" (''The Adventures of Dolas the Cannoneer''). It wa ...
''
Architecture
 The architecture in Poland under the Polish People's Republic had three major phases ŌĆō short-lived
The architecture in Poland under the Polish People's Republic had three major phases ŌĆō short-lived socialist realism
Socialist realism is a style of idealized realistic art that was developed in the Soviet Union and was the official style in that country between 1932 and 1988, as well as in other socialist countries after World War II. Socialist realism is ch ...
, modernism
Modernism is both a philosophy, philosophical and arts movement that arose from broad transformations in Western world, Western society during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The movement reflected a desire for the creation of new fo ...
and functionalism. Each of these styles or trends was either imposed by the government or communist doctrine.
Under Stalinism
Stalinism is the means of governing and Marxist-Leninist policies implemented in the Soviet Union from 1927 to 1953 by Joseph Stalin. It included the creation of a one-party totalitarian police state, rapid industrialization, the theory ...
in the late 1940s and 1950s, the Eastern Bloc countries adopted socialist realism, an idealized and monumental realistic art intended to promote communist values, such as the emancipation of the proletariat
The proletariat (; ) is the social class of wage-earners, those members of a society whose only possession of significant economic value is their labour power (their capacity to work). A member of such a class is a proletarian. Marxist philo ...
. This style became alternatively known as Stalinist Empire style due to its grandeur, excessive size and political message (a powerful state) it tried to convey. This expensive form greatly resembled a mixture of classicist architecture
Neoclassical architecture is an architectural style produced by the Neoclassical movement that began in the mid-18th century in Italy and France. It became one of the most prominent architectural styles in the Western world. The prevailing style ...
and Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts D├®coratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unite ...
, with archways, decorated cornices, mosaics, forged gates and columns. It was under this style that the first skyscrapers were erected in communist states. Stalin wanted to assure that Poland will remain under communist yoke and ordered the construction of one of the largest buildings in Europe at the time, the Palace of Culture and Science
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name pal─ütium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which ...
in Warsaw. With the permission of the Polish authorities who wouldn't dare to object, the construction started in 1952 and lasted until 1955. It was deemed a "gift from the Soviet Union to the Polish people" and at 237 meters in height it was an impressive landmark on European standards. With its proportions and shape it was to mediate between the Seven Sisters in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, ą£ąŠčüą║ą▓ą░, r=Moskva, p=m╔Ésk╦łva, a=ą£ąŠčüą║ą▓ą░.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
and the Empire State Building
The Empire State Building is a 102-story Art Deco skyscraper in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. The building was designed by Shreve, Lamb & Harmon and built from 1930 to 1931. Its name is derived from "Empire State", the nickname of the st ...
in New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
, but with style it possesses traditionally Polish and Art Deco architectural details.
 Following the Polish October in 1956, the concept of socialist realism was condemned. It was then that modernist architecture was promoted globally, with simplistic designs made of glass, steel and concrete. Due to previous extravagances, the idea of functionalism (serving for a purpose) was encouraged by Władysław Gomułka.
Following the Polish October in 1956, the concept of socialist realism was condemned. It was then that modernist architecture was promoted globally, with simplistic designs made of glass, steel and concrete. Due to previous extravagances, the idea of functionalism (serving for a purpose) was encouraged by Władysław Gomułka. Prefabrication
Prefabrication is the practice of assembling components of a structure in a factory or other manufacturing site, and transporting complete assemblies or sub-assemblies to the construction site where the structure is to be located. The term is u ...
was seen as a way to construct tower blocks or plattenbau in an efficient and orderly manner. A great influence on this type of architecture was Swiss-French architect and designer Le Corbusier
Charles-├ēdouard Jeanneret (6 October 188727 August 1965), known as Le Corbusier ( , , ), was a Swiss-French architect, designer, painter, urban planner, writer, and one of the pioneers of what is now regarded as modern architecture. He was ...
. Mass-prefabricated multi-family residential apartment blocks began to appear in Poland in the 1960s and their construction continued until the early 1990s, although the first examples of multi-dwelling units in Poland date back to the 1920s. The aim was to quickly urbanize rural areas, create space between individual blocks for green spaces and resettle people from densely-populated poorer districts to increase living conditions. The apartment blocks in Poland, commonly known as ''bloki'', were built on East German and Czechoslovak standards, alongside department stores, pavilions and public spaces. As of 2017, 44% of Poles reside in blocks built between the 1960s and 1980s.
Some groundbreaking architectural achievements were made during the People's Republic, most notably the reconstruction of Warsaw with its historical Old Town
In a city or town, the old town is its historic or original core. Although the city is usually larger in its present form, many cities have redesignated this part of the city to commemorate its origins after thorough renovations. There are ma ...
and the completion of Warszawa Centralna railway station
Warszawa Centralna, in English known as Warsaw Central Station, is the primary railway station in Warsaw, Poland. Completed in 1975, the station is located on the Warsaw Cross-City Line and features four underground island platforms with eight tr ...
in the 1970s under Edward Gierek's personal patronage. It was the most modern railway station building in that part of Europe when completed and was equipped with automatic glass doors and escalators, an unlikely sight in communist countries. Another example of pure late modernism was the Smyk Department Store, constructed in 1952 when socialist realism was still in effect; it was criticized for its appearance as it resembled the styles and motifs of the pre-war capitalist Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of ...
.
Education
intelligentsia
The intelligentsia is a status class composed of the university-educated people of a society who engage in the complex mental labours by which they critique, shape, and lead in the politics, policies, and culture of their society; as such, the in ...
or an educated class that would accept and favour socialist ideas over capitalism to maintain the communists in power for a long period.
Prior to the Second World War, education in the capitalist Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of ...
(1918ŌĆō1939) had many limitations and wasn't readily available to all, though under the 1932 J─Ödrzejewicz reform J─Ödrzejewicz reform was a major reform of the education in the Second Polish Republic, implemented in 1932. It reorganized the structure of Polish education, which diverged into three different systems during the era of partitions of Poland.Jaros ...
primary school was made compulsory. Furthermore, the pre-war system of education was in disarray; many educational facilities were much more accessible in wealthier western and central Poland than in the rural east (Kresy), particularly in the Polesie
Polesia, Polesie, or Polesye, uk, ą¤ąŠą╗č¢čüčüčÅ (Polissia), pl, Polesie, russian: ą¤ąŠą╗ąĄčüčīąĄ (Polesye) is a natural and historical region that starts from the farthest edge of Central Europe and encompasses Eastern Europe, including East ...
region where there was one large school per 100 square kilometers (39 square miles). Schools were also in desperate need of staff, tutors and teachers before 1939.
After the 1947 Polish legislative election
Parliamentary elections were held in Poland on 19 January 1947, Dieter Nohlen & Philip St├Čver (2010) ''Elections in Europe: A data handbook'', p1491 the first since World War II. According to the official results, the Democratic Bloc (''Blok De ...
, the communists took full control of the education in the newly formed Polish People's Republic. All private schools were nationalized, subjects that could question the socialist ideology (economics, finance) were either supervised or adjusted and religious studies were completely removed from the curriculum (secularization
In sociology, secularization (or secularisation) is the transformation of a society from close identification with religious values and institutions toward non-religious values and secular institutions. The ''secularization thesis'' expresses the ...
).
Primary as well as secondary, tertiary, vocational and higher education was made free. Attendance gradually grew, which put an end to illiteracy in rural areas. The communist government also introduced new beneficial content into the system; sports and physical education
Physical education, often abbreviated to Phys Ed. or P.E., is a subject taught in schools around the world. It is usually taught during primary and secondary education, and encourages psychomotor learning by using a play and movement explorati ...
were enforced and students were encouraged to learn foreign languages, especially German, Russian or French and from the 1980s also English. On July 15, 1961, two-year vocational career training was made obligatory to boost the number of skilled labourers and the minimum age of graduation rose to 15. Additionally, special schools were established for deaf, mute
Muteness is a speech disorder in which a person lacks the ability to speak.
Mute or the Mute may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment Film and television
* ''Mute'' (2005 film), a short film by Melissa Joan Hart
* ''Mute'' (2018 film), a scien ...
and blind children. Such institutions for the impaired were almost nonexistent in the Second Polish Republic. During the 1960s, thousands of modern schools were founded.
The number of universities nearly doubled between 1938 and 1963. Medical, agricultural, economical, engineering and sport faculties became separate colleges, under a universal communist model used in other countries of the Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc and the Soviet Bloc, was the group of socialist states of Central and Eastern Europe, East Asia, Southeast Asia, Africa, and Latin America under the influence of the Soviet Union that existed du ...
. Theological
Theology is the systematic study of the nature of the divine and, more broadly, of religious belief. It is taught as an academic discipline, typically in universities and seminaries. It occupies itself with the unique content of analyzing the ...
faculties were deemed unnecessary or potentially dangerous and were therefore removed from state universities. Philosophy
Philosophy (from , ) is the systematized study of general and fundamental questions, such as those about existence, reason, knowledge, values, mind, and language. Such questions are often posed as problems to be studied or resolved. Some ...
was also seen as superfluous. In order to strengthen the post-war Polish economy, the government created many common-labour faculties across the country, including dairying, fishing, tailoring, chemistry and mechanics to achieve a better economic output alongside efficiency. However, by 1980 the number of graduates from primary and secondary schools was so high that admission quotas for universities were introduced.
Religion
 The experiences in and after
The experiences in and after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposin ...
, wherein the large ethnic Polish population was decimated, its Jewish minority was annihilated by the Germans, the large German minority was forcibly expelled from the country at the end of the war, along with the loss of the eastern territories which had a significant population of Eastern Orthodox Belarusians and Ukrainians, led to Poland becoming more homogeneously Catholic than it had been.
The Polish anti-religious campaign was initiated by the communist government in Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
which, under the doctrine of Marxism
Marxism is a Left-wing politics, left-wing to Far-left politics, far-left method of socioeconomic analysis that uses a Materialism, materialist interpretation of historical development, better known as historical materialism, to understand S ...
, actively advocated for the disenfranchisement of religion and planned atheisation.Zdzislawa Walaszek. An Open Issue of Legitimacy: The State and the Church in Poland. Annals of the American Academy of Political and Social Science, Vol. 483, Religion and the State: The Struggle for Legitimacy and Power (January 1986), pp. 118ŌĆō134 The Catholic Church, as the religion of most Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
, was seen as a rival competing for the citizens' allegiance by the government, which attempted to suppress it. To this effect the communist state conducted anti-religious propaganda and persecution of clergymen and monasteries. As in most other Communist countries, religion was not outlawed as such (an exception being Communist Albania) and was permitted by the constitution, but the state attempted to achieve an atheistic society.
The Catholic Church in Poland provided strong resistance to Communist rule and Poland itself had a long history of dissent to foreign rule. The Polish nation rallied to the Church, as had occurred in neighbouring Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, which made it more difficult for the government to impose its antireligious policies as it had in the USSR, where the populace did not hold mass solidarity with the Russian Orthodox Church
, native_name_lang = ru
, image = Moscow July 2011-7a.jpg
, imagewidth =
, alt =
, caption = Cathedral of Christ the Saviour in Moscow, Russia
, abbreviation = ROC
, type ...
. It became the strongest anti-communist body during the epoch of Communism in Poland, and provided a more successful resistance than had religious bodies in most other Communist states.
The Catholic Church unequivocally condemned communist ideology. This led to the antireligious activity in Poland being compelled to take a more cautious and conciliatory line than in other Communist countries, largely failing in their attempt to control or suppress the Polish Church.
The state attempted to take control of minority churches, including the Polish Protestant and Polish Orthodox Church
The Polish Autocephalous Orthodox Church ( pl, Polski Autokefaliczny Ko┼øci├│┼é Prawos┼éawny), commonly known as the Polish Orthodox Church, or Orthodox Church of Poland, is one of the autocephalous Eastern Orthodox churches in full communion. Th ...
in order to use it as a weapon against the anti-communist efforts of the Roman Catholic Church in Poland, and it attempted to control the person who was named as Metropolitan for the Polish Orthodox Church; Metropolitan Dionizy (the post-war head of the POC) was arrested and retired from service after his release.
Following with the forcible conversion of Eastern Catholics in the USSR to Orthodoxy, the Polish government called on the Orthodox church in Poland to assume 'pastoral care
Pastoral care is an ancient model of emotional, social and spiritual support that can be found in all cultures and traditions.
The term is considered inclusive of distinctly non-religious forms of support, as well as support for people from rel ...
' of the eastern Catholics in Poland. After the removal of Metropolitan Dionizy from leadership of the Polish Orthodox Church, Metropolitan Macarius was placed in charge. He was from western Ukraine (previously eastern Poland) and who had been instrumental in the compulsory conversion of eastern Catholics to orthodoxy there. Polish security forces assisted him in suppressing resistance in his taking control of Eastern Catholic parishes. Many eastern Catholics who remained in Poland after the postwar border adjustments were resettled in Western Poland in the newly acquired territories from Germany. The state in Poland gave the POC a greater number of privileges than the Roman Catholic Church in Poland; the state even gave money to this Church, although it often defaulted on promised payments, leading to a perpetual financial crisis for the POC.
Demographics
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposin ...
, a third of Poland's population was composed of ethnic minorities. After the war, however, Poland's minorities were mostly gone, due to the 1945 revision of borders, and the Holocaust
The Holocaust, also known as the Shoah, was the genocide of European Jews during World War II. Between 1941 and 1945, Nazi Germany and its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe; a ...
. Under the National Repatriation Office
Pa┼ästwowy Urz─ģd Repatriacyjny (abbreviated PUR, translated into English as State Repatriation Office, State Office of Repatriation, National Repatriation Office or National Office of Repatriation) was a Polish communist governmental body created ...
(''Pa┼ästwowy Urz─ģd Repatriacyjny''), millions of Poles were forced to leave their homes in the eastern Kresy region and settle in the western former German territories
The former eastern territories of Germany (german: Ehemalige deutsche Ostgebiete) refer in present-day Germany to those territories east of the current eastern border of Germany i.e. OderŌĆōNeisse line which historically had been considered Ger ...
. At the same time, approximately 5 million remaining Germans (about 8 million had already fled or had been expelled and about 1 million had been killed in 1944ŌĆō46) were similarly expelled from those territories into the Allied occupation zones. Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
and Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, ąĀąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░ ąæąĄą╗ą░čĆčāčüčī, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
ian minorities found themselves now mostly within the borders of the Soviet Union; those who opposed this new policy (like the Ukrainian Insurgent Army in the Bieszczady Mountains region) were suppressed by the end of 1947 in the Operation Vistula.
 The population of Jews in Poland, which formed the largest Jewish community in pre-war Europe at about 3.3 million people, was all but destroyed by 1945. Approximately 3 million Jews died of starvation in
The population of Jews in Poland, which formed the largest Jewish community in pre-war Europe at about 3.3 million people, was all but destroyed by 1945. Approximately 3 million Jews died of starvation in ghetto
A ghetto, often called ''the'' ghetto, is a part of a city in which members of a minority group live, especially as a result of political, social, legal, environmental or economic pressure. Ghettos are often known for being more impoverished t ...
s and labor camp
A labor camp (or labour camp, see spelling differences) or work camp is a detention facility where inmates are forced to engage in penal labor as a form of punishment. Labor camps have many common aspects with slavery and with prisons (especi ...
s, were slaughtered at the German Nazi extermination camp
Nazi Germany used six extermination camps (german: Vernichtungslager), also called death camps (), or killing centers (), in Central Europe during World War II to systematically murder over 2.7 million peoplemostly Jewsin the Holocaust. The v ...
s or by the Einsatzgruppen
(, ; also ' task forces') were (SS) paramilitary death squads of Nazi Germany that were responsible for mass murder, primarily by shooting, during World War II (1939ŌĆō1945) in German-occupied Europe. The had an integral role in the im ...
death squads. Between 40,000 and 100,000 Polish Jews survived the Holocaust in Poland, and another 50,000 to 170,000 were repatriated from the Soviet Union, and 20,000 to 40,000 from Germany and other countries. At its postwar peak, there were 180,000 to 240,000 Jews in Poland, settled mostly in Warsaw, Łódź
Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of canti ...
, Krak├│w
Krak├│w (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Krak├│w was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
and Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, rou ...
."Jews in Poland Since 1939" (PDF), YIVO Institute for Jewish Research, ''The YIVO Encyclopedia of Jews in Eastern Europe'', Yale University Press, 2005 According to the national census, which took place on 14 February 1946, population of Poland was 23.9 million, out of which 32% lived in cities and towns, and 68% lived in the countryside. The 1950 census (3 December 1950) showed the population rise to 25 million, and the 1960 census (6 December 1960) placed the population of Poland at 29.7 million. tatistical Yearbook of Poland, Warsaw, 1965/ref> In 1950, Warsaw was again the biggest city, with the population of 804,000 inhabitants. Second was Łódź (pop. 620,000), then Kraków (pop. 344,000), Poznań (pop. 321,000), and Wrocław (pop. 309,000). Females were in the majority in the country. In 1931, there were 105.6 women for 100 men. In 1946, the difference grew to 118.5/100, but in subsequent years, number of males grew, and in 1960, the ratio was 106.7/100. Most Germans were expelled from Poland and the annexed east German territories at the end of the war, while many
Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, ąŻą║čĆą░茹Įčåč¢, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian. The majority ...
, Rusyns and Belarusians
, native_name_lang = be
, pop = 9.5ŌĆō10 million
, image =
, caption =
, popplace = 7.99 million
, region1 =
, pop1 = 600,000ŌĆō768,000
, region2 =
, pop2 ...
lived in territories incorporated into the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
. Small Ukrainian, Belarusian, Slovak, and Lithuanian
Lithuanian may refer to:
* Lithuanians
* Lithuanian language
* The country of Lithuania
* Grand Duchy of Lithuania
* Culture of Lithuania
* Lithuanian cuisine
* Lithuanian Jews as often called "Lithuanians" (''Lita'im'' or ''Litvaks'') by other Jew ...
minorities resided along the borders, and a German minority was concentrated near the southwestern city of Opole
Opole (; german: Oppeln ; szl, Ôpole) ;
* Silesian:
** Silesian PLS alphabet: ''Ôpole''
** Steuer's Silesian alphabet: ''Uopole''
* Silesian German: ''Uppeln''
* Czech: ''Opol├Ł''
* Latin: ''Oppelia'', ''Oppolia'', ''Opulia'' is a city loc ...
and in Masuria
Masuria (, german: Masuren, Masurian: ''Mazur├┐'') is a ethnographic and geographic region in northern and northeastern Poland, known for its 2,000 lakes. Masuria occupies much of the Masurian Lake District. Administratively, it is part of the ...
. Groups of Ukrainians and Polish Ruthenians also lived in western Poland, where they were forcefully resettled by the authorities.
As a result of the migrations and the Soviet Unions radically altered borders under the rule of Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; ŌĆō 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
, the population of Poland became one of the most ethnically homogeneous in the world. Virtually all people in Poland claim Polish nationality, with Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
as their native tongue.
Military
World War II
 The Polish People's Army (LWP) was initially formed during
The Polish People's Army (LWP) was initially formed during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposin ...
as the Polish 1st Tadeusz Ko┼øciuszko Infantry Division, but more commonly known as the Berling Army Berling may refer to:
*Berling, Moselle, France
* Berling (surname)
*Berlingr, a dwarf in the short story " S├Črla ├Š├Īttr"
See also
* Berlin (disambiguation)
* Berlinger (disambiguation)
*Berlingske
''Berlingske'', previously known as ''Berli ...
. Almost half of the soldiers and recruits in the Polish People's Army were Soviet. In March 1945, Red Army officers accounted for approximately 52% of the entire corps (15,492 out of 29,372). Around 4,600 of them remained by July 1946.
It was not the only Polish formation that fought along the Allied side, nor the first one in the East ŌĆō although the first Polish force formed in the USSR, the Anders Army
Anders' Army was the informal yet common name of the Polish Armed Forces in the East in the 1941ŌĆō42 period, in recognition of its commander W┼éadys┼éaw Anders. The army was created in the Soviet Union but, in March 1942, based on an understandi ...
, had by that time moved to Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
. The Polish forces soon grew beyond the 1st Division into two major commands ŌĆō the Polish First Army
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
commanded by Zygmunt Berling, and the Polish Second Army
The Polish Second Army ( pl, Druga Armia Wojska Polskiego, 2. AWP for short) was a Polish Army unit formed in the Soviet Union in 1944 as part of the People's Army of Poland. The organization began in August under the command of generals Karol Ś ...
headed by Karol ┼Üwierczewski. The Polish First Army participated in the VistulaŌĆōOder Offensive and the Battle of Kolberg (1945)
The Battle of Kolberg or Battle of Kołobrzeg (also, battle for Festung Kolberg) was the taking of the city of ''Kolberg'', now the city of Kołobrzeg, in Pomerania by the Soviet Army and its Polish allies from Nazi German forces during the ...
before taking part in its final offensive with the Battle of Berlin
The Battle of Berlin, designated as the Berlin Strategic Offensive Operation by the Soviet Union, and also known as the Fall of Berlin, was one of the last major offensives of the European theatre of World War II.
After the VistulaŌĆō ...
.
After the war
Following the Second World War, the Polish Army was reorganized into six (later seven) main military districts: the Warsaw Military District with its headquarters in Warsaw, theLublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of t ...
Military District, Krak├│w
Krak├│w (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Krak├│w was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
Military District, Łódź
Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of canti ...
Military District, Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John ...
Military District, the Pomeranian Military District
The Pomeranian Military District (Polish acronym POW) was a military district of the Polish Armed Forces from 1945 to 2011. Formally it was subordinate to the Minister of National Defence in the operational matters of defense and detached governm ...
with its headquarters in Toruń
)''
, image_skyline =
, image_caption =
, image_flag = POL Toruń flag.svg
, image_shield = POL Toruń COA.svg
, nickname = City of Angels, Gingerbread city, Copernicus Town
, pushpin_map = Kuyavian-Pom ...
and the Silesian Military District
Silesian Military District ( pl, ┼Ül─ģski Okr─Ög Wojskowy) was one of three military districts in Poland, the other two being the Pomeranian Military District and the Warsaw Military District. All three were disbanded by the end of 2011 due to the ...
in Katowice
Katowice ( , , ; szl, Katowicy; german: Kattowitz, yi, ū¦ūÉųĘūśūóūĢūĢūÖūź, Kattevitz) is the capital city of the Silesian Voivodeship in southern Poland and the central city of the Upper Silesian metropolitan area. It is the 11th most popul ...
.
Throughout the late 1940s and early 50s the Polish Army was under the command of Polish-born Marshal of the Soviet Union Konstantin Rokossovsky, who was intentionally given the title " Marshal of Poland" and was also Minister of National Defense. It was heavily tied into the Soviet military structures and was intended to increase Soviet influence as well as control over the Polish units in case of war. This process, however, was stopped in the aftermath of the Polish October in 1956. Rokossovsky, viewed as a Soviet puppet, was excluded from the Polish United Workers' Party and driven out back to the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
where he remained a hero until death.
Geography
 Geographically, the Polish People's Republic bordered the
Geographically, the Polish People's Republic bordered the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53┬░N to 66┬░N latitude and from ...
to the North; the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
(via the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, ąĀąŠčüčüąĖą╣čüą║ą░čÅ ąĪąŠą▓ąĄčéčüą║ą░čÅ ążąĄą┤ąĄčĆą░čéąĖą▓ąĮą░čÅ ąĪąŠčåąĖą░ą╗ąĖčüčéąĖč湥čüą║ą░čÅ ąĀąĄčüą┐čāą▒ą╗ąĖą║ą░, Ross├Łyskaya Sov├®tskaya Federat├Łvnaya Soci ...
(Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast (russian: ąÜą░ą╗ąĖąĮąĖąĮą│čĆą░╠üą┤čüą║ą░čÅ ąŠ╠üą▒ą╗ą░čüčéčī, translit=Kaliningradskaya oblast') is the westernmost federal subject of Russia. It is a semi-exclave situated on the Baltic Sea. The largest city and administr ...
), Lithuanian
Lithuanian may refer to:
* Lithuanians
* Lithuanian language
* The country of Lithuania
* Grand Duchy of Lithuania
* Culture of Lithuania
* Lithuanian cuisine
* Lithuanian Jews as often called "Lithuanians" (''Lita'im'' or ''Litvaks'') by other Jew ...
, Byelorussian and Ukrainian SSR
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, ąŻą║čĆą░čŚ╠üąĮčüčīą║ą░ ąĀą░ą┤čÅ╠üąĮčüčīą║ą░ ąĪąŠčåč¢ą░ą╗č¢čüčéąĖ╠üčćąĮą░ ąĀąĄčüą┐čā╠üą▒ą╗č¢ą║ą░, ; russian: ąŻą║čĆą░ąĖ╠üąĮčüą║ą░čÅ ąĪąŠą▓ąĄ╠üčéčüą║ą░čÅ ąĪąŠčåąĖą░ą╗ąĖčüčéąĖ╠üč湥čüą║ą░čÅ ąĀąĄčüą┐ ...
s) to the east; Czechoslovakia
, rue, ą¦ąĄčüčīą║ąŠčüą╗ąŠą▓ąĄąĮčīčüą║ąŠ, , yi, ūśū®ūóūøūÉūĪū£ūÉūĢūĢūÉū¦ūÖūÖ,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918ŌĆō19391945ŌĆō1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
to the south and East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
to the west. After World War II, Poland's borders were redrawn, following the decision taken at the Tehran Conference
The Tehran Conference (codenamed Eureka) was a strategy meeting of Joseph Stalin, Franklin Roosevelt, and Winston Churchill from 28 November to 1 December 1943, after the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran. It was held in the Soviet Union's embassy i ...
of 1943 at the insistence of the Soviet Union. Poland lost 77,000 km2 of territory in its eastern regions ( Kresy), gaining instead the smaller but much more industrialized (however ruined) so-called " Regained Territories" east of the Oder-Neisse line.
Administration
The Polish People's Republic was divided into several voivodeships (the Polish unit of administrative division). After World War II, the new administrative divisions were based on the pre-war ones. The areas in the East that were not annexed by the Soviet Union had their borders left almost unchanged. Newly acquired territories in the west and north were organized into the voivodeships ofSzczecin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major s ...
, Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, rou ...
, Olsztyn
Olsztyn ( , ; german: Allenstein ; Old Prussian: ''Aln─üsteini''
* Latin: ''Allenstenium'', ''Holstin'') is a city on the Łyna River in northern Poland. It is the capital of the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship, and is a city with county rights. ...
and partially joined to Gdańsk
Gda┼äsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gdu┼äsk;Stefan Ramu┼ét, ''S┼éownik j─Özyka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Krak├│w 1893, Gda┼äsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Gr├żsse, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
, Katowice Voivodeship, Katowice and Poznań Voivodeship, Poznań voivodeships. Two cities were granted voivodeship status: Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
and Łódź
Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of canti ...
.
In 1950, new voivodeships were created: Koszalin Voivodeship (1950ŌĆō1975), Koszalin ŌĆō previously part of Szczecin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major s ...
, Opole Voivodeship, Opole ŌĆō previously part of Katowice Voivodeship, Katowice, and Zielona G├│ra Voivodeship, Zielona G├│ra ŌĆō previously part of Pozna┼ä Voivodeship, Pozna┼ä, Wroc┼éaw
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, rou ...
and Szczecin
Szczecin (, , german: Stettin ; sv, Stettin ; Latin: ''Sedinum'' or ''Stetinum'') is the capital and largest city of the West Pomeranian Voivodeship in northwestern Poland. Located near the Baltic Sea and the German border, it is a major s ...
voivodeships. In addition, three other cities were granted the voivodeship status: Wrocław
Wrocław (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, rou ...
, Krak├│w
Krak├│w (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Krak├│w was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
and Poznań
Poznań () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John ...
.
In 1973, Poland's voivodeships were changed again. This reorganization of the administrative division of Poland was mainly a result of local government reform acts of 1973 to 1975. In place of three-level administrative division (voivodeship, county, commune), a new two-level administrative division was introduced (49 small voidships and communes). The three smallest voivodeships: Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
, Krak├│w
Krak├│w (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Krak├│w was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
and Łódź
Łódź, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of Łódź Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of canti ...
had a special status of municipal voivodeship; the city mayor (''prezydent miasta'') was also province governor.
References
Bibliography
* * *Notes
Further reading
External links
PRL
at Czas-PRL.pl
Internetowe Muzeum Polski Ludowej
at PolskaLudowa.com
Muzeum PRL
at MuzeumPRL.com
at Komunizm.eu
Propaganda komunistyczna
PRL Tube, a categorized collection of videos from the Polish Communist period
{{DEFAULTSORT:Poland, People's Republic Of Polish People's Republic, Eastern Bloc Former socialist republics Communist states Communism in Poland Soviet satellite states 1947 establishments in Poland 1989 disestablishments in Poland States and territories established in 1947 States and territories disestablished in 1989