

A mirror or looking glass is an object that
reflects an
image
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the direction of the image in an equal yet opposite angle from which the light shines upon it. This allows the viewer to see themselves or objects behind them, or even objects that are at an angle from them but out of their field of view, such as around a corner. Natural mirrors have existed since prehistoric times, such as the surface of water, but people have been manufacturing mirrors out of a variety of materials for thousands of years, like stone, metals, and glass. In modern mirrors, metals like
silver or
aluminium are often used due to their high
reflectivity, applied as a thin coating on
glass because of its naturally smooth and very
hard surface.
A mirror is a
wave reflector.
Light consists of waves, and when light waves reflect from the flat surface of a mirror, those waves retain the same degree of curvature and
vergence, in an equal yet opposite direction, as the original waves. This allows the waves to form an image when they are focused through a lens, just as if the waves had originated from the direction of the mirror. The light can also be pictured as
rays (imaginary lines radiating from the light source, that are always perpendicular to the waves). These rays are reflected at an equal yet opposite angle from which they strike the mirror (incident light). This property, called
specular reflection, distinguishes a mirror from objects that
diffuse light, breaking up the wave and scattering it in many directions (such as flat-white paint). Thus, a mirror can be any surface in which the texture or roughness of the surface is smaller (smoother) than the
wavelength of the waves.
When looking at a mirror, one will see a
mirror image
A mirror image (in a plane mirror) is a reflected duplication of an object that appears almost identical, but is reversed in the direction perpendicular to the mirror surface. As an optical effect it results from reflection off from substances ...
or reflected image of objects in the environment, formed by light emitted or scattered by them and reflected by the mirror towards one's eyes. This effect gives the illusion that those objects are behind the mirror, or (sometimes)
in front of it. When the surface is not flat, a mirror may behave like a reflecting
lens. A
plane mirror
A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat (planar) reflective surface. For light rays striking a plane mirror, the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence. The angle of the incidence is the angle between the incident ray and the surface n ...
yields a real-looking undistorted image, while a
curved mirror may distort, magnify, or reduce the image in various ways, while keeping the lines,
contrast,
sharpness
Sharpness ( ) is an English port in Gloucestershire, one of the most inland in Britain, and eighth largest in the South West. It is on the River Severn at , at a point where the tidal range, though less than at Avonmouth downstream ( typical sp ...
, colors, and other image properties intact.
A mirror is commonly used for inspecting oneself, such as during
personal grooming; hence the old-fashioned name "looking glass".
[ This use, which dates from prehistory,][ overlaps with uses in decoration and architecture. Mirrors are also used to view other items that are not directly visible because of obstructions; examples include rear-view mirrors in vehicles, security mirrors in or around buildings, and dentist's mirrors. Mirrors are also used in optical and scientific apparatus such as telescopes, lasers, cameras, periscopes, and industrial machinery.
According to ]superstitions
A superstition is any belief or practice considered by non-practitioners to be irrational or supernatural, attributed to fate or magic, perceived supernatural influence, or fear of that which is unknown. It is commonly applied to beliefs and ...
breaking a mirror is said to bring seven years of bad luck.
The terms "mirror" and "reflector" can be used for objects that reflect any other types of waves. An acoustic mirror reflects sound waves. Objects such as walls, ceilings, or natural rock-formations may produce echos, and this tendency often becomes a problem in acoustical engineering when designing houses, auditoriums, or recording studios. Acoustic mirrors may be used for applications such as parabolic microphone
A parabolic microphone is a microphone that uses a parabolic reflector to collect and focus sound waves onto a transducer, in much the same way that a parabolic antenna (e.g. satellite dish) does with radio waves. Though they lack high fidelity ...
s, atmospheric
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. A s ...
studies, sonar, and seafloor mapping.[ An atomic mirror reflects matter waves and can be used for atomic ]interferometry
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber opt ...
and atomic holography.
History
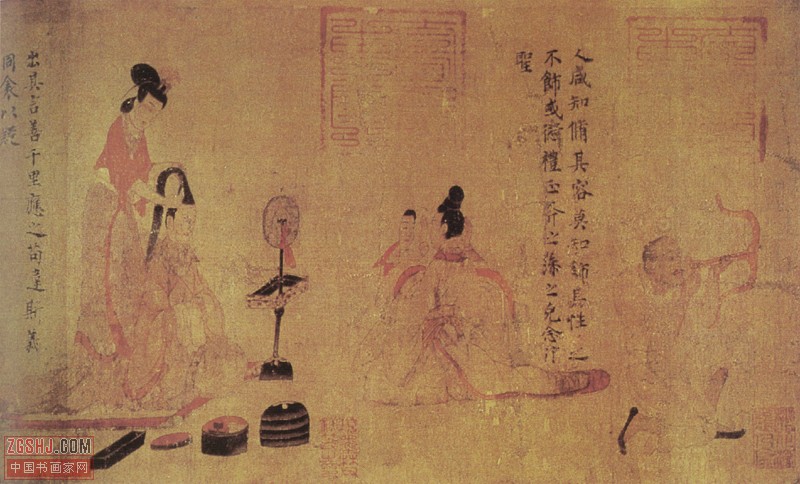



Prehistory
The first mirrors used by humans were most likely pools of dark, still water, or water collected in a primitive vessel of some sort. The requirements for making a good mirror are a surface with a very high degree of flatness (preferably but not necessarily with high reflectivity), and a surface roughness
Surface roughness, often shortened to roughness, is a component of surface finish (surface texture). It is quantified by the deviations in the direction of the normal vector of a real surface from its ideal form. If these deviations are large, ...
smaller than the wavelength of the light.
The earliest manufactured mirrors were pieces of polished stone such as obsidian
Obsidian () is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock.
Obsidian is produced from felsic lava, rich in the lighter elements s ...
, a naturally occurring volcanic glass.[ Examples of obsidian mirrors found in Anatolia (modern-day Turkey) have been dated to around 6000 BCE.][ Mirrors of polished copper were crafted in Mesopotamia from 4000 BCE,][ and in ancient Egypt from around 3000 BCE.][ Polished stone mirrors from Central and South America date from around 2000 BCE onwards.][
]
Bronze Age to Early Middle Ages
By the Bronze Age most cultures were using mirrors made from polished discs of bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
, copper, silver, or other metals.[ The people of Kerma in Nubia were skilled in the manufacturing of mirrors. Remains of their bronze kilns have been found within the temple of Kerma. In China, bronze mirrors were manufactured from around 2000 BC,]Greco-Roman
The Greco-Roman civilization (; also Greco-Roman culture; spelled Graeco-Roman in the Commonwealth), as understood by modern scholars and writers, includes the geographical regions and countries that culturally—and so historically—were di ...
Antiquity and throughout the Middle Ages in Europe.[ During the Roman Empire silver mirrors were in wide use by servants.][
Speculum metal is a highly reflective alloy of copper and tin that was used for mirrors until a couple of centuries ago. Such mirrors may have originated in China and India.][ Mirrors of speculum metal or any precious metal were hard to produce and were only owned by the wealthy.][
Common metal mirrors tarnished and required frequent polishing. Bronze mirrors had low reflectivity and poor color rendering, and stone mirrors were much worse in this regard.][ These defects explain the New Testament reference in ]1 Corinthians 13
1 Corinthians 13 is the thirteenth chapter of the First Epistle to the Corinthians in the New Testament of the Christian Bible. It is authored by Paul the Apostle and Sosthenes in Ephesus. This chapter covers the subject of Love. In the original ...
to seeing "as in a mirror, darkly."
The Greek philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ...
Socrates urged young people to look at themselves in mirrors so that, if they were beautiful, they would become worthy of their beauty, and if they were ugly, they would know how to hide their disgrace through learning.[
Glass began to be used for mirrors in the 1st century CE, with the development of ]soda-lime glass
Soda lime is a mixture of NaOH and CaO chemicals, used in granular form in closed breathing environments, such as general anaesthesia, submarines, rebreathers and recompression chambers, to remove carbon dioxide from breathing gases to prevent CO2 ...
and glass blowing.[ The Roman scholar Pliny the Elder claims that artisans in Sidon (modern-day Lebanon) were producing glass mirrors coated with lead or ]gold leaf
Gold leaf is gold that has been hammered into thin sheets (usually around 0.1 µm thick) by goldbeating and is often used for gilding. Gold leaf is available in a wide variety of karats and shades. The most commonly used gold is 22-kara ...
in the back. The metal provided good reflectivity, and the glass provided a smooth surface and protected the metal from scratches and tarnishing.[ However, there is no archeological evidence of glass mirrors before the third century.][
These early glass mirrors were made by blowing a glass bubble, and then cutting off a small circular section from 10 to 20 cm in diameter. Their surface was either concave or convex, and imperfections tended to distort the image. Lead-coated mirrors were very thin to prevent cracking by the heat of the molten metal.][ Due to the poor quality, high cost, and small size of glass mirrors, solid-metal mirrors (primarily of steel) remained in common use until the late nineteenth century.][
Silver-coated metal mirrors were developed in China as early as 500 CE. The bare metal was coated with an amalgam, then heated until the ]mercury
Mercury commonly refers to:
* Mercury (planet), the nearest planet to the Sun
* Mercury (element), a metallic chemical element with the symbol Hg
* Mercury (mythology), a Roman god
Mercury or The Mercury may also refer to:
Companies
* Merc ...
boiled away.[
]
Middle Ages and Renaissance

 The evolution of glass mirrors in the Middle Ages followed improvements in glassmaking technology. Glassmakers in France made flat glass plates by blowing glass bubbles, spinning them rapidly to flatten them, and cutting rectangles out of them. A better method, developed in Germany and perfected in
The evolution of glass mirrors in the Middle Ages followed improvements in glassmaking technology. Glassmakers in France made flat glass plates by blowing glass bubbles, spinning them rapidly to flatten them, and cutting rectangles out of them. A better method, developed in Germany and perfected in Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
by the 16th century, was to blow a cylinder of glass, cut off the ends, slice it along its length, and unroll it onto a flat hot plate.[ Venetian glassmakers also adopted lead glass for mirrors, because of its crystal-clarity and its easier workability. By the 11th century, glass mirrors were being produced in Moorish Spain.][
During the early Europe Renaissance, a fire-gilding technique developed to produce an even and highly reflective tin coating for glass mirrors. The back of the glass was coated with a tin-mercury amalgam, and the mercury was then evaporated by heating the piece. This process caused less thermal shock to the glass than the older molten-lead method.][ The date and location of the discovery is unknown, but by the 16th century Venice was a center of mirror production using this technique. These Venetian mirrors were up to square.
For a century, Venice retained the monopoly of the tin amalgam technique. Venetian mirrors in richly decorated frames served as luxury decorations for palaces throughout Europe, and were very expensive. For example, in the late seventeenth century, the Countess de Fiesque was reported to have traded an entire wheat farm for a mirror, considering it a bargain.][ However, by the end of that century the secret was leaked through industrial espionage. French workshops succeeded in large-scale industrialization of the process, eventually making mirrors affordable to the masses, in spite of the toxicity of mercury's vapor.][
]
Industrial Revolution
The invention of the ribbon machine
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. The filament is enclosed in a glass bulb with a vacuum or inert gas to protect the filament from oxida ...
in the late Industrial Revolution allowed modern glass panes to be produced in bulk.[ The Saint-Gobain factory, founded by royal initiative in France, was an important manufacturer, and ]Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; cs, Čechy ; ; hsb, Čěska; szl, Czechy) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. Bohemia can also refer to a wider area consisting of the historical Lands of the Bohemian Crown ruled by the Bohem ...
n and German glass, often rather cheaper, was also important.
The invention of the silvered-glass mirror is credited to German chemist Justus von Liebig
Justus Freiherr von Liebig (12 May 1803 – 20 April 1873) was a German scientist who made major contributions to agricultural and biological chemistry, and is considered one of the principal founders of organic chemistry. As a professor at t ...
in 1835.[ His wet deposition process involved the deposition of a thin layer of metallic silver onto glass through the chemical reduction of silver nitrate. This silvering process was adapted for mass manufacturing and led to the greater availability of affordable mirrors.
]
Contemporary technologies
Mirrors are often produced by the wet deposition of silver, or sometimes nickel or chromium (the latter used most often in automotive mirrors) via electroplating
Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct electric current. The part to be ...
directly onto the glass substrate.[
Glass mirrors for optical instruments are usually produced by ]vacuum deposition
Vacuum deposition is a group of processes used to deposit layers of material atom-by-atom or molecule-by-molecule on a solid surface. These processes operate at pressures well below atmospheric pressure (i.e., vacuum). The deposited layers can ...
methods. These techniques can be traced to observations in the 1920s and 1930s that metal was being ejected from electrodes in gas discharge lamps and condensed on the glass walls forming a mirror-like coating. The phenomenon, called sputtering, was developed into an industrial metal-coating method with the development of semiconductor technology in the 1970s.
A similar phenomenon had been observed with incandescent light bulbs: the metal in the hot filament would slowly sublimate and condense on the bulb's walls. This phenomenon was developed into the method of evaporation coating by Pohl and Pringsheim in 1912. John D. Strong
John Donovan Strong (1905-1992) was an American physicist and astronomer. Strong, one of the world’s foremost optical scientists, was known for being the first to detect water vapor in the atmosphere of Venus and for developing a number of innov ...
used evaporation coating to make the first aluminum-coated telescope mirrors in the 1930s.[ The first ]dielectric mirror
A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of mirror composed of multiple thin layers of dielectric material, typically deposited on a substrate of glass or some other optical material. By careful choice of the type and thickne ...
was created in 1937 by Auwarter using evaporated rhodium.[
The metal coating of glass mirrors is usually protected from abrasion and corrosion by a layer of paint applied over it. Mirrors for optical instruments often have the metal layer on the front face, so that the light does not have to cross the glass twice. In these mirrors, the metal may be protected by a thin transparent coating of a non-metallic ( dielectric) material. The first metallic mirror to be enhanced with a dielectric coating of silicon dioxide was created by Hass in 1937. In 1939 at the Schott Glass company, Walter Geffcken invented the first dielectric mirrors to use multilayer coatings.][
]
Burning mirrors
The Greek in Classical Antiquity were familiar with the use of mirrors to concentrate light. Parabolic mirrors were described and studied by the mathematician Diocles in his work ''On Burning Mirrors''.[ Ptolemy conducted a number of experiments with curved polished iron mirrors,][ and discussed plane, convex spherical, and concave spherical mirrors in his ''Optics''.][
Parabolic mirrors were also described by the Caliphate mathematician Ibn Sahl in the tenth century.][ The scholar Ibn al-Haytham discussed concave and convex mirrors in both ]cylindrical
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infini ...
and spherical geometries,[ carried out a number of experiments with mirrors, and solved the problem of finding the point on a convex mirror at which a ray coming from one point is reflected to another point.][
]
Types of mirrors

 Mirrors can be classified in many ways; including by shape, support, reflective materials, manufacturing methods, and intended application.
Mirrors can be classified in many ways; including by shape, support, reflective materials, manufacturing methods, and intended application.
By shape
Typical mirror shapes are planar, convex, and concave.
The surface of curved mirrors is often a part of a sphere. Mirrors that are meant to precisely concentrate parallel rays of light into a point are usually made in the shape of a paraboloid of revolution instead; they are used in telescopes (from radio waves to X-rays), in antennas to communicate with broadcast satellites, and in solar furnaces. A segmented mirror, consisting of multiple flat or curved mirrors, properly placed and oriented, may be used instead.
Mirrors that are intended to concentrate sunlight onto a long pipe may be a circular cylinder
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infini ...
or of a parabolic cylinder.
By structural material
The most common structural material for mirrors is glass, due to its transparency, ease of fabrication, rigidity, hardness, and ability to take a smooth finish.
Back-silvered mirrors
The most common mirrors consist of a plate of transparent glass, with a thin reflective layer on the back (the side opposite to the incident and reflected light) backed by a coating that protects that layer against abrasion, tarnishing, and corrosion. The glass is usually soda-lime glass, but lead glass may be used for decorative effects, and other transparent materials may be used for specific applications.
A plate of transparent plastic may be used instead of glass, for lighter weight or impact resistance. Alternatively, a flexible transparent plastic film may be bonded to the front and/or back surface of the mirror, to prevent injuries in case the mirror is broken. Lettering or decorative designs may be printed on the front face of the glass, or formed on the reflective layer. The front surface may have an anti-reflection coating.
Front-silvered mirrors
Mirrors which are reflective on the front surface (the same side of the incident and reflected light) may be made of any rigid material.[ The supporting material does not necessarily need to be transparent, but telescope mirrors often use glass anyway. Often a protective transparent coating is added on top of the reflecting layer, to protect it against abrasion, tarnishing, and corrosion, or to absorb certain wavelengths.
]
Flexible mirrors
Thin flexible plastic mirrors are sometimes used for safety, since they cannot shatter or produce sharp flakes. Their flatness is achieved by stretching them on a rigid frame. These usually consist of a layer of evaporated aluminum between two thin layers of transparent plastic.
By reflective material
 In common mirrors, the reflective layer is usually some metal like silver, tin, nickel, or
In common mirrors, the reflective layer is usually some metal like silver, tin, nickel, or chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hardne ...
, deposited by a wet process; or aluminium,[ deposited by sputtering or evaporation in vacuum. The reflective layer may also be made of one or more layers of transparent materials with suitable indices of refraction.
The structural material may be a metal, in which case the reflecting layer may be just the surface of the same. Metal concave dishes are often used to reflect infrared light (such as in ]space heater
A space heater is a device used to heat a single, small to medium sized area.
Operation
Electric space heaters fall into four main categories: fan heaters, ceramic, infrared, and oil-filled.
* Fan heaters are the cheapest, but are often the ...
s) or microwaves (as in satellite TV antennas). Liquid metal telescopes use a surface of liquid metal such as mercury.
Mirrors that reflect only part of the light, while transmitting some of the rest, can be made with very thin metal layers or suitable combinations of dielectric layers. They are typically used as beamsplitters. A dichroic mirror
A dichroic filter, thin-film filter, or interference filter is a color filter used to selectively pass light of a small range of colors while reflecting other colors. By comparison, dichroic mirrors and dichroic reflectors tend to be characteri ...
, in particular, has surface that reflects certain wavelengths of light, while letting other wavelengths pass through. A cold mirror is a dichroic mirror that efficiently reflects the entire visible light spectrum while transmitting infrared wavelengths. A hot mirror is the opposite: it reflects infrared light while transmitting visible light. Dichroic mirrors are often used as filters to remove undesired components of the light in cameras and measuring instruments.
In X-ray telescopes, the X-rays reflect off a highly precise metal surface at almost grazing angles, and only a small fraction of the rays are reflected.[ In ]flying relativistic mirrors
Flying may refer to:
* Flight, the process of flying
* Aviation, the creation and operation of aircraft
Music
Albums
* ''Flying'' (Grammatrain album), 1997
* ''Flying'' (Jonathan Fagerlund album), 2008
* ''Flying'' (UFO album), 1971
* ''Fl ...
conceived for X-ray lasers, the reflecting surface is a spherical shockwave
In physics, a shock wave (also spelled shockwave), or shock, is a type of propagating disturbance that moves faster than the local speed of sound in the medium. Like an ordinary wave, a shock wave carries energy and can propagate through a me ...
(wake wave) created in a low-density plasma
Plasma or plasm may refer to:
Science
* Plasma (physics), one of the four fundamental states of matter
* Plasma (mineral), a green translucent silica mineral
* Quark–gluon plasma, a state of matter in quantum chromodynamics
Biology
* Blood pla ...
by a very intense laser-pulse, and moving at an extremely high velocity.[
]
Nonlinear optical mirrors
A phase-conjugating mirror uses nonlinear optics to reverse the phase difference between incident beams. Such mirrors may be used, for example, for coherent beam combination. The useful applications are self-guiding of laser beams and correction of atmospheric distortions in imaging systems.[
]
Physical principles
 When a sufficiently narrow beam of light is reflected at a point of a surface, the surface's normal direction will be the bisector of the angle formed by the two beams at that point. That is, the direction vector towards the incident beams's source, the normal vector , and direction vector of the reflected beam will be coplanar, and the angle between and will be equal to the
When a sufficiently narrow beam of light is reflected at a point of a surface, the surface's normal direction will be the bisector of the angle formed by the two beams at that point. That is, the direction vector towards the incident beams's source, the normal vector , and direction vector of the reflected beam will be coplanar, and the angle between and will be equal to the angle of incidence
Angle of incidence is a measure of deviation of something from "straight on" and may refer to:
* Angle of incidence (aerodynamics), angle between a wing chord and the longitudinal axis, as distinct from angle of attack
In fluid dynamics, ang ...
between and , but of opposite sign.[
This property can be explained by the physics of an electromagnetic plane wave that is incident to a flat surface that is electrically conductive or where the speed of light changes abruptly, as between two materials with different indices of refraction.
* When parallel beams of light are reflected on a plane surface, the reflected rays will be parallel too.
* If the reflecting surface is concave, the reflected beams will be convergent, at least to some extent and for some distance from the surface.
* A convex mirror, on the other hand, will reflect parallel rays towards divergent directions.
More specifically, a concave parabolic mirror (whose surface is a part of a paraboloid of revolution) will reflect rays that are parallel to its axis into rays that pass through its focus. Conversely, a parabolic concave mirror will reflect any ray that comes from its focus towards a direction parallel to its axis. If a concave mirror surface is a part of a prolate ellipsoid, it will reflect any ray coming from one focus toward the other focus.][
A convex parabolic mirror, on the other hand, will reflect rays that are parallel to its axis into rays that seem to emanate from the focus of the surface, behind the mirror. Conversely, it will reflect incoming rays that converge toward that point into rays that are parallel to the axis. A convex mirror that is part of a prolate ellipsoid will reflect rays that converge towards one focus into divergent rays that seem to emanate from the other focus.][
Spherical mirrors do not reflect parallel rays to rays that converge to or diverge from a single point, or vice versa, due to ]spherical aberration
In optics, spherical aberration (SA) is a type of optical aberration, aberration found in optical systems that have elements with spherical surfaces. Lens (optics), Lenses and curved mirrors are prime examples, because this shape is easier to man ...
. However, a spherical mirror whose diameter is sufficiently small compared to the sphere's radius will behave very similarly to a parabolic mirror whose axis goes through the mirror's center and the center of that sphere; so that spherical mirrors can substitute for parabolic ones in many applications.[
A similar aberration occurs with parabolic mirrors when the incident rays are parallel among themselves but not parallel to the mirror's axis, or are divergent from a point that is not the focus – as when trying to form an image of an objet that is near the mirror or spans a wide angle as seen from it. However, this aberration can be sufficiently small if the object image is sufficiently far from the mirror and spans a sufficiently small angle around its axis.][
]
Mirror images
 Mirrors reflect an image to the observer. However, unlike a projected image on a screen, an image does not actually exist on the surface of the mirror. For example, when two people look at each other in a mirror, both see different images on the same surface. When the light waves converge through the lens of the eye they interfere with each other to form the image on the surface of the retina, and since both viewers see waves coming from different directions, each sees a different image in the same mirror. Thus, the images observed in a mirror depend upon the angle of the mirror with respect to the eye. The angle between the object and the observer is always twice the angle between the eye and the normal, or the direction perpendicular to the surface. This allows animals with binocular vision to see the reflected image with
Mirrors reflect an image to the observer. However, unlike a projected image on a screen, an image does not actually exist on the surface of the mirror. For example, when two people look at each other in a mirror, both see different images on the same surface. When the light waves converge through the lens of the eye they interfere with each other to form the image on the surface of the retina, and since both viewers see waves coming from different directions, each sees a different image in the same mirror. Thus, the images observed in a mirror depend upon the angle of the mirror with respect to the eye. The angle between the object and the observer is always twice the angle between the eye and the normal, or the direction perpendicular to the surface. This allows animals with binocular vision to see the reflected image with depth perception
Depth perception is the ability to perceive distance to objects in the world using the visual system and visual perception. It is a major factor in perceiving the world in three dimensions. Depth perception happens primarily due to stereopsis an ...
and in three dimensions.
The mirror forms a ''virtual image'' of whatever is in the opposite angle from the viewer, meaning that objects in the image appear to exist in a direct line of sight—behind the surface of the mirror—at an equal distance from their position in front of the mirror. Objects behind the observer, or between the observer and the mirror, are reflected back to the observer without any actual change in orientation; the light waves are simply reversed in a direction perpendicular to the mirror. However, when viewer is facing the object and the mirror is at an angle between them, the image appears inverted 180° along the direction of the angle.[''Mastering Physics for ITT-JEE, Volume 2'' By S. Chand & Co. 2012 Er. Rakesh Rathi Page 273--276]
Objects viewed in a (plane) mirror will appear laterally inverted (e.g., if one raises one's right hand, the image's left hand will appear to go up in the mirror), but not vertically inverted (in the image a person's head still appears above their body).[ However, a mirror does not actually "swap" left and right any more than it swaps top and bottom. A mirror swaps front and back. To be precise, it reverses the object in the direction perpendicular to the mirror surface (the normal), turning the three dimensional image inside out (the way a glove stripped off the hand can be turned inside out, turning a left-hand glove into a right-hand glove or vice versa). When a person raises their left hand, the actual left hand raises in the mirror, but gives the illusion of a right hand raising because the imaginary person in the mirror is literally inside-out, hand and all. If the person stands side-on to a mirror, the mirror really does reverse left and right hands, that is, objects that are physically closer to the mirror always appear closer in the virtual image, and objects farther from the surface always appear symmetrically farther away regardless of angle.
Looking at an image of oneself with the front-back axis flipped results in the perception of an image with its left-right axis flipped. When reflected in the mirror, a person's right hand remains directly opposite their real right hand, but it is perceived by the mind as the left hand in the image. When a person looks into a mirror, the image is actually front-back reversed (inside-out), which is an effect similar to the hollow-mask illusion. Notice that a mirror image is fundamentally different from the object (inside-out) and cannot be reproduced by simply rotating the object. An object and its mirror image are said to be chiral.
For things that may be considered as two-dimensional objects (like text), front-back reversal cannot usually explain the observed reversal. An image is a two-dimensional representation of a three-dimensional space, and because it exists in a two-dimensional plane, an image can be viewed from front or back. In the same way that text on a piece of paper appears reversed if held up to a light and viewed from behind, text held facing a mirror will appear reversed, because the image of the text is still facing away from the observer. Another way to understand the reversals observed in images of objects that are effectively two-dimensional is that the inversion of left and right in a mirror is due to the way human beings perceive their surroundings. A person's reflection in a mirror appears to be a real person facing them, but for that person to really face themselves (i.e.: twins) one would have to physically turn and face the other, causing an actual swapping of right and left. A mirror causes an illusion of left-right reversal because left and right were ''not'' swapped when the image appears to have turned around to face the viewer. The viewer's egocentric navigation (left and right with respect to the observer's point of view; i.e.: "my left...") is unconsciously replaced with their allocentric navigation (left and right as it relates another's point of view; "...your right") when processing the virtual image of the apparent person behind the mirror. Likewise, text viewed in a mirror would have to be physically turned around, facing the observer and away from the surface, actually swapping left and right, to be read in the mirror.]
Optical properties
Reflectivity
 The reflectivity of a mirror is determined by the percentage of reflected light per the total of the incident light. The reflectivity may vary with wavelength. All or a portion of the light not reflected is absorbed by the mirror, while in some cases a portion may also transmit through. Although some small portion of the light will be absorbed by the coating, the reflectivity is usually higher for first-surface mirrors, eliminating both reflection and absorption losses from the substrate.
The reflectivity is often determined by the type and thickness of the coating. When the thickness of the coating is sufficient to prevent transmission, all of the losses occur due to absorption. Aluminium is harder, less expensive, and more resistant to tarnishing than silver, and will reflect 85 to 90% of the light in the visible to near-ultraviolet range, but experiences a drop in its reflectance between 800 and 900 nm. Gold is very soft and easily scratched, costly, yet does not tarnish. Gold is greater than 96% reflective to near and far-infrared light between 800 and 12000 nm, but poorly reflects visible light with wavelengths shorter than 600 nm (yellow). Silver is expensive, soft, and quickly tarnishes, but has the highest reflectivity in the visual to near-infrared of any metal. Silver can reflect up to 98 or 99% of light to wavelengths as long as 2000 nm, but loses nearly all reflectivity at wavelengths shorter than 350 nm.
Dielectric mirrors can reflect greater than 99.99% of light, but only for a narrow range of wavelengths, ranging from a bandwidth of only 10 nm to as wide as 100 nm for tunable lasers. However, dielectric coatings can also enhance the reflectivity of metallic coatings and protect them from scratching or tarnishing. Dielectric materials are typically very hard and relatively cheap, however the number of coats needed generally makes it an expensive process. In mirrors with low tolerances, the coating thickness may be reduced to save cost, and simply covered with paint to absorb transmission.
The reflectivity of a mirror is determined by the percentage of reflected light per the total of the incident light. The reflectivity may vary with wavelength. All or a portion of the light not reflected is absorbed by the mirror, while in some cases a portion may also transmit through. Although some small portion of the light will be absorbed by the coating, the reflectivity is usually higher for first-surface mirrors, eliminating both reflection and absorption losses from the substrate.
The reflectivity is often determined by the type and thickness of the coating. When the thickness of the coating is sufficient to prevent transmission, all of the losses occur due to absorption. Aluminium is harder, less expensive, and more resistant to tarnishing than silver, and will reflect 85 to 90% of the light in the visible to near-ultraviolet range, but experiences a drop in its reflectance between 800 and 900 nm. Gold is very soft and easily scratched, costly, yet does not tarnish. Gold is greater than 96% reflective to near and far-infrared light between 800 and 12000 nm, but poorly reflects visible light with wavelengths shorter than 600 nm (yellow). Silver is expensive, soft, and quickly tarnishes, but has the highest reflectivity in the visual to near-infrared of any metal. Silver can reflect up to 98 or 99% of light to wavelengths as long as 2000 nm, but loses nearly all reflectivity at wavelengths shorter than 350 nm.
Dielectric mirrors can reflect greater than 99.99% of light, but only for a narrow range of wavelengths, ranging from a bandwidth of only 10 nm to as wide as 100 nm for tunable lasers. However, dielectric coatings can also enhance the reflectivity of metallic coatings and protect them from scratching or tarnishing. Dielectric materials are typically very hard and relatively cheap, however the number of coats needed generally makes it an expensive process. In mirrors with low tolerances, the coating thickness may be reduced to save cost, and simply covered with paint to absorb transmission.[
]
Surface quality
 Surface quality, or surface accuracy, measures the deviations from a perfect, ideal surface shape. Increasing the surface quality reduces distortion, artifacts, and aberration in images, and helps increase
Surface quality, or surface accuracy, measures the deviations from a perfect, ideal surface shape. Increasing the surface quality reduces distortion, artifacts, and aberration in images, and helps increase coherence
Coherence, coherency, or coherent may refer to the following:
Physics
* Coherence (physics), an ideal property of waves that enables stationary (i.e. temporally and spatially constant) interference
* Coherence (units of measurement), a deriv ...
, collimation, and reduce unwanted divergence in beams. For plane mirrors, this is often described in terms of flatness, while other surface shapes are compared to an ideal shape. The surface quality is typically measured with items like interferometer
Interferometry is a technique which uses the ''interference'' of superimposed waves to extract information. Interferometry typically uses electromagnetic waves and is an important investigative technique in the fields of astronomy, fiber op ...
s or optical flats, and are usually measured in wavelengths of light (λ). These deviations can be much larger or much smaller than the surface roughness. A normal household-mirror made with float glass
Float glass is a sheet of glass made by floating molten glass on a bed of molten metal, typically tin, although lead and other various low- melting-point alloys were used in the past. This method gives the sheet uniform thickness and very flat sur ...
may have flatness tolerances as low as 9–14λ per inch (25.4 mm), equating to a deviation of 5600 through 8800 nanometer
330px, Different lengths as in respect to the molecular scale.
The nanometre (international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: nm) or nanometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re ...
s from perfect flatness. Precision ground and polished mirrors intended for lasers or telescopes may have tolerances as high as λ/50 (1/50 of the wavelength of the light, or around 12 nm) across the entire surface.[ The surface quality can be affected by factors such as temperature changes, internal stress in the substrate, or even bending effects that occur when combining materials with different coefficients of thermal expansion, similar to a bimetallic strip.][
]
Surface roughness
Surface roughness
Surface roughness, often shortened to roughness, is a component of surface finish (surface texture). It is quantified by the deviations in the direction of the normal vector of a real surface from its ideal form. If these deviations are large, ...
describes the texture of the surface, often in terms of the depth of the microscopic scratches left by the polishing operations. Surface roughness determines how much of the reflection is specular and how much diffuses, controlling how sharp or blurry the image will be.
For perfectly specular reflection, the surface roughness must be kept smaller than the wavelength of the light. Microwaves, which sometimes have a wavelength greater than an inch (~25 mm) can reflect specularly off a metal screen-door, continental ice-sheets, or desert sand, while visible light, having wavelengths of only a few hundred nanometers (a few hundred-thousandths of an inch), must meet a very smooth surface to produce specular reflection. For wavelengths that are approaching or are even shorter than the diameter of the atoms, such as X-rays, specular reflection can only be produced by surfaces that are at a grazing incidence The angle of incidence, in geometric optics, is the angle between a ray incident on a surface and the line perpendicular (at 90 degree angle) to the surface at the point of incidence, called the normal. The ray can be formed by any waves, such as o ...
from the rays.
Surface roughness is typically measured in microns, wavelength, or grit size
upright=1.35, Sheets of sandpaper with different grit sizes (40 (coarse), 80, 150, 240, 600 (fine)).
Sandpaper and glasspaper are names used for a type of coated abrasive that consists of sheets of paper or cloth with abrasive material glued ...
, with ~80,000–100,000 grit or ~½λ–¼λ being "optical quality".[
]
Transmissivity
 Transmissivity is determined by the percentage of light transmitted per the incident light. Transmissivity is usually the same from both first and second surfaces. The combined transmitted and reflected light, subtracted from the incident light, measures the amount absorbed by both the coating and substrate. For transmissive mirrors, such as one-way mirrors,
Transmissivity is determined by the percentage of light transmitted per the incident light. Transmissivity is usually the same from both first and second surfaces. The combined transmitted and reflected light, subtracted from the incident light, measures the amount absorbed by both the coating and substrate. For transmissive mirrors, such as one-way mirrors, beam splitter
A beam splitter or ''beamsplitter'' is an optical device that splits a beam of light into a transmitted and a reflected beam. It is a crucial part of many optical experimental and measurement systems, such as interferometers, also finding wide ...
s, or laser output couplers, the transmissivity of the mirror is an important consideration. The transmissivity of metallic coatings are often determined by their thickness. For precision beam-splitters or output couplers, the thickness of the coating must be kept at very high tolerances to transmit the proper amount of light. For dielectric mirrors, the thickness of the coat must always be kept to high tolerances, but it is often more the number of individual coats that determine the transmissivity. For the substrate, the material used must also have good transmissivity to the chosen wavelengths. Glass is a suitable substrate for most visible-light applications, but other substrates such as zinc selenide or synthetic sapphire may be used for infrared or ultraviolet wavelengths.[
]
Wedge
Wedge errors are caused by the deviation of the surfaces from perfect parallelism. An optical wedge The wedge prism is a prism with a shallow angle between its input and output surfaces. This angle is usually 3 degrees or less. Refraction at the surfaces causes the prism to deflect light by a fixed angle. When viewing a scene through such a prism ...
is the angle formed between two plane-surfaces (or between the principle planes of curved surfaces) due to manufacturing errors or limitations, causing one edge of the mirror to be slightly thicker than the other. Nearly all mirrors and optics with parallel faces have some slight degree of wedge, which is usually measured in seconds
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds ...
or minutes of arc. For first-surface mirrors, wedges can introduce alignment deviations in mounting hardware. For second-surface or transmissive mirrors, wedges can have a prismatic effect on the light, deviating its trajectory or, to a very slight degree, its color, causing chromatic
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, intervals, chords, notes, musical styles, and kinds of harmony. They are very often used as a pair, ...
and other forms of aberration. In some instances, a slight wedge is desirable, such as in certain laser systems where stray reflections from the uncoated surface are better dispersed than reflected back through the medium.[
]
Surface defects
Surface defects are small-scale, discontinuous imperfections in the surface smoothness. Surface defects are larger (in some cases much larger) than the surface roughness, but only affect small, localized portions of the entire surface. These are typically found as scratches, digs, pits (often from bubbles in the glass), sleeks (scratches from prior, larger grit polishing operations that were not fully removed by subsequent polishing grits), edge chips, or blemishes in the coating. These defects are often an unavoidable side-effect of manufacturing limitations, both in cost and machine precision. If kept low enough, in most applications these defects will rarely have any adverse effect, unless the surface is located at an image plane where they will show up directly. For applications that require extremely low scattering of light, extremely high reflectance, or low absorption due to high energy levels that could destroy the mirror, such as lasers or Fabry-Perot interferometers, the surface defects must be kept to a minimum.[
]
Manufacturing
 Mirrors are usually manufactured by either polishing a naturally reflective material, such as speculum metal, or by applying a reflective coating to a suitable polished
Mirrors are usually manufactured by either polishing a naturally reflective material, such as speculum metal, or by applying a reflective coating to a suitable polished substrate
Substrate may refer to:
Physical layers
*Substrate (biology), the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the surface or medium on which an organism grows or is attached
** Substrate (locomotion), the surface over which an organism lo ...
.[
In some applications, generally those that are cost-sensitive or that require great durability, such as for mounting in a prison cell, mirrors may be made from a single, bulk material such as polished metal. However, metals consist of small crystals (grains) separated by grain boundaries that may prevent the surface from attaining optical smoothness and uniform reflectivity.][
]
Coating
Silvering
The coating of glass with a reflective layer of a metal is generally called " silvering", even though the metal may not be silver. Currently the main processes are electroplating
Electroplating, also known as electrochemical deposition or electrodeposition, is a process for producing a metal coating on a solid substrate through the reduction of cations of that metal by means of a direct electric current. The part to be ...
, "wet" chemical deposition, and vacuum deposition
Vacuum deposition is a group of processes used to deposit layers of material atom-by-atom or molecule-by-molecule on a solid surface. These processes operate at pressures well below atmospheric pressure (i.e., vacuum). The deposited layers can ...
[ Front-coated metal mirrors achieve reflectivities of 90–95% when new.
]
Dielectric coating
Applications requiring higher reflectivity or greater durability, where wide bandwidth is not essential, use dielectric coatings, which can achieve reflectivities as high as 99.997% over a limited range of wavelengths. Because they are often chemically stable and do not conduct electricity, dielectric coatings are almost always applied by methods of vacuum deposition, and most commonly by evaporation deposition. Because the coatings are usually transparent, absorption losses are negligible. Unlike with metals, the reflectivity of the individual dielectric-coatings is a function of Snell's law
Snell's law (also known as Snell–Descartes law and ibn-Sahl law and the law of refraction) is a formula used to describe the relationship between the angles of incidence and refraction, when referring to light or other waves passing through ...
known as the Fresnel equations, determined by the difference in refractive index between layers. Therefore, the thickness and index of the coatings can be adjusted to be centered on any wavelength. Vacuum deposition can be achieved in a number of ways, including sputtering, evaporation deposition, arc deposition, reactive-gas deposition, and ion plating, among many others.[
]
Shaping and polishing
Tolerances
Mirrors can be manufactured to a wide range of engineering tolerances, including reflectivity, surface quality, surface roughness
Surface roughness, often shortened to roughness, is a component of surface finish (surface texture). It is quantified by the deviations in the direction of the normal vector of a real surface from its ideal form. If these deviations are large, ...
, or transmissivity, depending on the desired application. These tolerances can range from wide, such as found in a normal household-mirror, to extremely narrow, like those used in lasers or telescopes. Tightening the tolerances allows better and more precise imaging or beam transmission over longer distances. In imaging systems this can help reduce anomalies ( artifacts), distortion or blur, but at a much higher cost. Where viewing distances are relatively close or high precision is not a concern, wider tolerances can be used to make effective mirrors at affordable costs.
Applications




Personal grooming
Mirrors are commonly used as aids to personal grooming.[ They may range from small sizes (portable), to full body sized; they may be handheld, mobile, fixed or adjustable. A classic example of an adjustable mirror is the cheval glass, which the user can tilt.
]
Safety and easier viewing
;Convex mirrors
 :Convex mirrors provide a wider field of view than flat mirrors,
:Convex mirrors provide a wider field of view than flat mirrors,[ and are often used on vehicles,][ especially large trucks, to minimize blind spots. They are sometimes placed at road junctions, and at corners of sites such as ]parking lot
A parking lot (American English) or car park (British English), also known as a car lot, is a cleared area intended for parking vehicles. The term usually refers to an area dedicated only for parking, with a durable or semi-durable surface ...
s to allow people to see around corners to avoid crashing into other vehicles or shopping carts. They are also sometimes used as part of security systems, so that a single video camera can show more than one angle at a time. Convex mirrors as decoration are used in interior design to provide a predominantly experiential effect.[
; Mouth mirrors or "dental mirrors"
:Dentists use mouth mirrors or "dental mirrors" to allow indirect vision and lighting within the mouth. Their reflective surfaces may be either flat or curved.][ Mouth mirrors are also commonly used by mechanics to allow vision in tight spaces and around corners in equipment.
; Rear-view mirrors
:Rear-view mirrors are widely used in and on vehicles (such as automobiles, or bicycles), to allow drivers to see other vehicles coming up behind them.][ On rear-view sunglasses, the left end of the left glass and the right end of the right glass work as mirrors.
]
One-way mirrors and windows
;One-way mirrors
:One-way mirrors (also called two-way mirrors) work by overwhelming dim transmitted light with bright reflected light.[ A true one-way mirror that actually allows light to be transmitted in one direction only without requiring external energy is not possible as it violates the second law of thermodynamics.:
;One-way windows
:One-way windows can be made to work with polarized light in the laboratory without violating the second law. This is an apparent paradox that stumped some great physicists, although it does not allow a practical one-way mirror for use in the real world.][ Optical isolators are one-way devices that are commonly used with lasers.
]
Signalling
With the sun as light source, a mirror can be used to signal by variations in the orientation of the mirror. The signal can be used over long distances, possibly up to on a clear day. Native American tribes and numerous militaries used this technique to transmit information between distant outposts.
Mirrors can also be used to attract the attention of search-and-rescue
Search and rescue (SAR) is the search for and provision of aid to people who are in distress or imminent danger. The general field of search and rescue includes many specialty sub-fields, typically determined by the type of terrain the search ...
parties. Specialized types of mirrors are available and are often included in military survival kits.
Technology
Televisions and projectors
Microscopic mirrors are a core element of many of the largest high-definition televisions and video projectors. A common technology of this type is Texas Instruments' DLP. A DLP chip is a postage stamp-sized microchip whose surface is an array of millions of microscopic mirrors. The picture is created as the individual mirrors move to either reflect light toward the projection surface ( pixel on), or toward a light-absorbing surface (pixel off).
Other projection technologies involving mirrors include LCoS. Like a DLP chip, LCoS is a microchip of similar size, but rather than millions of individual mirrors, there is a single mirror that is actively shielded by a liquid crystal
Liquid crystal (LC) is a state of matter whose properties are between those of conventional liquids and those of solid crystals. For example, a liquid crystal may flow like a liquid, but its molecules may be oriented in a crystal-like way. T ...
matrix with up to millions of pixels. The picture, formed as light, is either reflected toward the projection surface (pixel on), or absorbed by the activated LCD
A liquid-crystal display (LCD) is a flat-panel display or other electronically modulated optical device that uses the light-modulating properties of liquid crystals combined with polarizers. Liquid crystals do not emit light directly but in ...
pixels (pixel off). LCoS-based televisions and projectors often use 3 chips, one for each primary color.
Large mirrors are used in rear-projection televisions. Light (for example from a DLP as discussed above) is "folded" by one or more mirrors so that the television set is compact.
Solar power
 Mirrors are integral parts of a solar power plant. The one shown in the adjacent picture uses
Mirrors are integral parts of a solar power plant. The one shown in the adjacent picture uses concentrated solar power
Concentrated solar power (CSP, also known as concentrating solar power, concentrated solar thermal) systems generate solar power by using mirrors or lenses to concentrate a large area of sunlight into a receiver. Electricity is generated when ...
from an array of parabolic troughs.[
]
Instruments
 Telescopes and other precision instruments use ''front silvered'' or
Telescopes and other precision instruments use ''front silvered'' or first surface mirrors
A first-surface mirror or front-surface mirror (also commonly abbreviated FS mirror or FSM) is a mirror with the reflective surface being above a backing, as opposed to the conventional, second-surface mirror with the reflective surface behind a ...
, where the reflecting surface is placed on the front (or first) surface of the glass (this eliminates reflection from glass surface ordinary back mirrors have). Some of them use silver, but most are aluminium, which is more reflective at short wavelengths than silver.
All of these coatings are easily damaged and require special handling.
They reflect 90% to 95% of the incident light when new.
The coatings are typically applied by vacuum deposition
Vacuum deposition is a group of processes used to deposit layers of material atom-by-atom or molecule-by-molecule on a solid surface. These processes operate at pressures well below atmospheric pressure (i.e., vacuum). The deposited layers can ...
.
A protective overcoat is usually applied before the mirror is removed from the vacuum, because the coating otherwise begins to corrode as soon as it is exposed to oxygen and humidity in air. ''Front silvered'' mirrors have to be resurfaced occasionally to maintain their quality. There are optical mirrors such as mangin mirrors that are ''second surface mirrors'' (reflective coating on the rear surface) as part of their optical designs, usually to correct optical aberration
In optics, aberration is a property of optical systems, such as lenses, that causes light to be spread out over some region of space rather than focused to a point. Aberrations cause the image formed by a lens to be blurred or distorted, with th ...
s.[
] The reflectivity of the mirror coating can be measured using a reflectometer and for a particular metal it will be different for different wavelengths of light. This is exploited in some optical work to make cold mirrors and hot mirrors. A cold mirror is made by using a transparent substrate and choosing a coating material that is more reflective to visible light and more transmissive to infrared light.
A hot mirror is the opposite, the coating preferentially reflects infrared. Mirror surfaces are sometimes given thin film overcoatings both to retard degradation of the surface and to increase their reflectivity in parts of the spectrum where they will be used. For instance, aluminium mirrors are commonly coated with silicon dioxide or magnesium fluoride. The reflectivity as a function of wavelength depends on both the thickness of the coating and on how it is applied.
The reflectivity of the mirror coating can be measured using a reflectometer and for a particular metal it will be different for different wavelengths of light. This is exploited in some optical work to make cold mirrors and hot mirrors. A cold mirror is made by using a transparent substrate and choosing a coating material that is more reflective to visible light and more transmissive to infrared light.
A hot mirror is the opposite, the coating preferentially reflects infrared. Mirror surfaces are sometimes given thin film overcoatings both to retard degradation of the surface and to increase their reflectivity in parts of the spectrum where they will be used. For instance, aluminium mirrors are commonly coated with silicon dioxide or magnesium fluoride. The reflectivity as a function of wavelength depends on both the thickness of the coating and on how it is applied.
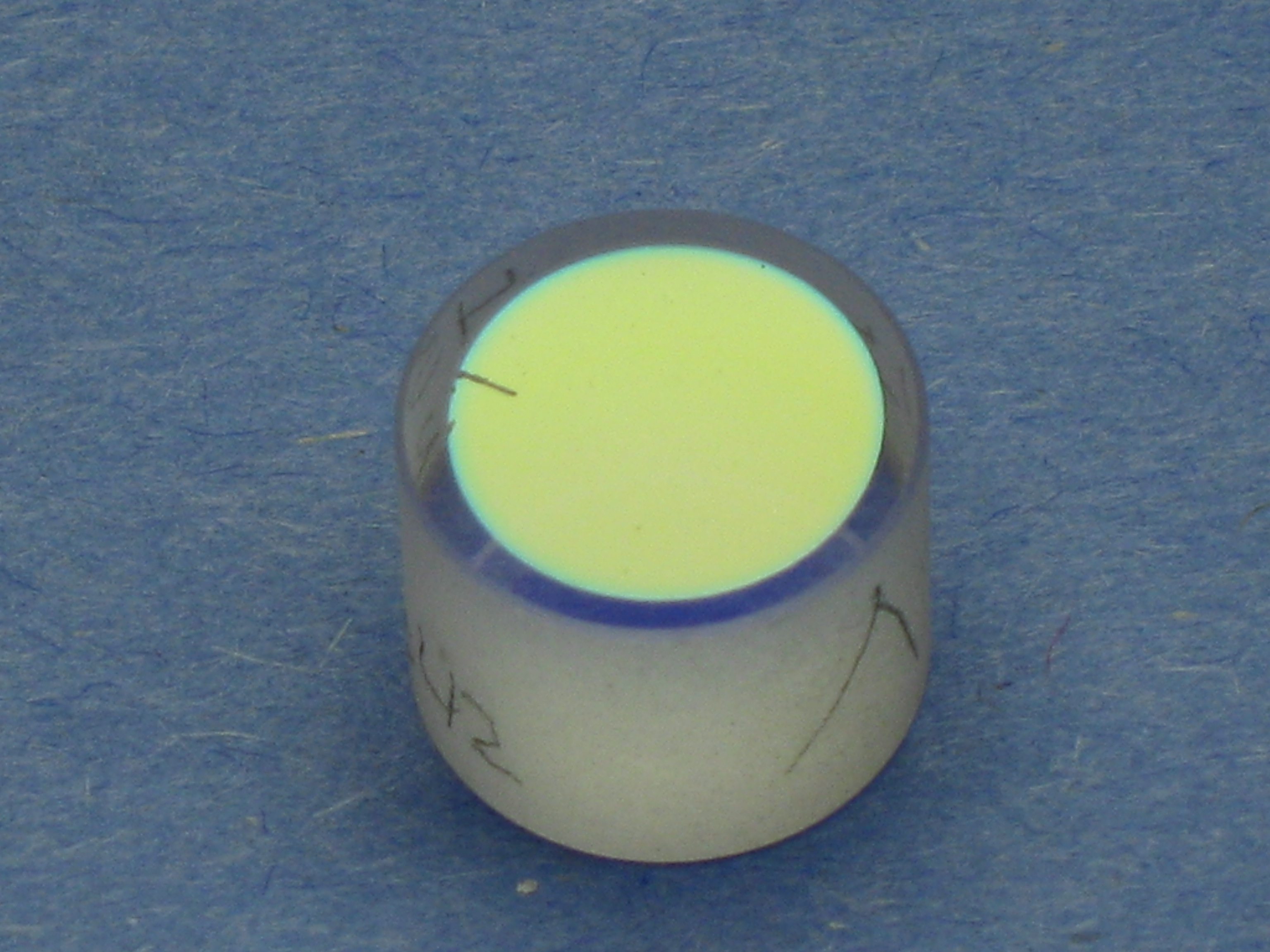
 For scientific optical work,
For scientific optical work, dielectric mirror
A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of mirror composed of multiple thin layers of dielectric material, typically deposited on a substrate of glass or some other optical material. By careful choice of the type and thickne ...
s are often used. These are glass (or sometimes other material) substrates on which one or more layers of dielectric material are deposited, to form an optical coating. By careful choice of the type and thickness of the dielectric layers, the range of wavelengths and amount of light reflected from the mirror can be specified. The best mirrors of this type can reflect >99.999% of the light (in a narrow range of wavelengths) which is incident on the mirror. Such mirrors are often used in lasers.
In astronomy, adaptive optics is a technique to measure variable image distortions and adapt a deformable mirror accordingly on a timescale of milliseconds, to compensate for the distortions.
Although most mirrors are designed to reflect visible light, surfaces reflecting other forms of electromagnetic radiation are also called "mirrors". The mirrors for other ranges of electromagnetic waves
In physics, electromagnetic radiation (EMR) consists of waves of the electromagnetic (EM) field, which propagate through space and carry momentum and electromagnetic radiant energy. It includes radio waves, microwaves, infrared, (visible) lig ...
are used in
optics and astronomy. Mirrors for radio waves (sometimes known as reflectors) are important elements of radio telescope
A radio telescope is a specialized antenna and radio receiver used to detect radio waves from astronomical radio sources in the sky. Radio telescopes are the main observing instrument used in radio astronomy, which studies the radio frequency ...
s.
Simple periscopes use mirrors.
Face-to-face mirrors
Two or more mirrors aligned exactly parallel and facing each other can give an infinite regress of reflections, called an infinity mirror
The infinity mirror (also sometimes called an infinite mirror) is a configuration of two or more parallel or nearly parallel mirrors, creating a series of smaller and smaller reflections that appear to recede to infinity. Often the front mirror ...
effect. Some devices use this to generate multiple reflections:
* Fabry–Pérot interferometer
In optics, a Fabry–Pérot interferometer (FPI) or etalon is an optical cavity made from two parallel reflecting surfaces (i.e.: thin mirrors). Optical waves can pass through the optical cavity only when they are in resonance with it. It is ...
* Laser (which contains an optical cavity An optical cavity, resonating cavity or optical resonator is an arrangement of mirrors or other optical elements that forms a cavity resonator for light waves. Optical cavities are a major component of lasers, surrounding the gain medium and provi ...
)
* 3D Kaleidoscope to concentrate light[
* momentum-enhanced ]solar sail
Solar sails (also known as light sails and photon sails) are a method of spacecraft propulsion using radiation pressure exerted by sunlight on large mirrors. A number of spaceflight missions to test solar propulsion and navigation have been p ...
[
]
Military applications
Tradition states that Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists ...
used a large array of mirrors to burn Roman ships during an attack on Syracuse. This has never been proven or disproved. On the TV show ''MythBusters
''MythBusters'' is a science entertainment television program, developed by Peter Rees and produced by Australia's Beyond Television Productions. The series premiered on the Discovery Channel on January 23, 2003. It was broadcast internatio ...
'', a team from MIT tried to recreate the famous "Archimedes Death Ray". They were unsuccessful at starting a fire on a ship.[ Previous attempts to set a boat on fire using only the bronze mirrors available in Archimedes' time were unsuccessful, and the time taken to ignite the craft would have made its use impractical, resulting in the ''MythBusters'' team deeming the myth "busted". It was however found that the mirrors made it very difficult for the passengers of the targeted boat to see; such a scenario could have impeded attackers and have provided the origin of the legend. (See solar power tower for a practical use of this technique.)
]
Seasonal lighting
 Due to its location in a steep-sided valley, the Italian town of Viganella gets no direct sunlight for seven weeks each winter. In 2006 a €100,000 computer-controlled mirror, 8×5 m, was installed to reflect sunlight into the town's piazza. In early 2007 the similarly situated village of Bondo, Switzerland, was considering applying this solution as well.
Due to its location in a steep-sided valley, the Italian town of Viganella gets no direct sunlight for seven weeks each winter. In 2006 a €100,000 computer-controlled mirror, 8×5 m, was installed to reflect sunlight into the town's piazza. In early 2007 the similarly situated village of Bondo, Switzerland, was considering applying this solution as well.[ In 2013, mirrors were installed to reflect sunlight into the town square in the Norwegian town of Rjukan.][ Mirrors can be used to produce enhanced lighting effects in greenhouses or conservatories.
]
Architecture
Mirrors are a popular design-theme in architecture, particularly with late modern and post-modernist high-rise buildings in major cities. Early examples include the Campbell Center in Dallas, which opened in 1972,[ and the John Hancock Tower (completed in 1976) in Boston.
More recently, two skyscrapers designed by architect Rafael Viñoly, the Vdara in Las Vegas and ]20 Fenchurch Street
20 Fenchurch Street is a commercial skyscraper in London that takes its name from its address on Fenchurch Street, in the historic City of London financial district. It has been nicknamed "The Walkie-Talkie" because of its distinctive shape, s ...
in London, have experienced unusual problems due to their concave curved-glass exteriors acting as respectively cylindrical and spherical reflectors for sunlight. In 2010, the ''Las Vegas Review Journal'' reported that sunlight reflected off the Vdara's south-facing tower could singe swimmers in the hotel pool, as well as melting plastic cups and shopping bags; employees of the hotel referred to the phenomenon as the "Vdara death ray",[ aka the " fryscraper." In 2013, sunlight reflecting off 20 Fenchurch Street melted parts of a ]Jaguar car
Jaguar (, ) is the luxury vehicle brand of Jaguar Land Rover, a British multinational corporation, multinational automaker, car manufacturer with its headquarters in Whitley, Coventry, England. Jaguar Cars was the company that was responsibl ...
parked nearby and scorching or igniting the carpet of a nearby barber-shop.[ This building had been nicknamed the "walkie-talkie" because its shape was supposedly similar to a certain model of two-way radio; but after its tendency to overheat surrounding objects became known, the nickname changed to the "walkie-scorchie".
]
Fine art
Paintings
 Painters depicting someone gazing into a mirror often also show the person's reflection. This is a kind of abstraction—in most cases the angle of view is such that the person's reflection should not be visible. Similarly, in movies and still photography an actor or actress is often shown ostensibly looking at him- or herself in a mirror, and yet the reflection faces the camera. In reality, the actor or actress sees only the camera and its operator in this case, not their own reflection. In the psychology of perception, this is known as the Venus effect.
The mirror is the central device in some of the greatest of European paintings:
* Édouard Manet's '' A Bar at the Folies-Bergère'' (1882)
* Titian's '' Venus with a Mirror''
*
Painters depicting someone gazing into a mirror often also show the person's reflection. This is a kind of abstraction—in most cases the angle of view is such that the person's reflection should not be visible. Similarly, in movies and still photography an actor or actress is often shown ostensibly looking at him- or herself in a mirror, and yet the reflection faces the camera. In reality, the actor or actress sees only the camera and its operator in this case, not their own reflection. In the psychology of perception, this is known as the Venus effect.
The mirror is the central device in some of the greatest of European paintings:
* Édouard Manet's '' A Bar at the Folies-Bergère'' (1882)
* Titian's '' Venus with a Mirror''
* Jan van Eyck
Jan van Eyck ( , ; – July 9, 1441) was a painter active in Bruges who was one of the early innovators of what became known as Early Netherlandish painting, and one of the most significant representatives of Early Northern Renaissance art. Ac ...
's ''Arnolfini Portrait
''The Arnolfini Portrait'' (or ''The Arnolfini Wedding'', ''The Arnolfini Marriage'', the ''Portrait of Giovanni Arnolfini and his Wife'', or other titles) is a 1434 oil painting on oak panel by the Early Netherlandish painter Jan van Eyck. It fo ...
''
* Pablo Picasso's '' Girl before a Mirror'' (1932)
* Diego Velázquez
Diego Rodríguez de Silva y Velázquez (baptized June 6, 1599August 6, 1660) was a Spanish painter, the leading artist in the court of King Philip IV of Spain and Portugal, and of the Spanish Golden Age. He was an individualistic artist of th ...
's '' Rokeby Venus''
* Diego Velázquez
Diego Rodríguez de Silva y Velázquez (baptized June 6, 1599August 6, 1660) was a Spanish painter, the leading artist in the court of King Philip IV of Spain and Portugal, and of the Spanish Golden Age. He was an individualistic artist of th ...
's '' Las Meninas'' (wherein the viewer is both the watcher - of a self-portrait in progress - and the watched) and the many adaptations of that painting in various media
* Veronese's ''Venus with a Mirror''
Artists have used mirrors to create works and to hone their craft:
* Filippo Brunelleschi
Filippo Brunelleschi ( , , also known as Pippo; 1377 – 15 April 1446), considered to be a founding father of Renaissance architecture, was an Italian architect, designer, and sculptor, and is now recognized to be the first modern engineer, p ...
discovered linear perspective with the help of the mirror.[
* Leonardo da Vinci called the mirror the "master of painters". He recommended, "When you wish to see whether your whole picture accords with what you have portrayed from nature take a mirror and reflect the actual object in it. Compare what is reflected with your painting and carefully consider whether both likenesses of the subject correspond, particularly in regard to the mirror."][
* Many self-portraits are made possible through the use of mirrors, such as great self-portraits by Dürer, ]Frida Kahlo
Magdalena Carmen Frida Kahlo y Calderón (; 6 July 1907 – 13 July 1954) was a Mexican painter known for her many portraits, self-portraits, and works inspired by the nature and artifacts of Mexico. Inspired by the country's popular culture, ...
, Rembrandt
Rembrandt Harmenszoon van Rijn (, ; 15 July 1606 – 4 October 1669), usually simply known as Rembrandt, was a Dutch Golden Age painter, printmaker and draughtsman. An innovative and prolific master in three media, he is generally consid ...
, and Van Gogh. M. C. Escher used special shapes of mirrors in order to achieve a much more complete view of his surroundings than by direct observation in '' Hand with Reflecting Sphere'' (1935; also known as ''Self-Portrait in Spherical Mirror'').
Mirrors are sometimes necessary to fully appreciate art work:
* István Orosz's anamorphic works are images distorted such that they only become clearly visible when reflected in a suitably shaped and positioned mirror.[
]
Sculpture
* Anamorphosis projecting sculpture into mirrors
Contemporary anamorphic artist Jonty Hurwitz uses cylindrical
A cylinder (from ) has traditionally been a three-dimensional solid, one of the most basic of curvilinear geometric shapes. In elementary geometry, it is considered a prism with a circle as its base.
A cylinder may also be defined as an infini ...
mirrors to project distorted sculptures.[
* Sculptures comprised entirely or in part of mirrors include:
** '' Infinity Also Hurts'', a mirror, glass and ]silicone
A silicone or polysiloxane is a polymer made up of siloxane (−R2Si−O−SiR2−, where R = organic group). They are typically colorless oils or rubber-like substances. Silicones are used in sealants, adhesives, lubricants, medicine, cooking ...
sculpture by artist Seth Wulsin
Seth Wulsin (born April 15, 1981 in Spring Valley, NY) is an independent journalist and contemporary artist working primarily with space, time and light through large-scale, site-specific, ephemeral sculpture, drawing and architectural perform ...
** '' Sky Mirror'', a public sculpture by artist Anish Kapoor
Other artistic mediums
 Some other contemporary artists use mirrors as the material of art:
* A
Some other contemporary artists use mirrors as the material of art:
* A Chinese magic mirror
The Chinese magic mirror () traces back to at least the 5th century, although their existence during the Han dynasty (206 BC – 24 AD) has been claimed. The mirrors were made out of solid bronze. The front was polished and could be used as a mi ...
is a device in which the face of the bronze mirror projects the same image that was cast on its back. This is due to minute curvatures on its front.[
* Specular holography uses a large number of curved mirrors embedded in a surface to produce three-dimensional imagery.
* Paintings on mirror surfaces (such as silkscreen printed glass mirrors)
* Special mirror installations:
** ''Follow Me'' mirror labyrinth by artist, Jeppe Hein (see also, Entertainment: Mirror mazes, below)
** ''Mirror Neon Cube'' by artist, Jeppe Hein
]
Religious function of the real and depicted mirror
In the Middle Ages mirrors existed in various shapes for multiple uses. Mostly they were used as an accessory for personal hygiene but also as tokens of courtly love, made from ivory in the ivory-carving centers in Paris, Cologne and the Southern Netherlands.[ They also had their uses in religious contexts as they were integrated in a special form of pilgrims badges or pewter/lead mirror boxes][ From the late 14th century. Burgundian ducal inventories show us that the dukes owned a mass of mirrors or objects with mirrors, not only with religious iconography or inscriptions, but combined with reliquaries, religious paintings or other objects that were distinctively used for personal piety.][ Considering mirrors in paintings and book illumination as depicted artifacts and trying to draw conclusions about their functions from their depicted setting, one of these functions is to be an aid in personal prayer to achieve self-knowledge and knowledge of God, in accord with contemporary theological sources. For example, the famous Arnolfini-Wedding by ]Jan van Eyck
Jan van Eyck ( , ; – July 9, 1441) was a painter active in Bruges who was one of the early innovators of what became known as Early Netherlandish painting, and one of the most significant representatives of Early Northern Renaissance art. Ac ...
shows a constellation of objects that can be recognized as one which would allow a praying man to use them for his personal piety: the mirror surrounded by scenes of the Passion to reflect on it and on oneself, a rosary
The Rosary (; la, , in the sense of "crown of roses" or "garland of roses"), also known as the Dominican Rosary, or simply the Rosary, refers to a set of prayers used primarily in the Catholic Church, and to the physical string of knots or b ...
as a device in this process, the veiled and cushioned bench to use as a prie-dieu, and the abandoned shoes that point in the direction in which the praying man kneeled.[ The metaphorical meaning of depicted mirrors is complex and many-layered, e.g. as an attribute of Mary, the "speculum sine macula" (mirror without blemish), or as attributes of scholarly and theological wisdom and knowledge as they appear in book illuminations of different evangelists and authors of theological treatises. Depicted mirrors – orientated on the physical properties of a real mirror – can be seen as metaphors of knowledge and reflection and are thus able to remind beholders to reflect and get to know themselves. The mirror may function simultaneously as a symbol and as a device of a moral appeal. That is also the case if it is shown in combination with virtues and vices, a combination which also occurs more frequently in the 15th century: the moralizing layers of mirror metaphors remind the beholder to examine himself thoroughly according to his own virtuous or vicious life. This is all the more true if the mirror is combined with iconography of death. Not only is Death as a corpse or skeleton holding the mirror for the still-living personnel of paintings, illuminations and prints, but the skull appears on the convex surfaces of depicted mirrors, showing the painted and real beholder his future face.][
]
Decoration
 Mirrors are frequently used in interior decoration and as ornaments:
* Mirrors, typically large and unframed, are frequently used in interior decoration to create an illusion of space and to amplify the apparent size of a room.
Mirrors are frequently used in interior decoration and as ornaments:
* Mirrors, typically large and unframed, are frequently used in interior decoration to create an illusion of space and to amplify the apparent size of a room.[ They come also framed in a variety of forms, such as the pier glass and the overmantel mirror.
* Mirrors are used also in some schools of feng shui, an ancient Chinese practice of placement and arrangement of space to achieve harmony with an environment.
* The softness of old mirrors is sometimes replicated by contemporary artisans for use in interior design. These reproduction antiqued mirrors are works of art and can bring color and texture to an otherwise hard, cold reflective surface.
* A decorative reflecting sphere of thin metal-coated glass, working as a reducing wide-angle mirror, is sold as a Christmas ornament called a ''bauble''.
* Some pubs and bars hang mirrors depicting the logo of a brand of liquor, beer or drinking establishment.
]
Entertainment
* Illuminated rotating disco balls covered with small mirrors are used to cast moving spots of light around a dance floor.
* The hall of mirrors, commonly found in amusement park
An amusement park is a park that features various attractions, such as rides and games, as well as other events for entertainment purposes. A theme park is a type of amusement park that bases its structures and attractions around a central ...
s, is an attraction in which a number of distorting mirrors produce unusual reflections of the visitor.
* Mirrors are employed in kaleidoscopes, personal entertainment-devices invented in Scotland by Sir David Brewster
Sir David Brewster KH PRSE FRS FSA Scot FSSA MICE (11 December 178110 February 1868) was a British scientist, inventor, author, and academic administrator. In science he is principally remembered for his experimental work in physical optics ...
.
* Mirrors are often used in magic to create an illusion. One effect is called Pepper's ghost.
* Mirror maze
A maze is a path or collection of paths, typically from an entrance to a goal. The word is used to refer both to branching tour puzzles through which the solver must find a route, and to simpler non-branching ("unicursal") patterns that lea ...
s, often found in amusement park
An amusement park is a park that features various attractions, such as rides and games, as well as other events for entertainment purposes. A theme park is a type of amusement park that bases its structures and attractions around a central ...
s , contain large numbers of mirrors and sheets of glass. The idea is to navigate the disorientating array without bumping into the walls. Mirrors in attractions like this are often made of Plexiglas to prevent breakages.[
]
Film and television
Mirrors appear in many movies and TV shows:
*''Black Swan
The black swan (''Cygnus atratus'') is a large waterbird, a species of swan which breeds mainly in the southeast and southwest regions of Australia. Within Australia, the black swan is nomadic, with erratic migration patterns dependent upon c ...
'' is a psychological horror film that frequently incorporates mirrors. Fractured mirrors are prominent in the film, and the character Nina stabs herself with a broken piece of mirror.
* ''Candyman'' is a horror film about a malevolent spirit summoned by speaking its name in front of a mirror.
* ''Conan the Destroyer
''Conan the Destroyer'' is a 1984 American epic sword and sorcery film directed by Richard Fleischer from a screenplay by Stanley Mann and a story by Roy Thomas and Gerry Conway. Based on the character Conan the Barbarian created by Robert E. ...
'' features a mirror-embedded chamber deep within Thoth-Amon's castle. The mirrors are first used in an illusory fashion to deceive Conan once he is separated by his companions, and during a battle sequence it is discovered that by breaking the mirrors he is able to damage and eventually defeat the otherwise-invulnerable wizard Thoth-Amon.
*'' Dead of Night'' is an anthology
In book publishing, an anthology is a collection of literary works chosen by the compiler; it may be a collection of plays, poems, short stories, songs or excerpts by different authors.
In genre fiction, the term ''anthology'' typically categ ...
horror film with one segment titled "The Haunted Mirror," in which a mirror casts a murderous spell.
*''Doctor Strange
Doctor Stephen Strange is a fictional character appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by Steve Ditko, the character first appeared in ''Strange Tales'' #110 (cover-dated July 1963). Doctor Strange serves as Sorce ...
'', '' Doctor Strange in the Multiverse of Madness'', and '' Spider-Man: No Way Home'' feature the fictional mirror dimension, a parallel dimension in the Marvel Universe
The Marvel Universe is a fictional shared universe where the stories in most American comic book titles and other media published by Marvel Comics take place. Super-teams such as the Avengers, the X-Men, the Fantastic Four, the Guardians of ...
that reflects objects like a mirror, but in different directions.
*'' Enter the Dragons iconic and final fight scene occurs in a mirrored room. The mirrors create multiple reflections of the fight movements but are eventually smashed.
*'' The Floorwalker'' and ''Duck Soup
Duck soup may refer to:
* ''Duck Soup'' (1933 film), starring the Marx Brothers
* ''Duck Soup'' (1927 film), featuring Laurel and Hardy
* Oritang, Korean duck soup
* "Duck Soup", an episode of '' Even Stevens''
* "Duck Soup", a song by Baba Broo ...
'' contain a mirror scene in which one person comically pretends to be the mirror reflection of someone else. This mirror scene has been imitated in other comedy films and TV shows.
*'' Hamlet'' has a throne room with mirrored walls. Hamlet, played by Kenneth Branagh, gives his famous speech with the words "to be or not to be," looking into these mirrors.
* ''Harry Potter and the Philosopher's Stone'' includes the magical Mirror of Erised.
*'' Inception'' contains mirrors created in a dream sequence. Ariadne creates two mirrors facing each other that form an infinite number of reflected mirrors.
*'' Last Night in Soho'' is a psychological horror movie with several mirror scenes. The character Ellie occasionally sees her mother's ghost in mirrors.
*'' The Matrix'' uses various reflections and mirrors throughout the film. Neo watches a broken mirror mend itself, and different objects create reflections.
* '' Mirror'' is a drama film by Andrei Tarkovsky
Andrei Arsenyevich Tarkovsky ( rus, Андрей Арсеньевич Тарковский, p=ɐnˈdrʲej ɐrˈsʲenʲjɪvʲɪtɕ tɐrˈkofskʲɪj; 4 April 1932 – 29 December 1986) was a Russian filmmaker. Widely considered one of the greates ...
that includes several scenes with mirrors and several scenes shot in reflection.
*'' Mirror Mirror'' is a fantasy comedy film based on Snow White that features a Mirror House and Mirror Queen.
* ''Mirrors'' is a horror film about haunted mirrors that reflect different scenes than those in front of them.
*'' Persona'' relies on mirror sequences to show how the two women, Bibi and Liv, reflect each other and become more alike.
* ''Poltergeist III
''Poltergeist III'' is a 1988 American supernatural horror film co-written and directed by Gary Sherman, and starring Tom Skerritt, Nancy Allen, and Lara Flynn Boyle in her film debut, with Heather O'Rourke and Zelda Rubinstein reprising their ...
'' features mirrors that do not reflect reality and which can be used as portals to an afterlife.
*''Psycho
Psycho may refer to:
Mind
* Psychopath
* Sociopath
* Someone with a personality disorder
* Someone with a psychological disorder
People with the nickname
* Karl Amoussou or Psycho, mixed martial artist
* Peter Ebdon or Psycho, English snook ...
'' by Alfred Hitchock has several shots with mirrors that reflect characters.
* ''Oculus'' is a horror film about a haunted mirror that causes people to hallucinate and commit acts of violence.
*'' Orpheus'' includes an important theme of mirrors in connection to aging and death.
*'' Taxi Driver'' has a notable scene with a mirror in which the character Travis, played by Robert De Niro
Robert Anthony De Niro Jr. ( , ; born August 17, 1943) is an American actor. Known for his collaborations with Martin Scorsese, he is considered to be one of the best actors of his generation. De Niro is the recipient of various accolades ...
, asks himself the famous line, "You talkin’ to me?"
*'' The Lady from Shanghai'' has a climatic hall of mirrors scene that has become a trope in cinema narratives.
*'' Raging Bull'' ends with the character Jake talking to himself in a mirror, a scene that was reused in ''Boogie Nights
''Boogie Nights'' is a 1997 American period comedy-drama film written and directed by Paul Thomas Anderson. It is set in Los Angeles's San Fernando Valley and focuses on a young nightclub dishwasher who becomes a popular star of pornographic fil ...
''.
*'' The Shining'' is a horror movie that includes several scenes with mirrors. Every time the character Jack encounters a ghost, a mirror is present.
* '' The 10th Kingdom'' miniseries
A miniseries or mini-series is a television series that tells a story in a predetermined, limited number of episodes. "Limited series" is another more recent US term which is sometimes used interchangeably. , the popularity of miniseries format h ...
requires the characters to use a magic mirror to travel between New York City (the 10th Kingdom) and the Nine Kingdoms of fairy tale
A fairy tale (alternative names include fairytale, fairy story, magic tale, or wonder tale) is a short story that belongs to the folklore genre. Such stories typically feature magic (paranormal), magic, incantation, enchantments, and mythical ...
.
*'' The Twilight Zone'' episode " The Mirror" features a mirror that the character Clemente believes can provide visions and information about enemies.
*'' Us'' is a horror film that includes a girl seeing a doppelgänger
A doppelgänger (), a compound noun formed by combining the two nouns (double) and (walker or goer) (), doppelgaenger or doppelganger is a biologically unrelated look-alike, or a double, of a living person.
In fiction and mythology, a doppelg ...
of herself in a house of mirrors
A house of mirrors or hall of mirrors is a traditional attraction at funfairs (carnivals) and amusement parks. The basic concept behind a house of mirrors is to be a maze-like puzzle. In addition to the maze, participants are also given mirro ...
in a funhouse. The mirror images reflect the similarities in the clones throughout the film.
*'' Vertigo'' includes several appearances of mirrors with both Scottie and Madeleine in the frame.
Literature
 Mirrors feature in literature:
* Christian Bible passages, 1 Corinthians 13:12 (" Through a Glass Darkly") and 2 Corinthians 3:18, reference a dim mirror-image or poor mirror-reflection.
*
Mirrors feature in literature:
* Christian Bible passages, 1 Corinthians 13:12 (" Through a Glass Darkly") and 2 Corinthians 3:18, reference a dim mirror-image or poor mirror-reflection.
* Narcissus
Narcissus may refer to:
Biology
* ''Narcissus'' (plant), a genus containing daffodils and others
People
* Narcissus (mythology), Greek mythological character
* Narcissus (wrestler) (2nd century), assassin of the Roman emperor Commodus
* Tiberiu ...
of Greek mythology wastes away while gazing, self-admiringly, at his reflection in water.
* The Song-dynasty history '' Zizhi Tongjian'' ''Comprehensive Mirror in Aid of Governance'' by Sima Guang is so titled because "mirror" (鑑, jiàn) is used metaphorically in Chinese to refer to gaining insight by reflecting on past experience or history.
* In the European fairy tale
A fairy tale (alternative names include fairytale, fairy story, magic tale, or wonder tale) is a short story that belongs to the folklore genre. Such stories typically feature magic (paranormal), magic, incantation, enchantments, and mythical ...
, '' Snow White'' (collected by the Brothers Grimm in 1812), the evil queen asks, " Mirror, mirror, on the wall... who's the fairest of them all?"
* In the Aarne-Thompson-Uther Index tale type ATU 329, "Hiding from the Devil (Princess)", the protagonist must find a way to hide from a princess, who, in many variants, owns a magical mirror that can see the whole world.
* In Tennyson's famous poem '' The Lady of Shalott'' (1833, revised in 1842), the titular character possesses a mirror that enables her to look out on the people of Camelot, as she is under a curse that prevents her from seeing Camelot directly.
* Hans Christian Andersen
Hans Christian Andersen ( , ; 2 April 1805 – 4 August 1875) was a Danish author. Although a prolific writer of plays, travelogues, novels, and poems, he is best remembered for his literary fairy tales.
Andersen's fairy tales, consisti ...
's fairy tale '' The Snow Queen'', features the devil, in a form of an evil troll,[ who made a magic mirror that distorts the appearance of everything that it reflects.
* Lewis Carroll's '' Through the Looking-Glass and What Alice Found There'' (1871) has become one of the best-loved exemplars of the use of mirrors in literature. The text itself utilizes a narrative that mirrors that of its predecessor, '' Alice's Adventures in Wonderland''.][
* In ]Oscar Wilde
Oscar Fingal O'Flahertie Wills Wilde (16 October 185430 November 1900) was an Irish poet and playwright. After writing in different forms throughout the 1880s, he became one of the most popular playwrights in London in the early 1890s. He is ...
's novel, '' The Picture of Dorian Gray'' (1890), a portrait serves as a magical mirror that reflects the true visage of the perpetually youthful protagonist, as well as the effect on his soul of each sinful act.[
* W. H. Auden's villanelle "Miranda" repeats the refrain: "My dear one is mine as mirrors are lonely".
* The short story '']Tlön, Uqbar, Orbis Tertius
"Tlön, Uqbar, Orbis Tertius" is a short story by the 20th-century Argentinian writer Jorge Luis Borges. The story was first published in the Argentinian journal '' Sur'', May 1940. The "postscript" dated 1947 is intended to be anachronistic, se ...
'' (1940) by Jorge Luis Borges begins with the phrase "I owe the discovery of Uqbar to the conjunction of a mirror and an encyclopedia" and contains other references to mirrors.
* ''The Trap'', a short story by H.P. Lovecraft and Henry S. Whitehead, centers around a mirror. "It was on a certain Thursday morning in December that the whole thing began with that unaccountable motion I thought I saw in my antique Copenhagen mirror. Something, it seemed to me, stirred—something reflected in the glass, though I was alone in my quarters."[
* Magical objects in the ''Harry Potter'' series (1997–2011) include the Mirror of Erised and two-way mirrors.
* Under ''Appendix: Variant Planes & Cosmologies'' of the '' Dungeons & Dragons'' '' Manual of the Planes'' (2000), is The Plane of Mirrors (page 204).][ It describes the Plane of Mirrors as a space existing behind reflective surfaces, and experienced by visitors as a long corridor. The greatest danger to visitors upon entering the plane is the instant creation of a mirror-self with the opposite alignment of the original visitor.
* ''The Mirror Thief'', a novel by Martin Seay (2016),][ includes a fictional account of industrial espionage surrounding mirror-manufacturing in 16th-century Venice.
* '' The Reaper's Image'', a short story by ]Stephen King
Stephen Edwin King (born September 21, 1947) is an American author of horror, supernatural fiction, suspense, crime, science-fiction, and fantasy novels. Described as the "King of Horror", a play on his surname and a reference to his high s ...
, concerns a rare Elizabethan mirror that displays the Reaper's image when viewed, which symbolises the death of the viewer.
* Kilgore Trout, a protagonist of Kurt Vonnegut's novel '' Breakfast of Champions'', believes that mirrors are windows to other universes, and refers to them as "leaks", a recurring motif in the book.
*In '' The Fellowship of the Ring'' by J. R. R. Tolkien, the Mirror of Galadriel
''The Lord of the Rings'' is an epic high-fantasy novel by English author and scholar J. R. R. Tolkien. Set in Middle-earth, intended to be Earth at some time in the distant past, the story began as a sequel to Tolkien's 1937 children's boo ...
allows one to see things of the past, present and possible future. The mirror additionally appears in the movie adaptation.
Mirror test
Only a few animal species have been shown to have the ability to recognize themselves in a mirror, most of them mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s. Experiments have found that the following animals can pass the mirror test:
* All great apes:
** Humans. Humans tend to fail the mirror test until they are about 18 months old, or what psychoanalysts call the " mirror stage".[
** ]Bonobo
The bonobo (; ''Pan paniscus''), also historically called the pygmy chimpanzee and less often the dwarf chimpanzee or gracile chimpanzee, is an endangered great ape and one of the two species making up the genus '' Pan,'' the other being the comm ...
s[
** ]Chimpanzee
The chimpanzee (''Pan troglodytes''), also known as simply the chimp, is a species of great ape native to the forest and savannah of tropical Africa. It has four confirmed subspecies and a fifth proposed subspecies. When its close relative th ...
s[
** Orangutans][
** Gorillas. Initially, it was thought that gorillas did not pass the test, but there are now several well-documented reports of gorillas (such as ]Koko
Koko or KOKO may refer to:
Animals
*Koko (gorilla) (1971–2018), a gorilla trained to communicate in American Sign Language
*Koko (dog) (2005–2012), the Australian kelpie in the 2011 film ''Red Dog''
*Koko (horse), an Irish racehorse that won ...
[) passing the test.
* Bottlenose dolphins][
* Orcas][
* ]Elephants
Elephants are the largest existing land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant, the African forest elephant, and the Asian elephant. They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and ...
[
* European magpies][
]
See also
* Anish Kapoor (artist working with mirrors)
* Aranmula kannadi
* Chirality (mathematics)
* Corner reflector
A corner reflector is a retroreflector consisting of three mutually perpendicular, intersecting flat surfaces, which reflects waves directly towards the source, but translated. The three intersecting surfaces often have square shapes. Radar co ...
* Deformable mirror
* Digital micromirror device
* Heliotrope (instrument)
* Honeycomb mirror
* List of telescope parts and construction
* Mirror armour
* Non-reversing mirror
A non-reversing mirror (sometimes referred to as a flip mirror) is a mirror that presents its subject as it would be seen from the mirror. A non-reversing mirror can be made by connecting two regular mirrors at their edges at a 90 degree angle. ...
* Mirror writing
* Mirrors in Mesoamerican culture
* Perfect mirror A perfect mirror is a mirror that reflects light (and electromagnetic radiation in general) perfectly, and does not transmit or absorb it.
General
Domestic mirrors are not perfect mirrors as they absorb a significant portion of the light which fal ...
* Periscope
* Selfie
* Spectrophobia
* TLV mirror
* Venus effect
References
Further reading
* ''Le miroir: révélations, science-fiction et fallacies. Essai sur une légende scientifique'', Jurgis Baltrušaitis, Paris, 1978. .
* ''On reflection'', Jonathan Miller, National Gallery Publications Limited (1998). .
* ''Lo specchio, la strega e il quadrante. Vetrai, orologiai e rappresentazioni del 'principium individuationis' dal Medioevo all'Età moderna'', Francesco Tigani, Roma, 2012. .
*Shrum, Rebecca K. 2017.
In the Looking Glass: Mirrors and Identity in Early America
'. Johns Hopkins University Press.
External links
*
*
*
How Mirrors Are Made (video)
Glass Association of North America (GANA)
July 2019 "The Ugly History of Beautiful Things: Mirrors" by Katy Kelleher for Longreads
{{Authority control
Glass applications
Reflective building components
Wallcoverings




 The evolution of glass mirrors in the Middle Ages followed improvements in glassmaking technology. Glassmakers in France made flat glass plates by blowing glass bubbles, spinning them rapidly to flatten them, and cutting rectangles out of them. A better method, developed in Germany and perfected in
The evolution of glass mirrors in the Middle Ages followed improvements in glassmaking technology. Glassmakers in France made flat glass plates by blowing glass bubbles, spinning them rapidly to flatten them, and cutting rectangles out of them. A better method, developed in Germany and perfected in  When a sufficiently narrow beam of light is reflected at a point of a surface, the surface's normal direction will be the bisector of the angle formed by the two beams at that point. That is, the direction vector towards the incident beams's source, the normal vector , and direction vector of the reflected beam will be coplanar, and the angle between and will be equal to the
When a sufficiently narrow beam of light is reflected at a point of a surface, the surface's normal direction will be the bisector of the angle formed by the two beams at that point. That is, the direction vector towards the incident beams's source, the normal vector , and direction vector of the reflected beam will be coplanar, and the angle between and will be equal to the  Mirrors reflect an image to the observer. However, unlike a projected image on a screen, an image does not actually exist on the surface of the mirror. For example, when two people look at each other in a mirror, both see different images on the same surface. When the light waves converge through the lens of the eye they interfere with each other to form the image on the surface of the retina, and since both viewers see waves coming from different directions, each sees a different image in the same mirror. Thus, the images observed in a mirror depend upon the angle of the mirror with respect to the eye. The angle between the object and the observer is always twice the angle between the eye and the normal, or the direction perpendicular to the surface. This allows animals with binocular vision to see the reflected image with
Mirrors reflect an image to the observer. However, unlike a projected image on a screen, an image does not actually exist on the surface of the mirror. For example, when two people look at each other in a mirror, both see different images on the same surface. When the light waves converge through the lens of the eye they interfere with each other to form the image on the surface of the retina, and since both viewers see waves coming from different directions, each sees a different image in the same mirror. Thus, the images observed in a mirror depend upon the angle of the mirror with respect to the eye. The angle between the object and the observer is always twice the angle between the eye and the normal, or the direction perpendicular to the surface. This allows animals with binocular vision to see the reflected image with  The reflectivity of a mirror is determined by the percentage of reflected light per the total of the incident light. The reflectivity may vary with wavelength. All or a portion of the light not reflected is absorbed by the mirror, while in some cases a portion may also transmit through. Although some small portion of the light will be absorbed by the coating, the reflectivity is usually higher for first-surface mirrors, eliminating both reflection and absorption losses from the substrate.
The reflectivity is often determined by the type and thickness of the coating. When the thickness of the coating is sufficient to prevent transmission, all of the losses occur due to absorption. Aluminium is harder, less expensive, and more resistant to tarnishing than silver, and will reflect 85 to 90% of the light in the visible to near-ultraviolet range, but experiences a drop in its reflectance between 800 and 900 nm. Gold is very soft and easily scratched, costly, yet does not tarnish. Gold is greater than 96% reflective to near and far-infrared light between 800 and 12000 nm, but poorly reflects visible light with wavelengths shorter than 600 nm (yellow). Silver is expensive, soft, and quickly tarnishes, but has the highest reflectivity in the visual to near-infrared of any metal. Silver can reflect up to 98 or 99% of light to wavelengths as long as 2000 nm, but loses nearly all reflectivity at wavelengths shorter than 350 nm.
Dielectric mirrors can reflect greater than 99.99% of light, but only for a narrow range of wavelengths, ranging from a bandwidth of only 10 nm to as wide as 100 nm for tunable lasers. However, dielectric coatings can also enhance the reflectivity of metallic coatings and protect them from scratching or tarnishing. Dielectric materials are typically very hard and relatively cheap, however the number of coats needed generally makes it an expensive process. In mirrors with low tolerances, the coating thickness may be reduced to save cost, and simply covered with paint to absorb transmission.
The reflectivity of a mirror is determined by the percentage of reflected light per the total of the incident light. The reflectivity may vary with wavelength. All or a portion of the light not reflected is absorbed by the mirror, while in some cases a portion may also transmit through. Although some small portion of the light will be absorbed by the coating, the reflectivity is usually higher for first-surface mirrors, eliminating both reflection and absorption losses from the substrate.
The reflectivity is often determined by the type and thickness of the coating. When the thickness of the coating is sufficient to prevent transmission, all of the losses occur due to absorption. Aluminium is harder, less expensive, and more resistant to tarnishing than silver, and will reflect 85 to 90% of the light in the visible to near-ultraviolet range, but experiences a drop in its reflectance between 800 and 900 nm. Gold is very soft and easily scratched, costly, yet does not tarnish. Gold is greater than 96% reflective to near and far-infrared light between 800 and 12000 nm, but poorly reflects visible light with wavelengths shorter than 600 nm (yellow). Silver is expensive, soft, and quickly tarnishes, but has the highest reflectivity in the visual to near-infrared of any metal. Silver can reflect up to 98 or 99% of light to wavelengths as long as 2000 nm, but loses nearly all reflectivity at wavelengths shorter than 350 nm.
Dielectric mirrors can reflect greater than 99.99% of light, but only for a narrow range of wavelengths, ranging from a bandwidth of only 10 nm to as wide as 100 nm for tunable lasers. However, dielectric coatings can also enhance the reflectivity of metallic coatings and protect them from scratching or tarnishing. Dielectric materials are typically very hard and relatively cheap, however the number of coats needed generally makes it an expensive process. In mirrors with low tolerances, the coating thickness may be reduced to save cost, and simply covered with paint to absorb transmission.
 Surface quality, or surface accuracy, measures the deviations from a perfect, ideal surface shape. Increasing the surface quality reduces distortion, artifacts, and aberration in images, and helps increase
Surface quality, or surface accuracy, measures the deviations from a perfect, ideal surface shape. Increasing the surface quality reduces distortion, artifacts, and aberration in images, and helps increase  Transmissivity is determined by the percentage of light transmitted per the incident light. Transmissivity is usually the same from both first and second surfaces. The combined transmitted and reflected light, subtracted from the incident light, measures the amount absorbed by both the coating and substrate. For transmissive mirrors, such as one-way mirrors,
Transmissivity is determined by the percentage of light transmitted per the incident light. Transmissivity is usually the same from both first and second surfaces. The combined transmitted and reflected light, subtracted from the incident light, measures the amount absorbed by both the coating and substrate. For transmissive mirrors, such as one-way mirrors,  Mirrors are usually manufactured by either polishing a naturally reflective material, such as speculum metal, or by applying a reflective coating to a suitable polished
Mirrors are usually manufactured by either polishing a naturally reflective material, such as speculum metal, or by applying a reflective coating to a suitable polished 



 :Convex mirrors provide a wider field of view than flat mirrors, and are often used on vehicles, especially large trucks, to minimize blind spots. They are sometimes placed at road junctions, and at corners of sites such as
:Convex mirrors provide a wider field of view than flat mirrors, and are often used on vehicles, especially large trucks, to minimize blind spots. They are sometimes placed at road junctions, and at corners of sites such as  Mirrors are integral parts of a solar power plant. The one shown in the adjacent picture uses
Mirrors are integral parts of a solar power plant. The one shown in the adjacent picture uses  Telescopes and other precision instruments use ''front silvered'' or
Telescopes and other precision instruments use ''front silvered'' or  The reflectivity of the mirror coating can be measured using a reflectometer and for a particular metal it will be different for different wavelengths of light. This is exploited in some optical work to make cold mirrors and hot mirrors. A cold mirror is made by using a transparent substrate and choosing a coating material that is more reflective to visible light and more transmissive to infrared light.
A hot mirror is the opposite, the coating preferentially reflects infrared. Mirror surfaces are sometimes given thin film overcoatings both to retard degradation of the surface and to increase their reflectivity in parts of the spectrum where they will be used. For instance, aluminium mirrors are commonly coated with silicon dioxide or magnesium fluoride. The reflectivity as a function of wavelength depends on both the thickness of the coating and on how it is applied.
The reflectivity of the mirror coating can be measured using a reflectometer and for a particular metal it will be different for different wavelengths of light. This is exploited in some optical work to make cold mirrors and hot mirrors. A cold mirror is made by using a transparent substrate and choosing a coating material that is more reflective to visible light and more transmissive to infrared light.
A hot mirror is the opposite, the coating preferentially reflects infrared. Mirror surfaces are sometimes given thin film overcoatings both to retard degradation of the surface and to increase their reflectivity in parts of the spectrum where they will be used. For instance, aluminium mirrors are commonly coated with silicon dioxide or magnesium fluoride. The reflectivity as a function of wavelength depends on both the thickness of the coating and on how it is applied.
 For scientific optical work,
For scientific optical work,  Painters depicting someone gazing into a mirror often also show the person's reflection. This is a kind of abstraction—in most cases the angle of view is such that the person's reflection should not be visible. Similarly, in movies and still photography an actor or actress is often shown ostensibly looking at him- or herself in a mirror, and yet the reflection faces the camera. In reality, the actor or actress sees only the camera and its operator in this case, not their own reflection. In the psychology of perception, this is known as the Venus effect.
The mirror is the central device in some of the greatest of European paintings:
* Édouard Manet's '' A Bar at the Folies-Bergère'' (1882)
* Titian's '' Venus with a Mirror''
*
Painters depicting someone gazing into a mirror often also show the person's reflection. This is a kind of abstraction—in most cases the angle of view is such that the person's reflection should not be visible. Similarly, in movies and still photography an actor or actress is often shown ostensibly looking at him- or herself in a mirror, and yet the reflection faces the camera. In reality, the actor or actress sees only the camera and its operator in this case, not their own reflection. In the psychology of perception, this is known as the Venus effect.
The mirror is the central device in some of the greatest of European paintings:
* Édouard Manet's '' A Bar at the Folies-Bergère'' (1882)
* Titian's '' Venus with a Mirror''
*  Some other contemporary artists use mirrors as the material of art:
* A
Some other contemporary artists use mirrors as the material of art:
* A 
 Mirrors are frequently used in interior decoration and as ornaments:
* Mirrors, typically large and unframed, are frequently used in interior decoration to create an illusion of space and to amplify the apparent size of a room. They come also framed in a variety of forms, such as the pier glass and the overmantel mirror.
* Mirrors are used also in some schools of feng shui, an ancient Chinese practice of placement and arrangement of space to achieve harmony with an environment.
* The softness of old mirrors is sometimes replicated by contemporary artisans for use in interior design. These reproduction antiqued mirrors are works of art and can bring color and texture to an otherwise hard, cold reflective surface.
* A decorative reflecting sphere of thin metal-coated glass, working as a reducing wide-angle mirror, is sold as a Christmas ornament called a ''bauble''.
* Some pubs and bars hang mirrors depicting the logo of a brand of liquor, beer or drinking establishment.
Mirrors are frequently used in interior decoration and as ornaments:
* Mirrors, typically large and unframed, are frequently used in interior decoration to create an illusion of space and to amplify the apparent size of a room. They come also framed in a variety of forms, such as the pier glass and the overmantel mirror.
* Mirrors are used also in some schools of feng shui, an ancient Chinese practice of placement and arrangement of space to achieve harmony with an environment.
* The softness of old mirrors is sometimes replicated by contemporary artisans for use in interior design. These reproduction antiqued mirrors are works of art and can bring color and texture to an otherwise hard, cold reflective surface.
* A decorative reflecting sphere of thin metal-coated glass, working as a reducing wide-angle mirror, is sold as a Christmas ornament called a ''bauble''.
* Some pubs and bars hang mirrors depicting the logo of a brand of liquor, beer or drinking establishment.
 Mirrors feature in literature:
* Christian Bible passages, 1 Corinthians 13:12 (" Through a Glass Darkly") and 2 Corinthians 3:18, reference a dim mirror-image or poor mirror-reflection.
*
Mirrors feature in literature:
* Christian Bible passages, 1 Corinthians 13:12 (" Through a Glass Darkly") and 2 Corinthians 3:18, reference a dim mirror-image or poor mirror-reflection.
*