|
Terra (satellite)
Terra (EOS AM-1) is a multi-national, NASA scientific research satellite in a Sun-synchronous orbit around the Earth that takes simultaneous measurements of Earth's atmosphere, land, and water to understand how Earth is changing and to identify the consequences for life on Earth. It is the flagship of the Earth Observing System (EOS) and the first satellite of the system which was followed by Aqua (launched in 2002) and Aura (launched in 2004). Terra was launched in 1999. The name "Terra" comes from the Latin word for Earth. A naming contest was held by NASA among U.S. high school students. The winning essay was submitted by Sasha Jones of Brentwood, Missouri. The identifier "AM-1" refers to its orbit, passing over the equator in the morning. Launch The satellite was launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base on December 18th, 1999, aboard an Atlas IIAS vehicle and began collecting data on February 24th, 2000. It was placed into a near-polar, sun-synchronous orbit at a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorological variables that are commonly measured are temperature, humidity, atmospheric pressure, wind, and precipitation. In a broader sense, climate is the state of the components of the climate system, including the atmosphere, hydrosphere, cryosphere, lithosphere and biosphere and the interactions between them. The climate of a location is affected by its latitude/longitude, terrain, altitude, land use and nearby water bodies and their currents. Climates can be classified according to the average and typical variables, most commonly temperature and precipitation. The most widely used classification scheme was the Köppen climate classification. The Thornthwaite system, in use since 1948, incorporates evapotranspiration along with temperature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Karl (2010)
Hurricane Karl was the most destructive tropical cyclone on record to strike the Mexican state of Veracruz. The eleventh tropical storm, sixth hurricane, and fifth and final major hurricane of the 2010 Atlantic hurricane season, Karl formed from an area of low pressure which had formed off of the northern coast Venezuela on September 11. It crossed the Caribbean and was upgraded to Tropical Storm Karl on September 14. The cyclone made landfall on the Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico as a strong tropical storm, and then rapidly strengthened in the Bay of Campeche before it made landfall near the city of Veracruz, on the central Mexican Gulf coast, as a major hurricane. This marked the first known time that a major hurricane existed in the Bay of Campeche. Afterwards, the storm rapidly weakened over the mountains of Mexico and dissipated on September 18. At least 22 people have been confirmed killed, most of which were in the state of Veracruz. Insured losses from the storm are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill
The ''Deepwater Horizon'' oil spill (also referred to as the "BP oil spill") was an industrial disaster that began on 20 April 2010 off of the coast of the United States in the Gulf of Mexico on the BP-operated Macondo Prospect, considered to be the largest marine oil spill in the history of the petroleum industry and estimated to be 8 to 31 percent larger in volume than the previous largest, the Ixtoc I oil spill, also in the Gulf of Mexico. The United States federal government estimated the total discharge at . After several failed efforts to contain the flow, the well was declared sealed on 19 September 2010. Reports in early 2012 indicated that the well site was still leaking. The ''Deepwater Horizon'' oil spill is regarded as one of the largest environmental disasters in world history. A massive response ensued to protect beaches, wetlands and estuaries from the spreading oil utilizing skimmer ships, floating booms, controlled burns and of oil dispersant. Due to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter Of 2009–10 In Europe
The winter of 2009–2010 in Europe was unusually cold. Globally, unusual weather patterns brought cold, moist air from the north. Weather systems were undergoing cyclogenesis from North American storms moving across the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and saw many parts of Europe experiencing heavy snowfall and record-low temperatures. This led to a number of deaths, widespread transport disruption, power failures and postponed sporting events. Cause The cold weather was caused by high pressure over Greenland and Iceland forcing weather patterns southward, a phenomenon described by meteorologists as the Arctic oscillation and also the North Atlantic oscillation which were negative compared to normal. The North Atlantic oscillation in Winter 2009/10 was lower than during any winter in over a century and this resulted in more easterly winds bringing cold air into Northern Europe from Siberia and the Arctic. Scientists have shown that El Niño, the quasi-biennial oscillation and so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has been described approximately as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing World Ocean. The Arctic Ocean includes the North Pole region in the middle of the Northern Hemisphere and extends south to about 60°N. The Arctic Ocean is surrounded by Eurasia and North America, and the borders follow topographic features: the Bering Strait on the Pacific side and the Greenland Scotland Ridge on the Atlantic side. It is mostly covered by sea ice throughout the year and almost completely in winter. The Arctic Ocean's surface temperature and salinity vary seasonally as the ice cover melts and freezes; its salinity is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of August 1, 2008
A total solar eclipse occurred at the Moon's descending node of the orbit on August 1, 2008. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. It had a Magnitude of eclipse, magnitude of 1.0394 that was visible from a narrow corridor through northern Canada (Nunavut), Greenland, central Russia, eastern Kazakhstan, western Mongolia and China. Occurring north of the arctic circle, it belonged to the so-called midnight sun eclipses. The largest city in the path of the eclipse was Novosibirsk in Russia. Occurring only 2.5 days after perigee (Perigee on July 29, 2008), the Moon's apparent diamete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Atlantic Anomaly
The South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA) is an area where Earth's inner Van Allen radiation belt comes closest to Earth's surface, dipping down to an altitude of . This leads to an increased flux of energetic particles in this region and exposes orbiting satellites to higher-than-usual levels of ionizing radiation. The effect is caused by the non-concentricity of Earth and its magnetic dipole. The SAA is the near-Earth region where Earth's magnetic field is weakest relative to an idealized Earth-centered dipole field. Definition The area of the SAA is confined by the intensity of Earth's magnetic field at less than 32,000 nanotesla at sea level, which corresponds to the dipolar magnetic field at ionospheric altitudes. However, the field itself varies in intensity as a gradient. Position and shape The Van Allen radiation belts are symmetric about the Earth's magnetic axis, which is tilted with respect to the Earth's rotational axis by an angle of approximately 11°. The intersection b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerosol
An aerosol is a suspension (chemistry), suspension of fine solid particles or liquid Drop (liquid), droplets in air or another gas. Aerosols can be natural or Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic. Examples of natural aerosols are fog or mist, dust, forest exudates, and geyser steam. Examples of anthropogenic aerosols include particulate air pollutants, mist from the discharge at Hydroelectric dam, hydroelectric dams, Irrigation, irrigation mist, Perfume, perfume from atomizers, smoke, steam from a kettle, Pesticide, sprayed pesticides, and medical treatments for respiratory illnesses. When a person inhales the contents of a vape pen or e-cigarette, they are inhaling an Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic aerosol. The liquid or solid particles in an aerosol have diameters typically less than micrometre, 1 μm (larger particles with a significant settling speed make the mixture a Suspension (chemistry), suspension, but the distinction is not clear-cut) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MOPITT
MOPITT (Measurements of Pollution in the Troposphere) is a payload scientific instrument launched into Earth orbit by NASA on board the Terra satellite in 1999. It is designed to monitor changes in pollution patterns and its effect in the lower atmosphere of the Earth. The instrument was funded by the Space Science Division of the Canadian Space Agency. Instrument MOPITT is a nadir sounding (vertically downward pointing) instrument that measures upwelling infrared radiation at 4.7 μm and 2.2-2.4 μm. It uses correlation spectroscopy to calculate total column observations and profiles of carbon monoxide in the lower atmosphere. Although observations of methane Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Ea ... were also planned, to date no data have been released. References ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
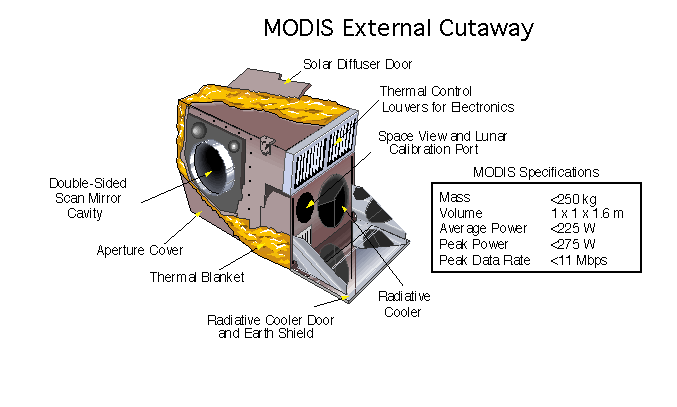
MODIS
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is a satellite-based sensor used for earth and climate measurements. There are two MODIS sensors in Earth orbit: one on board the Terra (EOS AM) satellite, launched by NASA in 1999; and one on board the Aqua (EOS PM) satellite, launched in 2002. MODIS has now been replaced by the VIIRS, which first launched in 2011 aboard the Suomi NPP satellite. The MODIS instruments were built by Santa Barbara Remote Sensing. They capture data in 36 spectral bands ranging in wavelength from 0.4 μm to 14.4 μm and at varying spatial resolutions (2 bands at 250 m, 5 bands at 500 m and 29 bands at 1 km). Together the instruments image the entire Earth every 1 to 2 days. They are designed to provide measurements in large-scale global dynamics including changes in Earth's cloud cover, radiation budget and processes occurring in the oceans, on land, and in the lower atmosphere. Support and calibration is provided by the MO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MISR
Misr or MISR may refer to: * Misr, the romanized Arabic name for Egypt * misr, singular of Arabic ''amsar'', which were early Arabic "garrison towns" * Misr (domain name), a top-level Internet domain name * Misr, a variant of the AKM assault rifle produced in Egypt * Misr Station, former name of Ramses Station, the main railroad station of Cairo * Misr Station, one of two main railroad stations in Alexandria Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ... * Multi-angle Imaging SpectroRadiometer, NASA's remote sensing instrument See also * {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |