Oregon pioneers on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Oregon () is a
 While there is considerable evidence that Paleo-Indians inhabited the region, the oldest evidence of habitation in Oregon was found at
While there is considerable evidence that Paleo-Indians inhabited the region, the oldest evidence of habitation in Oregon was found at
 The Lewis and Clark Expedition traveled through northern Oregon also in search of the
The Lewis and Clark Expedition traveled through northern Oregon also in search of the
 Oregon is north to south at longest distance, and east to west. With an area of , Oregon is slightly larger than the
Oregon is north to south at longest distance, and east to west. With an area of , Oregon is slightly larger than the
 Western Oregon's mountainous regions, home to three of the most prominent mountain peaks of the United States including
Western Oregon's mountainous regions, home to three of the most prominent mountain peaks of the United States including
 * Many species of mammals live in the state, which include opossums, shrews, moles, little pocket mice, great basin pocket mice,
* Many species of mammals live in the state, which include opossums, shrews, moles, little pocket mice, great basin pocket mice,
 Most of Oregon has a generally mild climate, though there is significant variation given the variety of landscapes across the state. The state's western region (west of the
Most of Oregon has a generally mild climate, though there is significant variation given the variety of landscapes across the state. The state's western region (west of the

 The
The  The Roma first reached Oregon in the 1890s. There is a substantial Roma population in Willamette Valley and around Portland.
The Roma first reached Oregon in the 1890s. There is a substantial Roma population in Willamette Valley and around Portland.
 * Total Employment (2016): 1,551,192
* Number of employer establishments (2016): 114,551
, Oregon ranks as the 17th highest in
* Total Employment (2016): 1,551,192
* Number of employer establishments (2016): 114,551
, Oregon ranks as the 17th highest in
 Oregon's diverse landscapes provide ideal environments for various types of farming. Land in the Willamette Valley owes its fertility to the
Oregon's diverse landscapes provide ideal environments for various types of farming. Land in the Willamette Valley owes its fertility to the
''Ecological Subregions of the United States''. Chapter 24.
U.S. Forest Service and Dept. of Agriculture. In 2016, the Willamette Valley region produced over of

 Vast forests have historically made Oregon one of the nation's major
Vast forests have historically made Oregon one of the nation's major

 Tourism is also a strong industry in the state. Tourism is centered on the state's natural features – mountains, forests, waterfalls, rivers, beaches and lakes, including
Tourism is also a strong industry in the state. Tourism is centered on the state's natural features – mountains, forests, waterfalls, rivers, beaches and lakes, including  Portland is home to the
Portland is home to the
 Oregon is also the home of large corporations in other industries. The world headquarters of Nike, Inc., Nike is located near Beaverton. Medford is home to Harry and David, which sells gift items under several brands. Medford is also home to the national headquarters of Lithia Motors. Portland is home to one of the West's largest trade book publishing houses, Graphic Arts Center Publishing. Oregon is also home to Mentor Graphics, Mentor Graphics Corporation, a world leader in electronic design automation located in Wilsonville, Oregon, Wilsonville and employs roughly 4,500 people worldwide.
Adidas, Adidas Corporations American Headquarters is located in Portland and employs roughly 900 full-time workers at its Portland campus. Nike, located in Beaverton, employs roughly 5,000 full-time employees at its campus. Nike's Beaverton campus is continuously ranked as a top employer in the Portland area-along with competitor Adidas. Intel, Intel Corporation employs 22,000 in Oregon with the majority of these employees located at the company's Hillsboro campus located about 30 minutes west of Portland. Intel has been a top employer in Oregon since 1974.
The U.S. Federal Government and Providence Health systems are respective contenders for top employers in Oregon with roughly 12,000 federal workers and 14,000 Providence Health workers.
In 2015, a total of seven companies headquartered in Oregon landed in the Fortune 1000: Nike, at 106; Precision Castparts Corp. at 302; Lithia Motors at 482; StanCorp Financial Group at 804; Schnitzer Steel Industries at 853; The Greenbrier Companies at 948; and Columbia Sportswear at 982.
Oregon is also the home of large corporations in other industries. The world headquarters of Nike, Inc., Nike is located near Beaverton. Medford is home to Harry and David, which sells gift items under several brands. Medford is also home to the national headquarters of Lithia Motors. Portland is home to one of the West's largest trade book publishing houses, Graphic Arts Center Publishing. Oregon is also home to Mentor Graphics, Mentor Graphics Corporation, a world leader in electronic design automation located in Wilsonville, Oregon, Wilsonville and employs roughly 4,500 people worldwide.
Adidas, Adidas Corporations American Headquarters is located in Portland and employs roughly 900 full-time workers at its Portland campus. Nike, located in Beaverton, employs roughly 5,000 full-time employees at its campus. Nike's Beaverton campus is continuously ranked as a top employer in the Portland area-along with competitor Adidas. Intel, Intel Corporation employs 22,000 in Oregon with the majority of these employees located at the company's Hillsboro campus located about 30 minutes west of Portland. Intel has been a top employer in Oregon since 1974.
The U.S. Federal Government and Providence Health systems are respective contenders for top employers in Oregon with roughly 12,000 federal workers and 14,000 Providence Health workers.
In 2015, a total of seven companies headquartered in Oregon landed in the Fortune 1000: Nike, at 106; Precision Castparts Corp. at 302; Lithia Motors at 482; StanCorp Financial Group at 804; Schnitzer Steel Industries at 853; The Greenbrier Companies at 948; and Columbia Sportswear at 982.
 Especially since the 1990 passage of Measure 5, which set limits on property tax levels, Oregon has struggled to fund higher education. Since then, Oregon has cut its higher education budget and now ranks 46th in the country in state spending per student. However, 2007 legislation funded the university system far beyond the governor's requested budget though still capping tuition increases at 3% per year. Oregon supports a total of seven public universities and one affiliate. It is home to three public research universities: The
Especially since the 1990 passage of Measure 5, which set limits on property tax levels, Oregon has struggled to fund higher education. Since then, Oregon has cut its higher education budget and now ranks 46th in the country in state spending per student. However, 2007 legislation funded the university system far beyond the governor's requested budget though still capping tuition increases at 3% per year. Oregon supports a total of seven public universities and one affiliate. It is home to three public research universities: The  UO is the state's highest nationally ranked and most selective public university by '' U.S. News & World Report'' and ''Forbes Magazine's List of America's Best Colleges, Forbes''. OSU is the state's only land-grant university, has the state's largest enrollment for fall 2014, and is the state's highest ranking university according to ''Academic Ranking of World Universities'', ''Washington Monthly'', and ''QS World University Rankings''. OSU receives more annual funding for research than all other public higher education institutions in Oregon combined. The state's urban Portland State University has Oregon's second largest enrollment.
The state has three regional universities: Western Oregon University in Monmouth, Oregon, Monmouth, Southern Oregon University in Ashland, and Eastern Oregon University in La Grande. The Oregon Institute of Technology has its campus in Klamath Falls, Oregon, Klamath Falls. The quasi-public Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) includes medical, dental, and nursing schools, and graduate programs in biomedical sciences in Portland and a science and engineering school in Hillsboro. The state also supports List of community colleges in Oregon, 17 community colleges.
UO is the state's highest nationally ranked and most selective public university by '' U.S. News & World Report'' and ''Forbes Magazine's List of America's Best Colleges, Forbes''. OSU is the state's only land-grant university, has the state's largest enrollment for fall 2014, and is the state's highest ranking university according to ''Academic Ranking of World Universities'', ''Washington Monthly'', and ''QS World University Rankings''. OSU receives more annual funding for research than all other public higher education institutions in Oregon combined. The state's urban Portland State University has Oregon's second largest enrollment.
The state has three regional universities: Western Oregon University in Monmouth, Oregon, Monmouth, Southern Oregon University in Ashland, and Eastern Oregon University in La Grande. The Oregon Institute of Technology has its campus in Klamath Falls, Oregon, Klamath Falls. The quasi-public Oregon Health & Science University (OHSU) includes medical, dental, and nursing schools, and graduate programs in biomedical sciences in Portland and a science and engineering school in Hillsboro. The state also supports List of community colleges in Oregon, 17 community colleges.
 Oregon is home to a wide variety of private colleges, the majority of which are located in the Portland area. The University of Portland and Marylhurst University are both Catholic universities located in or near Portland, affiliated with the Congregation of Holy Cross, and the Sisters of the Holy Names of Jesus and Mary, respectively. Reed College, a rigorous liberal arts college in Portland, was ranked by ''Forbes'' as the 52nd best college in the country in 2015.
Other private institutions in Portland include Lewis & Clark College; Multnomah University; Portland Bible College; Warner Pacific College; Cascade College; the National University of Natural Medicine; and Western Seminary, a theological graduate school. Pacific University is in the Portland suburb of Forest Grove. There are also private colleges further south in the Willamette Valley. McMinnville is home to Linfield College, while nearby Newberg is home to George Fox University. Salem is home to two private schools: Willamette University (the state's oldest, established during the provisional period) and Corban University. Also located near Salem is Mount Angel Abbey, Mount Angel Seminary, one of America's largest Roman Catholic seminaries. The state's second medical school, the College of Osteopathic Medicine of the Pacific, Northwest, is located in Lebanon. Eugene is home to three private colleges: Bushnell University, New Hope Christian College, and Gutenberg College.
Oregon is home to a wide variety of private colleges, the majority of which are located in the Portland area. The University of Portland and Marylhurst University are both Catholic universities located in or near Portland, affiliated with the Congregation of Holy Cross, and the Sisters of the Holy Names of Jesus and Mary, respectively. Reed College, a rigorous liberal arts college in Portland, was ranked by ''Forbes'' as the 52nd best college in the country in 2015.
Other private institutions in Portland include Lewis & Clark College; Multnomah University; Portland Bible College; Warner Pacific College; Cascade College; the National University of Natural Medicine; and Western Seminary, a theological graduate school. Pacific University is in the Portland suburb of Forest Grove. There are also private colleges further south in the Willamette Valley. McMinnville is home to Linfield College, while nearby Newberg is home to George Fox University. Salem is home to two private schools: Willamette University (the state's oldest, established during the provisional period) and Corban University. Also located near Salem is Mount Angel Abbey, Mount Angel Seminary, one of America's largest Roman Catholic seminaries. The state's second medical school, the College of Osteopathic Medicine of the Pacific, Northwest, is located in Lebanon. Eugene is home to three private colleges: Bushnell University, New Hope Christian College, and Gutenberg College.
 A writer in the
A writer in the


 Political opinions in Oregon are geographically split by the
Political opinions in Oregon are geographically split by the
 Oregon is home to three major professional sports teams: the Portland Trail Blazers of the National Basketball Association, NBA, the Portland Thorns FC of the National Women's Soccer League, NWSL and the Portland Timbers of Major League Soccer, MLS."MLS awards team to Portland for 2011"
Oregon is home to three major professional sports teams: the Portland Trail Blazers of the National Basketball Association, NBA, the Portland Thorns FC of the National Women's Soccer League, NWSL and the Portland Timbers of Major League Soccer, MLS."MLS awards team to Portland for 2011"
Portland Timbers, March 20, 2009. Until 2011, the only major professional sports team in Oregon was the Portland Trail Blazers of the National Basketball Association. From the 1970s to the 1990s, the Blazers were one of the most successful teams in the NBA in terms of both win–loss record and attendance. In the early 21st century, the team's popularity declined due to personnel and financial issues, but revived after the departure of controversial players and the acquisition of new players such as Brandon Roy and LaMarcus Aldridge, and still later Damian Lillard. The Blazers play in the Moda Center in Portland's Lloyd District, which also is home to the Portland Winterhawks of the junior ice hockey, junior Western Hockey League. The Portland Timbers play at Providence Park, just west of downtown Portland. The Timbers have a strong following, with the team regularly selling out its games. The Timbers repurposed the formerly multi-use stadium into a soccer-specific stadium in fall 2010, increasing the seating in the process. The Timbers operate Portland Thorns FC, a women's soccer team that has played in the National Women's Soccer League since the league's first season in 2013. The Thorns, who also play at Providence Park, have won two league championships, in the inaugural 2013 National Women's Soccer League season, 2013 season and also in 2017 National Women's Soccer League season, 2017, and have been by far the NWSL's attendance leader in each of the league's seasons. Eugene and Hillsboro have minor-league baseball teams: the Eugene Emeralds and the Hillsboro Hops both play in the High-A High-A West. Portland has had minor-league baseball teams in the past, including the Portland Beavers and Portland Rockies, who played most recently at Providence Park when it was known as PGE Park. Salem also previously had a Class A Short Season Northwest League team, the Salem-Keizer Volcanoes that was not included in the Minor League Baseball#Reorganization of 2021, 2021 Minor League Baseball reorganization. The Volcanoes ownership later formed the amateur Mavericks Independent Baseball League, which is fully based in Salem.
The Oregon State Beavers and the University of Oregon Ducks football teams of the Pac-12 Conference meet annually in the Oregon–Oregon State football rivalry. Both schools have had recent success in other sports as well: Oregon State won back-to-back College World Series, college baseball championships in 2006 and 2007, winning a third in 2018; and the University of Oregon won back-to-back NCAA Men's Cross Country Championship, NCAA men's cross country championships in 2007 and 2008.
Eugene and Hillsboro have minor-league baseball teams: the Eugene Emeralds and the Hillsboro Hops both play in the High-A High-A West. Portland has had minor-league baseball teams in the past, including the Portland Beavers and Portland Rockies, who played most recently at Providence Park when it was known as PGE Park. Salem also previously had a Class A Short Season Northwest League team, the Salem-Keizer Volcanoes that was not included in the Minor League Baseball#Reorganization of 2021, 2021 Minor League Baseball reorganization. The Volcanoes ownership later formed the amateur Mavericks Independent Baseball League, which is fully based in Salem.
The Oregon State Beavers and the University of Oregon Ducks football teams of the Pac-12 Conference meet annually in the Oregon–Oregon State football rivalry. Both schools have had recent success in other sports as well: Oregon State won back-to-back College World Series, college baseball championships in 2006 and 2007, winning a third in 2018; and the University of Oregon won back-to-back NCAA Men's Cross Country Championship, NCAA men's cross country championships in 2007 and 2008.
online
* * * * * * * * *
Oregon Encyclopedia
'
Oregon State Databases
at the American Library Association
State of Oregon
Oregon State Legislature
Oregon Constitution
TravelOregon.com
an official website of the Oregon Tourism Commission
Oregon State Parks
Oregon State Facts
from the United States Department of Agriculture
Oregon Historical Society
Oregon Blue Book
the online version of the Oregon Blue Book, state's official directory and fact book
Real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Oregon
from the United States Geological Survey * {{coord, 44, -121, dim:300000_region:US-OR_type:adm1st, name=State of Oregon, display=title Oregon, 1859 establishments in the United States Geography of the Pacific Northwest States and territories established in 1859 States of the United States States of the West Coast of the United States U.S. states with multiple time zones Contiguous United States
state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
in the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
region of the Western United States
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the Wes ...
. The Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
, while the Snake River
The Snake River is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest region in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, in turn, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. The Snake ...
delineates much of its eastern boundary with Idaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyom ...
. The 42° north parallel delineates the southern boundary with California
California is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, located along the West Coast of the United States, Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the List of states and territori ...
and Nevada
Nevada ( ; ) is a U.S. state, state in the Western United States, Western region of the United States. It is bordered by Oregon to the northwest, Idaho to the northeast, California to the west, Arizona to the southeast, and Utah to the east. N ...
.
Oregon has been home to many indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
nations for thousands of years. The first European traders, explorers, and settlers began exploring what is now Oregon's Pacific coast in the early-mid 16th century. As early as 1564, the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
began sending vessels northeast from the Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, riding the Kuroshio Current
The , also known as the Black or or the is a north-flowing, warm ocean current on the west side of the North Pacific Ocean basin. It was named for the deep blue appearance of its waters. Similar to the Gulf Stream in the North Atlantic, the Ku ...
in a sweeping circular route across the northern part of the Pacific. In 1592, Juan de Fuca
Juan de Fuca (10 June 1536, Cefalonia 23 July 1602, Cefalonia)Greek Consulate of Vancouver,Greek Pioneers: Juan de Fuca. was a Greeks, Greek maritime pilot, pilot who served Philip II of Spain, PhilipII of Spanish Empire, Spain. He is best know ...
undertook detailed mapping and studies of ocean currents in the Pacific Northwest, including the Oregon coast as well as the strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channe ...
now bearing his name. Spanish ships – 250 in as many years – would typically not land before reaching Cape Mendocino
Cape Mendocino (Spanish: ''Cabo Mendocino'', meaning "Cape of Mendoza"), which is located approximately north of San Francisco, is located on the Lost Coast entirely within Humboldt County, California, United States. At 124° 24' 34" W longitude ...
in California, but some landed or wrecked in what is now Oregon. Nehalem tales recount strangers and the discovery of items like chunks of beeswax
Beeswax (''cera alba'') is a natural wax produced by honey bees of the genus ''Apis''. The wax is formed into scales by eight wax-producing glands in the abdominal segments of worker bees, which discard it in or at the hive. The hive workers ...
and a lidded silver vase, likely connected to the 1707 wreck of the ''San Francisco Xavier''.
In 1843, an autonomous government was formed in the Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
, and the Oregon Territory
The Territory of Oregon was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from August 14, 1848, until February 14, 1859, when the southwestern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Oregon. Ori ...
was created in 1848. Oregon became the 33rd state of the U.S. on February 14, 1859. Today, with 4 million people over , Oregon is the ninth largest and 27th most populous U.S. state. The capital, Salem, is the second-most populous city in Oregon, with 169,798 residents. Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
, with 647,805, ranks as the 26th among U.S. cities. The Portland metropolitan area
The Portland metropolitan area is a metro area in the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington centered on the principal city of Portland, Oregon. The U.S. Office of Management and Budget (OMB) identifies it as the Portland–Vancouver–Hillsboro, ...
, which also includes the city of Vancouver, Washington
Vancouver is a city on the north bank of the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Washington, located in Clark County. Incorporated in 1857, Vancouver has a population of 190,915 as of the 2020 census, making it the fourth-largest city in Was ...
, to the north, ranks the 25th largest metro area in the nation, with a population of 2,453,168.
Oregon is one of the most geographically diverse states in the U.S., marked by volcanoes, abundant bodies of water, dense evergreen and mixed forests, as well as high deserts and semi-arid shrubland
Shrubland, scrubland, scrub, brush, or bush is a plant community characterized by vegetation dominated by shrubs, often also including grasses, herbs, and geophytes. Shrubland may either occur naturally or be the result of human activity. It m ...
s. At , Mount Hood
Mount Hood is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It was formed by a subduction zone on the Pacific coast and rests in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located about east-southeast of Portlan ...
, a stratovolcano
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and per ...
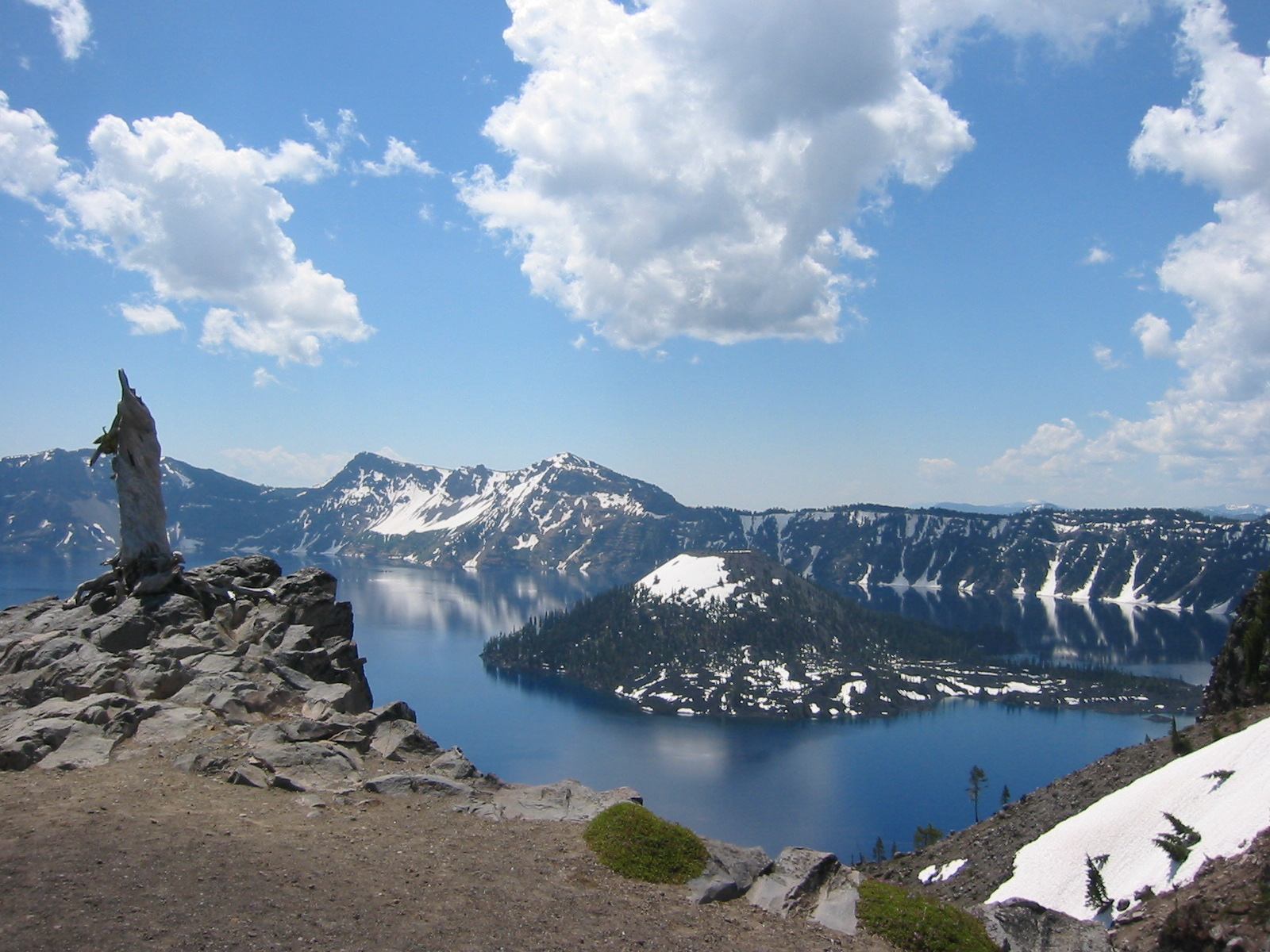
, is the state's highest point. Oregon's only national park, Crater Lake National Park
Crater Lake National Park is an American national park located in southern Oregon. Established in 1902, Crater Lake is the fifth-oldest national park in the United States and the only national park in Oregon. The park encompasses the caldera of ...
, comprises the caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
surrounding Crater Lake
Crater Lake (Klamath language, Klamath: ''Giiwas'') is a volcanic crater lake in south-central Oregon in the western United States. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and is famous for its deep blue color and water clarity. The ...
, the deepest lake in the United States. The state is also home to the single largest organism
The largest organisms now found on Earth can be determined according to various aspects of an organism's size, such as: mass, volume, area, length, height, or even genome size. Some organisms group together to form a superorganism (such as ants ...
in the world, ''Armillaria ostoyae
''Armillaria ostoyae'' (synonym ''Armillaria solidipes'') is a species of fungus (mushroom), pathogenic to trees, in the family Physalacriaceae. In the western United States, it is the most common variant of the group of species under the nam ...
'', a fungus that runs beneath of the Malheur National Forest
The Malheur National Forest is a United States National Forest, National Forest in the U.S. state of Oregon. It contains more than in the Blue Mountains (Pacific Northwest), Blue Mountains of eastern Oregon. The forest consists of Great Basin ...
.
Because of its diverse landscapes and waterways, Oregon's economy is largely powered by various forms of agriculture, fishing, and hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
power. Oregon is also the top lumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
producer of the contiguous United States, with the lumber industry dominating the state's economy during the 20th century. Technology is another one of Oregon's major economic forces, beginning in the 1970s with the establishment of the Silicon Forest
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
and the expansion of Tektronix
Tektronix, Inc., historically widely known as Tek, is an American company best known for manufacturing test and measurement devices such as oscilloscopes, logic analyzers, and video and mobile test protocol equipment.
Originally an independent ...
and Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
. Sportswear company Nike, Inc.
Nike, Inc. ( or ) is an American multinational corporation that is engaged in the design, development, manufacturing, and worldwide marketing and sales of footwear, apparel, equipment, accessories, and services. The company is headquartered ne ...
, headquartered in Beaverton, is the state's largest public corporation with an annual revenue of $30.6 billion.
Etymology
The origin of the state's name is a mystery. The earliest evidence of the name ''Oregon'' hasSpanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
origins. The term "orejón" (meaning "big ear") comes from the historical chronicle ''Relación de la Alta y Baja California'' (1598), written by Rodrigo Montezuma of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
; it made reference to the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
when the Spanish explorers penetrated into the North American territory that became part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. This chronicle is the first topographical and linguistic source with respect to the place name ''Oregon''. Another possible source is the Spanish word ''oregano
Oregano (, ; ''Origanum vulgare'') is a species of flowering plant in the mint family Lamiaceae. It was native to the Mediterranean region, but widely naturalised elsewhere in the temperate Northern Hemisphere.
Oregano is a woody perennial pla ...
'', which refers to a plant that grows in the southern part of the region. It is also possible that the American territory was named by the Spaniards, as there is a stream in Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
called the "Arroyo del Oregón" (which is located in the province of Ciudad Real
Ciudad Real (, ; en, "Royal City") is a municipality of Spain located in the autonomous community of Castile–La Mancha, capital of the province of Ciudad Real. It is the 5th most populated municipality in the region.
History
It was founde ...
), or that the "j" in the Spanish phrase "El Orejón" was later corrupted into a "g", and in context might refer to the 'earful' of the massive Columbia River at its mouth.
Another early use of the name, spelled ''Ouragon'', was by Major Robert Rogers Robert Rogers may refer to:
Politics
* Robert Rogers (Irish politician) (died 1719), Irish politician, MP for Cork City 1692–1699
*Robert Rogers (Manitoba politician) (1864–1936), Canadian politician
* Robert Rogers, Baron Lisvane (born 1950), ...
in a 1765 petition to the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of ...
. The term referred to the then-mythical River of the West (the Columbia River). By 1778, the spelling had shifted to ''Oregon''. Rogers wrote:
...from the Great Lakes towards the Head of the Mississippi, and from thence to the River called by the Indians Ouragon...One theory is that the name comes from the French word ''ouragan'' ("windstorm" or "hurricane"), which was applied to the River of the West based on Native American tales of powerful
Chinook wind
Chinook winds, or simply Chinooks, are two types of prevailing warm, generally westerly winds in western North America: Coastal Chinooks and interior Chinooks. The coastal Chinooks are persistent seasonal, wet, southwesterly winds blowing in from ...
s on the lower Columbia River, or perhaps from first-hand French experience with the Chinook winds of the Great Plains
The Great Plains (french: Grandes Plaines), sometimes simply "the Plains", is a broad expanse of flatland in North America. It is located west of the Mississippi River and east of the Rocky Mountains, much of it covered in prairie, steppe, an ...
. At the time, the River of the West was thought to rise in western Minnesota and flow west through the Great Plains.
Joaquin Miller
Cincinnatus Heine Miller (; September 8, 1837 – February 17, 1913), better known by his pen name Joaquin Miller (), was an American poet, author, and frontiersman. He is nicknamed the "Poet of the Sierras" after the Sierra Nevada, about which h ...
wrote in ''Sunset'' magazine in 1904:
The name, Oregon, is rounded down phonetically, from ''Ouve água''—Oragua, Or-a-gon, Oregon—given probably by the same Portuguese navigator that named the Farallones after his first officer, and it literally, in a large way, means cascades: "Hear the waters." You should steam up the Columbia and hear and feel the waters falling out of the clouds of Mount Hood to understand entirely the full meaning of the name ''Ouve a água'', Oregon.Another account, endorsed as the "most plausible explanation" in the book ''
Oregon Geographic Names
''Oregon Geographic Names'' is a compilation of the origin and meaning of place names in the U.S. state of Oregon, published by the Oregon Historical Society. The book was originally published in 1928. It was compiled and edited by Lewis A. McArth ...
'', was advanced by George R. Stewart
George Rippey Stewart (May 31, 1895 – August 22, 1980) was an American historian, toponymist, novelist, and a professor of English at the University of California, Berkeley. His 1959 book, ''Pickett's Charge'', a detailed history of the final ...
in a 1944 article in ''American Speech
''American Speech'' is a quarterly academic journal of the American Dialect Society, established in 1925 and currently published by Duke University Press. It focuses primarily on the English language used in the Western Hemisphere, but also publis ...
''. According to Stewart, the name came from an engraver's error in a French map published in the early 18th century, on which the Ouisiconsink (Wisconsin) River was spelled "Ouaricon-sint", broken on two lines with the ''-sint'' below, so there appeared to be a river flowing to the west named "Ouaricon".
According to the Oregon Tourism Commission, present-day Oregonians pronounce the state's name as "or-uh-gun, never or-ee-gone". After being drafted by the Detroit Lions
The Detroit Lions are a professional American football team based in Detroit. The Lions compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member of the National Football Conference (NFC) North Division. The team play their home games at Ford ...
in 2002, former Oregon Ducks
The Oregon Ducks are the intercollegiate athletic teams that represent the University of Oregon, located in Eugene. The Ducks compete at the National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I level as a member of the Pac-12 Conference. ...
quarterback Joey Harrington
John Joseph Harrington Jr. (born October 21, 1978) is a former American football quarterback who played in the National Football League (NFL) for seven seasons, primarily with the Detroit Lions. He played college football at Oregon, where he w ...
distributed "Orygun" stickers to members of the media as a reminder of how to pronounce the name of his home state. The stickers are sold by the University of Oregon Bookstore
The Duck Store is the bookstore for the University of Oregon in Eugene, Oregon, United States. It is a not-for-profit corporation governed by an elected Board of Directors composed mostly of students. It is independent of the University of Oregon ...
.
History
Humans have inhabited the area that is now Oregon for at least 15,000 years. In recorded history, mentions of the land date to as early as the 16th century. During the 18th and 19th centuries, European powers—and later the United States—quarreled over possession of the region until 1846, when the U.S. and Great Britain finalized division of the region. Oregon became a state on February 14, 1859, and has more than four million residents.Earliest inhabitants
 While there is considerable evidence that Paleo-Indians inhabited the region, the oldest evidence of habitation in Oregon was found at
While there is considerable evidence that Paleo-Indians inhabited the region, the oldest evidence of habitation in Oregon was found at Fort Rock Cave
Fort Rock Cave was the site of the earliest evidence of human habitation in the US state of Oregon before the excavation of Paisley Caves. Fort Rock Cave featured numerous well-preserved sagebrush sandals, ranging from 9,000 to 13,000 years old. ...
and the Paisley Caves
The Paisley Caves or the Paisley Five Mile Point Caves complex is a system of eight caves in an arid, desolate region of south-central Oregon, United States north of the present-day city of Paisley, Oregon. The caves are located in the Summer La ...
in Lake County. Archaeologist Luther Cressman
Luther Sheeleigh Cressman (October 24, 1897 – April 4, 1994) was an American field archaeologist, most widely known for his discoveries at Paleo-Indian sites such as Fort Rock Cave and Paisley Caves, sites related to the early settlement ...
dated material from Fort Rock to 13,200 years ago, and there is evidence supporting inhabitants in the region at least 15,000 years ago. By 8000 BC there were settlements throughout the state, with populations concentrated along the lower Columbia River, in the western valleys, and around coastal estuaries.
During the prehistoric period
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of ...
, the Willamette Valley region was flooded after the collapse of glacial dams from then Lake Missoula
Lake Missoula was a prehistoric proglacial lake in western Montana that existed periodically at the end of the last ice age between 15,000 and 13,000 years ago. The lake measured about and contained about of water, half the volume of Lake Mic ...
, located in what would later become Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
. These massive floods occurred during the last glacial period and filled the valley with of water.
By the 16th century, Oregon was home to many Native American groups, including the Chinook, Coquille (Ko-Kwell
The Coquille ( , sometimes spelled Ko-Kwel) are a Native American people who historically lived in the Coquille River watershed and nearby coast south of Coos Bay. They were signatories of the Oregon Coast Tribes Treaty of 1855 and were subsequ ...
), Bannock
Bannock may mean:
* Bannock (food), a kind of bread, cooked on a stone or griddle
* Bannock (Indigenous American), various types of bread, usually prepared by pan-frying
* Bannock people, a Native American people of what is now southeastern Oregon ...
, Chasta, Kalapuya
The Kalapuya are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American ethnic group, people, which had eight independent groups speaking three mutually intelligible dialects. The Kalapuya tribes' traditional homelands were the Willamette Va ...
, Klamath Klamath may refer to:
Ethnic groups
*Klamath people, a Native American people of California and Oregon
**Klamath Tribes, a federally recognized group of tribes in Oregon
*Klamath language, spoken by the Klamath people
Places in the United States
* ...
, Klickitat, Molalla, Nez Perce
The Nez Percé (; autonym in Nez Perce language: , meaning "we, the people") are an Indigenous people of the Plateau who are presumed to have lived on the Columbia River Plateau in the Pacific Northwest region for at least 11,500 years.Ames, K ...
, Takelma
The Takelma (also Dagelma) are a Native American people who originally lived in the Rogue Valley of interior southwestern Oregon.
Most of their villages were sited along the Rogue River. The name ''Takelma'' means "(Those) Along the River".
His ...
, Killamuk, Neah-kah-nie, Umatilla, and Umpqua.
European and pioneer settlement
The first Europeans to visit Oregon were Spanish explorers led byJuan Rodríguez Cabrillo
Juan Rodríguez Cabrillo ( pt, João Rodrigues Cabrilho; c. 1499 – January 3, 1543) was an Iberian maritime explorer best known for investigations of the West Coast of North America, undertaken on behalf of the Spanish Empire. He was the firs ...
, who sighted southern Oregon off the Pacific coast in 1543. Sailing from Central America on the ''Golden Hind
''Golden Hind'' was a galleon captained by Francis Drake in his circumnavigation of the world between 1577 and 1580. She was originally known as ''Pelican,'' but Drake renamed her mid-voyage in 1578, in honour of his patron, Sir Christopher Hat ...
'' in 1579 in search of the Strait of Anian
A strait is an Ocean, oceanic landform connecting two Sea, seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ...
during his circumnavigation of the Earth, the English explorer and privateer Sir Francis Drake
Sir Francis Drake ( – 28 January 1596) was an English explorer, sea captain, privateer, slave trader, naval officer, and politician. Drake is best known for his circumnavigation of the world in a single expedition, from 1577 to 1580 (t ...
briefly anchored at South Cove, Cape Arago, just south of Coos Bay
Coos Bay is an estuary where the Coos River enters the Pacific Ocean, the estuary is approximately 12 miles long and up to two miles wide. It is the largest estuary completely within Oregon state lines. The Coos Bay watershed covers an area of abou ...
, before sailing for what is now California. Martín de Aguilar, continuing separately from Sebastián Vizcaíno
Sebastián Vizcaíno (1548–1624) was a Spanish soldier, entrepreneur, explorer, and diplomat whose varied roles took him to New Spain, the Baja California peninsula, the California coast and Asia.
Early career
Vizcaíno was born in 154 ...
's scouting of California, reached as far north as Cape Blanco and possibly to Coos Bay in 1603. Exploration continued routinely in 1774, starting with the expedition of the frigate ''Santiago'' by Juan José Pérez Hernández
Juan José Pérez Hernández (born Joan Perés c. 1725 – November 3, 1775), often simply Juan Pérez, was an 18th-century Spanish explorer. He was the first known European to sight, examine, name, and record the islands near present-day Bri ...
, and the coast of Oregon became a valuable trade route to Asia. In 1778, British captain James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
also explored the coast.
French Canadians
French Canadians (referred to as Canadiens mainly before the twentieth century; french: Canadiens français, ; feminine form: , ), or Franco-Canadians (french: Franco-Canadiens), refers to either an ethnic group who trace their ancestry to Fren ...
, Scots, Métis
The Métis ( ; Canadian ) are Indigenous peoples who inhabit Canada's three Prairie Provinces, as well as parts of British Columbia, the Northwest Territories, and the Northern United States. They have a shared history and culture which derives ...
and other continental natives (e.g. Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
) trappers arrived in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, soon to be followed by Catholic clergy. Some traveled as members of the Lewis and Clark
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* "Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohead ...
and 1811 Astor expedition
The Pacific Fur Company (PFC) was an American fur trade venture wholly owned and funded by John Jacob Astor that functioned from 1810 to 1813. It was based in the Pacific Northwest, an area contested over the decades between the United Kingdom o ...
. Few stayed permanently such as Étienne Lussier, often referred to as the first "European" farmer in the state of Oregon. Evidence of the French Canadian presence can be found in numerous names of French origin such as Malheur Lake
Malheur Lake is one of the lakes in the Malheur National Wildlife Refuge in Harney County in the U.S. state of Oregon. Located about southeast of Burns, the lake is marsh fed by the Donner und Blitzen River from the south and the Silvies River ...
, Malheur River
The Malheur River (local pronunciation: "MAL-hyure") is a tributary of the Snake River in eastern Oregon in the United States. It drains a Great Basin Desert, high desert area, between the Harney Basin and the Blue Mountains (Oregon), Blue Moun ...
, Grande Ronde, Deschutes rivers and the city of La Grande. Furthermore, many of the early pioneers first came out West with the North West Company
The North West Company was a fur trading business headquartered in Montreal from 1779 to 1821. It competed with increasing success against the Hudson's Bay Company in what is present-day Western Canada and Northwestern Ontario. With great weal ...
and the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business div ...
before heading South of the Columbia for better farmland as the fur trade declined. French Prairie
French Prairie is located in Marion County, Oregon, United States, in the Willamette Valley between the Willamette River and the Pudding River, north of Salem. It was named for some of the earliest settlers of that part of the Oregon Country, Fr ...
by the Willamette River
The Willamette River ( ) is a major tributary of the Columbia River, accounting for 12 to 15 percent of the Columbia's flow. The Willamette's main stem is long, lying entirely in northwestern Oregon in the United States. Flowing northward b ...
and French Settlement by the Umpqua River
The Umpqua River ( ) on the Pacific coast of Oregon in the United States is approximately long. One of the principal rivers of the Oregon Coast and known for bass and shad, the river drains an expansive network of valleys in the mountains west ...
are known as early mixed ancestry settlements.  The Lewis and Clark Expedition traveled through northern Oregon also in search of the
The Lewis and Clark Expedition traveled through northern Oregon also in search of the Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arct ...
. They built their winter fort in 1805–06 at Fort Clatsop
Fort Clatsop was the encampment of the Lewis and Clark Expedition in the Oregon Country near the mouth of the Columbia River during the winter of 1805–1806. Located along the Lewis and Clark River at the north end of the Clatsop Plains approxim ...
, near the mouth of the Columbia River, staying at the encampment from December until March.
British explorer David Thompson also conducted overland exploration. In 1811, while working for the North West Company, Thompson became the first European to navigate the entire Columbia River. Stopping on the way, at the junction of the Snake River, he posted a claim to the region for Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
and the North West Company. Upon returning to Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-most populous city in Canada and List of towns in Quebec, most populous city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian ...
, he publicized the abundance of fur-bearing animals in the area.
Also in 1811, New Yorker John Jacob Astor
John Jacob Astor (born Johann Jakob Astor; July 17, 1763 – March 29, 1848) was a German-American businessman, merchant, real estate mogul, and investor who made his fortune mainly in a fur trade monopoly, by smuggling opium into China, and ...
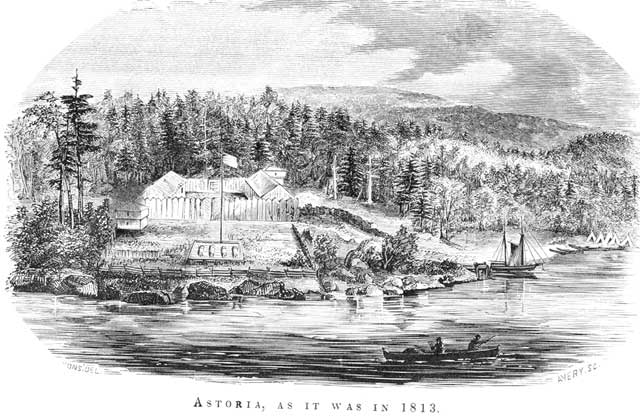
financed the establishment of Fort Astoria
Fort Astoria (also named Fort George) was the primary fur trading post of John Jacob Astor's Pacific Fur Company (PFC). A maritime contingent of PFC staff was sent on board the '' Tonquin'', while another party traveled overland from St. Louis. ...
at the mouth of the Columbia River as a western outpost to his Pacific Fur Company
The Pacific Fur Company (PFC) was an American fur trade venture wholly owned and funded by John Jacob Astor that functioned from 1810 to 1813. It was based in the Pacific Northwest, an area contested over the decades between the United Kingdom o ...
; this was the first permanent European settlement in Oregon.
In the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
, the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
gained control of all Pacific Fur Company posts. The Treaty of 1818
The Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, is an international treaty signed in 1818 betw ...
established joint British and American occupancy of the region west of the Rocky Mountains to the Pacific Ocean. By the 1820s and 1830s, the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business div ...
dominated the Pacific Northwest from its Columbia District
The Columbia District was a fur trading
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold ...
headquarters at Fort Vancouver
Fort Vancouver was a 19th century fur trading post that was the headquarters of the Hudson's Bay Company's Columbia Department, located in the Pacific Northwest. Named for Captain George Vancouver, the fort was located on the northern bank of th ...
(built-in 1825 by the district's chief factor, John McLoughlin
John McLoughlin, baptized Jean-Baptiste McLoughlin, (October 19, 1784 – September 3, 1857) was a French-Canadian, later American, Chief Factor and Superintendent of the Columbia District of the Hudson's Bay Company at Fort Vancouver fro ...
, across the Columbia from present-day Portland
Portland most commonly refers to:
* Portland, Oregon, the largest city in the state of Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States
* Portland, Maine, the largest city in the state of Maine, in the New England region of the northeas ...
).
In 1841, the expert trapper and entrepreneur Ewing Young
Ewing Young (1799-February 9, 1841) was an American fur trapper and trader from Tennessee who traveled in what was then the northern Mexico frontier territories of Santa Fe de Nuevo México and Alta California before settling in the Oregon Country. ...
died leaving considerable wealth and no apparent heir, and no system to probate
Probate is the judicial process whereby a will is "proved" in a court of law and accepted as a valid public document that is the true last testament of the deceased, or whereby the estate is settled according to the laws of intestacy in the sta ...
his estate. A meeting followed Young's funeral, at which a probate government was proposed. Doctor Ira Babcock
Doctor Ira Leonard Babcock (c. 1808 – March 21, 1888) was an American pioneer and doctor in the Oregon Country. A native of New York, he was selected as the first Supreme Judge with probate powers in February 1841 in what would become the stat ...
of Jason Lee Jason Lee may refer to:
Entertainment
*Jason Lee (actor) (born 1970), American film and TV actor and former professional skateboarder
*Jason Scott Lee (born 1966), Asian American film actor
* Jaxon Lee (Jason Christopher Lee, born 1968), American v ...
's Methodist Mission
The Methodist Mission was the Methodist Episcopal Church's 19th-century conversion efforts in the Pacific Northwest. Local Indigenous cultures were introduced to western culture and Christianity. Superintendent Jason Lee was the principal leader fo ...
was elected supreme judge. Babcock chaired two meetings in 1842 at Champoeg
Champoeg ( , historically Horner, John B. (1919). ''Oregon: Her History, Her Great Men, Her Literature''. The J.K. Gill Co.: Portland. p. 398.) is a former town in the U.S. state of Oregon. Now a ghost town, it was an important settlement in the W ...
, (halfway between Lee's mission and Oregon City), to discuss wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; plural, : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large Canis, canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of Canis lupus, subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been reco ...
and other animals of contemporary concern. These meetings were precursors to an all-citizen meeting in 1843, which instituted a provisional government headed by an executive committee
A committee or commission is a body of one or more persons subordinate to a deliberative assembly. A committee is not itself considered to be a form of assembly. Usually, the assembly sends matters into a committee as a way to explore them more ...
made up of David Hill, Alanson Beers Alanson Beers (August 19, 1808 – February 20, 1853) was an American pioneer and politician in the early days of the settlement of the Oregon Country. A blacksmith by trade, he was a reinforcement for the Methodist Mission in what would become the ...
, and Joseph Gale
Joseph Goff Gale (April 29, 1807 – December 13, 1881) was an American pioneer, trapper, entrepreneur, and politician who contributed to the early settlement of the Oregon Country. There he assisted in the construction of the first sailing vesse ...
. This government was the first acting public government of the Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
before annexation by the government of the United States. It was succeeded by a Second Executive Committee, made up of Peter G. Stewart, Osborne Russell
Osborne Russell (19 June 1814 – 1 May 1884) was a mountain man and politician who helped form the government of the U.S. state of Oregon. He was born in Maine.
Early life
Osborne Russell was born 19 June 1814, in the village of Bowdoinh ...
, and William J. Bailey
William J. Bailey (January 13, 1807 – February 5, 1876) was a British-born physician who migrated to the United States, where he became a pioneer and politician in the Oregon Country, particularly the Willamette Valley. Bailey participated in the ...
, and this committee was itself succeeded by George Abernethy
George Abernethy (October 7, 1807 – March 2, 1877) was an American politician, pioneer, notable entrepreneur, and first governor of Oregon under the provisional government based in the Willamette Valley, an area later a part of the American sta ...
, who was the first and only Governor of Oregon under the provisional government.
Also in 1841, Sir George Simpson, governor of the Hudson's Bay Company, reversed the Hudson's Bay Company's long-standing policy of discouraging settlement because it interfered with the lucrative fur trade. He directed that some 200 Red River Colony
The Red River Colony (or Selkirk Settlement), also known as Assiniboia, Assinboia, was a colonization project set up in 1811 by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk, on of land in British North America. This land was granted to Douglas by the Hud ...
settlers be relocated to HBC farms near Fort Vancouver, (the James Sinclair expedition), in an attempt to hold Columbia District.
Starting in 1842–43, the Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and Westward Expansion Trails, emigrant trail in the United States that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail spanned part of what ...
brought many new American settlers to the Oregon Country. Oregon's boundaries were disputed for a time, contributing to tensions between the U.K. and the U.S., but the border was defined peacefully in the 1846 Oregon Treaty
The Oregon Treaty is a treaty between the United Kingdom and the United States that was signed on June 15, 1846, in Washington, D.C. The treaty brought an end to the Oregon boundary dispute by settling competing American and British claims to t ...
. The border between the United States and British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English overseas possessions, English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland (island), Newfound ...
was set at the 49th parallel. The Oregon Territory
The Territory of Oregon was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from August 14, 1848, until February 14, 1859, when the southwestern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Oregon. Ori ...
was officially organized on August 13, 1848.
Settlement increased with the Donation Land Claim Act
The Donation Land Claim Act of 1850, sometimes known as the Donation Land Act, was a statute enacted by the United States Congress in late 1850, intended to promote homestead settlements in the Oregon Territory. It followed the Distribution-Preem ...
of 1850 and the forced relocation
Forced displacement (also forced migration) is an involuntary or coerced movement of a person or people away from their home or home region. The UNHCR defines 'forced displacement' as follows: displaced "as a result of persecution, conflict, g ...
of the native population to Indian reservations in Oregon
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
.
Statehood
In December 1844, Oregon passed its Black Exclusion Law, which prohibited African Americans from entering the territory while simultaneously prohibitingslavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
. Slave owners who brought their slaves with them were given three years before they were forced to free them. Any African Americans in the region after the law was passed were forced to leave, and those who did not comply were arrested and beaten. They received no less than twenty and no more than thirty-nine stripes across the back if they still did not leave. This process could be repeated every six months. Slavery played a major part in Oregon's history and even influenced its path to statehood. The territory's request for statehood was delayed several times, as members of Congress argued among themselves whether the territory should be admitted as a "free" or "slave" state. Eventually politicians from the South agreed to allow Oregon to enter as a "free" state, in exchange for opening slavery to the southwest United States.
Oregon was admitted to the Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
on February 14, 1859, though no one in Oregon knew it until March 15. Founded as a refuge from disputes over slavery, Oregon had a "whites only" clause in its original state Constitution. At the outbreak of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
, regular U.S. troops were withdrawn and sent east to aid the Union. Volunteer cavalry recruited in California were sent north to Oregon to keep peace and protect the populace. The First Oregon Cavalry served until June 1865.
Post-Reconstruction
Beginning in the 1880s, the growth of railroads expanded the state'slumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
, wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, and other agricultural markets, and the rapid growth of its cities. Due to the abundance of timber and waterway access via the Willamette River
The Willamette River ( ) is a major tributary of the Columbia River, accounting for 12 to 15 percent of the Columbia's flow. The Willamette's main stem is long, lying entirely in northwestern Oregon in the United States. Flowing northward b ...
, Portland became a major force in the lumber industry of the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though ...
, and quickly became the state's largest city. It would earn the nickname "Stumptown", and would later become recognized as one of the most dangerous port cities in the United States due to racketeering and illegal activities at the turn of the 20th century. In 1902, Oregon introduced direct legislation
Direct democracy or pure democracy is a form of democracy in which the electorate decides on policy initiatives without elected representatives as proxies. This differs from the majority of currently established democracies, which are represen ...
by the state's citizens through initiatives
In political science, an initiative (also known as a popular initiative or citizens' initiative) is a means by which a petition signed by a certain number of registered voters can force a government to choose either to enact a law or hold a ...
and referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
s, known as the Oregon System The Oregon Direct Legislation League was an organization of political activists founded by William S. U'Ren in the U.S. state of Oregon in 1898. U'Ren had been politically activated by reading the influential 1893 book ''Direct Legislation Through t ...
.
On May 5, 1945, six civilians were killed by a Japanese balloon bomb that exploded on Gearhart Mountain
Gearhart Mountain is a high mountain in Lake County and Klamath County, Oregon, in the United States. It is located in the Gearhart Mountain Wilderness of the Fremont–Winema National Forest, northeast of the Sprague River valley and the town ...
near Bly Bly may refer to:
Places
;In the United States
* Bly, Missouri, a ghost town
*Bly, Oregon, a small town in Oregon
Other
* Bly (surname)
*Bly, the fictional setting of ''The Turn of the Screw
''The Turn of the Screw'' is an 1898 horror nov ...
. They remained the only people on American soil whose deaths were attributed to an enemy balloon bomb explosion during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. The bombing site is now located in the Mitchell Recreation Area
Mitchell Recreation Area is a small picnic area located in the Fremont-Winema National Forests, Lake County, Oregon, near the unincorporated community of Bly. In it stands the Mitchell Monument, erected in 1950, which marks the only location in ...
.
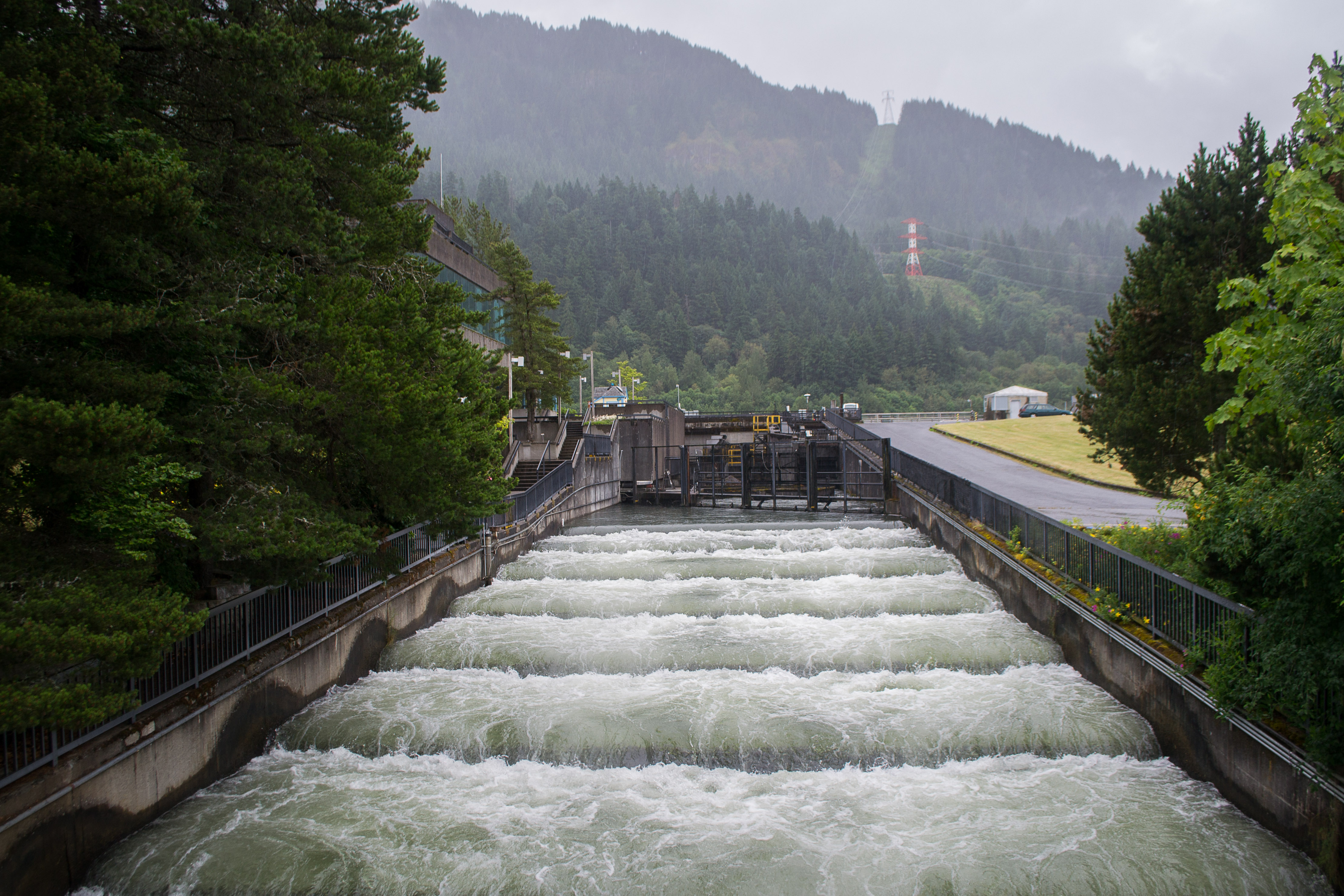
Industrial expansion began in earnest following the 1933–37 construction of the Bonneville Dam
Bonneville Lock and Dam consists of several run-of-the-river dam structures that together complete a span of the Columbia River between the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington at River Mile 146.1. The dam is located east of Portland, Oregon, ...
on the Columbia River. Hydroelectric power
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
, food, and lumber provided by Oregon helped fuel the development of the West, although the periodic fluctuations in the U.S. building industry have hurt the state's economy on multiple occasions. Portland, in particular, experienced a population boom between 1900 and 1930, tripling in size; the arrival of World War II also provided the northwest region of the state with an industrial boom, where Liberty ship
Liberty ships were a class of cargo ship built in the United States during World War II under the Emergency Shipbuilding Program. Though British in concept, the design was adopted by the United States for its simple, low-cost construction. Mass ...
s and aircraft carriers were constructed.
During the 1970s, the Pacific Northwest was particularly affected by the 1973 oil crisis
The 1973 oil crisis or first oil crisis began in October 1973 when the members of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC), led by Saudi Arabia, proclaimed an oil embargo. The embargo was targeted at nations that had supp ...
, with Oregon suffering a substantial shortage.
In 1972, The Oregon Beverage Container Act of 1971, popularly called the Bottle Bill, became the first law of its kind in the United States. The Bottle Bill system in Oregon was created to control litter. In practice, the system promotes recycling, not reusing, and the collected containers are generally destroyed and made into new containers. Ten states currently have similar laws.
In 1994, Oregon became the first U.S. state to legalize physician-assisted suicide
Assisted suicide is suicide undertaken with the aid of another person. The term usually refers to physician-assisted suicide (PAS), which is suicide that is assisted by a physician or other healthcare provider. Once it is determined that the p ...
through the Oregon Death with Dignity Act
Measure 16 of 1994 established the U.S. state of Oregon's Death with Dignity Act (ORS 127.800–995), which legalizes medical aid in dying (commonly referred to as physician-assisted suicide) with certain restrictions. Passage of this initiativ ...
. A measure to legalize recreational use of marijuana
Cannabis, also known as marijuana among other names, is a psychoactive drug from the cannabis plant. Native to Central or South Asia, the cannabis plant has been used as a drug for both recreational and entheogenic purposes and in various tra ...
in Oregon was approved on November 4, 2014, making Oregon only the second state at the time to have legalized gay marriage
Same-sex marriage, also known as gay marriage, is the marriage of two people of the same sex or gender. marriage between same-sex couples is legally performed and recognized in 33 countries, with the most recent being Mexico, constituting ...
, physician-assisted suicide, and recreational marijuana.
Geography
 Oregon is north to south at longest distance, and east to west. With an area of , Oregon is slightly larger than the
Oregon is north to south at longest distance, and east to west. With an area of , Oregon is slightly larger than the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
. It is the ninth largest state in the United States. Oregon's highest point is the summit of Mount Hood
Mount Hood is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It was formed by a subduction zone on the Pacific coast and rests in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located about east-southeast of Portlan ...
, at , and its lowest point is the sea level of the Pacific Ocean along the Oregon Coast. Oregon's mean elevation is . Crater Lake National Park
Crater Lake National Park is an American national park located in southern Oregon. Established in 1902, Crater Lake is the fifth-oldest national park in the United States and the only national park in Oregon. The park encompasses the caldera of ...
, the state's only national park, is the site of the deepest lake in the United States at . Oregon claims the D River
The D River is a river in Lincoln City, Oregon, United States. The once-nameless river was at one time the "shortest river in the world" in the ''Guinness World Records'' at .
World record dispute
The world's shortest title was lost in 1989 whe ...
as the shortest river in the world, though the state of Montana makes the same claim of its Roe River
The Roe River runs from Giant Springs to the Missouri River near Great Falls, Montana, United States. The Roe River is only long at its longest constant point, and had been named as the World's Shortest River by the '' Guinness Book of World ...
. Oregon is also home to Mill Ends Park
Mill Ends Park (sometimes mistakenly called Mill's End Park) is a tiny urban park, consisting of one tree, located in the median strip of Naito Parkway, SW Naito Parkway next to Tom McCall Waterfront Park along the Willamette River near SW Taylor ...
(in Portland), the smallest park in the world at .
Oregon is split into eight geographical regions. In Western Oregon
Western Oregon is a geographical term that is generally taken to mean the part of the U.S. state of Oregon within of the Oregon Coast, on the west side of the crest of the Cascade Range. The term is applied somewhat loosely, however, and is somet ...
: Oregon Coast
The Oregon Coast is a coastal region of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is bordered by the Pacific Ocean to its west and the Oregon Coast Range to the east, and stretches approximately from the California state border in the south to the Columbia ...
(west of the Coast Range), the Willamette Valley
The Willamette Valley ( ) is a long valley in Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. The Willamette River flows the entire length of the valley and is surrounded by mountains on three sides: the Cascade Range to the east, ...
, Rogue Valley
The Rogue Valley is a valley region in southwestern Oregon in the United States. Located along the middle Rogue River (Oregon), Rogue River and its tributaries in Josephine County, Oregon, Josephine and Jackson County, Oregon, Jackson counties, t ...
, Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, ...
and Klamath Mountains
The Klamath Mountains are a rugged and lightly populated mountain range in northwestern California and southwestern Oregon in the western United States. As a mountain system within both the greater Pacific Coast Ranges and the California Coast R ...
; and in Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and Eastern Oregon
Eastern Oregon is the eastern part of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is not an officially recognized geographic entity; thus, the boundaries of the region vary according to context. It is sometimes understood to include only the eight easternmost ...
: the Columbia Plateau
The Columbia Plateau is a geologic and geographic region that lies across parts of the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, and Idaho. It is a wide flood basalt plateau between the Cascade Range and the Rocky Mountains, cut through by the Columbia ...
, the High Desert, and the Blue Mountains.
Oregon lies in two time zone
A time zone is an area which observes a uniform standard time for legal, Commerce, commercial and social purposes. Time zones tend to follow the boundaries between Country, countries and their Administrative division, subdivisions instead of ...
s. Most of Malheur County is in the Mountain Time Zone
The Mountain Time Zone of North America keeps time by subtracting seven hours from Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) when standard time ( UTC−07:00) is in effect, and by subtracting six hours during daylight saving time ( UTC−06:00). The clo ...
, while the rest of the state lies in the Pacific Time Zone
The Pacific Time Zone (PT) is a time zone encompassing parts of western Canada, the western United States, and western Mexico. Places in this zone observe standard time by subtracting eight hours from Coordinated Universal Time ( UTC−08:00) ...
.
Geology and terrain
 Western Oregon's mountainous regions, home to three of the most prominent mountain peaks of the United States including
Western Oregon's mountainous regions, home to three of the most prominent mountain peaks of the United States including Mount Hood
Mount Hood is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It was formed by a subduction zone on the Pacific coast and rests in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located about east-southeast of Portlan ...
, were formed by the volcanic activity of the Juan de Fuca Plate, a tectonic plate
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
that poses a continued threat of volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates a ...
activity and earthquakes in the region. The most recent major activity was the 1700 Cascadia earthquake
The 1700 Cascadia earthquake occurred along the Cascadia subduction zone on January 26, 1700, with an estimated moment magnitude of 8.7–9.2. The megathrust earthquake involved the Juan de Fuca Plate from mid-Vancouver Island, south along the P ...
. Washington
Washington commonly refers to:
* Washington (state), United States
* Washington, D.C., the capital of the United States
** A metonym for the federal government of the United States
** Washington metropolitan area, the metropolitan area centered o ...
's Mount St. Helens
Mount St. Helens (known as Lawetlat'la to the indigenous Cowlitz people, and Loowit or Louwala-Clough to the Klickitat) is an active stratovolcano located in Skamania County, Washington, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United St ...
erupted in 1980, an event visible from northern Oregon and affecting some areas there.
The Columbia River, which forms much of Oregon's northern border, also played a major role in the region's geological evolution, as well as its economic and cultural development. The Columbia is one of North America's largest rivers, and one of two rivers to cut through the Cascades (the Klamath River
The Klamath River (Karuk: ''Ishkêesh'', Klamath: ''Koke'', Yurok: ''Hehlkeek 'We-Roy'') flows through Oregon and northern California in the United States, emptying into the Pacific Ocean. By average discharge, the Klamath is the second larges ...
in southern Oregon is the other). About 15,000 years ago, the Columbia repeatedly flooded much of Oregon during the Missoula Floods
The Missoula floods (also known as the Spokane floods or the Bretz floods or Bretz's floods) were cataclysmic glacial lake outburst floods that swept periodically across eastern Washington and down the Columbia River Gorge at the end of the last ...
; the modern fertility of the Willamette Valley is largely the result. Plentiful salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the ...
made parts of the river, such as Celilo Falls
Celilo Falls (Wyam, meaning "echo of falling water" or "sound of water upon the rocks," in several native languages) was a tribal fishing area on the Columbia River, just east of the Cascade Mountains, on what is today the border between the U.S. ...
, hubs of economic activity for thousands of years.
Today, Oregon's landscape varies from rain forest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainforest ...
in the Coast Range to barren desert in the southeast, which still meets the technical definition of a frontier
A frontier is the political and geographical area near or beyond a boundary. A frontier can also be referred to as a "front". The term came from French in the 15th century, with the meaning "borderland"—the region of a country that fronts o ...
. Oregon's geographical center
In geography, the centroid of the two-dimensional shape of a region of the Earth's surface (projected radially to sea level or onto a geoid surface) is known as its geographic centre or geographical centre or (less commonly) gravitational centre. I ...
is further west than any of the other 48 contiguous states (although the westernmost point of the lower 48 states is in Washington). Central Oregon
Central Oregon is a geographic region in the U.S. state of Oregon and is traditionally considered to be made up of Deschutes, Jefferson, and Crook counties. Other definitions include larger areas, often encompassing areas to the north towards the ...
's geographical features range from high desert and volcanic rock formations resulting from lava bed
Lava fields are large, mostly flat areas of surface or subaquatic lava flows. Such features are generally composed of highly fluid basalt lava, and can extend for tens or hundreds of miles across the underlying terrain.
Morphology and stru ...
s. The Oregon Badlands Wilderness
The Oregon Badlands Wilderness is a wilderness area located east of Bend, Oregon, Bend in Deschutes County, Oregon, Deschutes and Crook County, Oregon, Crook counties in the U.S. state of Oregon. The wilderness is managed by the Bureau of Land ...
is in this region of the state.
Flora and fauna
Typical of a western state, Oregon is home to a unique and diverse array of wildlife. Roughly 60 percent of the state is covered in forest, while the areas west of the Cascades are more densely populated by forest, making up around 80 percent of the landscape. Some 60 percent of Oregon's forests are within federal land. Oregon is the top timber producer of the lower 48 states. * Typical tree species include theDouglas fir
The Douglas fir (''Pseudotsuga menziesii'') is an evergreen conifer species in the pine family, Pinaceae. It is native to western North America and is also known as Douglas-fir, Douglas spruce, Oregon pine, and Columbian pine. There are three va ...
(the state tree
This is a list of U.S. state, federal district, and territory trees, including official trees of the following of the states, of the federal district, and of the territories.
Table
See also
* List of U.S. state, district, and territorial insign ...
), as well as redwood
Sequoioideae, popularly known as redwoods, is a subfamily of coniferous trees within the family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affini ...
, ponderosa pine
''Pinus ponderosa'', commonly known as the ponderosa pine, bull pine, blackjack pine, western yellow-pine, or filipinus pine is a very large pine tree species of variable habitat native to mountainous regions of western North America. It is the ...
, western red cedar
''Thuja plicata'' is an evergreen coniferous tree in the cypress family Cupressaceae, native to western North America. Its common name is western redcedar (western red cedar in the UK), and it is also called Pacific redcedar, giant arborvitae ...
, and hemlock. Ponderosa pine are more common in the Blue Mountains in the eastern part of the state and firs are more common in the west.
 * Many species of mammals live in the state, which include opossums, shrews, moles, little pocket mice, great basin pocket mice,
* Many species of mammals live in the state, which include opossums, shrews, moles, little pocket mice, great basin pocket mice, dark kangaroo mouse
The dark kangaroo mouse (''Microdipodops megacephalus'') is a species of rodent in the family Heteromyidae. It is found in California, Idaho, Nevada, Oregon and Utah in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), comm ...
, California kangaroo rat
The California kangaroo rat (''Dipodomys californicus'') is a species of rodent in the family Heteromyidae. However, populations are declining, having not fully recovered after the drought in California from 2013 to 2015 destroyed their habitat ( ...
, chisel-toothed kangaroo rat
The chisel-toothed kangaroo rat (''Dipodomys microps'') is a species of rodent in the family Heteromyidae.
There are 13 sub-species. Saltbush leaves are a major dietary component, requiring specialized physiology to eliminate the salt while reta ...
, ord's kangaroo rat
Ord's kangaroo rat (''Dipodomys ordii'') is a kangaroo rat native to western North America, specifically the Great Plains and the Great Basin, with its range extending from extreme southern Canada to central Mexico.
Ord's kangaroo rat has a fift ...
, bats, rabbits, pikas
A pika ( or ; archaically spelled pica) is a small, mountain-dwelling mammal found in Asia and North America. With short limbs, very round body, an even coat of fur, and no external tail, they resemble their close relative, the rabbit, but wi ...
, mountain beaver
The mountain beaver (''Aplodontia rufa'')Other names include mountain boomer, ground bear, giant mole, gehalis, lesser sasquatch, sewellel, suwellel, showhurll, showtl, and showte, as well as a number of Chinookan and other Native American terms ...
s, chipmunk
Chipmunks are small, striped rodents of the family Sciuridae. Chipmunks are found in North America, with the exception of the Siberian chipmunk which is found primarily in Asia.
Taxonomy and systematics
Chipmunks may be classified either as ...
s, squirrels, yellow-bellied marmot
The yellow-bellied marmot (''Marmota flaviventris''), also known as the rock chuck, is a large, stout-bodied ground squirrel in the marmot genus. It is one of fourteen species of marmots, and is native to mountainous regions of southwestern Cana ...
s, beavers (the state mammal), porcupine
Porcupines are large rodents with coats of sharp spines, or quills, that protect them against predation. The term covers two families of animals: the Old World porcupines of family Hystricidae, and the New World porcupines of family, Erethizont ...
s, coyote
The coyote (''Canis latrans'') is a species of canis, canine native to North America. It is smaller than its close relative, the wolf, and slightly smaller than the closely related eastern wolf and red wolf. It fills much of the same ecologica ...
s, wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; plural, : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large Canis, canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of Canis lupus, subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been reco ...
, fox
Foxes are small to medium-sized, omnivorous mammals belonging to several genera of the family Canidae. They have a flattened skull, upright, triangular ears, a pointed, slightly upturned snout, and a long bushy tail (or ''brush'').
Twelve sp ...
es black bears, raccoons, badgers, skunks, antelopes
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia.
Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mammal ...
, cougar
The cougar (''Puma concolor'') is a large Felidae, cat native to the Americas. Its Species distribution, range spans from the Canadian Yukon to the southern Andes in South America and is the most widespread of any large wild terrestrial mamm ...
s, bobcat
The bobcat (''Lynx rufus''), also known as the red lynx, is a medium-sized cat native to North America. It ranges from southern Canada through most of the contiguous United States to Oaxaca in Mexico. It is listed as Least Concern on the IUC ...
s, lynx
A lynx is a type of wild cat.
Lynx may also refer to:
Astronomy
* Lynx (constellation)
* Lynx (Chinese astronomy)
* Lynx X-ray Observatory, a NASA-funded mission concept for a next-generation X-ray space observatory
Places Canada
* Lynx, Ontar ...
es, deer, elk, and moose.
* Marine mammals include seals
Seals may refer to:
* Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly:
** Earless seal, or "true seal"
** Fur seal
* Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of a ...
, sea lion
Sea lions are pinnipeds characterized by external ear flaps, long foreflippers, the ability to walk on all fours, short and thick hair, and a big chest and belly. Together with the fur seals, they make up the family Otariidae, eared seals. ...
s, humpback whale
The humpback whale (''Megaptera novaeangliae'') is a species of baleen whale. It is a rorqual (a member of the family Balaenopteridae) and is the only species in the genus ''Megaptera''. Adults range in length from and weigh up to . The hump ...
s, killer whale
The orca or killer whale (''Orcinus orca'') is a toothed whale belonging to the oceanic dolphin family, of which it is the largest member. It is the only extant species in the genus ''Orcinus'' and is recognizable by its black-and-white pa ...
s, gray whale
The gray whale (''Eschrichtius robustus''), also known as the grey whale,Britannica Micro.: v. IV, p. 693. gray back whale, Pacific gray whale, Korean gray whale, or California gray whale, is a baleen whale that migrates between feeding and bree ...
s, blue whale
The blue whale (''Balaenoptera musculus'') is a marine mammal and a baleen whale. Reaching a maximum confirmed length of and weighing up to , it is the largest animal known to have ever existed. The blue whale's long and slender body can ...
s, sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the genus ''Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the sperm whale famil ...
s, pacific white-sided dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the ...
s, and bottlenose dolphin
Bottlenose dolphins are aquatic mammals in the genus ''Tursiops.'' They are common, cosmopolitan members of the family Delphinidae, the family of oceanic dolphins. Molecular studies show the genus definitively contains two species: the common ...
s.
* Notable birds include American widgeons, mallard duck
The mallard () or wild duck (''Anas platyrhynchos'') is a dabbling duck that breeds throughout the temperate and subtropical Americas, Eurasia, and North Africa, and has been introduced species, introduced to New Zealand, Australia, Peru, Bra ...
s, great blue heron
The great blue heron (''Ardea herodias'') is a large wading bird in the heron family Ardeidae, common near the shores of open water and in wetlands over most of North America and Central America, as well as the Caribbean and the Galápagos ...
s, bald eagle
The bald eagle (''Haliaeetus leucocephalus'') is a bird of prey found in North America. A sea eagle, it has two known subspecies and forms a species pair with the white-tailed eagle (''Haliaeetus albicilla''), which occupies the same niche as ...
s, golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known bird of p ...
s, western meadowlark
The western meadowlark (''Sturnella neglecta'') is a medium-sized icterid bird, about in length. It nests on the ground in open grasslands across western and central North America. It feeds mostly on bugs, but will also feed on seeds and berri ...
s (the state bird), barn owl
The barn owl (''Tyto alba'') is the most widely distributed species of owl in the world and one of the most widespread of all species of birds, being found almost everywhere except for the polar and desert regions, Asia north of the Himalaya ...
s, great horned owl
The great horned owl (''Bubo virginianus''), also known as the tiger owl (originally derived from early naturalists' description as the "winged tiger" or "tiger of the air"), or the hoot owl, is a large owl native to the Americas. It is an extrem ...
s, rufous hummingbirds, pileated woodpecker
The pileated woodpecker (''Dryocopus pileatus'') is a large, mostly black woodpecker native to North America. An insectivore, it inhabits deciduous forests in eastern North America, the Great Lakes, the boreal forests of Canada, and parts of the ...
s, wrens, towhee
A towhee is any one of a number of species of birds in the genus ''Pipilo'' or ''Melozone'' within the family Passerellidae (which also includes American sparrows, and juncos).
Towhees typically have longer tails than other Passerellidae. Most ...
s, sparrows, and buntings
The buntings are a group of Old World passerine birds forming the genus ''Emberiza'', the only genus in the family Emberizidae. The family contains 45 species. They are seed-eating birds with stubby, conical bills.
Taxonomy
The family Emberizi ...
.
Moose
The moose (in North America) or elk (in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is a member of the New World deer subfamily and is the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is the largest and heaviest extant species in the deer family. Most adult mal ...
have not always inhabited the state but came to Oregon in the 1960s; the Wallowa Valley Wallowa may refer to:
Places
*Wallowa, Oregon
*Wallowa County, Oregon
*Wallowa Lake
*Wallowa Lake State Park
*Wallowa Mountains
*Wallowa River
Other
*''Acacia calamifolia'', a shrub or tree
*''Acacia euthycarpa'', a shrub or tree
* ''The Wallo ...
herd numbered about 60 . Gray wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly un ...
were extirpated from Oregon around 1930 but have since found their way back; most reside in northeast Oregon, with two packs living in the south-central part. Although their existence in Oregon is unconfirmed, reports of grizzly bear
The grizzly bear (''Ursus arctos horribilis''), also known as the North American brown bear or simply grizzly, is a population or subspecies of the brown bear inhabiting North America.
In addition to the mainland grizzly (''Ursus arctos horri ...
s still turn up, and it is probable some still move into eastern Oregon from Idaho.
Oregon is home to what is considered the largest single organism in the world, an ''Armillaria solidipes
''Armillaria ostoyae'' (synonym ''Armillaria solidipes'') is a species of fungus (mushroom), pathogenic to trees, in the family Physalacriaceae. In the western United States, it is the most common variant of the group of species under the na ...
'' fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from th ...
beneath the Malheur National Forest
The Malheur National Forest is a United States National Forest, National Forest in the U.S. state of Oregon. It contains more than in the Blue Mountains (Pacific Northwest), Blue Mountains of eastern Oregon. The forest consists of Great Basin ...
of eastern Oregon.
Oregon has several National Park System sites, including Crater Lake National Park
Crater Lake National Park is an American national park located in southern Oregon. Established in 1902, Crater Lake is the fifth-oldest national park in the United States and the only national park in Oregon. The park encompasses the caldera of ...
in the southern part of the Cascades, John Day Fossil Beds National Monument
John Day Fossil Beds National Monument is a U.S. national monument in Wheeler and Grant counties in east-central Oregon. Located within the John Day River basin and managed by the National Park Service, the park is known for its well-preserved l ...
east of the Cascades, Lewis and Clark National Historical Park
The Lewis and Clark National Historical Park (including the former Fort Clatsop National Memorial), located in the vicinity of the mouth of the Columbia River, commemorates the Lewis and Clark Expedition. Administration of the park, which include ...
on the north coast, and Oregon Caves National Monument
Oregon Caves National Monument and Preserve is a protected area in the northern Siskiyou Mountains of southwestern Oregon in the United States. The 4,554-acre (1,843 ha) park, including the marble cave, is 20 miles (32 km) east of C ...
near the south coast.
Climate
Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, ...
) has an oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
, populated by dense evergreen
In botany, an evergreen is a plant which has foliage that remains green and functional through more than one growing season. This also pertains to plants that retain their foliage only in warm climates, and contrasts with deciduous plants, which ...
mixed forests. Western Oregon's climate is heavily influenced by the Pacific Ocean; the western third of Oregon is very wet in the winter, moderately to very wet during the spring and fall, and dry during the summer. The relative humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depe ...
of Western Oregon is high except during summer days, which are semi-dry to semi-humid; Eastern Oregon typically sees low humidity year-round.
The state's southwestern portion, particularly the Rogue Valley
The Rogue Valley is a valley region in southwestern Oregon in the United States. Located along the middle Rogue River (Oregon), Rogue River and its tributaries in Josephine County, Oregon, Josephine and Jackson County, Oregon, Jackson counties, t ...
, has a Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
with drier and sunnier winters and hotter summers, similar to Northern California
Northern California (colloquially known as NorCal) is a geographic and cultural region that generally comprises the northern portion of the U.S. state of California. Spanning the state's northernmost 48 counties, its main population centers incl ...
.
Oregon's northeastern portion has a steppe climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
, and its high terrain regions have a subarctic climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, ge ...
. Like Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
, Oregon, and the Pacific Northwest in general, is considered warm for its latitude, and the state has far milder winters at a given elevation than comparable latitudes elsewhere in North America, such as the Upper Midwest
The Upper Midwest is a region in the northern portion of the U.S. Census Bureau's Midwestern United States. It is largely a sub-region of the Midwest. Although the exact boundaries are not uniformly agreed-upon, the region is defined as referring ...
, Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
, Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
and New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
. However, the state ranks fifth for coolest summer temperatures of any state in the country, after Maine, Idaho, Wyoming, and Alaska.
The eastern two thirds of Oregon, which largely comprise high desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
, have cold, snowy winters and very dry summers. Much of the east is semiarid to arid like the rest of the Great Basin
The Great Basin is the largest area of contiguous endorheic basin, endorheic watersheds, those with no outlets, in North America. It spans nearly all of Nevada, much of Utah, and portions of California, Idaho, Oregon, Wyoming, and Baja California ...
, though the Blue Mountains are wet enough to support extensive forests. Most of Oregon receives significant snowfall, but the Willamette Valley, where 60 percent of the population lives, has considerably milder winters for its latitude and typically sees only light snowfall.
Oregon's highest recorded temperature is at Pendleton on August 10, 1898, and the lowest recorded temperature is at Seneca
Seneca may refer to:
People and language
* Seneca (name), a list of people with either the given name or surname
* Seneca people, one of the six Iroquois tribes of North America
** Seneca language, the language of the Seneca people
Places Extrat ...
on February 10, 1933.
Cities and towns
Oregon's population is largely concentrated in the Willamette Valley, which stretches from Eugene in the south (home of theUniversity of Oregon
The University of Oregon (UO, U of O or Oregon) is a public research university in Eugene, Oregon. Founded in 1876, the institution is well known for its strong ties to the sports apparel and marketing firm Nike, Inc, and its co-founder, billion ...
) through Corvallis (home of Oregon State University
Oregon State University (OSU) is a public land-grant, research university in Corvallis, Oregon. OSU offers more than 200 undergraduate-degree programs along with a variety of graduate and doctoral degrees. It has the 10th largest engineering co ...
) and Salem (the capital) to Portland (Oregon's largest city).
Astoria, at the mouth of the Columbia River, was the first permanent English-speaking settlement west of the Rockies
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
in what is now the United States. Oregon City, at the end of the Oregon Trail, was the Oregon Territory's first incorporated city, and was its first capital from 1848 until 1852, when the capital was moved to Salem. Bend, near the geographic center of the state, is one of the ten fastest-growing metropolitan areas in the United States. In southern Oregon, Medford is a rapidly growing metro area and is home to the Rogue Valley International-Medford Airport
A rogue is a person or entity that flouts accepted norms of behavior.
Rogue or rogues may also refer to:
Companies
* Rogue Ales, a microbrewery in Newport, Oregon
* Rogue Arts, a film production company
* Rogue Entertainment, a software comp ...
, the state's third-busiest airport. To the south, near the California border, is the city of Ashland. Eastern Oregon
Eastern Oregon is the eastern part of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is not an officially recognized geographic entity; thus, the boundaries of the region vary according to context. It is sometimes understood to include only the eight easternmost ...
is sparsely populated, but is home to Hermiston, which with a population of 18,000 is the largest and fastest-growing city in the region.
Demographics
Population

 The
The 2020 U.S. census
The United States census of 2020 was the twenty-fourth decennial United States census. Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2020. Other than a pilot study during the 2000 census, this was the first U.S. census to of ...
determined that the population of Oregon was 4,237,256 in 2020, a 10.71% increase over the 2010 census.
Oregon was the nation's "Top Moving Destination" in 2014, with two families moving into the state for every one moving out (66.4% to 33.6%). Oregon was also the top moving destination in 2013, and the second-most popular destination in 2010 through 2012.
As of the 2010 census, the population of Oregon was 3,831,074. The gender makeup of the state was 49.5% male and 50.5% female. 22.6% of the population were under the age of 18; 63.5% were between the ages of 18 and 64; and 12.5% were 65 years of age or older.
According to the 2020 census, 13.9% of Oregon's population was of Hispanic or Latino
''Hispanic'' and '' Latino'' are ethnonyms used to refer collectively to the inhabitants of the United States who are of Spanish or Latin American ancestry (). While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, for example, by the United States ...
origin (of any race) and 71.7% Non-Hispanic White
Non-Hispanic whites or Non-Latino whites are Americans who are classified as "white", and are not of Hispanic (also known as "Latino") heritage. The United States Census Bureau defines ''white'' to include European Americans, Middle Eastern Amer ...
, 2.0% African American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
, 1.5% Native American, 4.6% Asian
Asian may refer to:
* Items from or related to the continent of Asia:
** Asian people, people in or descending from Asia
** Asian culture, the culture of the people from Asia
** Asian cuisine, food based on the style of food of the people from Asi ...
, 1.5% Pacific Islander
Pacific Islanders, Pasifika, Pasefika, or rarely Pacificers are the peoples of the list of islands in the Pacific Ocean, Pacific Islands. As an ethnic group, ethnic/race (human categorization), racial term, it is used to describe the original p ...
, 10.5% one or more races.
According to the 2016 American Community Survey
The American Community Survey (ACS) is a demographics survey program conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. It regularly gathers information previously contained only in the long form of the decennial census, such as ancestry, citizenship, educati ...
, 12.4% of Oregon's population were of Hispanic or Latino
''Hispanic'' and '' Latino'' are ethnonyms used to refer collectively to the inhabitants of the United States who are of Spanish or Latin American ancestry (). While the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, for example, by the United States ...
origin (of any race): Mexican (10.4%), Puerto Rican (0.3%), Cuban
Cuban may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Cuba, a country in the Caribbean
* Cubans, people from Cuba, or of Cuban descent
** Cuban exile, a person who left Cuba for political reasons, or a descendant thereof
* Cuban citizen, a perso ...
(0.1%), and other Hispanic or Latino origin (1.5%). The five largest ancestry groups for White Oregonians were: German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
(19.1%), Irish
Irish may refer to:
Common meanings
* Someone or something of, from, or related to:
** Ireland, an island situated off the north-western coast of continental Europe
***Éire, Irish language name for the isle
** Northern Ireland, a constituent unit ...
(11.7%), English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
(11.3%), American
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, pe ...
(5.3%), and Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
(3.8%).
The state's most populous ethnic group, non-Hispanic White
Non-Hispanic whites or Non-Latino whites are Americans who are classified as "white", and are not of Hispanic (also known as "Latino") heritage. The United States Census Bureau defines ''white'' to include European Americans, Middle Eastern Amer ...
, has declined from 95.8% in 1970 to 77.8% in 2012. This decreased further to 71.7% in the 2020 census.
, 38.7% of Oregon's children under one year of age belonged to minority groups
The term 'minority group' has different usages depending on the context. According to its common usage, a minority group can simply be understood in terms of demographic sizes within a population: i.e. a group in society with the least number o ...
, meaning they had at least one parent who was not a non-Hispanic White. Of the state's total population, 22.6% was under the age 18, and 77.4% were 18 or older.
The center of population
In demographics, the center of population (or population center) of a region is a geographical point that describes a centerpoint of the region's population. There are several ways of defining such a "center point", leading to different geogr ...
of Oregon is located in Linn County, in the city of Lyons
Lyon,, ; Occitan: ''Lion'', hist. ''Lionés'' also spelled in English as Lyons, is the third-largest city and second-largest metropolitan area of France. It is located at the confluence of the rivers Rhône and Saône, to the northwest of th ...
. Around 60% of Oregon's population resides within the Portland metropolitan area
The Portland metropolitan area is a metro area in the U.S. states of Oregon and Washington centered on the principal city of Portland, Oregon. The U.S. Office of Management and Budget (OMB) identifies it as the Portland–Vancouver–Hillsboro, ...
.
, Oregon's population comprised 361,393 foreign-born residents. Of the foreign-born residents, the three largest groups are originally from countries in: Latin America (47.8%), Asia (27.4%), and Europe (16.5%).
Religious and secular communities
Oregon has frequently been cited by statistical agencies for having a smaller percentage of religious communities than other U.S. states. According to a 2009Gallup poll
Gallup, Inc. is an American analytics and advisory company based in Washington, D.C. Founded by George Gallup in 1935, the company became known for its public opinion polls conducted worldwide. Starting in the 1980s, Gallup transitioned its bu ...
, Oregon was paired with Vermont
Vermont () is a state in the northeast New England region of the United States. Vermont is bordered by the states of Massachusetts to the south, New Hampshire to the east, and New York to the west, and the Canadian province of Quebec to ...
as the two "least religious" states in the United States.
In the same 2009 Gallup poll, 69% of Oregonians identified themselves as being Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
. The largest Christian denominations in Oregon by number of adherents in 2010 were the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
with 398,738; The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints
The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, informally known as the LDS Church or Mormon Church, is a Nontrinitarianism, nontrinitarian Christianity, Christian church that considers itself to be the Restorationism, restoration of the ...
with 147,965; and the Assemblies of God
The Assemblies of God (AG), officially the World Assemblies of God Fellowship, is a group of over 144 autonomous self-governing national groupings of churches that together form the world's largest Pentecostal denomination."Assemblies of God". ...
with 45,492. Oregon also contains the largest community of Russian Old Believers
Old Believers or Old Ritualists, ''starovery'' or ''staroobryadtsy'' are Eastern Orthodox Christians who maintain the liturgical and ritual practices of the Russian Orthodox Church as they were before the reforms of Patriarch Nikon of Moscow bet ...
to be found in the United States. Judaism is the largest non-Christian religion in Oregon with more than 50,000 adherents, 47,000 of whom live in the Portland area. Recently, new kosher food and Jewish educational offerings have led to a rapid increase in Portland's Orthodox Jewish population. The Northwest Tibetan Cultural Association is headquartered in Portland. There are an estimated 6,000 to 10,000 Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abraha ...
in Oregon, most of whom live in and around Portland.
Most of the remainder of the population had no religious affiliation; the 2008 American Religious Identification Survey (ARIS)
The Institute for the Study of Secularism in Society and Culture (ISSSC) is located at Trinity College in Hartford, Connecticut. ISSSC was established in 2005 to advance the understanding of the role of secular values and the process of seculari ...
placed Oregon as tied with Nevada in fifth place of U.S. states having the highest percentage of residents identifying themselves as "non-religious", at 24 percent. Secular organizations include the Center for Inquiry
The Center for Inquiry (CFI) is a US nonprofit organization that works to mitigate belief in pseudoscience and the paranormal, as well as to fight the influence of religion in government.
History
The Center for Inquiry was established in 199 ...
(CFI), the Humanists of Greater Portland (HGP), and the United States Atheists (USA).
During much of the 1990s, a group of conservative Christians formed the Oregon Citizens Alliance
The Oregon Citizens Alliance (OCA) was a conservative Christian political activist organization, founded by Lon Mabon in the U.S. state of Oregon. It was founded in 1986 as a vehicle to challenge then–U.S. Senator Bob Packwood in the Republican p ...
, and unsuccessfully tried to pass legislation to prevent "gay sensitivity training" in public schools and legal benefits for homosexual couples.
* Since 2016, data for births of White Hispanic
White Latin Americans, or European Latin Americans, are Latin Americans who are considered white, typically due to European descent. Latin American countries have often tolerated intermarriage between different ethnic groups since the beginning ...
origin are not collected, but included in one ''Hispanic'' group; persons of Hispanic origin may be of any race.
* Births in table do not sum to 100% because Hispanics are counted both by their ethnicity and by their race.
Future projections
Projections from the U.S. Census Bureau show Oregon's population increasing to 4,833,918 by 2030, an increase of 41.3% compared to the state's population of 3,421,399 in 2000. The state's own projections forecast a total population of 5,425,408 in 2040.Economy
median household income
The median income is the income amount that divides a population into two equal groups, half having an income above that amount, and half having an income below that amount. It may differ from the mean (or average) income. Both of these are ways of ...
at $60,834. The gross domestic product (GDP) of Oregon in 2013 was $219.6 billion, a 2.7% increase from 2012; Oregon is the 25th wealthiest state by GDP. In 2003, Oregon was 28th in the U.S. by GDP. The state's per capita personal income (PCPI) in 2013 was $39,848, a 1.5% increase from 2012. Oregon ranks 33rd in the U.S. by PCPI, compared to 31st in 2003. The national PCPI in 2013 was $44,765.
Oregon's unemployment rate was 5.5% in September 2016, while the U.S. unemployment rate was 5.0% that month. Oregon has the third largest amount of food stamp users in the nation (21% of the population).
Agriculture
 Oregon's diverse landscapes provide ideal environments for various types of farming. Land in the Willamette Valley owes its fertility to the
Oregon's diverse landscapes provide ideal environments for various types of farming. Land in the Willamette Valley owes its fertility to the Missoula Floods
The Missoula floods (also known as the Spokane floods or the Bretz floods or Bretz's floods) were cataclysmic glacial lake outburst floods that swept periodically across eastern Washington and down the Columbia River Gorge at the end of the last ...
, which deposited lake sediment from Glacial Lake Missoula
Lake Missoula was a prehistoric proglacial lake in western Montana that existed periodically at the end of the last ice age between 15,000 and 13,000 years ago. The lake measured about and contained about of water, half the volume of Lake Mic ...
in western Montana onto the valley floor.McNab, W. Henry; Avers, Peter E (July 1994)''Ecological Subregions of the United States''. Chapter 24.
U.S. Forest Service and Dept. of Agriculture. In 2016, the Willamette Valley region produced over of
blueberries
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bi ...
. The industry is governed and represented by the Oregon Department of Agriculture
The Oregon Department of Agriculture (ODA) is responsible for agriculture in Oregon. This agency of the government of the U.S. state of Oregon promotes and regulates food production and safety. It is headed by the director of agriculture, appoin ...
.
Oregon is also one of four major world hazelnut (''Corylus avellana
''Corylus avellana'', the common hazel, is a species of flowering plant in the birch family Betulaceae. It is native to Europe and western Asia. It is an important component of the hedgerows that were the traditional field boundaries in lowland En ...
'') growing regions, and produces 95% of the domestic hazelnuts in the United States. While the history of the wine production in Oregon can be traced to before Prohibition
Prohibition is the act or practice of forbidding something by law; more particularly the term refers to the banning of the manufacture, storage (whether in barrels or in bottles), transportation, sale, possession, and consumption of alcoholic ...
, it became a significant industry beginning in the 1970s. In 2005, Oregon ranked third among U.S. states with 303 wineries. Due to regional similarities in climate and soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth or dirt, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support life. Some scientific definitions distinguish ''dirt'' from ''soil'' by restricting the former te ...
, the grapes planted in Oregon are often the same varieties found in the French regions of Alsace
Alsace (, ; ; Low Alemannic German/ gsw-FR, Elsàss ; german: Elsass ; la, Alsatia) is a cultural region and a territorial collectivity in eastern France, on the west bank of the upper Rhine next to Germany and Switzerland. In 2020, it had ...
and Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The c ...
. In 2014, 71 wineries opened in the state. The total is currently 676, which represents growth of 12% over 2013.
In the southern Oregon coast, commercially cultivated cranberries account for about 7 percent of U.S. production, and the cranberry ranks 23rd among Oregon's top 50 agricultural commodities. Cranberry cultivation in Oregon uses about in southern Coos and northern Curry
A curry is a dish with a sauce seasoned with spices, mainly associated with South Asian cuisine. In southern India, leaves from the curry tree may be included.
There are many varieties of curry. The choice of spices for each dish in tradit ...
counties, centered around the coastal city of Bandon. In the northeastern region of the state, particularly around Pendleton, both irrigated and dry land wheat is grown. Oregon farmer
A farmer is a person engaged in agriculture, raising living organisms for food or raw materials. The term usually applies to people who do some combination of raising field crops, orchards, vineyards, poultry, or other livestock. A farmer mig ...
s and ranchers also produce cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult mal ...
, sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated s ...
, dairy products, eggs and poultry
Poultry () are domesticated birds kept by humans for their eggs, their meat or their feathers. These birds are most typically members of the superorder Galloanserae (fowl), especially the order Galliformes (which includes chickens, quails, a ...
.
Caneberries
''Rubus'' is a large and diverse genus of flowering plants in the rose family, Rosaceae, subfamily Rosoideae, with over 1,350 species.
Raspberries, blackberries, and dewberries are common, widely distributed members of the genus. Most of thes ...
(''Rubus'') are farmed here. Stamen blight (''Hapalosphaeria deformans'') is significant here and throughout the PNW. Here it especially hinders commercial dewberries
The dewberries are a group of species in the genus ''Rubus'', section ''Rubus'', closely related to the blackberries. They are small trailing (rather than upright or high-arching) brambles with aggregate fruits, reminiscent of the raspberr ...
.
was first discovered in the 1990s on the California Central Coast
The Central Coast is an area of California, roughly spanning the coastal region between Point Mugu and Monterey Bay. It lies northwest of Los Angeles County and south of San Mateo County, San Mateo and Santa Clara County, Santa Clara counties, ...
and was quickly found here as well. ''P. ramorum'' is of economic concern due to its infestation of ''Rubus'' and ''Vaccinium
''Vaccinium'' is a common and widespread genus of shrubs or dwarf shrubs in the heath family (Ericaceae). The fruits of many species are eaten by humans and some are of commercial importance, including the cranberry, blueberry, bilberry (whort ...
'' spp. (including cranberry
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus ''Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species ''Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranberry ...
and blueberry
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' within the genus ''Vaccinium''. ''Vaccinium'' also includes cranberries, bi ...
).
es grown in the Willamette Valley
The Willamette Valley ( ) is a long valley in Oregon, in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. The Willamette River flows the entire length of the valley and is surrounded by mountains on three sides: the Cascade Range to the east, ...
are mostly sold directly and do not enter the more distant markets. OSU Extension recommends peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non-fu ...
and nectarine
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non-fuz ...
cultivars for Willamette: For peaches Springcrest, Gemfree, Early Redhaven, Harbelle, Sunhaven, Redhaven, Harken
Harken, Inc. is an international manufacturer specializing in performance sailing hardware, headquartered in Pewaukee, Wisconsin, United States. The company was founded in a 60-foot trailer in 1967 by brothers Peter Harken and Olaf Harken. Orig ...
, Redtop, July Elberta, Fairhaven, Canadian Harmony, Earlihale, Suncrest, Loring, Glohaven, Veteran
A veteran () is a person who has significant experience (and is usually adept and esteemed) and expertise in a particular occupation or field. A military veteran is a person who is no longer serving in a military.
A military veteran that has ...
, Biscoe, and Improved Elberta. For nectarines Juneglo, Harko, Redgold, and Fantasia
Fantasia International Film Festival (also known as Fantasia-fest, FanTasia, and Fant-Asia) is a film festival that has been based mainly in Montreal since its founding in 1996. Regularly held in July of each year, it is valued by both hardcore ...
.
An ('' Agrilus planipennis'') infestation has been sighted in Forest Grove, the first for Western North America
Western North America is the western edge of the North American continent that borders the Pacific Ocean. It consists of Alaska at the farthest north, down through the western Canadian province of British Columbia, the western U.S. states of Wa ...
. On June 30, 2022, an off-duty invasion biologist noticed an infested tree and the Emerald Ash Borer Readiness and Response Plan for Oregon finalized in March of the previous year was quickly enacted by state departments. The public is asked to report sightings to the state Department of Agriculture.
Forestry and fisheries

 Vast forests have historically made Oregon one of the nation's major
Vast forests have historically made Oregon one of the nation's major timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
-producing and logging states, but forest fires (such as the Tillamook Burn
The Tillamook Burn was a series of forest fires in the Northern Oregon Coast Range of Oregon in the United States that destroyed a total area of of old growth timber in what is now known as the Tillamook State Forest. There were four wildfire ...
), over-harvesting, and lawsuits over the proper management of the extensive federal forest holdings have reduced the timber produced. Between 1989 and 2011, the amount of timber harvested from federal lands in Oregon dropped about 90%, although harvest levels on private land have remained relatively constant.
Even the shift in recent years towards finished goods such as paper and building materials has not slowed the decline of the timber industry in the state. The effects of this decline have included Weyerhaeuser
Weyerhaeuser () is an American timberland company which owns nearly of timberlands in the U.S., and manages an additional of timberlands under long-term licenses in Canada. The company also manufactures wood products. It operates as a real e ...
's acquisition of Portland-based Willamette Industries
Willamette Industries, Inc. was a Fortune 500 forest products company based in Portland, Oregon, United States.Louisiana-Pacific
Louisiana-Pacific Corporation, commonly known as "LP", is an American building materials manufacturer. It was founded in 1973 and is currently based in Nashville, Tennessee. LP pioneered the U.S. production of oriented strand board (OSB) panels. ...
's corporate headquarters from Portland to Nashville
Nashville is the capital city of the U.S. state of Tennessee and the seat of Davidson County. With a population of 689,447 at the 2020 U.S. census, Nashville is the most populous city in the state, 21st most-populous city in the U.S., and the ...
, and the decline of former lumber company town
A company town is a place where practically all stores and housing are owned by the one company that is also the main employer. Company towns are often planned with a suite of amenities such as stores, houses of worship, schools, markets and re ...
s such as Gilchrist. Despite these changes, Oregon still leads the United States in softwood
file:Pinus sylvestris wood ray section 1 beentree.jpg, Scots Pine, a typical and well-known softwood
Softwood is wood from gymnosperm trees such as conifers. The term is opposed to hardwood, which is the wood from angiosperm trees. The main diff ...
lumber production; in 2011, was produced in Oregon, compared with in Washington, in Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, and in Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Miss ...
. The slowing of the timber and lumber industry
The wood industry or timber industry (sometimes lumber industry -- when referring mainly to sawed boards) is the industry concerned with forestry, logging, timber trade, and the production of primary forest products and wood products (e.g. furnitu ...
has caused high unemployment rates in rural areas.
Oregon has one of the largest salmon
Salmon () is the common name for several list of commercially important fish species, commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family (biology), family Salmonidae, which are native to tributary, tributaries of the ...
-fishing industries in the world, although ocean fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both ...
have reduced the river fisheries in recent years. Because of the abundance of waterways in the state, it is also a major producer of hydroelectric energy.
Tourism and entertainment

 Tourism is also a strong industry in the state. Tourism is centered on the state's natural features – mountains, forests, waterfalls, rivers, beaches and lakes, including
Tourism is also a strong industry in the state. Tourism is centered on the state's natural features – mountains, forests, waterfalls, rivers, beaches and lakes, including Crater Lake National Park
Crater Lake National Park is an American national park located in southern Oregon. Established in 1902, Crater Lake is the fifth-oldest national park in the United States and the only national park in Oregon. The park encompasses the caldera of ...
, Multnomah Falls
Multnomah Falls is a waterfall located on Multnomah Creek in the Columbia River Gorge, east of Troutdale, between Corbett and Dodson, Oregon, United States. The waterfall is accessible from the Historic Columbia River Highway and Interstate 84 ...
, the Painted Hills
The Painted Hills is a geologic site in Wheeler County, Oregon that is one of the three units of the John Day Fossil Beds National Monument along with Sheep Rock and Clarno. It totals and is located northwest of Mitchell, Oregon. The Painted ...
, the Deschutes River, and the Oregon Caves
Oregon Caves National Monument and Preserve is a protected area in the northern Siskiyou Mountains of southwestern Oregon in the United States. The 4,554-acre (1,843 ha) park, including the marble cave, is 20 miles (32 km) east of C ...
. Mount Hood and Mount Bachelor
Mount Bachelor, formerly named Bachelor Butte, is a dormant stratovolcano atop a shield volcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc and the Cascade Range of central Oregon. Named Mount Bachelor because it stands apart from the nearby Three Sisters, it ...
also draw visitors year-round for skiing
Skiing is the use of skis to glide on snow. Variations of purpose include basic transport, a recreational activity, or a competitive winter sport. Many types of competitive skiing events are recognized by the International Olympic Committee (IO ...
and other snow activities.
 Portland is home to the
Portland is home to the Oregon Museum of Science and Industry
The Oregon Museum of Science and Industry (OMSI, ) is a science and technology museum in Portland, Oregon, United States. It contains three auditoriums, including a large-screen theatre, planetarium, and exhibition halls with a variety of hands- ...
, the Portland Art Museum
The Portland Art Museum in Portland, Oregon, United States, was founded in 1892, making it one of the oldest art museums on the West Coast and seventh oldest in the US. Upon completion of the most recent renovations, the Portland Art Museum becam ...
, and the Oregon Zoo
The Oregon Zoo, originally the Portland Zoo and later the Washington Park Zoo, is a zoo located in Washington Park, Portland, Oregon, approximately southwest of downtown Portland. Founded in 1888, it is the oldest zoo west of the Mississippi Ri ...
, which is the oldest zoo west of the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
. The International Rose Test Garden
The International Rose Test Garden is a rose garden in Washington Park in Portland, Oregon, United States. There are over 10,000 rose bushes of approximately 650 varieties. The roses bloom from April through October with the peak coming in Jun ...
is another prominent attraction in the city. Portland has also been named the best city in the world for street food by several publications, including the '' U.S. News & World Report'' and CNN
CNN (Cable News Network) is a multinational cable news channel headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, U.S. Founded in 1980 by American media proprietor Ted Turner and Reese Schonfeld as a 24-hour cable news channel, and presently owned by ...
. Oregon is home to many breweries, and Portland has the largest number of breweries of any city in the world.
The state's coastal region produces significant tourism as well. The Oregon Coast Aquarium
__NOTOC__
The Oregon Coast Aquarium is an aquarium in Newport in the U.S. state of Oregon. Opened in 1992, the facility sits on along Yaquina Bay near the Pacific Ocean. The aquarium was home to Keiko, the orca who starred in the movie ''Free ...
comprises along Yaquina Bay
Yaquina Bay ( ) is a coastal estuarine community found in Newport, Oregon, United States. Yaquina Bay is a semi-enclosed body of water, approximately 8 km² (3.2 mi²) in area, with free connection to the Pacific Ocean, but also diluted ...
in Newport, and was also home to Keiko the orca whale. It has been noted as one of the top ten aquariums in North America. Fort Clatsop
Fort Clatsop was the encampment of the Lewis and Clark Expedition in the Oregon Country near the mouth of the Columbia River during the winter of 1805–1806. Located along the Lewis and Clark River at the north end of the Clatsop Plains approxim ...
in Warrenton features a replica of Lewis and Clark
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* "Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohead ...
's encampment at the mouth of the Columbia River in 1805. The Sea Lion Caves
Sea Lion Caves is a connected system of sea caves and caverns open to the Pacific Ocean in the U.S. state of Oregon. They are located north of Florence on U.S. Highway 101, about midpoint on the Oregon Coast. In this area Highway 101 follows ...
in Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico an ...
are the largest system of sea caverns in the United States, and also attract many visitors.
In Southern Oregon, the Oregon Shakespeare Festival
The Oregon Shakespeare Festival (OSF) is a regional repertory theatre in Ashland, Oregon, United States, founded in 1935 by Angus L. Bowmer. The Festival now offers matinee and evening performances of a wide range of classic and contemporary pla ...
, held in Ashland, is also a tourist draw, as is the Oregon Vortex
The Oregon Vortex is a roadside attraction that opened to tourists in 1930, located on Sardine Creek in Gold Hill, Oregon, in the United States. It consists of a number of interesting effects, which are gravity hill optical illusions, but whic ...
and the Wolf Creek Inn State Heritage Site
Wolf Creek Inn State Heritage Site is a state park in the U.S. state of Oregon, administered by the Oregon Parks and Recreation Department.
History
The Wolf Creek Inn was built along the Applegate Trail in 1883 for Henry Smith, a local entrepre ...
, a historic inn where Jack London
John Griffith Chaney (January 12, 1876 – November 22, 1916), better known as Jack London, was an American novelist, journalist and activist. A pioneer of commercial fiction and American magazines, he was one of the first American authors to ...
wrote his 1913 novel '' Valley of the Moon''.
Oregon has also historically been a popular region for film shoots due to its diverse landscapes, as well as its proximity to Hollywood
Hollywood usually refers to:
* Hollywood, Los Angeles, a neighborhood in California
* Hollywood, a metonym for the cinema of the United States
Hollywood may also refer to:
Places United States
* Hollywood District (disambiguation)
* Hollywood, ...
. Movies filmed in Oregon include: ''Animal House
''National Lampoon's Animal House'' is a 1978 American comedy film directed by John Landis and written by Harold Ramis, Douglas Kenney and Chris Miller. It stars John Belushi, Peter Riegert, Tim Matheson, John Vernon, Verna Bloom, Thomas Hu ...
'', ''Free Willy
''Free Willy'' is a 1993 American family drama film, directed by Simon Wincer, produced by Lauren Shuler Donner and Jennie Lew Tugend, written by Keith A. Walker and Corey Blechman from a story by Walker and distributed by Warner Bros. Pictures ...
'', ''The General (1927 film), The General'', ''The Goonies'', ''Kindergarten Cop'', ''One Flew Over the Cuckoo's Nest (film), One Flew Over the Cuckoo's Nest'', and ''Stand by Me (film), Stand By Me''. Oregon native Matt Groening, creator of ''The Simpsons'', has incorporated many references from his hometown of Portland into the TV series. Additionally, several television shows have been filmed throughout the state including ''Portlandia'', ''Grimm (TV series), Grimm'', ''Bates Motel (TV series), Bates Motel'', and ''Leverage (American TV series), Leverage''. The Oregon Film Museum is located in the old Clatsop County Jail in Astoria. Additionally, the Blockbuster (Bend, Oregon), last remaining Blockbuster store is located in Bend.
Technology
High technology industries located inSilicon Forest
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
have been a major employer since the 1970s. Tektronix
Tektronix, Inc., historically widely known as Tek, is an American company best known for manufacturing test and measurement devices such as oscilloscopes, logic analyzers, and video and mobile test protocol equipment.
Originally an independent ...
was the largest private employer in Oregon until the late 1980s. Intel Corporation, Intel's creation and expansion of several facilities in eastern Washington County, Oregon, Washington County continued the growth that Tektronix had started. Intel, the state's largest for-profit private employer, operates four large facilities, with Ronler Acres, Jones Farm and Hawthorn Farm all located in Hillsboro, Oregon, Hillsboro.
The spinoffs and startups that were produced by these two companies led to establishment of the so-called Silicon Forest
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
. The recession and Dot-com bubble, dot-com bust of 2001 hit the region hard; many high technology employers reduced the number of their employees or went out of business. Open Source Development Labs made news in 2004 when they hired Linus Torvalds, developer of the Linux kernel. In 2010, biotechnology giant Genentech opened a $400 million facility in Hillsboro, Oregon, Hillsboro to expand its production capabilities. Oregon is home to several large Data center, datacenters that take advantage of cheap power and a climate conducive to reducing cooling costs. Google operates a large datacenter in The Dalles, and Facebook built a large datacenter near Prineville, Oregon, Prineville in 2010. Amazon (company), Amazon opened a datacenter near Boardman, Oregon, Boardman in 2011, and a fulfillment center in Troutdale, Oregon, Troutdale in 2018.
Corporate headquarters
 Oregon is also the home of large corporations in other industries. The world headquarters of Nike, Inc., Nike is located near Beaverton. Medford is home to Harry and David, which sells gift items under several brands. Medford is also home to the national headquarters of Lithia Motors. Portland is home to one of the West's largest trade book publishing houses, Graphic Arts Center Publishing. Oregon is also home to Mentor Graphics, Mentor Graphics Corporation, a world leader in electronic design automation located in Wilsonville, Oregon, Wilsonville and employs roughly 4,500 people worldwide.
Adidas, Adidas Corporations American Headquarters is located in Portland and employs roughly 900 full-time workers at its Portland campus. Nike, located in Beaverton, employs roughly 5,000 full-time employees at its campus. Nike's Beaverton campus is continuously ranked as a top employer in the Portland area-along with competitor Adidas. Intel, Intel Corporation employs 22,000 in Oregon with the majority of these employees located at the company's Hillsboro campus located about 30 minutes west of Portland. Intel has been a top employer in Oregon since 1974.
The U.S. Federal Government and Providence Health systems are respective contenders for top employers in Oregon with roughly 12,000 federal workers and 14,000 Providence Health workers.
In 2015, a total of seven companies headquartered in Oregon landed in the Fortune 1000: Nike, at 106; Precision Castparts Corp. at 302; Lithia Motors at 482; StanCorp Financial Group at 804; Schnitzer Steel Industries at 853; The Greenbrier Companies at 948; and Columbia Sportswear at 982.
Oregon is also the home of large corporations in other industries. The world headquarters of Nike, Inc., Nike is located near Beaverton. Medford is home to Harry and David, which sells gift items under several brands. Medford is also home to the national headquarters of Lithia Motors. Portland is home to one of the West's largest trade book publishing houses, Graphic Arts Center Publishing. Oregon is also home to Mentor Graphics, Mentor Graphics Corporation, a world leader in electronic design automation located in Wilsonville, Oregon, Wilsonville and employs roughly 4,500 people worldwide.
Adidas, Adidas Corporations American Headquarters is located in Portland and employs roughly 900 full-time workers at its Portland campus. Nike, located in Beaverton, employs roughly 5,000 full-time employees at its campus. Nike's Beaverton campus is continuously ranked as a top employer in the Portland area-along with competitor Adidas. Intel, Intel Corporation employs 22,000 in Oregon with the majority of these employees located at the company's Hillsboro campus located about 30 minutes west of Portland. Intel has been a top employer in Oregon since 1974.
The U.S. Federal Government and Providence Health systems are respective contenders for top employers in Oregon with roughly 12,000 federal workers and 14,000 Providence Health workers.
In 2015, a total of seven companies headquartered in Oregon landed in the Fortune 1000: Nike, at 106; Precision Castparts Corp. at 302; Lithia Motors at 482; StanCorp Financial Group at 804; Schnitzer Steel Industries at 853; The Greenbrier Companies at 948; and Columbia Sportswear at 982.
Taxes and budgets
Oregon's wikt:Biennial, biennial state budget, $2.6 billion in 2017, comprises Fund accounting, General Funds, Federal funds, Federal Funds, Lottery Funds, and Other Funds. Oregon is one of Sales taxes in the United States, only five states that have no sales tax. Oregon voters have been resolute in their opposition to a sales tax, voting proposals down each of the nine times they have been presented. The last vote, for 1993's Measure 1, was defeated by a 75–25% margin. The state also has a minimum corporate tax of only $150 a year, amounting to 5.6% of the General Fund in the 2005–07 biennium; data about which businesses pay the minimum is not available to the public. As a result, the state relies on property tax, property and income taxes for its revenue. Oregon has the fifth highest personal income tax in the nation. According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Oregon ranked 41st out of the 50 states in taxes per capita in 2005 with an average amount paid of 1,791.45. A few local governments levy sales taxes on services: the city of Ashland, for example, collects a 5% sales tax on prepared food. The City of Portland imposes an Arts Education and Access Income Tax on residents over 18—a flat tax of $35 collected from individuals earning $1,000 or more per year and residing in a household with an annual income exceeding the federal poverty level. The tax funds Portland school teachers, and art focused non-profit organizations in Portland. The State of Oregon also allows transit district to levy an income tax on employers and the self-employed. The State currently collects the tax for TriMet and the Lane Transit District. Oregon is one of six states with a revenue limit. The "Kicker (Oregon tax rebate), kicker law" stipulates that when income tax collections exceed state economists' estimates by two percent or more, any excess must be returned to taxpayers. Since the enactment of the law in 1979, refunds have been issued for seven of the eleven biennia. In 2000, Ballot Measure 86 converted the "kicker" law from statute to the Oregon Constitution, and changed some of its provisions. Federal payments to county governments that were granted to replace timber revenue when logging in National Forests was restricted in the 1990s, have been under threat of suspension for several years. This issue dominates the future revenue of rural counties, which have come to rely on the payments in providing essential services. 55% of state revenues are spent on public education, 23% on human services (child protective services, Medicaid, and senior services), 17% on public safety, and 5% on other services.Healthcare
For health insurance, as of 2018 Cambia Health Solutions has the highest market share at 21%, followed by Providence Health & Services, Providence Health. In the Portland region, Kaiser Permanente leads. Providence and Kaiser are vertically integrated delivery systems which operate hospitals and offer insurance plans. Aside from Providence and Kaiser, hospital systems which are primarily Oregon-based include Legacy Health mostly covering Portland, Samaritan Health Services with five hospitals in various areas across the state, and Tuality Healthcare in the western Portland metropolitan area. In Southern Oregon, Asante runs several hospitals, including Rogue Regional Medical Center. Some hospitals are operated by multi-state organizations such as PeaceHealth and CommonSpirit Health. Some hospitals such Salem Hospital (Oregon), Salem Hospital operate independently of larger systems. Oregon Health & Science University is a Portland-based medical school that operates two hospitals and clinics. The Oregon Health Plan is the state's Medicaid managed care plan, and it is known for innovations. The Portland area is a mature managed care and two-thirds of Medicare enrollees are in Medicare Advantage plans.Education
Elementary, middle, and high school
In the 2013–2014 school year, the state had 567,000 students in public schools. There were 197 public school districts, served by 19 Education service district (Oregon), education service districts. In 2016, the largest school districts in the state were: Portland Public Schools (Oregon), Portland Public Schools, comprising 47,323 students; Salem-Keizer School District, comprising 40,565 students; Beaverton School District, comprising 39,625 students; Hillsboro School District, comprising 21,118 students; and North Clackamas School District, comprising 17,053 students. Approximately 90.5% of Oregon high school students graduate, improving on the national average of 88.3% as measured from the 2010 U.S. Census, 2010 U.S. census.Colleges and universities
 Especially since the 1990 passage of Measure 5, which set limits on property tax levels, Oregon has struggled to fund higher education. Since then, Oregon has cut its higher education budget and now ranks 46th in the country in state spending per student. However, 2007 legislation funded the university system far beyond the governor's requested budget though still capping tuition increases at 3% per year. Oregon supports a total of seven public universities and one affiliate. It is home to three public research universities: The
Especially since the 1990 passage of Measure 5, which set limits on property tax levels, Oregon has struggled to fund higher education. Since then, Oregon has cut its higher education budget and now ranks 46th in the country in state spending per student. However, 2007 legislation funded the university system far beyond the governor's requested budget though still capping tuition increases at 3% per year. Oregon supports a total of seven public universities and one affiliate. It is home to three public research universities: The University of Oregon
The University of Oregon (UO, U of O or Oregon) is a public research university in Eugene, Oregon. Founded in 1876, the institution is well known for its strong ties to the sports apparel and marketing firm Nike, Inc, and its co-founder, billion ...
(UO) in Eugene and Oregon State University
Oregon State University (OSU) is a public land-grant, research university in Corvallis, Oregon. OSU offers more than 200 undergraduate-degree programs along with a variety of graduate and doctoral degrees. It has the 10th largest engineering co ...
(OSU) in Corvallis, both Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified as research universities with very high research activity, and Portland State University which is classified as a research university with high research activity.
 Oregon is home to a wide variety of private colleges, the majority of which are located in the Portland area. The University of Portland and Marylhurst University are both Catholic universities located in or near Portland, affiliated with the Congregation of Holy Cross, and the Sisters of the Holy Names of Jesus and Mary, respectively. Reed College, a rigorous liberal arts college in Portland, was ranked by ''Forbes'' as the 52nd best college in the country in 2015.
Other private institutions in Portland include Lewis & Clark College; Multnomah University; Portland Bible College; Warner Pacific College; Cascade College; the National University of Natural Medicine; and Western Seminary, a theological graduate school. Pacific University is in the Portland suburb of Forest Grove. There are also private colleges further south in the Willamette Valley. McMinnville is home to Linfield College, while nearby Newberg is home to George Fox University. Salem is home to two private schools: Willamette University (the state's oldest, established during the provisional period) and Corban University. Also located near Salem is Mount Angel Abbey, Mount Angel Seminary, one of America's largest Roman Catholic seminaries. The state's second medical school, the College of Osteopathic Medicine of the Pacific, Northwest, is located in Lebanon. Eugene is home to three private colleges: Bushnell University, New Hope Christian College, and Gutenberg College.
Oregon is home to a wide variety of private colleges, the majority of which are located in the Portland area. The University of Portland and Marylhurst University are both Catholic universities located in or near Portland, affiliated with the Congregation of Holy Cross, and the Sisters of the Holy Names of Jesus and Mary, respectively. Reed College, a rigorous liberal arts college in Portland, was ranked by ''Forbes'' as the 52nd best college in the country in 2015.
Other private institutions in Portland include Lewis & Clark College; Multnomah University; Portland Bible College; Warner Pacific College; Cascade College; the National University of Natural Medicine; and Western Seminary, a theological graduate school. Pacific University is in the Portland suburb of Forest Grove. There are also private colleges further south in the Willamette Valley. McMinnville is home to Linfield College, while nearby Newberg is home to George Fox University. Salem is home to two private schools: Willamette University (the state's oldest, established during the provisional period) and Corban University. Also located near Salem is Mount Angel Abbey, Mount Angel Seminary, one of America's largest Roman Catholic seminaries. The state's second medical school, the College of Osteopathic Medicine of the Pacific, Northwest, is located in Lebanon. Eugene is home to three private colleges: Bushnell University, New Hope Christian College, and Gutenberg College.
Law and government
 A writer in the
A writer in the Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
book ''A Pacific Republic'', written in 1839, predicted the territory was to become an independent republic. Four years later, in 1843, settlers of the Willamette Valley voted in majority for a republic government. The Oregon Country functioned in this way until August 13, 1848, when Oregon was annexed by the United States and a territorial government was established. Oregon maintained a territorial government until February 14, 1859, when it was granted U.S. state, statehood.
Oregon state government has a separation of powers similar to the federal government of the United States, federal government. It has three branches:
* a legislature, legislative branch (the bicameral Oregon Legislative Assembly),
* an Executive (government), executive branch which includes an "administrative department" and Governor of Oregon, Oregon's governor serving as chief executive, and
* a Judiciary, judicial branch, headed by the Chief justice, Chief Justice of the Oregon Supreme Court.
Governors in Oregon serve four-year terms and are limited to two consecutive terms, but an unlimited number of total terms. Oregon has no Lieutenant governor (United States), lieutenant governor; in case the office of governor is vacated, ArticleV, Section 8a of the Oregon Constitution specifies that the Oregon Secretary of State, Secretary of State is first in line for succession. The other statewide officers are Oregon State Treasurer, Treasurer, Oregon Attorney General, Attorney General, Oregon Superintendent of Public Instruction, Superintendent, and Oregon Bureau of Labor and Industries, Labor Commissioner. The wikt:Biennial, biennial Oregon Legislative Assembly consists of a thirty-member Oregon State Senate, Senate and a sixty-member Oregon House of Representatives, House. The state supreme court has seven elected justices, currently including the only two openly gay state supreme court justices in the nation. They choose one of their own to serve a six-year term as Chief Justice.
The debate over whether to move to annual sessions is a long-standing battle in Oregon politics, but the voters have resisted the move from citizen legislators to professional lawmakers. Because Oregon's state budget is written in two-year increments and, there being no sales tax, state revenue is based largely on income taxes, it is often significantly over or under budget. Recent legislatures have had to be called into special sessions repeatedly to address revenue shortfalls resulting from economic downturns, bringing to a head the need for more frequent legislative sessions. Oregon Initiative 71, passed in 2010, mandates the legislature to begin meeting every year, for 160 days in odd-numbered years, and 35 days in even-numbered years.
Oregonians have voted for the Democratic Party (United States), Democratic presidential candidate in every election since 1988. In 2004 and 2006, Democrats won control of the State Senate, and then the House. Since the late 1990s, Oregon has been represented by four Democrats and one Republican Party (United States), Republican in the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives. Since 2009, the state has had two Democratic U.S. senators, Ron Wyden and Jeff Merkley. Oregon voters have elected Democratic governors in every election since 1986, most recently electing Kate Brown over Republican Bud Pierce in a 2016 special election for a two-year term, and re-electing her for a full four-year term over Republican Knute Buehler in 2018.
The base of Democratic support is largely concentrated in the urban centers of the Willamette Valley. The eastern two-thirds of the state beyond the Cascade Mountains typically votes Republican; in 2000 and 2004 United States presidential election, 2004, George W. Bush carried every county east of the Cascades. However, the region's sparse population means the more populous counties in the Willamette Valley usually outweigh the eastern counties in statewide elections.
In the 2002 general election, Oregon voters approved a Oregon Ballot Measure 25 (2002), ballot measure to increase the state minimum wage automatically each year according to inflationary changes, which are measured by the consumer price index (CPI). In the 2004 general election, Oregon voters passed ballot measures Oregon Ballot Measure 36 (2004), banning same-sex marriage and Oregon Ballot Measure 37 (2004), restricting land use regulation. In the Oregon's statewide elections, 2006, 2006 general election, voters restricted the use of Oregon Ballot Measure 39 (2006), eminent domain and extended the state's discount prescription drug coverage.
In the 2020 general election, Oregon voters approved a ballot measure to decriminalize the possession of small quantities of street drugs such as cocaine and heroin, becoming the first state in the country to do so after the drugs were originally made illegal. The state also approved a ballot measure to create a legal means of administering psilocybin for medicinal use.
Federal representation
Like all U.S. states, Oregon is represented by two United States Senate, senators. Following the 1980 United States census, 1980 census, Oregon had five Oregon's congressional districts, congressional districts. After Oregon was admitted to the Union, it began with a single member in the House of Representatives (La Fayette Grover, who served in the 35th United States Congress for less than a month). United States congressional apportionment, Congressional apportionment increased the size of the delegation following the censuses of 1890 United States Census, 1890, 1910 United States Census, 1910, 1940 United States Census, 1940, and 1980. Following the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, Oregon gained a sixth congressional seat. It will be filled in the 2022 United States House of Representatives elections, 2022 Congressional Elections. A United States congressional delegations from Oregon, detailed list of the past and present Congressional delegations from Oregon is available. The United States District Court for the District of Oregon hears federal cases in the state. The court has courthouses in Mark O. Hatfield United States Courthouse, Portland, Wayne L. Morse United States Courthouse, Eugene, Medford, and Pendleton. Also in Portland is the federal bankruptcy court, with a second branch in Eugene. Oregon (among other western states and territories) is in the United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit, 9th Court of Appeals. One of the court's meeting places is at the Pioneer Courthouse in downtown Portland, a National Historic Landmark built-in 1869.Politics

Cascade Range
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, ...
, with western Oregon being more Modern liberalism in the United States, liberal and Eastern Oregon
Eastern Oregon is the eastern part of the U.S. state of Oregon. It is not an officially recognized geographic entity; thus, the boundaries of the region vary according to context. It is sometimes understood to include only the eight easternmost ...
being Conservatism in the United States, conservative. In a 2008 analysis of the 2004 presidential election, a political analyst found that according to the application of a Likert scale, Oregon boasted both the most liberal Kerry voters and the most conservative Bush voters, making it the most politically polarized state in the country.
While Republicans typically win more counties by running up huge margins in the east, the Democratic tilt of the more populated west is usually enough to swing the entire state Democratic. In 2008, for instance, Republican Senate incumbent Gordon H. Smith lost his bid for a third term, even though he 2008 United States Senate election in Oregon, carried all but eight counties. His Democratic challenger, Jeff Merkley, won Multnomah County by 142,000 votes, more than double the overall margin of victory.
During Oregon's history, it has adopted many electoral reforms proposed during the Progressive Era, through the efforts of William Simon U'Ren, William S. U'Ren and his Direct Legislation League. Under his leadership, the state overwhelmingly approved a ballot measure in 1902 that created the initiative and referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
for citizens to introduce or approve proposed laws or amendments to the state constitution directly, making Oregon the first state to adopt such a system. Today, roughly half of U.S. states do so.
In following years, the primary election to select Political party, party candidates was adopted in 1904, and in 1908 the Oregon Constitution was amended to include recall of public officials. More recent amendments include the nation's first doctor-assisted suicide law, called the 1994 Oregon Ballot Measure 16, Death with Dignity Act (which was challenged, unsuccessfully, in 2005 by the Presidency of George W. Bush, Bush administration in a case heard by the Supreme Court of the United States, U.S. Supreme Court), 1998 Oregon Ballot Measure 67, legalization of medical cannabis, and among the nation's strongest Smart growth, anti-urban sprawl and pro-environment laws. More recently, Oregon Ballot Measure 37 (2004), 2004's Measure 37 reflects a backlash against such land-use laws. However, a further ballot measure in 2007, Oregon Ballot Measure 37 (2004)#Measure 49, Measure 49, curtailed many of the provisions of 37.
Of the List of Oregon ballot measures, measures placed on the ballot since 1902, the people have passed 99 of the 288 initiatives and 25 of the 61 referendums on the ballot, though not all of them survived challenges in courts (see ''Pierce v. Society of Sisters'', for an example). During the same period, the legislature has referred 363 measures to the people, of which 206 have passed.
Oregon pioneered the American use of postal voting, beginning with experimentation approved by the Oregon Legislative Assembly in 1981 and culminating with a Oregon Ballot Measure 60 (1998), 1998 ballot measure mandating that all counties conduct elections by mail. It remains one of just two states, the other being Washington, where Absentee ballot, voting by mail is the only method of voting.
In 1994, Oregon adopted the Oregon Health Plan, which made health care available to most of its citizens without private health insurance.
In the Electoral College (United States), U.S. Electoral College, Oregon casts seven votes. Oregon has supported Democratic candidates in the last nine elections. Democratic incumbent Barack Obama won the state by a margin of twelve percentage points, with over 54% of the popular vote in 2012. In the 2016 election, Hillary Clinton won Oregon by 11 percentage points. In the 2020 United States presidential election, 2020 election, Joe Biden won Oregon by 16 percentage points over his opponent, Donald Trump.
In a 2020 study, Oregon was ranked as the easiest state for citizens to vote in.
Secession to Idaho
In 2022, a movement called "Greater Idaho" or "Move" (i.e., "move" the state border) had propositions running through eastern Oregon counties to petition the Oregon Legislative Assembly, state legislature to permit a portion of the more-conservative eastern state to secede from Oregon to joinIdaho
Idaho ( ) is a state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. To the north, it shares a small portion of the Canada–United States border with the province of British Columbia. It borders the states of Montana and Wyom ...
.
Sports
 Oregon is home to three major professional sports teams: the Portland Trail Blazers of the National Basketball Association, NBA, the Portland Thorns FC of the National Women's Soccer League, NWSL and the Portland Timbers of Major League Soccer, MLS."MLS awards team to Portland for 2011"
Oregon is home to three major professional sports teams: the Portland Trail Blazers of the National Basketball Association, NBA, the Portland Thorns FC of the National Women's Soccer League, NWSL and the Portland Timbers of Major League Soccer, MLS."MLS awards team to Portland for 2011"Portland Timbers, March 20, 2009. Until 2011, the only major professional sports team in Oregon was the Portland Trail Blazers of the National Basketball Association. From the 1970s to the 1990s, the Blazers were one of the most successful teams in the NBA in terms of both win–loss record and attendance. In the early 21st century, the team's popularity declined due to personnel and financial issues, but revived after the departure of controversial players and the acquisition of new players such as Brandon Roy and LaMarcus Aldridge, and still later Damian Lillard. The Blazers play in the Moda Center in Portland's Lloyd District, which also is home to the Portland Winterhawks of the junior ice hockey, junior Western Hockey League. The Portland Timbers play at Providence Park, just west of downtown Portland. The Timbers have a strong following, with the team regularly selling out its games. The Timbers repurposed the formerly multi-use stadium into a soccer-specific stadium in fall 2010, increasing the seating in the process. The Timbers operate Portland Thorns FC, a women's soccer team that has played in the National Women's Soccer League since the league's first season in 2013. The Thorns, who also play at Providence Park, have won two league championships, in the inaugural 2013 National Women's Soccer League season, 2013 season and also in 2017 National Women's Soccer League season, 2017, and have been by far the NWSL's attendance leader in each of the league's seasons.
 Eugene and Hillsboro have minor-league baseball teams: the Eugene Emeralds and the Hillsboro Hops both play in the High-A High-A West. Portland has had minor-league baseball teams in the past, including the Portland Beavers and Portland Rockies, who played most recently at Providence Park when it was known as PGE Park. Salem also previously had a Class A Short Season Northwest League team, the Salem-Keizer Volcanoes that was not included in the Minor League Baseball#Reorganization of 2021, 2021 Minor League Baseball reorganization. The Volcanoes ownership later formed the amateur Mavericks Independent Baseball League, which is fully based in Salem.
The Oregon State Beavers and the University of Oregon Ducks football teams of the Pac-12 Conference meet annually in the Oregon–Oregon State football rivalry. Both schools have had recent success in other sports as well: Oregon State won back-to-back College World Series, college baseball championships in 2006 and 2007, winning a third in 2018; and the University of Oregon won back-to-back NCAA Men's Cross Country Championship, NCAA men's cross country championships in 2007 and 2008.
Eugene and Hillsboro have minor-league baseball teams: the Eugene Emeralds and the Hillsboro Hops both play in the High-A High-A West. Portland has had minor-league baseball teams in the past, including the Portland Beavers and Portland Rockies, who played most recently at Providence Park when it was known as PGE Park. Salem also previously had a Class A Short Season Northwest League team, the Salem-Keizer Volcanoes that was not included in the Minor League Baseball#Reorganization of 2021, 2021 Minor League Baseball reorganization. The Volcanoes ownership later formed the amateur Mavericks Independent Baseball League, which is fully based in Salem.
The Oregon State Beavers and the University of Oregon Ducks football teams of the Pac-12 Conference meet annually in the Oregon–Oregon State football rivalry. Both schools have had recent success in other sports as well: Oregon State won back-to-back College World Series, college baseball championships in 2006 and 2007, winning a third in 2018; and the University of Oregon won back-to-back NCAA Men's Cross Country Championship, NCAA men's cross country championships in 2007 and 2008.
Sister regions
* Fujian Province, * Taiwan Province (Republic of China), Taiwan Province, Taiwan, Republic of China (Taiwan) * Toyama Prefecture, * Jeollanam-do Province, Republic of Korea (South Korea) * Iraqi Kurdistan,See also
* Outline of Oregon (organized list of topics about Oregon) * Index of Oregon-related articles * Bibliography of Oregon history * Tax Fairness Oregon * ''''Notes
References
* * * * * Clucas, Richard A., Mark Henkels, and Brent Steel, eds. ''Oregon politics and government: progressives versus conservative populists'' (U of Nebraska Press, 2005)online
* * * * * * * * *
External links
* *Oregon Encyclopedia
'
Oregon State Databases
at the American Library Association
Government
State of Oregon
Oregon State Legislature
Oregon Constitution
Tourism and recreation
TravelOregon.com
an official website of the Oregon Tourism Commission
Oregon State Parks
Oregon State Facts
from the United States Department of Agriculture
History and culture
Oregon Historical Society
Oregon Blue Book
the online version of the Oregon Blue Book, state's official directory and fact book
Maps and geology
Real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of Oregon
from the United States Geological Survey * {{coord, 44, -121, dim:300000_region:US-OR_type:adm1st, name=State of Oregon, display=title Oregon, 1859 establishments in the United States Geography of the Pacific Northwest States and territories established in 1859 States of the United States States of the West Coast of the United States U.S. states with multiple time zones Contiguous United States