|
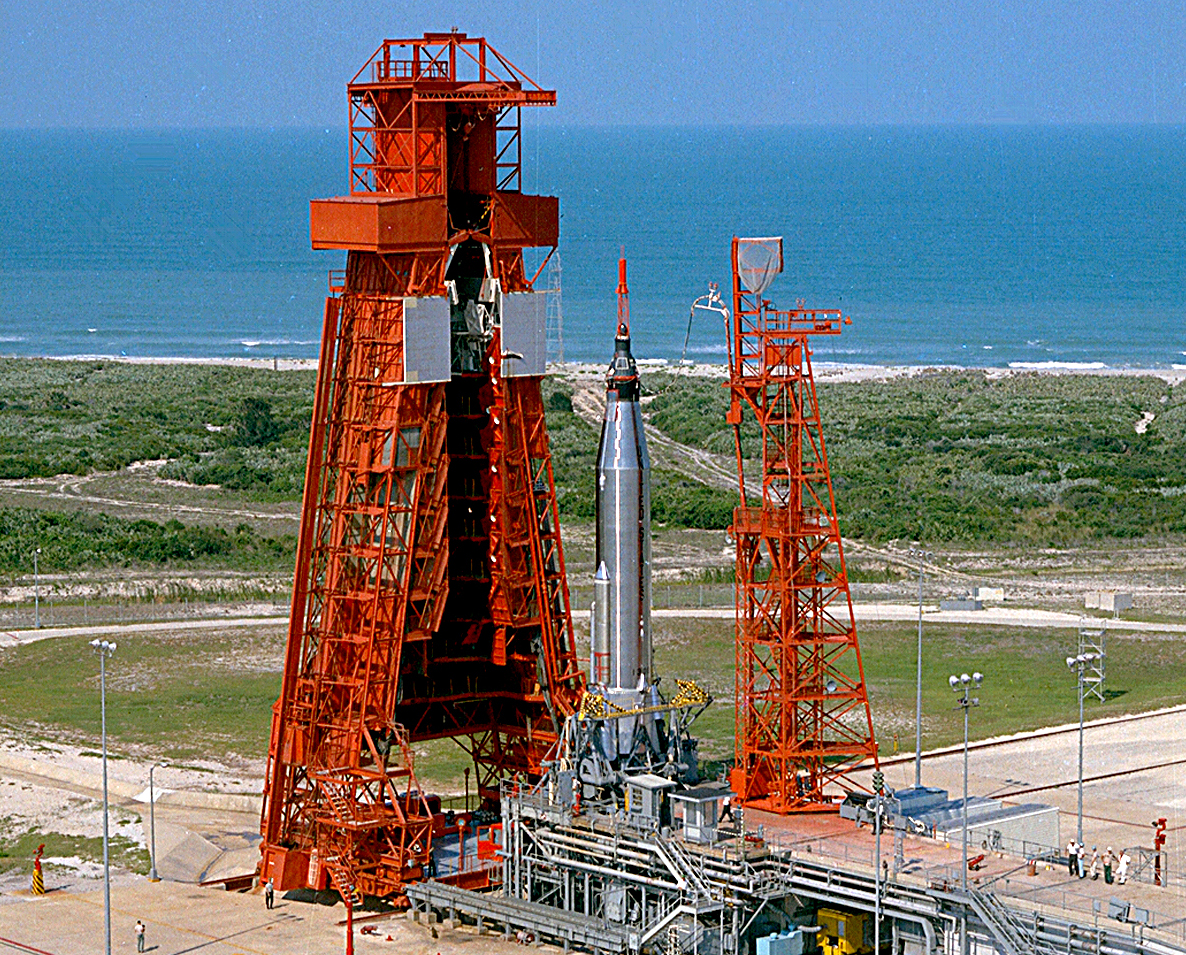
Mercury-Atlas 9
Mercury-Atlas 9 was the final crewed space mission of the U.S. Mercury program, launched on May 15, 1963, from Launch Complex 14 at Cape Canaveral, Florida. The spacecraft, named ''Faith 7'', completed 22 Earth orbits before splashing down in the Pacific Ocean, piloted by astronaut Gordon Cooper, then a United States Air Force major. The Atlas rocket was No. 130-D, and the Mercury spacecraft was No. 20. As of , this mission marks the last time an American was launched alone to conduct an entirely solo orbital mission. Flight directors * Chris KraftRed team * John HodgeBlue team Mission parameters *Mass: *Perigee: 161 km *Apogee: 267 km *Inclination: 32.5° * Period: 88.5 min Mission background Debate over Mercury project continuation The Mercury-Atlas 8 flight of Walter Schirra on October 3, 1962, had been so nearly perfect that some at NASA thought that the United States should quit while it was ahead and make MA-8 the last Mercury mission rather than ris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Slow-scan Television
Slow-scan television (SSTV) is a picture transmission method, used mainly by amateur radio operators, to transmit and receive static pictures via radio in monochrome or color. A literal term for SSTV is narrowband television. Analog broadcast television requires at least 6 MHz wide channels, because it transmits 25 or 30 picture frames per second (see ITU analog broadcast standards), but SSTV usually only takes up to a maximum of 3 kHz of bandwidth. It is a much slower method of still picture transmission, usually taking from about eight seconds to a couple of minutes, depending on the mode used, to transmit one image frame. Since SSTV systems operate on voice frequencies, amateurs use it on shortwave (also known as HF by amateur radio operators), VHF and UHF radio. History Concept The concept of SSTV was introduced by Copthorne Macdonald in 1957–58. He developed the first SSTV system using an electrostatic monitor and a vidicon tube. It was deemed suffi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Major (United States)
In the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Air Force, Air Force and United States Space Force, Space Force, major is a field officer above the military rank, rank of Captain (United States O-3), captain and below the rank of Lieutenant colonel (United States), lieutenant colonel. It is equivalent to the rank of Lieutenant commander (United States), lieutenant commander in the United States Navy, Navy and United States Coast Guard, Coast Guard. Although lieutenant commanders are considered junior officers by their services, majors are senior officers. The U.S. uniformed services pay grades, pay grade for the rank of major is O-4. The insignia for the rank consists of a golden Oak#Culture, oak leaf, with slight stylized differences between the versions of the different services. Promotion to the rank of major is governed by the United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense policies derived from the Defense Officer Personnel Manag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
McDonnell Aircraft Corporation
The McDonnell Aircraft Corporation was an American aerospace manufacturer based in St. Louis, Missouri. The company was founded on July 6, 1939, by James Smith McDonnell, and was best known for its military fighters, including the F-4 Phantom II, and crewed spacecraft including the Mercury capsule and Gemini capsule. McDonnell Aircraft later merged with the Douglas Aircraft Company to form McDonnell Douglas in 1967. History James McDonnell founded J.S. McDonnell & Associates in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, in 1928 to produce a small aircraft for family use.J.S. McDonnell & Associates, Early years: 1927-1938 (part 1) , Boeing.com. The economic depression from 1929 ruined his plans and the company collapsed. He went to work for [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vostok 1
Vostok 1 (, ) was the first spaceflight of the Vostok programme and the first human spaceflight, human orbital spaceflight in history. The Vostok 3KA space capsule was launched from Baikonur Cosmodrome on 12 April 1961, with Soviet astronaut, cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin aboard, making him the first human to reach orbital speed, orbital velocity around the Earth and to complete a full orbit around the Earth. The orbital spaceflight consisted of a single orbit around Earth which skimmed the upper atmosphere at at its lowest point. The flight took 108 minutes from launch to landing. Gagarin parachuted to the ground separately from his capsule after ejecting at altitude. Background The Space Race between the Soviet Union and the United States, the two Cold War superpowers, began just before the Soviet Union launched the world's first artificial satellite, Sputnik 1, in 1957. Both countries wanted to develop spaceflight technology quickly, particularly by launching the first successf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vostok Spacecraft
Vostok (, translated as "East") was a class of single-pilot crewed spacecraft built by the Soviet Union. The first human spaceflight was accomplished with Vostok 1 on April 12, 1961, by Soviet cosmonaut Yuri Gagarin. The Vostok programme made six crewed spaceflights from 1961 through 1963. This was followed in 1964 and 1965 by two flights of Vostok spacecraft modified for up to three pilots, identified as Voskhod. By the late 1960s, these were replaced with Soyuz spacecraft, which are still used . Development The Vostok spacecraft was originally designed for use both as a camera platform (for the Soviet Union's first spy satellite program, Zenit) and as a crewed spacecraft. This dual-use design was crucial in gaining Communist Party support for the program. The basic Vostok design has remained in use for some 40 years, gradually adapted for a range of other uncrewed satellites. The descent module design was reused, in heavily modified form, by the Voskhod program. Desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gemini Program
Project Gemini () was the second United States human spaceflight program to fly. Conducted after the first American crewed space program, Project Mercury, while the Apollo program was still in early development, Gemini was conceived in 1961 and concluded in 1966. The Gemini spacecraft carried a two-astronaut crew. Ten Gemini crews and 16 individual astronauts flew low Earth orbit (LEO) missions during 1965 and 1966. Gemini's objective was the development of space travel techniques to support the Apollo mission to Moon landing, land astronauts on the Moon. In doing so, it allowed the United States to catch up and overcome the lead in human spaceflight capability the Soviet Union had obtained in the early years of the Space Race, by demonstrating mission endurance up to just under 14 days, longer than the eight days required for a round trip to the Moon; methods of performing extravehicular activity (EVA) without tiring; and the orbital maneuvers necessary to achieve space rendezv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 contiguous states border Canada to the north and Mexico to the south, with the semi-exclave of Alaska in the northwest and the archipelago of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean. The United States asserts sovereignty over five Territories of the United States, major island territories and United States Minor Outlying Islands, various uninhabited islands in Oceania and the Caribbean. It is a megadiverse country, with the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, third-largest population, exceeding 340 million. Its three Metropolitan statistical areas by population, largest metropolitan areas are New York metropolitan area, New York, Greater Los Angeles, Los Angel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Walter Schirra
Walter Marty Schirra Jr. ( ; March 12, 1923 – May 3, 2007) was an American naval aviator, test pilot, and NASA astronaut. In 1959, he became one of the original seven astronauts chosen for Project Mercury, which was the United States' first effort to put humans into space. On October 3, 1962, he flew the six-orbit, nine-hour, Mercury-Atlas 8 mission, in a spacecraft he nicknamed ''Sigma 7'', becoming the fifth American and ninth human to travel into space. In December 1965, as part of the two-man Gemini program, he achieved the first space rendezvous, station-keeping his Gemini 6A spacecraft within of the sister Gemini 7 spacecraft. In October 1968, he commanded Apollo 7, an 11-day low Earth orbit shakedown test of the three-man Apollo Command/Service Module and the first crewed launch for the Apollo program. Before becoming an astronaut, Schirra graduated with a Bachelor of Science degree from the United States Naval Academy in 1945, and served at sea during World Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Orbital Period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets, exoplanets orbiting other stars, or binary stars. It may also refer to the time it takes a satellite orbiting a planet or moon to complete one orbit. For celestial objects in general, the orbital period is determined by a 360° revolution of one body around its primary, ''e.g.'' Earth around the Sun. Periods in astronomy are expressed in units of time, usually hours, days, or years. Its reciprocal is the orbital frequency, a kind of revolution frequency, in units of hertz. Small body orbiting a central body According to Kepler's Third Law, the orbital period ''T'' of two point masses orbiting each other in a circular or elliptic orbit is: :T = 2\pi\sqrt where: * ''a'' is the orbit's semi-major axis * ''G'' is the gravitationa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inclination
Orbital inclination measures the tilt of an object's orbit around a celestial body. It is expressed as the angle between a reference plane and the orbital plane or axis of direction of the orbiting object. For a satellite orbiting the Earth directly above the Equator, the plane of the satellite's orbit is the same as the Earth's equatorial plane, and the satellite's orbital inclination is 0°. The general case for a circular orbit is that it is tilted, spending half an orbit over the northern hemisphere and half over the southern. If the orbit swung between 20° north latitude and 20° south latitude, then its orbital inclination would be 20°. Orbits The inclination is one of the six orbital elements describing the shape and orientation of a celestial orbit. It is the angle between the orbital plane and the plane of reference, normally stated in degrees. For a satellite orbiting a planet, the plane of reference is usually the plane containing the planet's equator. For pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Apogee
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values. Apsides pertaining to orbits around different bodies have distinct names to differentiate themselves from other apsides. Apsides pertaining to geocentric orbits, orbits around the Earth, are at the farthest point called the ''apogee'', and at the nearest point the ''perigee'', like with orbits of satellites and the Moon around Earth. Apsides pertaining to orbits around the Sun are named ''aphelion'' for the farthest and ''perihelion'' for the nearest point in a heliocentric orbit. Earth's two apsides are the farthest point, ''aphelion'', and the nearest point, ''perihelion'', of its orbit around the host Sun. The terms ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion'' apply in the same way to the orbits of Jupiter and the other planets, the comets, and the asteroids of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |