|
Yaquina Bay
Yaquina Bay ( ) is a coastal estuarine community found in Newport, Oregon, United States. Yaquina Bay is a semi-enclosed body of water, approximately 8 km² (3.2 mi²) in area, with free connection to the Pacific Ocean, but also diluted with freshwater from the Yaquina River land drainage. The Bay is traversed by the Yaquina Bay Bridge. There are three small communities that border the Yaquina River and Bay; Newport (population approx. 9,989), Toledo (population approx. 3,459) and Elk City (population approx. 25). The Yaquina Bay in Newport is a popular tourist destination along the Pacific Coast Highway. It is also an important estuary for the ecology and economy of the area. History of Yaquina Bay Yaquina Bay is named after the Yaquina Tribe that occupied the territory along the Yaquina River. With the railroad addition In the late 1880s, many thought Yaquina Bay would be the commerce center for the Pacific Northwest. Wheat, lumber, and other goods were transported ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USACE Yaquina Bay Oregon
, colors = , anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day) , battles = , battles_label = Wars , website = , commander1 = Lieutenant general (United States), LTG Scott A. Spellmon , commander1_label = List of United States Army Corps of Engineers Chiefs of Engineers, Chief of Engineers and Commanding General of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers , commander2 = Major general (United States), MG]Richard J. Heitkamp, commander2_label = Deputy Chief of Engineers and Deputy Commanding General , commander3 = Major general (United States), MGKimberly M. Colloton, commander3_label = Deputy Commanding General for Military and International Operations , commander4 = Major general (United States), MG]William H. Graham, commander4_label = Deputy Command ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
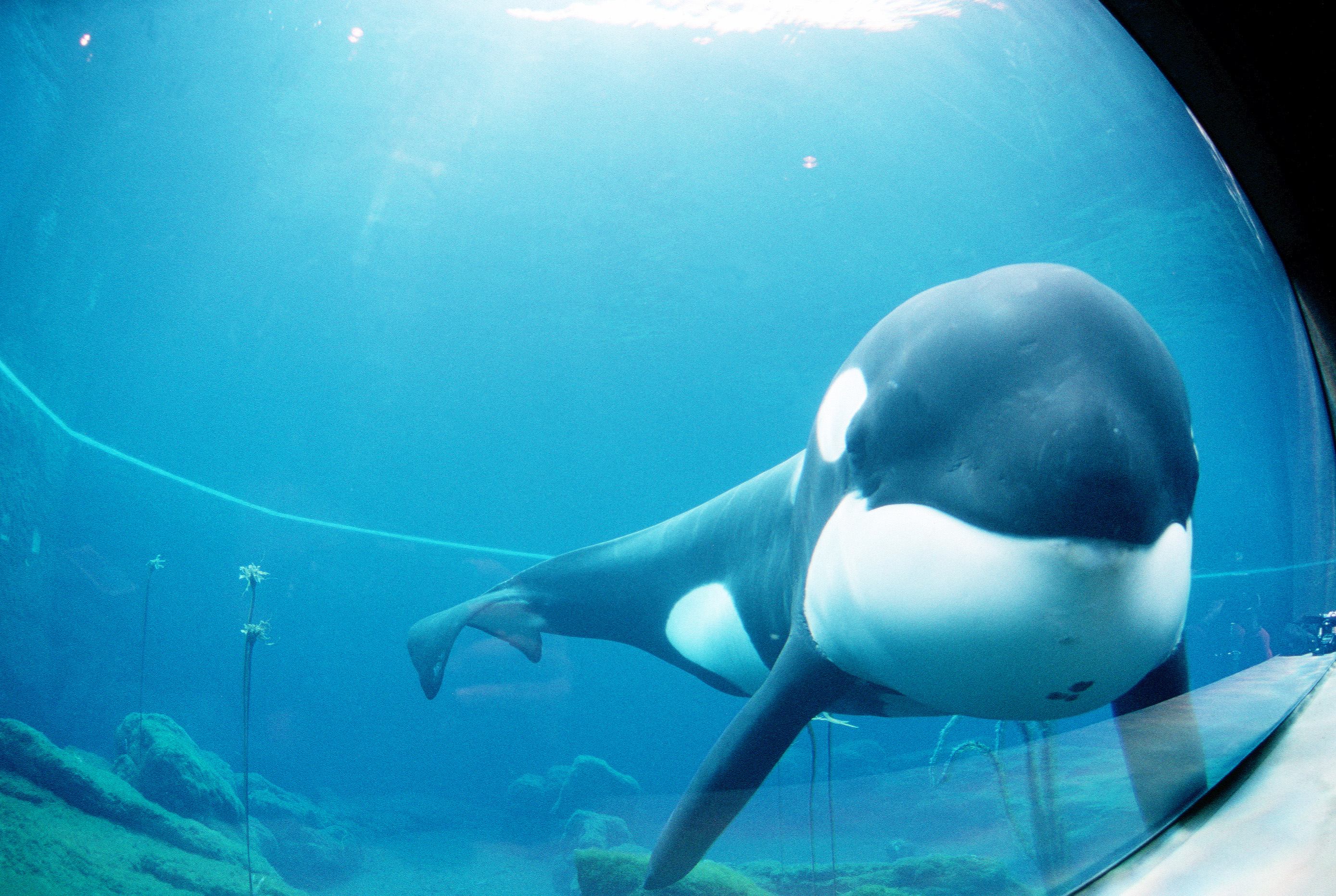
Oregon Coast Aquarium
__NOTOC__ The Oregon Coast Aquarium is an aquarium in Newport in the U.S. state of Oregon. Opened in 1992, the facility sits on along Yaquina Bay near the Pacific Ocean. The aquarium was home to Keiko, the orca who starred in the movie ''Free Willy'', from January 7, 1996 until September 9, 1998, when he was shipped to Vestmannaeyjar, Iceland. ''USA Today'' considers the Oregon Coast Aquarium world-class and ''Coastal Living'' magazine ranks it among the top ten aquariums in North America. History Newport business leaders proposed building an aquarium beginning in the early 1980s. They proposed a $7 million facility in 1982 as a way to boost the local economy. Two years later they incorporated as a non-profit, and increased fundraising efforts in 1987, collecting $11 million by 1991. Plans to turn along Yaquina Bay in Newport into a "world class" aquarium were finalized in 1990. The Aquarium was designed by SRG Architects, Portland: BIOS:Inc, of Seattle, and Walker/Macy Land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrea Lurida
''Ostrea lurida'', common name the Olympia oyster, after Olympia, Washington in the Puget Sound area, is a species of edible oyster, a marine bivalve mollusk in the family Ostreidae. This species occurs on the northern Pacific coast of North America. Over the years the role of this edible species of oyster has been partly displaced by the cultivation of non-native edible oyster species. ''Ostrea lurida'' is now known to be separate from a similar-appearing species, '' Ostrea conchaphila'', which occurs further south, south of Baja California, in Mexico. Molecular evidence has recently confirmed the separate status of the two species. However, previously, for a period of time, ''Ostrea lurida'' was considered to be merely a junior synonym of '' Ostrea conchaphila''. ''O. lurida'' has been found in archaeological excavations along the Central California coast of the Pacific Ocean, demonstrating that it was a marine species exploited by the Native American Chumash people. Large s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
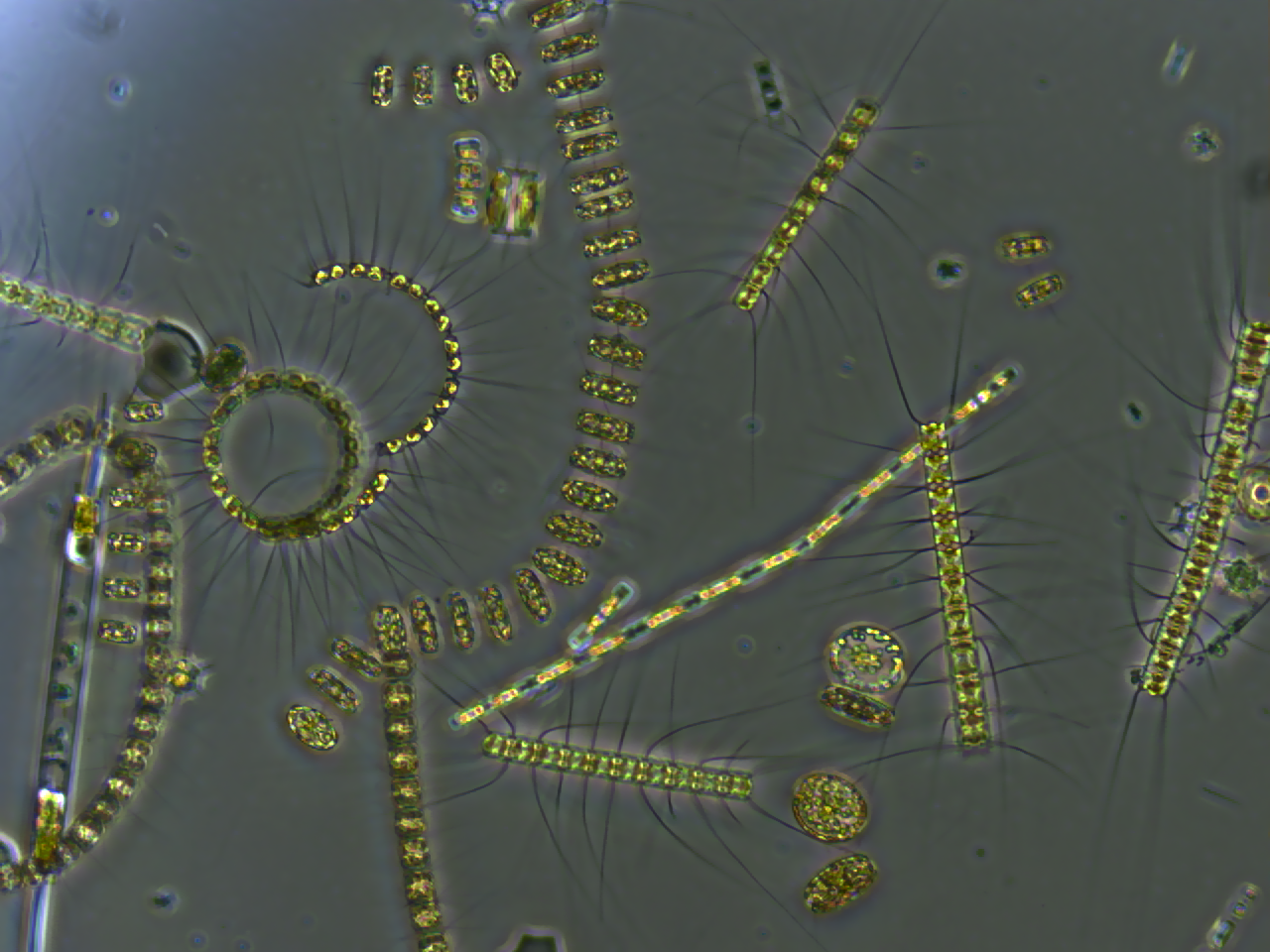
Diatom
A diatom (Neo-Latin ''diatoma''), "a cutting through, a severance", from el, διάτομος, diátomos, "cut in half, divided equally" from el, διατέμνω, diatémno, "to cut in twain". is any member of a large group comprising several genera of algae, specifically microalgae, found in the oceans, waterways and soils of the world. Living diatoms make up a significant portion of the Earth's biomass: they generate about 20 to 50 percent of the oxygen produced on the planet each year, take in over 6.7 billion metric tons of silicon each year from the waters in which they live, and constitute nearly half of the organic material found in the oceans. The shells of dead diatoms can reach as much as a half-mile (800 m) deep on the ocean floor, and the entire Amazon basin is fertilized annually by 27 million tons of diatom shell dust transported by transatlantic winds from the African Sahara, much of it from the Bodélé Depression, which was once made up of a system of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nutrient Cycle
A nutrient cycle (or ecological recycling) is the movement and exchange of inorganic and organic matter back into the production of matter. Energy flow is a unidirectional and noncyclic pathway, whereas the movement of mineral nutrients is cyclic. Mineral cycles include the carbon cycle, sulfur cycle, nitrogen cycle, water cycle, phosphorus cycle, oxygen cycle, among others that continually recycle along with other mineral nutrients into productive ecological nutrition. Outline The nutrient cycle is nature's recycling system. All forms of recycling have feedback loops that use energy in the process of putting material resources back into use. Recycling in ecology is regulated to a large extent during the process of decomposition. Ecosystems employ biodiversity in the food webs that recycle natural materials, such as mineral nutrients, which includes water. Recycling in natural systems is one of the many ecosystem services that sustain and contribute to the well-being of human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thalassinidea
Thalassinidea is a former infraorder of decapod crustaceans that live in burrows in muddy bottoms of the world's oceans. In Australian English, the littoral thalassinidean ''Trypaea australiensis'' is referred to as the ''yabby'' (a term which also refers to freshwater crayfish of the genus ''Cherax''), frequently used as bait for estuarine fishing; elsewhere, however, they are poorly known, and as such have few vernacular names, "mud lobster" and "ghost shrimp" counting among them. The burrows made by thalassinideans are frequently preserved, and the fossil record of thalassinideans reaches back to the late Jurassic. The group was abandoned when it became clear that it represented two separate lineages, now both recognised as infraorders: Gebiidea and Axiidea. Recent molecular analyses have shown that thalassinideans are most closely related to Brachyura (crabs) and Anomura (hermit crabs and their allies). There are believed to be 556 extant species of thalassinideans in 96 gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zostera Japonica
''Zostera japonica'' is a species of aquatic plant in the Zosteraceae family. It is referred to by the common names dwarf eelgrass or Japanese eelgrass, and is native to the seacoast of eastern Asia from Russia to Vietnam, and introduced to the western coast of North America. It is found in the intertidal zone and the shallow subtidal, and grows on sandy, muddy and silty substrates. Distribution and habitat It is considered native in the Russian Far East (Sakhalin, Kamchatka, Primorye, and the Kuril Islands), Japan, Korea, China, Korea, the Ryukyu Islands, Taiwan and Vietnam. It was first reported as being naturalized in British Columbia and in the US State of Washington, but is now considered invasive as far south as California. It is believed to have been introduced with a shipment of Japanese oysters some time in the first half of the twentieth century. This seagrass is mainly found in sheltered bays where the seabed is sand, mud or silt. It occurs in the intertidal zon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zostera Marina
''Zostera marina'' is a flowering vascular plant species as one of many kinds of seagrass, with this species known primarily by the English name of eelgrass with seawrack much less used, and refers to the plant after breaking loose from the submerged wetland soil, and drifting free with ocean current and waves to a coast seashore. It is a saline soft-sediment submerged plant native to marine environments on the coastlines of northern latitudes from subtropical to subpolar regions of North America and Eurasia. Distribution This species is the most wide-ranging marine flowering plant in the Northern Hemisphere. It lives in cooler ocean waters in the North Atlantic and North Pacific, and in the warmer southern parts of its range it dies off during warmer seasons. It grows in the Arctic region and endures several months of ice cover per year.Borum J., et al., (Eds.) (2004.European seagrasses: an introduction to monitoring and management.European Union: Monitoring & Managing of Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Lions (Lincoln County, Oregon Scenic Images) (lincD0021)
Sea lions are pinnipeds characterized by external ear flaps, long foreflippers, the ability to walk on all fours, short and thick hair, and a big chest and belly. Together with the fur seals, they make up the family Otariidae, eared seals. The sea lions have six extant and one extinct species (the Japanese sea lion) in five genera. Their range extends from the subarctic to tropical waters of the global ocean in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, with the notable exception of the northern Atlantic Ocean. They have an average lifespan of 20–30 years. A male California sea lion weighs on average about and is about long, while the female sea lion weighs and is long. The largest sea lions are Steller's sea lions, which can weigh and grow to a length of . Sea lions consume large quantities of food at a time and are known to eat about 5–8% of their body weight (about ) at a single feeding. Sea lions can move around in water and at their fastest they can reac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mudflat
Mudflats or mud flats, also known as tidal flats or, in Ireland, slob or slobs, are coastal wetlands that form in intertidal areas where sediments have been deposited by tides or rivers. A global analysis published in 2019 suggested that tidal flat ecosystems are as extensive globally as mangroves, covering at least of the Earth's surface. / They are found in sheltered areas such as bays, bayous, lagoons, and estuaries; they are also seen in freshwater lakes and salty lakes (or inland seas) alike, wherein many rivers and creeks end. Mudflats may be viewed geologically as exposed layers of bay mud, resulting from deposition of estuarine silts, clays and aquatic animal detritus. Most of the sediment within a mudflat is within the intertidal zone, and thus the flat is submerged and exposed approximately twice daily. A recent global remote sensing analysis estimated that approximately 50% of the global extent of tidal flats occurs within eight countries (Indonesia, China, Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zostera
''Zostera'' is a small genus of widely distributed seagrasses, commonly called marine eelgrass, or simply seagrass or eelgrass, and also known as seaweed by some fishermen and recreational boaters including yachtsmen. The genus ''Zostera'' contains 15 species. Ecology ''Zostera marina'' is found on sandy substrates or in estuaries, usually submerged or partially floating. Most ''Zostera'' are perennial. They have long, bright green, ribbon-like leaves, the width of which are about . Short stems grow up from extensive, white branching rhizomes. The flowers are enclosed in the sheaths of the leaf bases; the fruits are bladdery and can float. ''Zostera'' beds are important for sediment deposition, substrate stabilization, as substrate for epiphytic algae and micro-invertebrates, and as nursery grounds for many species of economically important fish and shellfish. ''Zostera'' often forms beds in bay mud in the estuarine setting. It is an important food for brant geese and wigeon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |