The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an
independent agency of the
U.S. federal government
The federal government of the United States (U.S. federal government or U.S. government) is the Federation#Federal governments, national government of the United States, a federal republic located primarily in North America, composed of 50 ...
responsible for the civil
space program,
aeronautics
Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study, design, and manufacturing of air flight–capable machines, and the techniques of operating aircraft and rockets within the atmosphere. The British Royal Aeronautical Society identifies ...
research, and
space research.
NASA was
established in 1958, succeeding the
National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in
space science
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider ...
.
NASA has since led most American
space exploration
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the exploration of space is carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration though is conducted both by robotic spacec ...
, including
Project Mercury,
Project Gemini
Project Gemini () was NASA's second human spaceflight program. Conducted between projects Mercury and Apollo, Gemini started in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual ...
, the 1968–1972
Apollo Moon landing missions, the
Skylab space station, and the
Space Shuttle. NASA supports the
International Space Station and oversees the development of the
Orion spacecraft and the
Space Launch System for the crewed lunar
Artemis program,
Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned
Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the
Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management for
uncrewed NASA launches.
NASA's science is focused on better understanding Earth through the
Earth Observing System; advancing
heliophysics through the efforts of the
Science Mission Directorate
The Science Mission Directorate (SMD) of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) engages the United States’ science community, sponsors scientific research, and develops and deploys satellites and probes in collaboration with NAS ...
's Heliophysics Research Program; exploring bodies throughout the
Solar System with advanced
robotic spacecraft
A robotic spacecraft is an uncrewed spacecraft, usually under telerobotic control. A robotic spacecraft designed to make scientific research measurements is often called a space probe. Many space missions are more suited to telerobotic rather t ...
such as ''
New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research ...
'' and
planetary rovers
Planetary means relating to a planet or planets. It can also refer to:
;Science
* Planetary habitability, the measure of an astronomical body's potential to develop and sustain life
* Planetary nebula, an astronomical object
;People
* Planetary ...
such as ''
Perseverance'';
and researching
astrophysics
Astrophysics is a science that employs the methods and principles of physics and chemistry in the study of astronomical objects and phenomena. As one of the founders of the discipline said, Astrophysics "seeks to ascertain the nature of the h ...
topics, such as the
Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
, through the
James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Spa ...
, and the
Great Observatories
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy regions of the electrom ...
and associated programs.
History
Creating a civil aeronautics and space agency

NASA traces its roots to the
National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). Despite being the birthplace of aviation, by 1914 the United States recognized that it was far behind Europe in aviation capability. Determined to regain American leadership in aviation, Congress created the
Aviation Section
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes fixed-wing and rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as lighter-than-air craft such as hot ai ...
of the U.S. Army Signal Corps in 1914 and established NACA in 1915 to foster aeronautical research and development. Over the next forty years NACA would conduct aeronautical research in support of the
U.S. Air Force, its predecessors in the
U.S. Army, the
U.S. Navy, and the civil aviation sector. After the end of
World War II, NACA became interested in the possibilities of guided missiles and supersonic aircraft, developing and testing the
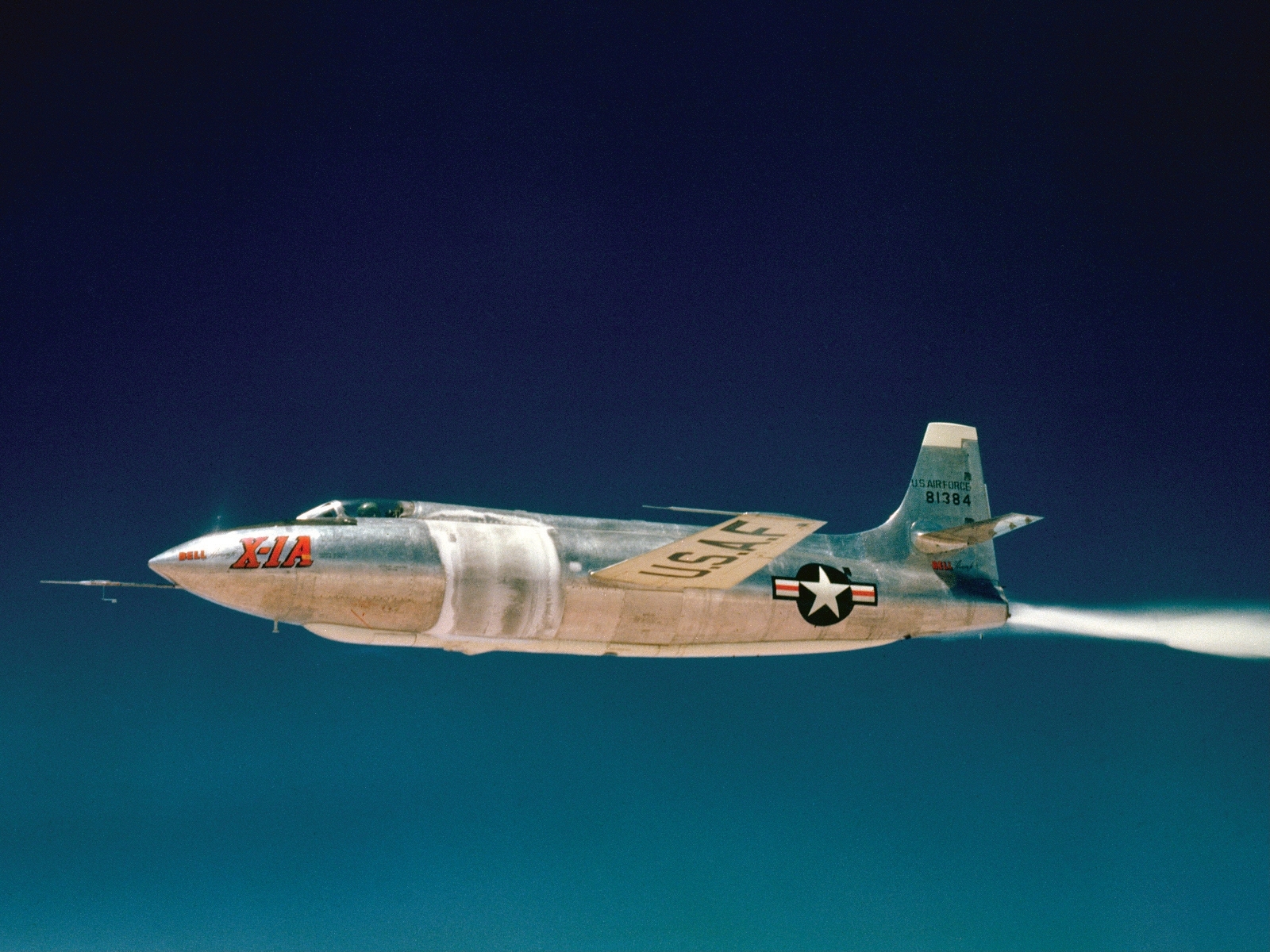
Bell X-1
The Bell X-1 (Bell Model 44) is a rocket engine–powered aircraft, designated originally as the XS-1, and was a joint National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics– U.S. Army Air Forces–U.S. Air Force supersonic research project built by Be ...
in a joint program with the
U.S. Air Force. NACA's interest in space grew out of its rocketry program at the Pilotless Aircraft Research Division.

The Soviet Union's launch of
Sputnik 1
Sputnik 1 (; see § Etymology) was the first artificial Earth satellite. It was launched into an elliptical low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on 4 October 1957 as part of the Soviet space program. It sent a radio signal back to Earth for t ...
ushered in the
Space Age and kicked off the
Space Race. Despite NACA's early rocketry program, the responsibility for launching the first American satellite fell to the
Naval Research Laboratory
The United States Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) is the corporate research laboratory for the United States Navy and the United States Marine Corps. It was founded in 1923 and conducts basic scientific research, applied research, technological ...
's
Project Vanguard. However, Project Vanguard was plauged by several issues and the
Army Ballistic Missile Agency would launch
Explorer 1
Explorer 1 was the first satellite launched by the United States in 1958 and was part of the U.S. participation in the International Geophysical Year (IGY). The mission followed the first two satellites the previous year; the Soviet Union's ...
, America's first satellite, on February 1, 1958.
The
Eisenhower Administration
Dwight D. Eisenhower's tenure as the 34th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1953, and ended on January 20, 1961. Eisenhower, a Republican from Kansas, took office following a landslide victory ov ...
decided to split the United States' military and civil spaceflight programs, which were organized together under
Defense Department's
Advanced Research Projects Agency. NASA was established on July 29, 1958 with the signing of the
National Aeronautics and Space Act and it began operations on October 1, 1958.
As the United States' premier aeronautics agency, NACA formed the core of NASA's new structure, absorbing its 8,000 employees and three major research laboratories. NASA also proceeded to absorb the Naval Research Laboratory's
Project Vanguard, the Army's
Jet Propulsion Laboratory, and the
Army Ballistic Missile Agency under
Wernher von Braun. This left NASA firmly as the United States' civil space lead and the Air Force as the military space lead.
First orbital and hypersonic flights

Plans for human spaceflight began in the U.S. Armed Forces prior to NASA's creation. The Air Force's
Man in Space Soonest and the Army's Project Adam served as the foundation for
Project Mercury, the first American program to put people in space. NASA established the
Space Task Group to manage the program, which would conduct sub-orbital flights with the Army's
Redstone rockets and orbital flights with the Air Force's
Atlas launch vehicles. While NASA intended for its first astronauts to be civilians, President Eisenhower directed that they be selected from the military. The
Mercury 7
The Mercury Seven were the group of seven astronauts selected to fly spacecraft for Project Mercury. They are also referred to as the Original Seven and Astronaut Group 1. Their names were publicly announced by NASA on April 9, 1959; these seve ...
astronauts included three Air Force pilots, three Navy aviators, and one Marine Corps pilot.

On May 5, 1961
Alan Shepard became the first American to enter space, performing a suborbital spaceflight in the
''Freedom 7''. This flight occurred less than a month after the Soviet Union's
Yuri Gagarin became the first human in space, executing a full orbital spaceflight. NASA's first orbital spaceflight was conducted by
John Glenn
John Herschel Glenn Jr. (July 18, 1921 – December 8, 2016) was an American Marine Corps aviator, engineer, astronaut, businessman, and politician. He was the third American in space, and the first American to orbit the Earth, circling ...
on February 20, 1962, in the
''Friendship 7'', conducting three full orbits before reentering. Glenn had to fly parts of his final two orbits manually due to a malfunction in the autopilot. The sixth and final Mercury mission was flown by
Gordon Cooper in May 1963, performing 22 orbits over 34 hours in the
''Faith 7''. The Mercury Program was a resounding success, achieving its objectives to orbit a human in space, develop tracking and control systems, and identify other issues associated with human spaceflight.
While much of NASA's attention turned to space, it did not forget its aeronautics mission. Early aeronautics research attempted to build upon the X-1's
supersonic flight
A supersonic aircraft is an aircraft capable of supersonic flight, that is, flying faster than the speed of sound (Mach number 1). Supersonic aircraft were developed in the second half of the twentieth century. Supersonic aircraft have been us ...
to build an aircraft capable of
hypersonic flight. The
North American X-15
The North American X-15 is a hypersonic rocket-powered aircraft. It was operated by the United States Air Force and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration as part of the X-plane series of experimental aircraft. The X-15 set speed an ...
was a joint NASA-U.S. Air Force program, with the hypersonic test aircraft becoming the first non-dedicated spacecraft to cross from the atmosphere to outer space. The X-15 also served as a testbed for Apollo program technologies and
ramjet and
scramjet propulsion.
Landing on the Moon

Escalations in the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
between the United States and Soviet Union prompted President
John F. Kennedy to charge NASA with landing an American on the Moon and returning him safely to Earth by the end of the 1960s, and installed
James E. Webb as NASA administrator to achieve this goal. On May 25, 1961, President Kennedy openly declared this goal in his Urgent National Needs speech to the
United States Congress, declaring:
Despite attacks on the goal of landing astronauts on the Moon from the former president Dwight Eisenhower and 1964 presidential candidate
Barry Goldwater
Barry Morris Goldwater (January 2, 1909 – May 29, 1998) was an American politician and United States Air Force officer who was a five-term U.S. Senator from Arizona (1953–1965, 1969–1987) and the Republican Party nominee for presiden ...
, President Kennedy was able to protect NASA's growing budget, of which 50% went directly to human spaceflight and it was later estimated that, at its height, 1 out of 20 Americans worked on some aspect of the Apollo Program.

To manage the Apollo Program, NASA required a more rigorous approach than it applied to Project Mercury. Mirroring the Department of Defense's program management concept using redundant systems in building the first intercontinental ballistic missiles, NASA requested the Air Force assign Major General
Samuel C. Phillips
Samuel Cochran Phillips (19 February 1921 – 31 January 1990) was a United States Air Force general who served as Director of NASA's Apollo program from 1964 to 1969, as commander of the Space and Missile Systems Organization (SAMSO) from 196 ...
to the space agency where he would serve as the director of the Appollo Program. Development of the
Saturn V rocket was led by
Wernher von Braun and his team at the
Marshall Space Flight Center
The George C. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), located in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama (Huntsville postal address), is the U.S. government's civilian rocketry and spacecraft propulsion research center. As the largest NASA center, MSFC's first ...
, derived from the Army Ballistic Missile Agency's original
Saturn I. The
Apollo spacecraft was designed and built by
North American Aviation
North American Aviation (NAA) was a major American aerospace manufacturer that designed and built several notable aircraft and spacecraft. Its products included: the T-6 Texan trainer, the P-51 Mustang fighter, the B-25 Mitchell bomber, the F ...
, while the
Apollo Lunar Module
The Apollo Lunar Module (LM ), originally designated the Lunar Excursion Module (LEM), was the lunar lander spacecraft that was flown between lunar orbit and the Moon's surface during the United States' Apollo program. It was the first crewed ...
was designed and built by
Grumman.
To develop the spaceflight skills and equipment required for a lunar mission, NASA initiated
Project Gemini
Project Gemini () was NASA's second human spaceflight program. Conducted between projects Mercury and Apollo, Gemini started in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual ...
. Using a modified Air Force
Titan II launch vehicle, the Gemini capsule could hold two astronauts for flights of over two weeks. Gemini pioneered the use of
fuel cells
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most bat ...
instead of legacy batteries and demonstrated
spacewalks and
rendezvous operations. NASA also needed more detained information about the Moon's geography and composition to prepare for a landing, using three uncrewed spacecraft programs.

The
Ranger Program was started in the 1950s as a response to Soviet lunar exploration but was generally considered to be a failure. The
Lunar Orbiter program had greater success, mapping the surface in preparation for Apollo landings and measured
Selenography, conducted meteoroid detection, and measured radiation levels. The
Surveyor program conducted uncrewed lunar landings and takeoffs, as well as taking surface and regolith observations.
Despite the setback caused by the
Apollo 1 fire, which killed three astronauts, the program proceeded.
Apollo 8
Apollo 8 (December 21–27, 1968) was the first crewed spacecraft to leave low Earth orbit and the first human spaceflight to reach the Moon. The crew orbited the Moon ten times without landing, and then departed safely back to Earth. These ...
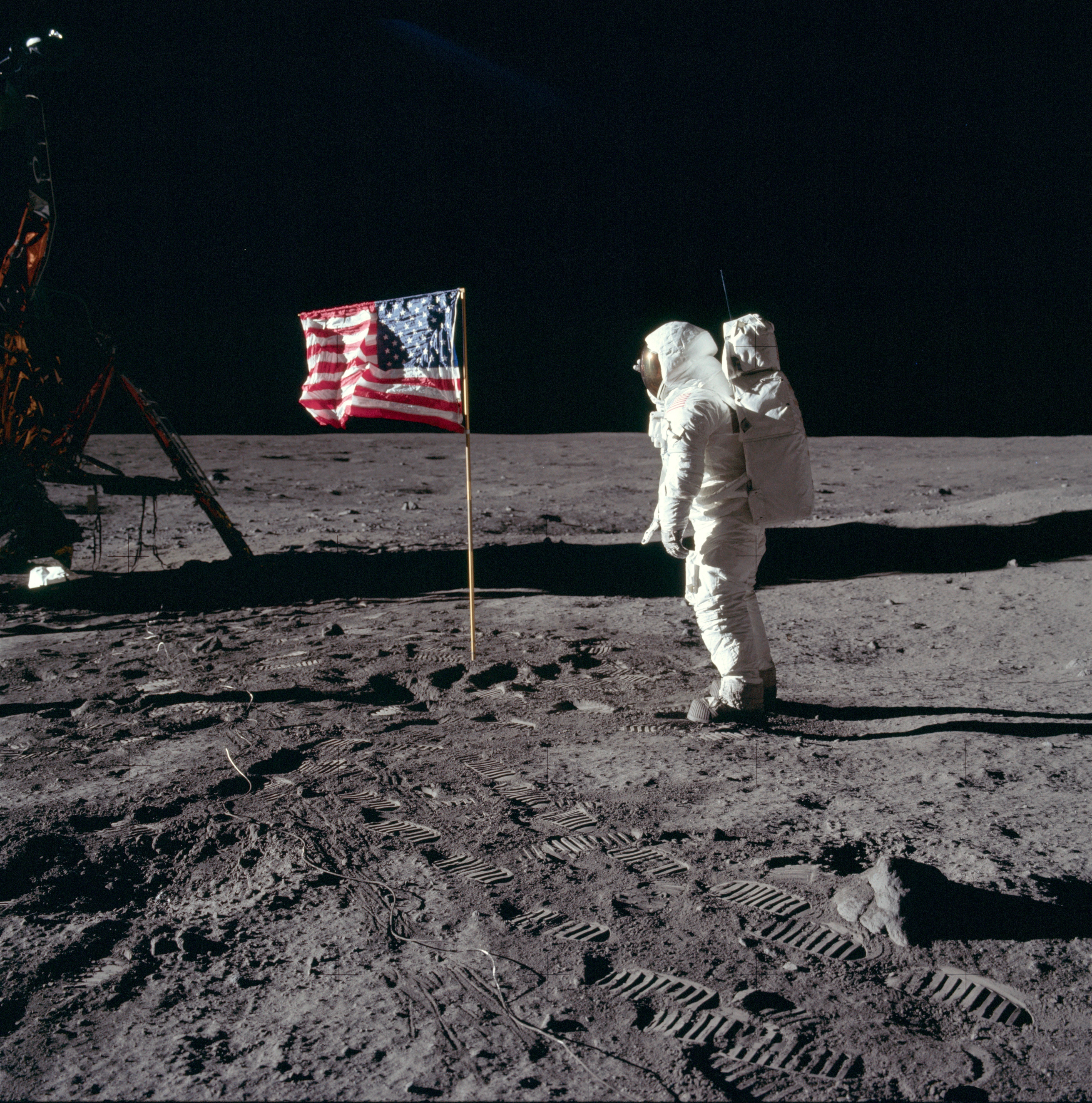
was the first circumlunar flight and the first lunar landing was conducted by
Apollo 11. Commanded by
Neil Armstrong
Neil Alden Armstrong (August 5, 1930 – August 25, 2012) was an American astronaut and aeronautical engineer who became the first person to walk on the Moon in 1969. He was also a naval aviator, test pilot, and university professor.
...
with astronauts
Buzz Aldrin and
Michael Collins Michael Collins or Mike Collins most commonly refers to:
* Michael Collins (Irish leader) (1890–1922), Irish revolutionary leader, soldier, and politician
* Michael Collins (astronaut) (1930–2021), American astronaut, member of Apollo 11 and Ge ...
, Apollo 11 was one of the most significant missions in NASA's history, marking the end of the Space Race when the Soviet's gave up lunar ambitions. As the first human to step on the surface of the Moon, Neil Armstrong uttered the now famous words:
NASA would conduct six total lunar landings as part of the Apollo Program, with
Apollo 17
Apollo 17 (December 7–19, 1972) was the final mission of NASA's Apollo program, the most recent time humans have set foot on the Moon or traveled beyond low Earth orbit. Commander Gene Cernan and Lunar Module Pilot Harrison Schmitt walked on ...
concluding the program in 1972.
 Wernher von Braun
Wernher von Braun had advocated for NASA to develop a space station since the agency was created. In 1973, Following the end of the Apollo lunar missions NASA launched its first space station,
Skylab, on the final launch of the Saturn V. Skylab repurposed a significant amount of former Apollo and Saturn hardware, with a repurposed Saturn V third stage serving as primary module for the space station. Damage to Skylab during launch required spacewalks by the first crew to make it habitable and operational. Skylab only hosted 9 missions and was decommissioned in 1974 and deorbited in 1979, two years prior to the Space Shuttle's launch and any possibility of boosting its orbit.
In 1975, the
Apollo–Soyuz mission was the first ever international spaceflight and a major diplomatic accomplishment between the Cold War rivals. Flown in 1975, a U.S. Apollo spacecraft docked with a Soviet
Soyuz capsule. It also was the last flight of the Apollo capsule.
Interplanetary exploration and space science
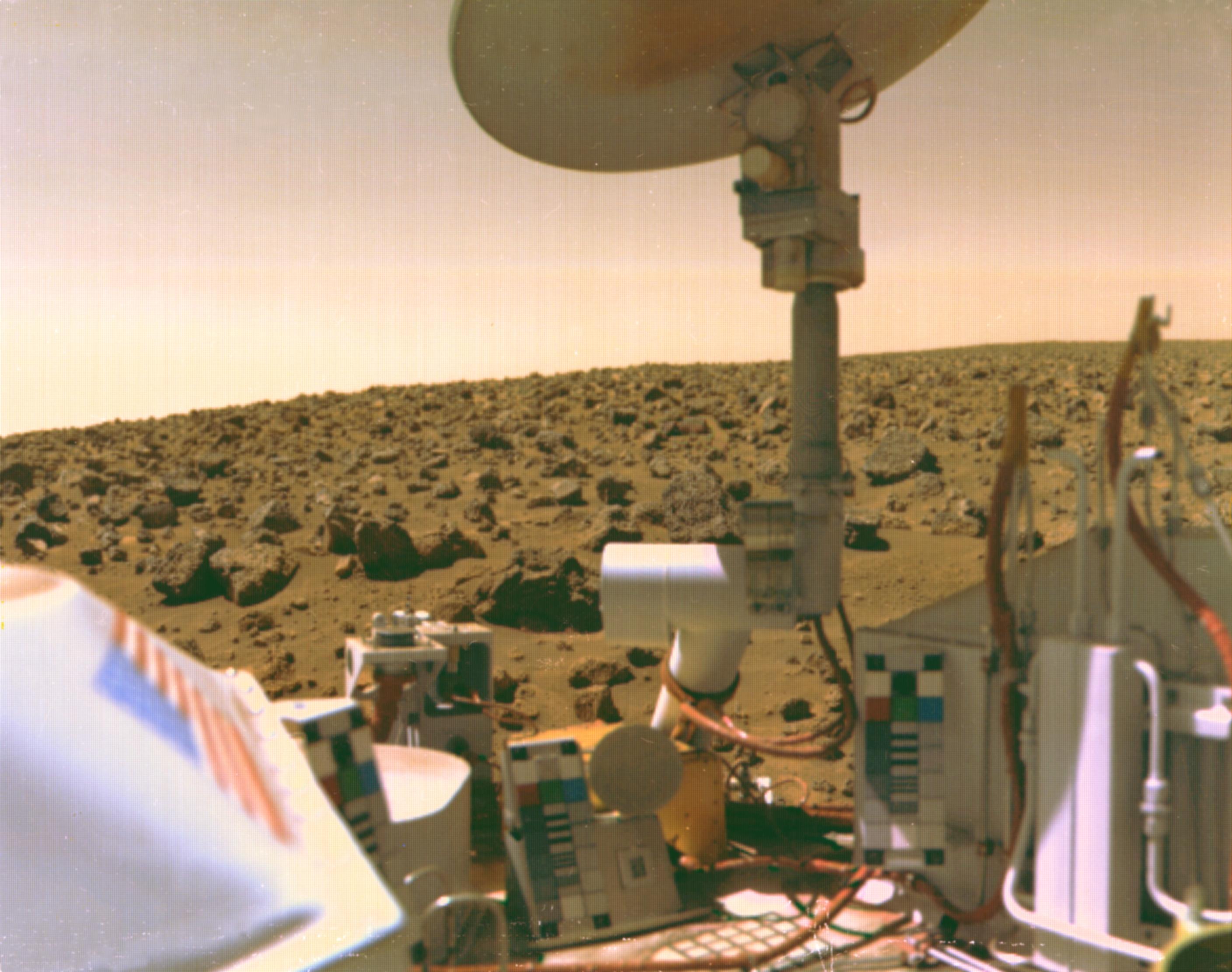

During the 1960s, NASA started its
space science
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider ...
and interplanetary probe program. The
Mariner program was its flagship program, launching probes to
Venus,
Mars, and
Mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
in the 1960s. The
Jet Propulsion Laboratory was the lead NASA center for robotic interplanetary exploration, making significant discoveries about the
inner planets. Despite these successes, Congress was unwilling to fund further interplanetary missions and NASA Administrator James Webb suspended all future interplanetary probes to focus resources on the Apollo program.
Following the conclusion of the Apollo program, NASA resumed launching interplanetary probes and expanded its
space science
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually consider ...
program. The first planet tagged for exploration was
Venus, sharing many similar characteristics to Earth. First visited by American
Mariner 2 spacecraft, Venus was observed to be a hot and inhospitable planet. Follow-on missions included the
Pioneer Venus project in the 1970s and
Magellan, which performed radar mapping of Venus' surface in the 1980s and 1990s. Future missions were flybys of Venus, on their way to other destinations in the Solar System.
Mars has long been a planet of intense fascination for NASA, being suspected of potentially having harbored life.
Mariner 5 was the first NASA spacecraft to flyby Mars, followed by
Mariner 6
A sailor, seaman, mariner, or seafarer is a person who works aboard a watercraft as part of its crew, and may work in any one of a number of different fields that are related to the operation and maintenance of a ship.
The profession of the s ...
and
Mariner 7.
Mariner 9
Mariner 9 (Mariner Mars '71 / Mariner-I) was a robotic spacecraft that contributed greatly to the exploration of Mars and was part of the NASA Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971 from LC-36B at Cape Canaveral Air ...
was the first orbital mission to Mars. Launched in 1975,
Viking program consisted of two landings on Mars in 1976. Follow-on missions would not be launched until 1996, with the
Mars Global Surveyor orbiter and
Mars Pathfinder, deploying the first Mars rover,
Sojourner
A sojourner is a person who resides temporarily in a place.
Sojourner may also refer to:
*Sojourner Truth (1797–1883), abolitionist and women's rights activist
*Albert Sojourner (1872–1951), member of the Mississippi House of Representatives
...
. During the early 2000s, the
2001 Mars Odyssey
''2001 Mars Odyssey'' is a robotic spacecraft orbiting the planet Mars. The project was developed by NASA, and contracted out to Lockheed Martin, with an expected cost for the entire mission of US$297 million. Its mission is to use spectr ...
orbiter reached the planet and in 2004 the ''
Sprit'' and ''
Opportunity'' rovers landed on the Red Planet. This was followed in 2005 by the
Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter and 2007 ''
Phoenix'' Mars lander. The 2012 landing of ''
Curiosity'' discovered that the radiation levels on Mars were equal to those on the
International Space Station, greatly increasing the possibility of Human exploration, and observed the key chemical ingredents for life to occur. In 2013, the Mars Atmosphere and Volatile EvolutioN (
MAVEN) mission observed the Martian upper atmospher and space environment and in 2018, the Interior exploration using Seismic Investigations Geodesy, and Heat Transport (
InSight) studied the Martian interior. The 2021 ''
Perseverance'' rover carried the first extraplanetary aircraft, a helicopter named ''
Ingenuity''.
NASA also launched missions to
Mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
in 2004, with the
MESSENGER
''MESSENGER'' was a NASA robotic space probe that orbited the planet Mercury between 2011 and 2015, studying Mercury's chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field. The name is a backronym for "Mercury Surface, Space Environment, Geoche ...
probe demonstrating as the first use of a
solar sail
Solar sails (also known as light sails and photon sails) are a method of spacecraft propulsion using radiation pressure exerted by sunlight on large mirrors. A number of spaceflight missions to test solar propulsion and navigation have been p ...
. NASA also launched probes to the
outer solar system starting in the 1960s.
Pioneer 10 was the first probe to the outer planets, flying by
Jupiter, while
Pioneer 11
''Pioneer 11'' (also known as ''Pioneer G'') is a robotic space probe launched by NASA on April 5, 1973, to study the asteroid belt, the environment around Jupiter and Saturn, solar winds, and cosmic rays. It was the first probe to encounter ...
provided the first close up view of the planet. Both probes became the first objects to leave the Solar System. The
Voyager program launched in 1977, conducting flybys of
Jupiter and
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
,
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth planet from the Sun and the farthest known planet in the Solar System. It is the fourth-largest planet in the Solar System by diameter, the third-most-massive planet, and the densest giant planet. It is 17 times ...
, and
Uranus on a trajectory to leave the Solar System. The
Galileo
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was ...
spacecraft, deployed from the Space Shuttle flight
STS-34, was the first spacecraft to orbit Jupiter, discovering evidence of subsurface oceans on the
Europa
Europa may refer to:
Places
* Europe
* Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace
* Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro
* Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development
* Europa Cliff ...
and observed that the moon may hold ice or liquid water. A joint NASA-
European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
-
Italian Space Agency mission,
Cassini–Huygens
''Cassini–Huygens'' ( ), commonly called ''Cassini'', was a space research, space-research mission by NASA, the European Space Agency (ESA), and the Italian Space Agency (ASI) to send a space probe to study the planet Saturn and its system, i ...
, was sent to
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
's moon of
Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
, which along with Mars and Europa, are the only objects non-Terran objects in the Solar System suspected of being capable of harboring life. Cassini discovered three new moons of Saturn and the
Huygens
Huygens (also Huijgens, Huigens, Huijgen/Huygen, or Huigen) is a Dutch patronymic surname, meaning "son of Hugo". Most references to "Huygens" are to the polymath Christiaan Huygens. Notable people with the surname include:
* Jan Huygen (1563– ...
probe entered Titan's atmosphere. The mission discovered evidence of liquid hydrocarbon lakes on Titan and subsurface water oceans on the moon of
Enceladus, which could harbor life. Finally launched in 2006, the
New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research ...
mission was the first spacecraft to visit
Pluto and the
Kuiper Belt
The Kuiper belt () is a circumstellar disc in the outer Solar System, extending from the orbit of Neptune at 30 astronomical units (AU) to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, but is far larger—20 times ...
.
Beyond interplanetary probes, NASA has a long tradition of launching
space telescopes. Launched in the 1960s, the
Orbiting Astronomical Observatory were NASA's first orbital telescopes, providing ultraviolet, gamma-ray, x-ray, and infrared observations. Not just looking up, NASA launched the
Orbiting Geophysical Observatory
Orbiting Geophysical Observatory (OGO) Program of NASA refers to the six satellites launched by the United States that were in use from September 1964 to 1972, designed to study the Earth's magnetosphere. The satellites successfully studied th ...
to look down at Earth and observe its interactions with the Sun. The
Uhuru satellite was the first dedicated x-ray telescope, mapping 85% of the sky and discovering a large number of
black holes
A black hole is a region of spacetime where gravity is so strong that nothing, including light or other electromagnetic waves, has enough energy to escape it. The theory of general relativity predicts that a sufficiently compact mass can def ...
.
Launched in the 1990s and early 2000s, the
Great Observatories program
NASA's series of Great Observatories satellites are four large, powerful space-based astronomical telescopes launched between 1990 and 2003. They were built with different technology to examine specific wavelength/energy regions of the electrom ...
are among NASA's most powerful telescopes. The
Hubble Space Telescope was launched in 1990 on
STS-31
STS-31 was the 35th mission of the NASA Space Shuttle program. The primary purpose of this mission was the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) into low Earth orbit. The mission used the Space Shuttle ''Discovery'' (the tenth missio ...
from the ''Discovery'' and could view galaxies 15 light years away. A major defect in the telescope's mirror could have cripped the program, had NASA not used computer enhancement to compensate for the imperfection and launched five Space Shuttle servicing flights to replace the damaged components. The
Compton Gamma Ray Observatory was launched from the ''Atlantis'' on
STS-37 in 1991, discovering a possible source of
antimatter at the center of the
Milky Way and observing that the majority of gamma-ray bursts occur outside of the Milky Way galaxy. The
Chandra X-ray Observatory was launched from the ''Columbia'' on
STS-93 in 1999, observing black holes,
quasars,
supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or when ...
, and
dark matter. It provided critical observations on the
Sagittarius A* black hole at the center of the Milky Way galaxy and the separation of dark and regular matter during galactic collisions. Finally, the
Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, f ...
is an infrared telescope and the last of the great observatories, launched in 2003 from a
Delta II rocket. It is in a trailing orbit aroud the Sun, following the Earth and discovered the existence of
brown dwarf stars.
Other telescopes, such as the
Cosmic Background Explorer and the
Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe
The Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe (WMAP), originally known as the Microwave Anisotropy Probe (MAP and Explorer 80), was a NASA spacecraft operating from 2001 to 2010 which measured temperature differences across the sky in the cosmic mic ...
, provided evidence to support the
Big Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
. The
James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Spa ...
, named after the NASA administrator who lead the Apollo program, is an infrared observatory launched in 2021. The James Webb Space Telescope is a direct successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, intended to observe the formation of the first galaxies. Other space telescopes include the
Kepler space telescope
The Kepler space telescope is a disused space telescope launched by NASA in 2009 to discover Earth-sized planets orbiting other stars. Named after astronomer Johannes Kepler, the spacecraft was launched into an Earth-trailing heliocentric orb ...
, launched in 2009 to identify planets orbiting extrasolar stars that may be Terran and possibly harbor life. The first exoplanet that the Keplar space telescope confirmed was
Kepler-22b, orbiting within the habitable zone of its star.
NASA also launched a number of different satellites to study Earth, such as
Television Infrared Observation Satellite (TIROS) in 1960, which was the first weather satellite. NASA and the
United States Weather Bureau cooperated on future TIROS and the second generation
Nimbus program of weather satellites. It also worked with the
Environmental Science Services Administration on a series of weather satellites and the agency launched its the experimental
Applications Technology Satellites
The Applications Technology Satellites (ATS) were a series of experimental satellites launched by NASA, under the supervision of, among others, Wernher von Braun. The program was launched in 1966 to test the feasibility of placing a satellite int ...
into geosynchronous orbit. NASA's first dedicated Earth observation satellite,
Landsat, was launched in 1972. This led to NASA and the
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration jointly developing the
Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite and discovering
Ozone depletion
Ozone depletion consists of two related events observed since the late 1970s: a steady lowering of about four percent in the total amount of ozone in Earth's atmosphere, and a much larger springtime decrease in stratospheric ozone (the ozone l ...
.
The Space Shuttle

NASA had been perusing
spaceplanes since the 1960s, blending the administration's dual aeronautics and space missions. NASA viewed a spaceplane as part of a larger program, providing routine and economical logistical support to a
space station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a human crew in orbit for an extended period of time, and is therefore a type of space habitat. It lacks major propulsion or landing systems. An orbital station or an orbital space station i ...
in Earth orbit that would be used as a hub for lunar and Mars missions. A reusable launch vehicle would end the need for expensive and expendable boosters like the Saturn V.
In 1969, NASA designated the
Johnson Space Center
The Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center (JSC) is NASA's center for human spaceflight (originally named the Manned Spacecraft Center), where human spaceflight training, research, and flight control are conducted. It was renamed in honor of the late U ...
as the lead center for developing the design, development, and manufacturing of the
Space Shuttle orbiter, while the
Marshall Space Flight Center
The George C. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), located in Redstone Arsenal, Alabama (Huntsville postal address), is the U.S. government's civilian rocketry and spacecraft propulsion research center. As the largest NASA center, MSFC's first ...
would lead the development of the launch system. NASA's series of
lifting body aircraft, culminating in the joint NASA-U.S. Air Force
Martin Marietta X-24
The Martin Marietta X-24 was an American experimental aircraft developed from a joint United States Air Force-NASA program named PILOT (1963–1975). It was designed and built to test lifting body concepts, experimenting with the concept of u ...
, directly informed the development of the Space Shuttle and future hypersonic flight aircraft. Official development of the
Space Shuttle began in 1972, with
Rockwell International contracted to design the orbiter and engines,
Martin Marietta
The Martin Marietta Corporation was an American company founded in 1961 through the merger of Glenn L. Martin Company and American-Marietta Corporation. In 1995, it merged with Lockheed Corporation to form Lockheed Martin.
History
Martin Mari ...
for the
external fuel tank
The Space Shuttle external tank (ET) was the component of the Space Shuttle launch vehicle that contained the liquid hydrogen Rocket propellant, fuel and liquid oxygen oxidizer. During lift-off and ascent it supplied the fuel and oxidizer und ...
, and
Morton Thiokol
Thiokol (variously Thiokol Chemical Corporation(/Company), Morton Thiokol Inc., Cordant Technologies Inc., Thiokol Propulsion, AIC Group, ATK Thiokol, ATK Launch Systems Group; finally Orbital ATK before becoming part of Northrop Grumman) was an ...
for the
solid rocket booster
A solid rocket booster (SRB) is a large solid propellant motor used to provide thrust in spacecraft launches from initial launch through the first ascent. Many launch vehicles, including the Atlas V, SLS and space shuttle, have used SRBs to give ...
s. NASA acquired six orbiters: the ''
Enterprise'', ''
Columbia
Columbia may refer to:
* Columbia (personification), the historical female national personification of the United States, and a poetic name for America
Places North America Natural features
* Columbia Plateau, a geologic and geographic region in ...
'', ''
Challenger
Challenger, Challengers, or The Challengers may refer to:
Entertainment
Comics and manga
* Challenger (character), comic book character
* ''Challengers'' (manga), manga by Hinako Takanaga
Film and TV
* ''The Challengers'' (TV series), a 1979 ...
'', ''
Discovery
Discovery may refer to:
* Discovery (observation), observing or finding something unknown
* Discovery (fiction), a character's learning something unknown
* Discovery (law), a process in courts of law relating to evidence
Discovery, The Discovery ...
'', ''
Atlantis'', and ''
Endeavour
Endeavour or endeavor may refer to:
People
Fictional characters
* Endeavour Morse, central character of the ''Inspector Morse'' novels by Colin Dexter
* Endeavor, the hero name for the character Enji Todoroki from the anime series ''My Hero A ...
''
The Space Shuttle program also allowed NASA to make dramatic changes to its
Astronaut Corps
Human spaceflight (also referred to as manned spaceflight or crewed spaceflight) is spaceflight with a crew or passengers aboard a spacecraft, often with the spacecraft being operated directly by the onboard human crew. Spacecraft can also be ...
. While almost all previous astronauts were Air Force or Naval test pilots, the Space Shuttle allowed NASA to begin recruiting more non-military scientific and technical experts. A prime example is
Sally Ride
Sally Kristen Ride (May 26, 1951 – July 23, 2012) was an American astronaut and physicist. Born in Los Angeles, she joined NASA in 1978, and in 1983 became the first American woman and the third woman to fly in space, after cosmonauts V ...
, who became the first American woman to fly in space on
STS-7. It also allowed NASA to accept exchange astronauts from U.S. allies and partners for the first time.
The first Space Shuttle flight occurred in 1981, when the ''Columbia'' launched on the
STS-1 mission, designed to serve as a flight test for the new spaceplane. NASA intended for the Space Shuttle to replace expendable launch systems like the Air Force's
Atlas,
Delta
Delta commonly refers to:
* Delta (letter) (Δ or δ), a letter of the Greek alphabet
* River delta, at a river mouth
* D (NATO phonetic alphabet: "Delta")
* Delta Air Lines, US
* Delta variant of SARS-CoV-2 that causes COVID-19
Delta may also re ...
, and
Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
and the
European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
's
Ariane
Ariane may refer to:
*Ariana (name), also Ariane, Arianne
Arts
* ''Ariane'' (Martinů), an opera by Bohuslav Martinů, first performed 1961
* ''Ariane'' (Massenet), an opera by Jules Massenet, first performed 1906
* ''Ariane'' (film), a 1931 ...
. The Space Shuttle's
Spacelab payload, developed by the
European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
, dramatically increased the scientific capabilities of shuttle missions over anything NASA was able to previously accomplish.

NASA launched its first commercial satellites on the
STS-5 mission and in 1984, the
STS-41-C
STS-41-C (formerly STS-13) was NASA's eleventh Space Shuttle mission, and the fifth mission of Space Shuttle ''Challenger''. The launch, which took place on April 6, 1984, marked the first direct ascent trajectory for a Space Shuttle mission. ...
mission conducted the world's first
on-orbit satellite servicing mission when the ''Challenge'' captured and repaired the malfunctioning
Solar Maximum Mission
The Solar Maximum Mission satellite (or SolarMax) was designed to investigate Sun, Solar phenomena, particularly solar flares. It was launched on February 14, 1980. The SMM was the first satellite based on the Multimission Modular Spacecraft bus ...
satellite. It also had the capability to return malfunctioning satellite to Earth, like it did with the
Palapa B2
Palapa is a series of Communications satellites owned by Indosat, an Indonesian telecommunications company (formerly by Perumtel and then by PT Satelit Palapa Indonesia/Satelindo). Starting with the first in July 1976, at which time Indone ...
and
Westar 6 satellites. Once returned to Earth, the satellites were repaired and relaunched.
Despite ushering in a new era of spaceflight, where NASA was contracting launch services to commercial companies, the Space Shuttle was criticized for not being as reusable and cost-effective as advertised. In 1986,
''Challenger'' disaster on the
STS-51L
STS-51-L was the 25th mission of the NASA Space Shuttle program and the final flight of Space Shuttle ''Challenger''.
Planned as the first Teacher in Space Project flight in addition to observing Halley's Comet for six days and performing a ...
mission resulted in the loss of the spacecraft and all seven astronauts on launch, grounding the entire space shuttle fleet for 36 months and forced the 44 commercial companies that contracted with NASA to deploy their satellites to return to expendable launch vehicles. When the Space Shuttle returned to flight with the
STS-26 mission, it had undergone significant modifications to improve its reliability and safety.

Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, the Russian Federation and United States initaited the
Shuttle-''Mir'' program. The first Russian cosmonaut flew on the
STS-60 mission in 1994 and the ''Discovery'' rendezvoused, but did not dock with, the Russian ''
Mir'' in the
STS-63 mission. This was followed by ''Atlantis
STS-71
STS-71 was the third mission of the US/Russian Shuttle-Mir Program and the first Space Shuttle docking to Russian space station ''Mir''. It started on June 27, 1995, with the launch of Space Shuttle ''Atlantis'' from launchpad 39A at the Kenn ...
mission where it accomplished the initial intended mission for the Space Shuttle, docking with a space station and transferring supplies and personnel. The Shuttle-''Mir'' program would continue until 1998, when a series of orbital accidents on the space station spelled an end to the program.
In 2003, a second space shuttle was lost when the ''Columbia'' was
lost
Lost may refer to getting lost, or to:
Geography
*Lost, Aberdeenshire, a hamlet in Scotland
* Lake Okeechobee Scenic Trail, or LOST, a hiking and cycling trail in Florida, US
History
*Abbreviation of lost work, any work which is known to have bee ...
upon reentry during the
STS-107 mission, resulting in the loss of the spacecraft and all seven astronauts. This accident marked the beginning of the end of the Space Shuttle program, with President
George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
directing that upon the completion of the International Space Station, the space shuttle be retired. In 2006, the Space Shuttle returned to flight and flew several additional missions, flying several mission to service the
Hubble Space Telescope, but was retired with the completion of the completion of the
STS-135 resupply mission to the International Space Station in 2011.
Space stations

NASA never gave up on the idea of a space station after Skylab's reentry in 1979. The agency began lobbing politicians to support building a space station as soon as the Space Shuttle began flying, selling it as an orbital laboratory, repair station, and a jumping off point for lunar and Mars missions. NASA found a strong advocate in President
Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
, who declared in a 1984 speech:
In 1985, NASA proposed the
Space Station ''Freedom'', which both the agency and President Reagan intended to be an international program. While this would add legitimacy to the program, there were concerns within NASA that the international component would dilute its authority within the project, having never been willing to work with domestic or international partners as true equals. There was also a concern with sharing sensitive space technologies with the Europeans, which had the potential to dilute America's technical lead. Ultimately, an international agreement to develop the Space Station ''Freedom'' program would be signed with thirteen countries in 1985, including the
European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
member states, Canada, and Japan.
Despite its status as the first international space program, the Space Station ''Freedom'' was controversial, with much of the debate centering on cost. Several redesigns to reduce cost were conducted in the early 1990s, stripping away much of its functions. However, despite calls for Congress to terminate the program it continued, in large part because by 1992 it had created 75,000 jobs across 39 states. By 1993, President
Bill Clinton attempted to significantly reduce NASA's budget and directed costs be significantly reduced, aerospace industry jobs were not lost, and the Russians be included.

In 1993, the Clinton Administration announced that the Space Station ''Freedom'' would become the
International Space Station in an agreement with the Russian Federation. This allowed the Russians to maintain their space program through an infusion of American currency to maintain their status as one of the two premier space programs. While the United States built and launched the majority of the International Space Station, Russia, Canada, Japan, and the European Space Agency all contributed components. Despite NASA's insistence that costs would be kept at a budget of $17.4, they kept rising and NASA had to transfer funds from other programs to keep the International Space Station solvent. Ultimately, the total cost of the station was $150 billion, with the United States paying for two-thirds.Following the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster in 2003, NASA was forced to rely on Russian
Soyuz launches for its astronauts and the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle accelerated the station's completion.
In the 1980s, right after the first flight of the Space Shuttle, NASA started a joint program with the Department of Defense to develop the
Rockwell X-30
The Rockwell X-30 was an advanced technology demonstrator project for the National Aero-Space Plane (NASP), part of a United States project to create a single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) spacecraft and passenger spaceliner. Started in 1986, it was canc ...
National Aerospace Plane. NASA realized that the Space Shuttle, while a massive technological accomplishment, would not be able to live up to all its promises. Designed to be a
single-stage-to-orbit
A single-stage-to-orbit (SSTO) vehicle reaches orbit from the surface of a body using only propellants and fluids and without expending tanks, engines, or other major hardware. The term usually, but not exclusively, refers to reusable vehicles ...
spaceplane, the X-30 had both civil and military applications. With the end of the
Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
, the X-30 was canceled in 1992 before reaching flight status.
Unleashing commercial space and return to the Moon
Following the 2003 Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster, President Bush started the
Constellation program to smoothly replace the Space Shuttle and expand space exploration beyond low Earth orbit. Constellation was intended to use a significant amount of former Space Shuttle equipment and return astronauts to the Moon. However, the Constellation program was canceled by the
Obama Administration
Barack Obama's tenure as the 44th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 2009, and ended on January 20, 2017. A Democrat from Illinois, Obama took office following a decisive victory over Republican ...
and former astronauts
Neil Armstrong
Neil Alden Armstrong (August 5, 1930 – August 25, 2012) was an American astronaut and aeronautical engineer who became the first person to walk on the Moon in 1969. He was also a naval aviator, test pilot, and university professor.
...
,
Gene Cernan, and
Jim Lovell sent a letter to President
Barack Obama to warn him that if the United States did not get new human spaceflight ability, the U.S. risked become a second or third-rate space power.
As early as the Reagan Administration, there had been calls for NASA to expand private sector involvement in space exploration rather than do it all in house. In the 1990s, NASA and Lockheed Martin entered into an agreement to develop the
Lockheed Martin X-33 and
VentureStar spaceplane, which was intended to replace the Space Shuttle. However, due to technical challenges the spacecraft was cancelled in 2001. Despite this, it was the first time a commercial space company directly expended a significant amount of its own resources into spacecraft development. The advent of
space tourism also forced NASA to challenge its assumption that only governments would have people in space. The first space tourist was
Dennis Tito, an American investment manager and former aerospace engineer who contracted with the Russians to fly to the International Space Station for four days, despite the opposition of NASA to the idea.
Advocates of this new commercial approach for NASA included former astronaut
Buzz Aldrin, who remarked that it would return NASA to its roots as a research and development agency, with commercial entities actually operating the space systems. Having corporations take over orbital operations would also allow NASA to focus all its efforts on deep space exploration and returning humans to the Moon and going to Mars. Embracing this approach, NASA's
Commercial Crew Program started by contracting cargo delivery to the International Space Station and flew its first operational contracted mission on
SpaceX Crew-1. This marked the first time since the retirement of the Space Shuttle that NASA was able to launch its own astronauts on an American spacecraft from the United States, ending a decade of reliance on the Russians.
In 2019, NASA announced the
Artemis program, intending to return to the Moon and establish a permanent human presence. This was paired with the
Artemis Accords
The Artemis Accords are a series of non-binding multilateral agreements between the United States government and other world governments participating in the Artemis Program, an American-led effort to return humans to the Moon by 2025, with the u ...
with partner nations to establish rules of behavior and norms of space commercialization on the Moon.
Active programs
Human spaceflight
International Space Station (1993–present)
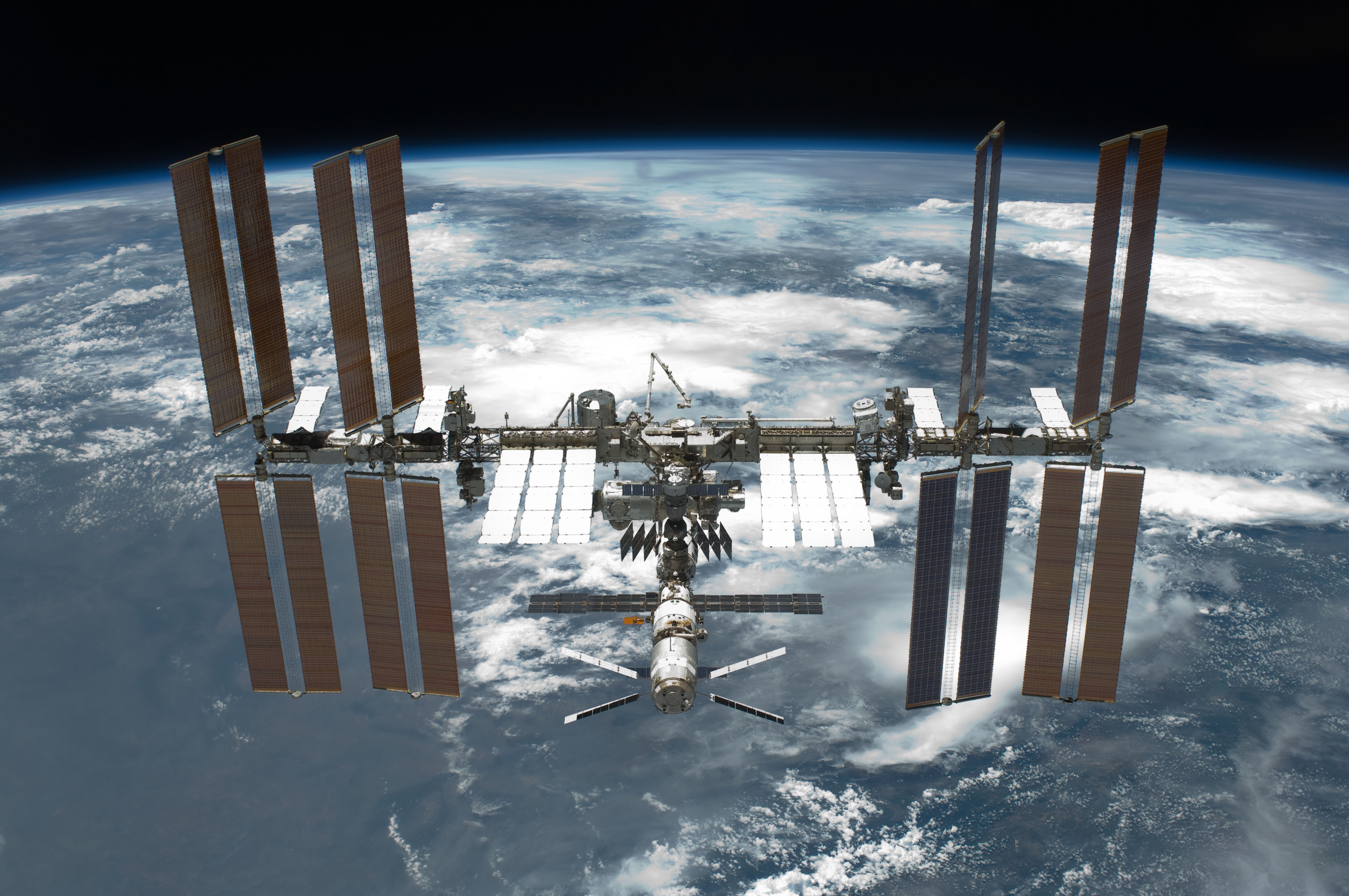

The
International Space Station (ISS) combines NASA's
Space Station ''Freedom'' project with the Soviet/Russian ''
Mir-2
''Mir''-2 was a Soviet space station project which began in February 1976. Some of the modules built for ''Mir''-2 have been incorporated into the International Space Station (ISS). The project underwent many changes, but was always based o ...
'' station, the European ''
Columbus
Columbus is a Latinized version of the Italian surname "''Colombo''". It most commonly refers to:
* Christopher Columbus (1451-1506), the Italian explorer
* Columbus, Ohio, capital of the U.S. state of Ohio
Columbus may also refer to:
Places ...
'' station, and the Japanese
Kibō laboratory module.
NASA originally planned in the 1980s to develop ''Freedom'' alone, but US budget constraints led to the merger of these projects into a single multi-national program in 1993, managed by NASA, the
Russian Federal Space Agency (RKA), the
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orb ...
(JAXA), the
European Space Agency
, owners =
, headquarters = Paris, Île-de-France, France
, coordinates =
, spaceport = Guiana Space Centre
, seal = File:ESA emblem seal.png
, seal_size = 130px
, image = Views in the Main Control Room (1205 ...
(ESA), and the
Canadian Space Agency
The Canadian Space Agency (CSA; french: Agence spatiale canadienne, ASC) is the national space agency of Canada, established in 1990 by the ''Canadian Space Agency Act''.
The president is Lisa Campbell, who took the position on September 3, 2020 ...
(CSA).
The station consists of pressurized modules, external
trusses,
solar arrays
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and c ...
and other components, which were
manufactured in various factories around the world, and have been launched by Russian
Proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
and
Soyuz rockets, and the US Space Shuttles.
The on-orbit assembly began in 1998, the completion of the
US Orbital Segment occurred in 2009 and the completion of the
Russian Orbital Segment occurred in 2010, though there are some debates of whether new modules should be added in the segment. The ownership and use of the space station is established in intergovernmental treaties and agreements
which divide the station into two areas and allow
Russia to retain full ownership of the Russian Orbital Segment (with the exception of ''
Zarya Zarya may refer to:
*Zorya, personification of dawn in Slavic mythology
* Zarya (antenna), a type of medium-wave broadcasting antenna used in former Soviet Union
*Zarya (ISS module) is a module of the International Space Station.
* ''Zarya'' (magazi ...
''),
with the US Orbital Segment allocated between the other international partners.
Long-duration missions to the ISS are referred to as
ISS Expeditions. Expedition crew members typically spend approximately six months on the ISS. The initial expedition crew size was three, temporarily decreased to two following the ''Columbia'' disaster. Since May 2009, expedition crew size has been six crew members. Crew size is expected to be increased to seven, the number the ISS was designed for, once the Commercial Crew Program becomes operational. The ISS has been continuously occupied for the past , having exceeded the previous record held by ''
Mir''; and has been visited by astronauts and cosmonauts from
15 different nations.
The station can be seen from the Earth with the naked eye and, as of , is the largest artificial satellite in Earth orbit with a mass and volume greater than that of any previous space station.
[International Space Station](_blank)
, Retrieved October 20, 2011 The Russian
Soyuz and American
Dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
spacecraft are used to send astronauts to and from the ISS. Several uncrewed cargo spacecraft provide service to the ISS; they are the Russian
Progress spacecraft which has done so since 2000, the European
Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV) since 2008, the Japanese
H-II Transfer Vehicle (HTV) since 2009, the (uncrewed)
Dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
since 2012, and the American
Cygnus spacecraft since 2013. The Space Shuttle, before its retirement, was also used for cargo transfer and would often switch out expedition crew members, although it did not have the capability to remain docked for the duration of their stay. Between the retirement of the Shuttle in 2011 and the commencement of crewed Dragon flights in 2020, American astronauts exclusively used the Soyuz for crew transport to and from the ISS The highest number of people occupying the ISS has been thirteen; this occurred three times during the late Shuttle ISS assembly missions.
The ISS program is expected to continue to 2030, after which the space station will be retired and destroyed in a controlled de-orbit.
Commercial Resupply Services (2008–present)
Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) are a contract solution to deliver cargo and supplies to the
International Space Station (ISS) on a commercial basis. NASA signed its first CRS contracts in 2008 and awarded $1.6 billion to
SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
for twelve cargo
Dragon
A dragon is a reptilian legendary creature that appears in the folklore of many cultures worldwide. Beliefs about dragons vary considerably through regions, but dragons in western cultures since the High Middle Ages have often been depicted as ...
and $1.9 billion to
Orbital Sciences for eight
Cygnus flights, covering deliveries to 2016. Both companies evolved or created their launch vehicle products to support the solution (SpaceX with The
Falcon 9 and Orbital with the
Antares).
SpaceX flew its first operational resupply mission (
SpaceX CRS-1) in 2012.
Orbital Sciences followed in 2014 (
Cygnus CRS Orb-1). In 2015, NASA extended CRS-1 to twenty flights for SpaceX and twelve flights for
Orbital ATK.
A second phase of contracts (known as CRS-2) was solicited in 2014; contracts were awarded in January 2016 to Orbital ATK
Cygnus,
Sierra Nevada Corporation
Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) is an American, privately held aerospace and national security contractor specializing in aircraft modification and integration, space components and systems, and related technology products for cybersecurity and ...
''
Dream Chaser
Dream Chaser is an American reusable lifting-body spaceplane being developed by Sierra Nevada Corporation (SNC) Space Systems. Originally intended as a crewed vehicle, the Dream Chaser Space System is set to be produced after the cargo varian ...
'', and SpaceX ''
Dragon 2'', for cargo transport flights beginning in 2019 and expected to last through 2024. In March 2022, NASA awarded an additional six CRS-2 missions each to both SpaceX and Northrop Grumman (formerly Orbital).
Northrop Grumman successfully delivered
Cygnus NG-17 to the ISS in February 2022. In July 2022, SpaceX launched its 25th CRS flight (
SpaceX CRS-25) and successfully delivered its cargo to the ISS. In late 2022, Sierra Nevada continued to assemble their Dream Chaser CRS solution; current estimates put its first launch in early 2023.
Commercial Crew Program (2011–present)
The Commercial Crew Program (CCP) provides
commercially operated crew transportation service to and from the
International Space Station (ISS) under contract to NASA, conducting crew rotations between the
expeditions of the
International Space Station program
The International Space Station programme is tied together by a complex set of legal, political and financial agreements between the fifteen nations involved in the project, governing ownership of the various components, rights to crewing and ...
. American
space manufacturer SpaceX
Space Exploration Technologies Corp. (SpaceX) is an American spacecraft manufacturer, launcher, and a satellite communications corporation headquartered in Hawthorne, California. It was founded in 2002 by Elon Musk with the stated goal of ...
began providing service in 2020, using the
Crew Dragon spacecraft, and NASA plans to add
Boeing when its
Boeing Starliner spacecraft becomes operational . NASA has contracted for six operational missions from Boeing and fourteen from SpaceX, ensuring sufficient support for ISS through 2030.
The spacecraft are owned and operated by the vendor, and crew transportation is provided to NASA as a commercial service. Each mission sends up to four astronauts to the ISS, with an option for a fifth passenger available. Operational flights occur approximately once every six months for missions that last for approximately six months. A spacecraft remains docked to the ISS during its mission, and missions usually overlap by at least a few days. Between the retirement of the
Space Shuttle in 2011 and the first operational CCP mission in 2020, NASA relied on the
Soyuz program to transport its astronauts to the ISS.
A Crew Dragon spacecraft is launched to space atop a
Falcon 9 Block 5 launch vehicle and the capsule returns to Earth via
splashdown in the ocean near Florida. The program's first operational mission,
SpaceX Crew-1, launched on 16 November 2020.
Boeing Starliner operational flights will now commence after its
final test flight which was launched atop an
Atlas V N22
Atlas V is an expendable launch system and the fifth major version in the Atlas launch vehicle family. It was originally designed by Lockheed Martin, now being operated by United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Lockheed Martin ...
launch vehicle. Instead of a splashdown, a Starliner capsule returns on land with
airbag
An airbag is a vehicle occupant-restraint system using a bag designed to inflate extremely quickly, then quickly deflate during a collision. It consists of the airbag cushion, a flexible fabric bag, an inflation module, and an impact sensor. Th ...
s at one of four designated sites in the western United States.
Artemis (2017–present)

Since 2017, NASA's
crewed spaceflight program has been the
Artemis program, which involves the help of US
commercial spaceflight companies and international partners such as
ESA,
JAXA
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orb ...
, and
CSA
CSA may refer to:
Arts and media
* Canadian Screen Awards, annual awards given by the Academy of Canadian Cinema & Television
* Commission on Superhuman Activities, a fictional American government agency in Marvel Comics
* Crime Syndicate of Amer ...
.
The goal of this program is to land "the first woman and the next man" on the
lunar south pole region by 2025. Artemis would be the first step towards the long-term goal of establishing a sustainable presence on the Moon, laying the foundation for companies to build a lunar economy, and eventually sending humans to
Mars.
The
Orion Crew Exploration Vehicle was held over from the canceled Constellation program for Artemis.
Artemis 1
Artemis 1, officially Artemis I and formerly Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), was an uncrewed Moon-orbiting mission. As the first major spaceflight of NASA's Artemis program, Artemis 1 marked the return of the agency to lunar exploration original ...
was the uncrewed initial launch of
Space Launch System (SLS) that would also send an Orion spacecraft on a
Distant Retrograde Orbit
A distant retrograde orbit (DRO), as most commonly conceived, is a spacecraft orbit around a moon>M2>>M3. So DRO is a general three-body problem solution. It's just that most practical near-term uses for the concept at three-body problems in our S ...
.
NASA's next major space initiative is to be the construction of the
Lunar Gateway, a small space station in lunar orbit. This space station will be designed primarily for non-continuous human habitation. The first tentative steps of returning to crewed lunar missions will be
Artemis 2
Artemis 2 (officially Artemis II) is the second scheduled mission of NASA's Artemis program, and the first scheduled crewed mission of NASA's Orion spacecraft, currently planned to be launched by the Space Launch System (SLS) in May 2024. The c ...
, which is to include the Orion crew module, propelled by the SLS, and is to launch in 2024.
This mission is to be a 10-day mission planned to briefly place a crew of four into a
Lunar flyby
A flyby () is a spaceflight operation in which a spacecraft passes in proximity to another body, usually a target of its space exploration mission and/or a source of a gravity assist to impel it towards another target. Spacecraft which are speci ...
.
The construction of the Gateway would begin with the proposed Artemis 3, which is planned to deliver a crew of four to
Lunar orbit
In astronomy, lunar orbit (also known as a selenocentric orbit) is the orbit of an object around the Moon.
As used in the space program, this refers not to the orbit of the Moon about the Earth, but to orbits by spacecraft around the Moon. The ...
along with the first modules of the Gateway. This mission would last for up to 30 days. NASA plans to build full scale deep space habitats such as the Lunar Gateway and the
Nautilus-X as part of its
Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships
Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships (NextSTEP) is a NASA program using a public-private partnership model that seeks commercial development of deep space exploration capabilities to support more extensive human space flight missi ...
(NextSTEP) program. In 2017, NASA was directed by the congressional NASA Transition Authorization Act of 2017 to get humans to Mars-orbit (or to the Martian surface) by the 2030s.
In support of the Artemis missions, NASA has been funding private companies to land robotic probes on the lunar surface in a program known as the
Commercial Lunar Payload Services
Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) is a NASA program to contract transportation services able to send small robotic landers and rovers to the Moon's south polar region mostly with the goals of scouting for lunar resources, testing in situ ...
. As of March 2022, NASA has awarded contracts for robotic lunar probes to companies such as
Intuitive Machines,
Firefly Space Systems
Firefly Alpha (Firefly α) is a two-stage orbital expendable launch vehicle developed by the American company Firefly Aerospace to compete in the commercial small satellite launch market. Alpha is intended to provide launch options for both ...
, and
Astrobotic.
On April 16, 2021, NASA announced they had selected the
SpaceX Lunar Starship as its Human Landing System. The agency's Space Launch System rocket will launch four astronauts aboard the Orion spacecraft for their multi-day journey to lunar orbit where they will transfer to SpaceX's Starship for the final leg of their journey to the surface of the Moon.
In November 2021, it was announced that the goal of landing astronauts on the Moon by 2024 had slipped to no earlier than 2025 due to numerous factors.
Artemis 1
Artemis 1, officially Artemis I and formerly Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1), was an uncrewed Moon-orbiting mission. As the first major spaceflight of NASA's Artemis program, Artemis 1 marked the return of the agency to lunar exploration original ...
launched on November 16, 2022 and returned to Earth safely on December 11, 2022. As of June 2022, NASA plans to launch
Artemis 2
Artemis 2 (officially Artemis II) is the second scheduled mission of NASA's Artemis program, and the first scheduled crewed mission of NASA's Orion spacecraft, currently planned to be launched by the Space Launch System (SLS) in May 2024. The c ...
in May 2024 and
Artemis 3 in December 2025.
Additional Artemis missions,
Artemis 4 and
Artemis 5
Artemis 5 (officially Artemis V) is the fifth planned mission and third crewed landing of NASA's Artemis Program. The mission will launch four astronauts on a Space Launch System rocket and an Orion to the south pole of the Moon. In additio ...
, are planned to launch after 2025.
Commercial LEO Development (2021–present)
The Commercial Low Earth Orbit Destinations program is an initiative by NASA to support work on commercial space stations that the agency hopes to have in place by the end of the current decade to replace the "International Space Station". The three selected companies are:
Blue Origin
Blue Origin, LLC is an American private spaceflight, privately funded aerospace manufacturer and sub-orbital spaceflight services company headquartered in Kent, Washington. Founded in 2000 by Jeff Bezos, the founder and executive chairman of Am ...
(et al.) with their
Orbital Reef
Orbital Reef is a planned low Earth orbit (LEO) space station designed by Blue Origin and Sierra Nevada Corporation's Sierra Space for commercial space activities and space tourism uses. Blue Origin has referred to it as a "mixed-use business ...
station concept,
Nanoracks (et al.) with their
Starlab Space Station
Starlab is the name given to the planned LEO space station designed by Nanoracks for commercial space activities uses. The company released preliminary plans in October 2021. The main structure of Starlab consists of a large inflatable habitat to ...
concept, and
Northrop Grumman with a station concept based on the HALO-module for the Gateway station.
Robotic exploration
NASA has conducted many uncrewed and robotic spaceflight programs throughout its history. More than 1,000 uncrewed missions have been designed to explore the Earth and the Solar System.
Mission selection process
NASA executes a mission development framework to plan, select, develop, and operate robotic missions. This framework defines cost, schedule and technical risk parameters to enable competitive selection of missions involving mission candidates that have been developed by principal investigators and their teams from across NASA, the broader U.S. Government research and development stakeholders, and industry. The mission development construct is defined by four umbrella programs.
=Explorer program
=
The Explorer program derives its origin from the earliest days of the U.S. Space program. In current form, the program consists of three classes of systems -
Small Explorers (SMEX),
Medium Explorers (MIDEX), and
University-Class Explorers (UNEX) missions. The NASA Explorer program office provides frequent flight opportunities for moderate cost innovative solutions from the heliophysics and astrophysics science areas. The Small Explorer missions are required to limit cost to NASA to below $150M (2022 dollars). Medium class explorer missions have typically involved NASA cost caps of $350M. The Explorer program office is based at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center.
=Discovery program
=
The NASA Discovery program develops and delivers robotic spacecraft solutions in the planetary science domain. Discovery enables scientists and engineers to assemble a team to deliver a solution against a defined set of objectives and competitively bid that solution against other candidate programs. Cost caps vary but recent mission selection processes were accomplished using a $500M cost cap to NASA. The Planetary Mission Program Office is based at the NASA Marshall Space Flight Center and manages both the Discovery and New Frontiers missions. The office is part of the Science Mission Directorate.
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson announced on June 2, 2021, that the ''
DAVINCI+'' and ''
VERITAS'' missions were selected to launch to Venus in the late 2020s, having beat out competing proposals for missions to Jupiter's volcanic moon Io and Neptune's large moon
Triton
Triton commonly refers to:
* Triton (mythology), a Greek god
* Triton (moon), a satellite of Neptune
Triton may also refer to:
Biology
* Triton cockatoo, a parrot
* Triton (gastropod), a group of sea snails
* ''Triton'', a synonym of ''Triturus' ...
that were also selected as Discovery program finalists in early 2020. Each mission has an estimated cost of $500 million, with launches expected between 2028 and 2030. Launch contracts will be awarded later in each mission's development.
=New Frontiers program
=
The New Frontiers program focuses on specific
Solar System exploration goals identified as top priorities by the planetary science community. Primary objectives include Solar System exploration employing medium class spacecraft missions to conduct high-science-return investigations. New Frontiers builds on the development approach employed by the Discovery program but provides for higher cost caps and schedule durations than are available with Discovery. Cost caps vary by opportunity; recent missions have been awarded based on a defined cap of $1 billion. The higher cost cap and projected longer mission durations result in a lower frequency of new opportunities for the program - typically one every several years. ''
OSIRIS-REx'' and ''
New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research ...
'' are examples of New Frontiers missions.
NASA has determined that the next opportunity to propose for the fifth round of New Frontiers missions will occur no later than the fall of 2024. Missions in NASA's New Frontiers Program tackle specific Solar System exploration goals identified as top priorities by the planetary science community. Exploring the Solar System with medium-class spacecraft missions that conduct high-science-return investigations is NASA's strategy to further understand the Solar System.
= Large strategic missions
=
Large strategic missions (formerly called Flagship missions) are strategic missions that are typically developed and managed by large teams that may span several NASA centers. The individual missions become the program as opposed to being part of a larger effort (see Discovery, New Frontiers, etc.). The
James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Spa ...
is a strategic mission that was developed over a period of more than 20 years. Strategic missions are developed on an ad-hoc basis as program objectives and priorities are established. Missions like Voyager, had they been developed today, would have been strategic missions. Three of the Great Observatories were strategic missions (the
Chandra X-ray Observatory,
Compton
Compton may refer to:
Places
Canada
* Compton (electoral district), a former Quebec federal electoral district
* Compton (provincial electoral district), a former Quebec provincial electoral district now part of Mégantic-Compton
* Compton, Que ...
, and the
Hubble Space Telescope). ''
Europa Clipper'' is the next large strategic mission in development by NASA.
Planetary science missions
NASA continues to play a material in exploration of the Solar System as it has for decades. Ongoing missions have current science objectives with respect to more than five extraterrestrial bodies within the Solar System – Moon (
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is a NASA robotic spacecraft currently orbiting the Moon in an eccentric polar mapping orbit. Data collected by LRO have been described as essential for planning NASA's future human and robotic missions t ...
), Mars (''
Perseverance'' rover), Jupiter (''
Juno
Juno commonly refers to:
*Juno (mythology), the Roman goddess of marriage and queen of the gods
*Juno (film), ''Juno'' (film), 2007
Juno may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Fictional characters
*Juno, in the film ''Jenny, Juno''
*Ju ...
''), asteroid
Bennu (''
OSIRIS-REx''), and Kuiper Belt Objects (''
New Horizons
''New Horizons'' is an Interplanetary spaceflight, interplanetary space probe that was launched as a part of NASA's New Frontiers program. Engineered by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) and the Southwest Research ...
''). The ''Juno'' extended mission will make multiple flybys of the Jovian moon Io in 2023 and 2024 after flybys of
Ganymede in 2021 and
Europa
Europa may refer to:
Places
* Europe
* Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace
* Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro
* Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development
* Europa Cliff ...
in 2022. ''
Voyager 1'' and ''
Voyager 2'' continue to provide science data back to Earth while continuing on their outward journeys into interstellar space.
On November 26, 2011, NASA's
Mars Science Laboratory mission was successfully launched for Mars. The ''
Curiosity'' rover successfully landed on Mars on August 6, 2012, and subsequently began its search for evidence of past or present life on Mars.
In September 2014, NASA's ''
MAVEN'' spacecraft, which is part of the
Mars Scout Program
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphe ...
, successfully entered Mars orbit and, as of October 2022, continues its study of the
atmosphere of Mars.
NASA's ongoing Mars investigations include in-depth surveys of Mars by the ''
Perseverance'' rover and ''
InSight'').
NASA's ''
Europa Clipper'', planned for launch in October 2024, will study the Galilean moon Europa through a series of flybys while in orbit around Jupiter. ''
Dragonfly
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threate ...
'' will send a mobile robotic
rotorcraft to Saturn's biggest moon,
Titan
Titan most often refers to:
* Titan (moon), the largest moon of Saturn
* Titans, a race of deities in Greek mythology
Titan or Titans may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Fictional entities
Fictional locations
* Titan in fiction, fictiona ...
. As of May 2021, ''Dragonfly'' is scheduled for launch in June 2027.
Astrophysics missions

The NASA Science Mission Directorate Astrophysics division manages the agency's astrophysics science portfolio. NASA has invested significant resources in the development, delivery, and operations of various forms of space telescopes. These telescopes have provided the means to study the cosmos over a large range of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The Great Observatories that were launched in the 1980s and 1990s have provided a wealth of observations for study by physicists across the planent. The first of them, the
Hubble Space Telescope, was delivered to orbit in 1990 and continues to function, in part due to prior servicing missions performed by the Space Shuttle. The other remaining active great observatory include the
Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), launched by
STS-93 in July 1999 and is now in a 64-hour
elliptical orbit studying X-ray sources that are not readily viewable from terrestrial observatories.

The
Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer
Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer, commonly known as IXPE or SMEX-14, is a space observatory with three identical telescopes designed to measure the polarization of cosmic X-rays of black holes, neutron stars, and pulsars. The observatory ...
(IXPE) is a space observatory designed to improve the understanding of X-ray production in objects such as neutron stars and pulsar wind nebulae, as well as stellar and supermassive black holes. IXPE launched in December 2021 and is an international collaboration between NASA and the
Italian Space Agency (ASI). It is part of the NASA
Small Explorers program (SMEX) which designs low-cost spacecraft to study heliophysics and astrophysics.
The
Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory
Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory, previously called the Swift Gamma-Ray Burst Explorer, is a NASA three-telescope space observatory for studying gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) and monitoring the afterglow in X-ray, and UV/Visible light at the location o ...
was launched in November 2004 and is Gamma-ray burst observatory that also monitors the afterglow in X-ray, and UV/Visible light at the location of a burst. The mission was developed in a joint partnership between
Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC empl ...
(GSFC) and an international consortium from the United States, United Kingdom, and Italy.
Pennsylvania State University
The Pennsylvania State University (Penn State or PSU) is a Public university, public Commonwealth System of Higher Education, state-related Land-grant university, land-grant research university with campuses and facilities throughout Pennsylvan ...
operates the mission as part of NASA's
Medium Explorer program (MIDEX).
The
Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope (FGST) is another gamma-ray focused space observatory that was launched to
low Earth orbit in June 2008 and is being used to perform
gamma-ray astronomy observations. In addition to NASA, the mission involves the
United States Department of Energy, and government agencies in France, Germany, Italy, Japan, and Sweden.
The
James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Spa ...
(JWST), launched in December 2021 on an
Ariane 5
Ariane 5 is a European heavy-lift space launch vehicle developed and operated by Arianespace for the European Space Agency (ESA). It is launched from the Centre Spatial Guyanais (CSG) in French Guiana. It has been used to deliver payloads int ...
rocket, operates in a
halo orbit
A halo orbit is a periodic, three-dimensional orbit near one of the L1, L2 or L3 Lagrange points in the three-body problem of orbital mechanics. Although a Lagrange point is just a point in empty space, its peculiar characteristic is that it ca ...
circling the Sun-Earth point.
JWST's high sensitivity in the infrared spectrum and its imaging resolution will allow it to view more distant, faint, or older objects than its predecessors, including Hubble.
Earth Sciences Program missions (1965–present)
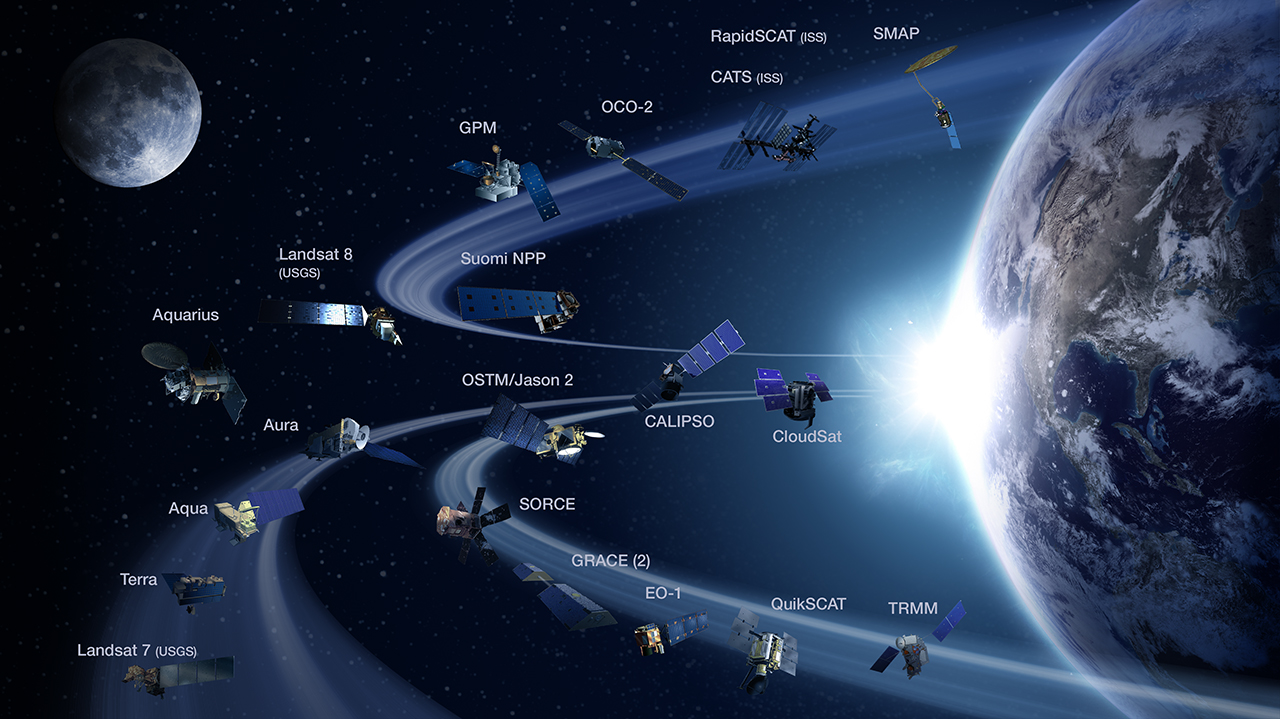
NASA Earth Science is a large, umbrella program comprising a range of terrestrial and space-based collection systems in order to better understand the Earth system and its response to natural and human-caused changes. Numerous systems have been developed and fielded over several decades to provide improved prediction for weather, climate, and other changes in the natural environment. Several of the current operating spacecraft programs include:
Aqua,
Aura
Aura most commonly refers to:
* Aura (paranormal), a field of luminous multicolored radiation around a person or object
* Aura (symptom), a symptom experienced before a migraine or seizure
Aura may also refer to:
Places Extraterrestrial
* 1488 ...
,
Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2 (OCO-2),
Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-on (GRACE FO), and
Ice, Cloud, and land Elevation Satellite 2 (ICESat-2).
In addition to systems already in orbit, NASA is designing a new set of Earth Observing Systems to study, assess, and generate responses for climate change, natural hazards, forest fires, and real-time agricultural processes. The GOES-T satellite (designated
GOES-18 after launch) joined the fleet of U.S. geostationary weather monitoring satellites in March 2022.
NASA also maintains the Earth Science Data Systems (ESDS) program to oversee the life cycle of NASA's Earth science data — from acquisition through processing and distribution. The primary goal of ESDS is to maximize the scientific return from NASA's missions and experiments for research and applied scientists, decision makers, and society at large.
The Earth Science program is managed by the Earth Science Division of the NASA Science Mission Directorate.
Space operations architecture
NASA invests in various ground and space-based infrastructures to support its science and exploration mandate. The agency maintains access to suborbital and orbital space launch capabilities and sustains ground station solutions to support its evolving fleet of spacecraft and remote systems.
Deep Space Network (1963–present)
The ''NASA Deep Space Network'' (''DSN'') serves as the primary ground station solution for NASA's interplanetary spacecraft and select Earth-orbiting missions.
The system employs ground station complexes near Barstow California in the United States, in Spain near Madrid, and in Australia near Canberra. The placement of these ground stations approximately 120 degrees apart around the planet provides the ability for communications to spacecraft throughout the
Solar System even as the Earth rotates about its axis on a daily basis. The system is controlled at a 24x7 operations center at JPL in Pasadena California which manages recurring communications linkages with up to 40 spacecraft. The system is managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL).
[
]
Near Space Network (1983–present)
 The Near Space Network (NSN) provides telemetry, commanding, ground-based tracking, data and communications services to a wide range of customers with satellites in low earth orbit (LEO), geosynchronous orbit (GEO), highly elliptical orbits (HEO), and lunar orbits. The NSN accumulates ground station and antenna assets from the Near-Earth Network and the '' Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System'' (''TDRS'') which operates in geosynchronous orbit providing continuous real-time coverage for launch vehicles and low earth orbit NASA missions.
The NSN consists of 19 ground stations worldwide operated by the US Government and by contractors including Kongsberg Satellite Services (KSAT), Swedish Space Corporation (SSC), and South African National Space Agency (SANSA). The ground network averages between 120 and 150 spacecraft contacts a day with TDRS engaging with systems on a near-continuous basis as needed; the system is managed and operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center.
The Near Space Network (NSN) provides telemetry, commanding, ground-based tracking, data and communications services to a wide range of customers with satellites in low earth orbit (LEO), geosynchronous orbit (GEO), highly elliptical orbits (HEO), and lunar orbits. The NSN accumulates ground station and antenna assets from the Near-Earth Network and the '' Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System'' (''TDRS'') which operates in geosynchronous orbit providing continuous real-time coverage for launch vehicles and low earth orbit NASA missions.
The NSN consists of 19 ground stations worldwide operated by the US Government and by contractors including Kongsberg Satellite Services (KSAT), Swedish Space Corporation (SSC), and South African National Space Agency (SANSA). The ground network averages between 120 and 150 spacecraft contacts a day with TDRS engaging with systems on a near-continuous basis as needed; the system is managed and operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center.
Sounding Rocket Program (1959–present)
 The ''NASA Sounding Rocket Program'' (''NSRP'') is located at the
The ''NASA Sounding Rocket Program'' (''NSRP'') is located at the Wallops Flight Facility
Wallops Flight Facility (WFF) is a rocket launch site on Wallops Island on the Eastern Shore of Virginia, United States, just east of the Delmarva Peninsula and approximately north-northeast of Norfolk. The facility is operated by the Goddard ...
and provides launch capability, payload development and integration, and field operations support to execute suborbital missions.[
In June 2022, NASA conducted its first rocket launch from a commercial spaceport outside the US. It launched a ]Black Brant IX
The Black Brant is a family of Canadian-designed sounding rockets originally built by Bristol Aerospace, since absorbed by Magellan Aerospace in Winnipeg, Manitoba. Over 800 Black Brants of various versions have been launched since they were firs ...
from the Arnhem Space Centre in Australia.
Launch Services Program (1990–present)
The NASA Launch Services Program (LSP) is responsible for procurement of launch services for NASA uncrewed missions and oversight of launch integration and launch preparation activity, providing added quality and mission assurance to meet program objectives. Since 1990, NASA has purchased expendable launch vehicle launch services directly from commercial providers, whenever possible, for its scientific and applications missions. Expendable launch vehicles can accommodate all types of orbit inclinations and altitudes and are ideal vehicles for launching Earth-orbit and interplanetary missions. LSP operates from Kennedy Space Center and falls under the NASA Space Operations Mission Directorate (SOMD).
Aeronautics Research
The ''Aeronautics Research Mission Directorate'' (''ARMD'') is one of five mission directorate
Directorate may refer to:
Contemporary
*Directorates of the Scottish Government
* Directorate-General, a type of specialised administrative body in the European Union
* Directorate-General for External Security, the French external intelligence ag ...
s within NASA, the other four being the Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate, the Space Operations Mission Directorate, the Science Mission Directorate
The Science Mission Directorate (SMD) of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) engages the United States’ science community, sponsors scientific research, and develops and deploys satellites and probes in collaboration with NAS ...
, and the Space Technology Mission Directorate. The ARMD is responsible for NASA's aeronautical
Aeronautics is the science or art involved with the study, design, and manufacturing of air flight–capable machines, and the techniques of operating aircraft and rockets within the atmosphere. The British Royal Aeronautical Society identifies ...
research, which benefits the commercial, military, and general aviation sectors. ARMD performs its aeronautics research at four NASA facilities: Ames Research Center and Armstrong Flight Research Center
The NASA Neil A. Armstrong Flight Research Center (AFRC) is an aeronautical research center operated by NASA. Its primary campus is located inside Edwards Air Force Base in California and is considered NASA's premier site for aeronautical res ...
in California, Glenn Research Center in Ohio, and Langley Research Center
The Langley Research Center (LaRC or NASA Langley), located in Hampton, Virginia, United States of America, is the oldest of NASA's field centers. It directly borders Langley Air Force Base and the Back River on the Chesapeake Bay. LaRC has fo ...
in Virginia.
NASA X-57 Maxwell aircraft (2016–present)
The ''NASA X-57 Maxwell'' is an experimental aircraft being developed by NASA to demonstrate the technologies required to deliver a highly efficient all-electric aircraft. The primary goal of the program is to develop and deliver all-electric technology solutions that can also achieve airworthiness certification with regulators. The program involves development of the system in several phases, or modifications, to incrementally grow the capability and operability of the system. The initial configuration of the aircraft has now completed ground testing as it approaches its first flights. In mid-2022, the X-57 was scheduled to fly before the end of the year. The development team includes staff from the NASA Armstrong, Glenn, and Langley centers along with number of industry partners from the United States and Italy.
Next Generation Air Transportation System (2007–present)
NASA is collaborating with the Federal Aviation Administration and industry stakeholders to modernize the United States National Airspace System (NAS). Efforts began in 2007 with a goal to deliver major modernization components by 2025.[ NASA contributions also include development of advanced automation concepts and tools that provide air traffic controllers, pilots, and other airspace users with more accurate real-time information about the nation's traffic flow, weather, and routing. Ames' advanced airspace modeling and simulation tools have been used extensively to model the flow of air traffic flow across the U.S., and to evaluate new concepts in airspace design, traffic flow management, and optimization.
]
Technology research
Nuclear in-space power and propulsion (ongoing)
NASA has made use of technologies such as the multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator
The multi-mission radioisotope thermoelectric generator (MMRTG) is a type of radioisotope thermoelectric generator (RTG) developed for NASA space missions such as the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), under the jurisdiction of the United States Depar ...
(MMRTG), which is a type of radioisotope thermoelectric generator used to power spacecraft. Shortages of the required plutonium-238 have curtailed deep space missions since the turn of the millennium.U.S. Department of Energy
The United States Department of Energy (DOE) is an executive department of the U.S. federal government that oversees U.S. national energy policy and manages the research and development of nuclear power and nuclear weapons in the United States. ...
. NASA's space nuclear technologies portfolio are led and funded by its Space Technology Mission Directorate.
Other initiatives
''Free Space Optics''. NASA contracted a third party to study the probability of using Free Space Optics (FSO) to communicate with Optical ( laser) Stations on the Ground (OGS) called laser-com RF networks for satellite communications.
''Water Extraction from Lunar Soil''. On July 29, 2020, NASA requested American universities to propose new technologies for extracting water from the lunar soil and developing power systems. The idea will help the space agency conduct sustainable
Specific definitions of sustainability are difficult to agree on and have varied in the literature and over time. The concept of sustainability can be used to guide decisions at the global, national, and individual levels (e.g. sustainable livin ...
exploration of the Moon.
Human Spaceflight Research (2005–present)
 NASA's
NASA's Human Research Program
The Human Research Program (HRP) was created in October 2005 at Johnson Space Center (JSC) in response to NASA's desire to move human research project management away from headquarters to the JSC. The HRP is an applied research and technology p ...
(HRP) is designed to study the effects of space on human health and also to provide countermeasures and technologies for human space exploration. The medical effects of space exploration are reasonably limited in low Earth orbit or in travel to the Moon. Travel to Mars, however, is significantly longer and deeper into space and significant medical issues can result. This includes bone loss, radiation exposure, vision changes, circadian rhythm disturbances, heart remodeling, and immune alterations. In order to study and diagnose these ill-effects, HRP has been tasked with identifying or developing small portable instrumentation with low mass, volume, and power to monitor the health of astronauts. To achieve this aim, on May 13, 2022, NASA and SpaceX Crew-4 astronauts successfully tested its rHEALTH ONE universal biomedical analyzer for its ability to identify and analyzer biomarkers, cells, microorganisms, and proteins in a spaceflight environment.
Planetary Defense (2016–present)
NASA established the Planetary Defense Coordination Office (''PDCO'') in 2016 to catalog and track potentially hazardous near-Earth objects (NEO), such as asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
s and comets and develop potential responses and defenses against these threats. The PDCO is chartered to provide timely and accurate information to the government and the public on close approaches by Potentially hazardous objects (PHOs) and any potential for impact. The office functions within the Science Mission Directorate Planetary Science division.
The PDCO augmented prior cooperative actions between the United States, the European Union, and other nations which had been scanning the sky for NEOs since 1998 in an effort called Spaceguard.
Near Earth object detection (1998–present)
From the 1990s NASA has run many NEO detection programs from Earth bases observatories, greatly increasing the number of objects that have been detected. However, many asteroids are very dark and the ones that are near the Sun are much harder to detect from Earth-based telescopes which observe at night, and thus face away from the Sun. NEOs inside Earth orbit only reflect a part of light also rather than potentially a "full Moon" when they are behind the Earth and fully lit by the Sun.
In 1998, the United States Congress gave NASA a mandate to detect 90% of near-Earth asteroids over diameter (that threaten global devastation) by 2008. This initial mandate was met by 2011. In 2005, the original USA Spaceguard mandate was extended by the George E. Brown, Jr.
George Edward Brown Jr. (March 6, 1920 – July 15, 1999) was an American Democratic Party (United States), Democratic politician from California. He represented suburban portions of Los Angeles County, California, Los Angeles County in the United ...
Near-Earth Object Survey Act, which calls for NASA to detect 90% of NEOs with diameters of or greater, by 2020 (compare to the 20-meter Chelyabinsk meteor
The Chelyabinsk meteor was a superbolide that entered Earth's atmosphere over the southern Ural (region), Ural region in Russia on 15 February 2013 at about 09:20 Yekaterinburg Time, YEKT (03:20 Coordinated Universal Time, UTC). It was caused ...
that hit Russia in 2013).
Involvement in current robotic missions
NASA has incorporated planetary defense objectives into several ongoing missions.
In 1999, NASA visited 433 Eros
Eros (minor planet designation: (433) Eros), provisional designation is a stony asteroid of the Amor group and the first discovered and second-largest near-Earth object with an elongated shape and a mean diameter of approximately . Visi ...
with the '' NEAR Shoemaker'' spacecraft which entered its orbit in 2000, closely imaging the asteroid with various instruments at that time. ''NEAR Shoemaker'' became the first spacecraft to successfully orbit and land on an asteroid, improving our understanding of these bodies and demonstrating our capacity to study them in greater detail.Dimorphos
(65803) Didymos I Dimorphos (provisional designation S/2003 (65803) 1) is a minor-planet moon of the near-Earth asteroid 65803 Didymos, with which it forms a binary system. It has a diameter of and has been characterised as a low-density rubb ...
asteroid. Scientists were seeking to determine whether an impact could alter the subsequent path of the asteroid; a concept that could be applied to future planetary defense. On September 26, 2022, DART hit its target. In the weeks following impact, NASA declared DART a success, confirming it had shortened Dimorphos' orbital period around Didymos by about 32 minutes, surpassing the pre-defined success threshold of 73 seconds.
NEO Surveyor, formerly called the Near-Earth Object Camera (NEOCam) mission, is a space-based infrared telescope under development to survey the Solar System for potentially hazardous asteroids
A potentially hazardous object (PHO) is a near-Earth object – either an asteroid or a comet – with an orbit that can make close approaches to the Earth and is large enough to cause significant regional damage in the event of impact. They are ...
. The spacecraft is scheduled to launch in 2026.
Study of Unidentified Aerial Phenomena (2022–present)
In June 2022, the head of the NASA Science Mission Directorate
The Science Mission Directorate (SMD) of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) engages the United States’ science community, sponsors scientific research, and develops and deploys satellites and probes in collaboration with NAS ...
, Thomas Zurbuchen
Thomas Hansueli Zurbuchen (born 1968) is a Swiss-American astrophysicist. From October 2016 until the end of 2022, he was the longest continually running Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate at NASA. Prior to this, he was ...
, confirmed that NASA would join the hunt for Unidentified Flying Objects (UFOs)/Unidentified Aerial Phenomena (UAPs). At a speech before the National Academies of Science, Engineering and Medicine, Zurbuchen said the space agency would bring a scientific perspective to efforts already underway by the Pentagon and intelligence agencies to make sense of dozens of such sightings. He said it was "high-risk, high-impact" research that the space agency should not shy away from, even if it is a controversial field of study.
Collaboration
NASA Advisory Council
In response to the Apollo 1 accident, which killed three astronauts in 1967, Congress directed NASA to form an Aerospace Safety Advisory Panel (ASAP) to advise the NASA Administrator on safety issues and hazards in NASA's air and space programs. In the aftermath of the Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster, Congress required that the ASAP submit an annual report to the NASA Administrator and to Congress. By 1971, NASA had also established the Space Program Advisory Council and the Research and Technology Advisory Council to provide the administrator with advisory committee support. In 1977, the latter two were combined to form the NASA Advisory Council (NAC).NASA Authorization Act of 2014
The NASA Authorization Act of 2014 () is a bill that would authorization bill, authorize the appropriations bill (United States), appropriation of $17.6 billion in fiscal year 2014 to the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). NASA ...
reaffirmed the importance of ASAP.
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)
NASA and NOAA have cooperated for decades on the development, delivery and operation of polar and geosynchronous weather satellites. The relationship typically involves NASA developing the space systems, launch solutions, and ground control technology for the satellites and NOAA operating the systems and delivering weather forecasting products to users. Multiple generations of NOAA Polar orbiting platforms have operated to provide detailed imaging of weather from low altitude. Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) provide near-real-time coverage of the western hemisphere to ensure accurate and timely understanding of developing weather phenomenon.
United States Space Force
The United States Space Force (USSF) is the space service branch of the United States Armed Forces, while the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) is an independent agency of the United States government responsible for civil spaceflight. NASA and the Space Force's predecessors in the Air Force have a long-standing cooperative relationship, with the Space Force supporting NASA launches out of Kennedy Space Center, Cape Canaveral Space Force Station, and Vandenberg Space Force Base, to include range support and rescue operations from Task Force 45. NASA and the Space Force also partner on matters such as defending Earth from asteroids. Space Force members can be NASA astronauts, with Colonel Michael S. Hopkins
Michael Scott Hopkins (born December 28, 1968) is a United States Space Force colonel and NASA astronaut. Hopkins was selected in June 2009 as a member of the NASA Astronaut Group 20. He made his first spaceflight as a Flight Engineer on Soyu ...
, the commander of SpaceX Crew-1, commissioned into the Space Force from the International Space Station on December 18, 2020.
U.S. Geological Survey
The Landsat program is the longest-running enterprise for acquisition of satellite imagery
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell ima ...
of Earth. It is a joint NASA / USGS program.Earth Resources Technology Satellite
Landsat 1 (LS-1), formerly named ERTS-A and ERTS-1, was the first satellite of the United States' Landsat program. It was a modified version of the Nimbus 4 Meteorology, meteorological satellite and was launched on July 23, 1972, by a Delta 01 ...
'' was launched. This was eventually renamed to '' Landsat 1'' in 1975. The most recent satellite in the series, ''Landsat 9
Landsat 9 is an Earth observation satellite launched on 27 September 2021 from Space Launch Complex-3E at Vandenberg Space Force Base on an Atlas V 401 launch vehicle. NASA is in charge of building, launching, and testing the satellite, while ...
'', was launched on September 27, 2021.
The instruments on the Landsat satellites have acquired millions of images. The images, archived in the United States and at Landsat receiving stations around the world, are a unique resource for global change research and applications in agriculture, cartography, geology, forestry, regional planning, surveillance
Surveillance is the monitoring of behavior, many activities, or information for the purpose of information gathering, influencing, managing or directing. This can include observation from a distance by means of electronic equipment, such as c ...
and education, and can be viewed through the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS) "EarthExplorer" website. The collaboration between NASA and USGS involves NASA designing and delivering the space system (satellite) solution, launching the satellite into orbit with the USGS operating the system once in orbit.[ As of October 2022, nine satellites have been built with eight of them successfully operating in orbit.
]
European Space Agency (ESA)
NASA collaborates with the European Space Agency on a wide range of scientific and exploration requirements. From participation with the Space Shuttle (the Spacelab missions) to major roles on the Artemis program (the Orion Service Module), ESA and NASA have supported the science and exploration missions of each agency. There are NASA payloads on ESA spacecraft and ESA payloads on NASA spacecraft. The agencies have developed joint missions in areas including heliophysics (e.g. Solar Orbiter) and astronomy ( Hubble Space Telescope, James Webb Space Telescope
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space telescope which conducts infrared astronomy. As the largest optical telescope in space, its high resolution and sensitivity allow it to view objects too old, distant, or faint for the Hubble Spa ...
).
Under the Artemis Gateway partnership, ESA will contribute habitation and refueling modules, along with enhanced lunar communications, to the Gateway.
NASA and ESA continue to advance cooperation in relation to Earth Science including climate change with agreements to cooperate on various missions including the Sentinel-6
The Sentinel-6 Michael Freilich (S6MF) is a radar altimeter satellite developed in partnership between several European and American organizations. It is part of the Jason satellite series and is named after Michael Freilich. S6MF includes ...
series of spacecraft
Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA)
NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency
The is the Japanese national air and space agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on 1 October 2003. JAXA is responsible for research, technology development and launch of satellites into orb ...
(JAXA) cooperate on a range of space projects. JAXA is a direct participant in the Artemis program, including the Lunar Gateway effort. JAXA's planned contributions to Gateway include I-Hab's environmental control and life support system, batteries, thermal control, and imagery components, which will be integrated into the module by the European Space Agency (ESA) prior to launch. These capabilities are critical for sustained Gateway operations during crewed and uncrewed time periods.
JAXA and NASA have collaborated on numerous satellite programs, especially in areas of Earth science. NASA has contributed to JAXA satellites and vice versa. Japanese instruments are flying on NASA's Terra and Aqua satellites, and NASA sensors have flown on previous Japanese Earth-observation missions. The NASA-JAXA Global Precipitation Measurement
Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) is a joint mission between JAXA and NASA as well as other international space agencies to make frequent (every 2–3 hours) observations of Earth's precipitation. It is part of NASA's Earth Systematic Missions ...
mission was launched in 2014 and includes both NASA- and JAXA-supplied sensors on a NASA satellite launched on a JAXA rocket. The mission provides the frequent, accurate measurements of rainfall over the entire globe for use by scientists and weather forecasters.
Roscosmos
NASA and Roscosmos have cooperated on the development and operation of the International Space Station since September 1993. The agencies have used launch systems from both countries to deliver station elements to orbit. Astronauts and Cosmonauts jointly maintain various elements of the station. Both countries provide access to the station via launch systems noting Russia's unique role as the sole provider of delivery of crew and cargo upon retirement of the space shuttle in 2011 and prior to commencement of NASA COTS and crew flights. In July 2022, NASA and Roscosmos signed a deal to share space station flights enabling crew from each country to ride on the systems provided by the other. Current geopolitical conditions in late 2022 make it unlikely that cooperation will be extended to other programs such as Artemis or lunar exploration.
Indian Space Research Organisation
In September 2014, NASA and Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO)
The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO; ) is the national space agency of India, headquartered in Bengaluru. It operates under the Department of Space (DOS) which is directly overseen by the Prime Minister of India, while the Chairman of ...
signed a partnership to collaborate on and launch a joint radar mission, the '' NASA-ISO Synthetic Aperature Radar'' (''NISAR
The NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission is a joint project between NASA and ISRO to co-develop and launch a dual-frequency synthetic aperture radar on an Earth observation satellite. The satellite will be the first radar imaging ...
'') mission. The mission is targeted to launch in 2024. NASA will provide the mission's L-band synthetic aperture radar, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder and payload data subsystem. ISRO provides the spacecraft bus, the S-band radar, the launch vehicle and associated launch services.
Artemis Accords
The Artemis Accords
The Artemis Accords are a series of non-binding multilateral agreements between the United States government and other world governments participating in the Artemis Program, an American-led effort to return humans to the Moon by 2025, with the u ...
have been established to define a framework for cooperating in the peaceful exploration and exploitation of the Moon, Mars, asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
s, and comets. The Accords were drafted by NASA and the U.S. State Department and are executed as a series of bilateral agreements between the United States and the participating countries. As of September 2022, 21 countries have signed the accords. They are Australia, Bahrain, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, France, Israel, Italy, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Luxembourg, Mexico, New Zealand, Poland, Romania, the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, Singapore, Ukraine, the United Arab Emirates, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
China National Space Administration
The Wolf Amendment was passed by the U.S. Congress into law in 2011 and prevents NASA from engaging in direct, bilateral cooperation with the Chinese government and China-affiliated organizations such as the China National Space Administration without the explicit authorization from Congress and the Federal Bureau of Investigation. The law has been renewed annually since by inclusion in annual appropriations bills.
Management
Leadership
The agency's administration is located at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC, and provides overall guidance and direction.
Strategic plan
NASA operates with four FY2022 strategic goals.
Budget
NASA budget requests are developed by NASA and approved by the administration prior to submission to the U.S. Congress. Authorized budgets are those that have been included in enacted appropriations bills that are approved by both houses of Congress and enacted into law by the U.S. president.
NASA fiscal year budget requests and authorized budgets are provided below.
Organization
NASA funding and priorities are developed through its six Mission Directorates.
Center-wide activities such as the Chief Engineer and Safety and Mission Assurance organizations are aligned to the headquarters function. The MSD budget estimate includes funds for these HQ functions. The administration operates 10 major field centers with several managing additional subordinate facilities across the country. Each is led by a Center Director (data below valid as of September 1, 2022).
Sustainability
Environmental impact
The exhaust gases produced by rocket propulsion systems, both in Earth's atmosphere and in space, can adversely affect the Earth's environment. Some hypergolic rocket propellants, such as hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ...
, are highly toxic prior to combustion, but decompose into less toxic compounds after burning. Rockets using hydrocarbon fuels, such as kerosene, release carbon dioxide and soot in their exhaust.LH2
Liquid hydrogen (LH2 or LH2) is the liquid state of the element hydrogen. Hydrogen is found naturally in the molecular H2 form.
To exist as a liquid, H2 must be cooled below its critical point of 33 K. However, for it to be in a fully liq ...
- fueled engines, like the SSME
The Aerojet Rocketdyne RS-25, also known as the Space Shuttle Main Engine (SSME), is a liquid-fuel cryogenic rocket engine that was used on NASA's Space Shuttle and is currently used on the Space Launch System (SLS).
Designed and manufacture ...
, is almost entirely water vapor.ion engines
An ion thruster, ion drive, or ion engine is a form of electric propulsion used for spacecraft propulsion. It creates thrust by accelerating ions using electricity.
An ion thruster ionizes a neutral gas by extracting some electrons out of ...
use harmless noble gases like xenon for propulsion.Environmental Protection Agency
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale f ...
recognized NASA as the first federal agency to directly use landfill gas
Landfill gas is a mix of different gases created by the action of microorganisms within a landfill as they decompose organic waste, including for example, food waste and paper waste. Landfill gas is approximately forty to sixty percent methane, ...
to produce energy at one of its facilities—the Goddard Space Flight Center
The Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) is a major NASA space research laboratory located approximately northeast of Washington, D.C. in Greenbelt, Maryland, United States. Established on May 1, 1959 as NASA's first space flight center, GSFC empl ...
, Greenbelt, Maryland.
In 2018, NASA along with other companies including Sensor Coating Systems, Pratt & Whitney
Pratt & Whitney is an American aerospace manufacturer with global service operations. It is a subsidiary of Raytheon Technologies. Pratt & Whitney's aircraft engines are widely used in both civil aviation (especially airlines) and military aviat ...
, Monitor Coating and UTRC launched the project CAUTION (CoAtings for Ultra High Temperature detectION). This project aims to enhance the temperature range of the Thermal History Coating up to and beyond. The final goal of this project is improving the safety of jet engines as well as increasing efficiency and reducing CO2 emissions.
Climate change
NASA also researches and publishes on climate change. Its statements concur with the global scientific consensus that the global climate is warming. Bob Walker, who has advised US President Donald Trump on space issues, has advocated that NASA should focus on space exploration and that its climate study operations should be transferred to other agencies such as NOAA
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditio ...
. Former NASA atmospheric scientist J. Marshall Shepherd countered that Earth science study was built into NASA's mission at its creation in the 1958 National Aeronautics and Space Act. NASA won the 2020 Webby People's Voice Award for Green in the category Web.
STEM Initiatives
'' Educational Launch of Nanosatellites (ELaNa)''. Since 2011, the ELaNa program has provided opportunities for NASA to work with university teams to test emerging technologies and commercial-off-the-shelf solutions by providing launch opportunities for developed CubeSats using NASA procured launch opportunities. By example, two NASA-sponsored CubeSats
A CubeSat is a class of miniaturized satellite based around a form factor consisting of cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than per unit, and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats ...
launched in June 2022 on a Virgin Orbit LauncherOne vehicle as the ELaNa 39 mission.
''Cubes in Space''. NASA started an annual competition in 2014 named "Cubes in Space". It is jointly organized by NASA and the global education company ''I Doodle Learning'', with the objective of teaching school students aged 11–18 to design and build scientific experiments to be launched into space on a NASA rocket or balloon. On June 21, 2017, the world's smallest satellite, KalamSAT, was launched.
Use of the metric system
US law requires the International System of Units
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most widely used system of measurement. E ...
to be used in all US Government programs, "except where impractical".
In 1969, Apollo 11 landed on the Moon using a mix of United States customary units
United States customary units form a system of measurement units commonly used in the United States and U.S. territories since being standardized and adopted in 1832. The United States customary system (USCS or USC) developed from English units ...
and metric units. In the 1980s, NASA started the transition towards the metric system, but was still using both systems in the 1990s. On September 23, 1999, a mixup between NASA's use of SI units and Lockheed Martin Space's use of US units resulted in the loss of the Mars Climate Orbiter.
In August 2007, NASA stated that all future missions and explorations of the Moon would be done entirely using the SI system. This was done to improve cooperation with space agencies of other countries that already use the metric system. As of 2007, NASA is predominantly working with SI units, but some projects still use US units, and some, including the International Space Station, use a mix of both.
Media presence
NASA TV
Approaching 40 years of service, the NASA TV channel airs content ranging from live coverage of crewed missions to video coverage of significant milestones for operating robotic spacecraft (e.g., rover landings on Mars for example) and domestic and international launches. The channel is delivered by NASA and is broadcast by satellite and over the Internet. The system initially started to capture archival footage of important space events for NASA managers and engineers and expanded as public interest grew. The Apollo 8
Apollo 8 (December 21–27, 1968) was the first crewed spacecraft to leave low Earth orbit and the first human spaceflight to reach the Moon. The crew orbited the Moon ten times without landing, and then departed safely back to Earth. These ...
Christmas Eve broadcast while in orbit around the Moon was received by more than a billion people. NASA's video transmission of the Apollo 11 Moon landing was awarded a primetime Emmy in commemoration of the 40th anniversary of the landing. The channel is a product of the U.S. Government and is widely available across many television and Internet platforms.
NASAcast
NASAcast is the official audio and video podcast of the NASA website. Created in late 2005, the podcast service contains the latest audio and video features from the NASA web site, including NASA TV's ''This Week at NASA'' and educational materials produced by NASA. Additional NASA podcasts, such as Science@NASA, are also featured and give subscribers an in-depth look at content by subject matter.
NASA EDGE
 NASA EDGE is a video podcast which explores different missions, technologies and projects developed by NASA. The program was released by NASA on March 18, 2007, and, , there have been 200 vodcasts produced. It is a
NASA EDGE is a video podcast which explores different missions, technologies and projects developed by NASA. The program was released by NASA on March 18, 2007, and, , there have been 200 vodcasts produced. It is a public outreach
Outreach is the activity of providing services to any population that might not otherwise have access to those services. A key component of outreach is that the group providing it is not stationary, but mobile; in other words, it involves meetin ...
vodcast sponsored by NASA's Exploration Systems Mission Directorate and based out of the Exploration and Space Operations Directorate at Langley Research Center
The Langley Research Center (LaRC or NASA Langley), located in Hampton, Virginia, United States of America, is the oldest of NASA's field centers. It directly borders Langley Air Force Base and the Back River on the Chesapeake Bay. LaRC has fo ...
in Hampton, Virginia. The NASA EDGE team takes an insiders look at current projects and technologies from NASA facilities around the United States, and it is depicted through personal interviews, on-scene broadcasts, computer animation
Computer animation is the process used for digitally generating animations. The more general term computer-generated imagery (CGI) encompasses both static scenes (still images) and dynamic images (moving images), while computer animation refe ...
s, and personal interviews with top scientists and engineers at NASA.
The show explores the contributions NASA has made to society as well as the progress of current projects in materials and space exploration
Space exploration is the use of astronomy and space technology to explore outer space. While the exploration of space is carried out mainly by astronomers with telescopes, its physical exploration though is conducted both by robotic spacec ...
. NASA EDGE vodcasts can be downloaded from the NASA website and from iTunes
iTunes () is a software program that acts as a media player, media library, mobile device management utility, and the client app for the iTunes Store. Developed by Apple Inc., it is used to purchase, play, download, and organize digital mul ...
.
In its first year of production, the show was downloaded over 450,000 times. the average download rate is more than 420,000 per month, with over one million downloads in December 2009 and January 2010.
Astronomy Picture of the Day
Gallery
See also
* List of crewed spacecraft
* List of NASA aircraft
* List of space disasters
This article lists verifiable spaceflight-related accidents and incidents resulting in human fatality or near-fatality during flight or training for crewed space missions, and testing, assembly, preparation or flight of crewed and robotic space ...
*
* : NASA people
*
*
*
*
Explanatory notes
References
Further reading
* Alexander, Joseph K. ''Science Advice to NASA: Conflict, Consensus, Partnership, Leadership'' (2019
excerpt
* Bizony, Piers et al. ''The NASA Archives. 60 Years in Space'' (2019)
* Brady, Kevin M. "NASA Launches Houston into Orbit How America's Space Program Contributed to Southeast Texas's Economic Growth, Scientific Development, and Modernization during the Late Twentieth Century." ''Journal of the West'' (2018) 57#4 pp 13–54.
* Bromberg, Joan Lisa. ''NASA and the Space Industry'' (Johns Hopkins UP, 1999).
* Clemons, Jack. ''Safely to Earth: The Men and Women Who Brought the Astronauts Home'' (2018
excerpt
* Dick, Steven J., and Roger D. Launius, eds. ''Critical Issues in the History of Spaceflight'' (NASA, 2006)
* Launius, Roger D. "Eisenhower, Sputnik, and the Creation of NASA." ''Prologue-Quarterly of the National Archives'' 28.2 (1996): 127–143.
* Pyle, Rod. ''Space 2.0: How Private Spaceflight, a Resurgent NASA, and International Partners are Creating a New Space Age'' (2019), overview of space exploratio
excerpt
* Spencer, Brett. "The Book and the Rocket: The Symbiotic Relationship between American Public Libraries and the Space Program, 1950–2015", ''Information & Culture'' 51, no. 4 (2016): 550–82.
* Weinzierl, Matthew. "Space, the final economic frontier." ''Journal of Economic Perspectives'' 32.2 (2018): 173–92
online
, review of economics literature
External links
*
*
*
NASA History Division
*
*
NODIS: NASA Online Directives Information System
*
NTRS: NASA Technical Reports Server
*
NASA History and the Challenge of Keeping the Contemporary Past
*
NASA podcasts
NASA Watch, an agency watchdog site
*
on howstuffworks.com
HowStuffWorks is an American commercial infotainment website founded by professor and author Marshall Brain, to provide its target audience an insight into the way many things work. The site uses various media to explain complex concepts, termino ...
{{Authority control
1958 establishments in Washington, D.C.
Articles containing video clips
Collier Trophy recipients
Government agencies established in 1958
Independent agencies of the United States government
Organizations based in Washington, D.C.
Webby Award winners
 NASA traces its roots to the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). Despite being the birthplace of aviation, by 1914 the United States recognized that it was far behind Europe in aviation capability. Determined to regain American leadership in aviation, Congress created the
NASA traces its roots to the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA). Despite being the birthplace of aviation, by 1914 the United States recognized that it was far behind Europe in aviation capability. Determined to regain American leadership in aviation, Congress created the  The Soviet Union's launch of
The Soviet Union's launch of  Plans for human spaceflight began in the U.S. Armed Forces prior to NASA's creation. The Air Force's Man in Space Soonest and the Army's Project Adam served as the foundation for Project Mercury, the first American program to put people in space. NASA established the Space Task Group to manage the program, which would conduct sub-orbital flights with the Army's Redstone rockets and orbital flights with the Air Force's Atlas launch vehicles. While NASA intended for its first astronauts to be civilians, President Eisenhower directed that they be selected from the military. The
Plans for human spaceflight began in the U.S. Armed Forces prior to NASA's creation. The Air Force's Man in Space Soonest and the Army's Project Adam served as the foundation for Project Mercury, the first American program to put people in space. NASA established the Space Task Group to manage the program, which would conduct sub-orbital flights with the Army's Redstone rockets and orbital flights with the Air Force's Atlas launch vehicles. While NASA intended for its first astronauts to be civilians, President Eisenhower directed that they be selected from the military. The  On May 5, 1961 Alan Shepard became the first American to enter space, performing a suborbital spaceflight in the ''Freedom 7''. This flight occurred less than a month after the Soviet Union's Yuri Gagarin became the first human in space, executing a full orbital spaceflight. NASA's first orbital spaceflight was conducted by
On May 5, 1961 Alan Shepard became the first American to enter space, performing a suborbital spaceflight in the ''Freedom 7''. This flight occurred less than a month after the Soviet Union's Yuri Gagarin became the first human in space, executing a full orbital spaceflight. NASA's first orbital spaceflight was conducted by  Escalations in the
Escalations in the  To manage the Apollo Program, NASA required a more rigorous approach than it applied to Project Mercury. Mirroring the Department of Defense's program management concept using redundant systems in building the first intercontinental ballistic missiles, NASA requested the Air Force assign Major General
To manage the Apollo Program, NASA required a more rigorous approach than it applied to Project Mercury. Mirroring the Department of Defense's program management concept using redundant systems in building the first intercontinental ballistic missiles, NASA requested the Air Force assign Major General  The Ranger Program was started in the 1950s as a response to Soviet lunar exploration but was generally considered to be a failure. The Lunar Orbiter program had greater success, mapping the surface in preparation for Apollo landings and measured Selenography, conducted meteoroid detection, and measured radiation levels. The Surveyor program conducted uncrewed lunar landings and takeoffs, as well as taking surface and regolith observations.
Despite the setback caused by the Apollo 1 fire, which killed three astronauts, the program proceeded.
The Ranger Program was started in the 1950s as a response to Soviet lunar exploration but was generally considered to be a failure. The Lunar Orbiter program had greater success, mapping the surface in preparation for Apollo landings and measured Selenography, conducted meteoroid detection, and measured radiation levels. The Surveyor program conducted uncrewed lunar landings and takeoffs, as well as taking surface and regolith observations.
Despite the setback caused by the Apollo 1 fire, which killed three astronauts, the program proceeded.  Wernher von Braun had advocated for NASA to develop a space station since the agency was created. In 1973, Following the end of the Apollo lunar missions NASA launched its first space station, Skylab, on the final launch of the Saturn V. Skylab repurposed a significant amount of former Apollo and Saturn hardware, with a repurposed Saturn V third stage serving as primary module for the space station. Damage to Skylab during launch required spacewalks by the first crew to make it habitable and operational. Skylab only hosted 9 missions and was decommissioned in 1974 and deorbited in 1979, two years prior to the Space Shuttle's launch and any possibility of boosting its orbit.
In 1975, the Apollo–Soyuz mission was the first ever international spaceflight and a major diplomatic accomplishment between the Cold War rivals. Flown in 1975, a U.S. Apollo spacecraft docked with a Soviet Soyuz capsule. It also was the last flight of the Apollo capsule.
Wernher von Braun had advocated for NASA to develop a space station since the agency was created. In 1973, Following the end of the Apollo lunar missions NASA launched its first space station, Skylab, on the final launch of the Saturn V. Skylab repurposed a significant amount of former Apollo and Saturn hardware, with a repurposed Saturn V third stage serving as primary module for the space station. Damage to Skylab during launch required spacewalks by the first crew to make it habitable and operational. Skylab only hosted 9 missions and was decommissioned in 1974 and deorbited in 1979, two years prior to the Space Shuttle's launch and any possibility of boosting its orbit.
In 1975, the Apollo–Soyuz mission was the first ever international spaceflight and a major diplomatic accomplishment between the Cold War rivals. Flown in 1975, a U.S. Apollo spacecraft docked with a Soviet Soyuz capsule. It also was the last flight of the Apollo capsule.
 During the 1960s, NASA started its
During the 1960s, NASA started its  NASA had been perusing spaceplanes since the 1960s, blending the administration's dual aeronautics and space missions. NASA viewed a spaceplane as part of a larger program, providing routine and economical logistical support to a
NASA had been perusing spaceplanes since the 1960s, blending the administration's dual aeronautics and space missions. NASA viewed a spaceplane as part of a larger program, providing routine and economical logistical support to a  NASA launched its first commercial satellites on the STS-5 mission and in 1984, the
NASA launched its first commercial satellites on the STS-5 mission and in 1984, the  Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, the Russian Federation and United States initaited the Shuttle-''Mir'' program. The first Russian cosmonaut flew on the STS-60 mission in 1994 and the ''Discovery'' rendezvoused, but did not dock with, the Russian '' Mir'' in the STS-63 mission. This was followed by ''Atlantis
Following the collapse of the Soviet Union, the Russian Federation and United States initaited the Shuttle-''Mir'' program. The first Russian cosmonaut flew on the STS-60 mission in 1994 and the ''Discovery'' rendezvoused, but did not dock with, the Russian '' Mir'' in the STS-63 mission. This was followed by ''Atlantis  NASA never gave up on the idea of a space station after Skylab's reentry in 1979. The agency began lobbing politicians to support building a space station as soon as the Space Shuttle began flying, selling it as an orbital laboratory, repair station, and a jumping off point for lunar and Mars missions. NASA found a strong advocate in President
NASA never gave up on the idea of a space station after Skylab's reentry in 1979. The agency began lobbing politicians to support building a space station as soon as the Space Shuttle began flying, selling it as an orbital laboratory, repair station, and a jumping off point for lunar and Mars missions. NASA found a strong advocate in President  In 1993, the Clinton Administration announced that the Space Station ''Freedom'' would become the International Space Station in an agreement with the Russian Federation. This allowed the Russians to maintain their space program through an infusion of American currency to maintain their status as one of the two premier space programs. While the United States built and launched the majority of the International Space Station, Russia, Canada, Japan, and the European Space Agency all contributed components. Despite NASA's insistence that costs would be kept at a budget of $17.4, they kept rising and NASA had to transfer funds from other programs to keep the International Space Station solvent. Ultimately, the total cost of the station was $150 billion, with the United States paying for two-thirds.Following the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster in 2003, NASA was forced to rely on Russian Soyuz launches for its astronauts and the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle accelerated the station's completion.
In the 1980s, right after the first flight of the Space Shuttle, NASA started a joint program with the Department of Defense to develop the
In 1993, the Clinton Administration announced that the Space Station ''Freedom'' would become the International Space Station in an agreement with the Russian Federation. This allowed the Russians to maintain their space program through an infusion of American currency to maintain their status as one of the two premier space programs. While the United States built and launched the majority of the International Space Station, Russia, Canada, Japan, and the European Space Agency all contributed components. Despite NASA's insistence that costs would be kept at a budget of $17.4, they kept rising and NASA had to transfer funds from other programs to keep the International Space Station solvent. Ultimately, the total cost of the station was $150 billion, with the United States paying for two-thirds.Following the Space Shuttle ''Columbia'' disaster in 2003, NASA was forced to rely on Russian Soyuz launches for its astronauts and the 2011 retirement of the Space Shuttle accelerated the station's completion.
In the 1980s, right after the first flight of the Space Shuttle, NASA started a joint program with the Department of Defense to develop the  The International Space Station (ISS) combines NASA's Space Station ''Freedom'' project with the Soviet/Russian ''
The International Space Station (ISS) combines NASA's Space Station ''Freedom'' project with the Soviet/Russian '' Since 2017, NASA's crewed spaceflight program has been the Artemis program, which involves the help of US commercial spaceflight companies and international partners such as ESA,
Since 2017, NASA's crewed spaceflight program has been the Artemis program, which involves the help of US commercial spaceflight companies and international partners such as ESA,  The NASA Science Mission Directorate Astrophysics division manages the agency's astrophysics science portfolio. NASA has invested significant resources in the development, delivery, and operations of various forms of space telescopes. These telescopes have provided the means to study the cosmos over a large range of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The Great Observatories that were launched in the 1980s and 1990s have provided a wealth of observations for study by physicists across the planent. The first of them, the Hubble Space Telescope, was delivered to orbit in 1990 and continues to function, in part due to prior servicing missions performed by the Space Shuttle. The other remaining active great observatory include the Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), launched by STS-93 in July 1999 and is now in a 64-hour elliptical orbit studying X-ray sources that are not readily viewable from terrestrial observatories.
The NASA Science Mission Directorate Astrophysics division manages the agency's astrophysics science portfolio. NASA has invested significant resources in the development, delivery, and operations of various forms of space telescopes. These telescopes have provided the means to study the cosmos over a large range of the electromagnetic spectrum.
The Great Observatories that were launched in the 1980s and 1990s have provided a wealth of observations for study by physicists across the planent. The first of them, the Hubble Space Telescope, was delivered to orbit in 1990 and continues to function, in part due to prior servicing missions performed by the Space Shuttle. The other remaining active great observatory include the Chandra X-ray Observatory (CXO), launched by STS-93 in July 1999 and is now in a 64-hour elliptical orbit studying X-ray sources that are not readily viewable from terrestrial observatories.
 The
The  NASA Earth Science is a large, umbrella program comprising a range of terrestrial and space-based collection systems in order to better understand the Earth system and its response to natural and human-caused changes. Numerous systems have been developed and fielded over several decades to provide improved prediction for weather, climate, and other changes in the natural environment. Several of the current operating spacecraft programs include: Aqua,
NASA Earth Science is a large, umbrella program comprising a range of terrestrial and space-based collection systems in order to better understand the Earth system and its response to natural and human-caused changes. Numerous systems have been developed and fielded over several decades to provide improved prediction for weather, climate, and other changes in the natural environment. Several of the current operating spacecraft programs include: Aqua,  The Near Space Network (NSN) provides telemetry, commanding, ground-based tracking, data and communications services to a wide range of customers with satellites in low earth orbit (LEO), geosynchronous orbit (GEO), highly elliptical orbits (HEO), and lunar orbits. The NSN accumulates ground station and antenna assets from the Near-Earth Network and the '' Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System'' (''TDRS'') which operates in geosynchronous orbit providing continuous real-time coverage for launch vehicles and low earth orbit NASA missions.
The NSN consists of 19 ground stations worldwide operated by the US Government and by contractors including Kongsberg Satellite Services (KSAT), Swedish Space Corporation (SSC), and South African National Space Agency (SANSA). The ground network averages between 120 and 150 spacecraft contacts a day with TDRS engaging with systems on a near-continuous basis as needed; the system is managed and operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center.
The Near Space Network (NSN) provides telemetry, commanding, ground-based tracking, data and communications services to a wide range of customers with satellites in low earth orbit (LEO), geosynchronous orbit (GEO), highly elliptical orbits (HEO), and lunar orbits. The NSN accumulates ground station and antenna assets from the Near-Earth Network and the '' Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System'' (''TDRS'') which operates in geosynchronous orbit providing continuous real-time coverage for launch vehicles and low earth orbit NASA missions.
The NSN consists of 19 ground stations worldwide operated by the US Government and by contractors including Kongsberg Satellite Services (KSAT), Swedish Space Corporation (SSC), and South African National Space Agency (SANSA). The ground network averages between 120 and 150 spacecraft contacts a day with TDRS engaging with systems on a near-continuous basis as needed; the system is managed and operated by the Goddard Space Flight Center.
 The ''NASA Sounding Rocket Program'' (''NSRP'') is located at the
The ''NASA Sounding Rocket Program'' (''NSRP'') is located at the  NASA's
NASA's  NASA EDGE is a video podcast which explores different missions, technologies and projects developed by NASA. The program was released by NASA on March 18, 2007, and, , there have been 200 vodcasts produced. It is a
NASA EDGE is a video podcast which explores different missions, technologies and projects developed by NASA. The program was released by NASA on March 18, 2007, and, , there have been 200 vodcasts produced. It is a