Mesoamerica on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Mesoamerica is a
Mesoamerica is a
 The term was first used by the
The term was first used by the
 Outside of the northern Maya lowlands,
Outside of the northern Maya lowlands,
 The history of human occupation in Mesoamerica is divided into stages or periods. These are known, with slight variation depending on region, as the Paleo-Indian, the
The history of human occupation in Mesoamerica is divided into stages or periods. These are known, with slight variation depending on region, as the Paleo-Indian, the
 The first complex civilization to develop in Mesoamerica was that of the
The first complex civilization to develop in Mesoamerica was that of the
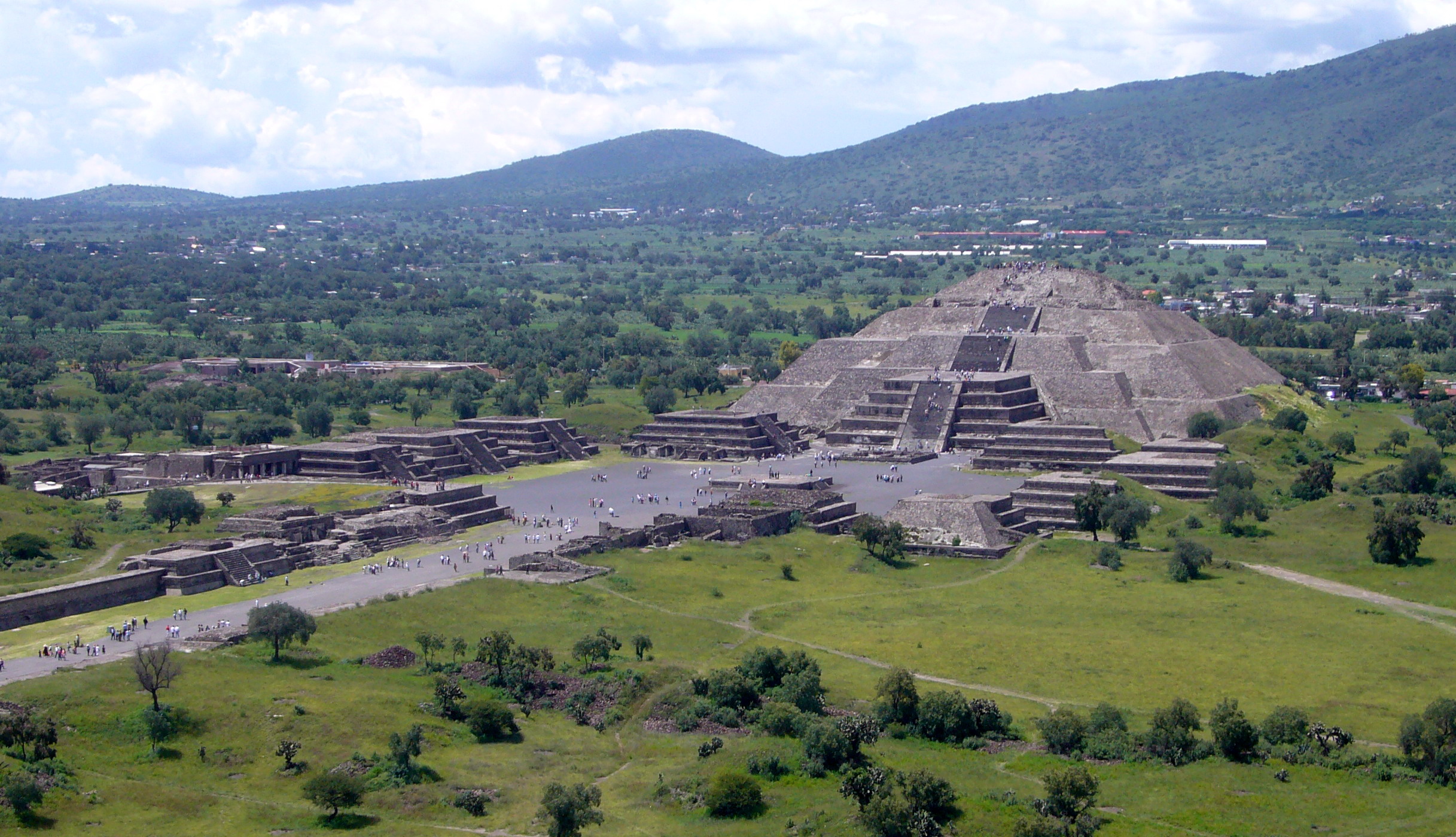 The Classic period is marked by the rise and dominance of several polities. The traditional distinction between the Early and Late Classic are marked by their changing fortune and their ability to maintain regional primacy. Of paramount importance are Teotihuacán in central Mexico and
The Classic period is marked by the rise and dominance of several polities. The traditional distinction between the Early and Late Classic are marked by their changing fortune and their ability to maintain regional primacy. Of paramount importance are Teotihuacán in central Mexico and
 The Late Classic period (beginning c. 600 CE until 909 CE) is characterized as a period of interregional competition and factionalization among the numerous regional polities in the Maya area. This largely resulted from the decrease in Tikal's socio-political and economic power at the beginning of the period. It was therefore during this time that other sites rose to regional prominence and were able to exert greater interregional influence, including Caracol,
The Late Classic period (beginning c. 600 CE until 909 CE) is characterized as a period of interregional competition and factionalization among the numerous regional polities in the Maya area. This largely resulted from the decrease in Tikal's socio-political and economic power at the beginning of the period. It was therefore during this time that other sites rose to regional prominence and were able to exert greater interregional influence, including Caracol,
 Generally applied to the Maya area, the Terminal Classic roughly spans the time between c. 800/850 and c. 1000 AD. Overall, it generally correlates with the rise to prominence of
Generally applied to the Maya area, the Terminal Classic roughly spans the time between c. 800/850 and c. 1000 AD. Overall, it generally correlates with the rise to prominence of
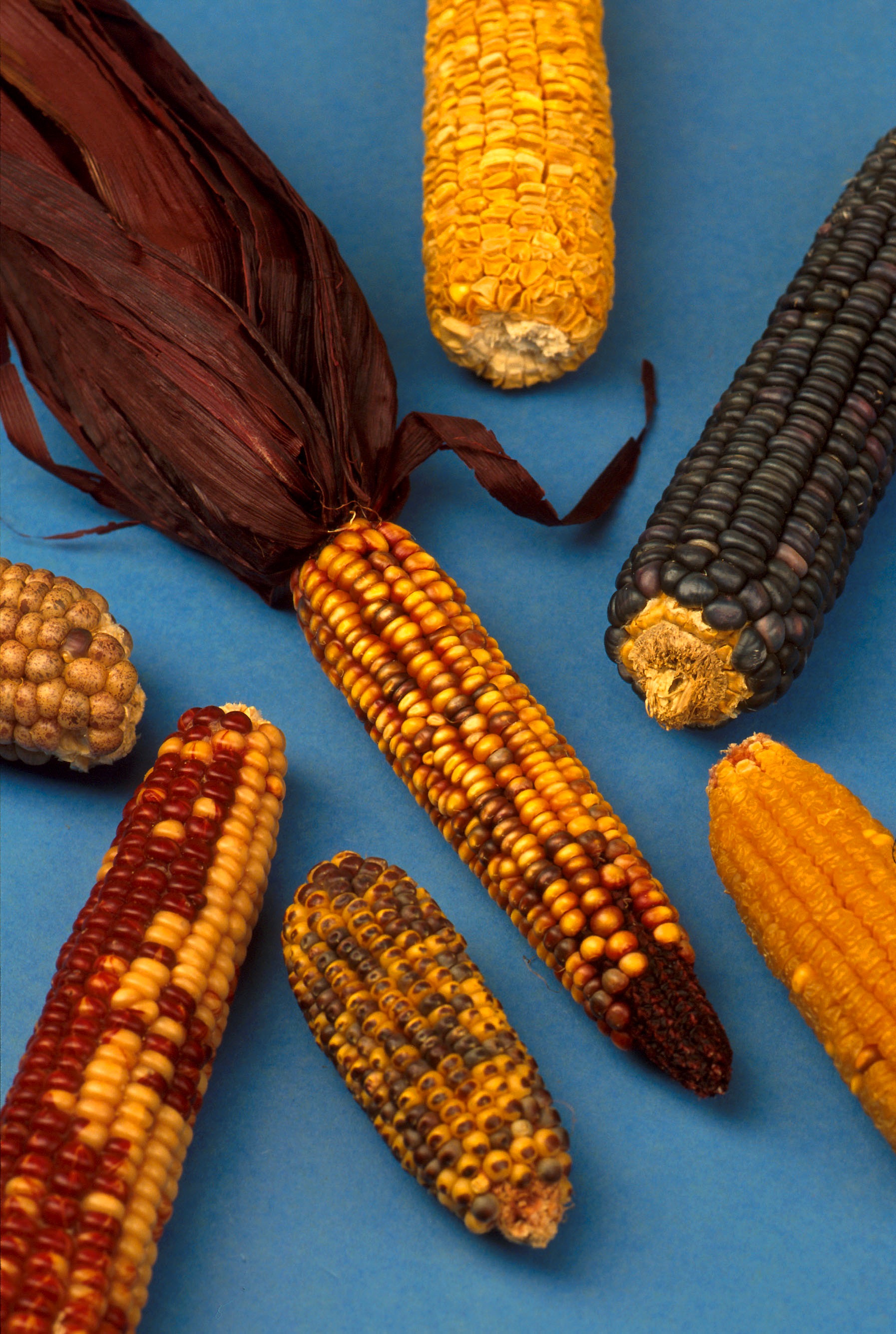


 By roughly 6000 BCE, hunter-gatherers living in the
By roughly 6000 BCE, hunter-gatherers living in the
 Ceremonial centers were the nuclei of Mesoamerican settlements. The temples provided spatial orientation, which was imparted to the surrounding town. The cities with their commercial and religious centers were always political entities, somewhat similar to the European
Ceremonial centers were the nuclei of Mesoamerican settlements. The temples provided spatial orientation, which was imparted to the surrounding town. The cities with their commercial and religious centers were always political entities, somewhat similar to the European
 Mesoamerican architecture is the collective name given to urban, ceremonial and public structures built by pre-Columbian civilizations in Mesoamerica. Although very different in styles, all kinds of mesoamerican architecture show some kind of interrelation, due to very significant cultural exchanges occurred during thousands of years. Among the most well-known structures in Mesoamerica, the flat-top
Mesoamerican architecture is the collective name given to urban, ceremonial and public structures built by pre-Columbian civilizations in Mesoamerica. Although very different in styles, all kinds of mesoamerican architecture show some kind of interrelation, due to very significant cultural exchanges occurred during thousands of years. Among the most well-known structures in Mesoamerica, the flat-top
 The Mesoamerican scripts deciphered to date are
The Mesoamerican scripts deciphered to date are
 The great breadth of the Mesoamerican pantheon of deities is due to the incorporation of ideological and religious elements from the first primitive religion of Fire, Earth, Water and Nature. Astral divinities (the sun, stars, constellations, and Venus) were adopted and represented in anthropomorphic,
The great breadth of the Mesoamerican pantheon of deities is due to the incorporation of ideological and religious elements from the first primitive religion of Fire, Earth, Water and Nature. Astral divinities (the sun, stars, constellations, and Venus) were adopted and represented in anthropomorphic,
 Autosacrifice, also called
Autosacrifice, also called

 The Mesoamerican ballgame was a sport with ritual associations played for over 3000 years by nearly all pre-Columbian peoples of Mesoamerica. The sport had different versions in different places during the millennia, and a modern version of the game,
The Mesoamerican ballgame was a sport with ritual associations played for over 3000 years by nearly all pre-Columbian peoples of Mesoamerica. The sport had different versions in different places during the millennia, and a modern version of the game,
 It has been argued that among Mesoamerican societies the concepts of
It has been argued that among Mesoamerican societies the concepts of
 Mesoamerican
Mesoamerican
Maya Culture
Mesoweb.com: a comprehensive site for Mesoamerican civilizations
Museum of the Templo Mayor
(Mexico)
National Museum of Anthropology and History
(Mexico)
concerning war in Mesoamerica
WAYEB: European Association of Mayanists
Open access international scientific journal devoted to the archaeological study of the American and Iberian peoples. It contains research articles on Mesoamerica. *
Vistas: Visual Culture in Spanish America, 1520–1820
' * {{Authority control Classic period in the Americas History of indigenous peoples of North America History of Belize History of El Salvador History of Guatemala History of Honduras History of Mexico History of Nicaragua Indigenous peoples of Central America Indigenous peoples in Mexico Pre-Columbian cultural areas Historical regions Regions of North America
historical region
Historical regions (or historical areas) are geographical regions which at some point in time had a cultural, ethnic, linguistic or political basis, regardless of latterday borders. They are used as delimitations for studying and analysing soci ...
and cultural area
In anthropology and geography, a cultural region, cultural sphere, cultural area or culture area refers to a geography with one relatively homogeneous human activity or complex of activities (culture). Such activities are often associated ...
in southern North America and most of Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
. It extends from approximately central Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
through Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wa ...
, Guatemala, El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by ...
, Honduras, Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean Sea, Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to ...
, and northern Costa Rica. Within this region pre-Columbian societies flourished for more than 3,000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas
Spain began colonization of the Americas, colonizing the Americas under the Crown of Castile and was spearheaded by the Spanish . The Americas were invaded and incorporated into the Spanish Empire, with the exception of Colonial Brazil, Braz ...
. Mesoamerica was the site of two of the most profound historical transformations in world history: primary urban generation, and the formation of New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
cultures out of the long encounters among indigenous, European, African and Asian cultures.
In the 16th century, Eurasian diseases such as smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by variola virus (often called smallpox virus) which belongs to the genus Orthopoxvirus. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) ce ...
and measles, which were endemic among the colonists but new to North America, caused the deaths of upwards of 90% of the indigenous people, resulting in great losses to their societies and cultures. Mesoamerica is one of the five areas in the world where ancient civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
C ...
arose independently (see cradle of civilization
A cradle of civilization is a location and a culture where civilization was created by mankind independent of other civilizations in other locations. The formation of urban settlements (cities) is the primary characteristic of a society that c ...
), and the second in the Americas. Norte Chico (Caral-Supe) in present-day Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal
, national_motto = "Fi ...
, arose as an independent civilization in the northern coastal region.
As a cultural area, Mesoamerica is defined by a mosaic of cultural traits developed and shared by its indigenous cultures. Beginning as early as 7000 BCE, the domestication of cacao, maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. ...
, beans
A bean is the seed of several plants in the family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food. They can be cooked in many different ways, including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes t ...
, tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word , ...
, avocado
The avocado (''Persea americana'') is a medium-sized, evergreen tree in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It is native to Americas, the Americas and was first domesticated by Mesoamerica, Mesoamerican tribes more than 5,000 years ago. Pre-Columb ...
, vanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus ''Vanilla (genus), Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the Mexican species, flat-leaved vanilla (''Vanilla planifolia, V. planifolia'').
Pollination is required to make the p ...
, squash and chili
Chili or chilli may refer to:
Food
* Chili pepper, the spicy fruit of plants in the genus ''Capsicum''; sometimes spelled "chilli" in the UK and "chile" in the southwestern US
* Chili powder, the dried, pulverized fruit of one or more varieties ...
, as well as the turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
and dog, resulted in a transition from paleo-Indian hunter-gatherer tribal groupings to the organization of sedentary agricultural villages. In the subsequent Formative period, agriculture and cultural traits such as a complex mythological and religious tradition, a vigesimal
vigesimal () or base-20 (base-score) numeral system is based on twenty (in the same way in which the decimal numeral system is based on ten). '' Vigesimal'' is derived from the Latin adjective '' vicesimus'', meaning 'twentieth'.
Places
In ...
numeric system, a complex calendric system, a tradition of ball playing, and a distinct architectural style
An architectural style is a set of characteristics and features that make a building or other structure notable or historically identifiable. It is a sub-class of style in the visual arts generally, and most styles in architecture relate closely ...
, were diffused through the area. Also in this period, villages began to become socially stratified and develop into chiefdom
A chiefdom is a form of hierarchical political organization in non-industrial societies usually based on kinship, and in which formal leadership is monopolized by the legitimate senior members of select families or 'houses'. These elites form a ...
s. Large ceremonial centers were built, interconnected by a network of trade routes for the exchange of luxury goods, such as obsidian, jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole gro ...
, cacao, cinnabar
Cinnabar (), or cinnabarite (), from the grc, κιννάβαρι (), is the bright scarlet to brick-red form of mercury(II) sulfide (HgS). It is the most common source ore for refining elemental mercury and is the historic source for the bri ...
, ''Spondylus
''Spondylus'' is a genus of bivalve molluscs, the only genus in the family Spondylidae.MolluscaBase (2019). MolluscaBase. Spondylus Linnaeus, 1758. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=t ...
'' shells, hematite
Hematite (), also spelled as haematite, is a common iron oxide compound with the formula, Fe2O3 and is widely found in rocks and soils. Hematite crystals belong to the rhombohedral lattice system which is designated the alpha polymorph of ...
, and ceramics. While Mesoamerican civilization knew of the wheel
A wheel is a circular component that is intended to rotate on an axle bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction with axles, allow heavy objects to be ...
and basic metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sci ...
, neither of these became technologically relevant.
Among the earliest complex civilizations was the Olmec
The Olmecs () were the earliest known major Mesoamerican civilization. Following a progressive development in Soconusco, they occupied the tropical lowlands of the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. It has been speculated that ...
culture, which inhabited the Gulf Coast of Mexico
The Gulf Coast of Mexico or East Coast of Mexico stretches along the Gulf of Mexico from the border between Mexico and the United States at Matamoros, Tamaulipas all the way to the tip of the Yucatán Peninsula at Cancún. It includes the coastal ...
and extended inland and southwards across the Isthmus of Tehuantepec
The Isthmus of Tehuantepec () is an isthmus in Mexico. It represents the shortest distance between the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. Before the opening of the Panama Canal, it was a major overland transport route known simply as t ...
. Frequent contact and cultural interchange between the early Olmec and other cultures in Chiapas, Oaxaca and Guatemala laid the basis for the Mesoamerican cultural area. All this was facilitated by considerable regional communications in ancient Mesoamerica, especially along the Pacific coast.
During this formative period distinct religious and symbolic traditions spread, as well as the development of artistic and architectural complexes. In the subsequent Preclassic period, complex urban polities began to develop among the Maya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a popu ...
, with the rise of centers such as Aguada fénix and Calakmul
Calakmul (; also Kalakmul and other less frequent variants) is a Maya archaeological site in the Mexican state of Campeche, deep in the jungles of the greater Petén Basin region. It is from the Guatemalan border. Calakmul was one of the larg ...
in Mexico; El Mirador
El Mirador (which translates as "the lookout", "the viewpoint", or "the belvedere") is a large pre-Columbian Middle and Late Preclassic (1000 BC - 250 AD) Mayan settlement, located in the north of the modern department of El Petén, Guatem ...
, and Tikal
Tikal () (''Tik’al'' in modern Mayan orthography) is the ruin of an ancient city, which was likely to have been called Yax Mutal, found in a rainforest in Guatemala. It is one of the largest archeological sites and urban centers of the pre-Co ...
in Guatemala, and the Zapotec at Monte Albán
Monte Albán is a large pre-Columbian archaeological site in the Santa Cruz Xoxocotlán Municipality in the southern Mexican state of Oaxaca (17.043° N, 96.767°W). The site is located on a low mountainous range rising above the plain in the c ...
. During this period, the first true Mesoamerican writing systems
Mesoamerica, along with Mesopotamia and China, is one of three known places in the world where writing is thought to have developed independently. Mesoamerican scripts deciphered to date are a combination of logographic and syllabic systems. ...
were developed in the Epi-Olmec and the Zapotec cultures. The Mesoamerican writing tradition reached its height in the Classic Maya logosyllabic script.
Mesoamerica is one of only six regions of the world where writing is known to have independently developed (the others being ancient Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
, Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal
, national_motto = "Fi ...
, India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
, Sumer, and China). In Central Mexico, the city of Teotihuacan
Teotihuacan (Spanish: ''Teotihuacán'') (; ) is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, northeast of modern-day Mexico City. Teotihuacan is known today as the ...
ascended at the height of the Classic period; it formed a military and commercial empire whose political influence stretched south into the Maya area and northward. Upon the collapse of Teotihuacán around 600 AD, competition between several important political centers in central Mexico, such as Xochicalco
Xochicalco () is a pre-Columbian archaeological site in Miacatlán Municipality in the western part of the Mexican state of Morelos. The name ''Xochicalco'' may be translated from Nahuatl as "in the house of Flowers". The site is located 38 ...
and Cholula, ensued. At this time during the Epi-Classic period, the Nahua people
The Nahuas () are a group of the indigenous people of Mexico, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, and Nicaragua. They comprise the largest indigenous group in Mexico and second largest in El Salvador. The Mexica (Aztecs) were of Nahua ethnicity, ...
s began moving south into Mesoamerica from the North, and became politically and culturally dominant in central Mexico, as they displaced speakers of Oto-Manguean languages
The Oto-Manguean or Otomanguean languages are a large family comprising several subfamilies of indigenous languages of the Americas. All of the Oto-Manguean languages that are now spoken are indigenous to Mexico, but the Manguean branch of the ...
.
During the early post-Classic period, Central Mexico was dominated by the Toltec
The Toltec culture () was a pre-Columbian Mesoamerican culture that ruled a state centered in Tula, Hidalgo, Mexico, during the Epiclassic and the early Post-Classic period of Mesoamerican chronology, reaching prominence from 950 to 1150 CE. Th ...
culture, and Oaxaca by the Mixtec
The Mixtecs (), or Mixtecos, are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples of Mexico inhabiting the region known as La Mixteca of Oaxaca and Puebla as well as La Montaña Region and Costa Chica Regions of the state of Guerrero. The Mixtec Cultur ...
. The lowland Maya area had important centers at Chichén Itzá and Mayapán
Mayapan (Màayapáan in Modern Maya; in Spanish Mayapán) is a Pre-Columbian Maya site a couple of kilometers south of the town of Telchaquillo in Municipality of Tecoh, approximately 40 km south-east of Mérida and 100 km west of ...
. Towards the end of the post-Classic period, the Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
s of Central Mexico built a tributary
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainag ...
empire covering most of central Mesoamerica.
The distinct Mesoamerican cultural tradition ended with the Spanish conquest
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its predec ...
in the 16th century. Over the next centuries, Mesoamerican indigenous cultures were gradually subjected to Spanish colonial rule. Aspects of the Mesoamerican cultural heritage still survive among the indigenous peoples who inhabit Mesoamerica. Many continue to speak their ancestral languages, and maintain many practices harking back to their Mesoamerican roots.
Etymology and definition
The term ''Mesoamerica'' literally means "middle America" in Greek. Middle America often refers to a larger area in the Americas, but it has also previously been used more narrowly to refer to Mesoamerica. An example is the title of the 16 volumes of ''The Handbook of Middle American Indians''. "Mesoamerica" is broadly defined as the area that is home to the Mesoamerican civilization, which comprises a group of peoples with close cultural and historical ties. The exact geographic extent of Mesoamerica has varied through time, as the civilization extended North and South from its heartland in southern Mexico. The term was first used by the
The term was first used by the German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
ethnologist
Ethnology (from the grc-gre, ἔθνος, meaning 'nation') is an academic field that compares and analyzes the characteristics of different peoples and the relationships between them (compare cultural, social, or sociocultural anthropology) ...
Paul Kirchhoff, who noted that similarities existed among the various pre-Columbian cultures
This list of pre-Columbian cultures includes those civilizations and cultures of the Americas which flourished prior to the European colonization of the Americas.
Cultural characteristics
Many pre-Columbian civilizations established permanent o ...
within the region that included southern Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
, Guatemala, Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wa ...
, El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by ...
, western Honduras, and the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
lowlands of Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest Sovereign state, country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean Sea, Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to ...
and northwestern Costa Rica. In the tradition of cultural history
Cultural history combines the approaches of anthropology and history to examine popular cultural traditions and cultural interpretations of historical experience. It examines the records and narrative descriptions of past matter, encompassing the ...
, the prevalent archaeological theory
Archaeological theory refers to the various intellectual frameworks through which archaeologists interpret archaeological data. Archaeological theory functions as the application of philosophy of science to archaeology, and is occasionally referred ...
of the early to middle 20th century, Kirchhoff defined this zone as a cultural area based on a suite of interrelated cultural similarities brought about by millennia of inter- and intra-regional interaction (i.e., diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical p ...
). Mesoamerica is recognized as a near-prototypical cultural area. This term is now fully integrated in the standard terminology of pre-Columbian anthropological
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of behavi ...
studies. Conversely, the sister terms Aridoamerica
Aridoamerica denotes an ecological region spanning Northern Mexico and the Southwestern United States, defined by the presence of the culturally significant staple foodstuff '' Phaseolus acutifolius'', a drought-resistant bean.Pratt and Nabha ...
and Oasisamerica
Oasisamerica is a term that was coined by Paul Kirchhoff (who also coined "Mesoamerica") and published in a 1954 article, and is used by some scholars, primarily Mexican anthropologists, for the broad cultural area defining pre-Columbian s ...
, which refer to northern Mexico and the western United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, respectively, have not entered into widespread usage.
Some of the significant cultural traits defining the Mesoamerican cultural tradition are:
* ''Horticulture and plant use'': sedentism
In cultural anthropology, sedentism (sometimes called sedentariness; compare sedentarism) is the practice of living in one place for a long time. , the large majority of people belong to sedentary cultures. In evolutionary anthropology and ar ...
based on maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. ...
agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled peop ...
; floating gardens; use of bark paper and agave
''Agave'' (; ; ) is a genus of monocots native to the hot and arid regions of the Americas and the Caribbean, although some ''Agave'' species are also native to tropical areas of North America, such as Mexico. The genus is primarily known ...
(see also maguey Maguey may refer to various American plants:
* Genus ''Agave'', especially
** Species ''Agave americana'', the century plant
** Species ''Agave salmiana''
* Genus '' Furcraea'', a source of natural fiber
* Maguey flowers, an edible flower
Other us ...
) for ritual purposes, as a medium for writing, and the use of agave for cooking and clothing; cultivation of cacao; grinding of corn softened with ashes or lime; harpoon-shaped digging stick
A digging stick, sometimes called a yam stick, is a wooden implement used primarily by subsistence-based cultures to dig out underground food such as roots and tubers, tilling the soil, or burrowing animals and anthills. It is a term used in a ...
* ''Clothing and personal articles'': lip plugs
The lip plate, also known as a lip plug, lip disc, or mouth plate is a form of body modification. Increasingly large discs (usually circular, and made from clay or wood) are inserted into a pierced hole in either the upper or lower lip, or both ...
, mirrors of polished stone, turbans, sandals with heels, textiles adorned with rabbit hair
Rabbit hair (also called rabbit fur, cony, coney, comb or lapin) is the fur of the common rabbit. It is most commonly used in the making of fur hats and coats, and is considered quite valuable today, although it was once a lower-priced commodi ...
* ''Architecture'': construction of stepped pyramids; stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and a ...
floors; ball courts with stone rings (see the use of natural rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, a ...
and the practice of the ritual Mesoamerican ballgame
The Mesoamerican ballgame ( nah, ōllamalīztli, , myn, pitz) was a sport with ritual associations played since at least 1650 BC by the pre-Columbian people of Ancient Mesoamerica. The sport had different versions in different places during ...
)
* ''Record keeping'': use of two different calendars
A calendar is a system of organizing days. This is done by giving names to periods of time, typically days, weeks, months and years. A date is the designation of a single and specific day within such a system. A calendar is also a physi ...
(a 260-day ritual calendar and a 365-day calendar based on the solar year
A tropical year or solar year (or tropical period) is the time that the Sun takes to return to the same position in the sky of a celestial body of the Solar System such as the Earth, completing a full cycle of seasons; for example, the time ...
); use of locally developed pictographic
A pictogram, also called a pictogramme, pictograph, or simply picto, and in computer usage an icon, is a graphic symbol that conveys its meaning through its pictorial resemblance to a physical object. Pictographs are often used in writing and gr ...
and hieroglyph
A hieroglyph (Greek for "sacred carvings") was a character of the ancient Egyptian writing system. Logographic scripts that are pictographic in form in a way reminiscent of ancient Egyptian are also sometimes called "hieroglyphs". In Neoplatonis ...
ic (logo-syllabic) writing systems
A writing system is a method of visually representing verbal communication, based on a script and a set of rules regulating its use. While both writing and speech are useful in conveying messages, writing differs in also being a reliable form ...
; numbers (see also vigesimal
vigesimal () or base-20 (base-score) numeral system is based on twenty (in the same way in which the decimal numeral system is based on ten). '' Vigesimal'' is derived from the Latin adjective '' vicesimus'', meaning 'twentieth'.
Places
In ...
(base 20) number system); "century" of fifty-two years; eighteen-month calendar; screen-fold books
* ''Commerce'': specialized markets, "department store" markets subdivided according to specialty
* ''Weapons and warfare'': wooden swords with stone chips set into the edges (see macuahuitl
A macuahuitl () is a weapon, a wooden club with several embedded obsidian blades. The name is derived from the Nahuatl language and means "hand-wood". Its sides are embedded with prismatic blades traditionally made from obsidian. Obsidian ...
), military orders (eagle knights and jaguar knights), clay pellets for blowguns, cotton-pad armor, traveling merchants who act as spies, wars for the purpose of securing sacrificial victims
* ''Ritual and myth'': practice of various forms of ritual sacrifice, including human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease gods, a human ruler, an authoritative/priestly figure or spirits of dead ancestors or as a retainer sacrifice, wherei ...
and quail sacrifice; paper and rubber as sacrificial offerings; pantheon of gods or spirits; acrobatic flier dance (see the Danza de los Voladores and the Totonac flier dance; 13 as a ritual number; ritual period of 20 x 13 = 260 days; mythic concept of one or more afterworlds and the difficult journey in reaching them; good and bad omen days; a religious complex based on a combination of shamanism
Shamanism is a religious practice that involves a practitioner (shaman) interacting with what they believe to be a Spirit world (Spiritualism), spirit world through Altered state of consciousness, altered states of consciousness, such as tranc ...
and natural deities, and a shared system of symbols
* ''Language'': a linguistic area
A sprachbund (, lit. "language federation"), also known as a linguistic area, area of linguistic convergence, or diffusion area, is a group of languages that share areal features resulting from geographical proximity and language contact. The lan ...
defined by a number of grammatical traits that have spread through the area by diffusion
Geography
Located on the Middle Americanisthmus
An isthmus (; ; ) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea counterpart of an isthm ...
joining North and South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the souther ...
between ''ca.'' 10° and 22° northern latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north po ...
, Mesoamerica possesses a complex combination of ecological systems, topographic zones, and environmental contexts. These different niches are classified into two broad categories: the lowlands (those areas between sea level
Mean sea level (MSL, often shortened to sea level) is an average surface level of one or more among Earth's coastal bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datuma standardise ...
and 1000 meters) and the ''altiplanos'', or highlands (situated between 1,000 and 2,000 meters above sea level). In the low-lying regions, sub-tropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north an ...
and tropical climate
Tropical climate is the first of the five major climate groups in the Köppen climate classification identified with the letter A. Tropical climates are defined by a monthly average temperature of 18 °C (64.4 °F) or higher in the cool ...
s are most common, as is true for most of the coastline along the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
and Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
and the Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea ( es, Mar Caribe; french: Mer des Caraïbes; ht, Lanmè Karayib; jam, Kiaribiyan Sii; nl, Caraïbische Zee; pap, Laman Karibe) is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico ...
. The highlands show much more climatic diversity, ranging from dry tropical to cold mountainous climates; the dominant climate is temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout t ...
with warm temperatures and moderate rainfall. The rainfall varies from the dry Oaxaca
)
, population_note =
, population_rank = 10th
, timezone1 = CST
, utc_offset1 = −6
, timezone1_DST = CDT
, utc_offset1_DST = −5
, postal_code_type = Postal ...
and north Yucatán
Yucatán (, also , , ; yua, Yúukatan ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán,; yua, link=no, Xóot' Noj Lu'umil Yúukatan. is one of the 31 states which comprise the federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate mun ...
to the humid southern Pacific and Caribbean lowlands.
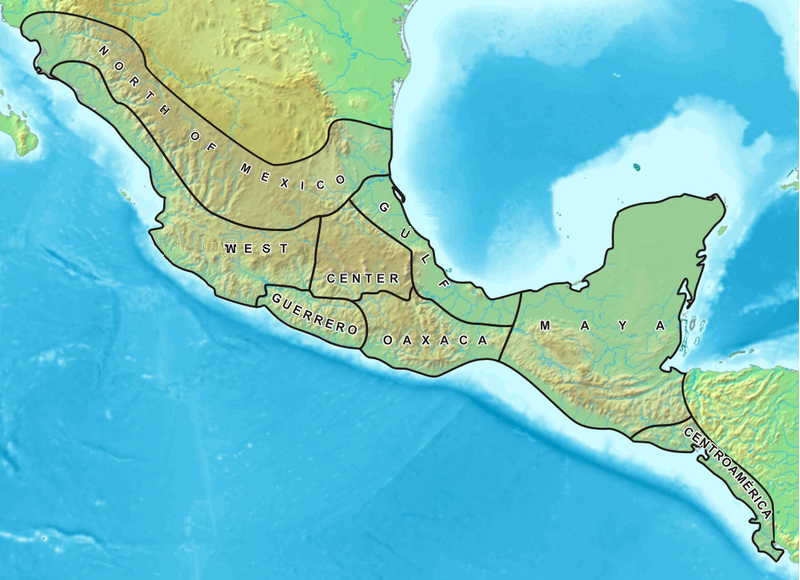
Cultural sub-areas
Several distinct sub-regions within Mesoamerica are defined by a convergence of geographic and cultural attributes. These sub-regions are more conceptual than culturally meaningful, and the demarcation of their limits is not rigid. The Maya area, for example, can be divided into two general groups: the lowlands and highlands. The lowlands are further divided into the southern and northern Maya lowlands. The southern Maya lowlands are generally regarded as encompassing northern Guatemala, southernCampeche
Campeche (; yua, Kaampech ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Campeche ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Campeche), is one of the 31 states which make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Located in southeast Mexico, it is bordered by ...
and Quintana Roo
Quintana Roo ( , ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Quintana Roo ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Quintana Roo), is one of the 31 states which, with Mexico City, constitute the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into 11 mu ...
in Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
, and Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wa ...
. The northern lowlands cover the remainder of the northern portion of the Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula (, also , ; es, Península de Yucatán ) is a large peninsula in southeastern Mexico and adjacent portions of Belize and Guatemala. The peninsula extends towards the northeast, separating the Gulf of Mexico to the north ...
. Other areas include Central Mexico, West Mexico, the Gulf Coast Lowlands, Oaxaca
)
, population_note =
, population_rank = 10th
, timezone1 = CST
, utc_offset1 = −6
, timezone1_DST = CDT
, utc_offset1_DST = −5
, postal_code_type = Postal ...
, the Southern Pacific Lowlands, and Southeast Mesoamerica (including northern Honduras).
Topography
There is extensive topographic variation in Mesoamerica, ranging from the high peaks circumscribing theValley of Mexico
The Valley of Mexico ( es, Valle de México) is a highlands plateau in central Mexico roughly coterminous with present-day Mexico City and the eastern half of the State of Mexico. Surrounded by mountains and volcanoes, the Valley of Mexico wa ...
and within the central Sierra Madre mountains to the low flatlands of the northern Yucatán Peninsula. The tallest mountain in Mesoamerica is Pico de Orizaba
Pico de Orizaba, also known as Citlaltépetl (from Nahuatl = star, and = mountain), is an inactive stratovolcano, the highest mountain in Mexico and the third highest in North America, after Denali of Alaska in the United States and Mount ...
, a dormant volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plat ...
located on the border of Puebla
Puebla ( en, colony, settlement), officially Free and Sovereign State of Puebla ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its cap ...
and Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
. Its peak elevation is 5,636 m (18,490 ft).
The Sierra Madre mountains, which consist of several smaller ranges, run from northern Mesoamerica south through Costa Rica. The chain is historically volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates ...
. In central and southern Mexico, a portion of the Sierra Madre chain is known as the Eje Volcánico Transversal, or the Trans-Mexican volcanic belt. There are 83 inactive and active volcanoes within the Sierra Madre range, including 11 in Mexico, 37 in Guatemala, 23 in El Salvador, 25 in Nicaragua, and 3 in northwestern Costa Rica. According to the Michigan Technological University, 16 of these are still active. The tallest active volcano is Popocatépetl
Popocatépetl (; Nahuatl: ) is an active stratovolcano located in the states of Puebla, Morelos, and Mexico in central Mexico. It lies in the eastern half of the Trans-Mexican volcanic belt. At it is the second highest peak in Mexico, after ...
at 5,452 m (17,887 ft). This volcano, which retains its Nahuatl
Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have small ...
name, is located 70 km (43 mi) southeast of Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley of ...
. Other volcanoes of note include Tacana on the Mexico–Guatemala border, Tajumulco and Santamaría in Guatemala, Izalco in El Salvador, Arenal in Costa Rica, and Concepción and Maderas on Ometepe
Ometepe is an island formed by two volcanoes rising out of Lake Nicaragua in the Republic of Nicaragua. Its name derives from the Nahuatl words ''ome'' (two) and ''tepetl'' (mountain), meaning "two mountains". It is the largest island in Lake N ...
, which is an island formed by both volcanoes rising out of Lake Cocibolca in Nicaragua.
One important topographic feature is the Isthmus of Tehuantepec
The Isthmus of Tehuantepec () is an isthmus in Mexico. It represents the shortest distance between the Gulf of Mexico and the Pacific Ocean. Before the opening of the Panama Canal, it was a major overland transport route known simply as t ...
, a low plateau that breaks up the Sierra Madre chain between the Sierra Madre del Sur
The Sierra Madre del Sur is a mountain range in southern Mexico, extending from southern Michoacán east through Guerrero, to the Isthmus of Tehuantepec in eastern Oaxaca.
Geography
The Sierra Madre del Sur joins with the Eje Volcánico Trans ...
to the north and the Sierra Madre de Chiapas
The Sierra Madre de Chiapas is a major mountain range in Central America. It crosses El Salvador, Guatemala, Mexico and Honduras. The Sierra Madre de Chiapas is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges that consists of an alm ...
to the south. At its highest point, the Isthmus
An isthmus (; ; ) is a narrow piece of land connecting two larger areas across an expanse of water by which they are otherwise separated. A tombolo is an isthmus that consists of a spit or bar, and a strait is the sea counterpart of an isthm ...
is 224 m (735 ft) above mean sea level. This area also represents the shortest distance between the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
and the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
in Mexico. The distance between the two coasts is roughly 200 km (120 mi). The northern side of the Isthmus is swampy and covered in dense jungle—but the Isthmus of Tehuantepec, as the lowest and most level point within the Sierra Madre mountain chain, was nonetheless a main transportation, communication, and economic route within Mesoamerica.
Bodies of water
 Outside of the northern Maya lowlands,
Outside of the northern Maya lowlands, river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the ...
s are common throughout Mesoamerica. Some of the more important ones served as loci of human occupation in the area. The longest river in Mesoamerica is the Usumacinta, which forms in Guatemala at the convergence of the Salinas or Chixoy and La Pasion River
Pasion (also Pasio; grc, Πασίων; before 430 – 370 BC) was a slave in Ancient Athens in the early 4th century BC, who rose to become a successful banker and Athenian citizen.
Life
Pasion was born some time before 430 BC.
It is unkn ...
and runs north for 970 km (600 mi)—480 km (300 mi) of which are navigable—eventually draining into the Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United S ...
. Other rivers of note include the Rio Grande de Santiago, the Grijalva River
Grijalva River, formerly known as ''Tabasco River'', ( es, Río Grijalva, known locally also as Río Grande de Chiapas, Río Grande and Mezcalapa River) is a long river in southeastern Mexico."Grijalva." '' Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dict ...
, the Motagua River
The Motagua River () is a river in Guatemala. It rises in the western highlands of Guatemala where it is also called Río Grande, and runs in an easterly direction to the Gulf of Honduras. The final few kilometres of the river form part of the ...
, the Ulúa River
The Ulúa River ( es, Río Ulúa, ) is a river in western Honduras. It rises in the central mountainous area of the country close to La Paz and runs approximately due northwards to the east end of the Gulf of Honduras at . En route, it is join ...
, and the Hondo River. The northern Maya lowlands, especially the northern portion of the Yucatán peninsula, are notable for their nearly complete lack of rivers (largely due to the absolute lack of topographic variation). Additionally, no lakes exist in the northern peninsula. The main source of water in this area is aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing, permeable rock, rock fractures, or unconsolidated materials ( gravel, sand, or silt). Groundwater from aquifers can be extracted using a water well. Aquifers vary greatly in their characteri ...
s that are accessed through natural surface openings called cenote
A cenote ( or ; ) is a natural pit, or sinkhole, resulting from the collapse of limestone bedrock that exposes groundwater. The regional term is specifically associated with the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, where cenotes were commonly used for ...
s.
With an area of 8,264 km2 (3,191 sq mi), Lake Nicaragua
Lake Nicaragua or Cocibolca or Granada ( es, Lago de Nicaragua, , or ) is a freshwater lake in Nicaragua. Of tectonic origin and with an area of , it is the largest lake in Central America, the 19th largest lake in the world (by area) and the t ...
is the largest lake in Mesoamerica. Lake Chapala
Lake Chapala ( es, Lago de Chapala, ) is Mexico's largest freshwater lake. It lies in the municipalities of Ocotlán, Chapala, Jocotepec, Poncitlán, and Jamay, in Jalisco, and in Venustiano Carranza and Cojumatlán de Régules, in Michoac ...
is Mexico's largest freshwater lake, but Lake Texcoco
Lake Texcoco ( es, Lago de Texcoco) was a natural lake within the "Anahuac" or Valley of Mexico. Lake Texcoco is best known as where the Aztecs built the city of Tenochtitlan, which was located on an island within the lake. After the Spanish con ...
is perhaps most well known as the location upon which Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was ...
, capital of the Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
Empire, was founded. Lake Petén Itzá
Lake Petén Itzá (''Lago Petén Itzá'', ) is a lake in the northern Petén Department in Guatemala. It is the third largest lake in Guatemala, after Lake Izabal and Lake Atitlán. It is located around . It has an area of , and is some long an ...
, in northern Guatemala, is notable as where the last independent Maya city, Tayasal (or Noh Petén), held out against the Spanish until 1697. Other large lakes include Lake Atitlán
Lake Atitlán ( es, links=no, Lago de Atitlán, ) is a lake in the Guatemalan Highlands of the Sierra Madre mountain range. The lake is located in the Sololá Department of southwestern Guatemala. It is known as the deepest lake in Central Ame ...
, Lake Izabal
Lake Izabal (), also known as the Golfo Dulce, is the largest lake in Guatemala with a surface area of 589.6 km² (145,693 acres or 227.6 sq mi) and a maximum depth is 18 m (59 ft). The Polochic River is the largest river that dra ...
, Lake Güija, Lemoa, and Lake Managua
Lake Managua ( es, Lago de Managua, ), also known as Lake Xolotlán (), is a lake in Nicaragua. At 1,042 km², it is approximately long and wide. Similarly to the name of Lake Nicaragua, its other name comes from the Nahuatl language, possi ...
.
Biodiversity
Almost allecosystem
An ecosystem (or ecological system) consists of all the organisms and the physical environment with which they interact. These biotic and abiotic components are linked together through nutrient cycles and energy flows. Energy enters the syst ...
s are present in Mesoamerica; the more well known are the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System
The Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System (MBRS), also popularly known as the Great Mayan Reef or Great Maya Reef, is a marine region that stretches over along the coasts of four countries – Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, and Honduras – from Isla ...
, the second largest in the world, and La Mosquitia (consisting of the Rio Platano Biosphere Reserve, Tawahka Asangni, Patuca National Park
Patuca National Park is a national park in Honduras. It was established on 1 January 1999 and covers an area of 3755.84 square kilometres.
References
{{authority control
National parks of Honduras
Protected areas established in 1999
Cent ...
, and Bosawas Biosphere Reserve) a rainforest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainfo ...
second in size in the Americas only to the Amazonas. The highlands present mixed and coniferous forest. The biodiversity is among the richest in the world, though the number of species in the red list of the IUCN grows every year.
Chronology and culture
 The history of human occupation in Mesoamerica is divided into stages or periods. These are known, with slight variation depending on region, as the Paleo-Indian, the
The history of human occupation in Mesoamerica is divided into stages or periods. These are known, with slight variation depending on region, as the Paleo-Indian, the Archaic
Archaic is a period of time preceding a designated classical period, or something from an older period of time that is also not found or used currently:
*List of archaeological periods
**Archaic Sumerian language, spoken between 31st - 26th cent ...
, the Preclassic (or Formative), the Classic
A classic is an outstanding example of a particular style; something of lasting worth or with a timeless quality; of the first or highest quality, class, or rank – something that exemplifies its class. The word can be an adjective (a '' ...
, and the Postclassic. The last three periods, representing the core of Mesoamerican cultural fluorescence, are further divided into two or three sub-phases. Most of the time following the arrival of the Spanish in the 16th century is classified as the Colonial period.
The differentiation of early periods (i.e., up through the end of the Late Preclassic) generally reflects different configurations of socio-cultural organization that are characterized by increasing socio-political complexity, the adoption of new and different subsistence strategies, and changes in economic organization (including increased interregional interaction). The Classic
A classic is an outstanding example of a particular style; something of lasting worth or with a timeless quality; of the first or highest quality, class, or rank – something that exemplifies its class. The word can be an adjective (a '' ...
period through the Postclassic are differentiated by the cyclical crystallization and fragmentation of the various political entities throughout Mesoamerica.
Paleo-Indian
The Mesoamerican Paleo-Indian period precedes the advent of agriculture and is characterized by a nomadic hunting and gathering subsistence strategy. Big-game hunting, similar to that seen in contemporaneous North America, was a large component of the subsistence strategy of the Mesoamerican Paleo-Indian. These sites had obsidian blades and Clovis-style flutedprojectile point
In North American archaeological terminology, a projectile point is an object that was hafted to a weapon that was capable of being thrown or projected, such as a javelin, dart, or arrow. They are thus different from weapons presumed to have ...
s.
Archaic
The Archaic period (8000–2000 BCE) is characterized by the rise of incipient agriculture in Mesoamerica. The initial phases of the Archaic involved the cultivation of wild plants, transitioning into informal domestication and culminating withsedentism
In cultural anthropology, sedentism (sometimes called sedentariness; compare sedentarism) is the practice of living in one place for a long time. , the large majority of people belong to sedentary cultures. In evolutionary anthropology and ar ...
and agricultural production by the close of the period. Transformations of natural environments have been a common feature at least since the mid Holocene. Archaic sites include ''Sipacate
Sipacate is a resort town and municipality on the Pacific coast of Guatemala, in Escuintla Department about west of Puerto San José. It is promoted as a venue for surfing. Being roughly in the center of the Guatemalan coastline, it is used as a ...
'' in Escuintla, Guatemala, where maize pollen samples date to c. 3500 BCE.
Preclassic/Formative
 The first complex civilization to develop in Mesoamerica was that of the
The first complex civilization to develop in Mesoamerica was that of the Olmec
The Olmecs () were the earliest known major Mesoamerican civilization. Following a progressive development in Soconusco, they occupied the tropical lowlands of the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. It has been speculated that ...
, who inhabited the gulf coast region of Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
throughout the Preclassic period. The main sites of the Olmec include San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán
San Lorenzo Tenochtitlán or San Lorenzo is the collective name for three related archaeological sites—San Lorenzo, Tenochtitlán and Potrero Nuevo—located in the southeast portion of the Mexican state of Veracruz. Along with La Venta and Tre ...
, La Venta
La Venta is a pre-Columbian archaeological site of the Olmec civilization located in the present-day Mexican state of Tabasco. Some of the artifacts have been moved to the museum "Parque - Museo de La Venta", which is in nearby Villahermos ...
, and Tres Zapotes
Tres Zapotes is a Mesoamerican archaeological site located in the south-central Gulf of Mexico, Gulf Lowlands of Mexico in the Papaloapan River plain. Tres Zapotes is sometimes referred to as the third major Olmec capital (after San Lorenzo Tenocht ...
. Specific dates vary, but these sites were occupied from roughly 1200 to 400 BCE. Remains of other early cultures interacting with the Olmec have been found at Takalik Abaj
Tak'alik Ab'aj (; ; ) is a pre-Columbian archaeological site in Guatemala. It was formerly known as Abaj Takalik; its ancient name may have been Kooja. It is one of several Mesoamerican sites with both Olmec and Maya features. The site flourishe ...
, Izapa
Izapa is a very large pre-Columbian archaeological site located in the Mexican state of Chiapas; it is best known for its occupation during the Late Formative period. The site is situated on the Izapa River, a tributary of the Suchiate River, ...
, and Teopantecuanitlan
Teopantecuanitlan is an archaeological site in the Mexican state of Guerrero that represents an unexpectedly early development of complex society for the region. The site dates to the Early to Middle Formative Periods, with the archaeologica ...
, and as far south as in Honduras. Research in the Pacific Lowlands of Chiapas and Guatemala suggest that Izapa
Izapa is a very large pre-Columbian archaeological site located in the Mexican state of Chiapas; it is best known for its occupation during the Late Formative period. The site is situated on the Izapa River, a tributary of the Suchiate River, ...
and the Monte Alto Culture
Monte Alto is an archaeological site on the Pacific Coast in what is now Guatemala.
History
Located 20 km southeast from Santa Lucía Cotzumalguapa in Escuintla, Monte Alto was occupied as early as 1800 BC, but has a fairly light presen ...
may have preceded the Olmec. Radiocarbon samples associated with various sculptures found at the Late Preclassic site of Izapa
Izapa is a very large pre-Columbian archaeological site located in the Mexican state of Chiapas; it is best known for its occupation during the Late Formative period. The site is situated on the Izapa River, a tributary of the Suchiate River, ...
suggest a date of between 1800 and 1500 BCE.
During the Middle and Late Preclassic period, the Maya civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, ar ...
developed in the southern Maya highlands and lowlands, and at a few sites in the northern Maya lowlands. The earliest Maya sites coalesced after 1000 BCE, and include Nakbe, El Mirador
El Mirador (which translates as "the lookout", "the viewpoint", or "the belvedere") is a large pre-Columbian Middle and Late Preclassic (1000 BC - 250 AD) Mayan settlement, located in the north of the modern department of El Petén, Guatem ...
, and Cerros. Middle to Late Preclassic Maya sites include Kaminaljuyú, Cival, Edzná, Cobá, Lamanai, Komchen, Dzibilchaltun, and San Bartolo, among others.
The Preclassic in the central Mexican highlands is represented by such sites as Tlapacoya, Tlatilco
Tlatilco was a large pre-Columbian village in the Valley of Mexico situated near the modern-day town of the same name in the Mexican Federal District. It was one of the first chiefdom centers to arise in the Valley, flourishing on the western sho ...
, and Cuicuilco
Cuicuilco is an important archaeological site located on the southern shore of Lake Texcoco in the southeastern Valley of Mexico, in what is today the borough of Tlalpan in Mexico City. Some historians believe this settlement goes back to 140 ...
. These sites were eventually superseded by Teotihuacán
Teotihuacan ( Spanish: ''Teotihuacán'') (; ) is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, northeast of modern-day Mexico City. Teotihuacan is known today as ...
, an important Classic-era site that eventually dominated economic and interaction spheres throughout Mesoamerica. The settlement of Teotihuacan is dated to the later portion of the Late Preclassic, or roughly 50 CE.
In the Valley of Oaxaca
The Central Valleys ( es, Valles Centrales) of Oaxaca, also simply known as the Oaxaca Valley, is a geographic region located within the modern-day state of Oaxaca in southern Mexico. In an administrative context, it has been defined as comprising ...
, San José Mogote
San José Mogote is a pre-Columbian archaeological site of the Zapotec, a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in the region of what is now the Mexican state of Oaxaca. A forerunner to the better-known Zapotec site of Monte Albán, San Jos� ...
represents one of the oldest permanent agricultural villages in the area, and one of the first to use pottery. During the Early and Middle Preclassic, the site developed some of the earliest examples of defensive palisades, ceremonial structures, the use of adobe
Adobe ( ; ) is a building material made from earth and organic materials. is Spanish for '' mudbrick''. In some English-speaking regions of Spanish heritage, such as the Southwestern United States, the term is used to refer to any kind of ...
, and hieroglyphic writing. Also of importance, the site was one of the first to demonstrate inherited status, signifying a radical shift in socio-cultural and political structure. San José Mogote was eventual overtaken by Monte Albán
Monte Albán is a large pre-Columbian archaeological site in the Santa Cruz Xoxocotlán Municipality in the southern Mexican state of Oaxaca (17.043° N, 96.767°W). The site is located on a low mountainous range rising above the plain in the c ...
, the subsequent capital of the Zapotec empire, during the Late Preclassic.
The Preclassic in western Mexico, in the states of Nayarit
Nayarit (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nayarit ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Nayarit), is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 20 municipalities and its ...
, Jalisco
Jalisco (, , ; Nahuatl: Xalixco), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Jalisco ; Nahuatl: Tlahtohcayotl Xalixco), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal ...
, Colima
Colima (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Colima ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Colima), is one of the 31 states that make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It shares its name with its capital and main city, Colima.
Colima i ...
, and Michoacán
Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo (; Purépecha: ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Michoacán de Ocampo), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of ...
also known as the Occidente, is poorly understood. This period is best represented by the thousands of figurines recovered by looters and ascribed to the "shaft tomb tradition
The Western Mexico shaft tomb tradition refers to a set of interlocked cultural traits found in the western Mexican states of Jalisco, Nayarit, and, to a lesser extent, Colima to its south, roughly dating to the period between 300 BCE and 400 C ...
".
Classic
Early Classic
 The Classic period is marked by the rise and dominance of several polities. The traditional distinction between the Early and Late Classic are marked by their changing fortune and their ability to maintain regional primacy. Of paramount importance are Teotihuacán in central Mexico and
The Classic period is marked by the rise and dominance of several polities. The traditional distinction between the Early and Late Classic are marked by their changing fortune and their ability to maintain regional primacy. Of paramount importance are Teotihuacán in central Mexico and Tikal
Tikal () (''Tik’al'' in modern Mayan orthography) is the ruin of an ancient city, which was likely to have been called Yax Mutal, found in a rainforest in Guatemala. It is one of the largest archeological sites and urban centers of the pre-Co ...
in Guatemala; the Early Classic's temporal limits generally correlate to the main periods of these sites. Monte Albán in Oaxaca is another Classic-period polity that expanded and flourished during this period, but the Zapotec capital exerted less interregional influence than the other two sites.
During the Early Classic, Teotihuacan participated in and perhaps dominated a far-reaching macro-regional interaction network. Architectural and artifact styles (talud-tablero, tripod slab-footed ceramic vessels) epitomized at Teotihuacan were mimicked and adopted at many distant settlements. Pachuca
Pachuca (; ote, Nju̱nthe), formally known as Pachuca de Soto, is the capital and largest city of the Mexican state of Hidalgo. It is located in the south-central part of the state. Pachuca de Soto is also the name of the municipality of whi ...
obsidian, whose trade and distribution is argued to have been economically controlled by Teotihuacan, is found throughout Mesoamerica.
Tikal came to dominate much of the southern Maya lowlands politically, economically, and militarily during the Early Classic. An exchange network centered at Tikal distributed a variety of goods and commodities throughout southeast Mesoamerica, such as obsidian imported from central Mexico (e.g., Pachuca) and highland Guatemala (e.g., El Chayal, which was predominantly used by the Maya during the Early Classic), and jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole gro ...
from the Motagua valley in Guatemala. Tikal was often in conflict with other polities in the Petén Basin
The Petén Basin is a geographical subregion of Mesoamerica, primarily located in northern Guatemala within the Department of El Petén, and into Campeche state in southeastern Mexico.
During the Late Preclassic and Classic periods of pre-Columb ...
, as well as with others outside of it, including Uaxactun
Uaxactun (pronounced ) is an ancient sacred place of the Maya civilization, located in the Petén Basin region of the Maya lowlands, in the present-day department of Petén, Guatemala. The site lies some north of the major center of Tikal. ...
, Caracol, Dos Pilas
Dos Pilas is a Pre-Columbian site of the Maya civilization located in what is now the department of Petén, Guatemala. It dates to the Late Classic Period, and was founded by an offshoot of the dynasty of the great city of Tikal in AD ...
, Naranjo
Naranjo is a Pre-Columbian Maya city in the Petén Basin region of Guatemala. It was occupied from about 500 BC to 950 AD, with its height in the Late Classic Period. The site is part of Yaxha-Nakum-Naranjo National Park. The city lies along the ...
, and Calakmul
Calakmul (; also Kalakmul and other less frequent variants) is a Maya archaeological site in the Mexican state of Campeche, deep in the jungles of the greater Petén Basin region. It is from the Guatemalan border. Calakmul was one of the larg ...
. Towards the end of the Early Classic, this conflict lead to Tikal's military defeat at the hands of Caracol in 562, and a period commonly known as the Tikal Hiatus.
Late Classic
 The Late Classic period (beginning c. 600 CE until 909 CE) is characterized as a period of interregional competition and factionalization among the numerous regional polities in the Maya area. This largely resulted from the decrease in Tikal's socio-political and economic power at the beginning of the period. It was therefore during this time that other sites rose to regional prominence and were able to exert greater interregional influence, including Caracol,
The Late Classic period (beginning c. 600 CE until 909 CE) is characterized as a period of interregional competition and factionalization among the numerous regional polities in the Maya area. This largely resulted from the decrease in Tikal's socio-political and economic power at the beginning of the period. It was therefore during this time that other sites rose to regional prominence and were able to exert greater interregional influence, including Caracol, Copán
Copán is an archaeological site of the Maya civilization in the Copán Department of western Honduras, not far from the border with Guatemala. This ancient Maya city mirrors the beauty of the physical landscape in which it flourished—a f ...
, Palenque
Palenque (; Yucatec Maya: ), also anciently known in the Itza Language as Lakamhaʼ ("Big Water or Big Waters"), was a Maya city state in southern Mexico that perished in the 8th century. The Palenque ruins date from ca. 226 BC to ca. 799 AD. Af ...
, and Calakmul (which was allied with Caracol and may have assisted in the defeat of Tikal), and Dos Pilas
Dos Pilas is a Pre-Columbian site of the Maya civilization located in what is now the department of Petén, Guatemala. It dates to the Late Classic Period, and was founded by an offshoot of the dynasty of the great city of Tikal in AD ...
Aguateca and Cancuén in the Petexbatún region of Guatemala. Around 710, Tikal arose again and started to build strong alliances and defeat its worst enemies. In the Maya area, the Late Classic ended with the so-called " Maya collapse", a transitional period coupling the general depopulation of the southern lowlands and development and florescence of centers in the northern lowlands.
Terminal Classic
Puuc
Puuc is the name of either a region in the Mexican state of Yucatán or a Maya architectural style prevalent in that region. The word ''puuc'' is derived from the Maya term for "hill". Since the Yucatán is relatively flat, this term was ext ...
settlements in the northern Maya lowlands, so named after the hills where they are mainly found. Puuc settlements are specifically associated with a unique architectural style (the "Puuc architectural style") that represents a technological departure from previous construction techniques. Major Puuc sites include Uxmal
Uxmal ( Yucatec Maya: ''Óoxmáal'' ) is an ancient Maya city of the classical period located in present-day Mexico. It is considered one of the most important archaeological sites of Maya culture, along with Palenque, Chichen Itza and Calakmul ...
, Sayil, Labna, Kabah, and Oxkintok. While generally concentrated within the area in and around the Puuc hills, the style has been documented as far away as at Chichen Itza
Chichen Itza , es, Chichén Itzá , often with the emphasis reversed in English to ; from yua, Chiʼchʼèen Ìitshaʼ () "at the mouth of the well of the Itza people" was a large pre-Columbian city built by the Maya people of the Termi ...
to the east and Edzna to the south.
Chichén Itzá was originally thought to have been a Postclassic site in the northern Maya lowlands. Research over the past few decades has established that it was first settled during the Early/Late Classic transition but rose to prominence during the Terminal Classic and Early Postclassic. During its apogee, this widely known site economically and politically dominated the northern lowlands. Its participation in the circum-peninsular exchange route, possible through its port site of Isla Cerritos, allowed Chichén Itzá to remain highly connected to areas such as central Mexico and Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
. The apparent "Mexicanization" of architecture at Chichén Itzá led past researchers to believe that Chichén Itzá existed under the control of a Toltec empire. Chronological data refutes this early interpretation, and it is now known that Chichén Itzá predated the Toltec; Mexican architectural styles are now used as an indicator of strong economic and ideological ties between the two regions.
Postclassic
The Postclassic (beginning 900–1000 CE, depending on area) is, like the Late Classic, characterized by the cyclical crystallization and fragmentation of various polities. The main Maya centers were located in the northern lowlands. Following Chichén Itzá, whose political structure collapsed during the Early Postclassic,Mayapán
Mayapan (Màayapáan in Modern Maya; in Spanish Mayapán) is a Pre-Columbian Maya site a couple of kilometers south of the town of Telchaquillo in Municipality of Tecoh, approximately 40 km south-east of Mérida and 100 km west of ...
rose to prominence during the Middle Postclassic and dominated the north for c. 200 years. After Mayapán's fragmentation, political structure in the northern lowlands revolved around large towns or city-states, such as Oxkutzcab and Ti’ho (Mérida, Yucatán
Mérida () is the capital of the Mexican state of Yucatán, and the largest city in southeastern Mexico. The city is also the seat of the eponymous Municipality. It is located in the northwest corner of the Yucatán Peninsula, about 35 km (22 m ...
), that competed with one another.
Toniná
Tonina (or Toniná in Spanish orthography) is a pre-Columbian archaeological site and ruined city of the Maya civilization located in what is now the Mexican state of Chiapas, some 13 km (8.1 mi) east of the town of Ocosingo.
The site ...
, in the Chiapas highlands, and Kaminaljuyú in the central Guatemala highlands, were important southern highland Maya centers. The latter site, Kaminaljuyú, is one of the longest occupied sites in Mesoamerica and was continuously inhabited from c. 800 BCE to around 1200 CE. Other important highland Maya groups include the K'iche' K'iche', K'ichee', or Quiché may refer to:
*K'iche' people of Guatemala, a subgroup of the Maya
*K'iche' language K'iche', K'ichee', or Quiché may refer to:
*K'iche' people K'iche', K'ichee', or Quiché may refer to:
* K'iche' people of Guatemala ...
of Utatlán, the Mam
Mam or MAM may refer to:
Places
* An Mám or Maum, a settlement in Ireland
* General Servando Canales International Airport in Matamoros, Tamaulipas, Mexico (IATA Code: MAM)
* Isle of Mam, a phantom island
* Mam Tor, a hill near Castleton in t ...
in Zaculeu, the Poqomam in Mixco Viejo
Mixco Viejo () ("Old Mixco"), occasionally spelt Mixcu Viejo, is an archaeological site in the north east of the Chimaltenango department of Guatemala, some to the north of Guatemala City and from the junction of the rivers Pixcaya and Mot ...
, and the Kaqchikel at Iximche
Iximcheʼ () (or Iximché using Spanish orthography) is a Pre-Columbian Mesoamerican archaeological site in the western highlands of Guatemala. Iximche was the capital of the Late Postclassic Kaqchikel Maya kingdom from 1470 until its aban ...
in the Guatemalan highlands. The Pipil resided in El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by ...
, while the Ch'orti' were in eastern Guatemala and northwestern Honduras.
In central Mexico, the early portion of the Postclassic correlates with the rise of the Toltec
The Toltec culture () was a pre-Columbian Mesoamerican culture that ruled a state centered in Tula, Hidalgo, Mexico, during the Epiclassic and the early Post-Classic period of Mesoamerican chronology, reaching prominence from 950 to 1150 CE. Th ...
and an empire based at their capital, Tula
Tula may refer to:
Geography
Antarctica
*Tula Mountains
* Tula Point
India
* Tulā, a solar month in the traditional Indian calendar
Iran
*Tula, Iran, a village in Hormozgan Province
Italy
*Tula, Sardinia, municipality (''comune'') in the pr ...
(also known as Tollan). Cholula, initially an important Early Classic center contemporaneous with Teotihuacan, maintained its political structure (it did not collapse) and continued to function as a regionally important center during the Postclassic. The latter portion of the Postclassic is generally associated with the rise of the Mexica and the Aztec Empire
The Aztec Empire or the Triple Alliance ( nci, Ēxcān Tlahtōlōyān, �jéːʃkaːn̥ t͡ɬaʔtoːˈlóːjaːn̥ was an alliance of three Nahua city-states: , , and . These three city-states ruled that area in and around the Valley of Mexic ...
. One of the more commonly known cultural groups in Mesoamerica, the Aztec politically dominated nearly all of central Mexico, the Gulf Coast, Mexico's southern Pacific Coast (Chiapas and into Guatemala), Oaxaca, and Guerrero
Guerrero is one of the 32 states that comprise the Administrative divisions of Mexico, 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in Municipalities of Guerrero, 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo and its largest city is Acap ...
.
The Tarascans (also known as the P'urhépecha) were located in Michoacán
Michoacán, formally Michoacán de Ocampo (; Purépecha: ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Michoacán de Ocampo ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Michoacán de Ocampo), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of ...
and Guerrero. With their capital at Tzintzuntzan, the Tarascan state was one of the few to actively and continuously resist Aztec domination during the Late Postclassic. Other important Postclassic cultures in Mesoamerica include the Totonac
The Totonac are an indigenous people of Mexico who reside in the states of Veracruz, Puebla, and Hidalgo. They are one of the possible builders of the pre-Columbian city of El Tajín, and further maintained quarters in Teotihuacán (a cit ...
along the eastern coast (in the modern-day states of Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
, Puebla
Puebla ( en, colony, settlement), officially Free and Sovereign State of Puebla ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Puebla), is one of the 32 states which comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 217 municipalities and its cap ...
, and Hidalgo). The Huastec resided north of the Totonac, mainly in the modern-day states of Tamaulipas
Tamaulipas (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Tamaulipas ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Tamaulipas), is a state in the northeast region of Mexico; one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal Entiti ...
and northern Veracruz. The Mixtec
The Mixtecs (), or Mixtecos, are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples of Mexico inhabiting the region known as La Mixteca of Oaxaca and Puebla as well as La Montaña Region and Costa Chica Regions of the state of Guerrero. The Mixtec Cultur ...
and Zapotec cultures, centered at Mitla
Mitla is the second-most important archeological site in the state of Oaxaca in Mexico, and the most important of the Zapotec culture. The site is located 44 km from the city of Oaxaca, in the upper end of the Tlacolula Valley, one of the ...
and Zaachila
Zaachila (the Zapotec name; Nahuatl: ''Teotzapotlan''; Mixtec: ''Ñuhu Tocuisi'') was a powerful Mesoamerican city in what is now Oaxaca, Mexico, from the city of Oaxaca. The city is named after Zaachila Yoo, the Zapotec ruler, in the late 14 ...
respectively, inhabited Oaxaca.
The Postclassic ends with the arrival of the Spanish and their subsequent conquest of the Aztec between 1519 and 1521. Many other cultural groups did not acquiesce until later. For example, Maya groups in the Petén area, including the Itza Itza may refer to:
* Itza people, an ethnic group of Guatemala
* Itzaʼ language, a Mayan language
* Itza Kingdom (disambiguation)
* Itza, Navarre, a town in Spain
See also
* Chichen Itza, a Mayan city
* Iza (disambiguation)
* Izza (disambiguat ...
at Tayasal and the Kowoj at Zacpeten, remained independent until 1697.
Some Mesoamerican cultures never achieved dominant status or left impressive archaeological remains but are nevertheless noteworthy. These include the Otomi
The Otomi (; es, Otomí ) are an indigenous people of Mexico inhabiting the central Mexican Plateau (Altiplano) region.
The Otomi are an indigenous people of Mexico who inhabit a discontinuous territory in central Mexico. They are linguisticall ...
, Mixe–Zoque groups (which may or may not have been related to the Olmecs), the northern Uto-Aztecan
Uto-Aztecan, Uto-Aztekan or (rarely in English) Uto-Nahuatl is a family of indigenous languages of the Americas, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The na ...
groups, often referred to as the Chichimeca
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajio region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" that de ...
, that include the Cora
Cora may refer to:
Science
* ''Cora'' (fungus), a genus of lichens
* ''Cora'' (damselfly), a genus of damselflies
* CorA metal ion transporter, a Mg2+ influx system
People
* Cora (name), a given name and surname
* Cora E. (born 1968), German hi ...
and Huichol
The Huichol or Wixárika are an indigenous people of Mexico and the United States living in the Sierra Madre Occidental range in the states of Nayarit, Jalisco, Zacatecas, and Durango, as well as in the United States in the states of California, ...
, the Chontales, the Huaves, and the Pipil, Xincan and Lencan peoples of Central America.
Chronology in chart form
Other characteristics
Subsistence

 By roughly 6000 BCE, hunter-gatherers living in the
By roughly 6000 BCE, hunter-gatherers living in the highlands
Highland is a broad term for areas of higher elevation, such as a mountain range or mountainous plateau.
Highland, Highlands, or The Highlands, may also refer to:
Places Albania
* Dukagjin Highlands
Armenia
* Armenian Highlands
Australia
* So ...
and lowlands of Mesoamerica began to develop agricultural practices with early cultivation of squash and chilli. The earliest example of maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. ...
dates to c. 4000 BCE and comes from Guilá Naquitz, a cave in Oaxaca. Earlier maize samples have been documented at the Los Ladrones cave site in Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Co ...
, c. 5500 BCE. Slightly thereafter, semi- agrarian communities began to cultivate other crops throughout Mesoamerica. Maize was the most common domesticate, but the common bean, tepary bean, scarlet runner bean, jicama
''Pachyrhizus erosus'', commonly known as jícama ( or ; Spanish ''jícama'' ; from Nahuatl ''xīcamatl'', ) Mexican turnip, is the name of a native Mexican vine, although the name most commonly refers to the plant's edible tuberous root. Jícam ...
, tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word , ...
and squash all became common cultivates by 3500 BCE. At the same time, these communities exploited cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor p ...
, yucca
''Yucca'' is a genus of perennial shrubs and trees in the family Asparagaceae, subfamily Agavoideae. Its 40–50 species are notable for their rosettes of evergreen, tough, sword-shaped leaves and large terminal panicles of white or whitish ...
, and agave
''Agave'' (; ; ) is a genus of monocots native to the hot and arid regions of the Americas and the Caribbean, although some ''Agave'' species are also native to tropical areas of North America, such as Mexico. The genus is primarily known ...
for fibers and textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not t ...
materials. By 2000 BCE, corn was the staple crop in the region, and remained so through modern times. The Ramón or Breadnut tree (''Brosimum alicastrum
''Brosimum alicastrum'', commonly known as the breadnut or ramon, is a tree species in the family Moraceae of flowering plants, whose other genera include figs and mulberries. The plant is known by a range of names in indigenous Mesoamerican ...
'') was an occasional substitute for maize in producing flour. Fruit was also important in the daily diet of Mesoamerican cultures. Some of the main ones consumed include avocado
The avocado (''Persea americana'') is a medium-sized, evergreen tree in the laurel family (Lauraceae). It is native to Americas, the Americas and was first domesticated by Mesoamerica, Mesoamerican tribes more than 5,000 years ago. Pre-Columb ...
, papaya
The papaya (, ), papaw, () or pawpaw () is the plant species ''Carica papaya'', one of the 21 accepted species in the genus '' Carica'' of the family Caricaceae. It was first domesticated in Mesoamerica, within modern-day southern Mexico and ...
, guava
Guava () is a common tropical fruit cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions. The common guava '' Psidium guajava'' (lemon guava, apple guava) is a small tree in the myrtle family (Myrtaceae), native to Mexico, Central America, ...
, mamey, zapote
Zapote the fifth district of the San José canton, in the San José province of Costa Rica. It is one of the administrative units surrounding San José downtown (officially composed of the districts of El Carmen, Merced, Hospital and Catedral ...
, and annona
''Annona'' (from Taíno ''annon'') is a genus of flowering plants in the pawpaw/ sugar apple family, Annonaceae. It is the second largest genus in the family after '' Guatteria'', containing approximately 166
.
Mesoamerica lacked animals suitable for domestication, most notably domesticated large ungulate
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraff ...
s. The lack of draft animals for transportation is one notable difference between Mesoamerica and the cultures of the South American Andes. Other animals, including the duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a fo ...
, dogs, and turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
, were domesticated
Domestication is a sustained multi-generational relationship in which humans assume a significant degree of control over the reproduction and care of another group of organisms to secure a more predictable supply of resources from that group. A ...
. Turkey was the first to be domesticated locally, around 3500 BCE. Dogs
The dog (''Canis familiaris'' or ''Canis lupus familiaris'') is a domesticated descendant of the wolf. Also called the domestic dog, it is derived from the extinct Pleistocene wolf, and the modern wolf is the dog's nearest living relativ ...
were the primary source of animal protein in ancient Mesoamerica, and dog bones are common in midden deposits throughout the region.
Societies of this region did hunt certain wild species for food. These animals included deer, rabbit
Rabbits, also known as bunnies or bunny rabbits, are small mammals in the family Leporidae (which also contains the hares) of the order Lagomorpha (which also contains the pikas). ''Oryctolagus cuniculus'' includes the European rabbit s ...
, birds, and various types of insects. They also hunted for luxury items, such as feline fur and bird plumage.
Mesoamerican cultures that lived in the lowlands and coastal plains settled down in agrarian communities somewhat later than did highland cultures due to the fact that there was a greater abundance of fruits and animals in these areas, which made a hunter-gatherer lifestyle more attractive. Fishing also was a major provider of food to lowland and coastal Mesoamericans creating a further disincentive to settle down in permanent communities.
Political organization
 Ceremonial centers were the nuclei of Mesoamerican settlements. The temples provided spatial orientation, which was imparted to the surrounding town. The cities with their commercial and religious centers were always political entities, somewhat similar to the European
Ceremonial centers were the nuclei of Mesoamerican settlements. The temples provided spatial orientation, which was imparted to the surrounding town. The cities with their commercial and religious centers were always political entities, somewhat similar to the European city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
, and each person could identify with the city where they lived.
Ceremonial centers were always built to be visible. Pyramids were meant to stand out from the rest of the city, to represent the gods and their powers. Another characteristic feature of the ceremonial centers is historic layers. All the ceremonial edifices were built in various phases, one on top of the other, to the point that what we now see is usually the last stage of construction. Ultimately, the ceremonial centers were the architectural translation of the identity of each city, as represented by the veneration of their gods and masters. Stela
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ''stelæ''), wh ...
e were common public monuments throughout Mesoamerica, and served to commemorate notable successes, events and dates associated with the rulers and nobility of the various sites.
Economy
Given that Mesoamerica was broken into numerous and diverse ecological niches, none of the societies that inhabited the area were self-sufficient, although very long-distance trade was common only for very rare goods, or luxury materials. For this reason, from the last centuries of theArchaic
Archaic is a period of time preceding a designated classical period, or something from an older period of time that is also not found or used currently:
*List of archaeological periods
**Archaic Sumerian language, spoken between 31st - 26th cent ...
period (8000 BC– 1000 BC) onward, regions compensated for the environmental inadequacies by specializing in the extraction of certain abundant natural resources and then trading them for necessary unavailable resources through established commercial trade networks.
The following is a list of some of the specialized resources traded from the various Mesoamerican sub-regions and environmental contexts:
* Pacific lowlands: cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus '' Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor p ...
and cochineal
The cochineal ( , ; ''Dactylopius coccus'') is a scale insect in the suborder Sternorrhyncha, from which the natural dye carmine is derived. A primarily sessile parasite native to tropical and subtropical South America through North Ameri ...
* Maya lowlands and the Gulf Coast: cacao, vanilla
Vanilla is a spice derived from orchids of the genus ''Vanilla (genus), Vanilla'', primarily obtained from pods of the Mexican species, flat-leaved vanilla (''Vanilla planifolia, V. planifolia'').
Pollination is required to make the p ...
, jaguar
The jaguar (''Panthera onca'') is a large cat species and the only living member of the genus ''Panthera'' native to the Americas. With a body length of up to and a weight of up to , it is the largest cat species in the Americas and the thi ...
skins, birds and bird feathers (especially quetzal
Quetzals () are strikingly colored birds in the trogon family. They are found in forests, especially in humid highlands, with the five species from the genus ''Pharomachrus'' being exclusively Neotropical, while a single species, the eared qu ...
and macaw
Macaws are a group of New World parrots that are long-tailed and often colorful. They are popular in aviculture or as companion parrots, although there are conservation concerns about several species in the wild.
Biology
Of the many diffe ...
)
* Central Mexico: Obsidian (Pachuca
Pachuca (; ote, Nju̱nthe), formally known as Pachuca de Soto, is the capital and largest city of the Mexican state of Hidalgo. It is located in the south-central part of the state. Pachuca de Soto is also the name of the municipality of whi ...
)
* Guatemalan highlands: Obsidian ( San Martin Jilotepeque, El Chayal, and Ixtepeque), pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Fe S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue giv ...
, and jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole gro ...
from the Motagua River
The Motagua River () is a river in Guatemala. It rises in the western highlands of Guatemala where it is also called Río Grande, and runs in an easterly direction to the Gulf of Honduras. The final few kilometres of the river form part of the ...
valley
* Coastal areas: salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quanti ...
, dry fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% ...
, shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
** Thin-shell structure
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard o ...
, and dye
A dye is a colored substance that chemically bonds to the substrate to which it is being applied. This distinguishes dyes from pigments which do not chemically bind to the material they color. Dye is generally applied in an aqueous solution and ...
s
Architecture
 Mesoamerican architecture is the collective name given to urban, ceremonial and public structures built by pre-Columbian civilizations in Mesoamerica. Although very different in styles, all kinds of mesoamerican architecture show some kind of interrelation, due to very significant cultural exchanges occurred during thousands of years. Among the most well-known structures in Mesoamerica, the flat-top
Mesoamerican architecture is the collective name given to urban, ceremonial and public structures built by pre-Columbian civilizations in Mesoamerica. Although very different in styles, all kinds of mesoamerican architecture show some kind of interrelation, due to very significant cultural exchanges occurred during thousands of years. Among the most well-known structures in Mesoamerica, the flat-top pyramids
A pyramid (from el, πυραμίς ') is a structure whose outer surfaces are triangular and converge to a single step at the top, making the shape roughly a pyramid in the geometric sense. The base of a pyramid can be trilateral, quadrilat ...
are a landmark feature of the most developed urban centers.
Two characteristics are most notable in Mesoamerican architecture. Firstly, the intimate connection between geography, astronomy and architecture: very often, urban centers or even single buildings are aligned to cardinal directions and/or along particular constellations. Secondly, iconography was considered integral part of architecture, with buildings often being adorned with images of religious and cultural significance.
Calendrical systems
Agriculturally based people historically divide the year into four seasons. These included the two solstices and the twoequinoxes
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun crosses the Earth's equator, which is to say, appears directly above the equator, rather than north or south of the equator. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise "due east" and se ...
, which could be thought of as the four "directional pillars" that support the year. These four times of the year were, and still are, important as they indicate seasonal changes that directly impact the lives of Mesoamerican agriculturalists.
The Maya closely observed and duly recorded the seasonal markers. They prepared almanacs recording past and recent solar and lunar eclipses, the phases of the moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width ...
, the periods of Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
and Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmos ...
, the movements of various other planets, and conjunctions of celestial bodies. These almanacs also made future predictions concerning celestial events. These tables are remarkably accurate, given the technology available, and indicate a significant level of knowledge among Maya astronomer
An astronomer is a scientist in the field of astronomy who focuses their studies on a specific question or field outside the scope of Earth. They observe astronomical objects such as stars, planets, moons, comets and galaxies – in either o ...
s.
Among the many types of calendars the Maya maintained, the most important include a 260-day cycle, a 360-day cycle or 'year', a 365-day cycle or year, a lunar cycle, and a Venus cycle, which tracked the synodic
Synodic, may refer to:
* Synodic day
* Synodic month
* Synodic orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it ...
period of Venus. Maya of the European contact period said that knowing the past aided in both understanding the present and predicting the future (Diego de Landa). The 260-day cycle was a calendar to govern agriculture, observe religious holidays, mark the movements of celestial bodies and memorialize public officials. The 260-day cycle was also used for divination, and (like the Catholic calendar of saints) to name newborns.
The names given to the days, months, and years in the Mesoamerican calendar came, for the most part, from animals, flowers, heavenly bodies, and cultural concepts that held symbolic significance in Mesoamerican culture. This calendar was used throughout the history of Mesoamerican by nearly every culture. Even today, several Maya groups in Guatemala, including the K'iche' K'iche', K'ichee', or Quiché may refer to:
*K'iche' people of Guatemala, a subgroup of the Maya
*K'iche' language K'iche', K'ichee', or Quiché may refer to:
*K'iche' people K'iche', K'ichee', or Quiché may refer to:
* K'iche' people of Guatemala ...
, Q'eqchi', Kaqchikel, and the Mixe people
The Mixe (Spanish ' or rarely ' ) are an indigenous people of Mexico inhabiting the eastern highlands of the state of Oaxaca. They speak the Mixe languages, which are classified in the Mixe–Zoque family, and are more culturally conservative tha ...
of Oaxaca continue using modernized forms of the Mesoamerican calendar.
Writing systems
 The Mesoamerican scripts deciphered to date are
The Mesoamerican scripts deciphered to date are logosyllabic
In a written language, a logogram, logograph, or lexigraph is a written character that represents a word or morpheme. Chinese characters (pronounced ''hanzi'' in Mandarin, '' kanji'' in Japanese, '' hanja'' in Korean) are generally logograms ...
combining the use of logograms
In a written language, a logogram, logograph, or lexigraph is a written character that represents a word or morpheme. Chinese characters (pronounced ''hanzi'' in Mandarin, ''kanji'' in Japanese, ''hanja'' in Korean) are generally logograms, ...
with a syllabary, and they are often called hieroglyph
A hieroglyph (Greek for "sacred carvings") was a character of the ancient Egyptian writing system. Logographic scripts that are pictographic in form in a way reminiscent of ancient Egyptian are also sometimes called "hieroglyphs". In Neoplatonis ...
ic scripts. Five or six different scripts have been documented in Mesoamerica, but archaeological dating methods, and a certain degree of self-interest, create difficulties in establishing priority and thus the forebear from which the others developed. The best documented and deciphered Mesoamerican writing system, and therefore the most widely known, is the classic Maya script
Maya script, also known as Maya glyphs, is historically the native writing system of the Maya civilization of Mesoamerica and is the only Mesoamerican writing system that has been substantially deciphered. The earliest inscriptions found which ...
. Others include the Olmec
The Olmecs () were the earliest known major Mesoamerican civilization. Following a progressive development in Soconusco, they occupied the tropical lowlands of the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. It has been speculated that ...
, Zapotec, and Epi-Olmec/Isthmian writing systems. An extensive Mesoamerican literature has been conserved partly in indigenous scripts and partly in the postinvasion transcriptions into Latin script
The Latin script, also known as Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greece, Greek city of Cumae, in southe ...
.
The other glyphic writing systems of Mesoamerica, and their interpretation, have been subject to much debate. One important ongoing discussion regards whether non-Maya Mesoamerican texts can be considered examples of true writing or whether non-Maya Mesoamerican texts are best understood as pictographic
A pictogram, also called a pictogramme, pictograph, or simply picto, and in computer usage an icon, is a graphic symbol that conveys its meaning through its pictorial resemblance to a physical object. Pictographs are often used in writing and gr ...
conventions that express ideas, specifically religious ones, but don't represent the phonetics of spoken language.
Mesoamerican writing is found in several mediums, including large stone monuments such as stelae
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek language, Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ...
, carved directly onto architecture, carved or painted over stucco (e.g., murals
A mural is any piece of graphic artwork that is painted or applied directly to a wall, ceiling or other permanent substrate. Mural techniques include fresco, mosaic, graffiti and marouflage.
Word mural in art
The word ''mural'' is a Spanis ...
), and on pottery
Pottery is the process and the products of forming vessels and other objects with clay and other ceramic materials, which are fired at high temperatures to give them a hard and durable form. Major types include earthenware, stoneware and po ...
. No Precolumbian Mesoamerican society is known to have had widespread literacy, and literacy was probably restricted to particular social classes, including scribes, painters, merchants, and the nobility.
The Mesoamerican book was typically written with brush and colored inks on a paper prepared from the inner bark of the ficus amacus. The book consisted of a long strip of the prepared bark, which was folded like a screenfold to define individual pages. The pages were often covered and protected by elaborately carved book boards. Some books were composed of square pages while others were composed of rectangular pages.
Following the Spanish conquests in the sixteenth century, Spanish friars taught indigenous scribes to write their languages in alphabetic texts. Many oral histories of the prehispanic period were subsequently recorded in alphabetic texts. The indigenous in central and southern Mexico continued to produce written texts in the colonial period, many with pictorial elements. An important scholarly reference work is the '' Handbook of Middle American Indians, Guide to Ethnohistorical Sources''. Mesoamerican codices survive from the Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
, Maya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a popu ...
, Mixtec
The Mixtecs (), or Mixtecos, are indigenous Mesoamerican peoples of Mexico inhabiting the region known as La Mixteca of Oaxaca and Puebla as well as La Montaña Region and Costa Chica Regions of the state of Guerrero. The Mixtec Cultur ...
, and Zapotec regions.
Arithmetic
Mesoamericanarithmetic
Arithmetic () is an elementary part of mathematics that consists of the study of the properties of the traditional operations on numbers—addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponentiation, and extraction of roots. In the 19th c ...
treated number
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers ...
s as having both literal and symbolic value, the result of the dualistic nature that characterized Mesoamerican ideology. As mentioned, the Mesoamerican numbering system was vigesimal (i.e., based on the number 20).
In representing numbers, a series of bars and dots were employed. Dots had a value of one, and bars had a value of five. This type of arithmetic was combined with a symbolic numerology: '2' was related to origins, as all origins can be thought of as doubling; '3' was related to household fire; '4' was linked to the four corners of the universe; '5' expressed instability; '9' pertained to the underworld and the night; '13' was the number for light, '20' for abundance, and '400' for infinity. The concept of zero was also used, and its representation at the Late Preclassic occupation of Tres Zapotes
Tres Zapotes is a Mesoamerican archaeological site located in the south-central Gulf of Mexico, Gulf Lowlands of Mexico in the Papaloapan River plain. Tres Zapotes is sometimes referred to as the third major Olmec capital (after San Lorenzo Tenocht ...
is one of the earliest uses of zero in human history.
Food, medicine, and science
Maize played an important role in Mesoamerican feasts due to its symbolic meaning and abundance. Gods were praised and named after. Companion planting was practiced in various forms by the indigenous peoples of the Americas. They domesticated squash 8,000 to 10,000 years ago, thenmaize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn ( North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. ...
, then common beans, forming the Three Sisters agricultural technique. The cornstalk served as a trellis
Trellis may refer to:
Structures
* Trellis (architecture), an architectural structure often used to support plants (especially vineyards)
* Trellis drainage pattern, a drainage system
Technology
* Trellis (graph), a special kind of graph used ...
for the beans to climb, and the beans fixed nitrogen, benefitting the maize.
Fray Bernardino de Sahagún
Bernardino de Sahagún, OFM (; – 5 February 1590) was a Franciscan friar, missionary priest and pioneering ethnographer who participated in the Catholic evangelization of colonial New Spain (now Mexico). Born in Sahagún, Spain, in 1499, he ...
collected extensive information on plants, animals, soil types, among other matters from native informants in Book 11, The Earthly Things, of the twelve-volume ''General History of the Things of New Spain,'' known as the Florentine Codex
The ''Florentine Codex'' is a 16th-century ethnographic research study in Mesoamerica by the Spanish Franciscan friar Bernardino de Sahagún. Sahagún originally titled it: ''La Historia General de las Cosas de Nueva España'' (in English: ''The ...
, compiled in the third quarter of the sixteenth century. Bernardino de Sahagún reported the ritualistic use of Psilocybe
''Psilocybe'' ( ) is a genus of gilled mushrooms, growing worldwide, in the family Hymenogastraceae. Most or nearly all species contain the psychedelic compounds psilocybin and psilocin.
Taxonomy
Taxonomic history
A 2002 study of the ...
mushrooms known to the Aztecs
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl l ...
as '' teōnanācatl'' (agglutinative form of ''teōtl'' (god, sacred) and ''nanācatl'' (mushroom) in Náhuatl
Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan languages, Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in ...
). An earlier work, the Badianus Manuscript or Libellus de Medicinalibus Indorum Herbis is another Aztec codex with written text and illustrations collected from the indigenous viewpoint. The ancient Aztecs used a variety of entheogens within their society.
Evidence shows that wild animals were captured and traded for symbolic and ritual purposes.
Mythology and worldview
Shared traits in Mesoamerican mythology are characterized by their common basis as a religion that—though in many Mesoamerican groups developed into complex polytheistic religious systems—retained some shamanistic elements. The great breadth of the Mesoamerican pantheon of deities is due to the incorporation of ideological and religious elements from the first primitive religion of Fire, Earth, Water and Nature. Astral divinities (the sun, stars, constellations, and Venus) were adopted and represented in anthropomorphic,
The great breadth of the Mesoamerican pantheon of deities is due to the incorporation of ideological and religious elements from the first primitive religion of Fire, Earth, Water and Nature. Astral divinities (the sun, stars, constellations, and Venus) were adopted and represented in anthropomorphic, zoomorphic
The word ''zoomorphism'' derives from the Greek ζωον (''zōon''), meaning "animal", and μορφη (''morphē''), meaning "shape" or "form". In the context of art, zoomorphism could describe art that imagines humans as non-human animals. It c ...
, and anthropozoomorphic sculptures, and in day-to-day objects. The qualities of these gods and their attributes changed with the passage of time and with cultural influences from other Mesoamerican groups. The gods are at once three: creator, preserver, and destroyer, and at the same time just one. An important characteristic of Mesoamerican religion was the dualism among the divine entities. The gods represented the confrontation between opposite poles: the positive, exemplified by light, the masculine, force, war, the sun, etc.; and the negative, exemplified by darkness, the feminine, repose, peace, the moon, etc.
The typical Mesoamerican cosmology sees the world as separated into a day world watched by the sun and a night world watched by the moon. More importantly, the three superposed levels of the world are united by a Ceiba
''Ceiba'' is a genus of trees in the family Malvaceae, native to tropical and subtropical areas of the Americas (from Mexico and the Caribbean to N Argentina) and tropical West Africa. Some species can grow to tall or more, with a straight, ...
tree (''Yaxche in Mayan). The geographic vision is also tied to the cardinal points. Certain geographical features are linked to different parts of this cosmovision. Thus mountains and tall trees connect the middle and upper worlds; caves connect the middle and nether worlds.
Sacrifice
Generally, sacrifice can be divided into two types: autosacrifice andhuman sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease gods, a human ruler, an authoritative/priestly figure or spirits of dead ancestors or as a retainer sacrifice, wherei ...
. The different forms of sacrifice are reflected in the imagery used to evoke ideological structure and sociocultural organization in Mesoamerica. In the Maya area, for example, stele depict bloodletting rituals performed by ruling elites, eagles and jaguars devouring human hearts, jade circles or necklaces that represented hearts, and plants and flowers that symbolized both nature and the blood that provided life. Imagery also showed pleas for rain or pleas for blood, with the same intention to replenish the divine energy. Ritual sacrifice was done in efforts to appease the gods, and was done with the purpose of protection of the population.
= Autosacrifice
= Autosacrifice, also called
Autosacrifice, also called bloodletting
Bloodletting (or blood-letting) is the withdrawal of blood from a patient to prevent or cure illness and disease. Bloodletting, whether by a physician or by leeches, was based on an ancient system of medicine in which blood and other bodily flu ...
, is the ritualized practice of drawing blood from oneself. It is commonly seen or represented through iconography as performed by ruling elites in highly ritualized ceremonies, but it was easily practiced in mundane sociocultural contexts (i.e., non-elites could perform autosacrifice). The act was typically performed with obsidian prismatic blade
In archaeology, a prismatic blade is a long, narrow, specialized stone flake tool with a sharp edge, like a small razor blade. Prismatic blades are flaked from stone cores through pressure flaking or direct percussion. This process results in a ...
s or stingray spines, and blood was drawn from piercing or cutting the tongue
The tongue is a muscular organ in the mouth of a typical tetrapod. It manipulates food for mastication and swallowing as part of the digestive process, and is the primary organ of taste. The tongue's upper surface (dorsum) is covered by taste bu ...
, earlobes, and/or genitals
A sex organ (or reproductive organ) is any part of an animal or plant that is involved in sexual reproduction. The reproductive organs together constitute the reproductive system. In animals, the testis in the male, and the ovary in the female, ...
(among other locations). Another form of autosacrifice was conducted by pulling a rope with attached thorns through the tongue or earlobes. The blood produced was then collected on amate
Amate ( es, amate from nah, āmatl ) is a type of bark paper that has been manufactured in Mexico since the precontact times. It was used primarily to create codices.
Amate paper was extensively produced and used for both communication, record ...
held in a bowl.
Autosacrifice was not limited to male rulers, as their female counterparts often performed these ritualized activities. They are typically shown performing the rope and thorns technique. A recently discovered queen's tomb in the Classic Maya site of Waka
Waka may refer to:
Culture and language
* Waka (canoe), a Polynesian word for canoe; especially, canoes of the Māori of New Zealand
** Waka ama, a Polynesian outrigger canoe
** Waka hourua, a Polynesian ocean-going canoe
** Waka taua, a Māor ...
(also known as El Perú) had a ceremonial stingray spine placed in her genital area, suggesting that women also performed bloodletting in their genitalia.
= Human sacrifice
= Sacrifice had great importance in the social and religious aspects of Mesoamerican culture. First, it showed death transformed into the divine. Death is the consequence of a human sacrifice, but it is not the end; it is but the continuation of the cosmic cycle. Death creates life—divine energy is liberated through death and returns to the gods, who are then able to create more life. Secondly, it justifies war, since the most valuable sacrifices are obtained through conflict. The death of the warrior is the greatest sacrifice and gives the gods the energy to go about their daily activities, such as the bringing of rain. Warfare and capturing prisoners became a method of social advancement and a religious cause. Finally, it justifies the control of power by the two ruling classes, the priests and the warriors. The priests controlled the religious ideology, and the warriors supplied the sacrifices. Historically it was also in discussion that those sacrificed were chosen by the gods, this idea of being "chosen" was decided by the gods. This was then displayed by acts, such as being struck by lightning. If someone was struck by lightning and a sacrifice was needed they would often be chosen by their population, as they believed they were chosen by the gods.Ballgame

 The Mesoamerican ballgame was a sport with ritual associations played for over 3000 years by nearly all pre-Columbian peoples of Mesoamerica. The sport had different versions in different places during the millennia, and a modern version of the game,
The Mesoamerican ballgame was a sport with ritual associations played for over 3000 years by nearly all pre-Columbian peoples of Mesoamerica. The sport had different versions in different places during the millennia, and a modern version of the game, ulama
In Islam, the ''ulama'' (; ar, علماء ', singular ', "scholar", literally "the learned ones", also spelled ''ulema''; feminine: ''alimah'' ingularand ''aalimath'' lural are the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious ...
, is still played in a few places.
Over 1300 ballcourts have been found throughout Mesoamerica. They vary considerably in size, but they all feature long narrow alleys with side-walls to bounce the balls against.
The rules of the ballgame are not known, but it was probably similar to volleyball, where the object is to keep the ball in play. In the most well-known version of the game, the players struck the ball with their hips, though some versions used forearms or employed rackets, bats, or handstones. The ball was made of solid rubber, and weighed up to 4 kg or more, with sizes that differed greatly over time or according to the version played.
While the game was played casually for simple recreation, including by children and perhaps even women, the game also had important ritual aspects, and major formal ballgames were held as ritual events, often featuring human sacrifice.
Astronomy
Mesoamericanastronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies astronomical object, celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and chronology of the Universe, evolution. Objects of interest ...
included a broad understanding of the cycles of planets and other celestial bodies. Special importance was given to the sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is a nearly perfect ball of hot plasma, heated to incandescence by nuclear fusion reactions in its core. The Sun radiates this energy mainly as light, ultraviolet, and infrared rad ...
, moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width ...
, and Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun. It is sometimes called Earth's "sister" or "twin" planet as it is almost as large and has a similar composition. As an interior planet to Earth, Venus (like Mercury) appears in Earth's sky never f ...
as the morning and evening star.
Observatories were built at some sites, including the round observatory at Ceibal and the "Observatorio" at Xochicalco
Xochicalco () is a pre-Columbian archaeological site in Miacatlán Municipality in the western part of the Mexican state of Morelos. The name ''Xochicalco'' may be translated from Nahuatl as "in the house of Flowers". The site is located 38 ...
. Often, the architectural organization of Mesoamerican sites was based on precise calculations derived from astronomical observations. Well-known examples of these include the El Castillo pyramid at Chichen Itza and the Observatorio at Xochicalco
Xochicalco () is a pre-Columbian archaeological site in Miacatlán Municipality in the western part of the Mexican state of Morelos. The name ''Xochicalco'' may be translated from Nahuatl as "in the house of Flowers". The site is located 38 ...
. A unique and common architectural complex found among many Mesoamerican sites are E-Groups, which are aligned so as to serve as astronomical observatories. The name of this complex is based on Uaxactun
Uaxactun (pronounced ) is an ancient sacred place of the Maya civilization, located in the Petén Basin region of the Maya lowlands, in the present-day department of Petén, Guatemala. The site lies some north of the major center of Tikal. ...
's "Group E", the first known observatory in the Maya area. Perhaps the earliest observatory documented in Mesoamerica is that of the Monte Alto culture
Monte Alto is an archaeological site on the Pacific Coast in what is now Guatemala.
History
Located 20 km southeast from Santa Lucía Cotzumalguapa in Escuintla, Monte Alto was occupied as early as 1800 BC, but has a fairly light presen ...
. This complex consisted of three plain stelae and a temple oriented with respect to the Pleiades
The Pleiades (), also known as The Seven Sisters, Messier 45 and other names by different cultures, is an asterism and an open star cluster containing middle-aged, hot B-type stars in the north-west of the constellation Taurus. At a distance ...
.
Symbolism of space and time
 It has been argued that among Mesoamerican societies the concepts of
It has been argued that among Mesoamerican societies the concepts of space
Space is the boundless three-dimensional extent in which objects and events have relative position and direction. In classical physics, physical space is often conceived in three linear dimensions, although modern physicists usually con ...
and time
Time is the continued sequence of existence and events that occurs in an apparently irreversible succession from the past, through the present, into the future. It is a component quantity of various measurements used to sequence events, t ...
are associated with the four cardinal compass points and linked together by the calendar. Dates or events were always tied to a compass direction, and the calendar specified the symbolic geographical characteristic peculiar to that period. Resulting from the significance held by the cardinal directions, many Mesoamerican architectural features, if not entire settlements, were planned and oriented with respect to directionality.
In Maya cosmology, each cardinal point was assigned a specific color and a specific jaguar deity (Bacab
Bacab () is the generic Yucatec Maya name for the four prehispanic aged deities of the interior of the earth and its water deposits. The Bacabs have more recent counterparts in the lecherous, drunken old thunder deities of the Gulf Coast regions. ...
). They are as follows:
* Hobnil, Bacab of the East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fa ...
, associated with the color red and the ''Kan'' years
* Can Tzicnal, Bacab of the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''no ...
, assigned the color white and the ''Muluc'' years
* Zac Cimi, Bacab of the West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
, associated with the color black and the ''Ix'' years
* Hozanek, Bacab of the South
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþa ...
, associated with the color yellow and the ''Cauac'' years.
Later cultures such as the Kaqchikel and K'iche' K'iche', K'ichee', or Quiché may refer to:
*K'iche' people of Guatemala, a subgroup of the Maya
*K'iche' language K'iche', K'ichee', or Quiché may refer to:
*K'iche' people K'iche', K'ichee', or Quiché may refer to:
* K'iche' people of Guatemala ...
maintain the association of cardinal directions with each color, but used different names.
Among the Aztec, the name of each day was associated with a cardinal point (thus conferring symbolic significance), and each cardinal direction was associated with a group of symbols. Below are the symbols and concepts associated with each direction:
* East: croco dile, the serpent, water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
, cane, and movement. The East was linked to the world priests and associated with vegetative fertility, or, in other words, tropical exuberance.
* North: wind, death, the dog, the jaguar, and flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and sta ...
(or chert
Chert () is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a ...
). The north contrasts with the east in that it is conceptualized as dry, cold, and oppressive. It is considered the nocturnal part of the universe and includes the dwellings of the dead. The dog ( xoloitzcuintle) has a very specific meaning, as it accompanies the deceased during the trip to the lands of the dead and helps them cross the river of death that leads into nothingness. (''See also'' Dogs in Mesoamerican folklore and myth).
* West: the house, the deer, the monkey
Monkey is a common name that may refer to most mammals of the infraorder Simiiformes, also known as the simians. Traditionally, all animals in the group now known as simians are counted as monkeys except the apes, which constitutes an incom ...
, the eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, j ...
, and rain. The west was associated with the cycles of vegetation, specifically the temperate high plains that experience light rains and the change of seasons.
* South: rabbit, the lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia al ...
, dried herbs, the buzzard
Buzzard is the common name of several species of birds of prey.
''Buteo'' species
* Archer's buzzard (''Buteo archeri'')
* Augur buzzard (''Buteo augur'')
* Broad-winged hawk (''Buteo platypterus'')
* Common buzzard (''Buteo buteo'')
* Eastern ...
, and flowers. It is related on the one hand to the luminous Sun and the noon heat, and on the other with rain filled with alcoholic drink. The rabbit, the principal symbol of the west, was associated with farmers and with pulque
Pulque (; nci, metoctli), or octli, is an alcoholic beverage made from the fermented sap of the maguey (agave) plant. It is traditional in central Mexico, where it has been produced for millennia. It has the color of milk, a rather viscous ...
.
Political and religious art
 Mesoamerican
Mesoamerican art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
istic expression was conditioned by ideology and generally focused on themes of religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural ...
and/or sociopolitical power. This is largely based on the fact that most works that survived the Spanish conquest were public monuments. These monuments were typically erected by rulers who sought to visually legitimize their sociocultural and political position; by doing so, they intertwined their lineage, personal attributes and achievements, and legacy with religious concepts. As such, these monuments were specifically designed for public display and took many forms, including stele, sculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sc ...
, architectural relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
s, and other types of architectural elements (e.g., roofcombs). Other themes expressed include tracking time, glorifying the city, and veneration of the gods—all of which were tied to explicitly aggrandizing the abilities and the reign of the ruler who commissioned the artwork.
The majority of artwork created during this historical time was in relation to these topics, religion and politics. Rulers were drawn and sculpted. Historical tales and events were then translated into pieces of art, and art was used to relay religious and political messages.
Music
Archaeological studies have never discovered any written music from thepre-Columbian era
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, ...
, but musical instruments were found, as well as carvings and depictions, that clearly show how music played a central role in the Mayan religious and societal structures, for example, as accompaniment to celebrations and funerals. Some Mesoamerican civilizations, such as the Maya, commonly played various instruments such as drums, flutes and whistles. Although most of the original Mayan music disappeared following the Spanish colonization, some of it mixed with the incoming Spanish music and exists to date.
See also
*Americas (terminology)
The Americas, also known as America,"America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 33: " 6c: from the feminine of ''Americus'', the Latinized first name of the expl ...
*Americas
*Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. ...
*Hispanic America
*Hispanic and Latino Americans
*Indigenous peoples of Mexico
*Indigenous peoples of the Americas
*Latin America
*Mesoamerican region
*Middle America (Americas)
*Painting in the Americas before European colonization
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Charles Gibson (historian), Gibson, Charles. ''The Aztecs Under Spanish Rule''. Stanford: Stanford University Press 1964. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Wauchope, Robert, general editor. ''Handbook of Middle American Indians''. Austin: University of Texas Press 1964–1976. * * *External links
Maya Culture
Mesoweb.com: a comprehensive site for Mesoamerican civilizations
Museum of the Templo Mayor
(Mexico)
National Museum of Anthropology and History
(Mexico)
concerning war in Mesoamerica
WAYEB: European Association of Mayanists
Open access international scientific journal devoted to the archaeological study of the American and Iberian peoples. It contains research articles on Mesoamerica. *
Vistas: Visual Culture in Spanish America, 1520–1820
' * {{Authority control Classic period in the Americas History of indigenous peoples of North America History of Belize History of El Salvador History of Guatemala History of Honduras History of Mexico History of Nicaragua Indigenous peoples of Central America Indigenous peoples in Mexico Pre-Columbian cultural areas Historical regions Regions of North America