|
Pioneer Venus Project
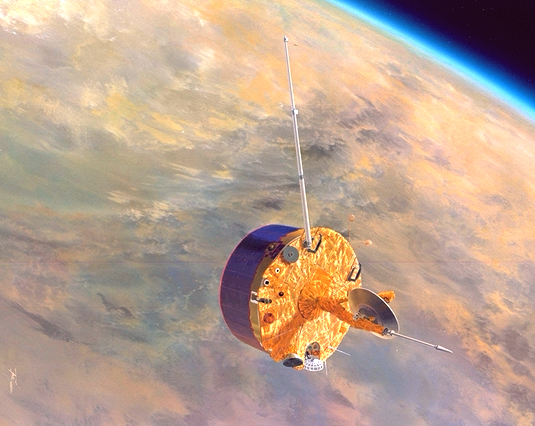
The Pioneer Venus project was part of the Pioneer program consisting of two spacecraft, the Pioneer Venus Orbiter and the Pioneer Venus Multiprobe, launched to Venus in 1978. The program was managed by NASA's Ames Research Center. The Pioneer Venus Orbiter entered orbit around Venus on December 4, 1978, and performed observations to characterize the atmosphere and surface of Venus. It continued to transmit data until October 1992. The Pioneer Venus Multiprobe deployed four small probes into the Venusian atmosphere on December 9, 1978. All four probes transmitted data throughout their descent to the surface. One probe survived the landing and transmitted data from the surface for over an hour. Overview The Pioneer mission consisted of two components, launched separately: an orbiter and a multiprobe. Orbiter The orbiter was launched on May 20, 1978 on an Atlas-Centaur rocket. The orbiter's mass was . The Pioneer Venus Orbiter was inserted into an elliptical orbit around V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arrival Of The Pioneer Venus Spacecraft At Venus (ARC-1978-AC78-0238)
Arrival(s) or The Arrival(s) may refer to: Film * ''The Arrival'' (1991 film), an American science fiction horror film * ''The Arrival'' (1996 film), an American-Mexican science fiction horror film * ''Arrival'' (film), a 2016 American science fiction film by Denis Villeneuve Literature * ''Arrival'' (novel), 2009, by Chris Morphew * ''Arrival'' (story collection) or ''Stories of Your Life and Others'', 2016, by Ted Chiang * ''The Arrival'' (graphic novel), 2006, by Shaun Tan * ''The Arrival'' (Applegate novel), a 2000 ''Animorphs'' novel by K.A. Applegate * ''The Arrivals'', a 2013 novel by Melissa Marr Music * Arrival (band), a British close-harmony pop-rock band with two eponymous albums Albums * ''Arrival'' (ABBA album) or the title instrumental (see below), 1976 * ''Arrival'' (Cymande album), 1981 * ''Arrival'' (Horace Parlan album) or the title instrumental, 1974 * ''Arrival'' (Jordan Rudess album), 1988 * ''Arrival'' (Journey album), 2000 * ''Arrival'' (Rosie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mass Spectrometer
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a '' mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated accor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
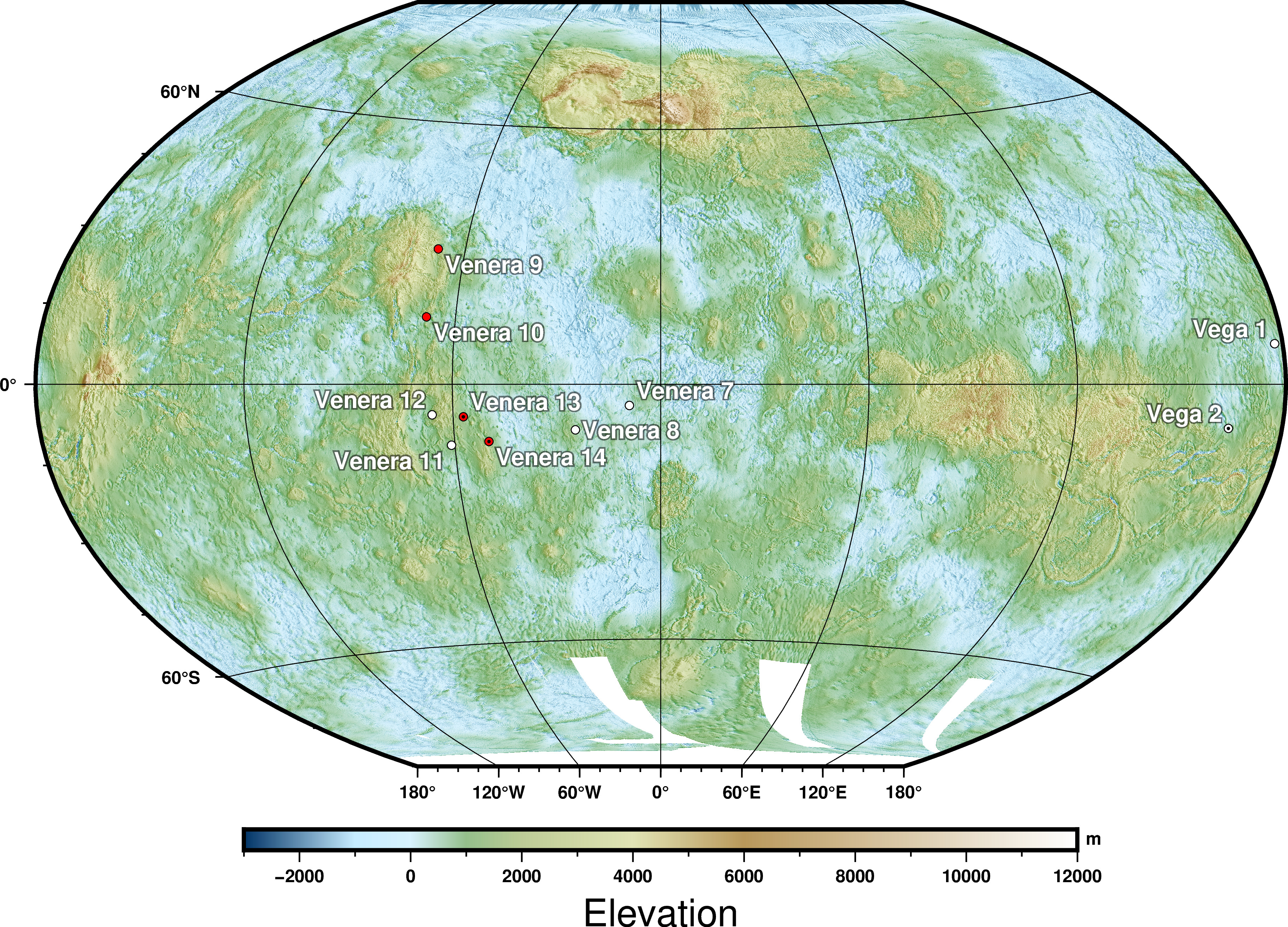
Venera
The Venera (, 'Venus') program was a series of space probes developed by the Soviet Union between 1961 and 1984 to gather information about the planet Venus. Thirteen probes successfully entered the Venusian atmosphere, including the two Venera-Halley probes. Ten of those successfully landed on the surface of the planet. Due to the extreme conditions, the probes could only survive for a short period on the surface, from 23 minutes to two hours. The ''Venera'' program established a number of precedents in space exploration, among them being the first human-made devices to enter the atmosphere of another planet ( Venera 3 on 1 March 1966), the first to make a soft landing on another planet ( Venera 7 on 15 December 1970), the first to return images from another planet's surface ( Venera 9 on 8 June 1975), the first to record sounds on another planet ( Venera 13 on 30 October 1981), and the first to perform high-resolution radar mapping scans ( Venera 15 on 2 June 1983). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Vega Program
Vega is the brightest star in the northern constellation of Lyra. It has the Bayer designation α Lyrae, which is Latinisation of names, Latinised to Alpha Lyrae and abbreviated Alpha Lyr or α Lyr. This star is List of star systems within 25–30 light-years, relatively close at only from the Sun, and one of the most luminous stars in the solar neighborhood, Sun's neighborhood. It is the list of brightest stars, fifth-brightest star in the night sky, and the second-brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus. Vega has been extensively studied by astronomers, leading it to be termed "arguably the next most important star in the sky after the Sun". Vega was the northern pole star around 12,000 BCE and will be so again around the year 13,727, when its declination will be . Vega was the first star other than the Sun to have its image and Astronomical spectroscopy, spectrum photographed. It was one of the first stars whose distance was estimated thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
1978 In Spaceflight
1978 saw the launch of the Pioneer Venus missions launched by the United States, on 20 May and 8 August. The Pioneer Venus Multiprobe landed four spacecraft on the planet, one of which transmitted data for 67 minutes before being destroyed by atmospheric pressure. ISEE-C, which was launched on 8 December, flew past comet 21P/Giacobini–Zinner in 1985, and Halley's Comet Halley's Comet is the only known List of periodic comets, short-period comet that is consistently visible to the naked eye from Earth, appearing every 72–80 years, though with the majority of recorded apparitions (25 of 30) occurring after ... in 1986.Hughes, J (1996) Larousse Desk Reference Encloypedia London RD Press Launches , colspan=8 style="background:white;", January , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", February , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", March , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", May , - , colspan=8 style="background:white;", June , - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nephelometer
A nephelometer or aerosol photometer is an instrument for measuring the concentration of suspended particulates in a liquid or gas colloid. A nephelometer measures suspended particulates by employing a light beam (source beam) and a light detector set to one side (often 90°) of the source beam. Particle density is then a function of the light reflected into the detector from the particles. To some extent, how much light reflects for a given density of particles is dependent upon properties of the particles such as their shape, color, and reflectivity. Nephelometers are calibrated to a known particulate, then use environmental factors (k-factors) to compensate lighter or darker colored dusts accordingly. K-factor is determined by the user by running the nephelometer next to an air sampling pump and comparing results. There are a wide variety of research-grade nephelometers on the market as well as open source varieties. Nephelometer uses The main uses of nephelometers relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radiant Flux
In radiometry, radiant flux or radiant power is the radiant energy emitted, reflected, transmitted, or received per unit time, and spectral flux or spectral power is the radiant flux per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the spectrum is taken as a function of frequency or of wavelength. The SI unit of radiant flux is the watt (W), one joule per second (), while that of spectral flux in frequency is the watt per hertz () and that of spectral flux in wavelength is the watt per metre ()—commonly the watt per nanometre (). Mathematical definitions Radiant flux Radiant flux, denoted ('e' for "energetic", to avoid confusion with photometric quantities), is defined as \begin \Phi_\mathrm &= \frac \\ ptQ_\mathrm &= \int_ \int_ \mathbf\cdot \hat\mathbf\, dA dt \end where * is the time; * is the radiant energy passing out of a closed surface ; * is the Poynting vector, representing the current density of radiant energy; * is the normal vector of a point on ; * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gas Chromatograph
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition. Typical uses of GC include testing the purity of a particular substance, or separating the different components of a mixture. In preparative chromatography, GC can be used to prepare pure compounds from a mixture. Gas chromatography is also sometimes known as vapor-phase chromatography (VPC), or gas–liquid partition chromatography (GLPC). These alternative names, as well as their respective abbreviations, are frequently used in scientific literature. Gas chromatography is the process of separating compounds in a mixture by injecting a gaseous or liquid sample into a mobile phase, typically called the carrier gas, and passing the gas through a stationary phase. The mobile phase is usually an inert gas or an unreactive gas such as helium, argon, nitrogen or hydrogen. The stationary phase can be solid or li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Satellite Bus
A satellite bus (or spacecraft bus) is the main body and structural component of a satellite or spacecraft, in which the payload and all scientific instruments are held. Bus-derived satellites are less customized than specially-produced satellites, but have specific equipment added to meet customer requirements, for example with specialized sensors or transponders, in order to achieve a specific mission. They are commonly used for geosynchronous satellites, particularly communications satellites, but are most commonly used in spacecraft which occupy low Earth orbit missions. Examples Some satellite bus examples include: * Boeing DS&S 702 * Lockheed Martin Space Systems A2100 * Moog Inc. SL-OMV, Meteor, Meteorite * * INVAP ARSAT-3K * Airbus D&S Eurostar * ISRO's I-1K, I-2K, I-3K, I-4K, I-6K, and Indian Mini Satellite bus * NASA Ames MCSB * SSL 1300 * family * Orbital ATK Star Bus family, inc GEOStar * Mitsubishi Electric DS2000 * Spacecraft bus of the Jam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pioneer Venus Orbiter And Multi-Probe - 1978 01565
Pioneer commonly refers to a person who is among the first at something that is new to a community. A pioneer as a settler is among the first settling at a place that is new to the settler community. A historic example are American pioneers, persons in American history who migrated westward to settle in what is now the Western and Midwestern United States. Pioneer, The Pioneer, or pioneering may also refer to: Companies and organizations *Pioneer Aerospace Corporation *Pioneer Chicken, an American fast-food restaurant chain *Pioneer Club Las Vegas, a casino in Las Vegas, Nevada, U.S. *Pioneer Corporation, a Japanese electronics manufacturer *Pioneer Energy, a Canadian gas station chain *Pioneer Entertainment, a Japanese anime company *Pioneer Fund, racist foundation, 1937 *Pioneer Hi-Bred, a U.S.-based agriculture company *Pioneer Hotel & Gambling Hall, Laughlin, Nevada, U.S. *Pioneer Instrument Company, an American aeronautical instrument manufacturer *Pioneer movement, a commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gamma-ray Burst
In gamma-ray astronomy, gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are extremely energetic events occurring in distant Galaxy, galaxies which represent the brightest and most powerful class of explosion in the universe. These extreme Electromagnetic radiation, electromagnetic emissions are second only to the Big Bang as the most energetic and luminous phenomenon ever known. Gamma-ray bursts can last from a few milliseconds to several hours. After the initial flash of gamma rays, a longer-lived afterglow is emitted, usually in the longer wavelengths of X-ray, ultraviolet, visible spectrum, optical, infrared, microwave or radio waves, radio frequencies. The intense radiation of most observed GRBs is thought to be released during a supernova or superluminous supernova as a high-mass star implodes to form a neutron star or a black hole. Short-duration (sGRB) events are a subclass of GRB signals that are now known to originate from the cataclysmic Neutron star merger, merger of binary neutron stars. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |