|
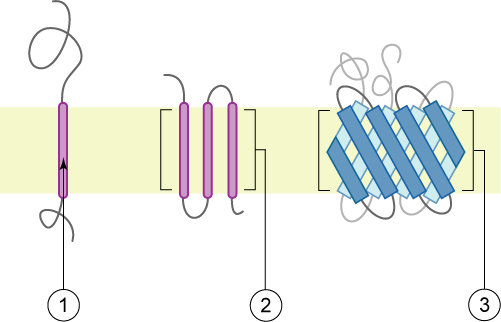
Single-pass Transmembrane Proteins
A single-pass membrane protein also known as single-spanning protein or bitopic protein is a transmembrane protein that spans the lipid bilayer only once. These proteins may constitute up to 50% of all transmembrane proteins, depending on the organism, and contribute significantly to the network of interactions between different proteins in cells, including interactions via transmembrane alpha helices. They usually include one or several water-soluble domains situated at the different sides of biological membranes, for example in single-pass transmembrane receptors. Some of them are small and serve as regulatory or structure-stabilizing subunits in large multi-protein transmembrane complexes, such as photosystems or the respiratory chain. A 2013 estimate identified about 1300 single-pass membrane proteins in the human genome. Topology-based classification Bitopic proteins are classified into 4 types, depending on their transmembrane topology and location of the transmembran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Targeting
:''This article deals with protein targeting in eukaryotes unless specified otherwise.'' Protein targeting or protein sorting is the biological mechanism by which proteins are transported to their appropriate destinations within or outside the cell. Proteins can be targeted to the inner space of an organelle, different intracellular membranes, the plasma membrane, or to the exterior of the cell via secretion. Information contained in the protein itself directs this delivery process. Correct sorting is crucial for the cell; errors or dysfunction in sorting have been linked to multiple diseases. History In 1970, Günter Blobel conducted experiments on protein translocation across membranes. Blobel, then an assistant professor at Rockefeller University, built upon the work of his colleague George Palade. Palade had previously demonstrated that non-secreted proteins were translated by free ribosomes in the cytosol, while secreted proteins (and target proteins, in general) were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danio Rerio
The zebrafish (''Danio rerio'') is a freshwater fish belonging to the minnow family (Cyprinidae) of the order Cypriniformes. Native to South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio (and thus often called a "tropical fish" although both tropical and subtropical). It is also found in private ponds. The zebrafish is an important and widely used vertebrate model organism in scientific research, for example in drug development, in particular pre-clinical development. It is also notable for its regenerative abilities, and has been modified by researchers to produce many transgenic strains. Taxonomy The zebrafish is a derived member of the genus ''Brachydanio'', of the family Cyprinidae. It has a sister-group relationship with '' Danio aesculapii''. Zebrafish are also closely related to the genus '' Devario'', as demonstrated by a phylogenetic tree of close species. Distribution Range The zebrafish is native to fresh water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Model Organism
A model organism (often shortened to model) is a non-human species that is extensively studied to understand particular biological phenomena, with the expectation that discoveries made in the model organism will provide insight into the workings of other organisms. Model organisms are widely used to research human disease when human experimentation would be unfeasible or unethical. This strategy is made possible by the common descent of all living organisms, and the conservation of metabolic and developmental pathways and genetic material over the course of evolution. Studying model organisms can be informative, but care must be taken when generalizing from one organism to another. In researching human disease, model organisms allow for better understanding the disease process without the added risk of harming an actual human. The species chosen will usually meet a determined taxonomic equivalency to humans, so as to react to disease or its treatment in a way that resembl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unicellular Organism
A unicellular organism, also known as a single-celled organism, is an organism that consists of a single cell, unlike a multicellular organism that consists of multiple cells. Organisms fall into two general categories: prokaryotic organisms and eukaryotic organisms. All prokaryotes are unicellular and are classified into bacteria and archaea. Many eukaryotes are multicellular, but some are unicellular such as protozoa, unicellular algae, and unicellular fungi. Unicellular organisms are thought to be the oldest form of life, with early protocells possibly emerging 3.8–4.0 billion years ago. Although some prokaryotes live in colonies, they are not specialised cells with differing functions. These organisms live together, and each cell must carry out all life processes to survive. In contrast, even the simplest multicellular organisms have cells that depend on each other to survive. Most multicellular organisms have a unicellular life-cycle stage. Gametes, for example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multicellular Organism
A multicellular organism is an organism that consists of more than one cell, in contrast to unicellular organism. All species of animals, land plants and most fungi are multicellular, as are many algae, whereas a few organisms are partially uni- and partially multicellular, like slime molds and social amoebae such as the genus '' Dictyostelium''. Multicellular organisms arise in various ways, for example by cell division or by aggregation of many single cells. Colonial organisms are the result of many identical individuals joining together to form a colony. However, it can often be hard to separate colonial protists from true multicellular organisms, because the two concepts are not distinct; colonial protists have been dubbed "pluricellular" rather than "multicellular". There are also multinucleate though technically unicellular organisms that are macroscopic, such as the xenophyophorea that can reach 20 cm. Evolutionary history Occurrence Multicellularity has evolve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prokaryotes
A prokaryote () is a single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. The word ''prokaryote'' comes from the Greek πρό (, 'before') and κάρυον (, 'nut' or 'kernel').Campbell, N. "Biology:Concepts & Connections". Pearson Education. San Francisco: 2003. In the two-empire system arising from the work of Édouard Chatton, prokaryotes were classified within the empire Prokaryota. But in the three-domain system, based upon molecular analysis, prokaryotes are divided into two domains: ''Bacteria'' (formerly Eubacteria) and '' Archaea'' (formerly Archaebacteria). Organisms with nuclei are placed in a third domain, Eukaryota. In the study of the origins of life, prokaryotes are thought to have arisen before eukaryotes. Besides the absence of a nucleus, prokaryotes also lack mitochondria, or most of the other membrane-bound organelles that characterize the eukaryotic cell. It was once thought that prokaryotic cellular components within the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eukaryote
Eukaryotes () are organisms whose cells have a nucleus. All animals, plants, fungi, and many unicellular organisms, are Eukaryotes. They belong to the group of organisms Eukaryota or Eukarya, which is one of the three domains of life. Bacteria and Archaea (both prokaryotes) make up the other two domains. The eukaryotes are usually now regarded as having emerged in the Archaea or as a sister of the Asgard archaea. This implies that there are only two domains of life, Bacteria and Archaea, with eukaryotes incorporated among archaea. Eukaryotes represent a small minority of the number of organisms, but, due to their generally much larger size, their collective global biomass is estimated to be about equal to that of prokaryotes. Eukaryotes emerged approximately 2.3–1.8 billion years ago, during the Proterozoic eon, likely as flagellated phagotrophs. Their name comes from the Greek εὖ (''eu'', "well" or "good") and κάρυον (''karyon'', "nut" or "kernel"). E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genome
In the fields of molecular biology and genetics, a genome is all the genetic information of an organism. It consists of nucleotide sequences of DNA (or RNA in RNA viruses). The nuclear genome includes protein-coding genes and non-coding genes, other functional regions of the genome such as regulatory sequences (see non-coding DNA), and often a substantial fraction of 'junk' DNA with no evident function. Almost all eukaryotes have mitochondria and a small mitochondrial genome. Algae and plants also contain chloroplasts with a chloroplast genome. The study of the genome is called genomics. The genomes of many organisms have been sequenced and various regions have been annotated. The International Human Genome Project reported the sequence of the genome for ''Homo sapiens'' in 200The Human Genome Project although the initial "finished" sequence was missing 8% of the genome consisting mostly of repetitive sequences. With advancements in technology that could handle seq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrinsically Disordered Protein
In molecular biology, an intrinsically disordered protein (IDP) is a protein that lacks a fixed or ordered three-dimensional structure, typically in the absence of its macromolecular interaction partners, such as other proteins or RNA. IDPs range from fully unstructured to partially structured and include random coil, molten globule-like aggregates, or flexible linkers in large multi-domain proteins. They are sometimes considered as a separate class of proteins along with globular, fibrous and membrane proteins. IDPs are a very large and functionally important class of proteins and their discovery has disproved the idea that three-dimensional structures of proteins must be fixed to accomplish their biological functions. For example, IDPs have been identified to participate in weak multivalent interactions that are highly cooperative and dynamic, lending them importance in DNA regulation and in cell signaling. Many IDPs can also adopt a fixed three-dimensional structure after bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globular Protein
In biochemistry, globular proteins or spheroproteins are spherical ("globe-like") proteins and are one of the common protein types (the others being fibrous, disordered and membrane proteins). Globular proteins are somewhat water-soluble (forming colloids in water), unlike the fibrous or membrane proteins. There are multiple fold classes of globular proteins, since there are many different architectures that can fold into a roughly spherical shape. The term globin can refer more specifically to proteins including the globin fold. Globular structure and solubility The term globular protein is quite old (dating probably from the 19th century) and is now somewhat archaic given the hundreds of thousands of proteins and more elegant and descriptive structural motif vocabulary. The globular nature of these proteins can be determined without the means of modern techniques, but only by using ultracentrifuges or dynamic light scattering techniques. The spherical structure is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amino Acid Residue
Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers specifically polypeptides formed from sequences of amino acids, the monomers of the polymer. A single amino acid monomer may also be called a ''residue'' indicating a repeating unit of a polymer. Proteins form by amino acids undergoing condensation reactions, in which the amino acids lose one water molecule per reaction in order to attach to one another with a peptide bond. By convention, a chain under 30 amino acids is often identified as a peptide, rather than a protein. To be able to perform their biological function, proteins fold into one or more specific spatial conformations driven by a number of non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic packing. To understand the functions of proteins at a molecular level, it is often necessary to determine their three-dimensional structure. This is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |