|
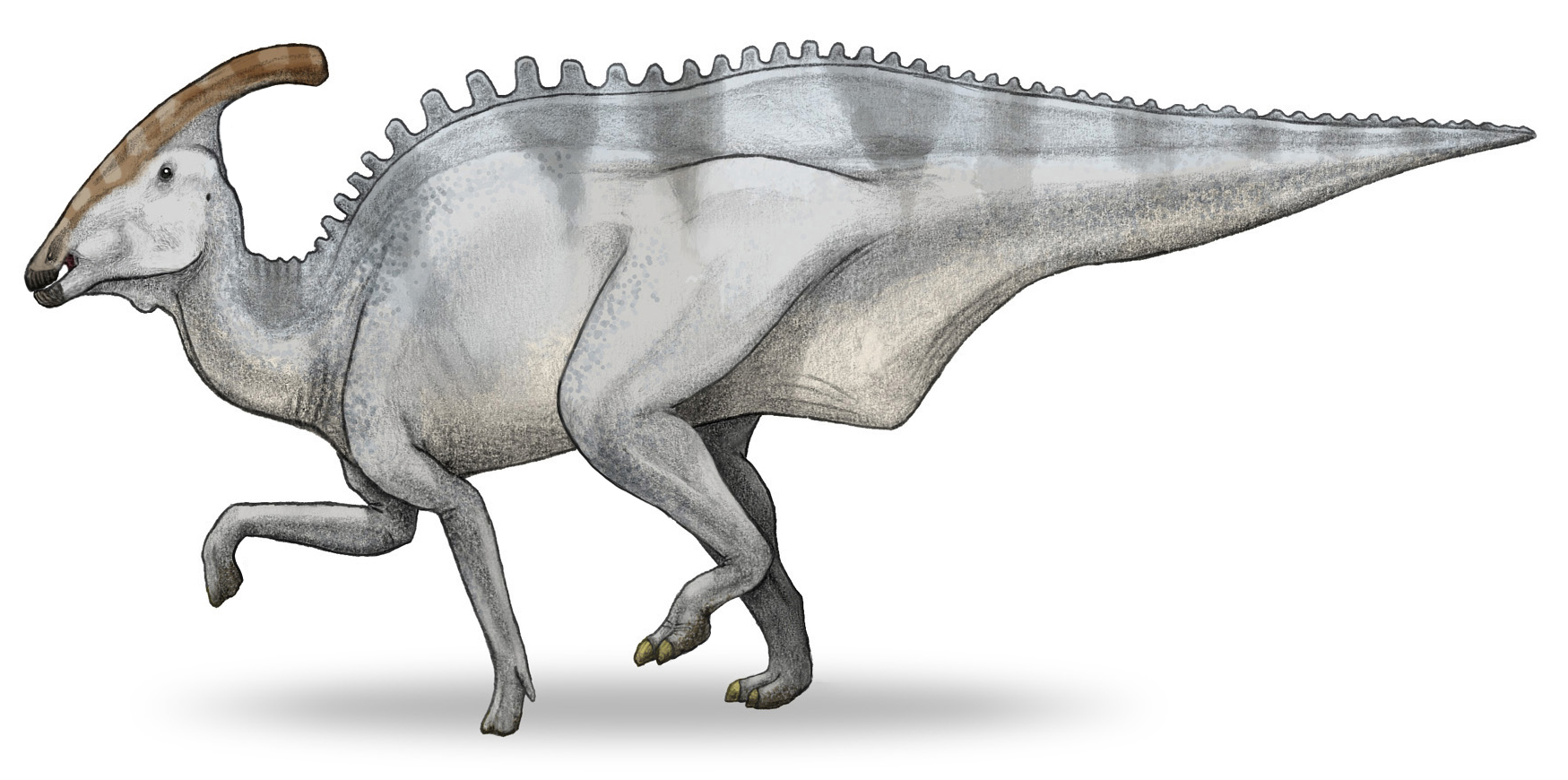
Parasaurolophus
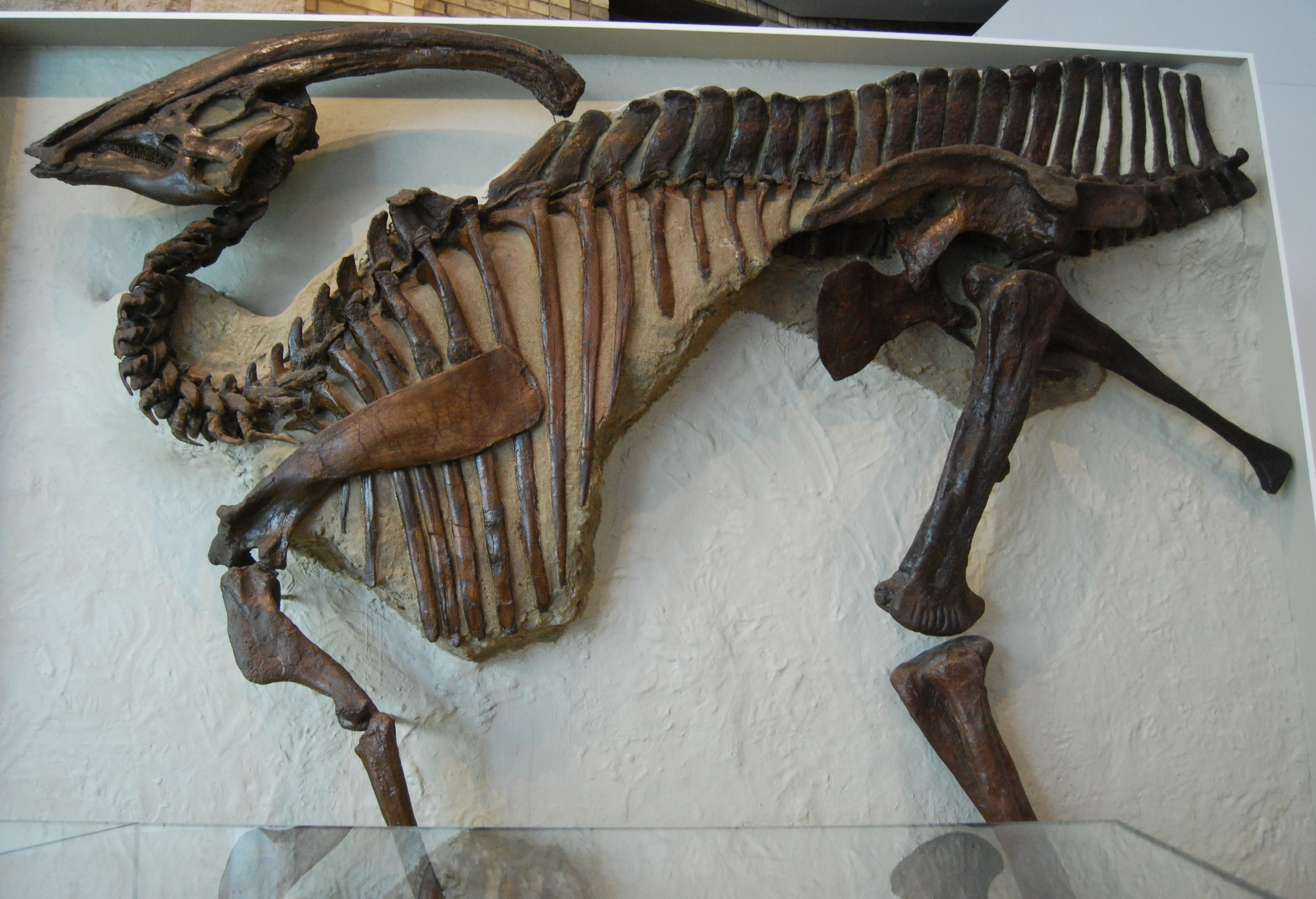
''Parasaurolophus'' (; meaning "near crested lizard" in reference to ''Saurolophus)'' is a genus of herbivorous hadrosaurid ornithopod dinosaur that lived in what is now North America and possibly Asia during the Late Cretaceous Period, about 76.5–73 million years ago. It was a herbivore that walked both as a biped and as a quadruped. Three species are universally recognized: ''P. walkeri'' (the type species), ''P. tubicen'', and the short-crested ''P. cyrtocristatus''. Additionally, a fourth species, ''P. jiayinensis'', has been proposed, although it is more commonly placed in the separate genus '' Charonosaurus''. Remains are known from Alberta (Canada), New Mexico and Utah (United States), and possibly Heilongjiang (China). The genus was first described in 1922 by William Parks from a skull and partial skeleton found in Alberta. ''Parasaurolophus'' was a hadrosaurid, part of a diverse family of Cretaceous dinosaurs known for their range of bizarre head adornmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charonosaurus
''Charonosaurus'' ( ; meaning "Charon's lizard") is a genus of dinosaur whose fossils were discovered by Godefroit, Zan & Jin in 2000 on the south bank of the Amur River, dividing China from Russia. It is monotypic, consisting of the species ''C. jiayinensis''. Description ''Charonosaurus'' is a very large lambeosaurine hadrosaur, estimated around in length and in body mass.Holtz, Thomas R. Jr. (2012) ''Dinosaurs: The Most Complete, Up-to-Date Encyclopedia for Dinosaur Lovers of All Ages,'Winter 2011 Appendix./ref> It is known from a partial skull (Holotype: CUST J-V1251-57 (Changchun University of Sciences and Technology, Changchun, Jilin Province, China) found in the Late Maastrichtian Yuliangze Formation, west of Jiayin village, Heilongjiang Province, northeastern China. Adult and juvenile hadrosaur remains discovered in the same area and formation likely represent the same taxon and supply information on most of the postcranial skeleton; the femur length was up to 1.3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hadrosauridae
Hadrosaurids (), or duck-billed dinosaurs, are members of the ornithischian family Hadrosauridae. This group is known as the duck-billed dinosaurs for the flat duck-bill appearance of the bones in their snouts. The ornithopod family, which includes genera such as '' Edmontosaurus'' and '' Parasaurolophus'', was a common group of herbivores during the Late Cretaceous Period. Hadrosaurids are descendants of the Upper Jurassic/Lower Cretaceous iguanodontian dinosaurs and had a similar body layout. Hadrosaurs were among the most dominant herbivores during the Late Cretaceous in Asia and North America, and during the close of the Cretaceous several lineages dispersed into Europe, Africa, South America and Antarctica. Like other ornithischians, hadrosaurids had a predentary bone and a pubic bone which was positioned backwards in the pelvis. Unlike more primitive iguanodonts, the teeth of hadrosaurids are stacked into complex structures known as dental batteries, which acted as ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1922 In Paleontology
Arthropods Insects Archosauromorphs Newly named phytosaurs Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Plesiosaurs New taxa Synapsids Non-mammalian References {{portal, Paleontology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithopod
Ornithopoda () is a clade of ornithischian dinosaurs, called ornithopods (), that started out as small, bipedal running grazers and grew in size and numbers until they became one of the most successful groups of herbivores in the Cretaceous world, dominating the North American land. Their major evolutionary advantage was the progressive development of a chewing apparatus that became the most sophisticated ever developed by a non-avian dinosaur, rivaling that of modern mammals such as the domestic cow. They reached their apex of diversity and ecological dominance in the hadrosaurids (colloquially known as 'duck-bills'), before they were wiped out by the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event along with all other non- avian dinosaurs. Members are known from all seven continents, though they are generally rare in the Southern Hemisphere. History of research In 1870, Thomas Henry Huxley listed Iguanodontidae (coined by Cope a year earlier) as one of his three families of dinosa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Wiman
Carl Johan Josef Ernst Wiman (March 10, 1867 – June 15, 1944) was a Swedish palaeontologist, the first professor of palaeontology and historical geology at Uppsala University, and the father of Swedish vertebrate palaeontology. Wiman was instrumental in the construction of the Palaeontological Museum of Uppsala University (now part of the Museum of Evolution), which contains the largest collection of Chinese fossil vertebrate material outside China. He is responsible for naming the genera ''Helopus'' (renamed ''Euhelopus'' because ''Helopus'' was already in use) and '' Tanius'', and the species ''Pentaceratops fenestratus'' and '' Parasaurolophus tubicen''. He was also the first to suggest that the hollow cranial crests of lambeosaurine duckbill dinosaurs could be used as a horn-like noisemaker. Early life Family Wiman was born on 10 March 1867 in the recently inaugurated Märsta railway station, located on Husby-Odensala, Stockholm. Wiman's father was a Swed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Museum Of Natural History
The Field Museum of Natural History (FMNH), also known as The Field Museum, is a natural history museum in Chicago, Illinois, and is one of the largest such museums in the world. The museum is popular for the size and quality of its educational and scientific programs, and its extensive scientific-specimen and artifact collections. The permanent exhibitions, which attract up to two million visitors annually, include fossils, current cultures from around the world, and interactive programming demonstrating today's urgent conservation needs. The museum is named in honor of its first major benefactor, Marshall Field, the department-store magnate. The museum and its collections originated from the 1893 World's Columbian Exposition and the artifacts displayed at the fair. The museum maintains a temporary exhibition program of traveling shows as well as in-house produced topical exhibitions. The professional staff maintains collections of over 24 million specimens and objects t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Parks (paleontologist)
William Arthur Parks (11 December 1868 – 3 October 1936) was a Canadian geologist and paleontologist, following in the tradition of Lawrence Lambe. Parks was born in Hamilton, Ontario. After graduating with a Bachelor of Arts in 1892, Parks joined the University of Toronto's staff, where he taught geology, paleontology, and mineralogy. He went on to earn a PhD in 1900. He wrote 80 scientific papers in his lifetime. Parks died in Toronto, Ontario, in 1936. Named taxa * 1919 ''Kritosaurus incurvimanus'' * 1922 ''Parasaurolophus walkeri'' * 1923 ''Corythosaurus intermedius'' * 1923 ''Lambeosaurus lambei'' * 1924 '' Dyoplosaurus acutosquameus'' * 1925 '' Arrhinoceratops brachyops'' * 1925 '' Neomeryx finni'' * 1926 ''Struthiomimus brevitertius'' (type species of '' Dromiceiomimus'') * 1928 '' Struthiomimus samueli'' * 1928 ''Albertosaurus arctunguis'' * 1931 ''Tetragonosaurus praeceps'' * 1931 ''Tetragonosaurus erectofrons ''Lambeosaurus'' ( , meaning " Lambe's lizard") is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saurolophus
''Saurolophus'' (; meaning "lizard crest") is a genus of large hadrosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of Asia and North America, that lived in what is now the Horseshoe Canyon and Nemegt formations about 70 million to 68 million years ago. It is one of the few genera of dinosaurs known from multiple continents. The type species, ''S. osborni'', was described by Barnum Brown in 1912 from Canadian fossils. A second valid species, ''S. angustirostris'', is represented by numerous specimens from Mongolia, and was described by Anatoly Konstantinovich Rozhdestvensky. ''Saurolophus'' is distinguished by a spike-like crest which projects up and back from the skull. It was a herbivorous dinosaur which could move about either bipedally or quadrupedally. Discovery and history Barnum Brown recovered the first described remains of ''Saurolophus'' in 1911, including a nearly complete skeleton ( AMNH 5220). Now on display in the American Museum of Natural History, this s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadruped
Quadrupedalism is a form of locomotion where four limbs are used to bear weight and move around. An animal or machine that usually maintains a four-legged posture and moves using all four limbs is said to be a quadruped (from Latin ''quattuor'' for "four", and ''pes'', ''pedis'' for "foot"). Quadruped animals are found among both vertebrates and invertebrates. Quadrupeds vs. tetrapods Although the words ‘quadruped’ and ‘tetrapod’ are both derived from terms meaning ‘four-footed’, they have distinct meanings. A tetrapod is any member of the taxonomic unit Tetrapoda (which is defined by descent from a specific four-limbed ancestor), whereas a quadruped actually uses four limbs for locomotion. Not all tetrapods are quadrupeds and not all entities that could be described as ‘quadrupedal’ are tetrapods. This last meaning includes certain artificial objects; almost all quadruped ''organisms'' are tetrapods (with the exception of some raptorial arthropods adapte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Period (geology)
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bipedalism
Bipedalism is a form of terrestrial locomotion where an organism moves by means of its two rear limbs or legs. An animal or machine that usually moves in a bipedal manner is known as a biped , meaning 'two feet' (from Latin ''bis'' 'double' and ''pes'' 'foot'). Types of bipedal movement include walking, running, and hopping. Several groups of modern species are habitual bipeds whose normal method of locomotion is two-legged. In the Triassic period some groups of archosaurs (a group that includes crocodiles and dinosaurs) developed bipedalism; among the dinosaurs, all the early forms and many later groups were habitual or exclusive bipeds; the birds are members of a clade of exclusively bipedal dinosaurs, the theropods. Within mammals, habitual bipedalism has evolved multiple times, with the macropods, kangaroo rats and mice, springhare, hopping mice, pangolins and hominin apes ( australopithecines, including humans) as well as various other extinct groups evolving th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |