Parasaurolophus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Parasaurolophus'' (; meaning "near crested lizard" in reference to '' Saurolophus)'' is a
 Meaning "near crested lizard", the name ''Parasaurolophus'' is derived from the
Meaning "near crested lizard", the name ''Parasaurolophus'' is derived from the
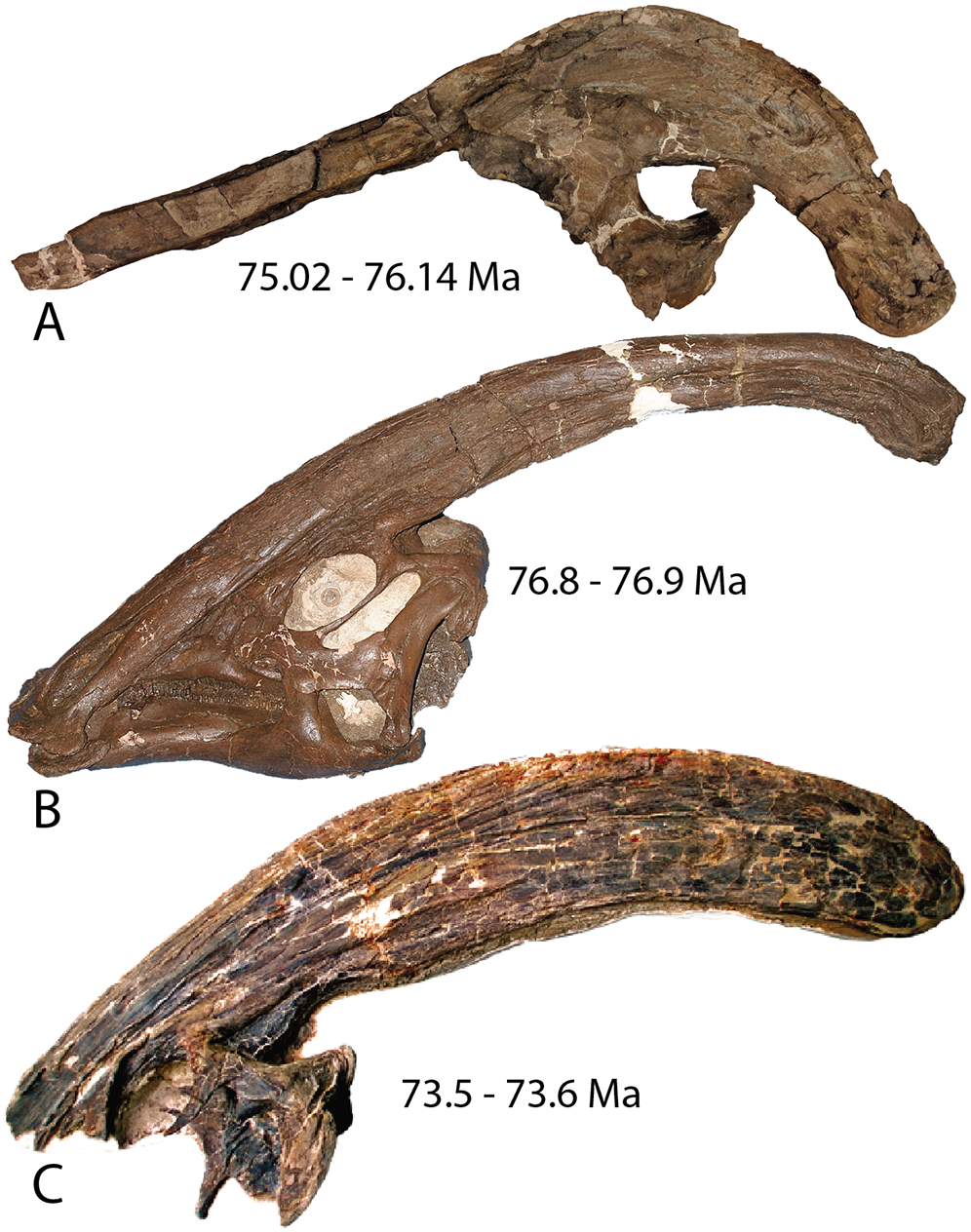 ''Parasaurolophus'' is known from three certain species, ''P. walkeri'', ''P. tubicen'', and ''P. cyrtocristatus''. All of them can be distinguished from each other, and have many differences. The first named species, therefore the type, is ''P. walkeri''. One certain specimen, from the Dinosaur Park Formation is referred to it, but many more are almost certainly referable. Like stated above, it is different from the other two species, with it having a simpler internal structure than ''P. tubicen'', a straighter crest and different internal structuring than ''P. cyrtocristatus''.
The next named species is ''P. tubicen'', which is the largest of the ''Parasaurolophus'' species. It lived in New Mexico, where three specimens are known, and can be differentiated from its other species. It possesses a long and straight crest, with a very complex interior compared to the other species. All known specimens of ''P. tubicen'' come from the De-Na-Zin Member of the
''Parasaurolophus'' is known from three certain species, ''P. walkeri'', ''P. tubicen'', and ''P. cyrtocristatus''. All of them can be distinguished from each other, and have many differences. The first named species, therefore the type, is ''P. walkeri''. One certain specimen, from the Dinosaur Park Formation is referred to it, but many more are almost certainly referable. Like stated above, it is different from the other two species, with it having a simpler internal structure than ''P. tubicen'', a straighter crest and different internal structuring than ''P. cyrtocristatus''.
The next named species is ''P. tubicen'', which is the largest of the ''Parasaurolophus'' species. It lived in New Mexico, where three specimens are known, and can be differentiated from its other species. It possesses a long and straight crest, with a very complex interior compared to the other species. All known specimens of ''P. tubicen'' come from the De-Na-Zin Member of the
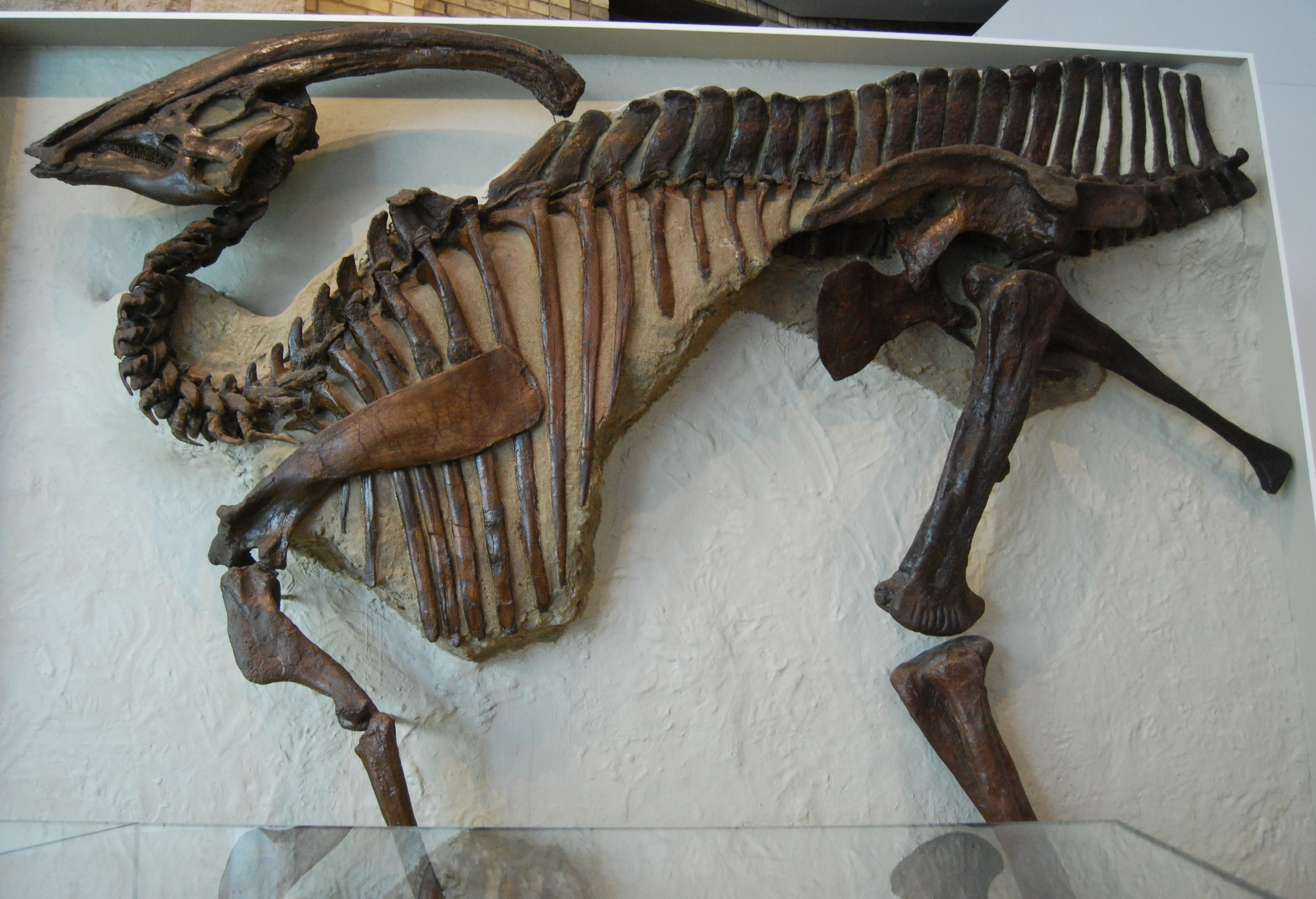
 Like most dinosaurs, the skeleton of ''Parasaurolophus'' is incompletely known. The length of the
Like most dinosaurs, the skeleton of ''Parasaurolophus'' is incompletely known. The length of the  Like other hadrosaurids, it was able to walk on either two legs or four. It probably preferred to forage for food on four legs, but ran on two. The
Like other hadrosaurids, it was able to walk on either two legs or four. It probably preferred to forage for food on four legs, but ran on two. The
 The following cladogram is after the 2007 redescription of '' Lambeosaurus magnicristatus'' (Evans and Reisz, 2007):
The following cladogram is after the 2007 redescription of '' Lambeosaurus magnicristatus'' (Evans and Reisz, 2007):

 ''Parasaurolophus'' is known from many adult specimens, and a juvenile described in 2013, numbered RAM 140000 and nicknamed Joe, after a volunteer at the Raymond M. Alf Museum of Paleontology (RAM). The juvenile was discovered in the
''Parasaurolophus'' is known from many adult specimens, and a juvenile described in 2013, numbered RAM 140000 and nicknamed Joe, after a volunteer at the Raymond M. Alf Museum of Paleontology (RAM). The juvenile was discovered in the  The skull of RAM 14000 is almost complete, with the left side only lacking a piece of the
The skull of RAM 14000 is almost complete, with the left side only lacking a piece of the
 Many hypotheses have been advanced as to what functions the cranial crest of ''Parasaurolophus'' performed, but most have been discredited. It is now believed that it may have had several functions: visual display for identifying species and sex, sound amplification for communication, and thermoregulation. It is not clear which was most significant at what times in the evolution of the crest and its internal nasal passages.
Many hypotheses have been advanced as to what functions the cranial crest of ''Parasaurolophus'' performed, but most have been discredited. It is now believed that it may have had several functions: visual display for identifying species and sex, sound amplification for communication, and thermoregulation. It is not clear which was most significant at what times in the evolution of the crest and its internal nasal passages.
 Many early suggestions focused on adaptations for an aquatic lifestyle, following the hypothesis that hadrosaurids were amphibious, a common line of thought until the 1960s. Thus,
Many early suggestions focused on adaptations for an aquatic lifestyle, following the hypothesis that hadrosaurids were amphibious, a common line of thought until the 1960s. Thus,
 Barnum Brown (1912) noted the presence of fine striations near the back of the crest that he hypothesized could be associated with the presence of a frill of skin, comparable to the one found in the modern basilisk lizard. His hypothesis was seemingly supported by skin preserved above the neck and back of ''Corythosaurus'' and ''Edmontosaurus''. Subsequently, reconstructions of ''Parasaurolophus'' with a substantial frill of skin between the crest and neck appeared in influential paleoart including murals by Charles R. Knight and in the Walt Disney animated film ''Fantasia''. This led to the frill being depicted in many other sources, though the advent of the now-debunked "snorkel" hypothesis, and conflation of the frill hypothesis with the idea that the crest serves as an anchor point for neck ligaments, along with lack of strong evidence for its presence, has seen it fall out of favor in most modern depictions.
Barnum Brown (1912) noted the presence of fine striations near the back of the crest that he hypothesized could be associated with the presence of a frill of skin, comparable to the one found in the modern basilisk lizard. His hypothesis was seemingly supported by skin preserved above the neck and back of ''Corythosaurus'' and ''Edmontosaurus''. Subsequently, reconstructions of ''Parasaurolophus'' with a substantial frill of skin between the crest and neck appeared in influential paleoart including murals by Charles R. Knight and in the Walt Disney animated film ''Fantasia''. This led to the frill being depicted in many other sources, though the advent of the now-debunked "snorkel" hypothesis, and conflation of the frill hypothesis with the idea that the crest serves as an anchor point for neck ligaments, along with lack of strong evidence for its presence, has seen it fall out of favor in most modern depictions.
 ''Parasaurolophus walkeri'', from the
''Parasaurolophus walkeri'', from the
 In the
In the
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of herbivorous
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
hadrosaurid
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which inclu ...
ornithopod
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (), that started out as small, bipedal running grazers and grew in size and numbers until they became one of the most successful groups of herbivores in the Cretaceous wo ...
dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
that lived in what is now North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Car ...
and possibly Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an area ...
during the Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
Period
Period may refer to:
Common uses
* Era, a length or span of time
* Full stop (or period), a punctuation mark
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Period (music), a concept in musical composition
* Periodic sentence (or rhetorical period), a concept ...
, about 76.5–73 million years ago. It was a herbivore
A herbivore is an animal anatomically and physiologically adapted to eating plant material, for example foliage or marine algae, for the main component of its diet. As a result of their plant diet, herbivorous animals typically have mouthpart ...
that walked both as a biped
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
and as a quadruped
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion where four limbs are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four limbs is said to be a quadruped (from Latin ''quattuor' ...
. Three species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
are universally recognized: ''P. walkeri'' (the type species
In zoological nomenclature, a type species (''species typica'') is the species name with which the name of a genus or subgenus is considered to be permanently taxonomically associated, i.e., the species that contains the biological type specimen ...
), ''P. tubicen'', and the short-crested ''P. cyrtocristatus''. Additionally, a fourth species, ''P. jiayinensis'', has been proposed, although it is more commonly placed in the separate genus ''Charonosaurus
''Charonosaurus'' ( ; meaning " Charon's lizard") is a genus of dinosaur whose fossils were discovered by Godefroit, Zan & Jin in 2000 on the south bank of the Amur River, dividing China from Russia. It is monotypic, consisting of the species ...
''. Remains are known from Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
(Canada), New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Tiguex
, OfficialLang = None
, Languages = English, Spanish ( New Mexican), Navajo, Ker ...
and Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
(United States), and possibly Heilongjiang
Heilongjiang () formerly romanized as Heilungkiang, is a province in northeast China. The standard one-character abbreviation for the province is (). It was formerly romanized as "Heilungkiang". It is the northernmost and easternmost province ...
(China). The genus was first described in 1922 by William Parks from a skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
and partial skeleton found in Alberta.
''Parasaurolophus'' was a hadrosaurid
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which inclu ...
, part of a diverse family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ...
of Cretaceous dinosaurs known for their range of bizarre head adornments which were likely used for communication and better hearing. This genus is known for its large, elaborate cranial crest, which at its largest forms a long curved tube projecting upwards and back from the skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, the ...
. ''Charonosaurus
''Charonosaurus'' ( ; meaning " Charon's lizard") is a genus of dinosaur whose fossils were discovered by Godefroit, Zan & Jin in 2000 on the south bank of the Amur River, dividing China from Russia. It is monotypic, consisting of the species ...
'' from China, which may have been its closest relative, had a similar skull and potentially a similar crest. Visual recognition of both species and sex, acoustic resonance, and thermoregulation
Thermoregulation is the ability of an organism to keep its body temperature within certain boundaries, even when the surrounding temperature is very different. A thermoconforming organism, by contrast, simply adopts the surrounding temperature ...
have been proposed as functional explanations for the crest. It is one of the rarer hadrosaurids, known from only a handful of good specimens.
Discovery and naming
 Meaning "near crested lizard", the name ''Parasaurolophus'' is derived from the
Meaning "near crested lizard", the name ''Parasaurolophus'' is derived from the Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''para''/παρα "beside" or "near", ''saurus''/ "lizard" and ''lophos''/λοφος "crest". It is based on ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
768, a skull and partial skeleton missing most of the tail and the hind legs below the knees, which was found by a field party from the University of Toronto
The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 as King's College, the first institution ...
in 1920 near Sand Creek along the Red Deer River
The Red Deer River is a river in Alberta and a small portion of Saskatchewan, Canada. It is a major tributary of the South Saskatchewan River and is part of the larger Saskatchewan-Nelson system that empties into Hudson Bay.
Red Deer River ...
in Alberta, Canada. These rocks are now known as the Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian s ...
-age Upper Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
Dinosaur Park Formation
The Dinosaur Park Formation is the uppermost member of the Belly River Group (also known as the Judith River Group), a major geologic unit in southern Alberta. It was deposited during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, between about 76. ...
. William Parks named the specimen ''P. walkeri'' in honor of Sir Byron Edmund Walker, chairman of the Board of Trustees of the Royal Ontario Museum
The Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) is a museum of art, world culture and natural history in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is one of the largest museums in North America and the largest in Canada. It attracts more than one million visitors every year ...
. ''Parasaurolophus'' remains are rare in Alberta, with only one other partial skull from (probably) the Dinosaur Park Formation, and three Dinosaur Park specimens lacking skulls, possibly belonging to the genus. In some faunal lists, there is a mention of possible ''P. walkeri'' material in the Hell Creek Formation
The Hell Creek Formation is an intensively studied division of mostly Upper Cretaceous and some lower Paleocene rocks in North America, named for exposures studied along Hell Creek, near Jordan, Montana. The formation stretches over portions of ...
of Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
, a rock unit of late Maastrichtian age. This occurrence is not noted by Sullivan and Williamson in their 1999 review of the genus, and has not been further elaborated upon elsewhere.
In 1921, Charles H. Sternberg recovered a partial skull ( PMU.R1250) from what is now known as the slightly younger Kirtland Formation
The Kirtland Formation (originally the Kirtland Shale) is a sedimentary geological formation.
Description
The Kirtland Formation is the product of alluvial muds and overbank sand deposits from the many channels draining the coastal plain th ...
in San Juan County, New Mexico. This specimen was sent to Uppsala
Uppsala (, or all ending in , ; archaically spelled ''Upsala'') is the county seat of Uppsala County and the List of urban areas in Sweden by population, fourth-largest city in Sweden, after Stockholm, Gothenburg, and Malmö. It had 177,074 inha ...
, Sweden, where Carl Wiman
Carl Johan Josef Ernst Wiman (March 10, 1867 – June 15, 1944) was a Swedish palaeontologist, the first professor of palaeontology and historical geology at Uppsala University, and the father of Swedish vertebrate palaeontology.
Wiman was ...
described it as a second species, ''P. tubicen'', in 1931. The specific epithet is derived from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''tǔbǐcěn'' "trumpeter". A second, nearly complete ''P. tubicen'' skull ( NMMNH P-25100) was found in New Mexico in 1995. Using computed tomography of this skull, Robert Sullivan and Thomas Williamson gave the genus a monograph
A monograph is a specialist work of writing (in contrast to reference works) or exhibition on a single subject or an aspect of a subject, often by a single author or artist, and usually on a scholarly subject.
In library cataloging, ''monograph ...
ic treatment in 1999, covering aspects of its anatomy and taxonomy, and the functions of its crest. Williamson later published an independent review of the remains, disagreeing with the taxonomic conclusions.
John Ostrom
John Harold Ostrom (February 18, 1928 – July 16, 2005) was an American paleontologist who revolutionized modern understanding of dinosaurs in the 1960s.
As first proposed by Thomas Henry Huxley in the 1860s, Ostrom showed that dinosaurs were ...
described another good specimen ( FMNH P27393) from New Mexico as ''P. cyrtocristatus'' in 1961. It includes a partial skull with a short, rounded crest, and much of the postcrania Postcrania (postcranium, adjective: postcranial) in zoology and vertebrate paleontology is all or part of the skeleton apart from the skull. Frequently, fossil remains, e.g. of dinosaurs or other extinct tetrapods, consist of partial or isolated sk ...
l skeleton except for the feet, neck, and parts of the tail. Its specific name is derived from the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''curtus'' "shortened" and ''cristatus'' "crested". The specimen was found in either the top of the Fruitland Formation
The Fruitland Formation is a geologic formation found in the San Juan Basin in the states of New Mexico and Colorado, in the United States of America. It contains fossils dating it to the Campanian age of the late Cretaceous.
or, more likely, the base of the overlying Kirtland Formation. The range of this species was in 1979, when David B. Weishampel and James A. Jensen described a partial skull with a similar crest (BYU
Brigham Young University (BYU, sometimes referred to colloquially as The Y) is a private research university in Provo, Utah. It was founded in 1875 by religious leader Brigham Young and is sponsored by the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day S ...
2467) from the Campanian-age Kaiparowits Formation
The Kaiparowits Formation is a sedimentary rock formation found in the Kaiparowits Plateau in Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument, in the southern part of Utah in the western United States. It is over 2800 feet (850 m) thick, and is ...
of Garfield County, Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to it ...
. Since then, another skull has been found in Utah with the short/round ''P. cyrtocristatus'' crest morphology.
Species
 ''Parasaurolophus'' is known from three certain species, ''P. walkeri'', ''P. tubicen'', and ''P. cyrtocristatus''. All of them can be distinguished from each other, and have many differences. The first named species, therefore the type, is ''P. walkeri''. One certain specimen, from the Dinosaur Park Formation is referred to it, but many more are almost certainly referable. Like stated above, it is different from the other two species, with it having a simpler internal structure than ''P. tubicen'', a straighter crest and different internal structuring than ''P. cyrtocristatus''.
The next named species is ''P. tubicen'', which is the largest of the ''Parasaurolophus'' species. It lived in New Mexico, where three specimens are known, and can be differentiated from its other species. It possesses a long and straight crest, with a very complex interior compared to the other species. All known specimens of ''P. tubicen'' come from the De-Na-Zin Member of the
''Parasaurolophus'' is known from three certain species, ''P. walkeri'', ''P. tubicen'', and ''P. cyrtocristatus''. All of them can be distinguished from each other, and have many differences. The first named species, therefore the type, is ''P. walkeri''. One certain specimen, from the Dinosaur Park Formation is referred to it, but many more are almost certainly referable. Like stated above, it is different from the other two species, with it having a simpler internal structure than ''P. tubicen'', a straighter crest and different internal structuring than ''P. cyrtocristatus''.
The next named species is ''P. tubicen'', which is the largest of the ''Parasaurolophus'' species. It lived in New Mexico, where three specimens are known, and can be differentiated from its other species. It possesses a long and straight crest, with a very complex interior compared to the other species. All known specimens of ''P. tubicen'' come from the De-Na-Zin Member of the Kirtland Formation
The Kirtland Formation (originally the Kirtland Shale) is a sedimentary geological formation.
Description
The Kirtland Formation is the product of alluvial muds and overbank sand deposits from the many channels draining the coastal plain th ...
.
In 1961, the third species, ''P. cyrtocristatus'' was named by John Ostrom
John Harold Ostrom (February 18, 1928 – July 16, 2005) was an American paleontologist who revolutionized modern understanding of dinosaurs in the 1960s.
As first proposed by Thomas Henry Huxley in the 1860s, Ostrom showed that dinosaurs were ...
. Its three known specimens, have been found in the Fruitland and Kaiparowits
The Paiute Indian Tribe of Utah is a federally recognized tribe of Southern Paiute and Ute Indians in southwestern Utah.
Reservation
The Paiute Indian Tribe of Utah (PITU) has a reservation composed of ten separate parcels of land, located in fo ...
formations from Utah and New Mexico. The second specimen, the first known from the Kaiparowits Formation, was originally unassigned to a specific taxon. Of the ''Parasaurolophus'' species, ''P. cyrtocristatus'' is the smallest, and has the most curved crest. Because of its possession of the two above features, it has often been speculated that it was a female of ''P. walkeri'' or ''P. tubicen'', which were males, although ''P. tubicen'' lived approximately a million years later. As noted by Thomas Williamson, the type material of ''P. cyrtocristatus'' is about 72% the size of ''P. tubicen'', close to the size at which other lambeosaurines are interpreted to begin showing definitive sexual dimorphism
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
in their crests (~70% of adult size). Even though many scientists have supported the possible fact of ''P. cyrtocristatus'' being a female, many other studies have found that it is not, because of the differences in age, distribution, and the large differences in the crest and its internal structure.
A study published in '' PLoS ONE'' in 2014 found that one more species could be referred to ''Parasaurolophus''. This study, led by Xing, found ''Charonosaurus
''Charonosaurus'' ( ; meaning " Charon's lizard") is a genus of dinosaur whose fossils were discovered by Godefroit, Zan & Jin in 2000 on the south bank of the Amur River, dividing China from Russia. It is monotypic, consisting of the species ...
jiayensis'' was actually nested deeply inside ''Parasaurolophus'', which created the new species ''P. jiayensis''. If this species is indeed inside ''Parasaurolophus'', then the genus lasted until the K-Pg extinction, and is known from two continents.
Description
type specimen
In biology, a type is a particular wiktionary:en:specimen, specimen (or in some cases a group of specimens) of an organism to which the scientific name of that organism is formally attached. In other words, a type is an example that serves to a ...
of ''P. walkeri'' is estimated at , and its body mass is estimated at according to Gregory S. Paul. Allometry-based body mass estimate indicates that it reached more than in body mass. Its skull is about long, including the crest, whereas the type skull of ''P. tubicen'' is over long, indicating a larger animal. Its single known forelimb was relatively short for a hadrosaurid, with a short but wide shoulder blade. The thighbone
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates with ...
measures long in ''P. walkeri'' and is robust for its length when compared to other hadrosaurids. The upper arm
In human anatomy, the arm refers to the upper limb in common usage, although academically the term specifically means the upper arm between the glenohumeral joint (shoulder joint) and the elbow joint. The distal part of the upper limb between th ...
and pelvic
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
bones were also heavily built.
 Like other hadrosaurids, it was able to walk on either two legs or four. It probably preferred to forage for food on four legs, but ran on two. The
Like other hadrosaurids, it was able to walk on either two legs or four. It probably preferred to forage for food on four legs, but ran on two. The neural spines
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
of the vertebra
The spinal column, a defining synapomorphy shared by nearly all vertebrates,Hagfish are believed to have secondarily lost their spinal column is a moderately flexible series of vertebrae (singular vertebra), each constituting a characteristic ...
e were tall, as was common in lambeosaurines; tallest over the hips, they increased the height of the back. Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have diffe ...
impressions are known for ''P. walkeri'', showing uniform tubercle-like scales but no larger structures.
Skull
The most noticeable feature was the cranial crest, which protruded from the rear of the head and was made up of thepremaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammal has b ...
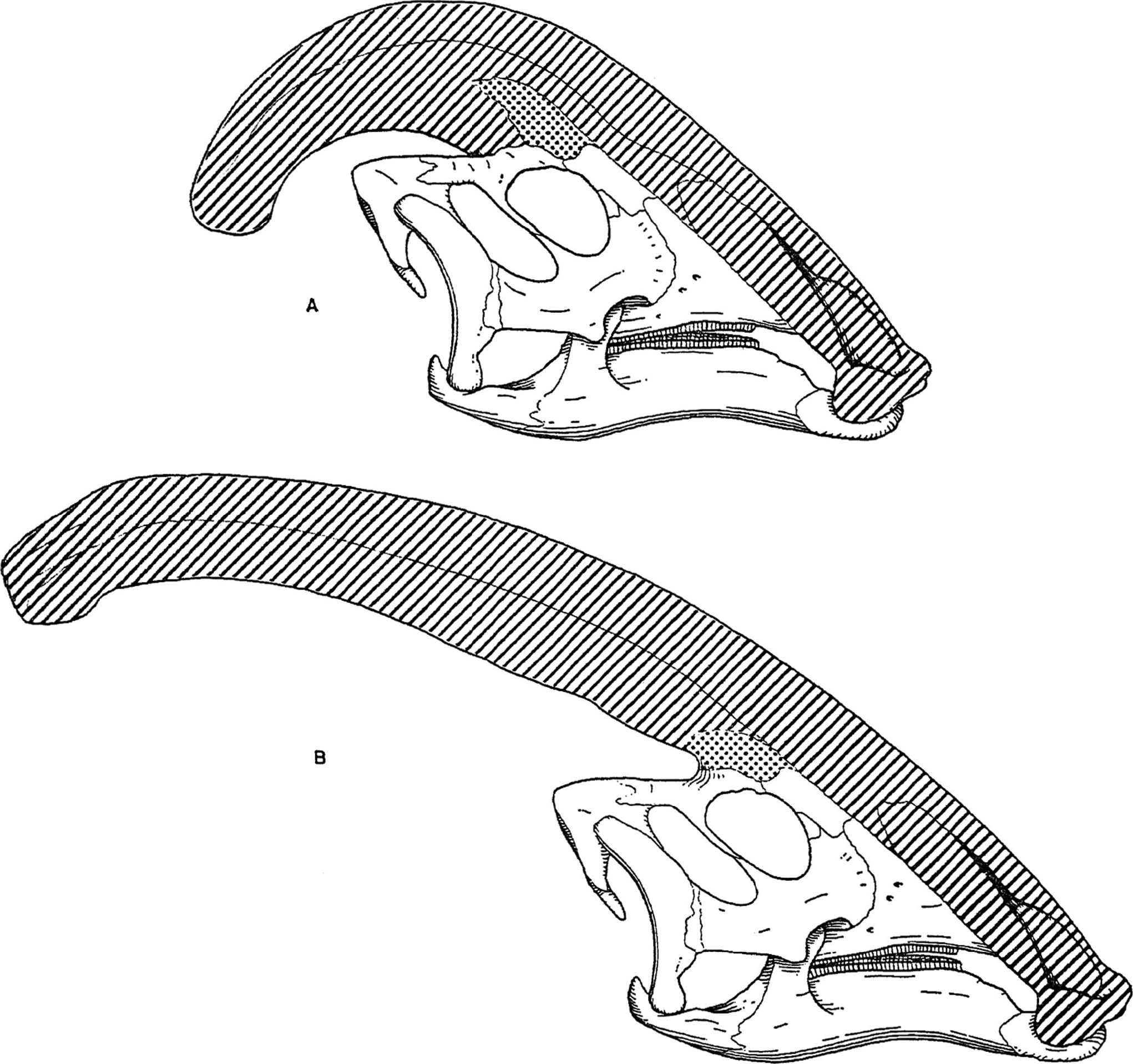
and nasal bones. The crest was hollow, with distinct tubes leading from each nostril to the end of the crest before reversing direction and heading back down the crest and into the skull. The tubes were simplest in ''P. walkeri'', and more complex in ''P. tubicen'', where some tubes were blind and others met and separated. While ''P. walkeri'' and ''P. tubicen'' had long crests with only slight curvature, ''P. cyrtocristatus'' had a short crest with a more circular profile.
Classification
As its name implies, ''Parasaurolophus'' was initially thought to be closely related to '' Saurolophus'' because of its superficially similar crest. However, it was soon reassessed as a member of thelambeosaurine
Lambeosaurinae is a group of crested hadrosaurid dinosaurs.
Classification
Lambeosaurines have been traditionally split into the tribes or clades Parasaurolophini ('' Parasaurolophus'', ''Charonosaurus'', others (?).) and Lambeosaurini (''Cor ...
subfamily of hadrosaurids—''Saurolophus'' is a hadrosaurine. It is usually interpreted as a separate offshoot of the lambeosaurines, distinct from the helmet-crested ''Corythosaurus
''Corythosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid "duck-billed" dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period, about 77–75.7 million years ago. It lived in what is now North America. Its name means "helmet lizard", derived from Greek κόρυ� ...
'', ''Hypacrosaurus
''Hypacrosaurus'' (meaning "near the highest lizard" reek υπο-, ''hypo-'' = less + ακρος, ''akros'', high because it was almost but not quite as large as ''Tyrannosaurus'') was a genus of duckbill dinosaur similar in appearance to ''Co ...
'', and ''Lambeosaurus
''Lambeosaurus'' ( , meaning " Lambe's lizard") is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur that lived about 75 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceous period (Campanian stage) of North America. This bipedal/quadrupedal, herbivorous dinosaur is k ...
''. Its closest known relative appears to be ''Charonosaurus
''Charonosaurus'' ( ; meaning " Charon's lizard") is a genus of dinosaur whose fossils were discovered by Godefroit, Zan & Jin in 2000 on the south bank of the Amur River, dividing China from Russia. It is monotypic, consisting of the species ...
'', a lambeosaurine with a similar skull (but no complete crest yet) from the Amur
The Amur (russian: река́ Аму́р, ), or Heilong Jiang (, "Black Dragon River", ), is the world's List of longest rivers, tenth longest river, forming the border between the Russian Far East and Northeast China, Northeastern China (Inne ...
region of northeastern China, and the two may form a clade
A clade (), also known as a monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that are monophyletic – that is, composed of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants – on a phylogenetic tree. Rather than the English term, ...
Parasaurolophini
Parasaurolophini is a tribe of derived corythosaurian lambeosaurine hadrosaurids that are native to Asia, and North America. It is defined as everything closer to ''Parasaurolophus walkeri'' than to '' Lambeosaurus lambei''. It currently contain ...
. ''P. cyrtocristatus'', with its short, rounder crest, may be the most basal of the three known ''Parasaurolophus'' species, or it may represent subadult
A juvenile is an individual organism that has not yet reached its adult form, sexual maturity or size. Juveniles can look very different from the adult form, particularly in colour, and may not fill the same niche as the adult form. In many o ...
or female specimens of ''P. tubicen''.
 The following cladogram is after the 2007 redescription of '' Lambeosaurus magnicristatus'' (Evans and Reisz, 2007):
The following cladogram is after the 2007 redescription of '' Lambeosaurus magnicristatus'' (Evans and Reisz, 2007):
Paleobiology

Diet and feeding
As a hadrosaurid, ''Parasaurolophus'' was a largebipedal
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' ...
/quadrupedal
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion where four limbs are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four limbs is said to be a quadruped (from Latin ''quattuor ...
herbivore, eating plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclud ...
s with a sophisticated skull that permitted a grinding motion analogous to chewing
Chewing or mastication is the process by which food is crushed and ground by teeth. It is the first step of digestion, and it increases the surface area of foods to allow a more efficient break down by enzymes. During the mastication process, th ...
. Its teeth were continually being replaced; they were packed into dental batteries containing hundreds of teeth, only a relative handful of which were in use at any time. It used its beak to crop plant material, which was held in the jaws by a cheek
The cheeks ( la, buccae) constitute the area of the face below the eyes and between the nose and the left or right ear. "Buccal" means relating to the cheek. In humans, the region is innervated by the buccal nerve. The area between the inside ...
-like organ. Vegetation could have been taken from the ground up to a height of around . As noted by Bob Bakker, lambeosaurines have narrower beaks than hadrosaurines, implying that ''Parasaurolophus'' and its relatives could feed more selectively than their broad-beaked, crestless counterparts. ''Parasaurolophus'' had a diet consisting of leaves, twigs and pine needles which would imply that it was a browser.
Growth
 ''Parasaurolophus'' is known from many adult specimens, and a juvenile described in 2013, numbered RAM 140000 and nicknamed Joe, after a volunteer at the Raymond M. Alf Museum of Paleontology (RAM). The juvenile was discovered in the
''Parasaurolophus'' is known from many adult specimens, and a juvenile described in 2013, numbered RAM 140000 and nicknamed Joe, after a volunteer at the Raymond M. Alf Museum of Paleontology (RAM). The juvenile was discovered in the Kaiparowits Formation
The Kaiparowits Formation is a sedimentary rock formation found in the Kaiparowits Plateau in Grand Staircase–Escalante National Monument, in the southern part of Utah in the western United States. It is over 2800 feet (850 m) thick, and is ...
in 2009. Excavated by the joint expedition by museum and The Webb Schools
The Webb Schools is the collective name for two private schools for grades 9-12, founded by Thompson Webb, located in Claremont, California. The Webb School of California for boys was established in 1922, and the Vivian Webb School for girls in 1 ...
, the juvenile has been identified as around only one year old when it died. Referred to ''Parasaurolophus'' sp., the juvenile is the most complete, as well as youngest ''Parasaurolophus'' ever found, and measures . This individual fits neatly into the currently known ''Parasaurolophus'' growth stages, and lived approximately 75 million years ago. Even though no complete skull of the intermediate age between RAM 14000 and adult ''Parasaurolophus'' has been found yet, a partial braincase of about the right size is known. At 25% of the total adult size, the juvenile show that crest growth of ''Parasaurolophus'' began sooner than in related genera, such as ''Corythosaurus''. It has been suggested that ''Parasaurolophus'' adults bore such large crests, especially when compared to the related ''Corythosaurus'', because of this difference in age between when their crests started developing. Its age also means that ''Parasaurolophus'' had a very fast growth rate, which took place in about a year. The crest of the juvenile is not long and tubular like the adults, but low and hemispherical.
 The skull of RAM 14000 is almost complete, with the left side only lacking a piece of the
The skull of RAM 14000 is almost complete, with the left side only lacking a piece of the maxilla
The maxilla (plural: ''maxillae'' ) in vertebrates is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The t ...
. However, the skull was split down the middle by erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distin ...
, possibly when it was resting on the bottom of a river bed
A stream bed or streambed is the bottom of a stream or river (bathymetry) or the physical confine of the normal water flow ( channel). The lateral confines or channel margins are known as the stream banks or river banks, during all but flood ...
. The two sides are displaced slightly, with some bones of the right being moved off the main block, also by erosion. After reconstruction, the skull viewed from the side resembles other juvenile lambeosaurines found, being roughly a trapezoid
A quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides is called a trapezoid () in American and Canadian English. In British and other forms of English, it is called a trapezium ().
A trapezoid is necessarily a Convex polygon, convex quadri ...
in shape.
A partial cranial endocast for RAM 14000 was reconstructed from CT scan data, the first ever for a ''Parasaurolophus'' of any ontogenetic stage. The endocast was reconstructed in two sections, one on the portion of the braincase articulated with the left half of the skull and the remainder on the disarticulated portion of the braincase. Their relative position was then approximated based on cranial landmarks and comparison with other hadrosaurids. Because of weathering, many of the smaller neural canals and foramina could not be identified for certain.
Cranial crest
Differences in crests
As for other lambeosaurines, it is believed that the cranial crest of ''Parasaurolophus'' changed with age and was asexually dimorphic
Sexual dimorphism is the condition where the sexes of the same animal and/or plant species exhibit different morphological characteristics, particularly characteristics not directly involved in reproduction. The condition occurs in most ani ...
characteristic in adults. James Hopson
James Allen Hopson (born 1935) is an American paleontologist and professor (now retired) at the University of Chicago. His work has focused on the evolution of the synapsids (a group of amniotes that includes the mammals), and has been focused ...
, one of the first researchers to describe lambeosaurine crests in terms of such distinctions, suggested that ''P. cyrtocristatus'', with its small crest, was the female form of ''P. tubicen''. Thomas Williamson suggested it was the juvenile form. Neither hypothesis became widely accepted. As only six good skulls, one juvenile braincase, and one recently discovered juvenile skull are known, additional material will help clear up these potential relationships. Williamson noted that in any case, juvenile ''Parasaurolophus'' probably had small, rounded crests like ''P. cyrtocristatus'', that probably grew faster as individuals approached sexual maturity
Sexual maturity is the capability of an organism to reproduce. In humans it might be considered synonymous with adulthood, but here puberty is the name for the process of biological sexual maturation, while adulthood is based on cultural definitio ...
. Recent restudy of a juvenile braincase previously assigned to ''Lambeosaurus'', now assigned to ''Parasaurolophus'', provides evidence that a small tubular crest was present in juveniles. This specimen preserves a small upward flaring of the frontal bone
The frontal bone is a bone in the human skull. The bone consists of two portions.'' Gray's Anatomy'' (1918) These are the vertically oriented squamous part, and the horizontally oriented orbital part, making up the bony part of the forehead, pa ...
s that was similar to but smaller than what is seen in adult specimens; in adults, the frontals formed a platform that supported the base of the crest. This specimen also indicates that the growth of the crest in ''Parasaurolophus'' and the facial profile of juvenile individuals differed from the ''Corythosaurus''-''Hypacrosaurus''-''Lambeosaurus'' model, in part because the crest of ''Parasaurolophus'' lacks the thin bony 'coxcomb' that makes up the upper portion of the crest of the other three lambeosaurines.
Rejected function hypotheses
 Many early suggestions focused on adaptations for an aquatic lifestyle, following the hypothesis that hadrosaurids were amphibious, a common line of thought until the 1960s. Thus,
Many early suggestions focused on adaptations for an aquatic lifestyle, following the hypothesis that hadrosaurids were amphibious, a common line of thought until the 1960s. Thus, Alfred Sherwood Romer
Alfred Sherwood Romer (December 28, 1894 – November 5, 1973) was an American paleontologist and biologist and a specialist in vertebrate evolution.
Biography
Alfred Romer was born in White Plains, New York, the son of Harry Houston Romer an ...
proposed it served as a snorkel, Martin Wilfarth that it was an attachment for a mobile proboscis
A proboscis () is an elongated appendage from the head of an animal, either a vertebrate or an invertebrate. In invertebrates, the term usually refers to tubular mouthparts used for feeding and sucking. In vertebrates, a proboscis is an elong ...
used as a breathing tube or for food gathering, Charles M. Sternberg that it served as an airtrap to keep water out of the lung
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in humans and most other animals, including some snails and a small number of fish. In mammals and most other vertebrates, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of t ...
s, and Ned Colbert that it served as an air reservoir for prolonged stays underwater.
Other proposals were more mechanical in nature. William Parks, in 1922, suggested that the crest was joined to the vertebrae above the shoulders by ligament
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the:
* Peritoneal li ...
s or muscles, and helped with moving and supporting the head. This is unlikely, because in all modern archosaurs, the nuchal ligament attaches to the neck or base of the skull.Manucci, F, Dempsey, M, Tanke, D H., et al. Description and etiology of paleopathological lesions in the type specimen of Parasaurolophus walkeri (Dinosauria: Hadrosauridae), with proposed reconstructions of the nuchal ligament J. Anat. 2020; 00: 1– 15. https://doi.org/10.1111/joa.13363 Othenio Abel
Othenio Lothar Franz Anton Louis Abel (June 20, 1875 – July 4, 1946) was an Austrian paleontologist and evolutionary biologist. Together with Louis Dollo, he was the founder of "paleobiology" and studied the life and environment of fossilized or ...
proposed it was used as a weapon in combat among members of the same species, and Andrew Milner suggested that it could be used as a foliage deflector, like the helmet crest (called a 'casque') of the cassowary
Cassowaries ( tpi, muruk, id, kasuari) are flightless birds of the genus ''Casuarius'' in the order Casuariiformes. They are classified as ratites (flightless birds without a keel on their sternum bones) and are native to the tropical forest ...
. Still, other proposals made housing specialized organs the major function. Halszka Osmólska
Halszka Osmólska (September 15, 1930 – March 31, 2008) was a Polish paleontologist who had specialized in Mongolian dinosaurs.
Biography
She was born in 1930 in Poznań. In 1949, she began to study biology at Faculty of Biology and Earth Scie ...
suggested that it housed salt gland
The salt gland is an organ for excreting excess salts. It is found in the cartilaginous fishes subclass elasmobranchii (sharks, rays, and skates), seabirds, and some reptiles. Salt glands can be found in the rectum of sharks. Birds and reptiles ...
s, and John Ostrom suggested that it housed expanded areas for olfactory tissue and much improved sense of smell
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, it ...
of the lambeosaurines, which had no obvious defensive capabilities.
Most of these hypotheses have been discredited or rejected. For example, there is no hole at the end of the crest for a snorkeling function. There are no muscle scars for a proboscis and it is dubious that an animal with a beak would need one. As a proposed airlock, it would not have kept out water. The proposed air reservoir would have been insufficient for an animal the size of ''Parasaurolophus''. Other hadrosaurids had large heads without needing large hollow crests to serve as attachment points for supporting ligaments. Also, none of the proposals explain why the crest has such a shape, why other lambeosaurines should have crests that look much different but perform a similar function, how crestless or solid-crested hadrosaurids got along without such capabilities, or why some hadrosaurids had solid crests. These considerations particularly impact hypotheses based on increasing the capabilities of systems already present in the animal, such as the salt gland and olfaction hypotheses, and indicate that these were not primary functions of the crest. Additionally, work on the nasal cavity of lambeosaurines shows that olfactory nerves and corresponding sensory tissue were largely outside the portion of the nasal passages in the crest, so the expansion of the crest had little to do with the sense of smell.
Temperature regulation hypothesis
The large surface area andvascularization
Angiogenesis is the physiological process through which new blood vessels form from pre-existing vessels, formed in the earlier stage of vasculogenesis. Angiogenesis continues the growth of the vasculature by processes of sprouting and splitting ...
of the crest also suggests a thermoregulatory function. The first to propose the cranial crests of lambeosaurines related to temperature regulation was Wheeler (1978). He proposed that there was a nerve connection between the crest and the brain
A brain is an organ that serves as the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals. It is located in the head, usually close to the sensory organs for senses such as vision. It is the most complex organ in a v ...
, so that the latter could be cooled by the former. The next people to publish a related idea were Teresa Maryańska
Teresa Maryańska (1937 – 3 October 2019) was a Polish paleontologist who specialized in Mongolian dinosaurs, particularly pachycephalosaurians and ankylosaurians. Peter Dodson (1998 p. 9) states that in 1974 Maryanska together with Hals ...
and Osmólska, who realized that like modern lizards, dinosaurs could have possessed salt glands, and cooled off by osmo-regulation. In 2006 Evans published an argument about the functions of lambeosaurine crests, and supported why this could be a causing factor for the evolution of the crest.
Behavioral hypotheses
''Parasaurolophus'' is often hypothesized to have used its crest as a resonating chamber to produce low frequency sounds to alert other members of a group or its species. This function was originally suggested by Wiman in 1931 when he described ''P. tubicen''. He noted that the crest's internal structures are similar to those of a swan and theorized that an animal could use its elongated nasal passages to create noise. However, the nasal tubes of ''Hypacrosaurus'', ''Corythosaurus'', and ''Lambeosaurus'' are much more variable and complicated than the airway of ''Parasaurolophus''. A large amount of material and data supports the hypothesis that the large, tubular crest of ''Parasaurolophus'' was a resonating chamber. Weishampel in 1981 suggested that ''Parasaurolophus'' made noises ranging between the frequencies 55 and 720 Hz, although there was some difference in the range of individual species because of the crest size, shape, and nasal passage length, most obvious in ''P. cyrtocristatus'' (interpreted as a possible female). Hopson found that there is anatomical evidence that hadrosaurids had a strong hearing. There is at least one example, in the related ''Corythosaurus'', of a slender stapes (reptilian ear bone) in place, which combined with a large space for an eardrum implies a sensitive middle ear. Furthermore, the hadrosaurid lagena is elongate like a crocodilian's, indicating that the auditory portion of the inner ear was well-developed. Based on the similarity of hadrosauridinner ears
The inner ear (internal ear, auris interna) is the innermost part of the vertebrate ear. In vertebrates, the inner ear is mainly responsible for sound detection and balance. In mammals, it consists of the bony labyrinth, a hollow cavity in the ...
to those of crocodiles
Crocodiles (family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to include all extant memb ...
, he also proposed that adult hadrosaurids were sensitive to high frequencies, such as their offspring might produce. According to Weishampel, this is consistent with parents and offspring communicating.
Computer modeling of a well-preserved specimen of ''P. tubicen'', with more complex air passages than those of ''P. walkeri'', has allowed the reconstruction of the possible sound its crest produced. The main path resonates at around 30 Hz, but the complicated sinus anatomy causes peaks and valleys in the sound.
The other main behavioral theory is that the crest was used for intra-species recognition. This means that the crest could have been used for species recognition, as a warning signal, and for other, non-sexual uses. These could have been some of the reasons crests evolved in ''Parasaurolophus'' and other hadrosaurids. Instead, social and physiological
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemical ...
functions have become more supported as function(s) of the crest, focusing on visual
The visual system comprises the sensory organ (the eye) and parts of the central nervous system (the retina containing photoreceptor cells, the optic nerve, the optic tract and the visual cortex) which gives organisms the sense of sight (the ...
and auditory identification and communication. As a large object, the crest has clear value as a visual signal and sets this animal apart from its contemporaries. The large size of hadrosaurid eye sockets
In anatomy, the orbit is the cavity or socket of the skull in which the eye and its appendages are situated. "Orbit" can refer to the bony socket, or it can also be used to imply the contents. In the adult human, the volume of the orbit is , o ...
and the presence of sclerotic ring
Sclerotic rings are rings of bone found in the eyes of many animals in several groups of vertebrates, except for mammals and crocodilians. They can be made up of single bones or multiple segments and take their name from the sclera. They are bel ...
s in the eyes imply acute vision and diurnal habits, evidence that sight was important to these animals. If, as is commonly illustrated, a skin frill extended from the crest to the neck or back, the proposed visual display would have been even showier. As is suggested by other lambeosaurine skulls, the crest of ''Parasaurolophus'' likely permitted both species identification (such as separating it from ''Corythosaurus'' or ''Lambeosaurus'') and sexual identification by shape and size.
Soft tissue frill
 Barnum Brown (1912) noted the presence of fine striations near the back of the crest that he hypothesized could be associated with the presence of a frill of skin, comparable to the one found in the modern basilisk lizard. His hypothesis was seemingly supported by skin preserved above the neck and back of ''Corythosaurus'' and ''Edmontosaurus''. Subsequently, reconstructions of ''Parasaurolophus'' with a substantial frill of skin between the crest and neck appeared in influential paleoart including murals by Charles R. Knight and in the Walt Disney animated film ''Fantasia''. This led to the frill being depicted in many other sources, though the advent of the now-debunked "snorkel" hypothesis, and conflation of the frill hypothesis with the idea that the crest serves as an anchor point for neck ligaments, along with lack of strong evidence for its presence, has seen it fall out of favor in most modern depictions.
Barnum Brown (1912) noted the presence of fine striations near the back of the crest that he hypothesized could be associated with the presence of a frill of skin, comparable to the one found in the modern basilisk lizard. His hypothesis was seemingly supported by skin preserved above the neck and back of ''Corythosaurus'' and ''Edmontosaurus''. Subsequently, reconstructions of ''Parasaurolophus'' with a substantial frill of skin between the crest and neck appeared in influential paleoart including murals by Charles R. Knight and in the Walt Disney animated film ''Fantasia''. This led to the frill being depicted in many other sources, though the advent of the now-debunked "snorkel" hypothesis, and conflation of the frill hypothesis with the idea that the crest serves as an anchor point for neck ligaments, along with lack of strong evidence for its presence, has seen it fall out of favor in most modern depictions.
Paleopathology
''Parasaurolophus walkeri'' is known from one specimen which might contain apathology
Pathology is the study of the causes and effects of disease or injury. The word ''pathology'' also refers to the study of disease in general, incorporating a wide range of biology research fields and medical practices. However, when used in ...
. The skeleton shows a v-shaped gap or notch in the vertebrae at the base of the neck. Originally thought to be pathologic, Parks published a second interpretation of this, as a ligament attachment to support the head. The crest would attach to the gap via muscles or ligaments, and be used to support the head while bearing a frill, like predicted to exist in some hadrosaurids. One other possibility, is that during preparation, the specimen was damaged, creating the possible pathology. The notch, however, is still considered more likely to be a pathology, even though some illustrations of ''Parasaurolophus'' restore the skin flap.
Another possible pathology was noticed by Parks, and from around the notch. In the fourth, fifth, and sixth vertebrae, directly anterior to the notch, the neural spines were damaged. The fourth had an obvious fracture, with the other two possessing a swelling at the base of the break.
Analysis of the pathology undertaken by Bertozzo ''et al.,'' published in December 2020, suggests the pathology to the shoulder and thoracic ribs in the holotype of ''P. walkeri'' was plausibly the result of the dinosaur being hit by a falling tree, perhaps during a severe storm. Based on the regrowth of bone, it is suggested that the hadrosaur survived for at least one to four months to perhaps years after being injured. None of the pathologies on the holotype individual are believed to have caused or contributed to its death.
Paleoecology
Alberta
Dinosaur Park Formation
The Dinosaur Park Formation is the uppermost member of the Belly River Group (also known as the Judith River Group), a major geologic unit in southern Alberta. It was deposited during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, between about 76. ...
, was a member of a diverse and well-documented fauna
Fauna is all of the animal life present in a particular region or time. The corresponding term for plants is ''flora'', and for fungi, it is '' funga''. Flora, fauna, funga and other forms of life are collectively referred to as '' biota''. Zoo ...
of prehistoric animals, including well-known dinosaurs such as the horned
A horn is a permanent pointed projection on the head of various animals that consists of a covering of keratin and other proteins surrounding a core of live bone. Horns are distinct from antlers, which are not permanent.
In mammals, true horns ...
''Centrosaurus
''Centrosaurus'' ( ; ) is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Canada. Their remains have been found in the Dinosaur Park Formation, dating from 76.5 to 75.5 million years ago.
Discovery and naming
The firs ...
'', ''Chasmosaurus
''Chasmosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of ceratopsid dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period of North America. Its name means 'opening lizard', referring to the large openings ( fenestrae) in its frill (Greek ''chasma'' meaning 'opening' or 'hollow' ...
'', and '' Styracosaurus''; fellow duckbills ''Gryposaurus
''Gryposaurus'' (meaning "hooked-nosed (Greek ''grypos'') lizard"; sometimes incorrectly translated as "griffin (Latin ''gryphus'') lizard") was a genus of duckbilled dinosaur that lived about 80 to 75 million years ago, in the Late Cretaceo ...
'' and ''Corythosaurus''; tyrannosaurid
Tyrannosauridae (or tyrannosaurids, meaning "tyrant lizards") is a family of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that comprises two subfamilies containing up to thirteen genera, including the eponymous ''Tyrannosaurus''. The exact number of genera ...
''Gorgosaurus
''Gorgosaurus'' ( ; ) is a genus of tyrannosaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in western North America during the Late Cretaceous Period (Campanian), between about 76.6 and 75.1 million years ago. Fossil remains have been found in the Ca ...
''; and armored
Armour (British English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or f ...
''Edmontonia
''Edmontonia'' is a genus of panoplosaurin nodosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period. It is part of the Nodosauridae, a family within Ankylosauria. It is named after the Edmonton Formation (now the Horseshoe Canyon Formation in Ca ...
'', ''Euoplocephalus
''Euoplocephalus'' ( ) is a genus of very large, herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaurs, living during the Late Cretaceous of Canada. It has only one named species, ''Euoplocephalus tutus''.
The first fossil of ''Euoplocephalus'' was found in 1897 i ...
'' and ''Dyoplosaurus
''Dyoplosaurus'' (meaning “double-armoured lizard”) is a monospecific genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur from Alberta that lived during the Late Cretaceous (middle Campanian, ~76.5–75 Ma) in what is now the Dinosaur Park Formation. ''Dyoplosau ...
''. It was a rare constituent of this fauna. The Dinosaur Park Formation is interpreted as a low-relief setting of river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
s and floodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudi ...
s that became more swamp
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
y and influenced by marine conditions over time as the Western Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway (also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, the North American Inland Sea, and the Western Interior Sea) was a large inland sea that split the continent of North America into two landmasses. The ancient sea ...
transgressed westward. The climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologic ...
was warmer than present-day Alberta, without frost
Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor in an above-freezing atmosphere coming in contact with a solid surface whose temperature is below freezing, and resulting in a phase change from water vapor (a gas) ...
, but with wetter and drier seasons. Conifer
Conifers are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a single ...
s were apparently the dominant canopy
Canopy may refer to:
Plants
* Canopy (biology), aboveground portion of plant community or crop (including forests)
* Canopy (grape), aboveground portion of grapes
Religion and ceremonies
* Baldachin or canopy of state, typically placed over an ...
plants, with an understory
In forestry and ecology, understory (American English), or understorey (Commonwealth English), also known as underbrush or undergrowth, includes plant life growing beneath the forest canopy without penetrating it to any great extent, but abov ...
of fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes except t ...
s, tree fern
The tree ferns are arborescent (tree-like) ferns that grow with a trunk elevating the fronds above ground level, making them trees. Many extant tree ferns are members of the order Cyatheales, to which belong the families Cyatheaceae (scaly tree ...
s, and angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s.
Some of the less common hadrosaurs in the Dinosaur Park Formation of Dinosaur Provincial Park, such as ''Parasaurolophus'', may represent the remains of individuals who died while migrating through the region. They might also have had a more upland habitat where they may have nested or fed. The presence of ''Parasaurolophus'' and ''Kritosaurus'' in northern latitude fossil sites may represent faunal exchange between otherwise distinct northern and southern biomes in Late Cretaceous North America. Both taxa are uncommon outside of the southern biome, where, along with ''Pentaceratops
''Pentaceratops'' ("five-horned face") is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsid dinosaur from the late Cretaceous Period of what is now North America. Fossils of this animal were first discovered in 1921, but the genus was named in 1923 when its ty ...
'', they are predominate members of the fauna.
New Mexico
 In the
In the Fruitland Formation
The Fruitland Formation is a geologic formation found in the San Juan Basin in the states of New Mexico and Colorado, in the United States of America. It contains fossils dating it to the Campanian age of the late Cretaceous.
of New Mexico, ''P. cyrtocristatus'' shared its habitat with other ornithischians and theropods. Specifically, its contemporaries were the ceratopsia
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic. ...
n ''Pentaceratops sternbergii
''Pentaceratops'' ("five-horned face") is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsid dinosaur from the late Cretaceous Period of what is now North America. Fossils of this animal were first discovered in 1921, but the genus was named in 1923 when its t ...
''; the pachycephalosaur
Pachycephalosauria (; from Greek παχυκεφαλόσαυρος for 'thick headed lizards') is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs. Along with Ceratopsia, it makes up the clade Marginocephalia. With the exception of two species, most pachyc ...
''Stegoceras novomexicanum
''Stegoceras'' is a genus of pachycephalosaurid (dome-headed) dinosaur that lived in what is now North America during the Late Cretaceous period, about 77.5 to 74 million years ago (mya). The first specimens from Alberta, Canada, were describ ...
''; and some unidentified fossils belonging to Tyrannosauridae
Tyrannosauridae (or tyrannosaurids, meaning "tyrant lizards") is a family of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that comprises two subfamilies containing up to thirteen genera, including the eponymous ''Tyrannosaurus''. The exact number of genera ...
, ?''Ornithomimus
''Ornithomimus'' (; "bird mimic") is a genus of ornithomimid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now North America. ''Ornithomimus'' was a swift bipedal theropod which fossil evidence indicates was covered in feathers, equippe ...
'', ?Troodontidae
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinosaurian lineages. More recent fossil disco ...
, ?''Saurornitholestes langstoni
''Saurornitholestes'' ("lizard-bird thief") is a genus of carnivorous dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur from the late Cretaceous of Canada (Alberta) and the United States (Montana, New Mexico, Alabama, North Carolina, and South Carolina).
Two spec ...
'', ?''Struthiomimus
''Struthiomimus'' (meaning "ostrich mimic", from the Ancient Greek, Greek στρούθειος/''stroutheios'' meaning "of the ostrich" and μῖμος/''mimos'' meaning "mimic" or "imitator") is a genus of Ornithomimidae, ornithomimid dinosaurs ...
'', Ornithopoda
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (), that started out as small, bipedal running grazers and grew in size and numbers until they became one of the most successful groups of herbivores in the Cretaceous worl ...
, ?''Chasmosaurus
''Chasmosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of ceratopsid dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period of North America. Its name means 'opening lizard', referring to the large openings ( fenestrae) in its frill (Greek ''chasma'' meaning 'opening' or 'hollow' ...
'', ?''Corythosaurus
''Corythosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid "duck-billed" dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period, about 77–75.7 million years ago. It lived in what is now North America. Its name means "helmet lizard", derived from Greek κόρυ� ...
'', Hadrosaurinae, Hadrosauridae, and Ceratopsidae
Ceratopsidae (sometimes spelled Ceratopidae) is a family of ceratopsian dinosaurs including ''Triceratops'', '' Centrosaurus'', and ''Styracosaurus''. All known species were quadrupedal herbivores from the Upper Cretaceous. All but one species are ...
. When ''Parasaurolophus'' existed, the Fruitland Formation was swampy, positioned in the lowlands, and close to the shore of the Cretaceous Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway (also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, the North American Inland Sea, and the Western Interior Sea) was a large inland sea that split the continent of North America into two landmasses. The ancient se ...
. The lowermost part of the Fruitland Formation is just younger than 75.56 ± 0.41 mya, with the uppermost boundary dating to 74.55 ± 0.22 mya.
Existing slightly later than the species from the Fruitland Formation, ''P. tubicen'' is also found in New Mexico, in the Kirtland Formation
The Kirtland Formation (originally the Kirtland Shale) is a sedimentary geological formation.
Description
The Kirtland Formation is the product of alluvial muds and overbank sand deposits from the many channels draining the coastal plain th ...
. Numerous vertebrate groups are from this formation, including fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
es, crurotarsan
Crurotarsi is a clade of archosauriform reptiles that includes crocodilians and stem-crocodilians and possibly bird-line archosaurs too if the extinct, crocodile-like phytosaurs are more distantly related to crocodiles than traditionally thoug ...
s, ornithischians, saurischia
Saurischia ( , meaning "reptile-hipped" from the Greek ' () meaning 'lizard' and ' () meaning 'hip joint') is one of the two basic divisions of dinosaurs (the other being Ornithischia), classified by their hip structure. Saurischia and Ornithis ...
ns, pterosaur
Pterosaurs (; from Greek ''pteron'' and ''sauros'', meaning "wing lizard") is an extinct clade of flying reptiles in the order, Pterosauria. They existed during most of the Mesozoic: from the Late Triassic to the end of the Cretaceous (228 to ...
s, and turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked tu ...
s. The fishes are represented by the two species '' Melvius chauliodous'' and '' Myledalphus bipartitus''. The crurotarsans include '' Brachychampsa montana'' and '' Denazinosuchus kirtlandicus''. Ornithischians from the formation are represented by the hadrosaurid
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which inclu ...
s '' Anasazisaurus horneri'', '' Naashoibitosaurus ostromi'', '' Kritosaurus navajovius'', and ''P. tubicen''; the ankylosaurid
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known Ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Pal ...
s '' Ahshislepelta minor'' and ''Nodocephalosaurus kirtlandensis
''Nodocephalosaurus'' (meaning "knob headed lizard") is a monotypic taxon, monospecific genus of ankylosauridae, ankylosaurid dinosaur from New Mexico that lived during the Late Cretaceous (late Campanian to early Maastrichtian stage, 73.49 to 73 ...
''; the ceratopsians ''Pentaceratops sternbergii'' and '' Titanoceratops ouranos''; and the pachycephalosaurs ''Stegoceras novomexicanum'' and '' Sphaerotholus goodwini''. Saurischians include the tyrannosaurid
Tyrannosauridae (or tyrannosaurids, meaning "tyrant lizards") is a family of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that comprises two subfamilies containing up to thirteen genera, including the eponymous ''Tyrannosaurus''. The exact number of genera ...
''Bistahieversor sealeyi
''Bistahieversor'' (meaning "Bistahi destroyer"), also known as the "Bisti Beast", is a genus of eutyrannosaurian tyrannosauroid dinosaur; the genus contains only a single known species, ''B. sealeyi'', described in 2010, from the Late Cretaceo ...
''; the ornithomimid
Ornithomimidae (meaning "bird-mimics") is a family of theropod dinosaurs which bore a superficial resemblance to modern ostriches. Ornithomimids were fast, omnivorous or herbivorous dinosaurs known mainly from the Late Cretaceous Period of Laura ...
''Ornithomimus'' sp.; and the troodontid
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinosaurian lineages. More recent fossil disco ...
"Saurornitholestes
''Saurornitholestes'' ("lizard-bird thief") is a genus of carnivorous dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur from the late Cretaceous of Canada (Alberta) and the United States (Montana, New Mexico, Alabama, North Carolina, and South Carolina).
Two spec ...
" ''robustus''. One pterosaur is known, named '' Navajodactylus boerei''. Turtles are fairly plentiful, and are known from '' Denazinemys nodosa'', ''Basilemys nobilis
''Basilemys'' () is a large, terrestrial trionychoid turtle from the Upper Cretaceous. In Greek, the word "Basil" means royal or kingly and the word "Emys" means turtle. Therefore, ''Basilemys'' means King Turtle. ''Basilemys'' has been found in r ...
'', '' Neurankylus baueri'', '' Plastomenus robustus''. and '' Thescelus hemispherica''. Unidentified taxa are known, including the crurotarsan ?''Leidyosuchus
''Leidyosuchus'' (meaning " Leidy's crocodile") is an extinct genus of alligatoroid from the Late Cretaceous of Alberta. It was named in 1907 by Lawrence Lambe, and the type species is ''L. canadensis''. It is known from a number of specimens fro ...
'', and the theropods
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally ca ...
?''Struthiomimus'', Troodontidae and Tyrannosauridae. The beginning of the Kirtland Formation dates to 74.55 ± 0.22 mya, with the formation ending at around 73.05 ± 0.25 mya.
Utah
Argon-argon radiometric dating indicates that the Kaiparowits Formation was deposited between 76.6 and 74.5 million years ago, during the Campanian stage of the LateCretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of th ...
period. During the Late Cretaceous period, the site of the Kaiparowits Formation was located near the western shore of the Western Interior Seaway
The Western Interior Seaway (also called the Cretaceous Seaway, the Niobraran Sea, the North American Inland Sea, and the Western Interior Sea) was a large inland sea that split the continent of North America into two landmasses. The ancient sea ...
, a large inland sea that split North America into two landmasses, Laramidia
Laramidia was an island continent that existed during the Late Cretaceous period (99.6–66 Ma), when the Western Interior Seaway split the continent of North America in two. In the Mesozoic era, Laramidia was an island land mass separated from A ...
to the west and Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, Ca ...
to the east. The plateau where dinosaurs lived was an ancient floodplain dominated by large channels and abundant wetland peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and is the most efficien ...
swamps, ponds and lakes, and was bordered by highlands. The climate was wet and humid, and supported an abundant and diverse range of organisms. This formation contains one of the best and most continuous records of Late Cretaceous terrestrial life in the world.
''Parasaurolophus'' shared its paleoenvironment
Paleoecology (also spelled palaeoecology) is the study of interactions between organisms and/or interactions between organisms and their environments across geologic timescales. As a discipline, paleoecology interacts with, depends on and informs ...
with other dinosaurs, such as dromaeosaurid
Dromaeosauridae () is a family of feathered theropod dinosaurs. They were generally small to medium-sized feathered carnivores that flourished in the Cretaceous Period. The name Dromaeosauridae means 'running lizards', from Greek ('), meaning ...
theropod
Theropoda (; ), whose members are known as theropods, is a dinosaur clade that is characterized by hollow bones and three toes and claws on each limb. Theropods are generally classed as a group of saurischian dinosaurs. They were ancestrally c ...
s, the troodontid
Troodontidae is a clade of bird-like theropod dinosaurs. During most of the 20th century, troodontid fossils were few and incomplete and they have therefore been allied, at various times, with many dinosaurian lineages. More recent fossil disco ...
'' Talos sampsoni'', ornithomimids
Ornithomimidae (meaning "bird-mimics") is a family of theropod dinosaurs which bore a superficial resemblance to modern ostriches. Ornithomimids were fast, omnivorous or herbivorous dinosaurs known mainly from the Late Cretaceous Period of Lauras ...
like ''Ornithomimus velox
''Ornithomimus'' (; "bird mimic") is a genus of ornithomimid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now North America. ''Ornithomimus'' was a swift bipedal theropod which fossil evidence indicates was covered in feathers, equipped ...
'', tyrannosaurids
Tyrannosauridae (or tyrannosaurids, meaning "tyrant lizards") is a family (biology), family of coelurosaurian Theropoda, theropod dinosaurs that comprises two subfamilies containing up to thirteen genus, genera, including the eponymous ''Tyrannos ...
like ''Albertosaurus
''Albertosaurus'' (; meaning "Alberta lizard") is a genus of tyrannosaurid theropod dinosaurs that lived in western North America during the Late Cretaceous Period, about 71 million years ago. The type species, ''A. sarcophagus'', wa ...
'' and ''Teratophoneus
''Teratophoneus'' ("monstrous murderer"; Greek: ''teras'', "monster" and ''phoneus'', "murderer") is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur which lived during the late Cretaceous period (late Campanian age, about 77 to 76 million years ago) in what i ...
'', armored ankylosaurids, the duckbilled hadrosaur ''Gryposaurus monumentensis
''Gryposaurus'' (meaning "hooked-nosed (Greek ''grypos'') lizard"; sometimes incorrectly translated as " griffin (Latin ''gryphus'') lizard") was a genus of duckbilled dinosaur that lived about 80 to 75 million years ago, in the Late Cretac ...
'', the ceratopsians
Ceratopsia or Ceratopia ( or ; Greek: "horned faces") is a group of herbivorous, beaked dinosaurs that thrived in what are now North America, Europe, and Asia, during the Cretaceous Period, although ancestral forms lived earlier, in the Jurassic ...
''Utahceratops gettyi
''Utahceratops'' is an extinct genus of ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 76.4~75.5 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now Utah. ''Utahceratops'' was a large-sized, robustly-built, ground-dwelling, quadrupe ...
'', ''Nasutoceratops titusi
''Nasutoceratops'' is an extinct genus of ceratopsian dinosaur. It is a basal Centrosaurinae, centrosaurine which lived during the Late Cretaceous period (geology), Period (late Campanian, about 76.0-75.5 Mya (unit), Ma). Fossils have been found ...
'' and ''Kosmoceratops richardsoni
''Kosmoceratops'' () is a genus of ceratopsid dinosaur that lived in North America about 76–75.9 million years ago during the Late Cretaceous period. Specimens were discovered in Utah in the Kaiparowits Formation of the Grand Staircase–Esca ...
'' and the oviraptorosauria
Oviraptorosaurs ("egg thief lizards") are a group of feathered maniraptoran dinosaurs from the Cretaceous Period of what are now Asia and North America. They are distinct for their characteristically short, beaked, parrot-like skulls, with or wi ...
n ''Hagryphus giganteus
''Hagryphus'' (meaning " Ha's griffin") is a monospecific genus of caenagnathid dinosaur from southern Utah that lived during the Late Cretaceous (upper Campanian stage, 75.95 Ma) in what is now the Kaiparowits Formation of the Grand Staircase– ...
''. Paleofauna present in the Kaiparowits Formation included chondrichthyans
Chondrichthyes (; ) is a class that contains the cartilaginous fishes that have skeletons primarily composed of cartilage. They can be contrasted with the Osteichthyes or ''bony fishes'', which have skeletons primarily composed of bone tissue. C ...
(sharks and rays), frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely Carnivore, carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order (biology), order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-f ...
s, salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All ten ...
s, turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked tu ...
s, lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia alt ...
s and crocodilia
Crocodilia (or Crocodylia, both ) is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles, known as crocodilians. They first appeared 95 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period ( Cenomanian stage) and are the closest living ...
ns like the apex predator
An apex predator, also known as a top predator, is a predator at the top of a food chain, without natural predators of its own.
Apex predators are usually defined in terms of trophic dynamics, meaning that they occupy the highest trophic lev ...
''Deinosuchus
''Deinosuchus'' () is an extinct genus of alligatoroid crocodilian, related to modern alligators and caimans, that lived 82 to 73 million years ago (Ma), during the late Cretaceous period. The name translates as "terrible crocodile" and i ...
''. A variety of early mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s were present including multituberculate
Multituberculata (commonly known as multituberculates, named for the multiple tubercles of their teeth) is an extinct order of rodent-like mammals with a fossil record spanning over 130 million years. They first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, a ...
s, marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a po ...
s, and insectivora
The order Insectivora (from Latin ''insectum'' "insect" and ''vorare'' "to eat") is a now-abandoned biological grouping within the class of mammals. Some species have now been moved out, leaving the remaining ones in the order Eulipotyphla, wi ...
ns.
See also
*Timeline of hadrosaur research
A timeline is a display of a list of events in chronological order. It is typically a graphic design showing a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it, and usually contemporaneous events.
Timelines can use any suitable scale represent ...
References
Footnotes
Citations
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* * * * * * {{Taxonbar, from=Q203583 Late Cretaceous dinosaurs of North America Lambeosaurines Fossil taxa described in 1922 Taxa named by William Parks Kirtland fauna Dinosaur Park fauna Paleontology in Alberta Paleontology in New Mexico Paleontology in Utah Kaiparowits Formation Campanian genus first appearances Campanian genus extinctions Ornithischian genera