Permian South America on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Permian ( ) is a
The ICS International Chronostratigraphic Chart
Episodes 36: 199-204. For most of the 20th century, the Permian was divided into the Early and Late Permian, with the Kungurian being the last stage of the Early Permian. Glenister and colleagues in 1992 proposed a tripartite scheme, advocating that the Roadian-Capitanian was distinct from the rest of the Late Permian, and should be regarded as a separate epoch. The tripartite split was adopted after a formal proposal by Glenister et al. (1999). Historically, most marine biostratigraphy of the Permian was based on
Proposal of Guadalupian and component Roadian, Wordian and Capitanian stages as international standards for the middle Permian series
''Permophiles'', 34, 3–11. The Roadian was named in 1968 in reference to the Road Canyon Member of the
''The Global Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) for the boundary between the Capitanian and Wuchiapingian Stage (Permian)''
Episodes 29(4), pp. 253–262'' The Wuchiapinginan and Changhsingian were first introduced in 1962, by J. Z. Sheng as the "Wuchiaping Formation" and "Changhsing Formation" within the Lopingian series. The GSSP for the base of the Wuchiapingian is located at Penglaitan, Guangxi, China and was ratified in 2004. The boundary is defined by the first appearance of ''Clarkina postbitteri postbitteri'''''' The Changhsingian was originally derived from the Changxing Limestone, a geological unit first named by the Grabau in 1923, ultimately deriving from
 During the Permian, all the
During the Permian, all the
 At the start of the Permian, the Earth was still in the
At the start of the Permian, the Earth was still in the
/ref> In addition to becoming warmer, the climate became notably more arid at the end of the Carboniferous and beginning of the Permian, with a significant trend of increasing aridification being observed over the course of the Cisuralian, particularly during the AWE.

 Insects, which had first appeared and become abundant during the preceding Carboniferous, experienced a dramatic increase in diversification during the Early Permian. Towards the end of the Permian, there was a substantial drop in both origination and extinction rates. The dominant insects during the Permian Period were early representatives of Paleoptera,
Insects, which had first appeared and become abundant during the preceding Carboniferous, experienced a dramatic increase in diversification during the Early Permian. Towards the end of the Permian, there was a substantial drop in both origination and extinction rates. The dominant insects during the Permian Period were early representatives of Paleoptera,
 The terrestrial fossil record of the Permian is patchy and temporally discontinuous. Early Permian records are dominated by equatorial Europe and North America, while those of the Middle and Late Permian are dominated by temperate
The terrestrial fossil record of the Permian is patchy and temporally discontinuous. Early Permian records are dominated by equatorial Europe and North America, while those of the Middle and Late Permian are dominated by temperate
File:EdaphosaurusDB.jpg, '' Edaphosaurus pogonias'' and '' Platyhystrix'' – Early Permian, North America and Europe
File:Dimetr eryopsDB.jpg, '' Dimetrodon grandis'' and ''
 Four
Four  The oldest likely record of Ginkgoales (the group containing ''
The oldest likely record of Ginkgoales (the group containing ''
 The Permian ended with the most extensive extinction event recorded in
The Permian ended with the most extensive extinction event recorded in
Accessed 1 April 2013. Another hypothesis involves ocean venting of hydrogen sulfide gas. Portions of the
University of California offers a more modern Permian stratigraphy
* * ttp://www.geo-lieven.com/erdzeitalter/perm/perm.htm Examples of Permian Fossils
Permian (chronostratigraphy scale)
* {{Authority control Geological periods
geologic period
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochr ...
and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Year#Abbreviations yr and ya, Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 ...
Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic
The Paleozoic (or Palaeozoic) Era is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The name ''Paleozoic'' ( ;) was coined by the British geologist Adam Sedgwick in 1838
by combining the Greek words ''palaiós'' (, "old") and ' ...
Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
.
The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsid
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes reptil ...
s and the sauropsids
Sauropsida ("lizard faces") is a clade of amniotes, broadly equivalent to the class Reptilia. Sauropsida is the sister taxon to Synapsida, the other clade of amniotes which includes mammals as its only modern representatives. Although early sy ...
( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa
Panthalassa, also known as the Panthalassic Ocean or Panthalassan Ocean (from Greek "all" and "sea"), was the superocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea, the latest in a series of supercontinents in the history of Earth. During th ...
. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their amphibian ancestors.
Various authors recognise at least three, and possibly four extinction events in the Permian. The end of the Early Permian ( Cisuralian) saw a major faunal turnover, with most lineages of primitive "pelycosaur
Pelycosaur ( ) is an older term for basal or primitive Late Paleozoic synapsids, excluding the therapsids and their descendants. Previously, the term ''mammal-like reptile'' had been used, and pelycosaur was considered an order, but this is ...
" synapsids becoming extinct, being replaced by more advanced therapsids
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented mo ...
. The end of the Capitanian
In the geologic timescale, the Capitanian is an age or stage of the Permian. It is also the uppermost or latest of three subdivisions of the Guadalupian Epoch or Series. The Capitanian lasted between and million years ago. It was preceded by ...
Stage of the Permian was marked by the major Capitanian mass extinction event
The Capitanian mass extinction event, also known as the end-Guadalupian extinction event or the pre-Lopingian crisis was an extinction event that predated the end-Permian extinction event and occurred around 260 million years ago during a period ...
, associated with the eruption of the Emeishan Traps. The Permian (along with the Paleozoic) ended with the Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic (P–T, P–Tr) extinction event, also known as the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian Extinction and colloquially as the Great Dying, formed the boundary between the Permian and Triassic geologic periods, as ...
, the largest mass extinction in Earth's history (which is the last of the three or four crises that occurred in the Permian), in which nearly 81% of marine species and 70% of terrestrial species died out, associated with the eruption of the Siberian Traps
The Siberian Traps (russian: Сибирские траппы, Sibirskiye trappy) is a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the traps is one of the largest ...
. It took well into the Triassic for life to recover from this catastrophe; on land, ecosystems took 30 million years to recover.
Etymology and history
Prior to the introduction of the term "Permian", rocks of equivalent age in Germany had been named theRotliegend
The Rotliegend, Rotliegend Group or Rotliegendes (german: the underlying red) is a lithostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) of latest Carboniferous to Guadalupian (middle Permian) age that is found in the subsurface of large areas in wes ...
and Zechstein
The Zechstein (German either from ''mine stone'' or ''tough stone'') is a unit of sedimentary rock layers of Middle to Late Permian (Guadalupian to Lopingian) age located in the European Permian Basin which stretches from the east coast of Englan ...
, and in Great Britain as the New Red Sandstone
The New Red Sandstone, chiefly in British geology, is composed of beds of red sandstone and associated rocks laid down throughout the Permian (300 million years ago) to the end of the Triassic (about 200 million years ago), that under ...
.
The term "Permian" was introduced into geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Ea ...
in 1841 by Sir Roderick Impey Murchison, president of the Geological Society of London
The Geological Society of London, known commonly as the Geological Society, is a learned society based in the United Kingdom. It is the oldest national geological society in the world and the largest in Europe with more than 12,000 Fellows.
Fe ...
, after extensive Russian explorations undertaken with Édouard de Verneuil
Philippe Édouard Poulletier de Verneuil (13 February 180529 May 1873) was a French paleontologist.Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
in the years 1840 and 1841. Murchison identified "vast series of beds of marl, schist, limestone, sandstone and conglomerate” that succeeded Carboniferous strata in the region. Murchison, in collaboration with Russian geologists, named the period after the surrounding Russian region and the city of Perm, which itself take their name from the medieval kingdom of Permia
Great Perm, or simply Perm, in Latin ''Permia'', was a medieval historical region in what is now the Perm Krai of the Russian Federation. Cherdyn is said to have been its capital.
The origin of the name ''Perm'' is uncertain. Most common expl ...
that occupied the same region hundreds of years prior, and which now lies in the Perm Krai
Perm Krai (russian: Пе́рмский край, r=Permsky kray, p=ˈpʲɛrmskʲɪj ˈkraj, ''Permsky krai'', , ''Perem lador'') is a federal subject of Russia (a krai) that came into existence on December 1, 2005 as a result of the 2004 re ...
of Russia. Between 1853 and 1867, Jules Marcou
Jules Marcou (April 20, 1824 – April 17, 1898) was a French-Swiss-American geologist.
Biography
He was born at Salins, in the ''département'' of Jura, in France. He was educated at Besançon and at the Collège Saint Louis, Paris. After co ...
recognised Permian strata in a large area of North America from the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
to the Colorado River
The Colorado River ( es, Río Colorado) is one of the principal rivers (along with the Rio Grande) in the Southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The river drains an expansive, arid watershed that encompasses parts of seven U.S. s ...
and proposed the name "Dyassic", from "Dyas" and "Trias", though Murchison rejected this in 1871. The Permian system was controversial for over a century after its original naming, with the United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, ...
until 1941 considering the Permian a subsystem of the Carboniferous equivalent to the Mississippian and Pennsylvanian.
Geology
The Permian Period is divided into threeepochs
In chronology and periodization, an epoch or reference epoch is an instant in time chosen as the origin of a particular calendar era. The "epoch" serves as a reference point from which time is measured.
The moment of epoch is usually decided by ...
, from oldest to youngest, the Cisuralian, Guadalupian, and Lopingian. Geologists divide the rocks of the Permian into a stratigraphic
Stratigraphy is a branch of geology concerned with the study of rock layers (strata) and layering (stratification). It is primarily used in the study of sedimentary and layered volcanic rocks.
Stratigraphy has three related subfields: lithostra ...
set of smaller units called stages
Stage or stages may refer to:
Acting
* Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions
* Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage"
* ''The Stage'', a weekly British theatre newspaper
* S ...
, each formed during corresponding time intervals called ages. Stages can be defined globally or regionally. For ''global'' stratigraphic correlation, the International Commission on Stratigraphy
The International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), sometimes referred to unofficially as the "International Stratigraphic Commission", is a daughter or major subcommittee grade scientific daughter organization that concerns itself with stratigr ...
(ICS) ratify global stages based on a Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point
A Global Boundary Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) is an internationally agreed upon reference point on a stratigraphic section which defines the lower boundary of a stage on the geologic time scale. The effort to define GSSPs is conducted b ...
(GSSP) from a single formation
Formation may refer to:
Linguistics
* Back-formation, the process of creating a new lexeme by removing or affixes
* Word formation, the creation of a new word by adding affixes
Mathematics and science
* Cave formation or speleothem, a secondar ...
(a stratotype A stratotype or type section in geology is the physical location or outcrop of a particular reference exposure of a stratigraphic sequence or stratigraphic boundary. If the stratigraphic unit is layered, it is called a stratotype, whereas the stan ...
) identifying the lower boundary of the stage. The ages of the Permian, from youngest to oldest, are:Cohen, K.M., Finney, S.C., Gibbard, P.L. & Fan, J.-X. (2013; updatedThe ICS International Chronostratigraphic Chart
Episodes 36: 199-204. For most of the 20th century, the Permian was divided into the Early and Late Permian, with the Kungurian being the last stage of the Early Permian. Glenister and colleagues in 1992 proposed a tripartite scheme, advocating that the Roadian-Capitanian was distinct from the rest of the Late Permian, and should be regarded as a separate epoch. The tripartite split was adopted after a formal proposal by Glenister et al. (1999). Historically, most marine biostratigraphy of the Permian was based on
ammonoids
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish) ...
; however, ammonoid localities are rare in Permian stratigraphic sections, and species characterise relatively long periods of time. All GSSPs for the Permian are based around the first appearance datum
First appearance datum (FAD) is a term used by geologists and paleontologists to designate the first appearance of a species in the geologic record. FADs are determined by identifying the geologically oldest fossil discovered, to date, of a particu ...
of specific species of conodont, an enigmatic group of jawless chordate
A chordate () is an animal of the phylum Chordata (). All chordates possess, at some point during their larval or adult stages, five synapomorphies, or primary physical characteristics, that distinguish them from all the other taxa. These fi ...
s with hard tooth-like oral elements. Conodonts are used as index fossils
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Bio ...
for most of the Palaeozoic and the Triassic.
Cisuralian
The Cisuralian Series is named after the strata exposed on the western slopes of the Ural Mountains in Russia and Khazakhstan. The name was proposed by J. B. Waterhouse in 1982 to comprise the Asselian, Sakmarian, and Artinskian stages. The Kungurian was later added to conform to the Russian "Lower Permian".Albert Auguste Cochon de Lapparent
Albert Auguste Cochon de Lapparent (30 December 18395 May 1908) was a French geologist.
Life
He was born at Bourges. After studying at the École polytechnique from 1858 to 1860 he became ''ingénieur au corps des mines'', and took part in draw ...
in 1900 had proposed the "Uralian Series", but the subsequent inconsistent usage of this term meant that it was later abandoned.
The Asselian was named by the Russian stratigrapher V.E. Ruzhenchev in 1954, after the Assel River
Assel (russian: Ассель; ba, Әселе, ''Äsele'') is a river in Russia, that flows through Bashkortostan and the Orenburg Oblast. The river mouth is 14 km along the left bank of the Bolshoy Ik. The river is 51 km long and th ...
in the southern Ural Mountains. The GSSP for the base of the Asselian is located in the Aidaralash River valley near Aqtöbe
Aktobe ( kz, Ақтөбе, Aqtöbe; russian: Актобе, Aktobe) is a city on the Ilek River in Kazakhstan. It is the administrative center of Aktobe Region. In 2020, it had a population of 500,757 people.
Aktobe is located in the west of K ...
, Kazakhstan, which was ratified in 1996. The beginning of the stage is defined by the first appearance of '' Streptognathodus postfusus.''
The Sakmarian is named in reference to the Sakmara River
The Sakmara (russian: Сакмара; ba, Һаҡмар, Haqmar) is a river in Russia that drains the southern tip of the Ural Mountains south into the river Ural. It is long, and has a drainage basin of . It is a right tributary of the Ural, whic ...
in the southern Urals, and was coined by Alexander Karpinsky in 1874. The GSSP for the base of the Sakmarian is located at the Usolka section in the southern Urals, which was ratified in 2018. The GSSP is defined by the first appearance of '' Sweetognathus binodosus''.
The Artinskian was named after the city of Arti in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia. It was named by Karpinsky in 1874. The Artinskian currently lacks a defined GSSP. The proposed definition for the base of the Artinskian is the first appearance of ''Sweetognathus aff. S. whitei.''
The Kungurian takes its name after Kungur
Kungur (russian: Кунгу́р) is a town in the southeast of Perm Krai, Russia, located in the Ural Mountains at the confluence of the rivers Iren and Shakva with the Sylva ( Kama's basin). Population: 64,800 (1959); 36,000 (1939).
His ...
, a city in Perm Krai. The stage was introduced by Alexandr Antonovich Stukenberg in 1890. The Kungurian currently lacks a defined GSSP. Recent proposals have suggested the appearance of ''Neostreptognathodus pnevi'' as the lower boundary.
Guadalupian
The Guadalupian Series is named after theGuadalupe Mountains
The Guadalupe Mountains ( es, Sierra de Guadalupe) are a mountain range located in West Texas and southeastern New Mexico. The range includes the highest summit in Texas, Guadalupe Peak, , and the "signature peak" of West Texas, El Capitan, both ...
in Texas and New Mexico, where extensive marine sequences of this age are exposed. It was named by George Herbert Girty in 1902.Glenister, B.F., Wardlaw, B.R. et al. 1999Proposal of Guadalupian and component Roadian, Wordian and Capitanian stages as international standards for the middle Permian series
''Permophiles'', 34, 3–11. The Roadian was named in 1968 in reference to the Road Canyon Member of the
Word Formation
In linguistics, word formation is an ambiguous term that can refer to either:
* the processes through which words can change (i.e. morphology), or
* the creation of new lexemes in a particular language
Morphological
A common method of word for ...
in Texas. The GSSP for the base of the Roadian is located 42.7m above the base of the Cutoff Formation
The Cutoff Formation is a geologic formation in Texas and New Mexico, US. It preserves fossils dating back to the Permian period.
Description
The Cutoff Formation consists of feet of thin limestone beds interbedded with dark shale and sandsto ...
in Stratotype Canyon, Guadalupe Mountains, Texas, and was ratified in 2001. The beginning of the stage is defined by the first appearance of ''Jinogondolella nankingensis''.
The Wordian was named in reference to the Word Formation by Johan August Udden in 1916, Glenister and Furnish in 1961 was the first publication to use it as a chronostratigraphic term as a substage of the Guadalupian Stage. The GSSP for the base of the Wordian is located in Guadalupe Pass, Texas, within the sediments of the Getaway Limestone Member of the Cherry Canyon Formation, which was ratified in 2001. The base of the Wordian is defined by the first appearance of the conodont ''Jinogondolella aserrata.''
The Capitanian is named after the Capitan Reef in the Guadalupe Mountains of Texas, named by George Burr Richardson
George Burr Richardson, MS, PhD (1872 - 1949) was a geologist who, among other endeavors, participated in extensive field work for the United States Geological Survey (USGS) in Alaska, Pennsylvania, California, Texas, Colorado, and Utah.
In Texas, ...
in 1904, and first used in a chronostratigraphic sense by Glenister and Furnish in 1961 as a substage of the Guadalupian Stage. The Captianian was ratified as an international stage by the ICS in 2001. The GSSP for the base of the Captianian is located at Nipple Hill in the southeast Guadalupe Mountains of Texas, and was ratified in 2001, the beginning of the stage is defined by the first appearance of ''Jinogondolella postserrata.''
Lopingian
The Lopingian was first introduced by Amadeus William Grabau in 1923 as the “Loping Series” afterLeping
Leping () is a county-level city in the northeast of Jiangxi province, China. It is under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Jingdezhen.
Administrative divisions
Leping City has 2 subdistricts, 14 towns and 2 townships.
;2 subdis ...
, Jiangxi
Jiangxi (; ; formerly romanized as Kiangsi or Chianghsi) is a landlocked province in the east of the People's Republic of China. Its major cities include Nanchang and Jiujiang. Spanning from the banks of the Yangtze river in the north int ...
, China. Originally used as a lithostraphic unit, T.K. Huang in 1932 raised the Lopingian to a series, including all Permian deposits in South China that overlie the Maokou Limestone. In 1995, a vote by the Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy of the ICS adopted the Lopingian as an international standard chronostratigraphic unit.''; 2006''The Global Stratotype Section and Point (GSSP) for the boundary between the Capitanian and Wuchiapingian Stage (Permian)''
Episodes 29(4), pp. 253–262'' The Wuchiapinginan and Changhsingian were first introduced in 1962, by J. Z. Sheng as the "Wuchiaping Formation" and "Changhsing Formation" within the Lopingian series. The GSSP for the base of the Wuchiapingian is located at Penglaitan, Guangxi, China and was ratified in 2004. The boundary is defined by the first appearance of ''Clarkina postbitteri postbitteri'''''' The Changhsingian was originally derived from the Changxing Limestone, a geological unit first named by the Grabau in 1923, ultimately deriving from
Changxing County
() is a county of the prefecture-level city of Huzhou, in the northwest of Zhejiang province, China. Situated on the southwest shore of Lake Tai, it borders the provinces of Jiangsu to the north and Anhui to the west. It has a total area of an ...
, Zhejiang
Zhejiang ( or , ; , Chinese postal romanization, also romanized as Chekiang) is an East China, eastern, coastal Provinces of China, province of the People's Republic of China. Its capital and largest city is Hangzhou, and other notable citie ...
.The GSSP for the base of the Changhsingian is located 88 cm above the base of the Changxing Limestone in the Meishan D section, Zhejiang, China and was ratified in 2005, the boundary is defined by the first appearance of ''Clarkina wangi.''
The GSSP for the base of the Triassic is located at the base of Bed 27c at the Meishan D section, and was ratified in 2001. The GSSP is defined by the first appearance of the conodont '' Hindeodus parvus''.
Regional stages
The Russian Tatarian Stage includes the Lopingian, Capitanian and part of the Wordian, while the underlying Kazanian includes the rest of the Wordian as well at the Roadian. In North America, the Permian is divided into the Wolfcampian (which includes the Nealian and the Lenoxian stages) corresponding to the Asselian through lower Kungurian; the Leonardian (Hessian and Cathedralian stages) corresponding to the upper Kungurian; the Guadalupian; and the Ochoan, corresponding to the Lopingian.Paleogeography
 During the Permian, all the
During the Permian, all the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
's major landmasses were collected into a single supercontinent known as Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
, with the microcontinental terranes of Cathaysia
Cathaysia was a microcontinent or a group of terranes that rifted off Gondwana during the Late Paleozoic. They mostly correspond to modern territory of China, which were split into the North China and South China blocks.
Terminology
The terms " ...
to the east. Pangaea straddled the equator and extended toward the poles, with a corresponding effect on ocean currents in the single great ocean ("Panthalassa
Panthalassa, also known as the Panthalassic Ocean or Panthalassan Ocean (from Greek "all" and "sea"), was the superocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea, the latest in a series of supercontinents in the history of Earth. During th ...
", the "universal sea"), and the Paleo-Tethys Ocean
The Paleo-Tethys or Palaeo-Tethys Ocean was an ocean located along the northern margin of the paleocontinent Gondwana that started to open during the Middle Cambrian, grew throughout the Paleozoic, and finally closed during the Late Triassic; exi ...
, a large ocean that existed between Asia and Gondwana. The Cimmeria continent rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-grabe ...
ed away from Gondwana and drifted north to Laurasia, causing the Paleo-Tethys Ocean to shrink. A new ocean was growing on its southern end, the Neotethys Ocean, an ocean that would dominate much of the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
Era. The Central Pangean Mountains
The Central Pangean Mountains were an extensive northeast–southwest trending mountain range in the central portion of the supercontinent Pangaea during the Carboniferous, Permian and Triassic periods. They were formed as a result of collision ...
, which began forming due to the collision of Laurasia and Gondwana during the Carboniferous, reached their maximum height during the early Permian around 295 million years ago, comparable to the present Himalayas
The Himalayas, or Himalaya (; ; ), is a mountain range in Asia, separating the plains of the Indian subcontinent from the Tibetan Plateau. The range has some of the planet's highest peaks, including the very highest, Mount Everest. Over 10 ...
, but became heavily eroded as the Permian progressed. The Kazakhstania
Kazakhstania ( kk, Qazaqstaniya), the Kazakh terranes, or the Kazakhstan Block, is a geological region in Central Asia which consists of the area roughly centered on Lake Balkhash, north and east of the Aral Sea, south of the Siberian craton and ...
block collided with Baltica during the Cisuralian, while the North China Craton
The North China Craton is a continental crustal block with one of Earth's most complete and complex records of igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic processes. It is located in northeast China, Inner Mongolia, the Yellow Sea, and North Korea. Th ...
, the South China Block
The Yangtze Plate, also called the South China Block or the South China Subplate, comprises the bulk of southern China. It is separated on the east from the Okinawa Plate by a rift that forms the Okinawa Trough which is a back-arc basin, on the so ...
and Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
fused to each other and Pangea by the end of the Permian.
Large continental landmass interiors experience climates with extreme variations of heat and cold (" continental climate") and monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal osci ...
conditions with highly seasonal rainfall patterns. Deserts seem to have been widespread on Pangaea. Such dry conditions favored gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, '' Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμν ...
s, plants with seeds enclosed in a protective cover, over plants such as fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes exce ...
s that disperse spores in a wetter environment. The first modern trees ( conifers, ginkgo
''Ginkgo'' is a genus of non-flowering seed plants. The scientific name is also used as the English name. The order to which it belongs, Ginkgoales, first appeared in the Permian, 270 million years ago, and is now the only living genus with ...
s and cycad
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants of a species are either male o ...
s) appeared in the Permian.
Three general areas are especially noted for their extensive Permian deposits—the Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
(where Perm itself is located), China, and the southwest of North America, including the Texas red beds. The Permian Basin in the U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
s of Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
and New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ke ...
is so named because it has one of the thickest deposits of Permian rocks in the world.
Paleoceanography
Sea levels dropped slightly during the earliest Permian (Asselian). The sea level was stable at several tens of metres above present during the Early Permian, but there was a sharp drop beginning during the Roadian, culminating in the lowest sea level of the entire Palaeozoic at around present sea level during the Wuchiapingian, followed by a slight rise during the Changhsingian.Climate
Late Paleozoic icehouse
The late Paleozoic icehouse, also known as the Late Paleozoic Ice Age (LPIA) and formerly known as the Karoo ice age, was an ice age that began in the Late Devonian and ended in the Late Permian, occurring from 360 to 255 million years ago (Mya), ...
, which began in the latest Devonian. At the beginning of the Pennsylvanian around 323 million years ago, glaciers began to form around the South Pole
The South Pole, also known as the Geographic South Pole, Terrestrial South Pole or 90th Parallel South, is one of the two points where Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface. It is the southernmost point on Earth and lies antipod ...
, which would grow to cover a vast area. This area extended from the southern reaches of the Amazon basin and covered large areas of southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number o ...
, as well as most of Australia and Antarctica. Cyclothems
In geology, cyclothems are alternating stratigraphy, stratigraphic sequences of Marine (ocean), marine and non-marine sediments, sometimes interbedded with coal seams. Historically, the term was defined by the European coal geologists who worked ...
indicate that the size of the glaciers were controlled by Milankovitch cycles
Milankovitch cycles describe the collective effects of changes in the Earth's movements on its climate over thousands of years. The term was coined and named after Serbian geophysicist and astronomer Milutin Milanković. In the 1920s, he hypot ...
akin to recent ice age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gre ...
s, with glacial period
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betwe ...
s and interglacials. The oldest cyclotherms are around 313 million years old while the youngest are around 293 million years old, corresponding to the coldest part of the Late Paleozoic icehouse. Deep ocean temperatures during this time were cold due to the influx of cold bottom waters generated by seasonal melting of the ice cap. By 287 million years ago, temperatures warmed and the South Pole ice cap retreated in what was known as the Artinskian Warming Event (AWE), though glaciers would remain present in the upland regions of eastern Australia, the Transantarctic Mountains
The Transantarctic Mountains (abbreviated TAM) comprise a mountain range of uplifted (primarily sedimentary) rock in Antarctica which extend, with some interruptions, across the continent from Cape Adare in northern Victoria Land to Coats Land. ...
, and the mountainous regions of far northern Siberia until the end of the Permian. The Permian was cool in comparison to most other geologic time periods, with modest Pole to Equator temperature gradients. This was interrupted by the Emeishan Thermal Excursion in the late part of the Capitanian, around 260 million years ago, corresponding to the eruption of the Emeishan Traps. The end of the Permian is marked by the much larger temperature excursion at the Permian-Triassic boundary, corresponding to the eruption of the Siberian Traps
The Siberian Traps (russian: Сибирские траппы, Sibirskiye trappy) is a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the traps is one of the largest ...
, which released more than 5 teratonnes of CO2 , more than doubling atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations.Alt URL/ref> In addition to becoming warmer, the climate became notably more arid at the end of the Carboniferous and beginning of the Permian, with a significant trend of increasing aridification being observed over the course of the Cisuralian, particularly during the AWE.
Life

Marine invertebrates
Permian marine deposits are rich infossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved ...
mollusks, echinoderm
An echinoderm () is any member of the phylum Echinodermata (). The adults are recognisable by their (usually five-point) radial symmetry, and include starfish, brittle stars, sea urchins, sand dollars, and sea cucumbers, as well as the s ...
s, and brachiopod
Brachiopods (), phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of trochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, w ...
s. Brachiopods were highly diverse during the Permian. The extinct order Productida was the predominant group of Permian brachiopods, accounting for up to about half of all Permian brachiopod genera. Conodonts experienced their lowest diversity of their entire evolutionary history during the Permian. Amongst ammonoids
Ammonoids are a group of extinct marine mollusc animals in the subclass Ammonoidea of the class Cephalopoda. These molluscs, commonly referred to as ammonites, are more closely related to living coleoids (i.e., octopuses, squid and cuttlefish) ...
, Goniatitida
Goniatids, informally goniatites, are ammonoid cephalopods that form the order Goniatitida, derived from the more primitive Agoniatitida during the Middle Devonian some 390 million years ago (around Eifelian stage). Goniatites (goniatitids) sur ...
were a major group during the Early-Mid Permian, but declined during the Late Permian. Members of the order Prolecanitida
Prolecanitida is an order of extinct ammonoid cephalopods with discoidal to thinly lenticular shells with goniatitic or ceratitic sutures and which retained the simple retrochoanitic siphuncle with backward extending septal necks. As typical fo ...
were less diverse. The Ceratitida
Ceratitida is an order that contains almost all ammonoid cephalopod genera from the Triassic as well as ancestral forms from the Upper Permian, the exception being the phylloceratids which gave rise to the great diversity of post Triassic ammon ...
originated from the family Daraelitidae
The Daraelitidae form a family in the ammonoid order Prolecanitida from the Upper Mississippian - Middle Permian characterized by discoidal shells with no prominent sculpture, moderately large umbilicus, and goniatitic or ceratitic sutures with ...
within Prolecanitida during the mid-Permian, and extensively diversified during the Late Permian. Only three families of trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the ...
are known from the Permian, Proetidae, Brachymetopidae and Phillipsiidae. Diversity, origination and extinction rates during the Early Permian were low. Trilobites underwent a diversification during the Kungurian-Wordian, the last in their evolutionary history, before declining during the Late Permian. By the Changhsingian, only a handful (4-6) genera remained.
Terrestrial biota
Terrestrial life in the Permian included diverse plants,fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s, and various types of tetrapods
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids (reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids ( pelycosaurs, extinct therapsi ...
. The period saw a massive desert covering the interior of Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
. The warm zone spread in the northern hemisphere, where extensive dry desert appeared. The rocks formed at that time were stained red by iron oxides, the result of intense heating by the sun of a surface devoid of vegetation cover. A number of older types of plants and animals died out or became marginal elements.
The Permian began with the Carboniferous flora still flourishing. About the middle of the Permian a major transition in vegetation began. The swamp-loving lycopod
Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants known as lycopods, lycophytes or other terms including the component lyco-. Members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts. They have dichotomously branching s ...
trees of the Carboniferous, such as ''Lepidodendron
''Lepidodendron'' is an extinct genus of primitive vascular plants belonging to the family Lepidodendraceae, part of a group of Lycopodiopsida known as scale trees or arborescent lycophytes, related to quillworts and lycopsids (club mosses). Th ...
'' and ''Sigillaria
''Sigillaria'' is a genus of extinct, spore-bearing, arborescent (tree-like) plants. It was a lycopodiophyte, and is related to the lycopsids, or club-mosses, but even more closely to quillworts, as was its associate ''Lepidodendron''.
Fossil ...
'', were progressively replaced in the continental interior by the more advanced seed ferns and early conifers as a result of the Carboniferous rainforest collapse. At the close of the Permian, lycopod and equisete swamps reminiscent of Carboniferous flora survived only on a series of equatorial islands in the Paleo-Tethys Ocean
The Paleo-Tethys or Palaeo-Tethys Ocean was an ocean located along the northern margin of the paleocontinent Gondwana that started to open during the Middle Cambrian, grew throughout the Paleozoic, and finally closed during the Late Triassic; exi ...
that later would become South China.
The Permian saw the radiation of many important conifer groups, including the ancestors of many present-day families. Rich forests were present in many areas, with a diverse mix of plant groups. The southern continent saw extensive seed fern forests of the ''Glossopteris
''Glossopteris'' tymology: from Ancient Greek γλῶσσα (glôssa, " tongue ") + πτερίς (pterís, " fern ")is the largest and best-known genus of the extinct Permian order of seed ferns known as Glossopteridales (also known as Arberia ...
'' flora. Oxygen levels were probably high there. The ginkgos and cycad
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants of a species are either male o ...
s also appeared during this period.
Insects
 Insects, which had first appeared and become abundant during the preceding Carboniferous, experienced a dramatic increase in diversification during the Early Permian. Towards the end of the Permian, there was a substantial drop in both origination and extinction rates. The dominant insects during the Permian Period were early representatives of Paleoptera,
Insects, which had first appeared and become abundant during the preceding Carboniferous, experienced a dramatic increase in diversification during the Early Permian. Towards the end of the Permian, there was a substantial drop in both origination and extinction rates. The dominant insects during the Permian Period were early representatives of Paleoptera, Polyneoptera
The cohort Polyneoptera is a proposed taxonomic ranking for the Orthoptera (grasshoppers, crickets, etc.) and all other Neopteran insects believed to be more closely related to Orthoptera than to any other insect orders. These winged insects, no ...
, and Paraneoptera
Paraneoptera or Acercaria is a superorder of insects which includes lice (bark lice and true lice), thrips, and hemipterans, the true bugs. It also includes the extinct order Permopsocida, known from fossils dating from the Early Permian to the ...
. Palaeodictyopteroidea
The Palaeodictyopteroidea or Paleodictyopterida are an extinct superorder of Palaeozoic beaked insects, characterised by unique mouthparts consisting of 5 stylets. They represent the first important terrestrial herbivores, and the first major gr ...
, which had represented the dominant group of insects during the Carboniferous, declined during the Permian. This is likely due to competition by Hemiptera, due to their similar mouthparts and therefore ecology. Primitive relatives of damselflies and dragonflies
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threa ...
( Meganisoptera), which include the largest flying insects of all time, also declined during the Permian. Holometabola
Endopterygota (from Ancient Greek ''endon'' 'inner' + ''pterón'' 'wing' + New Latin ''-ota'' 'having'), also known as Holometabola, is a superorder of insects within the infraclass Neoptera that go through distinctive larval, pupal, and adult st ...
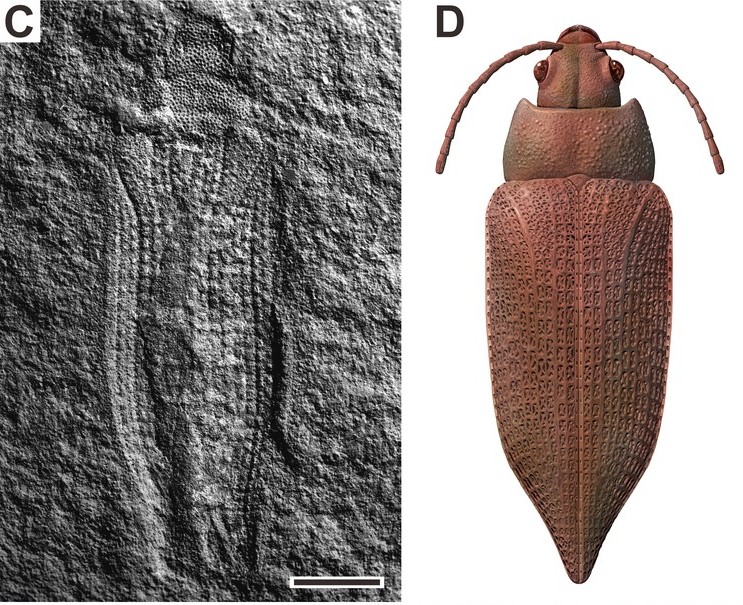
, the largest group of modern insects, also diversified during this time. The earliest known beetle
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 describ ...
s, appear at the beginning of the Permian. Early beetles such as members of Permocupedidae likely xylophagous
Xylophagy is a term used in ecology to describe the habits of an herbivorous animal whose diet consists primarily (often solely) of wood. The word derives from Greek ''ξυλοφάγος'' (''xulophagos'') "eating wood", from ''ξύλον'' (') ...
feeding on decaying wood. Several lineages, such as Schizophoridae expanded into aquatic habitats by the Late Permian. Members of the modern orders Archostemata and Adephaga are known from the Late Permian. Complex wood boring traces found in the Late Permian of China suggest that members of Polyphaga, the most diverse group of modern beetles, were also present in the Permian.
Tetrapods
 The terrestrial fossil record of the Permian is patchy and temporally discontinuous. Early Permian records are dominated by equatorial Europe and North America, while those of the Middle and Late Permian are dominated by temperate
The terrestrial fossil record of the Permian is patchy and temporally discontinuous. Early Permian records are dominated by equatorial Europe and North America, while those of the Middle and Late Permian are dominated by temperate Karoo Supergroup
The Karoo Supergroup is the most widespread stratigraphic unit in Africa south of the Kalahari Desert. The supergroup consists of a sequence of units, mostly of nonmarine origin, deposited between the Late Carboniferous and Early Jurassic, a peri ...
sediments of South Africa and the Ural region of European Russia. Early Permian terrestrial faunas of North America and Europe were dominated by primitive pelycosaur
Pelycosaur ( ) is an older term for basal or primitive Late Paleozoic synapsids, excluding the therapsids and their descendants. Previously, the term ''mammal-like reptile'' had been used, and pelycosaur was considered an order, but this is ...
synapsid
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes reptil ...
s including the herbivorous edaphosaurids
Edaphosauridae is a family of mostly large (up to 3 meters or more) Late Carboniferous to Early Permian synapsids. Edaphosaur fossils are so far known only from North America and Europe.
Characteristics
They were the earliest known herbivorous a ...
, and carnivorous sphenacodontids, diadectids
Diadectidae is an extinct family of early tetrapods that lived in what is now North America and Europe during the Late Carboniferous and Early Permian in Asia during the Late Permian. They were the first herbivorous tetrapods, and also the first ...
and amphibians.Huttenlocker, A. K., and E. Rega. 2012. The Paleobiology and Bone Microstructure of Pelycosaurian-grade Synapsids. Pp. 90–119 in A. Chinsamy (ed.) Forerunners of Mammals: Radiation, Histology, Biology. Indiana University Press.
Amniotes
A faunal turnover occurred at the transition between the Cisuralian and Guadalupian, with the decline of amphibians and the replacement of pelycosaurs with more advancedtherapsid
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more ...
s. If terrestrial deposition ended around the end of the Cisuralian in North America and began in Russia during the early Guadalupian, a continuous record of the transition is not preserved. Uncertain dating has led to suggestions that there is a global hiatus in the terrestrial fossil record during the late Kungurian and early Roadian, referred to as "Olson's Gap" that obscures the nature of the transition. Other proposals have suggested that the North American and Russian records overlap, with the latest terrestrial North American deposition occurring during the Roadian, suggesting that there was an extinction event, dubbed "Olson's Extinction
Olson's Extinction was a mass extinction that occurred in the late Cisuralian or early Guadalupian of the Permian period and which predated the Permian–Triassic extinction event.
It is named after Everett C. Olson. There was a sudden change b ...
". The Middle Permian faunas of South Africa and Russia are dominated by therapsid
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more ...
s, most abundantly by the diverse Dinocephalia
Dinocephalians (terrible heads) are a clade of large-bodied early therapsids that flourished in the Early and Middle Permian between 279.5 and 260 million years ago (Ma), but became extinct during the Capitanian mass extinction event. Dinocephal ...
. Dinocephalians become extinct at the end of the Middle Permian, during the Capitanian mass extinction event
The Capitanian mass extinction event, also known as the end-Guadalupian extinction event or the pre-Lopingian crisis was an extinction event that predated the end-Permian extinction event and occurred around 260 million years ago during a period ...
. Late Permian faunas are dominated by advanced therapsids such as the predatory sabertoothed gorgonopsia
Gorgonopsia (from the Greek Gorgon, a mythological beast, and 'aspect') is an extinct clade of sabre-toothed therapsids from the Middle to Upper Permian roughly 265 to 252 million years ago. They are characterised by a long and narrow skull, a ...
ns and herbivorous beaked dicynodont
Dicynodontia is an extinct clade of anomodonts, an extinct type of non-mammalian therapsid. Dicynodonts were herbivorous animals with a pair of tusks, hence their name, which means 'two dog tooth'. Members of the group possessed a horny, typic ...
s, alongside large herbivorous pareiasaur parareptiles. The Archosauromorpha, the group of reptiles that would give rise to the pseudosuchia
Pseudosuchia is one of two major divisions of Archosauria, including living crocodilians and all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds. Pseudosuchians are also informally known as "crocodilian-line archosaurs". Prior to ...
ns, dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s, and pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 ...
s in the following Triassic, first appeared and diversified during the Late Permian, including the first appearance of the Archosauriformes
Archosauriformes (Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles that developed from archosauromorph ancestors some time in the Latest Permian (roughly 252 million years ago). It was defined by Jacques Gauthier ...
during the latest Permian. Cynodonts, the group of therapsids ancestral to modern mammals, first appeared and gained a worldwide distribution during the Late Permian. Another group of therapsids, the therocephalia
Therocephalia is an extinct suborder of eutheriodont therapsids (mammals and their close relatives) from the Permian and Triassic. The therocephalians ("beast-heads") are named after their large skulls, which, along with the structure of their ...
ns (such as ''Lycosuchus
''Lycosuchus'' ("wolf crocodile") is an extinct genus of carnivorous therocephalians which lived in the Middle Permian 265—260 Ma existing for approximately . As a member of the Lycosuchidae, the genus represents one of the earliest divergi ...
''), arose in the Middle Permian. There were no flying vertebrates, though the extinct lizard like reptile family Weigeltisauridae
Weigeltisauridae is a family of gliding neodiapsid reptiles that lived during the Late Permian, between 258 and 252 million years ago. Fossils of weigeltisaurids have been found in Madagascar, Germany, Great Britain, and Russia. A possible weigelt ...
from the Late Permian had extendable wings like modern gliding lizards, and are the oldest known gliding vertebrates.
Synapsid
Synapsids + (, 'arch') > () "having a fused arch"; synonymous with ''theropsids'' (Greek, "beast-face") are one of the two major groups of animals that evolved from basal amniotes, the other being the sauropsids, the group that includes reptil ...
s (the group that would later include mammals) thrived and diversified greatly at this time. Permian synapsids included some large members such as '' Dimetrodon''. The special adaptations of synapsids enabled them to flourish in the drier climate of the Permian and they grew to dominate the vertebrates.
Amphibians
Permian stem-amniotes consisted oftemnospondyli
Temnospondyli (from Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carb ...
, lepospondyli
Lepospondyli is a diverse taxon of early tetrapods. With the exception of one late-surviving lepospondyl from the Late Permian of Morocco ('' Diplocaulus minumus''), lepospondyls lived from the Early Carboniferous ( Mississippian) to the Early Pe ...
and batrachosaurs. Temnospondyls reached a peak of diversity in the Cisuralian, with a substantial decline during the Guadalupian-Lopingian following Olson's extinction, with the family diversity dropping below Carboniferous levels.
Embolomeres, a group of aquatic crocodile-like reptilliomorphs that previously had its last records in the Cisuralian, are now known to have persisted into the Lopingian in China.
Modern amphibians ( lissamphibians) are suggested to have originated during Permian, descending from a lineage of dissorophoid
Dissorophoideans are a clade of medium-sized, temnospondyl amphibians that appeared during the Moscovian in Euramerica, and continued through to the Late Permian and the Early Triassic of Gondwana. They are distinguished by various details of the ...
temnospondyls.
Eryops
''Eryops'' (; from Greek , , 'drawn-out' + , , 'face', because most of its skull was in front of its eyes) is a genus of extinct, amphibious temnospondyls. It contains the single species , the fossils of which are found mainly in early Permian (a ...
'' – Early Permian, North America
File:Ocher fauna DB.jpg, Ocher fauna, '' Estemmenosuchus uralensis'' and ''Eotitanosuchus
''Eotitanosuchus'' ("dawn giant crocodile") is an extinct genus of biarmosuchian therapsids whose fossils were found in the town of Ochyor in Perm Krai, Russia. It lived about 267 million years ago. The only species is ''Eotitanosuchus olsoni''. ...
'' – Middle Permian, Ural Region
File:Titanophoneus 3.jpg, '' Titanophoneus'' and ''Ulemosaurus
''Ulemosaurus'' is an extinct genus of dinocephalian therapsids that lived 265 to 260 million years ago, at Isheevo in Russian Tatarstan. It was a tapinocephalid, a group of bulky herbivores which flourished in the Middle Permian. ''Ulemosaurus'' ...
'' – Ural Region
File:Inostrancevia 4DB.jpg, '' Inostrancevia alexandri'' and ''Scutosaurus
''Scutosaurus'' ("shield lizard") is an extinct genus of pareiasaur parareptiles. Its genus name refers to large plates of armor scattered across its body. It was a large anapsid reptile that, unlike most reptiles, held its legs underneath its ...
'' – Late Permian, North European Russia (Northern Dvina)
Fish
The diversity of fish during the Permian is relatively low compared to the following Triassic. The dominant group of bony fishes during the Permian were the "Paleopterygii" a paraphyletic grouping of Actinopterygii that lie outside ofNeopterygii
Neopterygii (from Greek νέος ''neos'' 'new' and πτέρυξ ''pteryx'' 'fin') is a subclass of ray-finned fish (Actinopterygii). Neopterygii includes the Holostei and the Teleostei, of which the latter comprise the vast majority of extant ...
. The earliest unequivocal members of Neopterygii appear during the Early Triassic, but a Permian origin is suspected. The diversity of coelacanth
The coelacanths ( ) are fish belonging to the order Actinistia that includes two extant species in the genus ''Latimeria'': the West Indian Ocean coelacanth (''Latimeria chalumnae''), primarily found near the Comoro Islands off the east coast ...
s is relatively low throughout the Permian in comparison to other marine fishes, though there is an increase in diversity during the terminal Permian (Changhsingian), corresponding with the highest diversity in their evolutionary history during the Early Triassic. Diversity of freshwater fish faunas was generally low and dominated by lungfish
Lungfish are freshwater vertebrates belonging to the order Dipnoi. Lungfish are best known for retaining ancestral characteristics within the Osteichthyes, including the ability to breathe air, and ancestral structures within Sarcopterygii, i ...
and "Paleopterygians". The last common ancestor of all living lungfish is thought to have existed during the Early Permian. Though the fossil record is fragmentary, lungfish appear to have undergone an evolutionary diversification and size increase in freshwater habitats during the Early Permian, but subsequently declined during the middle and late Permian. Permian chondrichthyan faunas are poorly known. Members of the chondrichthyan clade Holocephali
Holocephali ("complete heads"), sometimes given the term Euchondrocephali, is a subclass of cartilaginous fish in the class Chondrichthyes. The earliest fossils are of teeth and come from the Devonian period. Little is known about these primitiv ...
, which contains living chimaeras, reached their apex of diversity during the Carboniferous-Permian, the most famous Permian representative being the "buzz-saw shark" ''Helicoprion
''Helicoprion'' is an extinct genus of shark-like eugeneodont fish. Almost all fossil specimens are of spirally arranged clusters of the individuals' teeth, called "tooth whorls", which in life were embedded in the lower jaw. As with most extin ...
,'' known for its unusual spiral shaped spiral tooth whorl in the lower jaw. Hybodonts
Hybodontiformes, commonly called hybodonts, are an extinct group of shark-like chondrichthyans, which existed from the late Devonian to the Late Cretaceous. They form the group of Elasmobranchii closest to neoselachians, the clade of modern sh ...
, a group of shark-like chondrichtyans, were widespread and abundant members of marine and freshwater faunas throughout the Permian. Xenacanthiformes, another extinct group of shark-like chondrichtyans, were common in freshwater habitats, and represented the apex predators of freshwater ecosystems.
Flora
floristic provinces
A phytochorion, in phytogeography, is a geographic area with a relatively uniform composition of plant species. Adjacent phytochoria do not usually have a sharp boundary, but rather a soft one, a transitional area in which many species from both r ...
in the Permian are recognised, the Angaran, Euramerican, Gondwanan, and Cathaysian realms. The Carboniferous Rainforest Collapse would result in the replacement of lycopsid
Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants known as lycopods, lycophytes or other terms including the component lyco-. Members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts. They have dichotomously branching s ...
-dominated forests with tree-fern
The tree ferns are arborescent (tree-like) ferns that grow with a trunk elevating the fronds above ground level, making them trees. Many extant tree ferns are members of the order Cyatheales, to which belong the families Cyatheaceae (scaly tree ...
dominated ones during the late Carboniferous in Euramerica, and result in the differentiation of the Cathaysian floras from those of Euramerica. The Gondwanan floristic region was dominated by Glossopteridales
Glossopteridales is an extinct order of plants belonging to Pteridospermatophyta, or seed ferns, also known as Arberiales and Ottokariales. They arose at the beginning of the Permian () on the southern continent of Gondwana, but became extinct a ...
, a group of woody gymnosperm plants, for most of the Permian, extending to high southern latitudes. The ecology of the most prominent glossopterid, ''Glossopteris
''Glossopteris'' tymology: from Ancient Greek γλῶσσα (glôssa, " tongue ") + πτερίς (pterís, " fern ")is the largest and best-known genus of the extinct Permian order of seed ferns known as Glossopteridales (also known as Arberia ...
'', has been compared to that of bald cypress
''Taxodium distichum'' (bald cypress, swamp cypress; french: cyprès chauve;
''cipre'' in Louisiana) is a deciduous conifer in the family Cupressaceae. It is native to the southeastern United States. Hardy and tough, this tree adapts to a wide ...
, living in mire
A mire, peatland, or quagmire is a wetland area dominated by living peat-forming plants. Mires arise because of incomplete decomposition of organic matter, usually litter from vegetation, due to water-logging and subsequent anoxia. All types ...
s with waterlogged soils. The tree-like calamites
''Calamites'' is a genus of extinct arborescent (tree-like) horsetails to which the modern horsetails (genus ''Equisetum'') are closely related. Unlike their herbaceous modern cousins, these plants were medium-sized trees, growing to heights o ...
, distant relatives of modern horsetails
''Equisetum'' (; horsetail, snake grass, puzzlegrass) is the only living genus in Equisetaceae, a family of ferns, which reproduce by spores rather than seeds.
''Equisetum'' is a " living fossil", the only living genus of the entire subclass ...
, lived in coal swamps and grew in bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, ...
-like vertical thickets. A mostly complete specimen of ''Arthropitys
''Arthropitys'' is an extinct genus of calamitacean equisetale. The petrified fossils of ''Arthropitys bistriata'', the type species, can be found at Chemnitz petrified forest, Chemnitz, Germany.
History
Petrified trunks of tree ferns, see ...
'' from the Early Permian Chemnitz petrified forest
The Chemnitz petrified forest is a petrified forest in Chemnitz, Germany.
Most of the trunks are exhibited in the Museum of Natural History in Chemnitz inside of Kulturkaufhaus Tietz , including slices of trunks with polished edges. A small colle ...
of Germany demonstrates that they had complex branching patterns similar to modern angiosperm trees.
 The oldest likely record of Ginkgoales (the group containing ''
The oldest likely record of Ginkgoales (the group containing ''Ginkgo
''Ginkgo'' is a genus of non-flowering seed plants. The scientific name is also used as the English name. The order to which it belongs, Ginkgoales, first appeared in the Permian, 270 million years ago, and is now the only living genus with ...
'' and its close relatives) is '' Trichopitys heteromorpha'' from the earliest Permian of France. The oldest known fossils definitively assignable to modern cycad
Cycads are seed plants that typically have a stout and woody (ligneous) trunk with a crown of large, hard, stiff, evergreen and (usually) pinnate leaves. The species are dioecious, that is, individual plants of a species are either male o ...
s are known from the Late Permian. In Cathaysia, where a wet tropical frost free climate prevailed, the Noeggerathiales
Noeggerathiales is a now- extinct order of vascular plants. The fossil range of the order extends from the Upper Carboniferous to the upper Permian (Lopingian). Due to gaps in the fossil record, the group is incompletely known and poorly defined, ...
, an extinct group of tree fern-like progymnosperm
The progymnosperms are an extinct group of woody, spore-bearing plants that is presumed to have evolved from the trimerophytes, and eventually gave rise to the gymnosperms, ancestral to acrogymnosperms and angiosperms (flowering plants). They ...
s were a common component of the flora The earliest Permian (~ 298 million years ago) Cathyasian Wuda Tuff flora, representing a coal swamp community, has an upper canopy consisting of lycopsid
Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants known as lycopods, lycophytes or other terms including the component lyco-. Members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts. They have dichotomously branching s ...
tree ''Sigillaria
''Sigillaria'' is a genus of extinct, spore-bearing, arborescent (tree-like) plants. It was a lycopodiophyte, and is related to the lycopsids, or club-mosses, but even more closely to quillworts, as was its associate ''Lepidodendron''.
Fossil ...
,'' with a lower canopy consisting of Marattialean tree ferns, and Noeggerathiales. Early conifers appeared in the Late Carboniferous, represented by primitive walchia
''Walchia'' is a fossil conifer, Cupressaceae, cypress-like genus found in upper Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian (Carboniferous) and lower Permian (about 310-290 Mya (unit), Mya) rocks of Europe and North America. A forest of In situ, in-s ...
n conifers, but were replaced with more derived voltzialeans during the Permian. Permian conifers were very similar morphologically to their modern counterparts, and were adapted to stressed dry or seasonally dry climatic conditions. Bennettitales
Bennettitales (also known as cycadeoids) is an extinct order of seed plants that first appeared in the Permian period and became extinct in most areas toward the end of the Cretaceous. Bennettitales are among the most common Mesozoic seed plants ...
, which would go on to become in widespread the Mesozoic, first appeared during the Cisuralian in China. Lyginopterids, which had declined in the late Pennsylvanian and subsequently have a patchy fossil record, survived into the Late Permian in Cathaysia and equatorial east Gondwana.
Permian–Triassic extinction event
paleontology
Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ...
: the Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic (P–T, P–Tr) extinction event, also known as the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian Extinction and colloquially as the Great Dying, formed the boundary between the Permian and Triassic geologic periods, as ...
. 90 to 95% of marine species became extinct, as well as 70% of all land organisms. It is also the only known mass extinction of insects. Recovery from the Permian–Triassic extinction event was protracted; on land, ecosystems took 30 million years to recover. Trilobite
Trilobites (; meaning "three lobes") are extinct marine arthropods that form the class Trilobita. Trilobites form one of the earliest-known groups of arthropods. The first appearance of trilobites in the fossil record defines the base of the ...
s, which had thrived since Cambrian times, finally became extinct before the end of the Permian. Nautiloids
Nautiloids are a group of marine cephalopods (Mollusca) which originated in the Late Cambrian and are represented today by the living ''Nautilus'' and ''Allonautilus''. Fossil nautiloids are diverse and speciose, with over 2,500 recorded species ...
, a subclass of cephalopods, surprisingly survived this occurrence.
There is evidence that magma, in the form of flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reac ...
, poured onto the Earth's surface in what is now called the Siberian Traps
The Siberian Traps (russian: Сибирские траппы, Sibirskiye trappy) is a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the traps is one of the largest ...
, for thousands of years, contributing to the environmental stress that led to mass extinction. The reduced coastal habitat and highly increased aridity probably also contributed. Based on the amount of lava estimated to have been produced during this period, the worst-case scenario is the release of enough carbon dioxide from the eruptions to raise world temperatures five degrees Celsius.Palaeos: Life Through Deep Time > The Permian PeriodAccessed 1 April 2013. Another hypothesis involves ocean venting of hydrogen sulfide gas. Portions of the
deep ocean
The deep sea is broadly defined as the ocean depth where light begins to fade, at an approximate depth of 200 metres (656 feet) or the point of transition from continental shelves to continental slopes. Conditions within the deep sea are a combin ...
will periodically lose all of its dissolved oxygen allowing bacteria that live without oxygen to flourish and produce hydrogen sulfide gas. If enough hydrogen sulfide accumulates in an anoxic zone, the gas can rise into the atmosphere. Oxidizing gases in the atmosphere would destroy the toxic gas, but the hydrogen sulfide would soon consume all of the atmospheric gas available. Hydrogen sulfide levels might have increased dramatically over a few hundred years. Models of such an event indicate that the gas would destroy ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the lo ...
in the upper atmosphere allowing ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
radiation to kill off species that had survived the toxic gas. There are species that can metabolize hydrogen sulfide.
Another hypothesis builds on the flood basalt eruption theory. An increase in temperature of five degrees Celsius would not be enough to explain the death of 95% of life. But such warming could slowly raise ocean temperatures until frozen methane reservoirs below the ocean floor near coastlines melted, expelling enough methane (among the most potent greenhouse gases) into the atmosphere to raise world temperatures an additional five degrees Celsius. The frozen methane hypothesis helps explain the increase in carbon-12 levels found midway in the Permian–Triassic boundary layer. It also helps explain why the first phase of the layer's extinctions was land-based, the second was marine-based (and starting right after the increase in C-12 levels), and the third land-based again.
See also
*List of fossil sites
This list of fossil sites is a worldwide list of localities known well for the presence of fossils. Some entries in this list are notable for a single, unique find, while others are notable for the large number of fossils found there. Many of t ...
''(with link directory)''
* Olson's Extinction
Olson's Extinction was a mass extinction that occurred in the late Cisuralian or early Guadalupian of the Permian period and which predated the Permian–Triassic extinction event.
It is named after Everett C. Olson. There was a sudden change b ...
* List of Permian tetrapods
References
Further reading
*External links
University of California offers a more modern Permian stratigraphy
* * ttp://www.geo-lieven.com/erdzeitalter/perm/perm.htm Examples of Permian Fossils
Permian (chronostratigraphy scale)
* {{Authority control Geological periods