|
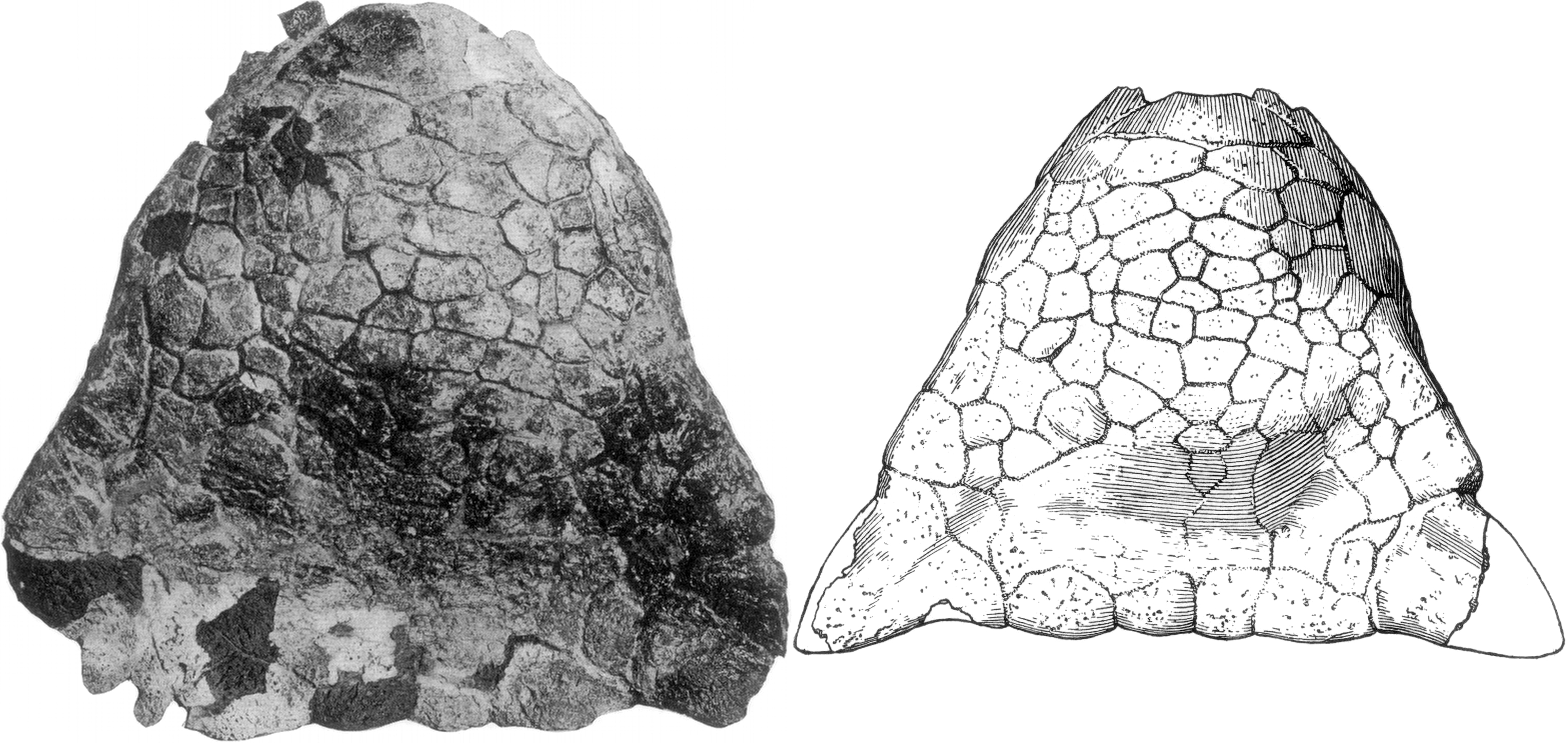
Dyoplosaurus
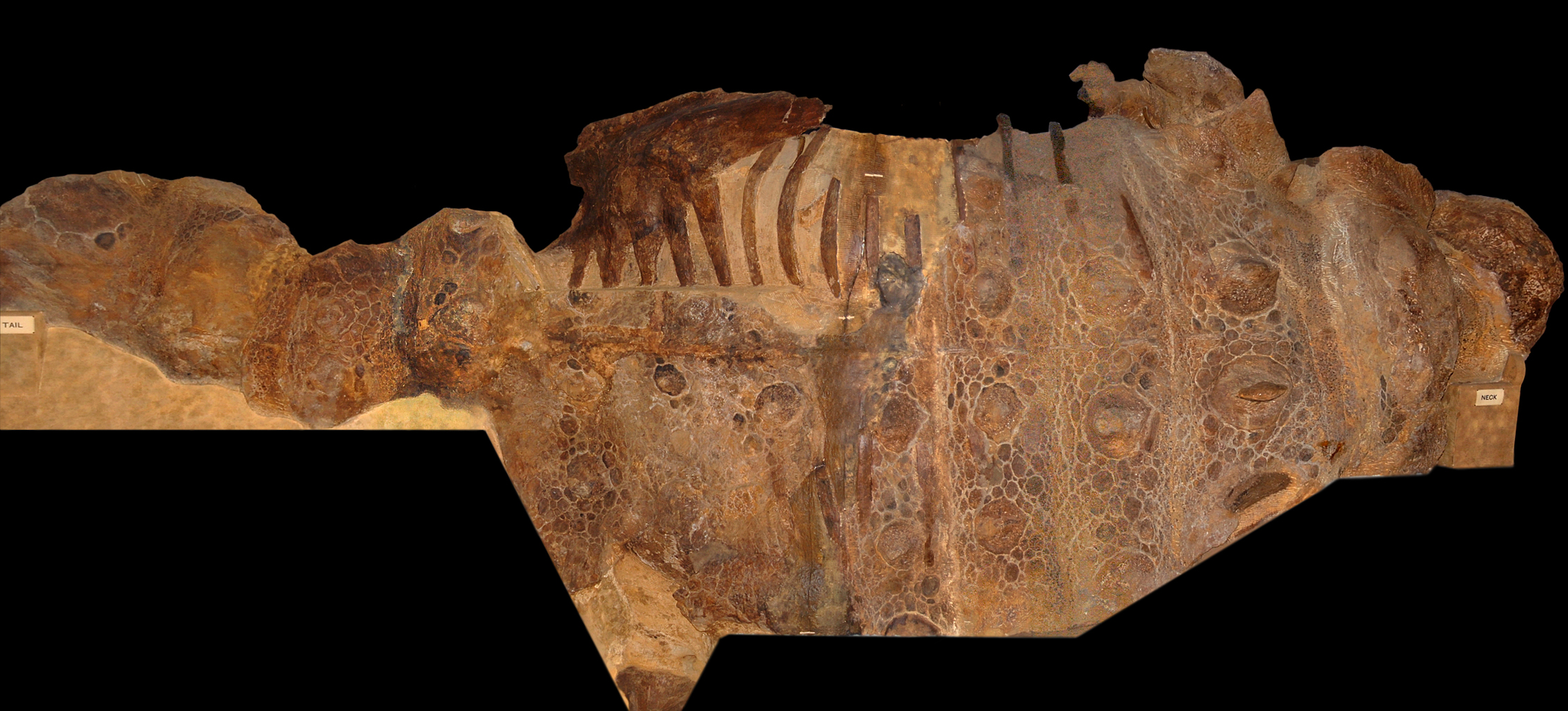
''Dyoplosaurus'' (meaning “double-armoured lizard”) is a monospecific genus of ankylosaurid dinosaur from Alberta that lived during the Late Cretaceous (middle Campanian, ~76.5–75 Ma) in what is now the Dinosaur Park Formation. ''Dyoplosaurus'' represents a close relative of ''Scolosaurus'' and ''Anodontosaurus'', two ankylosaurids known from the Horseshoe Canyon and Dinosaur Park Formation. Discovery and naming The holotype specimen was obtained in 1919 from the bottom ten metres of the Dinosaur Park Formation by Levi Sternberg, near what is now the Red Deer River in Alberta, Canada. The holotype specimen, ROM 784, consists of a partial skull roof, mandible fragments with teeth, osteoderms, skin impressions, articulated post-thoracic vertebrae, partial thoracic ribs, a partial ilium, both ischia, tail club, associated radius, metacarpal, femur, tibia, fibula, and pes. The holotype is currently housed at the Royal Ontario Museum. Two specimens were referred to ''Dyoplosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scolosaurus
''Scolosaurus'' is an extinct genus of ankylosaurid dinosaurs within the subfamily Ankylosaurinae. It is known from the lower levels of the Dinosaur Park Formation and upper levels of the Oldman Formation in the Late Cretaceous (latest middle Campanian stage, about 76.5 Ma ago) of Alberta, Canada. It contains two species, ''S. cutleri'' and ''S. thronus''. The type species, ''S. cutleri'', measured up to in length and in body mass. Discovery ''Scolosaurus'' was named by Franz Nopcsa von Felső-Szilvás in 1928, based on holotype NHMUK R.5161, a nearly complete specimen that preserves the entire skeleton except for the distal end of the tail, the right forelimb, the right hindlimb, and the skull. The rare preservation of osteoderms and skin impression are also present. The fossil skeleton was discovered by William Edmund Cutler, an independent fossil collector in 1914 at Quarry 80 of the Deadlodge Canyon locality. It was collected from the bottom of the Dinosaur Park ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euoplocephalus
''Euoplocephalus'' ( ) is a genus of very large, herbivorous ankylosaurid dinosaurs, living during the Late Cretaceous of Canada. It has only one named species, ''Euoplocephalus tutus''. The first fossil of ''Euoplocephalus'' was found in 1897 in Alberta. In 1902, it was named ''Stereocephalus'', but that name had already been given to an insect, so it was changed in 1910. Later, many more ankylosaurid remains were found from the Campanian of North America and often made separate genera. In 1971, Walter Coombs concluded that they all belonged to ''Euoplocephalus'' which then would be one of the best-known dinosaurs. Recently however, experts have come to the opposite conclusion, limiting the authentic finds of ''Euoplocephalus'' to about a dozen specimens. These include a number of almost complete skeletons, so much is nevertheless known about the build of the animal. ''Euoplocephalus'' reached in length and in body mass. Its body was low-slung and very flat and wide, standin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anodontosaurus
''Anodontosaurus'' is an extinct genus of ankylosaurid dinosaurs within the subfamily Ankylosaurinae. It is known from the entire span of the Late Cretaceous Horseshoe Canyon Formation (mid Late Campanian to "middle" Maastrichtian stage, about 72.8-67 Ma ago) of southern Alberta, Canada. It contains two species, ''A. lambei'' and ''A. inceptus''. Discovery ''Anodontosaurus'' was named by Charles Mortram Sternberg in 1928, based on holotype CMN 8530, a partially preserved skeleton including the skull, half ring, armor and other postcranial remains.C. M. Sternberg (1929) "A toothless armoured dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous of Alberta." ''Canada Department of Mines Geological Survey Bulletin (Geological Series)'' 54(49):28-33 The badly crushed skeleton was collected by Sternberg in 1916 from a Canadian Museum of Nature quarry, 8 miles southwest of Morrin. It was collected from the upper part of the Lower Horseshoe Canyon Formation (unit 2), dating to the latest Campanian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur Park Formation
The Dinosaur Park Formation is the uppermost member of the Belly River Group (also known as the Judith River Group), a major geologic unit in southern Alberta. It was deposited during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, between about 76.5 and 74.4 million years ago. It was deposited in alluvial and coastal plain environments, and it is bounded by the nonmarine Oldman Formation below it and the marine Bearpaw Formation above it.Eberth, D.A. 2005. The geology. In: Currie, P.J., and Koppelhus, E.B. (eds), Dinosaur Provincial Park: A Spectacular Ancient Ecosystem Revealed. Indiana University Press: Bloomington and Indianapolis, p.54-82. . The Dinosaur Park Formation contains dense concentrations of dinosaur skeletons, both articulated and disarticulated, which are often found with preserved remains of soft tissues. Remains of other animals such as fish, turtles, and crocodilians, as well as plant remains, are also abundant. The formation has been named after Dinosaur Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosauridae
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known Ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. These animals were mainly herbivorous and were obligate quadrupeds, with leaf-shaped teeth and robust, scute-covered bodies. Ankylosaurids possess a distinctly domed and short snout, wedge-shaped osteoderms on their skull, scutes along their torso, and a tail club. Ankylosauridae is exclusively known from the northern hemisphere, with specimens found in western North America, Europe, and East Asia. The first discoveries within this family were of the genus ''Ankylosaurus'', by Peter Kaiser and Barnum Brown in Montana in 1906. Brown went on to name Ankylosauridae and the subfamily Ankylosaurinae in 1908. Anatomy Ankylosaurids are stout, solidly built, armoured dinosaurs. They possess accessory ossifications on c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosaurid Tail Clubs
Ankylosauridae () is a family of armored dinosaurs within Ankylosauria, and is the sister group to Nodosauridae. The oldest known Ankylosaurids date to around 122 million years ago and went extinct 66 million years ago during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. These animals were mainly herbivorous and were obligate quadrupeds, with leaf-shaped teeth and robust, scute-covered bodies. Ankylosaurids possess a distinctly domed and short snout, wedge-shaped osteoderms on their skull, scutes along their torso, and a tail club. Ankylosauridae is exclusively known from the northern hemisphere, with specimens found in western North America, Europe, and East Asia. The first discoveries within this family were of the genus ''Ankylosaurus'', by Peter Kaiser and Barnum Brown in Montana in 1906. Brown went on to name Ankylosauridae and the subfamily Ankylosaurinae in 1908. Anatomy Ankylosaurids are stout, solidly built, armoured dinosaurs. They possess accessory ossifications on c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Arbour
Victoria Megan Arbour is a Canadian evolutionary biologist and vertebrate palaeontologist at Royal BC Museum, where she is Curator of Palaeontology. An "expert on the armoured dinosaurs known as ankylosaurs", Arbour analyzes fossils and creates 3-D computer models. She named the possible pterosaur '' Gwawinapterus'' from Hornby Island, and a partial ornithischian dinosaur from Sustut Basin, British Columbia (now named ''Ferrisaurus''), and has participated in the naming of the ankylosaurs ''Zuul'', ''Zaraapelta'', ''Crichtonpelta'', and ''Ziapelta''. Early life and education Born in 1983, Arbour is from Halifax, Nova Scotia. Her mother, a math teacher, and father, a soil scientist, supported her science interests. Arbour completed a B.Sc. Honours Thesis supervised by Milton Graves, ''An ornithischian dinosaur from the Sustut Basin, British Columbia, Canada'', and graduated from Dalhousie University in 2006. She completed her master's thesis, ''Evolution, biomechanics, and func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosaurinae
Ankylosaurinae is a subfamily of ankylosaurid dinosaurs, existing from the Early Cretaceous about 105 million years ago until the end of the Late Cretaceous, about 66 mya. Many genera are included in the clade, such as ''Ankylosaurus'', ''Pinacosaurus'', ''Euoplocephalus'', and ''Saichania''. Features Ankylosaurines are defined as being closer relatives to ''Ankylosaurus'' than to ''Shamosaurus''. Diagnostic features of ankylosaurines include the nuchal shelf that obscures the occiput in dorsal view, and the quadrate condyle which is obscured lightly by the quadratojugal boss. Phylogeny The following cladogram is based on the 50% majority rule phylogenetic analysis In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ... of Arbour & Currie (2015): References Ankylosaur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosaurus
''Ankylosaurus'' is a genus of armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of the non-avian dinosaurs. It was named by Barnum Brown in 1908; it is monotypic, containing only ''A. magniventris''. The generic name means "fused" or "bent lizard", and the specific name means "great belly". A handful of specimens have been excavated to date, but a complete skeleton has not been discovered. Though other members of Ankylosauria are represented by more extensive fossil material, ''Ankylosaurus'' is often considered the archetypal member of its group, despite having some unusual features. Possibly the largest-known ankylosaurid, ''Ankylosaurus'' is estimated to have been between long and to have weighed between . It was quadrupedal, with a broad, robust body. It had a wide, low skull, with two horns pointing backward from the b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinacosaurus
''Pinacosaurus'' (meaning "Plank lizard") is a genus of ankylosaurid thyreophoran dinosaur that lived in Asia during the Late Cretaceous (Santonian-Campanian, roughly 75 million to 71 million years ago), mainly in Mongolia and China. The first remains of the genus were found in 1923, and the type species ''Pinacosaurus grangeri'' was named in 1933. ''Pinacosaurus mephistocephalus'' named in 1999, is a second possibly valid species differing from the type species in details of the skull armour. Of ''Pinacosaurus grangeri'' many skeletons have been found, more than of any other ankylosaur. These predominantly consist of juveniles that perhaps lived in herds roaming the desert landscape of their habitat. ''Pinacosaurus'' was a medium-sized ankylosaurine, about five metres long and weighed up to two tonnes. Its body was flat and low-slung but not as heavily built as in some other members of the Ankylosaurinae. The head was protected by bone tiles, hence its name. Each nostril was for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1924 In Paleontology
Dinosaurs Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Plesiosaurs New taxa Synapsids Non-mammalian References {{portal, Paleontology 1920s in paleontology Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fossi ... Paleontology 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Parks (paleontologist)
William Arthur Parks (11 December 1868 – 3 October 1936) was a Canadian geologist and paleontologist, following in the tradition of Lawrence Lambe. Parks was born in Hamilton, Ontario. After graduating with a Bachelor of Arts in 1892, Parks joined the University of Toronto's staff, where he taught geology, paleontology, and mineralogy. He went on to earn a PhD in 1900. He wrote 80 scientific papers in his lifetime. Parks died in Toronto, Ontario, in 1936. Named taxa * 1919 '' Kritosaurus incurvimanus'' * 1922 ''Parasaurolophus walkeri'' * 1923 '' Corythosaurus intermedius'' * 1923 ''Lambeosaurus lambei'' * 1924 ''Dyoplosaurus acutosquameus'' * 1925 ''Arrhinoceratops brachyops'' * 1925 '' Neomeryx finni'' * 1926 '' Struthiomimus brevitertius'' (type species of ''Dromiceiomimus'') * 1928 ''Struthiomimus samueli'' * 1928 '' Albertosaurus arctunguis'' * 1931 '' Tetragonosaurus praeceps'' * 1931 '' Tetragonosaurus erectofrons'' * 1933 ''Struthiomimus currelli'' * 1933 '' Struthi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |