|
Cygnus CRS Orb-1
Orbital-1, also known as Orb-1, was the second flight of the Orbital Sciences Cygnus cargo spacecraft, its second flight to the International Space Station (ISS) and the third launch of the company's Antares launch vehicle. The mission launched on 9 January 2014 at 18:07:05 UTC. Spacecraft Orb-1 was the first of eight contracted flights by Orbital Sciences under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services (CRS-1) contract. This was the maiden flight of the Castor 30B second stage. Orbital Sciences continued its naming of Cygnus spacecraft in tribute to former astronauts. This vehicle was named the S.S. ''C. Gordon Fullerton'' for C. Gordon Fullerton, the NASA astronaut who died on 21 August 2013. This Cygnus cargo mission launched the Nanoracks CubeSat Deployer to the ISS's Kibō module. Launch and early operations The launch of Orb-1 was scheduled for November 2013, but a series of delays pushed the date to 20 December 2013. The Antares launch vehicle rolled out from the W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Logistics
Space logistics is "the theory and practice of driving space system design for operability and supportability, and of managing the flow of materiel, services, and information needed throughout a space system lifecycle." It includes terrestrial logistics in support of space travel, including any additional "design and development, acquisition, storage, movement, distribution, maintenance, evacuation, and disposition of space materiel", movement of people in space (both routine and for medical and other emergencies), and contracting and supplying any required support services for maintaining space travel. The space logistics research and practice primarily focus on the modeling and management of the astro-logistics supply chain from Earth and on to destinations throughout the solar system as well as the system architecture strategies to minimize both logistics requirements and operational costs of human and robotic operations in space. History As early as 1960, Wernher von Braun s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Sciences Corporation
Orbital Sciences Corporation (commonly referred to as Orbital) was an American company specializing in the design, manufacture, and launch of small- and medium- class space and launch vehicle systems for commercial, military and other government customers. In 2014, Orbital merged with Alliant Techsystems to create a new company called Orbital ATK, Inc., which in turn was purchased by Northrop Grumman in 2018. The remnants of the former Orbital Sciences Corporation today are a subsidiary of Northrop Grumman, known as Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems. Orbital was headquartered in Dulles, Virginia and publicly traded on the New York Stock Exchange with the ticker symbol ORB. Orbital's primary products were satellites and launch vehicles, including low Earth orbit (LEO), geosynchronous Earth orbit and planetary spacecraft for communications, remote sensing, scientific and defense missions; ground- and air-launched launch vehicles that delivered satellites into orbit; missile de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Virginia
West Virginia is a state in the Appalachian, Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States.The Census Bureau and the Association of American Geographers classify West Virginia as part of the Southern United States while the Bureau of Labor Statistics classifies the state as a part of the Mid-Atlantic regionMid-Atlantic Home : Mid-Atlantic Information Office: U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics" www.bls.gov. Archived. It is bordered by Pennsylvania to the north and east, Maryland to the east and northeast, Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, and Ohio to the northwest. West Virginia is the 10th-smallest state by area and ranks as the 12th-least populous state, with a population of 1,793,716 residents. The capital and largest city is Charleston. West Virginia was admitted to the Union on June 20, 1863, and was a key border state during the American Civil War. It was the only state to form by separating from a Confederate state, the second to sepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut [Massachusett writing systems, məhswatʃəwiːsət],'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It borders on the Atlantic Ocean and Gulf of Maine to the east, Connecticut and Rhode Island to the south, New Hampshire and Vermont to the north, and New York (state), New York to the west. The state's capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city, as well as its cultural and financial center, is Boston. Massachusetts is also home to the urban area, urban core of Greater Boston, the largest metropolitan area in New England and a region profoundly influential upon American History of the United States, history, academia, and the Economy of the United States, research economy. Originally dependent on agriculture, fishing, and trade. Massachusetts was transformed into a manuf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no) , anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind" , Former = Province of South Carolina , seat = Columbia , LargestCity = Charleston , LargestMetro = Greenville (combined and metro) Columbia (urban) , BorderingStates = Georgia, North Carolina , OfficialLang = English , population_demonym = South Carolinian , Governor = , Lieutenant Governor = , Legislature = General Assembly , Upperhouse = Senate , Lowerhouse = House of Representatives , Judiciary = South Carolina Supreme Court , Senators = , Representative = 6 Republicans1 Democrat , postal_code = SC , TradAbbreviation = S.C. , area_rank = 40th , area_total_sq_mi = 32,020 , area_total_km2 = 82,932 , area_land_sq_mi = 30,109 , area_land_km2 = 77,982 , area_water_sq_mi = 1,911 , area_water_km2 = 4,949 , area_water_percent = 6 , population_rank = 23rd , population_as_of = 2022 , 2010Pop = 5282634 , population ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Health Threat From Cosmic Rays
Health threats from cosmic rays are the dangers posed by cosmic rays to astronauts on interplanetary missions or any missions that venture through the Van-Allen Belts or outside the Earth's magnetosphere. They are one of the greatest barriers standing in the way of plans for interplanetary travel by crewed spacecraft, but space radiation health risks also occur for missions in low Earth orbit such as the International Space Station (ISS). In October 2015, the NASA Office of Inspector General issued a health hazards report related to space exploration, including a human mission to Mars. The deep-space radiation environment The radiation environment of deep space is different from that on the Earth's surface or in low Earth orbit, due to the much larger flux of high-energy galactic cosmic rays (GCRs), along with radiation from solar proton events (SPEs) and the radiation belts. Galactic cosmic rays (GCRs) consist of high energy protons (85%), alpha particles (14%) and oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20140106 Antares CRS Orb-1 Rocket At MARS Pad 0A (201401060004HQ)
Fourteen or 14 may refer to: * 14 (number), the natural number following 13 and preceding 15 * one of the years 14 BC, AD 14, 1914, 2014 Music * 14th (band), a British electronic music duo * ''14'' (David Garrett album), 2013 *''14'', an unreleased album by Charli XCX * "14" (song), 2007, from ''Courage'' by Paula Cole Other uses * ''Fourteen'' (film), a 2019 American film directed by Dan Sallitt * ''Fourteen'' (play), a 1919 play by Alice Gerstenberg * ''Fourteen'' (manga), a 1990 manga series by Kazuo Umezu * ''14'' (novel), a 2013 science fiction novel by Peter Clines * ''The 14'', a 1973 British drama film directed by David Hemmings * Fourteen, West Virginia, United States, an unincorporated community * Lot Fourteen, redevelopment site in Adelaide, South Australia, previously occupied by the Royal Adelaide Hospital * "The Fourteen", a nickname for NASA Astronaut Group 3 * Fourteen Words, a phrase used by white supremacists and Nazis See also * 1/4 (other) * Fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kibō (ISS Module)
The Japanese Experiment Module (JEM), nicknamed , is a Japanese science module for the International Space Station (ISS) developed by JAXA. It is the largest single ISS module, and is attached to the ''Harmony'' module. The first two pieces of the module were launched on Space Shuttle missions STS-123 and STS-124. The third and final components were launched on STS-127. Components In initial configuration, ''Kibō'' consisted of six major elements: * Pressurized Module (PM) * Exposed Facility (EF) * Experiment Logistics Module (ELM) Pressurized Section (ELM-PS) * Experiment Logistics Module (ELM) Exposed Section (ELM-ES) * Japanese Experiment Module remote manipulator system (JEMRMS) * Inter-orbit communication system (ICS) Pressurized Module The Pressurized Module (PM) is the core component connected to the port hatch of ''Harmony''. It is cylindrical in shape and contains twenty-three International Standard Payload Racks (ISPRs), ten of which are dedicated to sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
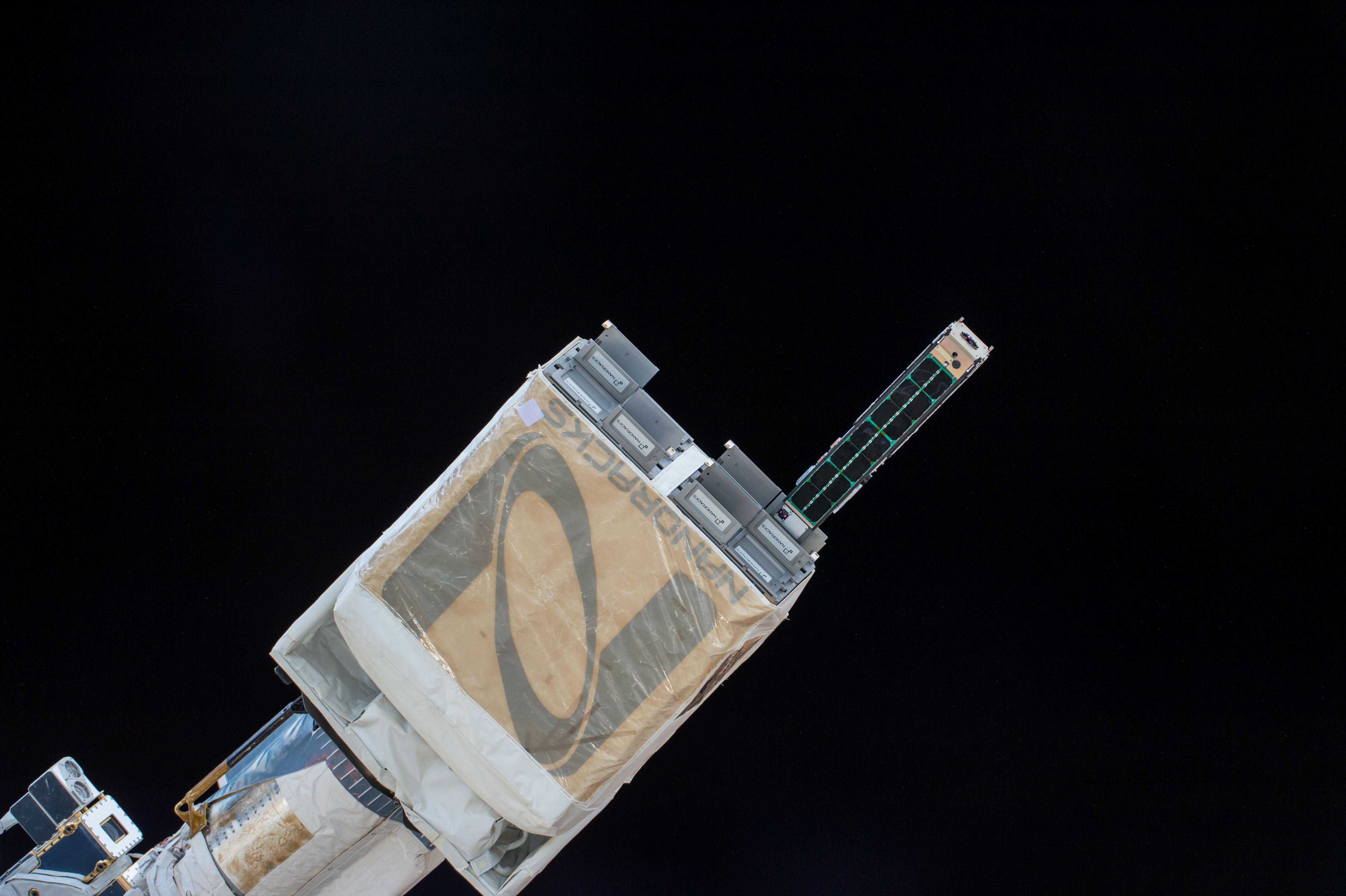
Nanoracks CubeSat Deployer
The Nanoracks CubeSat Deployer (NRCSD) is a device to deploy CubeSats into orbit from the International Space Station (ISS). In 2014, two CubeSat deployers were on board the International Space Station (ISS): the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Small Satellite Orbital Deployer (J-SSOD) and the Nanoracks CubeSat Deployer (NRCSD). The J-SSOD is the first of its kind to deploy small satellites from the International Space Station (ISS). The NRCSD is the first commercially operated small satellite deployer from the ISS, maximizing full capabilities of each airlock cycle of deployments. CubeSats belong to a class of research spacecraft called nanosatellites. The basic cube-shaped satellites measure on each side, weigh less than , and have a volume of about , although there are CubeSats which are built and deployed with sizes of multiples of 10 cm in length. , one method of getting CubeSats to orbit is to transport them aboard a larger spacecraft as part of a cargo load to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castor (rocket Stage)
The Castor family of solid-fuel rocket stages and boosters built by Thiokol (now Northrop Grumman) and used on a variety of launch vehicles. They were initially developed as the second-stage motor of the Scout rocket. The design was based on the MGM-29 Sergeant, a surface-to-surface missile developed for the United States Army at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Versions Flown versions Castor 1 :The Castor 1 was first used for a successful suborbital launch of a Scout X-1 rocket on September 2, 1960. :It was long, in diameter, and had a burn time of 27 seconds. Castor 1 stages were also used as strap-on boosters for launch vehicles using Thor first stages, including the Delta-D. (A Delta-D was used in 1964 to launch Syncom-3, the first satellite placed in a geostationary orbit.) Castor 1 stages were used in 141 launch attempts of Scout and Delta rockets, only 2 of which were failures. They were also used on some thrust-assisted Thor-Agena launchers. The last launch usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |