|
MHC Class III
MHC class III is a group of proteins belonging the class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC). Unlike other MHC types such as MHC class I and MHC class II, of which their structure and functions in immune response are well defined, MHC class III are poorly defined structurally and functionally. They are not involved in antigen binding (the process called antigen presentation, a classic function of MHC proteins). Only few of them are actually involved in immunity while many are signalling molecules in other cell communications. They are mainly known from their genes because their gene cluster is present between those of class I and class II. The gene cluster was discovered when genes (specifically those of complement components C2, C4, and factor B) were found in between class I and class II genes on the short (p) arm of human chromosome 6. It was later found that it contains many genes for different signalling molecules such as tumour necrosis factors (TNFs) and heat sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
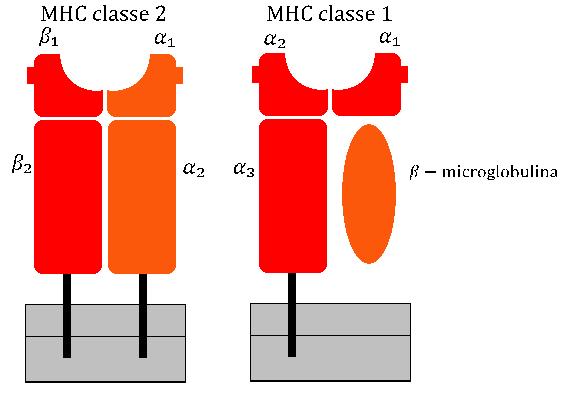
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. This locus got its name because it was discovered via the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules: binding an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bringing the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own phenotype or of other biologic entities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrophage
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris, and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that are specific to healthy body cells on their surface. The process is called phagocytosis, which acts to defend the host against infection and injury. These large phagocytes are found in essentially all tissues, where they patrol for potential pathogens by amoeboid movement. They take various forms (with various names) throughout the body (e.g., histiocytes, Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, and others), but all are part of the mononuclear phagocyte system. Besides phagocytosis, they play a critical role in nonspecific defense (innate immunity) and also help initiate specific defense mechanisms (adaptive immunity) by recruiting other immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genes On Human Chromosome 6
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gene– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LST1
Leukocyte-specific transcript 1 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LST1'' gene In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-6-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NCR3
Natural cytotoxicity triggering receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NCR3'' gene. NCR3 has also been designated as CD337 (cluster of differentiation 337) and as NKp30. NCR3 belongs to the family of NCR membrane receptors together with NCR1 (NKp46) and NCR2 (NKp44). Identification NKp30 receptor was first identified in 1999. According to Western blot analysis specific monoclonal antibodies reacted with 30kDa molecule, therefore was the protein named NKp30. Structure Gene for NKp30 is located in the MHC class III region of the human MHC locus and encodes 190 amino acid long type I transmembrane receptor which belongs to immunoglobulin super family (IgSF). NKp30 has a mass of 30 kDa and includes one Ig-like extracellular domain which is 138 amino acids long, a 19 amino acid transmembrane (TM) domain and a 33 amino acid cytoplasmic tail. The Ig-like domain consists of 2 antiparallel beta-sheets linked by a disulphide bond. The extracellular domain conta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gray Short-tailed Opossum
The gray short-tailed opossum (''Monodelphis domestica'') is a small South American member of the family Didelphidae. Unlike most other marsupials, the gray short-tailed opossum does not have a true pouch. The scientific name ''Monodelphis'' is derived from Greek and means "single womb" (referring to the lack of a pouch) and the Latin word ''domestica'' which means "domestic" (chosen because of the species' habit of entering human dwellings). It was the first marsupial to have its genome sequenced. The gray short-tailed opossum is used as a research model in science, and is also frequently found in the exotic pet trade. It is also known as the Brazilian opossum, rainforest opossum and in a research setting the laboratory opossum. Description Gray short-tailed opossums are relatively small animals, with a superficial resemblance to voles. In the wild they have head-body length of and weigh ; males are larger than females. However, individuals kept in captivity are typically mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenopus Tropicalis
The western clawed frog (''Xenopus tropicalis'') is a species of frog in the family Pipidae, also known as tropical clawed frog. It is the only species in the genus ''Xenopus'' to have a diploid genome. Its genome has been sequenced, making it a significant model organism for genetics that complements the related species ''Xenopus laevis'' (the African clawed frog), a widely used vertebrate model for developmental biology. ''X. tropicalis'' also has a number of advantages over ''X. laevis'' in research, such as a much shorter generation time (<5 months), smaller size ( body length), and a larger number of eggs per . It is found in , |
CYP21
Steroid 21-hydroxylase (also known as steroid 21-monooxygenase, cytochrome P450C21, 21α-hydroxylase and less commonly 21β-hydroxylase) is an enzyme that Hydroxylation, hydroxylates steroids at the C21 position and is involved in biosynthesis of aldosterone and cortisol. The enzyme converts progesterone and 17α-Hydroxyprogesterone, 17α-hydroxyprogesterone into 11-Deoxycorticosterone, 11-deoxycorticosterone and 11-Deoxycortisol, 11-deoxycortisol, respectively, within metabolic pathways that ultimately lead to aldosterone and cortisol. Deficiency in the enzyme may cause Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency, congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Steroid 21-hydroxylase is a member of the cytochrome P450 family of monooxygenase enzymes that uses an iron containing heme enzyme cofactor, cofactor to oxidize substrates. The enzyme is localized in endoplasmic reticulum membranes of adrenal cortex, and is encoded by the gene in humans, which is located near the ''CY ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STK19
Serine/threonine-protein kinase 19 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''STK19'' gene. This gene encodes a serine/threonine kinase A serine/threonine protein kinase () is a kinase enzyme, in particular a protein kinase, that phosphorylates the OH group of the amino-acid residues serine or threonine, which have similar side chains. At least 350 of the 500+ human prote ... which localizes predominantly to the nucleus. Its specific function is unknown; it is possible that phosphorylation of this protein is involved in transcriptional regulation. This gene localizes to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region on chromosome 6 and expresses two transcript variants. See also * RCCX References Further reading * * * * * * * * * EC 2.7.11 {{gene-6-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alu Element
An Alu element is a short stretch of DNA originally characterized by the action of the ''Arthrobacter luteus (Alu)'' restriction endonuclease. ''Alu'' elements are the most abundant transposable elements, containing over one million copies dispersed throughout the human genome. ''Alu'' elements were thought to be selfish or parasitic DNA, because their sole known function is self reproduction. However, they are likely to play a role in evolution and have been used as genetic markers. They are derived from the small cytoplasmic 7SL RNA, a component of the signal recognition particle. ''Alu'' elements are highly conserved within primate genomes and originated in the genome of an ancestor of Supraprimates. ''Alu'' insertions have been implicated in several inherited human diseases and in various forms of cancer. The study of Alu elements has also been important in elucidating human population genetics and the evolution of primates, including the evolution of humans. Alu fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Endogenous Retrovirus
Endogenous retroviruses (ERVs) are endogenous viral elements in the genome that closely resemble and can be derived from retroviruses. They are abundant in the genomes of jawed vertebrates, and they comprise up to 5–8% of the human genome (lower estimates of ~1%). ERVs are a vertically inherited proviral sequence and a subclass of a type of gene called a transposon, which can normally be packaged and moved within the genome to serve a vital role in gene expression and in regulation. ERVs however lack most transposon functions, are typically not infectious and are often defective genomic remnants of the retroviral replication cycle. They are distinguished as germline provirus retroelements due to their integration and reverse-transcription into the nuclear genome of the host cell. Researchers have suggested that retroviruses evolved from a type of transposon called a retrotransposon, a Class I element; these genes can mutate and instead of moving to another location in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |