|
Puuc
Puuc is the name of either a region in the Mexican state of Yucatán or a Maya architectural style prevalent in that region. The word ''puuc'' is derived from the Maya term for "hill". Since the Yucatán is relatively flat, this term was extended to encompass the large karstic range of hills in the southern portion of the state, hence, the terms Puuc region or Puuc hills. The Puuc hills extend into northern Campeche and western Quintana Roo. The term Puuc is also used to designate the architectural style of ancient Maya sites located within the Puuc hills, hence, the term Puuc architecture. This architectural style began at the end of the Late Classic period but experienced its greatest extent during the Terminal Classic period. Puuc architecture In the florescence of Puuc architecture (such as at the ancient Maya site of Uxmal) buildings were decorated with carefully cut veneer stones set into a concrete core. The lower portion of the façades are blank with a flat surf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayil
Sayil is a Maya archaeological site in the Mexican state of Yucatán, in the southwest of the state, south of Uxmal. It was incorporated together with Uxmal as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1996. Sayil flourished principally, albeit briefly, during the Terminal Classic period. A number of badly damaged monuments suggest that Sayil was governed by a local royal dynasty,Sharer & Traxler 2006, p.545. with wealth among lineages based, at least in part, upon control of the best agricultural lands.Carmean ''et al.'' 2005, p.435 Location The site is located in the karst limestone hills of the Puuc region of the northern Yucatan Peninsula. Sayil is located south of the contemporary Puuc archaeological site of Kabah, from in Xlapak and from Labna. It was built in a shallow valley among low, steep hills.Sharer & Traxler 2006, p.546. The Puuc region that includes the site of Sayil possesses well defined wet and dry seasons and is characterised by a near absence of surface wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayil2
Sayil is a Maya archaeological site in the Mexican state of Yucatán, in the southwest of the state, south of Uxmal. It was incorporated together with Uxmal as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1996. Sayil flourished principally, albeit briefly, during the Terminal Classic period. A number of badly damaged monuments suggest that Sayil was governed by a local royal dynasty,Sharer & Traxler 2006, p.545. with wealth among lineages based, at least in part, upon control of the best agricultural lands.Carmean ''et al.'' 2005, p.435 Location The site is located in the karst limestone hills of the Puuc region of the northern Yucatan Peninsula. Sayil is located south of the contemporary Puuc archaeological site of Kabah, from in Xlapak and from Labna. It was built in a shallow valley among low, steep hills.Sharer & Traxler 2006, p.546. The Puuc region that includes the site of Sayil possesses well defined wet and dry seasons and is characterised by a near absence of surface wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maya Civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, architecture, mathematics, calendar, and astronomical system. The Maya civilization developed in the Maya Region, an area that today comprises southeastern Mexico, all of Guatemala and Belize, and the western portions of Honduras and El Salvador. It includes the northern lowlands of the Yucatán Peninsula and the highlands of the Sierra Madre, the Mexican state of Chiapas, southern Guatemala, El Salvador, and the southern lowlands of the Pacific littoral plain. Today, their descendants, known collectively as the Maya, number well over 6 million individuals, speak more than twenty-eight surviving Mayan languages, and reside in nearly the same area as their ancestors. The Archaic period, before 2000 BC, saw the first developments in agricul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
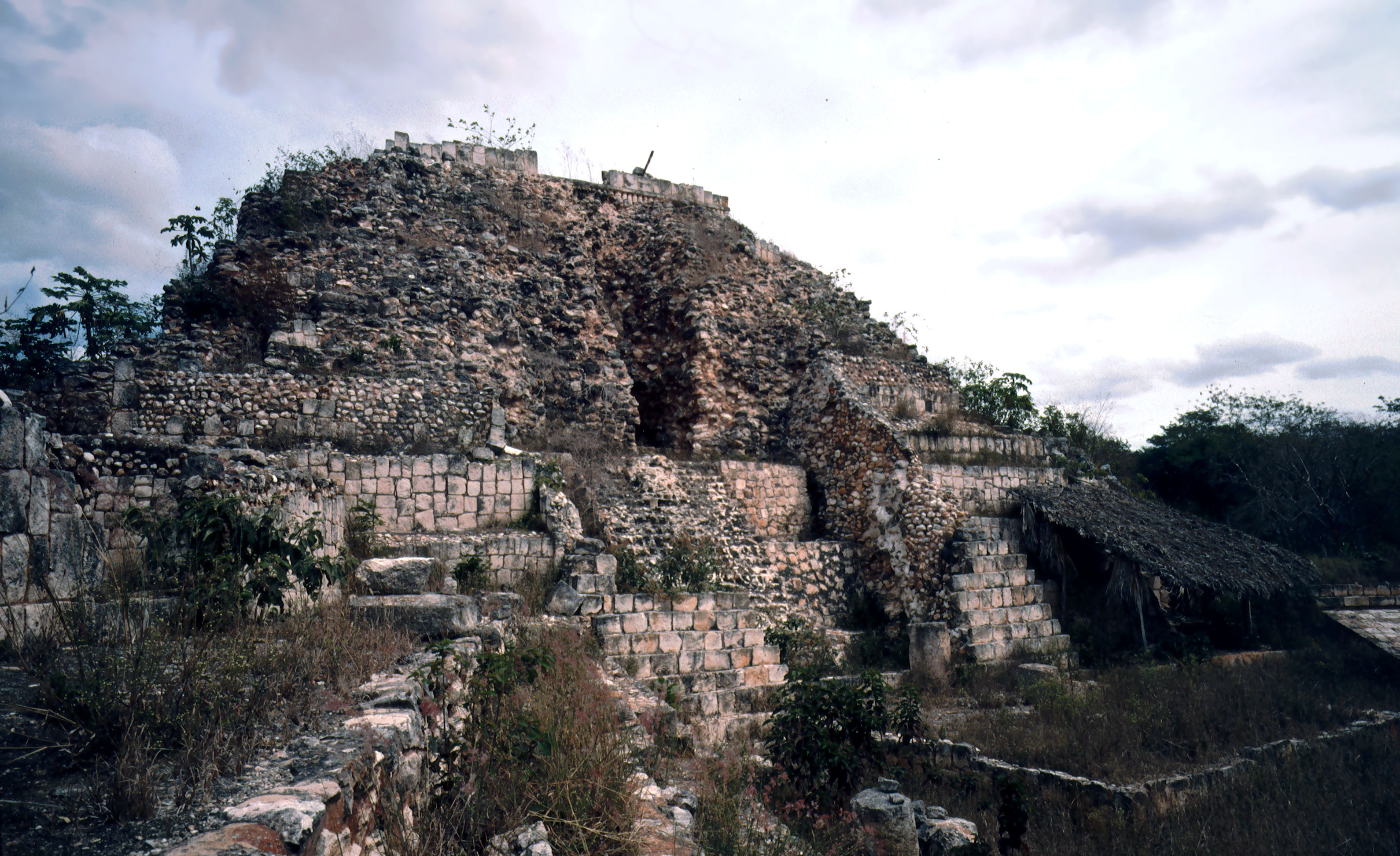
Xlapak
Xlapak (or Xlapac) is a small Maya archaeological site in the Yucatan Peninsula of southeastern Mexico. It is located in the heart of the Puuc region, about from the archaeological site of Labná and a similar distance from Sayil, lying directly between the two sites. It consists of three main groups in a valley of the Puuc Hills in Yucatán State,Toscano Hernández & Huchim Herrera 2004, p.84. a region of karst limestone forming the only major topographical feature of the peninsula. The closest town is Oxkutzcab, about to the northeast. The site dates from the Late to Terminal Classic periods and was sited in an area suitable for agriculture. Restoration at Xlapak, and other nearby archaeological sites, was carried out in the first half of the 20th century by the Mexican '' Instituto de Antropologia e Historia'' (Institute of Anthropology and History). Further archaeological investigation was carried out in 1965 under the direction of César A. Sáenz. The site The site c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabah, Yucatán
Kabah (also spelled Kabaah, Kabáh, Kahbah and Kaba) is a Maya archaeological site in the Puuc region of western Yucatan, south of Mérida. Kabah is south of Uxmal, connected to that site by an long raised causeway wide with monumental arches at each end. Kabah is the second largest ruin of the Puuc region after Uxmal. The site is on Fed. 261, approximately south from Mérida, Yucatán, towards Campeche, Campeche, and is a popular tourism destination. Ruins extend for a considerable distance on both sides of the highway; many of the more distant structures are little visited, and some are still overgrown with forest. , a program was ongoing to clear and restore more buildings, as well as archeological excavations under the direction of archeologist Ramón Carrasco. Kabah was declared a Yucatán state park in 1993. History The name ''Kabah'' or ''Kabaah'' was first suggested by Estanislao Carrillo in 1846 and is usually taken to be archaic Maya language for "strong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
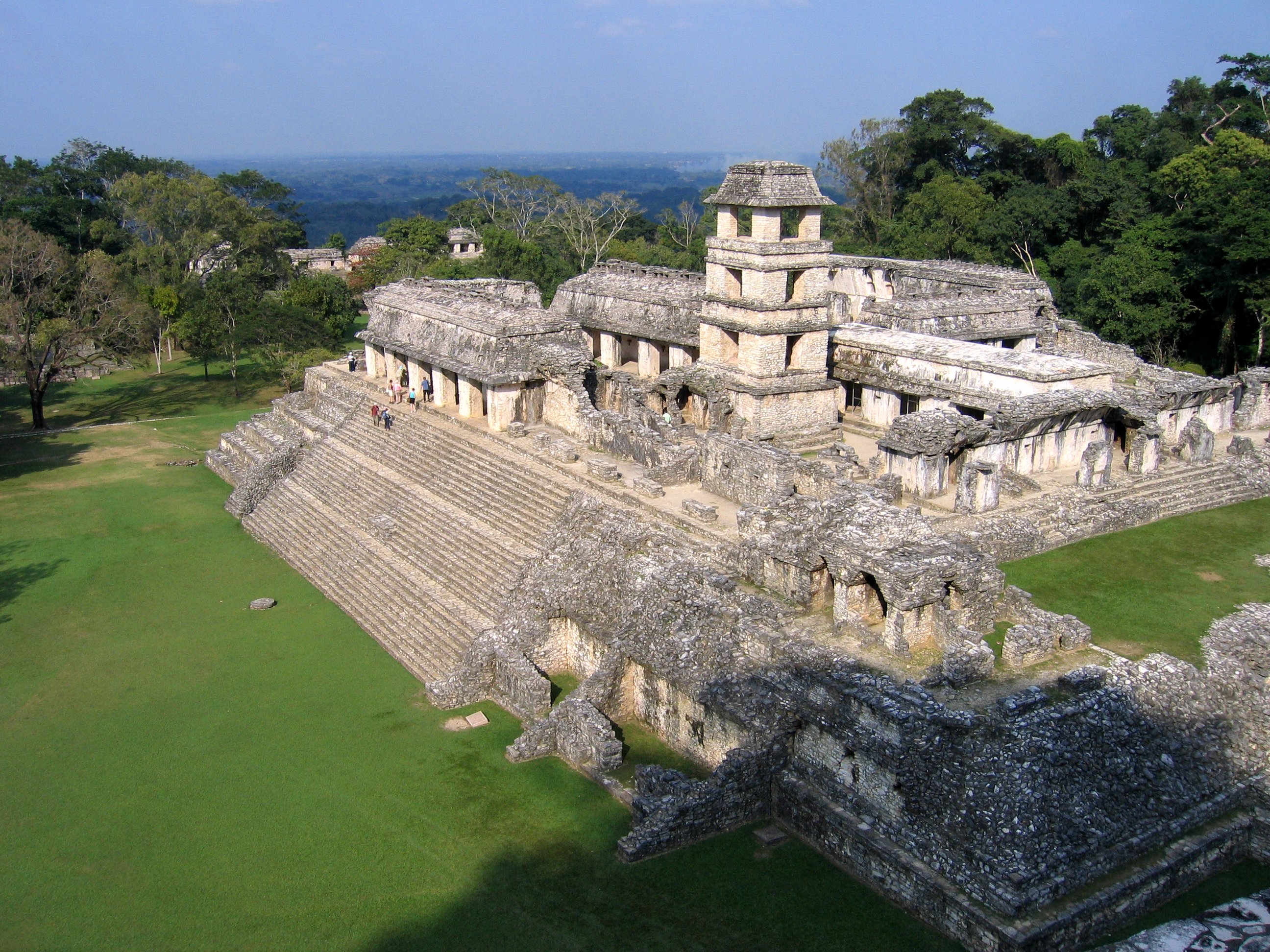
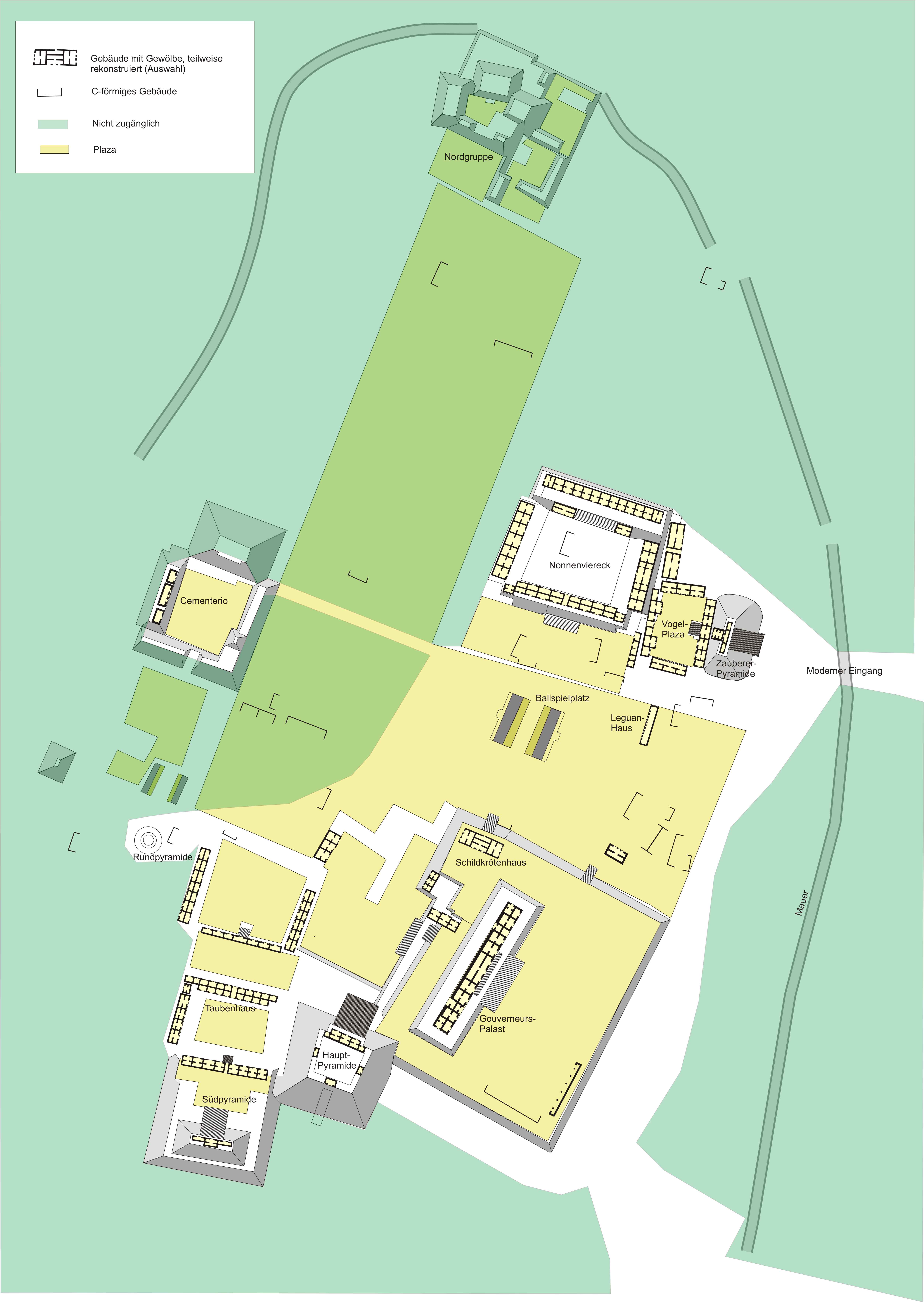
Uxmal
Uxmal (Yucatec Maya: ''Óoxmáal'' ) is an ancient Maya city of the classical period located in present-day Mexico. It is considered one of the most important archaeological sites of Maya culture, along with Palenque, Chichen Itza and Calakmul in Mexico, Caracol and Xunantunich in Belize, and Tikal in Guatemala. It is located in the Puuc region of the eastern Yucatán Peninsula, and is considered one of the Maya cities most representative of the region's dominant architectural style. It has been designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site in recognition of its significance. Uxmal is located 62 km south of Mérida, capital of Yucatán state in Mexico. Its buildings are noted for their size and decoration. Ancient roads called ''sacbes'' connect the buildings, and also were built to other cities in the area such as Chichén Itzá in modern-day Mexico, Caracol and Xunantunich in modern-day Belize, and Tikal in modern-day Guatemala. Its buildings are typical of the Puuc style, wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerican Architecture
Mesoamerican architecture is the set of architectural traditions produced by pre-Columbian cultures and civilizations of Mesoamerica, traditions which are best known in the form of public, ceremonial and urban monumental buildings and structures. The distinctive features of Mesoamerican architecture encompass a number of different regional and historical styles, which however are significantly interrelated. These styles developed throughout the different phases of Mesoamerican history as a result of the intensive cultural exchange between the different cultures of the Mesoamerican culture area through thousands of years. Mesoamerican architecture is mostly noted for its pyramids, which are the largest such structures outside of Ancient Egypt. One interesting and widely researched topic is the relation between cosmovision, religion, geography, and architecture in Mesoamerica. Much seems to suggest that many traits of Mesoamerican architecture were governed by religious and mytho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labna
Labna (or Labná in Spanish orthography) is a Mesoamerican archaeological site and ceremonial center of the pre-Columbian Maya civilization, located in the Puuc Hills region of the Yucatán Peninsula. It is situated to the south of the large Maya site of Uxmal, in the southwest of the present-day state of Yucatán, Mexico. It was incorporated with Uxmal as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1996. The site is a comparatively small and compact one. Among its notable structures is a large two-storey 'palace' (''"El Palacio"''), which is one of the longest contiguous structures in the Puuc region at approximately 120 m (393.7 ft) in length. From the palace, a ceremonial road (''sacbe'') extends to an elaborately decorated gateway arch (''"El Arco"''). This structure is 3 m (9.8 ft) wide and 6 m high, with well-reserved bas-reliefs. The arch is not an entrance to the city, but rather is a passageway between public areas. Next to this gateway stands ''"El Mirador"' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xculoc
Xculoc is a village in Campeche, Mexico. This settlement of Maya people is located 20 kilometres south of Uxmal and the same distance west of Sayil.Kramer, K., ''Maya Children: Helpers at the Farm'' (Harvard University Press, 2005), p. 55. Ancient Puuc Puuc is the name of either a region in the Mexican state of Yucatán or a Maya architectural style prevalent in that region. The word ''puuc'' is derived from the Maya term for "hill". Since the Yucatán is relatively flat, this term was ex ... style Mayan building ruins are located in Xculoc. References {{coord, 20, 11, N, 89, 50, W, display=title, region:MX_type:city_source:GNS-enwiki Populated places in Campeche Maya sites in Campeche Maya Classic Period ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campeche
Campeche (; yua, Kaampech ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Campeche ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Campeche), is one of the 31 states which make up the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. Located in southeast Mexico, it is bordered by the states of Tabasco to the southwest, Yucatán to the northeast, and Quintana Roo to the east; to the southeast by the Orange Walk district of Belize, and by the Petén department of Guatemala to the south. It has a coastline to the west with the Gulf of Mexico. The state capital, also called Campeche, was declared a World Heritage Site in 1997. The formation of the state began with the city, which was founded in 1540 as the Spanish began the conquest of the Yucatán Peninsula. The city was a rich and important port during the colonial period, but it declined after Mexico's independence. Campeche was part of the province of Yucatán but split off in the mid-19th century, mostly due to political friction with the city of Mérida. Much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yucatán (state)
Yucatán (, also , , ; yua, Yúukatan ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán,; yua, link=no, Xóot' Noj Lu'umil Yúukatan. is one of the 31 states which comprise the federal entities of Mexico. It comprises 106 separate municipalities, and its capital city is Mérida. It is located on the northern part of the Yucatán Peninsula. It is bordered by the states of Campeche to the southwest and Quintana Roo to the southeast, with the Gulf of Mexico off its northern coast. Before the arrival of Spaniards in the Yucatán Peninsula, the name of this region was ''Mayab''. In the Yucatec Maya language, ''mayab'' means "flat", and is the source of the word "Maya" itself. The peninsula was a very important region for the Maya civilization, which reached the peak of its development here, where the Mayans founded the cities of Chichen Itza, Izamal, Motul, Mayapan, Ek' Balam and Ichcaanzihóo (also called Ti'ho), now Mérida. After the Spanish conquest of Yucatán (e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesoamerican Chronology
Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of pre-Columbian, prehispanic Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian (first human habitation until 3500 BCE); the Archaic (before 2600 BCE), the Preclassic or Formative (2500 BCE – 250 CE), the Classic (250–900 CE), and the Postclassic (); as well as the post European contact Colonial Period (1521–1821), and Postcolonial, or the period after independence from Spain (1821–present). The periodisation of Mesoamerica by researchers is based on archaeological, ethnohistorical, and modern cultural anthropology research dating to the early twentieth century. Archaeologists, ethnohistorians, historians, and cultural anthropologists continue to work to develop cultural histories of the region. Overview Paleo-Indian period 10,000–3500 BCE The Paleo-Indian (less frequently, ''Lithic stage, Lithic'') period or era is that which spans from the first signs of human presence in the region, to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)