MHC2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large
 Classical MHC molecules present epitopes to the TCRs of CD8+ T lymphocytes. Nonclassical molecules (MHC class IB) exhibit limited polymorphism, expression patterns, and presented antigens; this group is subdivided into a group encoded within MHC loci (e.g., HLA-E, -F, -G), as well as those not (e.g., stress ligands such as ULBPs, Rae1, and H60); the antigen/ligand for many of these molecules remain unknown, but they can interact with each of CD8+ T cells, NKT cells, and NK cells. The evolutionary oldest nonclassical MHC class I lineage in human was deduced to be the lineage that includes the CD1 and PROCR (alias EPCR) molecules and this lineage may have been established before the origin of tetrapod species. However, the only nonclassical MHC class I lineage for which evidence exists that it was established before the evolutionary separation of Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish) and Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish plus tetrapods) is lineage Z of which members are found, together in each species with classical MHC class I, in lungfish and throughout ray-finned fishes; why the Z lineage was well conserved in ray-finned fish but lost in tetrapods is not understood.
Classical MHC molecules present epitopes to the TCRs of CD8+ T lymphocytes. Nonclassical molecules (MHC class IB) exhibit limited polymorphism, expression patterns, and presented antigens; this group is subdivided into a group encoded within MHC loci (e.g., HLA-E, -F, -G), as well as those not (e.g., stress ligands such as ULBPs, Rae1, and H60); the antigen/ligand for many of these molecules remain unknown, but they can interact with each of CD8+ T cells, NKT cells, and NK cells. The evolutionary oldest nonclassical MHC class I lineage in human was deduced to be the lineage that includes the CD1 and PROCR (alias EPCR) molecules and this lineage may have been established before the origin of tetrapod species. However, the only nonclassical MHC class I lineage for which evidence exists that it was established before the evolutionary separation of Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish) and Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish plus tetrapods) is lineage Z of which members are found, together in each species with classical MHC class I, in lungfish and throughout ray-finned fishes; why the Z lineage was well conserved in ray-finned fish but lost in tetrapods is not understood.
 Peptides are processed and presented by two classical pathways:
* In MHC class II,
Peptides are processed and presented by two classical pathways:
* In MHC class II, 
 Human MHC class I and II are also called
Human MHC class I and II are also called
''Molecular Individuality''
ĆöGerman online book (2012)
NetMHC 3.0 server
Ćöpredicts binding of peptides to a number of different MHC (HLA) alleles
ĆöCardiff University
The story of 2YF6: A Chicken MHC
RCSB Protein Data Bank: Molecule of the MonthŌĆöMajor Histocompatibility Complex
dbMHC Home, NCBI's database of the Major Histocompatibility Complex
{{Authority control Gene families Glycoproteins Immune system Single-pass transmembrane proteins
locus
Locus (plural loci) is Latin for "place". It may refer to:
Entertainment
* Locus (comics), a Marvel Comics mutant villainess, a member of the Mutant Liberation Front
* ''Locus'' (magazine), science fiction and fantasy magazine
** ''Locus Award' ...
on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell
Cell most often refers to:
* Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life
Cell may also refer to:
Locations
* Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery ...
surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system ...
. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules.
This locus got its name because it was discovered via the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules: binding an antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bringing the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell rec ...
. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
, also called white blood cells
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from mult ...
(WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transpo ...
, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune disease
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
s.
In a cell, protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, respo ...
molecules of the host's own phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
or of other biologic entities are continually synthesized and degraded. Each MHC molecule on the cell surface displays a small peptide (a molecular fraction of a protein) called an epitope
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The epitope is the specific piece of the antigen to which an antibody binds. The p ...
. The presented self-antigens prevent an organism
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells (cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and ...
's immune system
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinte ...
from targeting its own cells. The presentation of pathogen-derived proteins results in the elimination of the infected cell by the immune system.
Diversity of an individual's self-antigen presentation, mediated by MHC self-antigens, is attained in at least three ways: (1) an organism's MHC repertoire is polygenic
A polygene is a member of a group of non-epistatic genes that interact additively to influence a phenotypic trait, thus contributing to multiple-gene inheritance (polygenic inheritance, multigenic inheritance, quantitative inheritance), a type of ...
(via multiple, interacting genes); (2) MHC expression is codominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the Phenotype, effect of a different variant of the same gene on Homologous chromosome, the other copy of the chromosome. The first ...
(from both sets of inherited alleles
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ß╝ä╬╗╬╗╬┐Žé ''├Īllos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
); (3) MHC gene variants are highly polymorphic (diversely varying from organism to organism within a species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
). Sexual selection
Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which members of one biological sex mate choice, choose mates of the other sex to mating, mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of t ...
has been observed in male mice choosing to mate with females with different MHCs. Also, at least for MHC I presentation, there has been evidence of antigenic peptide splicing, which can combine peptides from different proteins, vastly increasing antigen diversity.
Discovery
The first descriptions of the MHC were made by British immunologist Peter Gorer in 1936. MHC genes were first identified in inbred mice strains.Clarence Little
Clarence Cook Little (October 6, 1888 ŌĆō December 22, 1971) was an American genetics, cancer, and tobacco researcher and academic administrator, as well as a eugenicist.
Early life
C. C. Little was born in Brookline, Massachusetts and atte ...
transplanted tumors across different strains and found rejection of transplanted tumors according to strains of host versus donor. George Snell selectively bred two mouse strains, attained a new strain nearly identical to one of the progenitor strains, but differing crucially in histocompatibility
Histocompatibility, or tissue compatibility, is the property of having the same, or sufficiently similar, alleles of a set of genes called human leukocyte antigens (HLA), or major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Each individual expresses many uni ...
ŌĆöthat is, tissue compatibility upon transplantationŌĆöand thereupon identified an MHC locus
Locus (plural loci) is Latin for "place". It may refer to:
Entertainment
* Locus (comics), a Marvel Comics mutant villainess, a member of the Mutant Liberation Front
* ''Locus'' (magazine), science fiction and fantasy magazine
** ''Locus Award' ...
. Later Jean Dausset
Jean-Baptiste-Gabriel-Joachim Dausset (19 October 1916 ŌĆō 6 June 2009) was a French immunologist born in Toulouse, France. Dausset received the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1980 along with Baruj Benacerraf and George Davis Snell fo ...
demonstrated the existence of MHC genes in humans and described the first human leucocyte antigen, the protein which we call now HLA-A2. Some years later┬Ā Baruj Benacerraf showed that polymorphic MHC genes not only determine an individualŌĆÖs unique constitution of antigens but also regulate the interaction among the various cells of the immunological system. These three scientists have been awarded the 1980 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discoveries concerning ŌĆ£genetically determined structures on the cell surface that regulate immunological reactionsŌĆØ.
The first fully sequenced and annotated MHC was published for humans in 1999 by a consortium of sequencing centers from the UK, USA and Japan in ''Nature''. It was a "virtual MHC" since it was a mosaic from different individuals. A much shorter MHC locus from chickens was published in the same issue of ''Nature''. Many other species have been sequenced and the evolution of the MHC was studied, e.g. in the gray short-tailed opossum
Opossums () are members of the marsupial order Didelphimorphia () endemic to the Americas. The largest order of marsupials in the Western Hemisphere, it comprises 93 species in 18 genera. Opossums originated in South America and entered North ...
(''Monodelphis domestica
The gray short-tailed opossum (''Monodelphis domestica'') is a small South American member of the family Didelphidae. Unlike most other marsupials, the gray short-tailed opossum does not have a true pouch. The scientific name ''Monodelphis'' is ...
''), a marsupial
Marsupials are any members of the mammalian infraclass Marsupialia. All extant marsupials are endemic to Australasia, Wallacea and the Americas. A distinctive characteristic common to most of these species is that the young are carried in a po ...
, MHC spans 3.95 Mb, yielding 114 genes, 87 shared with humans. Marsupial MHC genotypic
The genotype of an organism is its complete set of genetic material. Genotype can also be used to refer to the alleles or variants an individual carries in a particular gene or genetic location. The number of alleles an individual can have in a ...
variation lies between eutherian mammals and bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweigh ...
s, taken as the minimal MHC encoding, but is closer in organization to that of nonmammals
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
. The IPD-MHC Database was created which provides a centralised repository for sequences of the Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) from a number of different species. The database contains 77 species for the release from 2019-12-19.
Genes
The MHC locus is present in alljawed vertebrates
Gnathostomata (; from Greek: (') "jaw" + (') "mouth") are the jawed vertebrates. Gnathostome diversity comprises roughly 60,000 species, which accounts for 99% of all living vertebrates, including humans. In addition to opposing jaws, living ...
, it is assumed to have arisen about 450 million years ago. Despite the difference in the number of genes included in the MHC of different species, the overall organization of the locus is rather similar. Usual MHC contains about a hundred genes and pseudogenes, not all of them are involved in immunity. In human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
s, the MHC region occurs on chromosome 6
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans more than 170 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total ...
, between the flanking genetic marker A genetic marker is a gene or DNA sequence with a known location on a chromosome that can be used to identify individuals or species. It can be described as a variation (which may arise due to mutation or alteration in the genomic loci) that can be ...
s '' MOG'' and '' COL11A2'' (from 6p22.1 to 6p21.3 about 29Mb to 33Mb on the hg38 assembly), and contains 224 genes spanning 3.6 megabase pairs
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA ...
(3 600 000 bases). About half have known immune functions. The human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
MHC is also called the HLA (human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of th ...
) complex (often just the HLA). Similarly, there is SLA (Swine leukocyte antigens), BoLA (Bovine leukocyte antigens), DLA for dogs, etc. However, historically, the MHC in mice
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus' ...
is called the Histocompatibility system 2 or just the H-2, in rats - RT1, and in chicken - B-locus.
The MHC gene family is divided into three subgroups: MHC class I
MHC class I molecules are one of two primary classes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules (the other being MHC class II) and are found on the cell surface of all nucleated cells in the bodies of vertebrates. They also occur on plat ...
, MHC class II
MHC Class II molecules are a class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules normally found only on professional antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, mononuclear phagocytes, some endothelial cells, thymic epithelial ce ...
, and MHC class III
MHC class III is a group of proteins belonging the class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Unlike other MHC types such as MHC class I and MHC class II, of which their structure and functions in immune response are well defined, MHC class ...
. Among all those genes present in MHC, there are two types of genes coding for the proteins MHC class I
MHC class I molecules are one of two primary classes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules (the other being MHC class II) and are found on the cell surface of all nucleated cells in the bodies of vertebrates. They also occur on plat ...
molecules and MHC class II
MHC Class II molecules are a class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules normally found only on professional antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, mononuclear phagocytes, some endothelial cells, thymic epithelial ce ...
molecules that are directly involved in the antigen presentation
Antigen presentation is a vital immune process that is essential for T cell immune response triggering. Because T cells recognize only fragmented antigens displayed on cell surfaces, antigen processing must occur before the antigen fragment, now ...
. These genes are highly polymorphic, 19031 alleles of class I HLA, and 7183 of class II HLA are deposited for human in the IMGT database.
Proteins
MHC class I
MHC class I
MHC class I molecules are one of two primary classes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules (the other being MHC class II) and are found on the cell surface of all nucleated cells in the bodies of vertebrates. They also occur on plat ...
molecules are expressed in some nucleated
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, ...
cells and also in platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek ╬ĖŽüŽī╬╝╬▓╬┐Žé, "clot" and ╬║ŽŹŽä╬┐Žé, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby ini ...
sŌĆöin essence all cells but red blood cell
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "holl ...
s. It presents epitopes to killer T cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell r ...
s, also called cytotoxic T lymphocyte
A cytotoxic T cell (also known as TC, cytotoxic T lymphocyte, CTL, T-killer cell, cytolytic T cell, CD8+ T-cell or killer T cell) is a T cell, T lymphocyte (a type of white blood cell) that kills cancer cells, cells that are infected by intracel ...
s (CTLs). A CTL expresses CD8 receptors, in addition to T-cell receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding b ...
s (TCR)s. When a CTL's CD8 receptor docks to a MHC class I molecule, if the CTL's TCR fits the epitope within the MHC class I molecule, the CTL triggers the cell to undergo programmed cell death by apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ß╝ĆŽĆŽīŽĆŽäŽēŽā╬╣Žé, ap├│pt┼Źsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes incl ...
. Thus, MHC class I helps mediate cellular immunity
Cell-mediated immunity or cellular immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibodies. Rather, cell-mediated immunity is the activation of phagocytes, antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and the release of various cytokines in ...
, a primary means to address intracellular pathogen
Intracellular parasites are microparasites that are capable of growing and reproducing inside the cells of a host.
Types of parasites
There are two main types of intracellular parasites: Facultative and Obligate.
Facultative intracellular para ...
s, such as virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea.
Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1 ...
es and some bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among ...
, including bacterial L forms, bacterial genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
''Mycoplasma
''Mycoplasma'' is a genus of bacteria that, like the other members of the class ''Mollicutes'', lack a cell wall around their cell membranes. Peptidoglycan (murein) is absent. This characteristic makes them naturally resistant to antibiotics ...
'', and bacterial genus ''Rickettsia
''Rickettsia'' is a genus of nonmotile, gram-negative, nonspore-forming, highly pleomorphic bacteria that may occur in the forms of cocci (0.1 ╬╝m in diameter), bacilli (1ŌĆō4 ╬╝m long), or threads (up to about 10 ╬╝m long). The term "rickett ...
''. In humans, MHC class I comprises HLA-A
HLA-A is a group of human leukocyte antigens (HLA) that are encoded by the HLA-A locus, which is located at human chromosome 6p21.3. HLA is a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigen specific to humans. HLA-A is one of three major types of ...
, HLA-B
HLA-B (major histocompatibility complex, class I, B) is a human gene that provides instructions for making a protein that plays a critical role in the immune system. HLA-B is part of a family of genes called the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) compl ...
, and HLA-C
HLA-C belongs to the MHC (human = HLA) class I heavy chain receptors. The C receptor is a heterodimer consisting of a HLA-C mature gene product and ╬▓2-microglobulin. The mature C chain is anchored in the membrane. MHC Class I molecules, like HLA ...
molecules.
The first crystal structure of Class I MHC molecule, human HLA-A2, was published in 1989. The structure revealed that MHC-I molecules are heterodimers
In biochemistry, a protein dimer is a macromolecular complex formed by two protein monomers, or single proteins, which are usually non-covalently bound. Many macromolecules, such as proteins or nucleic acids, form dimers. The word ''dimer'' ha ...
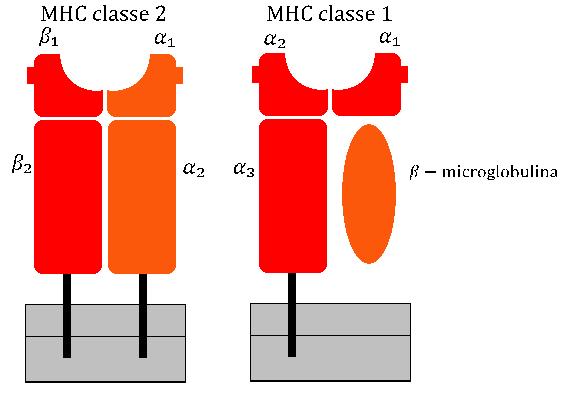
, they have polymorphic heavy ╬▒-subunit whose gene occurs inside the MHC locus and small invariant ╬▓2 microglobulin subunit whose gene is located usually outside of it. Polymorphic heavy chain of MHC-I molecule contains N-terminal extra-cellular region composed by three domains, ╬▒1, ╬▒2, and ╬▒3, transmembrane helix to hold MHC-I molecule on the cell surface and short cytoplasmic tail. Two domains, ╬▒1 and ╬▒2 form deep peptide-binding groove between two long ╬▒-helices and the floor of the groove formed by eight ╬▓-strands. Immunoglobulin-like domain ╬▒3 involved in the interaction with CD8
CD8 (cluster of differentiation 8) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). Along with the TCR, the CD8 co-receptor plays a role in T cell signaling and aiding with cytotoxic T cell-antigen int ...
co-receptor. ╬▓2 microglobulin provides stability of the complex and participates in the recognition of peptide-MHC class I complex by CD8
CD8 (cluster of differentiation 8) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). Along with the TCR, the CD8 co-receptor plays a role in T cell signaling and aiding with cytotoxic T cell-antigen int ...
co-receptor. The peptide is non-covalently bound to MHC-I, it is held by the several pockets on the floor of the peptide-binding groove. Amino acid side-chains that are most polymorphic in human alleles fill up the central and widest portion of the binding groove, while conserved side-chains are clustered at the narrower ends of the groove.
 Classical MHC molecules present epitopes to the TCRs of CD8+ T lymphocytes. Nonclassical molecules (MHC class IB) exhibit limited polymorphism, expression patterns, and presented antigens; this group is subdivided into a group encoded within MHC loci (e.g., HLA-E, -F, -G), as well as those not (e.g., stress ligands such as ULBPs, Rae1, and H60); the antigen/ligand for many of these molecules remain unknown, but they can interact with each of CD8+ T cells, NKT cells, and NK cells. The evolutionary oldest nonclassical MHC class I lineage in human was deduced to be the lineage that includes the CD1 and PROCR (alias EPCR) molecules and this lineage may have been established before the origin of tetrapod species. However, the only nonclassical MHC class I lineage for which evidence exists that it was established before the evolutionary separation of Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish) and Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish plus tetrapods) is lineage Z of which members are found, together in each species with classical MHC class I, in lungfish and throughout ray-finned fishes; why the Z lineage was well conserved in ray-finned fish but lost in tetrapods is not understood.
Classical MHC molecules present epitopes to the TCRs of CD8+ T lymphocytes. Nonclassical molecules (MHC class IB) exhibit limited polymorphism, expression patterns, and presented antigens; this group is subdivided into a group encoded within MHC loci (e.g., HLA-E, -F, -G), as well as those not (e.g., stress ligands such as ULBPs, Rae1, and H60); the antigen/ligand for many of these molecules remain unknown, but they can interact with each of CD8+ T cells, NKT cells, and NK cells. The evolutionary oldest nonclassical MHC class I lineage in human was deduced to be the lineage that includes the CD1 and PROCR (alias EPCR) molecules and this lineage may have been established before the origin of tetrapod species. However, the only nonclassical MHC class I lineage for which evidence exists that it was established before the evolutionary separation of Actinopterygii (ray-finned fish) and Sarcopterygii (lobe-finned fish plus tetrapods) is lineage Z of which members are found, together in each species with classical MHC class I, in lungfish and throughout ray-finned fishes; why the Z lineage was well conserved in ray-finned fish but lost in tetrapods is not understood.
MHC class II
MHC class II
MHC Class II molecules are a class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules normally found only on professional antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, mononuclear phagocytes, some endothelial cells, thymic epithelial ce ...
can be conditionally expressed by all cell types, but normally occurs only on "professional" antigen-presenting cells
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a cell that displays antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize these complexes using ...
(APCs): macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M Žå, M╬” or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''╬╝╬▒╬║ŽüŽīŽé'' (') = large, ''Žå╬▒╬│╬Ąß┐¢╬Į'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cel ...
s, B cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or ...
s, and especially dendritic cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. The ...
(DCs). An APC takes up an antigenic protein, performs antigen processing Antigen processing, or the cytosolic pathway, is an immunological process that prepares antigens for presentation to special cells of the immune system called T lymphocytes. It is considered to be a stage of antigen presentation pathways. This pro ...
, and returns a molecular fraction of itŌĆöa fraction termed the epitope
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The epitope is the specific piece of the antigen to which an antibody binds. The p ...
ŌĆöand displays it on the APC's surface coupled within an MHC class II molecule (antigen presentation
Antigen presentation is a vital immune process that is essential for T cell immune response triggering. Because T cells recognize only fragmented antigens displayed on cell surfaces, antigen processing must occur before the antigen fragment, now ...
). On the cell's surface, the epitope can be recognized by immunologic structures like T-cell receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding b ...
s (TCRs). The molecular region which binds to the epitope is the paratope
In immunology, a paratope, also known as an antigen-binding site, is the part of an antibody which recognizes and binds to an antigen. It is a small region at the tip of the antibody's antigen-binding fragment and contains parts of the antibody' ...
.
On surfaces of helper T cells are CD4 receptors, as well as TCRs. When a naive helper T cell's CD4 molecule docks to an APC's MHC class II molecule, its TCR can meet and bind the epitope coupled within the MHC class II. This event primes the naive T cell
In immunology, a naive T cell (Th0 cell) is a T cell that has differentiated in the thymus, and successfully undergone the positive and negative processes of central selection in the thymus. Among these are the naive forms of helper T cells ( CD ...
. According to the local milieu, that is, the balance of cytokine
Cytokines are a broad and loose category of small proteins (~5ŌĆō25 kDa) important in cell signaling. Cytokines are peptides and cannot cross the lipid bilayer of cells to enter the cytoplasm. Cytokines have been shown to be involved in autocrin ...
s secreted by APCs in the microenvironment, the naive helper T cell
The T helper cells (Th cells), also known as CD4+ cells or CD4-positive cells, are a type of T cell that play an important role in the adaptive immune system. They aid the activity of other immune cells by releasing cytokines. They are considere ...
(Th0) polarizes into either a memory Th cell or an effector Th cell of phenotype
In genetics, the phenotype () is the set of observable characteristics or traits of an organism. The term covers the organism's morphology or physical form and structure, its developmental processes, its biochemical and physiological proper ...
either type 1 (Th1), type 2 (Th2), type 17 (Th17), or regulatory/suppressor (Treg), as so far identified, the Th cell's terminal differentiation.
MHC class II thus mediates immunization toŌĆöor, if APCs polarize Th0 cells principally to Treg cells, immune tolerance
Immune tolerance, or immunological tolerance, or immunotolerance, is a state of unresponsiveness of the immune system to substances or tissue that would otherwise have the capacity to elicit an immune response in a given organism. It is induced by ...
ofŌĆöan antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
. The polarization during primary exposure to an antigen is key in determining a number of chronic disease
A chronic condition is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term ''chronic'' is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three mo ...
s, such as inflammatory bowel diseases
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine, as well ...
and asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, cou ...
, by skewing the immune response that memory Th cells coordinate when their memory recall is triggered upon secondary exposure to similar antigens. B cells express MHC class II to present antigens to Th0, but when their B cell receptor
The B cell receptor (BCR) is a transmembrane protein on the surface of a B cell. A B cell receptor is composed of a membrane-bound immunoglobulin molecule and a signal transduction moiety. The former forms a type 1 transmembrane receptor protein, ...
s bind matching epitopes, interactions which are not mediated by MHC, these activated B cells secrete soluble immunoglobulins: antibody
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the ...
molecules mediating humoral immunity
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is named so because it in ...
.
Class II MHC molecules are also heterodimers, genes for both ╬▒ and ╬▓ subunits are polymorphic and located within MHC class II subregion. Peptide-binding groove of MHC-II molecules is forms by N-terminal domains of both subunits of the heterodimer, ╬▒1 and ╬▓1, unlike MHC-I molecules, where two domains of the same chain are involved. In addition, both subunits of MHC-II contain transmembrane helix and immunoglobulin domains ╬▒2 or ╬▓2 that can be recognized by CD4 co-receptors. In this way MHC molecules chaperone which type of lymphocytes may bind to the given antigen with high affinity, since different lymphocytes express different T-Cell Receptor (TCR) co-receptors.
MHC class II molecules in humans have five to six
isotypes. Classical molecules present peptides to CD4+ lymphocytes. Nonclassical molecules, accessories, with intracellular functions, are not exposed on cell membranes, but in internal membranes, assisting with the loading of antigenic peptides onto classic MHC class II molecules. The important nonclassical MHC class II molecule DM is only found from the evolutionary level of lungfish, although also in more primitive fishes both classical and nonclassical MHC class II are found.
MHC class III
Class III molecules have physiologic roles unlike classes I and II, but are encoded between them in the short arm of human chromosome 6. Class III molecules include several secreted proteins with immune functions: components of thecomplement system
The complement system, also known as complement cascade, is a part of the immune system that enhances (complements) the ability of antibodies and phagocytic cells to clear microbes and damaged cells from an organism, promote inflammation, and at ...
(such as C2, C4, and B factor), cytokines (such as TNF-╬▒
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-╬▒) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
, LTA, and LTB), and heat shock protein
Heat shock proteins (HSP) are a family of proteins produced by cells in response to exposure to stressful conditions. They were first described in relation to heat shock, but are now known to also be expressed during other stresses including expo ...
s.
Function
MHC is the tissue-antigen that allows the immune system (more specifically T cells) to bind to, recognize, and tolerate itself (autorecognition). MHC is also the chaperone for intracellular peptides that are complexed with MHCs and presented toT cell receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding b ...
s (TCRs) as potential foreign antigens. MHC interacts with TCR and its co-receptors to optimize binding conditions for the TCR-antigen interaction, in terms of antigen binding affinity and specificity, and signal transduction effectiveness.
Essentially, the MHC-peptide complex is a complex of auto-antigen/allo-antigen. Upon binding, T cells should in principle tolerate the auto-antigen, but activate when exposed to the allo-antigen. Disease states occur when this principle is disrupted.
Antigen presentation
Antigen presentation is a vital immune process that is essential for T cell immune response triggering. Because T cells recognize only fragmented antigens displayed on cell surfaces, antigen processing must occur before the antigen fragment, now ...
: MHC molecules bind to both T cell receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding b ...
and CD4/CD8
CD8 (cluster of differentiation 8) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that serves as a co-receptor for the T-cell receptor (TCR). Along with the TCR, the CD8 co-receptor plays a role in T cell signaling and aiding with cytotoxic T cell-antigen int ...
co-receptors on T lymphocytes
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell rec ...
, and the antigen epitope
An epitope, also known as antigenic determinant, is the part of an antigen that is recognized by the immune system, specifically by antibodies, B cells, or T cells. The epitope is the specific piece of the antigen to which an antibody binds. The p ...
held in the peptide-binding groove of the MHC molecule interacts with the variable Ig-Like domain of the TCR to trigger T-cell activation
Autoimmune reaction
An autoimmune disease is a condition arising from an abnormal immune response to a functioning body part. At least 80 types of autoimmune diseases have been identified, with some evidence suggesting that there may be more than 100 types. Nearly a ...
: Having some MHC molecules increases the risk of autoimmune diseases more than having others. HLA-B27
Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) B27 (subtypes B*2701-2759) is a class I surface antigen encoded by the B locus in the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) on chromosome 6 and presents antigenic peptides (derived from self and non-self antigens) to ...
is an example. It is unclear how exactly having the HLA-B27 tissue type increases the risk of ankylosing spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hip ...
and other associated inflammatory diseases, but mechanisms involving aberrant antigen presentation or T cell activation have been hypothesized.
Tissue allorecognition
Allorecognition is the ability of an individual organism to distinguish its own tissues from those of another. It manifests itself in the recognition of antigens expressed on the surface of cells of non-self origin. Allorecognition has been descri ...
: MHC molecules in complex with peptide epitopes are essentially ligands for TCRs. T cells become activated by binding to the peptide-binding grooves of any MHC molecule that they were not trained to recognize during positive selection
In population genetics, directional selection, is a mode of negative natural selection in which an extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, causing the allele frequency to shift over time in the direction of that phenotype. Under dir ...
in the thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. ...
.
Antigen processing and presentation
phagocytes
Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek ', "to eat" or "devour", and "-cyte", the suffix in biology denoting "cell", from the Greek '' ...
such as macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M Žå, M╬” or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''╬╝╬▒╬║ŽüŽīŽé'' (') = large, ''Žå╬▒╬│╬Ąß┐¢╬Į'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
and immature dendritic cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. The ...
take up entities by phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (Ōēź 0.5 ╬╝m), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is ...
into phagosomes
In cell biology, a phagosome is a vesicle formed around a particle engulfed by a phagocyte via phagocytosis. Professional phagocytes include macrophages, neutrophils, and dendritic cells (DCs).
A phagosome is formed by the fusion of the cell me ...
ŌĆöthough B cells
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or ...
exhibit the more general endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. E ...
into endosomes
Endosomes are a collection of intracellular sorting organelles in eukaryotic cells. They are parts of endocytic membrane transport pathway originating from the trans Golgi network. Molecules or ligands internalized from the plasma membrane can ...
ŌĆöwhich fuse with lysosomes
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane prote ...
whose acidic enzymes cleave the uptaken protein into many different peptides. Via physicochemical dynamics in molecular interaction with the particular MHC class II variants borne by the host, encoded in the host's genome, a particular peptide exhibits immunodominance and loads onto MHC class II molecules. These are trafficked to and externalized on the cell surface.
* In MHC class I, any nucleated cell normally presents cytosolic peptides, mostly self peptides derived from protein turnover and defective ribosomal products. During viral infection, intracellular microorganism infection, or cancerous transformation, such proteins degraded in the proteosome
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases.
Proteasomes are part of a major mechanism by whi ...
are as well loaded onto MHC class I molecules and displayed on the cell surface. T lymphocytes can detect a peptide displayed at 0.1%-1% of the MHC molecules.

T lymphocyte recognition restrictions
In their development in thethymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. ...
, T lymphocytes are selected to recognize MHC molecules of the host, but not recognize other self antigens. Following selection, each T lymphocyte shows dual specificity: The TCR recognizes self MHC, but only non-self antigens.
MHC restriction occurs during lymphocyte development in the thymus through a process known as positive selection
In population genetics, directional selection, is a mode of negative natural selection in which an extreme phenotype is favored over other phenotypes, causing the allele frequency to shift over time in the direction of that phenotype. Under dir ...
. T cells that do not receive a positive survival signal ŌĆö mediated mainly by thymic epithelial cells presenting self peptides bound to MHC molecules ŌĆö to their TCR undergo apoptosis. Positive selection ensures that mature T cells can functionally recognize MHC molecules in the periphery (i.e. elsewhere in the body).
The TCRs of T lymphocytes recognise only sequential epitopes, also called linear epitope
In immunology, a linear epitope (also sequential epitope) is an epitopeŌĆöa binding site on an antigenŌĆöthat is recognized by antibodies by its linear sequence of amino acids (i.e. primary structure). In contrast, most antibodies recognize a con ...
s, of only peptides and only if coupled within an MHC molecule. (Antibody molecules secreted by activated B cells, though, recognize diverse epitopesŌĆöpeptide
Peptides (, ) are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. Long chains of amino acids are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides.
A ...
, lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include ...
, carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogenŌĆōoxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or ma ...
, and nucleic acid
Nucleic acids are biopolymers, macromolecules, essential to all known forms of life. They are composed of nucleotides, which are the monomers made of three components: a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group and a nitrogenous base. The two main cl ...
ŌĆöand recognize conformational epitope
In immunology, a conformational epitope is a sequence of sub-units (usually amino acids) composing an antigen that come in direct contact with a receptor of the immune system.
An ''antigen'' is any substance that the immune system can recognize ...
s, which have three-dimensional
Three-dimensional space (also: 3D space, 3-space or, rarely, tri-dimensional space) is a geometric setting in which three values (called ''parameters'') are required to determine the position of an element (i.e., point). This is the informal ...
structure.)
In sexual mate selection
MHC molecules enable immune system surveillance of the population of protein molecules in a host cell, and greater MHC diversity permits greater diversity ofantigen presentation
Antigen presentation is a vital immune process that is essential for T cell immune response triggering. Because T cells recognize only fragmented antigens displayed on cell surfaces, antigen processing must occur before the antigen fragment, now ...
. In 1976, Yamazaki ''et al'' demonstrated a sexual selection
Sexual selection is a mode of natural selection in which members of one biological sex mate choice, choose mates of the other sex to mating, mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of t ...
mate choice
Mate choice is one of the primary mechanisms under which evolution can occur. It is characterized by a "selective response by animals to particular stimuli" which can be observed as behavior.Bateson, Paul Patrick Gordon. "Mate Choice." Mate Choic ...
by male mice for females of a different MHC. Similar results have been obtained with fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of li ...
. Some data find lower rates of early pregnancy loss
Miscarriage, also known in medical terms as a spontaneous abortion and pregnancy loss, is the death of an embryo or fetus before it is able to survive independently. Miscarriage before 6 weeks of gestation is defined by ESHRE as biochemical lo ...
in human couples of dissimilar MHC genes.
MHC may be related to mate choice in some human populations, a theory that found support by studies by Ober and colleagues in 1997, as well as by Chaix and colleagues in 2008. However, the latter findings have been controversial. If it exists, the phenomenon might be mediated by olfaction
The sense of smell, or olfaction, is the special sense through which smells (or odors) are perceived. The sense of smell has many functions, including detecting desirable foods, hazards, and pheromones, and plays a role in taste.
In humans, it ...
, as MHC phenotype appears strongly involved in the strength and pleasantness of perceived odour of compounds from sweat
Perspiration, also known as sweating, is the production of fluids secreted by the sweat glands in the skin of mammals.
Two types of sweat glands can be found in humans: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. The eccrine sweat glands are distribut ...
. Fatty acid esters
In chemistry, an ester is a compound derived from an oxoacid (organic or inorganic) in which at least one hydroxyl group () is replaced by an alkoxy group (), as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. Glycerides are ...
ŌĆösuch as methyl undecanoate, methyl decanoate, methyl nonanoate, methyl octanoate, and methyl hexanoateŌĆöshow strong connection to MHC.
In 1995, Claus Wedekind
Claus Wedekind is a Swiss biological researcher notable for his 1995 study that determined a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) dependent mate preference in humans.
This study is often known as the "sweaty T-shirt study". In it, men each wor ...
found that in a group of female college students who smelled T-shirts worn by male students for two nights (without deodorant, cologne, or scented soaps), by far most women chose shirts worn by men of dissimilar MHCs, a preference reversed if the women were on oral contraceptives. In 2005 in a group of 58 subjects, women were more indecisive when presented with MHCs like their own, although with oral contraceptives, the women showed no particular preference. No studies show the extent to which odor preference determines mate selection (or vice versa).
Evolutionary diversity
Mostmammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s have MHC variants similar to those of humans, who bear great allelic diversity, especially among the nine classical genesŌĆöseemingly due largely to gene duplication
Gene duplication (or chromosomal duplication or gene amplification) is a major mechanism through which new genetic material is generated during molecular evolution. It can be defined as any duplication of a region of DNA that contains a gene. ...
ŌĆöthough human MHC regions have many pseudogene
Pseudogenes are nonfunctional segments of DNA that resemble functional genes. Most arise as superfluous copies of functional genes, either directly by DNA duplication or indirectly by Reverse transcriptase, reverse transcription of an mRNA trans ...
s. The most diverse loci, namely HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C, have roughly 6000, 7200, and 5800 known alleles, respectively. Many HLA alleles are ancient, sometimes of closer homology
Homology may refer to:
Sciences
Biology
*Homology (biology), any characteristic of biological organisms that is derived from a common ancestor
* Sequence homology, biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences
*Homologous chrom ...
to a chimpanzee MHC alleles than to some other human alleles of the same gene.
MHC allelic diversity has challenged evolutionary biologists
Evolutionary biology is the subfield of biology that studies the evolution, evolutionary processes (natural selection, common descent, speciation) that produced the Biodiversity, diversity of life on Earth. It is also defined as the study of ...
for explanation. Most posit balancing selection Balancing selection refers to a number of selective processes by which multiple alleles (different versions of a gene) are actively maintained in the gene pool of a population at frequencies larger than expected from genetic drift alone. Balancing ...
(see polymorphism (biology)
In biology, polymorphism is the occurrence of two or more clearly different morphs or forms, also referred to as alternative ''phenotypes'', in the population of a species. To be classified as such, morphs must occupy the same habitat at the s ...
), which is any natural selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charle ...
process whereby no single allele is absolutely most fit, such as frequency-dependent selection Frequency-dependent selection is an evolutionary process by which the fitness (biology), fitness of a phenotype or genotype depends on the phenotype or genotype composition of a given population.
* In positive frequency-dependent selection, the fit ...
and heterozygote advantage
A heterozygote advantage describes the case in which the heterozygous genotype has a higher relative fitness (biology), fitness than either the homozygous Dominance (genetics), dominant or homozygous recessive gene, recessive genotype. Loci exhib ...
. Pathogenic coevolution, as a type of balancing selection, posits that common alleles are under greatest pathogenic pressure, driving positive selection of uncommon allelesŌĆömoving targets, so to say, for pathogens. As pathogenic pressure on the previously common alleles decreases, their frequency in the population stabilizes, and remain circulating in a large population. Genetic drift
Genetic drift, also known as allelic drift or the Wright effect, is the change in the frequency of an existing gene variant (allele) in a population due to random chance.
Genetic drift may cause gene variants to disappear completely and there ...
is also a major driving force in some species. It is possible that the combined effects of some or all of these factors cause the genetic diversity.
MHC diversity has also been suggested as a possible indicator for conservation, because large, stable populations tend to display greater MHC diversity, than smaller, isolated populations. Small, fragmented populations that have experienced a population bottleneck
A population bottleneck or genetic bottleneck is a sharp reduction in the size of a population due to environmental events such as famines, earthquakes, floods, fires, disease, and droughts; or human activities such as specicide, widespread violen ...
typically have lower MHC diversity. For example, relatively low MHC diversity has been observed in the cheetah
The cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus'') is a large cat native to Africa and central Iran. It is the fastest land animal, estimated to be capable of running at with the fastest reliably recorded speeds being , and as such has evolved specialized ...
(''Acinonyx jubatus''), Eurasian beaver
The Eurasian beaver (''Castor fiber'') or European beaver is a beaver species that was once widespread in Eurasia, but was hunted to near-extinction for both its fur and castoreum. At the turn of the 20th century, only about 1,200 beavers survi ...
(''Castor fiber''), and giant panda
The giant panda (''Ailuropoda melanoleuca''), also known as the panda bear (or simply the panda), is a bear species endemic to China. It is characterised by its bold black-and-white coat and rotund body. The name "giant panda" is sometimes us ...
(''Ailuropoda melanoleuca''). In 2007 low MHC diversity was attributed a role in disease susceptibility in the Tasmanian devil
The Tasmanian devil (''Sarcophilus harrisii'') (palawa kani: purinina) is a carnivorous marsupial of the family Dasyuridae. Until recently, it was only found on the island state of Tasmania, but it has been reintroduced to New South Wales in ...
(''Sarcophilus harrisii''), native to the isolated island of Tasmania
)
, nickname =
, image_map = Tasmania in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Tasmania in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdi ...
, such that an antigen of a transmissible tumor, involved in devil facial tumour disease
Devil facial tumour disease (DFTD) is an aggressive non-viral clonally transmissible cancer which affects Tasmanian devils, a marsupial native to Australia. DFTD was first described in 1996. In the subsequent decade the disease ravaged Tasmania's ...
, appears to be recognized as a ''self antigen''. To offset inbreeding
Inbreeding is the production of offspring from the mating or breeding of individuals or organisms that are closely related genetically. By analogy, the term is used in human reproduction, but more commonly refers to the genetic disorders and o ...
, efforts to sustain genetic diversity in populations of endangered species and of captive animals have been suggested.
In ray-finned fish like rainbow trout, allelic polymorphism in MHC class II is reminiscent of that in mammals and predominantly maps to the peptide binding groove. However, in MHC class I of many teleost fishes, the allelic polymorphism is much more extreme than in mammals in the sense that the sequence identity levels between alleles can be very low and the variation extends far beyond the peptide binding groove. It has been speculated that this type of MHC class I allelic variation contributes to allograft rejection, which may be especially important in fish to avoid grafting of cancer cells through their mucosal skin.
The MHC locus (6p21.3) has 3 other paralogous loci in the human genome, namely 19pl3.1, 9q33-q34, and 1q21-q25. It is believed that the loci arouse from the two-round duplications in vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () ( chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, ...
s of a single ProtoMHC locus, and the new domain organizations of the MHC genes were a result of later cis-duplication and exon shuffling in a process termed "the MHC Big Bang." Genes in this locus are apparently linked to intracellular intrinsic immunity in the basal Metazoan
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals Heterotroph, consume organic material, Cellular respiration#Aerobic respiration, breathe oxygen, are Motility, able to move, ca ...
''Trichoplax adhaerens
''Trichoplax adhaerens'' is one of the three named species in the phylum Placozoa. The others are ''Hoilungia hongkongensis'' and ''Polyplacotoma mediterranea''. The Placozoa is a basal group of multicellular animals (metazoa). ''Trichoplax'' ar ...
''.
In transplant rejection
In a transplant procedure, as of an organ orstem cells
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type o ...
, MHC molecules themselves act as antigen
In immunology, an antigen (Ag) is a molecule or molecular structure or any foreign particulate matter or a pollen grain that can bind to a specific antibody or T-cell receptor. The presence of antigens in the body may trigger an immune response. ...
s and can provoke immune response in the recipient, thus causing transplant rejection. MHC molecules were identified and named after their role in transplant rejection between mice of different strains, though it took over 20 years to clarify MHC's role in presenting peptide antigens to cytotoxic T lymphocytes
A cytotoxic T cell (also known as TC, cytotoxic T lymphocyte, CTL, T-killer cell, cytolytic T cell, CD8+ T-cell or killer T cell) is a T lymphocyte (a type of white blood cell) that kills cancer cells, cells that are infected by intracellular pa ...
(CTLs).
Each human cell expresses six MHC class I alleles (one HLA-A, -B, and -C allele from each parent) and six to eight MHC class II alleles (one HLA-DP and -DQ, and one or two HLA-DR from each parent, and combinations of these). The MHC variation in the human population is high, at least 350 alleles for HLA-A genes, 620 alleles for HLA-B, 400 alleles for DR, and 90 alleles for DQ. Any two individuals who are not identical twins will express differing MHC molecules. All MHC molecules can mediate transplant rejection, but HLA-C and HLA-DP, showing low polymorphism, seem least important.
When maturing in the thymus, T lymphocytes are selected for their TCR incapacity to recognize self antigens, yet T lymphocytes can react against the donor MHC's peptide-binding groove, the variable region of MHC holding the presented antigen's epitope for recognition by TCR, the matching paratope
In immunology, a paratope, also known as an antigen-binding site, is the part of an antibody which recognizes and binds to an antigen. It is a small region at the tip of the antibody's antigen-binding fragment and contains parts of the antibody' ...
. T lymphocytes of the recipient take the incompatible peptide-binding groove as nonself antigen.
Transplant rejection has various types known to be mediated by MHC (HLA):
* Hyperacute rejection occurs when, before the transplantation, the recipient has preformed anti-HLA antibodies, perhaps by previous blood transfusions (donor tissue that includes lymphocytes expressing HLA molecules), by anti-HLA generated during pregnancy (directed at the father's HLA displayed by the fetus), or by previous transplantation;
* Acute cellular rejection occurs when the recipient's T lymphocytes are activated by the donor tissue, causing damage via mechanisms such as direct cytotoxicity from CD8 cells.
* Acute humoral rejection and chronic disfunction occurs when the recipient's anti-HLA antibodies form directed at HLA molecules present on endothelial cells
The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vessel ...
of the transplanted tissue.
In all of the above situations, immunity is directed at the transplanted organ, sustaining lesions. A cross-reaction test between potential donor cells and recipient serum seeks to detect presence of preformed anti-HLA antibodies in the potential recipient that recognize donor HLA molecules, so as to prevent hyperacute rejection. In normal circumstances, compatibility between HLA-A, -B, and -DR molecules is assessed. The higher the number of incompatibilities, the lower the five-year survival rate. Global databases of donor information enhance the search for compatible donors.
The involvement in allogeneic transplant rejection appears to be an ancient feature of MHC molecules, because also in fish associations between transplant rejections and (mis-)matching of MHC class I and MHC class II were observed.
HLA biology
human leukocyte antigen
The human leukocyte antigen (HLA) system or complex is a complex of genes on chromosome 6 in humans which encode cell-surface proteins responsible for the regulation of the immune system. The HLA system is also known as the human version of th ...
(HLA). To clarify the usage, some of the biomedical literature uses HLA to refer specifically to the HLA protein molecules and reserves MHC for the region of the genome that encodes for this molecule, but this is not a consistent convention.
The most studied HLA genes are the nine classical MHC genes: ''HLA-A
HLA-A is a group of human leukocyte antigens (HLA) that are encoded by the HLA-A locus, which is located at human chromosome 6p21.3. HLA is a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigen specific to humans. HLA-A is one of three major types of ...
, HLA-B
HLA-B (major histocompatibility complex, class I, B) is a human gene that provides instructions for making a protein that plays a critical role in the immune system. HLA-B is part of a family of genes called the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) compl ...
, HLA-C
HLA-C belongs to the MHC (human = HLA) class I heavy chain receptors. The C receptor is a heterodimer consisting of a HLA-C mature gene product and ╬▓2-microglobulin. The mature C chain is anchored in the membrane. MHC Class I molecules, like HLA ...
, HLA-DPA1
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DP alpha 1, also known as HLA-DPA1, is a human gene.
Function
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the HLA class II alpha chain paralogues. The class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting o ...
, HLA-DPB1
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DP(W2) beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HLA-DPB1'' gene.
HLA-DPB belongs to the HLA class II beta chain paralogues. This class II molecule is a heterodimer consisting of an alpha ( ...
, HLA-DQA1
Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DQ alpha 1, also known as HLA-DQA1, is a human gene present on short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.3) and also denotes the genetic locus which contains this gene. The protein encoded by this gene is one of tw ...
, HLA-DQB1, HLA-DRA
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DR alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HLA-DRA gene. HLA-DRA encodes the alpha subunit of HLA-DR. Unlike the alpha chains of other Human MHC class II molecules, the alpha subunit is pra ...
'', and ''HLA-DRB1
HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB1 beta chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HLA-DRB1'' gene. DRB1 encodes the most prevalent beta subunit of HLA-DR. DRB1 alleles, especially those encoding amino acid sequence changes at ...
''. In humans, the MHC gene cluster is divided into three regions: classes I, II, and III. The A, B and C genes belong to MHC class I, whereas the six D genes belong to class II.
MHC alleles are expressed in codominant fashion. This means the allele
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ß╝ä╬╗╬╗╬┐Žé ''├Īllos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
s (variants) inherited from both parents are expressed equally:
* Each person carries 2 alleles of each of the 3 class-I genes, (''HLA-A, HLA-B'' and ''HLA-C''), and so can express six different types of MHC-I (see figure).
* In the class-II locus, each person inherits a pair of HLA-DP genes (DPA1 and DPB1, which encode ╬▒ and ╬▓ chains), a couple of genes'' HLA-DQ'' (''DQA1'' and ''DQB1'', for ╬▒ and ╬▓ chains), one gene ''HLA-DR╬▒'' (''DRA1''), and one or more genes ''HLA-DR╬▓'' (''DRB1'' and ''DRB3, -4'' or ''-5''). That means that one heterozygous
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism.
Mo ...
individual can inherit six or eight functioning class-II alleles, three or more from each parent. The role of ''DQA2'' or ''DQB2'' is not verified. The ''DRB2, DRB6, DRB7, DRB8'' and ''DRB9'' are pseudogenes.
The set of alleles that is present in each chromosome is called the MHC haplotype
A haplotype ( haploid genotype) is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent.
Many organisms contain genetic material ( DNA) which is inherited from two parents. Normally these organisms have their DNA or ...
. In humans, each HLA allele is named with a number. For instance, for a given individual, his haplotype might be HLA-A2, HLA-B5, HLA-DR3, etc... Each heterozygous individual will have two MHC haplotypes, one each from the paternal and maternal chromosomes.
The MHC genes are highly polymorphic; many different alleles exist in the different individuals inside a population. The polymorphism is so high, in a mixed population (non endogamic), no two individuals have exactly the same set of MHC molecules, with the exception of identical twins
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two em ...
.
The polymorphic regions in each allele are located in the region for peptide contact. Of all the peptides that could be displayed by MHC, only a subset will bind strongly enough to any given HLA allele, so by carrying two alleles for each gene, each encoding specificity for unique antigens, a much larger set of peptides can be presented.
On the other hand, inside a population, the presence of many different alleles ensures there will always be an individual with a specific MHC molecule able to load the correct peptide to recognize a specific microbe. The evolution of the MHC polymorphism ensures that a population will not succumb to a new pathogen or a mutated one, because at least some individuals will be able to develop an adequate immune response to win over the pathogen. The variations in the MHC molecules (responsible for the polymorphism) are the result of the inheritance of different MHC molecules, and they are not induced by recombination, as it is the case for the antigen receptors
Receptor may refer to:
*Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a n ...
.
Because of the high levels of allelic
An allele (, ; ; modern formation from Greek ß╝ä╬╗╬╗╬┐Žé ''├Īllos'', "other") is a variation of the same sequence of nucleotides at the same place on a long DNA molecule, as described in leading textbooks on genetics and evolution.
::"The chro ...
diversity found within its genes, MHC has also attracted the attention of many evolution
Evolution is change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. These characteristics are the expressions of genes, which are passed on from parent to offspring during reproduction. Variation ...
ary biologists.
See also
*Cell-mediated immunity
Cell-mediated immunity or cellular immunity is an immune response that does not involve antibodies. Rather, cell-mediated immunity is the activation of phagocytes, antigen-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocytes, and the release of various cytokines in ...
* Disassortative sexual selection
* Humoral immunity
Humoral immunity is the aspect of immunity that is mediated by macromolecules - including secreted antibodies, complement proteins, and certain antimicrobial peptides - located in extracellular fluids. Humoral immunity is named so because it in ...
* MHC multimer MHC multimers are oligomeric forms of MHC molecules, designed to identify and isolate T-cells with high affinity to specific antigens amid a large group of unrelated T-cells. Multimers generally range in size from dimers to octamers; however, some ...
* Pheromone
A pheromone () is a secreted or excreted chemical factor that triggers a social response in members of the same species. Pheromones are chemicals capable of acting like hormones outside the body of the secreting individual, to affect the behavio ...
* Streptamer
* Transplant rejection
Transplant rejection occurs when Organ transplant, transplanted tissue is rejected by the recipient's immune system, which destroys the transplanted tissue. Transplant rejection can be lessened by determining the molecular similitude between don ...
Notes and references
Bibliography
*External links
*''Molecular Individuality''
ĆöGerman online book (2012)
NetMHC 3.0 server
Ćöpredicts binding of peptides to a number of different MHC (HLA) alleles
ĆöCardiff University
The story of 2YF6: A Chicken MHC
RCSB Protein Data Bank: Molecule of the MonthŌĆöMajor Histocompatibility Complex
dbMHC Home, NCBI's database of the Major Histocompatibility Complex
{{Authority control Gene families Glycoproteins Immune system Single-pass transmembrane proteins