|
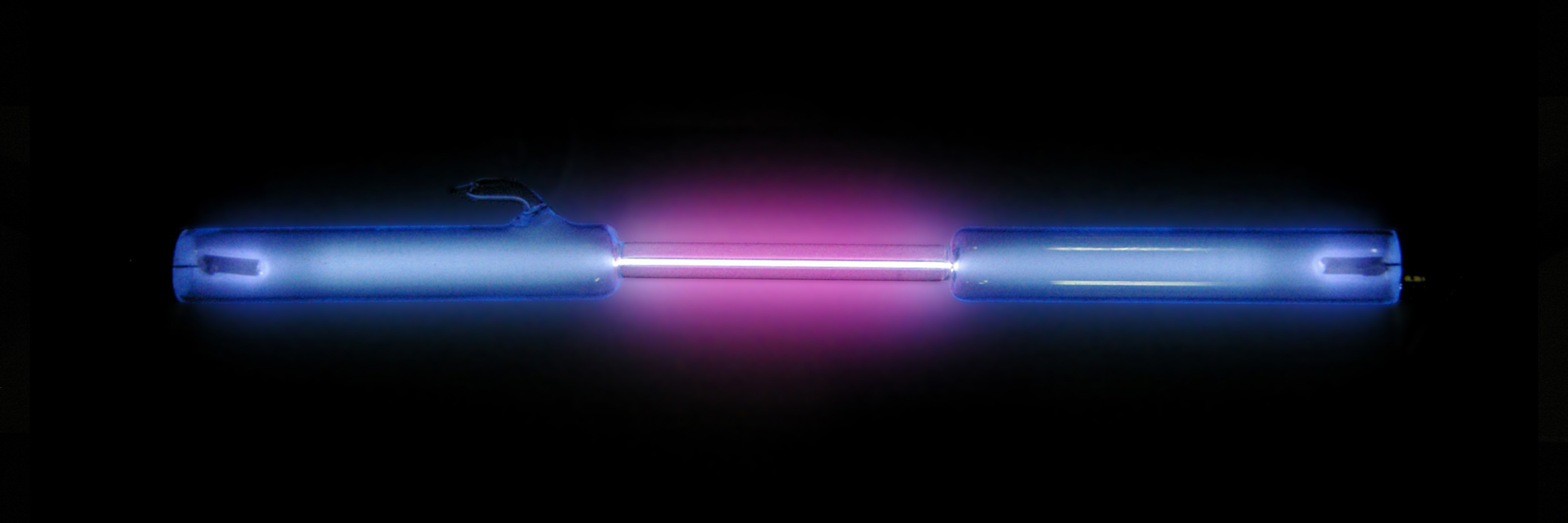
Antimatter
In modern physics, antimatter is defined as matter composed of the antiparticles (or "partners") of the corresponding subatomic particle, particles in "ordinary" matter, and can be thought of as matter with reversed charge and parity, or going backward in time (see CPT symmetry). Antimatter occurs in natural processes like cosmic ray collisions and some types of radioactive decay, but only a tiny fraction of these have successfully been bound together in experiments to form antiatoms. Minuscule numbers of antiparticles can be generated at particle accelerators, but total artificial production has been only a few nanograms. No Macroscopic scale, macroscopic amount of antimatter has ever been assembled due to the extreme cost and difficulty of production and handling. Nonetheless, antimatter is an essential component of widely available applications related to beta decay, such as positron emission tomography, radiation therapy, and industrial imaging. In theory, a particle and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Antihelium
In modern physics, antimatter is defined as matter composed of the antiparticles (or "partners") of the corresponding particles in "ordinary" matter, and can be thought of as matter with reversed charge and parity, or going backward in time (see CPT symmetry). Antimatter occurs in natural processes like cosmic ray collisions and some types of radioactive decay, but only a tiny fraction of these have successfully been bound together in experiments to form antiatoms. Minuscule numbers of antiparticles can be generated at particle accelerators, but total artificial production has been only a few nanograms. No macroscopic amount of antimatter has ever been assembled due to the extreme cost and difficulty of production and handling. Nonetheless, antimatter is an essential component of widely available applications related to beta decay, such as positron emission tomography, radiation therapy, and industrial imaging. In theory, a particle and its antiparticle (for example, a proto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic particles. In everyday as well as scientific usage, ''matter'' generally includes atoms and anything made up of them, and any particles (or combination of particles) that act as if they have both rest mass and volume. However it does not include massless particles such as photons, or other energy phenomena or waves such as light or heat. Matter exists in various states (also known as phases). These include classical everyday phases such as solid, liquid, and gas – for example water exists as ice, liquid water, and gaseous steam – but other states are possible, including plasma, Bose–Einstein condensates, fermionic condensates, and quark–gluon plasma. Usually atoms can be imagined as a nucleus of protons and neu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Positron
The positron or antielectron is the particle with an electric charge of +1''elementary charge, e'', a Spin (physics), spin of 1/2 (the same as the electron), and the same Electron rest mass, mass as an electron. It is the antiparticle (antimatter counterpart) of the electron. When a positron collides with an electron, annihilation occurs. If this collision occurs at low energies, it results in the production of two or more photons. Positrons can be created by positron emission radioactive decay (through weak interactions), or by pair production from a sufficiently energetic photon which is interacting with an atom in a material. History Theory In 1928, Paul Dirac published a paper proposing that electrons can have both a positive and negative charge. This paper introduced the Dirac equation, a unification of quantum mechanics, special relativity, and the then-new concept of electron Spin (physics), spin to explain the Zeeman effect. The paper did not explicitly predict a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
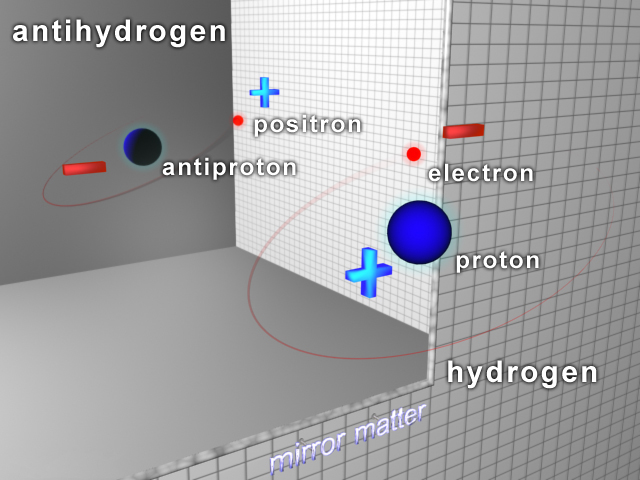
Antihydrogen
Antihydrogen () is the antimatter counterpart of hydrogen. Whereas the common hydrogen atom is composed of an electron and proton, the antihydrogen atom is made up of a positron and antiproton. Scientists hope that studying antihydrogen may shed light on the question of why there is more matter than antimatter in the observable universe, known as the baryon asymmetry problem. Antihydrogen is produced artificially in particle accelerators. Experimental history Accelerators first detected hot antihydrogen in the 1990s. ATHENA studied cold in 2002. It was first trapped by the Antihydrogen Laser Physics Apparatus (ALPHA Collaboration, ALPHA) team at CERN in 2010, who then measured the structure and other important properties. ALPHAAEgIS and GBAR plan to further cool and study atoms. 1s–2s transition measurement In 2016, the Antiproton Decelerator#ALPHA, ALPHA experiment measured the atomic electron transition between the two lowest energy levels of antihydrogen, 1s–2s. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Antiproton
The antiproton, , (pronounced ''p-bar'') is the antiparticle of the proton. Antiprotons are stable, but they are typically short-lived, since any collision with a proton will cause both particles to be annihilated in a burst of energy. The existence of the antiproton with electric charge of , opposite to the electric charge of of the proton, was predicted by Paul Dirac in his 1933 Nobel Prize lecture. Dirac received the Nobel Prize for his 1928 publication of his Dirac equation that predicted the existence of positive and negative solutions to Einstein's energy equation (E = mc^2) and the existence of the positron, the antimatter analog of the electron, with opposite charge and spin. The antiproton was first experimentally confirmed in 1955 at the Bevatron particle accelerator by University of California, Berkeley physicists Emilio Segrè and Owen Chamberlain, for which they were awarded the 1959 Nobel Prize in Physics. In terms of valence quarks, an antiproton consists o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Antiparticle
In particle physics, every type of particle of "ordinary" matter (as opposed to antimatter) is associated with an antiparticle with the same mass but with opposite physical charges (such as electric charge). For example, the antiparticle of the electron is the positron (also known as an antielectron). While the electron has a negative electric charge, the positron has a positive electric charge, and is produced naturally in certain types of radioactive decay. The opposite is also true: the antiparticle of the positron is the electron. Some particles, such as the photon, are their own antiparticle. Otherwise, for each pair of antiparticle partners, one is designated as the normal particle (the one that occurs in matter usually interacted with in daily life). The other (usually given the prefix "anti-") is designated the ''antiparticle''. Particle–antiparticle pairs can annihilate each other, producing photons; since the charges of the particle and antiparticle are opposite, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mass–energy Equivalence
In physics, mass–energy equivalence is the relationship between mass and energy in a system's rest frame. The two differ only by a multiplicative constant and the units of measurement. The principle is described by the physicist Albert Einstein's formula: E = mc^2. In a reference frame where the system is moving, its relativistic energy and relativistic mass (instead of rest mass) obey the same formula. The formula defines the energy () of a particle in its rest frame as the product of mass () with the speed of light squared (). Because the speed of light is a large number in everyday units (approximately ), the formula implies that a small amount of mass corresponds to an enormous amount of energy. Rest mass, also called invariant mass, is a fundamental physical property of matter, independent of velocity. Massless particles such as photons have zero invariant mass, but massless free particles have both momentum and energy. The equivalence principle implies that w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cosmic Ray
Cosmic rays or astroparticles are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk are deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Neutrino
A neutrino ( ; denoted by the Greek letter ) is an elementary particle that interacts via the weak interaction and gravity. The neutrino is so named because it is electrically neutral and because its rest mass is so small ('' -ino'') that it was long thought to be zero. The rest mass of the neutrino is much smaller than that of the other known elementary particles (excluding massless particles). The weak force has a very short range, the gravitational interaction is extremely weak due to the very small mass of the neutrino, and neutrinos do not participate in the electromagnetic interaction or the strong interaction. Consequently, neutrinos typically pass through normal matter unimpeded and with no detectable effect. Weak interactions create neutrinos in one of three leptonic flavors: # electron neutrino, # muon neutrino, # tau neutrino, Each flavor is associated with the correspondingly named charged lepton. Although neutrinos were long believed to be mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up quark, up and down quark, down quarks. Electrons are extremely lightweight particles that orbit the positively charged atomic nucleus, nucleus of atoms. Their negative charge is balanced by the positive charge of protons in the nucleus, giving atoms their overall electric charge#Charge neutrality, neutral charge. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, each consisting of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a number of orbiting electrons equal to the number of protons. The configuration and energy levels of these orbiting electrons determine the chemical properties of an atom. Electrons are bound to the nucleus to different degrees. The outermost or valence electron, valence electrons are the least tightly bound and are responsible for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered ''radioactive''. Three of the most common types of decay are Alpha decay, alpha, Beta decay, beta, and Gamma ray, gamma decay. The weak force is the Fundamental interactions, mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetic force, electromagnetic and nuclear forces. Radioactive decay is a randomness, random process at the level of single atoms. According to quantum mechanics, quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay, regardless of how long the atom has existed. However, for a significant number of identical atoms, the overall decay rate can be expressed as a decay constant or as a half-life. The half-lives of radioactive atoms have a huge range: f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
CPT Symmetry
Charge, parity, and time reversal symmetry is a fundamental symmetry of physical laws under the simultaneous transformations of charge conjugation (C), parity transformation (P), and time reversal (T). CPT is the only combination of C, P, and T that is observed to be an exact symmetry of nature at the fundamental level. The CPT theorem says that CPT symmetry holds for all physical phenomena, or more precisely, that any Lorentz invariant local quantum field theory with a Hermitian Hamiltonian must have CPT symmetry. In layman terms, this stipulates that an antimatter, mirrored, and time reversed universe would behave exactly the same as our regular universe. History The CPT theorem appeared for the first time, implicitly, in the work of Julian Schwinger in 1951 to prove the connection between spin and statistics. In 1954, Gerhart Lüders and Wolfgang Pauli derived more explicit proofs, so this theorem is sometimes known as the Lüders–Pauli theorem. At about the same t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |