|
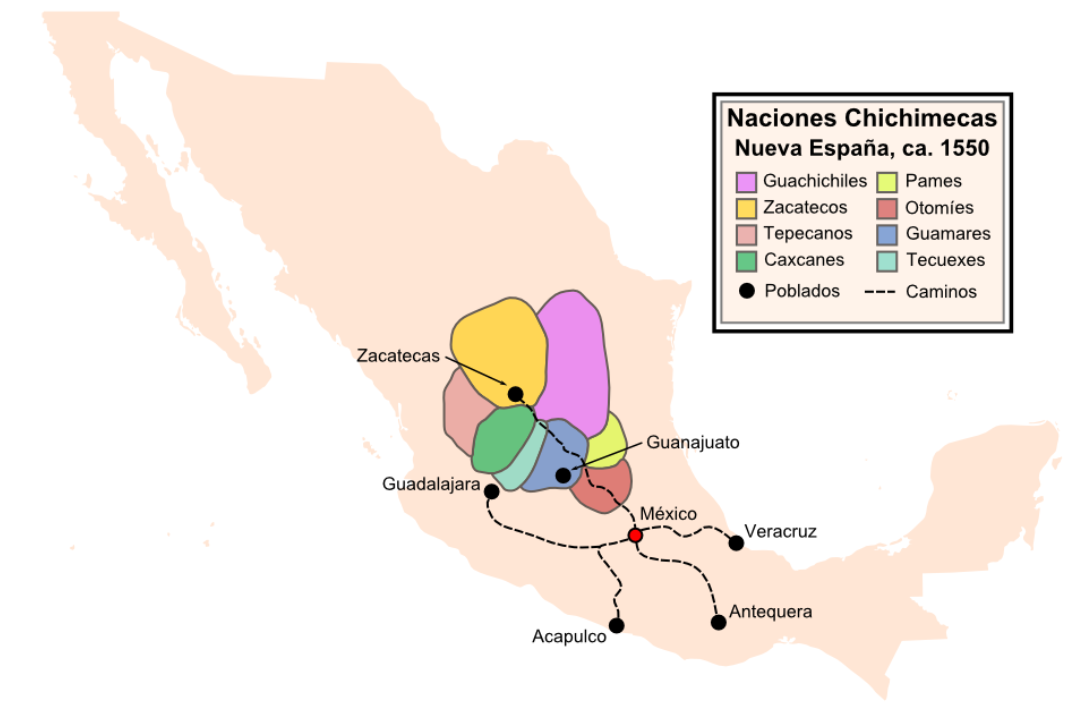
Chichimeca
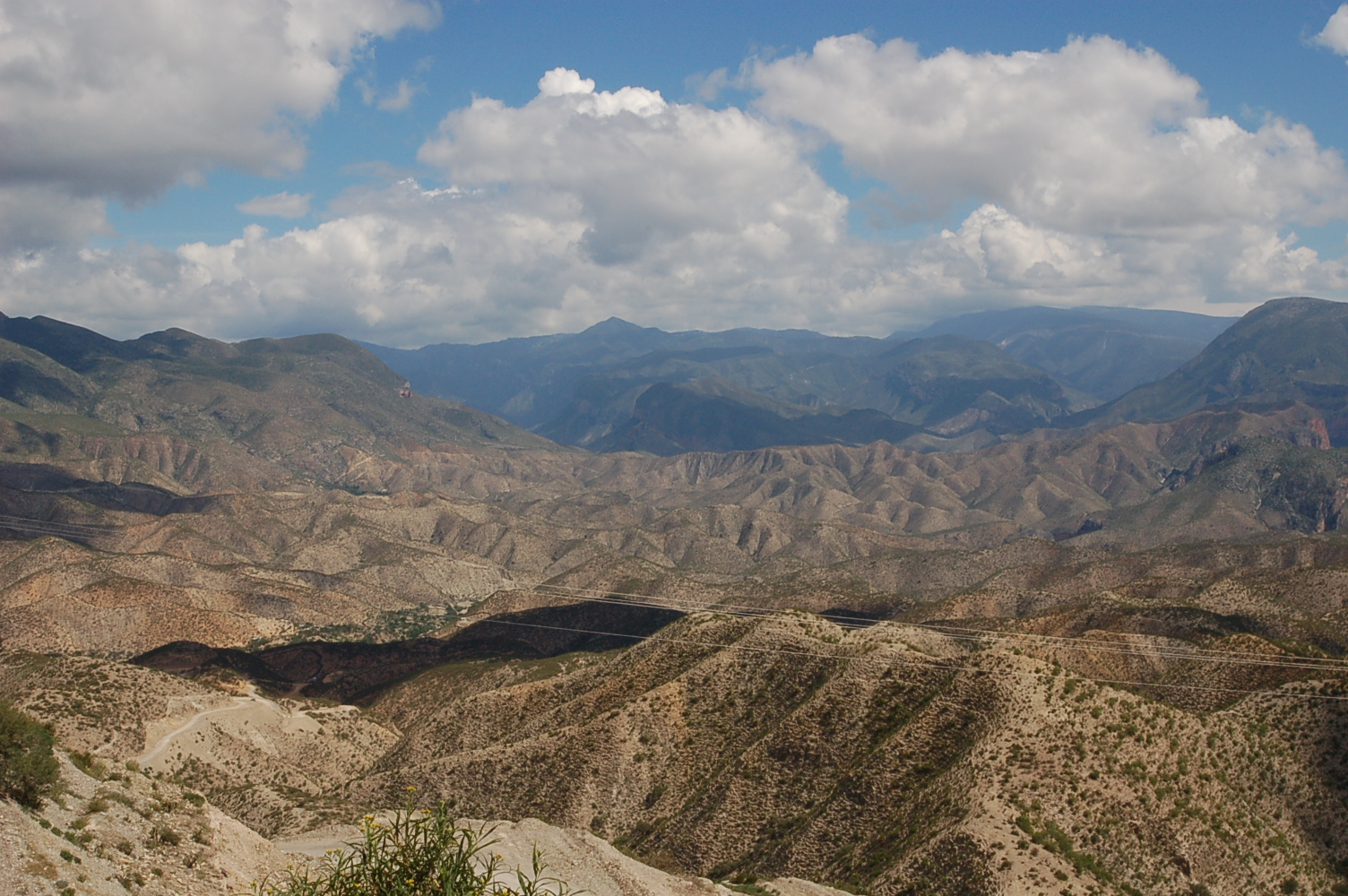
Chichimeca () is the name that the Nahua peoples of Mexico generically applied to nomadic and semi-nomadic peoples who were established in present-day Bajio region of Mexico. Chichimeca carried the meaning as the Roman term "barbarian" that described Germanic tribes. The name, with its pejorative sense, was adopted by the Spanish Empire. For the Spanish, in the words of scholar Charlotte M. Gradie, "the Chichimecas were a wild, nomadic people who lived north of the Valley of Mexico. They had no fixed dwelling places, lived by hunting, wore little clothes and fiercely resisted foreign intrusion into their territory, which happened to contain silver mines the Spanish wished to exploit." In spite of not having temples or idols, they practiced animal sacrifice, and they were feared for their expertise and brutality in war. The Spanish invasion resulted in a "drastic population decline of all the peoples known collectively as Chichimecas, and to the eventual disappearance as peoples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chichimeca War
The Chichimeca War (1550–90) was a military conflict between the Spanish Empire and the Chichimeca Confederation established in the territories today known as the Central Mexican Plateau, called by the Conquistadores La Gran Chichimeca. The epicenter of the hostilities was the region now called the Bajío. The Chichimeca War is recorded as the longest and most expensive military campaign confronting the Spanish Empire and indigenous people in Mesoamerica. The forty-year conflict was settled through several peace treaties driven by the Spaniards which led to the pacification and, ultimately, the streamlined integration of the native populations into the New Spain society. The Chichimeca War (1550-1590) began eight years after the two-year Mixtón War. It can be considered a continuation of the rebellion as the fighting did not come to a halt in the intervening years. Unlike in the Mixtón rebellion, the Caxcanes were now allied with the Spanish. The war was fought in what are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Guanajuato
Guanajuato (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Guanajuato), is one of the 32 states that make up the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 46 municipalities and its capital city is Guanajuato. Guanajuato is in central Mexico. It is bordered by the states of Jalisco to the west, Zacatecas to the northwest, San Luis Potosí to the north, Querétaro to the east, and Michoacán to the south. It covers an area of . The state is home to several historically important cities, especially those along the "Bicentennial Route", which retraces the path of Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla's insurgent army at the beginning of the Mexican War of Independence. This route begins at Dolores Hidalgo, and passes through the Sanctuary of Atotonilco, San Miguel de Allende, Celaya, and the capital of Guanajuato. Other important cities in the state include León, the state's biggest city, Salamanca, and Irapuato. The first town established by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanajuato
Guanajuato (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Guanajuato ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Guanajuato), is one of the 32 states that make up the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 46 municipalities and its capital city is Guanajuato. Guanajuato is in central Mexico. It is bordered by the states of Jalisco to the west, Zacatecas to the northwest, San Luis Potosí to the north, Querétaro to the east, and Michoacán to the south. It covers an area of . The state is home to several historically important cities, especially those along the "Bicentennial Route", which retraces the path of Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla's insurgent army at the beginning of the Mexican War of Independence. This route begins at Dolores Hidalgo, and passes through the Sanctuary of Atotonilco, San Miguel de Allende, Celaya, and the capital of Guanajuato. Other important cities in the state include León, the state's biggest city, Salamanca, and Irapuato. The first town established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chichimeca Jonaz People
The Chichimeca Jonaz are an indigenous people of Mexico, living in the states of Guanajuato and San Luis Potosí. In Guanajuato, the Chichimeca Jonaz people live in a community in San Luis de la Paz municipality. The settlement is 2,070 m above sea level. They call this place ''Rancho Úza'' or ''Misión Chichimeca''. They are descendants of the Pame people, who fought in the Chichimeca War (1550-1590) in the Chichimeca Confederation. In the 2000 General Census by INEGI 2,641 people named themselves as speakers of the Chichimeca Jonaz language. Of these 1,433 speakers lived in Guanajuato, and the other 115 in San Luis Potosí. Their language belongs to the Pamean sub-branch of the Oto-Pamean languages, Oto-Pamean branch of the Oto-Manguean language family, the closest relative of the Chichimeca Jonaz language is the Pame language. Spanish colonization of the Americas During the ensuing Spanish colonization of the Americas, the Chichimecas Jonaz descendants, whom are the Pame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierra Gorda
The Sierra Gorda () is an ecological region centered on the northern third of the Mexican state of Querétaro and extending into the neighboring states of Guanajuato, Hidalgo and San Luis Potosí. Within Querétaro, the ecosystem extends from the center of the state starting in parts of San Joaquín and Cadereyta de Montes municipalities and covering all of the municipalities of Peñamiller, Pinal de Amoles, Jalpan de Serra, Landa de Matamoros and Arroyo Seco, for a total of 250 km2 of territory. The area is extremely rugged with high steep mountains and deep canyons. As part of the Huasteca Karst, it also contains many formations due to erosion of limestone, especially pit caves known locally as sótanos. The area is valued for its very wide diversity of plant and animal life, which is due to the various microenvironments created by the ruggedness of the terrain and wide variation in rainfall. This is due to the mountains’ blocking of moisture coming in from the Gulf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pame People
The north Pame, or Xi'iuy (alternate spelling: Xi'úi, Xi'ui, Xi'oi, or Xiyui), as they refer to themselves, the south Pame, or Ñáhu, Nyaxu (in Hidalgo), and the Pame in Querétaro or Re Nuye Eyyä, are an Indigenous people of central Mexico primarily living in the state of San Luis Potosí. When Spanish colonists arrived and conquered their traditional territory in the sixteenth century, which "extended from the modern state of Tamaulipas in the north to Hidalgo and the area around Mexico City in the south along the Sierra Madre," they renamed "the area ''Pamería'', and applied the name Pame to all of the peoples there." Estimates for population of the Pames at the time of contact with Spanish colonists in 1519 range between 40,000 and 70,000. In 1794, the population was estimated at around 25,000. Recent figures for the Pame have estimated the population to be approximately 10,000 people. The Pames, along with the Chichimeca-Jonaz of the Sierra Gorda in eastern Guanajuato, are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Gran Chichimeca
La Gran Chichimeca was a term used by the Spanish ''conquistadores'' of the 16th century to refer to an area of the northern central Mexican ''altiplano'' (plateau), a territory which today is encompassed by the modern Mexican states of Jalisco, Aguascalientes, Nayarit, Guanajuato and Zacatecas. They derived the term from the Aztec who referred to the nomadic tribes of the area as “chichimeca”. The Nahuatl name ''Chīchīmēcah'' (plural, ; singular ''Chīchīmēcatl'') means "inhabitants of Chichiman"; the placename Chichiman itself means "Area of Milk". It is sometimes said to be related to ''chichi'' "dog", but the i's in ''chichi'' are short while those in ''Chīchīmēcah'' are long, a phonemic distinction in Nahuatl. The word could either have a negative "barbarous" sense, or a positive " noble savage" sense. Seventy years after the 1521 fall of the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan (present-day Mexico City), the Spaniards had failed to subdue the north of New Spain, La Gran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Jalisco
Jalisco (, , ; Nahuatl: Xalixco), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Jalisco ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Jalisco ; Nahuatl: Tlahtohcayotl Xalixco), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is located in Western Mexico and is bordered by six states, which are Nayarit, Zacatecas, Aguascalientes, Guanajuato, Michoacán, and Colima. Jalisco is divided into 125 municipalities, and its capital and largest city is Guadalajara. Jalisco is one of the most economically and culturally important states in Mexico, owing to its natural resources as well as its long history and culture. Many of the characteristic traits of Mexican culture, particularly outside Mexico City, are originally from Jalisco, such as mariachi, ranchera music, birria, tequila, jaripeo, etc., hence the state's motto: "Jalisco es México." Economically, it is ranked third in the country, with industries centered in the Guadalajara metropolitan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbarian
A barbarian (or savage) is someone who is perceived to be either Civilization, uncivilized or primitive. The designation is usually applied as a generalization based on a popular stereotype; barbarians can be members of any nation judged by some to be less civilized or orderly (such as a tribal society) but may also be part of a certain "primitive" culture, cultural group (such as nomads) or social class (such as bandits) both within and outside one's own nation. Alternatively, they may instead be admired and romanticised as noble savages. In idiomatic or figurative usage, a "barbarian" may also be an individual reference to a brutal, cruel, warlike, and insensitive person. The term originates from the el, βάρβαρος (''barbaros'' pl. βάρβαροι ''barbaroi''). In Ancient Greece, the Greeks used the term not only towards those who did not speak Greek and follow classical Greek customs, but also towards Greek populations on the fringe of the Greek world with peculiar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Luis Potosí
San Luis Potosí (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of San Luis Potosí ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de San Luis Potosí), is one of the 32 states which compose the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 58 municipalities and its capital city is San Luis Potosí City. Located in Central Mexico, San Luis Potosí is bordered by seven other Mexican states: Nuevo León to the north; Tamaulipas to the north-east; Veracruz to the east; Hidalgo, Querétaro and Guanajuato to the south; and Zacatecas to north-west. In addition to the capital city, other major cities in the state include Ciudad Valles, Matehuala, Rioverde, and Tamazunchale. History In pre-Columbian times, the territory now occupied by the state of San Luis Potosí contained parts of the cultural areas of Mesoamerica and Aridoamerica. Its northern and western-central areas were inhabited by the Otomi and Chichimeca tribes. These indigenous groups were nomadic hunter-gatherers. Although many indigenou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnohistory (journal)
''Ethnohistory'' is a peer-reviewed academic journal established in 1954 and published quarterly by Duke University Press Duke University Press is an academic publisher and university press affiliated with Duke University. It was founded in 1921 by William T. Laprade as The Trinity College Press. (Duke University was initially called Trinity College). In 1926 Du ... on behalf of the American Society for Ethnohistory. It publishes articles and reviews in the fields of ethnohistory, historical anthropology and social and cultural history. Like its sponsoring professional society, ''Ethnohistory'' has represented a meeting ground between scholars in the disciplines of history and anthropology. Geography and other disciplines have been increasingly represented in its pages over time. Founded by scholars focused primarily on studies of Native North America, the journal has, over its history, progressively become more global in scope. References Quarterly journals Publications ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |