List Of Ancient Cities In Dacia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Dacian and
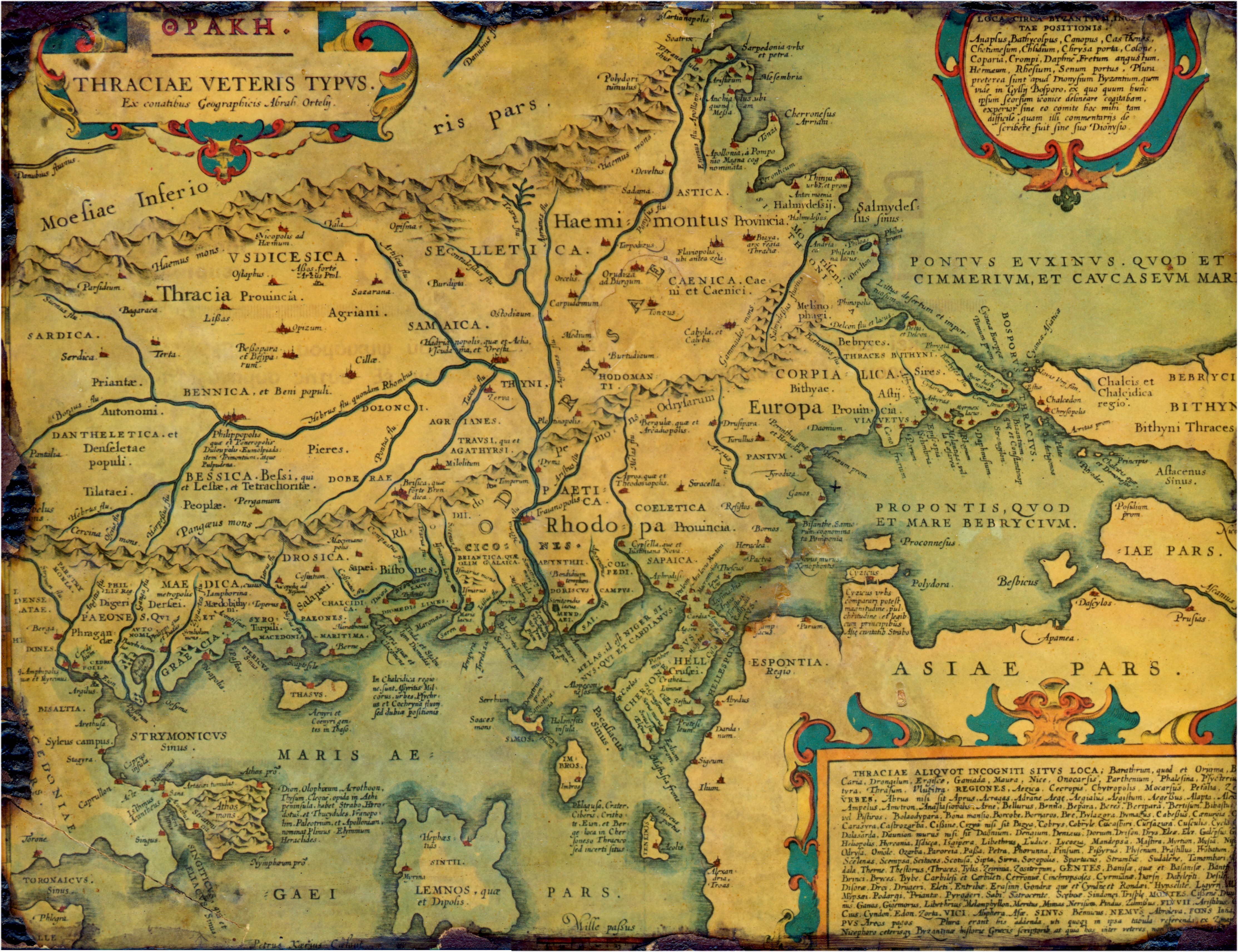
 * Abritus
*
* Abritus
*
Sorin Olteanu's Project: Linguae Thraco-Daco-Moesorum - Toponyms Section
Placenames in the Compilation 'notitia dignitatum' (Cnd)
Dacian Map
Thracians and Dacians
Thracians 700-46 BC
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ancient Cities in Thrace And Dacia Geography of ancient Thrace Ancient Thrace Celtic towns Thracian towns Greek colonies in Thrace Greek colonization Former populated places in the Balkans Archaeological sites in Romania Balkans-related lists
Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied t ...
, but some were Celt
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
ic, Greek, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
, Paeonian, or Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
.
A number of cities in Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus r ...
and Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to t ...
were built on or close to the sites of preexisting Dacian or Thracian settlements. Some settlements in this list may have a double entry, such as the Paeonian ''Astibo'' and Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
''Astibus''. It is believed that Thracians did not build true cities even if they were named as such; the largest Thracian settlements were large villages.The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond ,, 1992, page 612: "Thrace possessed only fortified areas and cities such as Cabassus would have been no more than large villages. In general the population lived in villages and hamlets..." The only known attempt to build a polis
''Polis'' (, ; grc-gre, πόλις, ), plural ''poleis'' (, , ), literally means "city" in Greek. In Ancient Greece, it originally referred to an administrative and religious city center, as distinct from the rest of the city. Later, it also ...
by the Thracians was Seuthopolis
Seuthopolis (Ancient Greek: Σευθόπολις) was an ancient hellenistic-type city founded by the Thracian king Seuthes III between 325–315 BC and the capital of the Odrysian kingdom.
Its ruins are now located at the bottom of the Koprinka ...
.,The Thracians 700 BC-AD 46 by Christopher Webber, , 2001, page 1, "...the city of Seuthopolis seems to be the only significant town in Thrace not built by Greeks..." although Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
considered the Thracian cities with "bria" ending polises. Some of the Dacian settlements and fortresses employed the traditional Murus Dacicus construction technique.
Note: Throughout these lists, an asterisk indicates that the toponym
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
is reconstructed.
Daco-Thracian
Many city names were composed of an initial lexical element affixed to ''-dava'', ''-daua'', ''-deva'', ''-deba'', ''-daba'', or ''-dova'', which meant "city" or "town" Endings on more southern regions are exclusively ''-bria'' ("town, city"), ''-disza'', ''-diza'', ''-dizos'' ("fortress, walled settlement"), ''-para'', ''-paron'', ''-pera'', ''-phara'' ("town, village").Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
translated -bria as polis, but that may not be accurate. Thracian ''-disza'', ''-diza'', and ''-dizos'' are derived from Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
''*dheigh-'', "to knead clay", hence to "make bricks", "build walls", "wall", "walls", and so on. These Thracian lexical items show a satemization
Languages of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European family are classified as either centum languages or satem languages according to how the dorsal consonants (sounds of "K", "G" and "Y" type) of the reconstructed Proto-Indo-European langu ...
of PIE
A pie is a baked dish which is usually made of a pastry dough casing that contains a filling of various sweet or savoury ingredients. Sweet pies may be filled with fruit (as in an apple pie), nuts ( pecan pie), brown sugar ( sugar pie), swe ...
''*gh-''. Cognates include Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic peri ...
''teichos'' ("wall, fort, fortified town", as in the town of Didymoteicho) and Avestan
Avestan (), or historically Zend, is an umbrella term for two Old Iranian languages: Old Avestan (spoken in the 2nd millennium BCE) and Younger Avestan (spoken in the 1st millennium BCE). They are known only from their conjoined use as the scrip ...
''da?za'' ("wall").
It is suggested that the "dava" endings are from the Dacian language, while the rest from the Thracian language
The Thracian language () is an extinct and poorly attested language, spoken in ancient times in Southeast Europe by the Thracians. The linguistic affinities of the Thracian language are poorly understood, but it is generally agreed that it was ...
. However "dava" towns can be found as south as Sandanski and Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the c ...
. Some "dava" toponyms contain the same linguistic features as "diza" toponyms, e.g. Pirodiza and Pirodava. The first written mention of the name "Dacians" is in Roman sources. Strabo specified that the Daci are the Getae, identified as a Thracian tribe. The Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often consid ...
, Getae
The Getae ( ) or Gets ( ; grc, Γέται, singular ) were a Thracian-related tribe that once inhabited the regions to either side of the Lower Danube, in what is today northern Bulgaria and southern Romania. Both the singular form ''Get'' an ...
and their kings were always considered as Thracians by the ancients (Dio Cassius, Trogus Pompeius, Appian, Strabo, Herodotus and Pliny the Elder) and were said to speak the same language. The Dacian language is considered a variety of the Thracian language
The Thracian language () is an extinct and poorly attested language, spoken in ancient times in Southeast Europe by the Thracians. The linguistic affinities of the Thracian language are poorly understood, but it is generally agreed that it was ...
. Such lexical differentiation -dava vs. para, would be hardly enough evidence to separate Dacian from Thracian, thus they are classified as dialects. It is also possible that '-dava' and '-bria' mean two different things in the same language, rather than meaning the same thing in two different languages. Thus bria could have been used for urbanized settlements, similar in scale and design to those of the "civilised" peoples like Greeks and Romans, whereas '-dava' could mean a settlement which is rural, being situated in the steppe-like part of the Thracian lands.
* Abydos Abydos may refer to:
*Abydos, a progressive metal side project of German singer Andy Kuntz
* Abydos (Hellespont), an ancient city in Mysia, Asia Minor
* Abydos (''Stargate''), name of a fictional planet in the '' Stargate'' science fiction universe ...
* Acidava
Acidava (''Acidaua'') was a Dacian and later Roman fortress on the Olt river near the lower Danube. The settlements remains are located in today's Enoşeşti, Olt County, Oltenia, Romania.
History
After the Roman conquest of Dacia by Roman Em ...
(''Acidaua''), a fortress town close to the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
, located in today's Piatra-Olt
Piatra-Olt is a town in Olt County, Oltenia, Romania. The town administers five villages: Bistrița Nouă, Criva de Jos, Criva de Sus, Enoșești and Piatra. The town is an important railway station and road intersection. It officially became a tow ...
, Olt County, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
* Acmonia
* Abdera
* Acatapara
* Aedava
Aedava (also known as Aedeva, Aedabe, Aedeba, Aedadeba) was a Dacian settlement located south of the Danube in Moesia (present-day northern Bulgaria). In his ''De Aedificiis'', the 6th century AD historian Procopius placed Aedava on the Danubian ...
(''Aedeva'', ''Aedabe'', ''Aedeba'' or ''Aedadeba''), placed by Procopius on the Danubian road
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
between Augustae and Variana, in Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
(the present Northern Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
)
* Aedeva
Aedava (also known as Aedeva, Aedabe, Aedeba, Aedadeba) was a Dacian settlement located south of the Danube in Moesia (present-day northern Bulgaria). In his ''De Aedificiis'', the 6th century AD historian Procopius placed Aedava on the Danubian ...
, modern Pernik
* Agatapara
* Ahypara
* Aiadava
Aiadava (''Aiadaba'' or ''Aeadaba'', gr, Αἰάδαβα) was a Dacian town in the Remesiana region, present day Bela Palanka, Serbia.
After the Romans conquered Moesia in the 75 BC, the new castrum (imperial domain with estates) and municip ...
(''Aiadaba'' or ''Aeadaba'', gr, Αἰάδαβα), a locality in the Remesiana region in present-day Bela Palanka, Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
* Aizis
Aizis (''Aixis'', ''Aixim'', ''Airzis'', ''Azizis'', ''Azisis'', ''Aizisis'', ''Alzisis'', ''Aigis'', ''Aigizidava ', ''Zizis'', grc, Αίζισίς) was a Dacian town mentioned by Emperor Trajan in his work ''Dacica''. Located at ''Dealul Ru ...
* Alaaibria (''Aixis'', ''Aixim'', ''Airzis'', ''Azizis'', ''Azisis'', ''Aizisis'', ''Alzisis'', ''Aigis'', ''Aigizidava*'', ''Zizis''), mentioned by Emperor Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
in Dacica
''Dacica'' (or ''De bello dacico'') is a Latin work by Roman Emperor Trajan, written in the spirit of Julius Caesar's commentaries like ''De Bello Gallico'', and describing Trajan's campaigns in Dacia.
It is assumed to be based on Criton of He ...
* Amutria
Amutria (''Amutrion'', ''Amutrium'', ''Admutrium'', ''Ad Mutrium'', ''Ad Mutriam'', grc, Ἀμούτριον) was a Dacian town close to the Danube and included in the Roman road network, after the conquest of Dacia.
The name is homonymous with ...
(''Amutrion'', ''Amutrium'', grc, Ἀμούτριον), a Dacian town close to the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
, possibly today's Motru
Motru () is a city in Romania, Gorj County. It is situated on the river Motru in western Oltenia. The county capital Târgu Jiu is located about 35 km northeast. The city administers eight villages: Dealu Pomilor, Horăști, Însurăței, ...
, Gorj County
Gorj County () is a county ( județ) of Romania, in Oltenia, with its capital city at Târgu Jiu. ''Gorj'' comes from the Slavic ''Gor(no)-'' Jiu (“upper Jiu”), in contrast with Dolj (“lower Jiu”).
Demographics
In 2011, the county had a ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
* Apulon
Apulon (''Apoulon'', ''Apula'') was a Dacian fortress city close to modern Alba Iulia, Romania. The Latin name of Apulum is derived. The exact location is believed by many archaeologists to be the Dacian fortifications on top of ''Piatra Craivi ...
(''Apoulon'', ''Apula''), a fortress city close to modern Alba-Iulia
Alba Iulia (; german: Karlsburg or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''Weißenburg''; hu, Gyulafehérvár; la, Apulum) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the Mureș River in the historical ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
from which the Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
name of Apulum is derived
* Arcina ('' Arcinna''), a fortress town in Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and so ...
* Apsynthus
* Arcobadara
Arcobara (previously identified as Arcobadara (''Arkobadara'', grc, Ἀρκοβάδαρα) Cristian Găzdac, Corneliu Gaiu, Elena Marchiş: "Arcobadara (Ilişua)", Ed. Mega Publishing House, Cluj-Napoca, 2011) was a Dacian town mentioned by Pt ...
* Argedava
Argedava (''Argedauon'', ''Sargedava'', ''Sargedauon'', ''Zargedava'', ''Zargedauon'', grc, Αργεδαυον, Σαργεδαυον) was an important Dacian town mentioned in the Decree of Dionysopolis (48 BC), and potentially located ...
(''Argedauon'', ''Sargedava'', ''Sargedauon'', ''Zargedava'', ''Zargedauon'', grc, Αργεδαυον, Σαργεδαυον), mentioned in the Decree of Dionysopolis The Decree of Dionysopolis was written around 48 BC by the citizens of Dionysupolis, Dionysopolis (today's Balchik, on the Black Sea coast of Bulgaria) to Akornion, who traveled far away in a diplomatic mission to meet somebody's farther in ''Argeda ...
, potentially the dava discovered at Popești, a district in the town of Mihăilești
Mihăilești is a town located in Giurgiu County, Muntenia, Romania. It administers three villages: Drăgănescu, Novaci and Popești. It officially became a town in 1989, as a result of the Romanian rural systematization program.
The town stand ...
, Giurgiu County
Giurgiu () is a county (''județ'') of Romania on the border with Bulgaria, in Muntenia, with the capital city at Giurgiu.
Demographics
In 2011, it had a population of 265,494 and the population density was .
* Romanians – over 96%
* Roman ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
and maybe Burebista
Burebista ( grc, Βυρεβίστας, Βοιρεβίστας) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area locat ...
's court or capital
* Argidava
Argidava (''Argidaua'', ''Arcidava'', ''Arcidaua'', ''Argedava'', ''Argedauon'', ''Argedabon'', ''Sargedava'', ''Sargedauon'', ''Zargedava'', ''Zargedauon'', grc, Ἀργίδαυα, Αργεδαυον, Αργεδαβον, Σαργεδαυον) ...
(''Argidaua'', ''Arcidava'', ''Arcidaua'', ''Argedava'', ''Argedauon'', ''Sargedava'', ''Sargedauon'', ''Zargedava'', ''Zargedauon'', grc, Ἀργίδαυα, Αργεδαυον, Σαργεδαυον), potentially Burebista
Burebista ( grc, Βυρεβίστας, Βοιρεβίστας) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area locat ...
's court or capital, located in today's Vărădia, Caraș-Severin County
Caraș-Severin () is a county ( județ) of Romania on the border with Serbia. The majority of its territory lies within the historical region of Banat, with a few northeastern villages considered part of Transylvania. The county seat is Reșița ...
, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
* Artanes, modern Lom
* Arutela
The Roman castra Arutela is a historical monument, situated between Paușa and Căciulata, near the town Călimănești. It is estimated to have been constructed between 137 – 138 A.D. The building lies on the left bank of the Olt River, ne ...
* Apulon
Apulon (''Apoulon'', ''Apula'') was a Dacian fortress city close to modern Alba Iulia, Romania. The Latin name of Apulum is derived. The exact location is believed by many archaeologists to be the Dacian fortifications on top of ''Piatra Craivi ...
* Atipara
Atipara is a village in Barisal District in the Barisal Division of southern-central Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the ...
* Authiparu
* Bergula
* Berzobis
Berzovia ( hu, Zsidovin) is a commune in Caraș-Severin County, Banat, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europ ...
, ancient Bârzava, Romania
* Bataldeua
* Bazopara
* Bediza
* Belaidipara
* Bendipara
* Beodiza
* Bergula, modern ( Luleburgaz)
* Beripara
* Beroea
Beroea (or Berea) was an ancient city of the Hellenistic period and Roman Empire now known as Veria (or Veroia) in Macedonia, Northern Greece. It is a small city on the eastern side of the Vermio Mountains north of Mount Olympus. The town is menti ...
, modern Stara Zagora
Stara Zagora ( bg, Стара Загора, ) is the sixth-largest city in Bulgaria, and the administrative capital of the homonymous Stara Zagora Province.
Name
The name comes from the Slavic root ''star'' ("old") and the name of the medieva ...
* Bessapara of the Bessi
The Bessi (; grc, Βῆσσοι, or , ) were a Thracian tribe that inhabited the upper valley of the Hebros and the lands between the Haemus and Rhodope mountain ranges in historical Thrace.
Geography
The exact geographic location of the Bes ...
tribe, today Sinitovo
* Bizye, capital of the Odrysae
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria and ...
* Bolbabria
* Bortudiza
* Bospara
* Bregedava
* Breierphara, near modern Komotini
Komotini ( el, Κομοτηνή, tr, Gümülcine, bg, Комотини) is a city in the region of East Macedonia and Thrace, northeastern Greece. It is the capital of the Rhodope. It was the administrative centre of the Rhodope-Evros super-pr ...
* Brentopara
* Briparon
* Buatpara
* Buricodava
Buricodava was a Dacian town.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
* Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fertile/Happy Dacia') was a Roman province, provinc ...
* Buridava
Buridava (''Burridava'') was a Dacian town. situated in Dacia, later Dacia Apulensis, now Romania, on the banks of the river Aluta, now Olt.
Ancient sources
Ptolemy's Geographia
Tabula Peutingeriana
Etymology
The name is Geto- ...
(''Burridava
Buridava (''Burridava'') was a Dacian town. situated in Dacia, later Dacia Apulensis, now Romania, on the banks of the river Aluta, now Olt.
Ancient sources
Ptolemy's Geographia
Tabula Peutingeriana
Etymology
The name is Geto- ...
''), today's Ocnele Mari
Ocnele Mari is a town located in Vâlcea County, Oltenia, Romania. The town administers eight villages: Buda, Cosota, Făcăi, Gura Suhașului, Lunca, Ocnița, Slătioarele, and Țeica.
The town is situated in the central part of the county, at ...
, Romania
* Burtudiza
* Busipara
* Buteridava
Buteridava was a Dacian town.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black ...
* Cabassus
* Capidava
Capidava (''Kapidaua'', ''Cappidava'', ''Capidapa'', ''Calidava'', ''Calidaua'') was an important Geto-Dacian center on the right bank of the Danube. After the Roman conquest, it became a civil and military center, as part of the province of ...
('' Kapidaua''), a fortress town on the southern side of the lower Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
* Caria
Caria (; from Greek: Καρία, ''Karia''; tr, Karya) was a region of western Anatolia extending along the coast from mid-Ionia (Mycale) south to Lycia and east to Phrygia. The Ionians, Ionian and Dorians, Dorian Greeks colonized the west of i ...
, modern Shabla
* Carsidava
Carsidava ( grc, Καρσίδαυα) was a Dacian town. Recent research placed Carsidava near Soroca town in MoldovaVasile Itaiuc, Descoperirea fortificatiei antice Carsidava la marginea orasului Soroca. International Conference "Cultural research" ...
or Karsidaua
* Cedonia
Sibiu ( , , german: link=no, Hermannstadt , la, Cibinium, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Härmeschtat'', hu, Nagyszeben ) is a city in Romania, in the historical region of Transylvania. Located some north-west of Bucharest, the city straddles the Cib ...
, near Sibiu
Sibiu ( , , german: link=no, Hermannstadt , la, Cibinium, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Härmeschtat'', hu, Nagyszeben ) is a city in Romania, in the historical region of Transylvania. Located some north-west of Bucharest, the city straddles the Ci ...
* Chesdupara
* Cleipadava
* Crenides
* Cumidava
Cumidava (also Comidava, Komidava, grc, Κομίδαυα) was originally a Dacian settlement, and later a Roman military camp on the site of the modern city of Râşnov (15 km from Braşov) in Romania.
Etymology
After the Roman conquest ...
(''Comidava
Cumidava (also Comidava, Komidava, grc, Κομίδαυα) was originally a Dacian settlement, and later a Roman military camp on the site of the modern city of Râşnov (15 km from Braşov) in Romania.
Etymology
After the Roman conquest ...
'', '' Komidaua''), ancient Râșnov, Romania
* Cumlideva
* Cypasis
Cypasis or Kypasis ( grc, Κύπασις) was an Emporium of the Cardia, on the east of the Hebrus River, on the Bay of Melas.
Its site is located north of the mouth of the Kavak River in European Turkey
East Thrace or Eastern Thrace ( t ...
* Danedebai
Danedevae (''Danedebai'', grc, Δανεδέβαι) was a Dacian town.
Ancient sources
Ptolemy's Geographia
Tabula Peutingeriana
Etymology
History
Dacian town
Roman times
Archaeology
See also
* Dacian davae
* ...
,
* Dausdava ('' Dausadava'', '' Dausdavua''), "The shrine of wolves", a fortress town close to the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
* Debelt
Debelt (Bulgarian: Дебелт) is a village in Burgas Province in southeastern Bulgaria. It is located in the municipality of Sredets.
History
Debelt is located near the ruins of the city of Develtos. During the Russo-Turkish War of 1828-1829, ...
* Dentheletica, capital of the Dentheletae tribe, modern Kyustendil
* Desudaba or Maedius of the Maedi tribe, modern Sandanski
* Diacum
* Dierna
* Dinogetia
Dinogetia was an ancient Geto-Dacian settlement and later Roman fortress located on the right (southern) bank of the Danube near the place where it joins the Siret. The Dinogetia site is situated in Northern Dobruja 8 kilometres east of Galați ...
, located above the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
delta
* Docidava
Docidava (''Dokidava'', ''Dakidawa''?, grc, Δοκίδαυα) was a Dacian town in north-western Roman Dacia.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
* Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as D ...
or Dokidaua
* Dodopara
* Drabeskos Draviskos ( el, Δραβήσκος) is a village in Serres regional unit, located 45 km southeast of the city of Serres. Since 2011 it is a municipal unit of the Municipality of Nea Zichni. Until 1926 it was named "Zdravik".
History Antiquity
...
* Drobeta
''Drobeta'' is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker (entomologist), Francis Walker in 1858.
Species
* ''Drobeta albicauda'' (Hampson, 1910)
* ''Drobeta albirufa'' (Druce, 1909)
* ''Drobeta andrevia'' ...
, located on the left bank of the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
at Turnu Severin
Drobeta-Turnu Severin (), colloquially Severin, is a city in Mehedinți County, Oltenia, Romania, on the northern bank of the Danube, close to the Iron Gates. "Drobeta" is the name of the ancient Dacian and Roman towns at the site, and the modern ...
* Drusipara
Drizipara (or ''Druzipara, Drousipara. Drusipara'') now Büyükkarıştıran (Büyükkarıştıran) in Lüleburgaz district was a city and a residential episcopal see in the Roman province of Europa in the civil diocese of Thrace. It is now a tit ...
* Egeta
* Ergines
* Eumolpias, later Pulpudeva
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the ...
translating ''Philippopolis'', the name resulted in modern Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the c ...
, prehistoric settlement
* Gatae
The Battle of Gatae was an engagement fought in roughly 103 AD during the Roman Emperor Trajan's war with the kingdom of Dacia.
There is no serious historical evidence giving an exact place or time to the battle, nor any troop positions, numeric ...
* Gazoros Gazoros or Gazorus (Greek: ) was a town mentioned by Ptolemy to be in the region of Edonis or Odomantike and also by inscriptions of Hellenistic and Roman times. Later in the 4th century BC, it was annexed to the Macedonian kingdom and made a polis ...
* Gellipara
* Genucla Genucla is the name of an ancient fortress of the Getae, located on the riverbank of the Danube or on an island on the river. It is mentioned by Dio Cassius in his ''History of Rome'' (''Historia Romana''), in Book LI (51), chapter 26. The author ...
, settlement located south of the Danube
* Germania
Germania ( ; ), also called Magna Germania (English: ''Great Germania''), Germania Libera (English: ''Free Germania''), or Germanic Barbaricum to distinguish it from the Roman province of the same name, was a large historical region in north- ...
, "hot water", modern Sapareva Banya, site of the Dentheletae tribe
* Germisara "hot water"
* Gildova
Gildava (''Gildoba'', ''Gildova'', grc, Γιλδαβα) was a Dacian town.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
* Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fe ...
(''Gildoba
Gildava (''Gildoba'', ''Gildova'', grc, Γιλδαβα) was a Dacian town.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
* Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, 'Fe ...
''), located along the Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
river
* Giridava
Giridava (''Giridaua'', ''Geridava'') was a Dacian town, situated in Moesia, modern northern Bulgaria.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its ...
* Hesdupara
* Iamphorynna Iamphorina or Iamphorynna was the capital of the Maedi, a Thracian tribe in ancient Macedonia. It was taken by Philip V of Macedon in 211 BCE. Writing in the 19th century, William Martin Leake placed it at Ivorina (Vrania), in the upper valley ...
, capital of the Maedi tribe
* Itadeba ('' Itadava'')
* Isgipara
* Ismara
Ismarus or Ismaros ( grc, Ἴσμαρος) was a city of the Cicones, in ancient Thrace, mentioned by Homer in the ''Odyssey''.
Homeric Ismarus
After their departure from Troy, Odysseus and his companions stop at Ismaros. They sack the town, and ...
* Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the larges ...
(Olbia
Olbia (, ; sc, Terranoa; sdn, Tarranoa) is a city and commune of 60,346 inhabitants (May 2018) in the Italian insular province of Sassari in northeastern Sardinia, Italy, in the historical region of Gallura. Called ''Olbia'' in the Roman age, ...
)
* Jidava
Jidava was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia.
Since 1969, the site has been administered by the Argeș County Museum.''Enciclopedia Argeșului și Muscelului'' site, p. 123
Gallery
File:Jidava - Plan.svg, The plan of the castrum
File:Castru ...
, near Câmpulung Muscel
Câmpulung (also spelled ''Cîmpulung'', , german: Langenau, Old Romanian ''Dlăgopole'', ''Длъгополе'' (from Middle Bulgarian)), or ''Câmpulung Muscel'', is a municipality in the Argeș County, Muntenia, Romania. It is situated amon ...
, Romania
* Jidova
* Kabyle of the Kabileti tribe, capital of the Odrysae
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria and ...
* Keliadeva
* Keirpara
* Keriparon
* Kipsela, modern Ipsala
* Kirpiza
* Kistidiza
* Klepidaua
* Krabnopara
* Krasalopara
* Kuimedaba
* Longinopara
* Lygos, modern Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
* Malva
''Malva'' is a genus of herbaceous annual, biennial, and perennial plants in the family Malvaceae. It is one of several closely related genera in the family to bear the common English name mallow. The genus is widespread throughout the temper ...
, a Dacian settlement where Roman Romula
Romula or Malva was an ancient city in Roman Dacia, later the village of Reşca, Dobrosloveni Commune, Olt County, Romania. It was the capital of Dacia Malvensis, one of the three subdivisions of the province of Dacia.
History
The Roman ci ...
was built
* Marcodava (Dacia)
Marcodava ( grc, Μαρκόδαυα) was a Dacian town, north-west of Apulon.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, ...
('' Markodaua'')
* Maskiobria
* Melsambria, modern Nessebar
Nesebar (often transcribed as Nessebar and sometimes as Nesebur, bg, Несебър, pronounced ) is an ancient city and one of the major seaside resorts on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast, located in Burgas Province. It is the administrative centr ...
* Melta, modern Lovech
* Murideba
Murideva (''Murideba'', grc, Μουριδεβά) was a Dacian town in Scythia Minor, not far from Zaldapa.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
* Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia ...
* Mutzipara* Napoca, ancient Cluj-Napoca
; hu, kincses város)
, official_name=Cluj-Napoca
, native_name=
, image_skyline=
, subdivision_type1 = Counties of Romania, County
, subdivision_name1 = Cluj County
, subdivision_type2 = Subdivisions of Romania, Status
, subdivision_name2 ...
, Romania
* Naulochas, modern Obzor
Obzor ( bg, Обзор ) is a small town and seaside resort on the Black Sea coast of Bulgaria. It is part of Nesebar Municipality, Burgas Province. On February 28th, 2021, the citizens of Obzor and six nearby villages voted in a referendum to sepa ...
* Nentinava ('' Netindaua''), ancient Slobozia, Romania
* Nentivava, ancient Olteniţa, Romania
* Netindava
* Nipsa near Panisus
* Oescus
Oescus, Palatiolon or Palatiolum ( bg, Улпия Ескус, ) was an important ancient city on the Danube river in Roman Moesia. It later became known as ''Ulpia Oescus''. It lay northwest of the modern Bulgarian city of Pleven, near the v ...
of the Triballi
The Triballi ( grc, Τριβαλλοί, Triballoí, lat, Triballi) were an ancient people who lived in northern Bulgaria in the region of Roman Oescus up to southeastern Serbia, possibly near the territory of the Morava Valley in the late Iron A ...
tribe
* Odryssa or Uscudama
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
, modern Edirne, capital of the Odrysae
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria and ...
or Bessi
The Bessi (; grc, Βῆσσοι, or , ) were a Thracian tribe that inhabited the upper valley of the Hebros and the lands between the Haemus and Rhodope mountain ranges in historical Thrace.
Geography
The exact geographic location of the Bes ...
tribe
* Onokarsis, capital residence of the Odrysae
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria and ...
, possibly modern Starosel
Starosel ( bg, Старосел) is a village in central Bulgaria, Hisarya Municipality, Plovdiv Province. It lies at the foot of the Sredna Gora mountain range along the shores of Pyasachnik River.
Starosel is known for the abundance of ...
* Orsudisza
* Ostudiza
* Patridava ('' Patridaua'')
* Patruissa
* Pelendava ('' Pelendova''), ancient Craiova
Craiova (, also , ), is Romania's 6th Cities in Romania, largest city and capital of Dolj County, and situated near the east bank of the river Jiu River, Jiu in central Oltenia. It is a longstanding political center, and is located at approximatel ...
, Romania
* Perburidava
Perburidava was a Dacian town.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Bl ...
* Perperikon
* Pinon
* Piroboridava
Piroboridava ( grc, Πιροβορίδαυα) was a Dacian town mentioned by Ptolemy, and archaeologically identified at Poiana, Galați, Romania. Second part name of the city Dacian dava shows significance of the tribal city.
See also
* D ...
* Petra
Petra ( ar, ٱلْبَتْرَاء, Al-Batrāʾ; grc, Πέτρα, "Rock", Nabataean Aramaic, Nabataean: ), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu or Raqēmō, is an historic and archaeological city in southern Jordan. It is adjacent to t ...
, fort of Maedi
* Petrodava ('' Petrodaua''), located in Piatra Neamț
Piatra Neamț (; german: Kreuzburg an der Bistrița (Siret), Bistritz; hu, Karácsonkő) is the capital city of Neamț County, in the historical region of Western Moldavia, in northeastern Romania. Because of its privileged location in the Easter ...
* Piroboridava
Piroboridava ( grc, Πιροβορίδαυα) was a Dacian town mentioned by Ptolemy, and archaeologically identified at Poiana, Galați, Romania. Second part name of the city Dacian dava shows significance of the tribal city.
See also
* D ...
(''Piroboridaua'')
* Pizos
* Polondava
Polondava (''Polonda'', grc, Πολόνδα, Πάλοδα) was a Dacian town, north of Dinogetia.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
* Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ...
* Polymbria
* Potaissa
Turda (; hu, Torda, ; german: link=no, Thorenburg; la, Potaissa) is a city in Cluj County, Transylvania, Romania. It is located in the southeastern part of the county, from the county seat, Cluj-Napoca, to which it is connected by the Europ ...
(''Patavissa''), ancient Turda, Romania
* Predava
* Priskupera
* Quemedava
Quemedava was an ancient Dacian city in Dardania mentioned by Procopius.Ethnic continuity in the Carpatho-Danubian area by Elemér Illyés,1988,,p. 223
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Illyria
* List of ancient cities in Thr ...
, mentioned by Procopius in DardaniaEthnic continuity in the Carpatho-Danubian area by Elemér Illyés, 1988, , page 223
* Ramidava
Ramidava ( grc, Ραμίδαυα) was a Dacian town.
See also
* Dava (Dacian), Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
* Roman Dacia
References
Ancient
*
Modern
*
Further reading
Dacian tow ...
(''Rhamidaua'')
* Ratiaria
* Recidava
* Remesiana
* Romboses
* Rusidava
Rusidava (or Zusidava) was a Dacian town mentioned in Tabula Peutingeriana between Acidava and Pons Aluti, today's Drăgășani, Vâlcea County, Romania.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
* Roman Da ...
(''Rusidava
Rusidava (or Zusidava) was a Dacian town mentioned in Tabula Peutingeriana between Acidava and Pons Aluti, today's Drăgășani, Vâlcea County, Romania.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
* Roman Da ...
'')
* Ruconium
* Sacidava ('' Sacidaba'')
* Sagadava
* Salmydessos
Salmydessus or Salmydessos ( grc, Σαλμυδησσός), also Halmydessus or Halmydessos (Ἁλμυδισσός), was a coast-town of ancient Thrace, on the Euxine, about northwest of the entrance of the Bosporus. The eastern offshoots of the Ha ...
, modern Kıyıköy
Kıyıköy, formerly Midye, ancient/medieval Medea ( bg, Мидия, el, Μήδεια), is a small town on the Black Sea coast in the district of Vize in Kırklareli Province in northwestern Turkey. It is from Vize and away from Kırklareli. ...
, residence of the Odrysae
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria and ...
* Sandava
''Sandava'' is a genus of moths of the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker in 1863.
Species
*''Sandava micrastigma'' (Kaye, 1901) Trinidad
*''Sandava scitisignata
''Sandava scitisignata'', the fungi snout, is a moth of t ...
* Sangidaua
* Sarmizegetusa (''Sarmisegetuza
Sarmizegetusa Regia, also Sarmisegetusa, Sarmisegethusa, Sarmisegethuza, Ζαρμιζεγεθούσα (''Zarmizegethoúsa'') or Ζερμιζεγεθούση (''Zermizegethoúsē''), was the capital and the most important military, religious and ...
''), Decebalus's capital and holy place
* Scaidava
Scaidava ( grc, Σκεδεβά) was a Dacian town between Iatrus and Trimammium ( Ablanovo).
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
* Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; o ...
('' Skedeba'')
* Scaptopara, of the Dentheletae tribe, modern Blagoevgrad
* Scaripara
* Scedabria
* Scelabria
* Scept
* Selymbria
Selymbria ( gr, Σηλυμβρία),Demosthenes, '' de Rhod. lib.'', p. 198, ed. Reiske. or Selybria (Σηλυβρία), or Selybrie (Σηλυβρίη), was a town of ancient Thrace on the Propontis, 22 Roman miles east from Perinthus, and 44 Roman ...
, modern Silivri
Silivri, formerly Selymbria (Greek: Σηλυμβρία), is a city and a district in Istanbul Province along the Sea of Marmara in Turkey, outside the urban core of Istanbul, containing many holiday and weekend homes for residents of the city. The ...
in European TurkeyAn Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 465: "Megara was principal or sole founder of...Kalchedo...Selymbria...Byzantion...Astakos...Herakleia pontike and possible Olbia..."
* Serdica
Serdika or Serdica (Bulgarian: ) is the historical Roman name of Sofia, now the capital of Bulgaria.
Currently, Serdika is the name of a district located in the city. It includes four neighbourhoods: "Fondovi zhilishta"; "Banishora", "Orlandovts ...
of the Serdi tribe, modern Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and ha ...
* Setidava Setidava, mentioned by Ptolemy in his Geography, was a Dacian outpost in north central Europe. This town, with the typical Dacian location name ending of ''- dava'', was mentioned in Ptolemy's Germania, who placed it north of Calisia (''Kalisia'') ...
('' Setidaua''), mentioned by Ptolemy as a thriving settlement
* Seuthopolis
Seuthopolis (Ancient Greek: Σευθόπολις) was an ancient hellenistic-type city founded by the Thracian king Seuthes III between 325–315 BC and the capital of the Odrysian kingdom.
Its ruins are now located at the bottom of the Koprinka ...
* Singidava ('' Singidaua'')
* Sintica of the Sintoi
The Sintians (; grc-gre, Σίντιες), "the Raiders, the Plunderers", from Ancient Greek ''sinteis'', "destructive") were known to the Greeks as pirates and raiders; they are also referred to as a Thracian people who once inhabited the area ...
tribe
* Skaripara
* Skaskopara
* Spinopara
* Stratopara
* Strupil
* Subzupara
* Sucidava ('' Suvidava'', '' Sukidaua''), located in Corabia
Corabia () is a small Danube port located in Olt County, Oltenia, Romania, which used to be part of the now-dissolved Romanați County before World War II. Across the Danube from Corabia lies the Bulgarian village of Gigen.
History
Beneath Co ...
, Olt County, Romania
* Susudava, mentioned by Ptolemy as a thriving settlement
* Sykidaba
* Tamasidava
Tamasidava ( grc, Ταμασίδαυα) was a Dacian town mentioned by Ptolemy.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
* Roman Dacia
Roman Dacia ( ; also known as Dacia Traiana, ; or Dacia Felix, ' ...
('' Tamasidaua'')
* Tarpodiza
* Tapae
Tapae was a fortified settlement, guarding Sarmizegetusa, the main political centre of Dacia. Its location was on the Iron Gates of Transylvania, a natural passage breaking between Țarcului and Poiana Ruscă Mountains and connecting Banat to Ț ...
, a Dacian outpost guarding Sarmisegetuza and the site of two major battles between Dacians and Romans
* Teichos
Teichus or Teichos ( grc, Τεῖχος), also known as Teichus/Teichos of the Dymaeans ( grc, Τεῖχος Δυμαίων, Teichos Dymaion), was a fortified settlement in the territory of Dyme, in ancient Achaea, near the promontory Araxus, which ...
, residence of the Odryssae
* Therma of the Mygdones tribe, modern Thessaloniki
Thessaloniki (; el, Θεσσαλονίκη, , also known as Thessalonica (), Saloniki, or Salonica (), is the second-largest city in Greece, with over one million inhabitants in its Thessaloniki metropolitan area, metropolitan area, and the capi ...
*Thermidava Thermidava is a toponym used by Ptolemy in relation to a settlement in the route of the Roman army during the Dacian campaign (101-106 CE) of Emperor Trajan. In the context of Ptolemy's narrative the settlement was located along the Lissus- Naissus ...
, placed by Ptolemy on the Lissus Lissus or Lissos ( el, Λίσσος) could be:
* Lissus (Crete), an ancient Greek city in Crete
* Lissos (Illyria), an ancient city in Illyria, the present day city of Lezhë in Albania
* Lissus, a river in Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη ...
- Naissus route. The toponym is most probably a misreading of a settlement which most scholars in contemporary research locate near present-day Banat
Banat (, ; hu, Bánság; sr, Банат, Banat) is a geographical and historical region that straddles Central and Eastern Europe and which is currently divided among three countries: the eastern part lies in western Romania (the counties of T ...
, Serbia.
* Thynia
In the ancient world, Thynia (, el, Θυνία) was a region of Europe along the northern coast of the Propontis, opposite Bithynia on the Asian side.W.H.Race, ''Apollonius Rhodius: Argonautica'', Loeb Classical Library (2008), introductory maps ...
, town of the Thyni
The Thyni ( el, Θυνοί) were a Thracian tribe that lived in south-eastern Thrace. The Thyni were closely related to the Bithynians, with whom they often exchanged troops and royal marriages, later a section of the Thyni, along with the Bithyni ...
* Tibiscum
Tibiscum (''Tibisco'', ''Tibiscus'', ''Tibiskon'') was a Dacian town mentioned by Ptolemy, later a Roman castra and municipium. The ruins of the ancient settlement are located in Jupa, Caraș-Severin County, Romania.
See also
* Dacian dav ...
* Tirista
''Tirista'' is a genus of moths in the family Sesiidae.
Species
*'' Tirista argentifrons'' Walker, 865
__NOTOC__
Year 865 ( DCCCLXV) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Event ...
('' Tsirista'')
* Tranopara
* Tranupara
* Tsgipera
* Tsierna ('' Dierna'')
* Tyrida
Tirida, also known as Stabulum Diomedis or Stabulo Diomedis (both Latin for 'Diomedes's stable'), was a town of ancient Thrace. Pliny the Elder writes "Oppidum fuit Tirida, Diomedis equorum stabulis dirum." This Diomedes was the king of the Biston ...
* Tyrodiza
Tyrodiza ( grc, Τυρόδιζα) was a Greek city in ancient Thrace, located in the region of the Propontis. It appears to have flourished between 550 BCE and 330 BCE, and is identified with the place called Tiristasis (Τειρίστα� ...
* Urdoviza, modern Kiten
* Utidava ('' Utidaua'')
* Zalcdaba
* Zaldapa
Zaldapa (''Zeldepa'', grc, Ζάλδαπα, Ζέλδεπα) was a large Late Roman fortified city in Scythia Minor/Moesia, located near today's Abrit, Bulgaria.
It was originally an ancient Thracian settlement from around the 8th century BC. The ...
* Zargidava
Zargidava ( grc, Ζαργίδαυα) was a Dacian town mentioned by Ptolemy.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, ...
('' Zargidaua'')
* Zburulus
* Sarmicegetusa
* Zeugma
* Zesutera
* Zidava
Zidava was a Dacian fortified town in present-day Alba County, in the Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the ...
* Zikideva Zicídeva ( el, Ζικίδεβα) was an Early Byzantine town, tentatively identified with the late antique settlement excavated on the top of Tsarevets hill, near modern Veliko Tarnovo in northern Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, Българи ...
* Zimnicea
Zimnicea () is a town in Teleorman County, Romania (in the historic region of Muntenia), a port on the Danube opposite the Bulgarian city of Svishtov.
Geography
Zimnicea is situated on the left bank of the Danube river. It is the southernmost pla ...
, site where Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, wikt:Ἀλέξανδρος, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the Ancient Greece, ancient Greek kingdom of Maced ...
fought the Dacians
* Ziridava
Ziridava (''Ziridaua'', grc, italic=yes, Ζιρίδαυα) was a Dacian town located between Apulon and Tibiscum, mentioned by Ptolemy in the area of the Dacian tribe of Biephi (today's Romania, Banat region).
Ancient sources Ptolemy's ' ...
(''Ziridaua''), identified archaeologically with Pecica, Arad, Romania
* Zirmai
* Zisnudeba
* Zisnedeva ('' Zisnudeva'', '' Zisnudeba''), located in Dacian Moesia
Moesia (; Latin: ''Moesia''; el, Μοισία, Moisía) was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans south of the Danube River, which included most of the territory of modern eastern Serbia, Kosovo, north-eastern Alban ...
* Zucidaua
* Zurobara
Zurobara ( grc, italic=yes, Ζουρόβαρα) was a Dacian town located in the northwest of today's Romanian Banat. It was positioned by the Tibiscus (Timiș) river, north of Sarmizegetusa Regia and south of Ziridava.
This town was attested ...
* Zusidava

Unknown names
:Aghireșu
Aghireșu ( hu, Egeres; german: Erldorf) is a commune in Cluj County, Transylvania, Romania.
The commune has an area of 105.79 km2 and a population of 7156 people (2007). It is composed of eleven villages: Aghireșu, Aghireșu-Fabrici (''E ...
: Ardan
: Ardeu
: Arpașu de Sus
: Augustin
: Băile Tușnad
: Băleni-Români
: Bănița
Bănița ( hu, Banica, german: Bansdorf) is a commune in Hunedoara County, Transylvania, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the ...
: Bâzdâna
: Beidaud
Beidaud is a commune in Tulcea County, Northern Dobruja, Romania.
The commune includes three villages:
* Beidaud
* Neatârnarea (''Caildere'' until 1908)
* Sarighiol de Deal
The commune's name is of Turkish origin, being a compound of the words ...
: Bocșa
: Boroșneu Mic
: Boșorod
Boșorod ( hu, Bosoród, german: Bosendorf) is a commune in Hunedoara County, Transylvania, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe ...
: Botfei
: Breaza
: Bretea Mureșană
Ilia ( hu, Marosillye, german: Elienmarkt) is a commune in Hunedoara County, Romania. The commune lies in the historical province of Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural ...
: Bucium
The ''bucium'' (, also called ''trâmbiţă'' or ''tulnic'') is a type of alphorn used by mountain dwellers and by shepherds in Romania and Moldova. The word is derived from Latin '' bucinum'', originally meaning "curved horn", an instrument ...
: Căpâlna
Căpâlna ( hu, Feketekápolna) is a commune in Bihor County, Crișana, Romania with a population of 1,663 people (2011). It is composed of five villages: Căpâlna, Ginta (''Gyanta''), Rohani (''Rohány''), Săldăbagiu Mic (''Körösszáldobág ...
: Cernat
: Cetățeni
Cetățeni is a commune in Argeș County, Muntenia, Romania. It is composed of three villages: Cetățeni, Lăicăi, and Valea Cetățuia.
The commune is situated at a distance of from Pitești and from Câmpulung, right next to Dâmbovița Coun ...
: Cioclovina
: Clopotiva
: "Costești-Blidaru"
: "Costești-Cetățuie"
: Cotnari
Cotnari () is a village and the center of the eponymous commune in Iași County, Romania, in the historical region of Western Moldavia. It is located north-west of Iași and south of Hârlău, in a major wine-producing region of Romania, and is fa ...
: Coțofenii din Dos
Coțofenii din Dos is a commune in Dolj County, Oltenia, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders B ...
: Covasna
Covasna (, hu, Kovászna, , german: Kowasna) is a town in Covasna County, Transylvania, Romania, at an altitude of . It is known for its natural mineral waters and mofettas.
The town administers one village, Chiuruș ( hu, Csomakőrös). The ...
: Cozia
: Crăsanii de Jos
: Crivești
: Crizbav
Crizbav ( hu, Krizba, german: Krebsbach) is a commune in Brașov County, Transylvania, Romania. It is composed of two villages, Crizbav and Cutuș (''Kutastelep'').
At the 2011 census, 83.1% of inhabitants were Romanians and 16.1% Hungarians.
...
: Cuciulata
Hoghiz (german: Warmwasser; hu, Hévíz or ''Olthévíz'') is a commune in Brașov County, Transylvania, Romania. It is composed of six villages: Bogata Olteană (''Oltbogát''), Cuciulata (''Katscheloden''; ''Kucsuláta''), Dopca (''Dopich''; '' ...
: "Cucuiș - Dealul Golu"
: "Cucuiș - Vârful Berianului"
: Cugir
Cugir (; German: ''Kudsir, Kudschir'', Hungarian: ''Kudzsir'') is a town in Alba County, Romania. Declared a town in 1968, it administers seven villages: Bocșitura (Hungarian ''Boksiturahavas'', German ''Potschitur''), Bucuru (''Bukuruhavas''/' ...
: Cârlomănești
: Dalboșeț
Dalboșeț ( hu, Dalbosec) is a commune in Caraș-Severin County, western Romania with a population of 1,919 people. It is composed of seven villages: Bârz, Boina, Boinița, Dalboșeț, Prislop, Reșița Mică (''Kisresica'') and Șopotu Vechi (' ...
: Densuș
Densuș ( hu, Demsus, german: Demsdorf) is a commune in Hunedoara County, Transylvania, Romania and the site of Densuș Church. It is composed of seven villages: Criva, Densuș, Hățăgel (''Hacazsel''), Peșteana (''Nagypestény''), Peștenița ( ...
: Divici
: Drajna de Sus
: Dumitrița
Dumitrița (german: Waltersdorf; hu, Kisdemeter) is a commune in Bistrița-Năsăud County, Transylvania, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and ...
: Eliseni
: Feldioara
Feldioara (german: Marienburg, ; hu, Földvár or ''Barcaföldvár'') is a commune in Brașov County, Transylvania, Romania, about 15 kilometres from the city of Brașov. It is composed of three villages: Colonia Reconstrucția (''Bohntelep''), ...
: "Fețele Albe"
: Grădiștea de Munte
: Iedera de Jos
: Feleac
: Jigodin
Miercurea Ciuc (; hu, Csíkszereda, ; german: Szeklerburg) is the county seat of Harghita County, Romania. It lies in the Székely Land, a mainly Hungarian-speaking ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania, and is situated in the Olt Rive ...
: Liubcova
Berzasca ( hu, Berszászka, german: Bersaska, sr, Берзаска ''Berzaska'') is a commune in Caraș-Severin County, in the Banat region of western Romania with a population of 3,123 people. It is composed of five villages: Berzasca, Bigăr, ...
: Mala Kopania
Mala may refer to:
Comics
* Mala (Amazon), an Amazon from Wonder Woman's side of the DC Universe
* Mala (Kryptonian), a villain from Superman's corner of the DC Universe
Films and television
* ''Mala'' (1941 film), a Bollywood drama film
* , a ...
: Marca Marca may refer to:
Places
* Marca, Sălaj, a commune in Sălaj County, Romania
* Marca, a tributary of the Barcău in Sălaj County, Romania
* an alternative name for Merca, Somalia
* Marca District, in the province Recuay, Peru
* Marçà, a vil ...
: Mataraua
Belciugatele is a commune in Călărași County, Muntenia, Romania. It is composed of five villages: Belciugatele, Cândeasca, Cojești, Mataraua and Măriuța.
As of 2007 the population of Belciugatele is 1,878.
The ruins of a Dacian fortress
...
: Merești
Merești ( or colloquially ''Almás'', Hungarian pronunciation:, meaning "Place of Apples on the Homorod") is a commune in Harghita County, Romania. It lies in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania. It is composed o ...
: Moinești
: Monariu
Budacu de Jos (german: Deutsch-Budak; hu, Szászbudak) is a commune in Bistrița-Năsăud County, Transylvania, Romania. It is composed of five villages: Budacu de Jos, Buduș (''Alsóbudak'';''Budesdorf''), Jelna (''Kiszsolna''; ''Senndorf''), Mo ...
: Monor
Monor is a town in Pest county, Hungary. It is situated immediately southeast of Üllő municipality and Ferenc Liszt International Airport - southeast of Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It ...
: Moșna
: Ocolișu Mic
: Odorheiu Secuiesc
: Olteni
Olteni is a commune in Teleorman County, Muntenia, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgar ...
: Orăștie Mountains
Orăștie (; german: link=no, Broos, hu, Szászváros, la, Saxopolis) is a city in Hunedoara County, south-western Transylvania, central Romania.
History
7th–9th century – On the site of an old swamp was a human settlement, now ...
: Petrila
: Petroșani
: "Piatra Roșie"
: Pietroasa Mică
: Pinticu
Teaca (german: Tekendorf,Tekendorf in Nordsiebenbürgen : Ortsmonographie; Ilse Schliessleder-Fronius, 1989 hu, Teke) is a commune in Bistrița-Năsăud County, Transylvania, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the ...
: Pisculești
Tinosu is a communes of Romania, commune in Prahova County, Muntenia, Romania. It is composed of three villages: Predești, Pisculești, and Tinosu.
The Tinosu (archaeological site), ruins of a Dacian fortified town is located near the villages of ...
: Poiana cu Cetate
Grajduri is a commune in Iași County, Western Moldavia, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hunga ...
: Polovragi
Polovragi is a commune in Gorj County, Oltenia, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to th ...
: Ponor
: Popești (Călărași)
: Porumbenii Mari
Porumbeni ( hu, Nagygalambfalva ) is a commune in Harghita County, Romania. It lies in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania, and is composed of two villages, Porumbenii Mari (the commune center; ''Nagygalambfalva'') ...
: Praid
: Racoș
Racoș (also ''Racoșul de Jos''; german: Unter-Krebsdorf; hu, Alsórákos) is a commune in Brașov County, Transylvania, Romania. It is composed of two villages, Mateiaș (''Mátéfalva'') and Racoș.
The commune is located at the northern edg ...
: Racu
Racu ( hu, Csíkrákos, , meaning "Place with the Crabs of Csík") is a commune in Harghita County, Romania. It lies in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania.
Component villages
The commune is composed of two vill ...
: Radovanu - Gorgana I
: Radovanu - Jidovescu
: Roadeș
: Rovinari
: Rușor
: Sacalasău
: Satu Mare (Harghita)
: Satu Nou
: Sânzieni
: Seimeni
Seimeni (plural of ''Seimen'') designates the group of flintlock-armed infantry mercenaries charged with guarding the ''hospodar'' (ruler) and his court in 17th and 18th century Wallachia and Moldavia. They were mostly of Serb and other Balkan or ...
: Socol
Socol ( ro, Socol, sr, Сокол/Sokol, or Соколовац/Sokolovac, hu, Nérasolymos) is a commune in Caraș-Severin County, Romania (in the '' Clisura Dunării'' area of Banat). In 2011, the population of the commune numbered 1,873 peopl ...
: Sprâncenata
Sprâncenata is a commune in Olt County, Muntenia, Romania.
Position
Sprâncenata is situated in the Wallachian Plain, on the left bank of the Olt River. It is composed of four villages: Sprâncenata and Bârseștii de Sus, which are located alon ...
: Stâncești
: Stoina
Stoina is a commune in Gorj County, Oltenia, Romania. It is composed of seven villages: Ciorari, Mielușei, Păișani, Stoina, Toiaga, Ulmet and Urda de Sus.
References
*
Communes in Gorj County
Localities in Oltenia
{{Gorj-geo-stub ...
: Șeica Mică
Șeica Mică (german: Kleinschelken; hu, Kisselyk) is a commune located in Sibiu County, Transylvania, Romania. It is composed of two villages, Soroștin (''Schorsten''; ''Sorostély'') and Șeica Mică.
Tourism
* the fortified church of Șe ...
: Tășad
The Tășad (also: ''Valea Mare'') is a left tributary of the river Crișul Repede in Romania. It discharges into the Crișul Repede in Oșorhei, near Oradea
Oradea (, , ; german: Großwardein ; hu, Nagyvárad ) is a city in Romania, located in ...
: Telița
Telița is a commune in Anenii Noi District, Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north ...
: Teliu
Teliu ( hu, Keresztvár, Nyén, Nyény; german: Kreuzburg) is a commune in Brașov County, Transylvania, Romania. It is composed of a single village, Teliu.
The commune is located in the eastern part of the county, on the banks of the river Teli ...
: Tilișca
Tilișca (german: Tilischen; hu, Tilicske) is a commune in Sibiu County, Transylvania, Romania, in the Cindrel Mountains, west of the county capital Sibiu, in the Mărginimea Sibiului
Mărginimea Sibiului ( hu, Szeben-Hegyalja) is an area whi ...
: Timișu de Jos
Predeal (; hu, Predeál) is a town in Brașov County, Transylvania, Romania. Predeal, a mountain resort town, is the highest town in Romania. It is located in the Prahova Valley at an elevation of over .
The town administers three villages: ...
: Turia
: Unip
The United National Independence Party (UNIP) is a political party in Zambia. It governed the country from 1964 to 1991 under the socialist President (government title), presidency of Kenneth Kaunda, and was the sole legal party in the country ...
: Uroi
Simeria (; german: Fischdorf; hu, Piski) is a town in Hunedoara County, Transylvania, Romania, and an important railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled ...
: Valea Seacă
: Viișoara Moșneni
: Zemplín
: Zetea
Zetea ( hu, Zetelaka, Hungarian pronunciation: ) is a commune in the central part of Harghita County, Romania. The commune lies in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania.
Component villages
The commune is composed ...
Thraco-Illyrian
* Chesdupara * Daradapara *Scupi
Scupi (''Σκούποι'' in ancient greek) is an archaeological site located between Zajčev Rid (''Зајчев Рид'' 'Rabbit Hill') and the Vardar River, several kilometers from the center of Skopje in North Macedonia. A Roman military camp w ...
of the Dardani
The Dardani (; grc, Δαρδάνιοι, Δάρδανοι; la, Dardani) or Dardanians were a Paleo-Balkan people, who lived in a region that was named Dardania after their settlement there. They were among the oldest Balkan peoples, and their ...
tribe
* Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous provice of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians an ...
Greek and Macedon
Thrace, from Strymon to Nestos
* Amphipolis, founded by colonists fromAthens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
* Akontisma
Acontisma or Akontisma ( grc, Ἀχόντισμα), also called Hercontroma or Herkontroma, was a settlement in ancient Macedon near the border of ancient Thrace, Thrace on the coast and on the Via Egnatia, 8 or 9 miles (13 to 15 km) eastward of N ...
An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 856
* Antisara
* Creston, modern Kilkis
* Datos Datus or Datos ( grc, Δάτος), also Datum or Daton (Δάτον and Δᾶτον), was an ancient Greek city located in Macedonia, specifically in the region between the river Strymon and the river Nestos. It was founded by colonists from Thaso ...
, founded by colonists from Thasos
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 855: "The Thasians... they founded Krenides and Daton"
* Drabeskos Draviskos ( el, Δραβήσκος) is a village in Serres regional unit, located 45 km southeast of the city of Serres. Since 2011 it is a municipal unit of the Municipality of Nea Zichni. Until 1926 it was named "Zdravik".
History Antiquity
...
* Eion, founded by colonists from Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
* Ennea Hodoi
* Galepsus, founded by colonists from Thasos
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
* Gasoros
* Heraclea Sintica
Heraclea Sintica, Heracleia Sintica, Хераклея Синтика in Bulgarian or Herakleia Sintike ( grc, Ἡράκλεια Σιντική), or Heraclea ex Sintiis, also known as Heraclea Strymonus or Herakleia Strymonos (Ἡράκλεια Στ ...
* Krenides, founded by colonists from Thasos
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
* Mastira
''Mastira'' is a genus of spiders in the family Thomisidae. It was first described in 1891 by Tamerlan Thorell. , it contains 10 species.
Species
''Mastira'' comprises the following species:
*''Mastira adusta'' (L. Koch, 1867) – New Guinea, ...
, mentioned by Demosthenes (341 BCE) in his "The Oration on the State of the Chersonesus". This town was unknown to the scholar Harpocration (100-200 CE), who suggests that instead of "Mastira" we should read " Bastira", a known Thracian town of that name.
* Myrkinos Myrcinus or Myrkinos ( grc, Μύρκινος or Μύρκιννος) was an ancient Greek city located in Macedonian Thrace, in the region of Edonis between the Strymon and the Nestos Rivers, on the left bank of the Strymon. It was within the terri ...
, founded by colonists from Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' (exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in a ...
An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 782, "The Thasians are said to have colonised the Hedonian city of Myrkinos, Galepsos and Oisyme..." in 497 BC
* Neapolis, founded by colonists from Thasos
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
, modern Kavala
Kavala ( el, Καβάλα, ''Kavála'' ) is a city in northern Greece, the principal seaport of eastern Macedonia and the capital of Kavala regional unit.
It is situated on the Bay of Kavala, across from the island of Thasos and on the Egnat ...
* Oesyme
Oesyme or Oisyme ( grc-x-attic, Οἰσύμη, grc-x-doric, Οἰσύμα) and Aisyme or Aesyme ( grc, Αἰσύμη) was an ancient Greek ''polis'' (city-state) located in ancient Thrace and later in Macedonia. It was within the region of Pier ...
, founded by colonists from Thasos
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
* ParoikopolisAn Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 857
* Pergamos
Pergamos (; tr, Beyarmudu) is a Turkish Cypriot village in Larnaca District, Cyprus, 4 km north of Pyla, almost surrounded by the British Sovereign Base Area (SBA) at Dhekelia.PRIO web site http://www.prio-cyprus-displacement.net/default. ...
* Phagres
Phagres ( grc, Φάγρης) was a ancient Greek, Greek city located in ancient Thrace and later in kingdom of Macedon, Macedon, in the region between the river Strymon (river), Strymon and the river Nestos (river), Nestos called Edonis (region), E ...
, founded by colonists from Thasos
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
* Philippi
Philippi (; grc-gre, Φίλιπποι, ''Philippoi'') was a major Greek city northwest of the nearby island, Thasos. Its original name was Crenides ( grc-gre, Κρηνῖδες, ''Krenides'' "Fountains") after its establishment by Thasian colon ...
, founded by Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king ('' basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ...
, rebuilt Crenides
* Philippopolis (modern Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the c ...
)
* Pistyros
Pistyrus or Pistyros ( grc, Πίστυρος), or Pistirus or Pistiros (Πίστιρος), or Bistirus or Bistiros (Βίστιρος), also known as Pisteira (Πίστειρα),Harpocration, p. 124. 11; Schol. ad Aesch. Pers. 2. was an ancient Gre ...
, founded by colonists from Thasos
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
* Sirra Sirra ( grc, Σίρρα) or ( grc, Σέρραι) was an ancient Greek polis (after the 4th century BC) located in Thrace, in the region between the river Strymon and the river Nestos. The city ethnic name was ( grc, Σειραίος) or ( grc, Σ ...
, founded by Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king ('' basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ...
, rebuilt town of the Siriopeoni, modern Serres
* Skapte Hyle
* Skotoussa
Skotoussa ( el, Σκοτούσσα, ) is a village and a former municipality in the Serres (regional unit), Serres regional unit, Greece. Population 5,135 (2011). Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Irakleia, Serr ...
* Tristolos
Thrace, from Nestos to Hebros
* Abdera, founded by colonists fromKlazomenai
Klazomenai ( grc, Κλαζομεναί) or Clazomenae was an ancient Greek city on the coast of Ionia and a member of the Ionian League. It was one of the first cities to issue silver coinage. Its ruins are now located in the modern town Urla n ...
* Ainos Ainos may refer to:
*Aenus (Thrace), an ancient Greek city in Thrace, near the Aegean coast
*Mount Ainos, on the island Cefalonia
*Ainu people of Japan
{{disambiguation ...
('' Poltymbria'') founded by colonists from Alopeke, Mytilene, and Kyme
* Bergepolis Bergepolis ( grc, Βεργέπολις) was a Greek town located in ancient Thrace, in the region between the river Nestos to the river Hebros. It was founded by colonists from Abdera. Bergepolis was an urban center dependent on Abdera. Bergepoli ...
, founded by colonists from Abdera
* Doriskos
Doriscus ( grc-gre, Δορίσκος and Δωρίσκος, ''Dorískos'') was a settlement in ancient Thrace (modern-day Greece), on the northern shores of Aegean Sea, in a plain west of the river Hebrus (river), Hebrus. It was notable for remaini ...
* Drys, founded by colonists from Samothrace
Samothrace (also known as Samothraki, el, Σαμοθράκη, ) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. It is a municipality within the Evros regional unit of Thrace. The island is long and is in size and has a population of 2,859 (2011 ...
* Dikaia
Dikaia ( el, Δίκαια, ) is a village in the northern part of the Evros regional unit in Greece. Dikaia was the seat of the former municipality of Trigono, and is part of the municipality Orestiada since 2011. In 2011 its population was 561 ...
, founded by colonists from Samos
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the -wide Mycale Strait. It is also a separate ...
The Histories by Herodotus, Carolyn Dewald, and Robin Waterfield, 2008, page 442: "... bed of the Lisus, Xerxes passed the Greek towns of Maronea, Dicaea, and Abdera. His route also took him past a ..."
* Kypsela
* Larissa
Larissa (; el, Λάρισα, , ) is the capital and largest city of the Thessaly region in Greece. It is the fifth-most populous city in Greece with a population of 144,651 according to the 2011 census. It is also capital of the Larissa regiona ...
* Maroneia, founded by colonists from Chios
Chios (; el, Χίος, Chíos , traditionally known as Scio in English) is the fifth largest Greek island, situated in the northern Aegean Sea. The island is separated from Turkey by the Chios Strait. Chios is notable for its exports of mastic ...
* Menebria, founded by colonists from Samothrace
Samothrace (also known as Samothraki, el, Σαμοθράκη, ) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. It is a municipality within the Evros regional unit of Thrace. The island is long and is in size and has a population of 2,859 (2011 ...
on a town named Melsambria, modern Nessebar
Nesebar (often transcribed as Nessebar and sometimes as Nesebur, bg, Несебър, pronounced ) is an ancient city and one of the major seaside resorts on the Bulgarian Black Sea Coast, located in Burgas Province. It is the administrative centr ...
* Orthagoria
Orthagoria ( grc, Ὀρθαγορία) or Orthagoreia (Ὀρθαγορεία) was an ancient Greek town of ancient Thrace, located on the coast of the Aegean Sea. Pliny the Elder says ''Ortagurea'' (perhaps the same as Orthagoria) was the old name ...
* Sale, founded by colonists from Samothrace
Samothrace (also known as Samothraki, el, Σαμοθράκη, ) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. It is a municipality within the Evros regional unit of Thrace. The island is long and is in size and has a population of 2,859 (2011 ...
* Stryme Stryme ( grc, Στρύμη) was an ancient Greek city on the south coast of ancient Thrace, a little to the west of Mesembria, between which and Stryme flowed the small river Lissus, which the army of Xerxes I is said to have drunk dry. It was found ...
, founded from colonists from Thasos
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
* Zone
Zone or The Zone may refer to:
Places Climate and altitude zones
* Death zone (originally the lethal zone), altitudes above a certain point where the amount of oxygen is insufficient to sustain human life for an extended time span
* Frigid zone, ...
, founded by colonists from Samothrace
Samothrace (also known as Samothraki, el, Σαμοθράκη, ) is a Greek island in the northern Aegean Sea. It is a municipality within the Evros regional unit of Thrace. The island is long and is in size and has a population of 2,859 (2011 ...
Inland Thrace
*Alexandropolis Maedica
Alexandropolis ( grc, Ἀλεξανδρόπολις, Alexandrόpolis, Alexander's city) in the Thracian region of Maedians, was the first town founded in 340 BC by Alexander the Great (he was sixteen years old), after defeating a local Thrac ...
* Beroea
Beroea (or Berea) was an ancient city of the Hellenistic period and Roman Empire now known as Veria (or Veroia) in Macedonia, Northern Greece. It is a small city on the eastern side of the Vermio Mountains north of Mount Olympus. The town is menti ...
, founded by Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king ('' basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ...
in 342 BC
* Philippopolis, Pulpudeva ('' Philippopolis''), today's city of Plovdiv
Plovdiv ( bg, Пловдив, ), is the second-largest city in Bulgaria, standing on the banks of the Maritsa river in the historical region of Thrace. It has a population of 346,893 and 675,000 in the greater metropolitan area. Plovdiv is the c ...
in Bulgaria, founded by Philip II of Macedon
Philip II of Macedon ( grc-gre, Φίλιππος ; 382 – 21 October 336 BC) was the king ('' basileus'') of the ancient kingdom of Macedonia from 359 BC until his death in 336 BC. He was a member of the Argead dynasty, founders of the ...
in a town formerly called ''Eumolpias''.
* Stanimachos, founded by colonists from Istiaia
Istiaia ( el, Ιστιαία, , before 1913: Ξηροχώρι - ''Xirochori''2.537 Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Istiaia-Aidipsos, of which it is the seat and a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an are ...
, modern Asenovgrad
Asenovgrad ( bg, Асеновград ) is List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, a town in central southern Bulgaria, part of Plovdiv Province. It is the largest town in Bulgaria that is not a province center. Previously known as ''Stanimaka'' ( ...
* Pistiros
Pistiros (Ancient Greek, ''Πίστιρος'') was an inland Ancient Greek emporion, or trade center, in Ancient Thrace. It is located near the modern city of Vetren, in the westernmost part of the Maritsa River valley.
The identification of the ...
, founded by Pistyrians from the coast
Thracian Chersonesos
*Aegospotami
Aegospotami ( grc, Αἰγὸς Ποταμοί, ''Aigos Potamoi'') or AegospotamosMish, Frederick C., Editor in Chief. “Aegospotami.” '' Webster’s Ninth New Collegiate Dictionary''. 9th ed. Springfield, MA: Merriam-Webster Inc., 1985. , (in ...
(''Aegospotamos'')
* Alokopennesos, founded by colonists from Aeolis
* Araplos
* Callipolis
* Chersonesos
Chersonesus ( grc, Χερσόνησος, Khersónēsos; la, Chersonesus; modern Russian and Ukrainian: Херсоне́с, ''Khersones''; also rendered as ''Chersonese'', ''Chersonesos'', contracted in medieval Greek to Cherson Χερσών; ...
(''Agora
The agora (; grc, ἀγορά, romanized: ', meaning "market" in Modern Greek) was a central public space in ancient Greek city-states. It is the best representation of a city-state's response to accommodate the social and political order of t ...
''), founded by colonists from Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
* Derris
''Derris'' is genus of leguminous plants found in Southeast Asia and the southwest Pacific islands, including New Guinea. The roots of '' D. elliptica'' contain rotenone, a strong insecticide and fish poison.
Despite the secondary compounds foun ...
* Elaious
Elaeus ( grc, Ἐλαιοῦς ''Elaious'', later ''Elaeus''), the “Olive City”, was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek city located in Thrace, on the Thracian Chersonese. Elaeus was located at the southern end of the Hellespont (now the Dard ...
, founded by colonists from Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
* Ide
* Kardia, founded by colonists from Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation, by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 636: "In the archaic period Athens colonised Sigeion, Elaious, Chersonesus, Paktye, Sestus, Kardia..."
* Kressa
* Krithotai
Crithote or Krithote ( grc, Κριθωτή or Κριθώτη) was an ancient Greek city located in Thrace, located in the region of the Thracian Chersonesos. It was on the Hellespont north of Gallipolis, and was an Athenian colony founded by Miltia ...
, founded by colonists from Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
* Limnae, founded by colonists from Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' (exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in a ...
* Madytos
Madytos ( el, Μάδυτος) is a former municipality in the Thessaloniki regional unit, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Volvi, of which it is a municipal unit. Its population was 2,460 in 2011. The ...
, founded by colonists from Lesbos
* Pactya, founded by colonists from Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
* Paion
Paion ( el, Παΐων) is a former municipality in Achaea, West Greece, Greece. Its population in 2011 was 1,055. The seat of the municipality was in Dafni. The municipality was created after the Greek War of Independence and was dissolved in ...
* Sestos
Sestos ( el, Σηστός, la, Sestus) was an ancient city in Thrace. It was located at the Thracian Chersonese peninsula on the European coast of the Hellespont, opposite the ancient city of Abydos, and near the town of Eceabat in Turkey.
In ...
, founded by colonists from Lesbos
Propontic Thrace
*Athyra
''Athyra'' is a fantasy novel by American writer Steven Brust, the sixth book in his Vlad Taltos series, set in the fantasy world of Dragaera. Originally published in 1993, by Ace Books, it was reprinted in 2003 along with ''Orca'' in the omn ...
* Byzantion, founded by colonists from Megara
Megara (; el, Μέγαρα, ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis Island, Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, befo ...
on a town called Lygos, modern Istanbul
Istanbul ( , ; tr, İstanbul ), formerly known as Constantinople ( grc-gre, Κωνσταντινούπολις; la, Constantinopolis), is the List of largest cities and towns in Turkey, largest city in Turkey, serving as the country's economic, ...
* Bisanthe
Bisanthe ( grc, Βισάνθη) was a great city in ancient Thrace, on the coast of the Propontis, which had been founded by the Samians. About 400 BCE, Bisanthe belonged to the kingdom of the Thracian prince Seuthes II. At a later period its ...
, founded by colonists from Samos
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the -wide Mycale Strait. It is also a separate ...
* Daminon Teichos Daminon Teichos ( grc, Δαμινόν τεῖχος), also Daunium or Daunion (Δαύνιον), was a Greek city in ancient Thrace, located in the region of the Propontis.
It is cited in the '' Periplus of Pseudo-Scylax'' in its recitation of the ...
* Ergiske
* Heraclea (''Perinthus
Perinthus or Perinthos ( grc, ἡ Πέρινθος) was a great and flourishing town of ancient Thrace, situated on the Propontis. According to John Tzetzes, it bore at an early period the name of Mygdonia (Μυγδονία). It lay 22 miles west ...
'')
* Heraion, founded by colonists from Samos
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the -wide Mycale Strait. It is also a separate ...
* Lysimachia
* Neapolis (Thracian Chersonese)
Neapolis ( grc, Νεάπολις) was a Greek city in ancient Thrace, located on the Propontis. It also bore the name Heraclea or Herakleia (Ἡράκλεια). It was a member of the Delian League and appears in Athenian tribute registers between ...
, founded by colonists from Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
* Orestias
Orestias ( el, Ὀρεστιάς) was an ancient Greek settlement next to the Maritsa (or Evros) river, near or at the site of present-day Edirne, and close to the current border between Turkey and Greece.
Legends claim that Orestias was founded ...
, rebuilt
* Perinthus
Perinthus or Perinthos ( grc, ἡ Πέρινθος) was a great and flourishing town of ancient Thrace, situated on the Propontis. According to John Tzetzes, it bore at an early period the name of Mygdonia (Μυγδονία). It lay 22 miles west ...
, founded by colonists from Samos
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the -wide Mycale Strait. It is also a separate ...
* Rhaedestus
Bisanthe ( grc, Βισάνθη) was a great city in ancient Thrace, on the coast of the Propontis, which had been founded by the Samians. About 400 BCE, Bisanthe belonged to the kingdom of the Thracian prince Seuthes II. At a later period its ...
, founded by colonists from Samos
Samos (, also ; el, Σάμος ) is a Greek island in the eastern Aegean Sea, south of Chios, north of Patmos and the Dodecanese, and off the coast of western Turkey, from which it is separated by the -wide Mycale Strait. It is also a separate ...
* Serrion Teichos
* Selymbria
Selymbria ( gr, Σηλυμβρία),Demosthenes, '' de Rhod. lib.'', p. 198, ed. Reiske. or Selybria (Σηλυβρία), or Selybrie (Σηλυβρίη), was a town of ancient Thrace on the Propontis, 22 Roman miles east from Perinthus, and 44 Roman ...
, modern Silivri
Silivri, formerly Selymbria (Greek: Σηλυμβρία), is a city and a district in Istanbul Province along the Sea of Marmara in Turkey, outside the urban core of Istanbul, containing many holiday and weekend homes for residents of the city. The ...
in European Turkey, of Thracian etymology
* Tyrodiza
Tyrodiza ( grc, Τυρόδιζα) was a Greek city in ancient Thrace, located in the region of the Propontis. It appears to have flourished between 550 BCE and 330 BCE, and is identified with the place called Tiristasis (Τειρίστα� ...
, of Thracian etymology
West Pontic coast
* Aegyssos, modern Tulcea * Aquae Calidae * Ahtopol, founded by colonists fromAthens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
* Anchialos, modern Pomorie, founded by colonists from Appolonia
* Apollonia, modern Sozopol, founded by IoniansAn Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, Index
* Berga
Berga () is the capital of the ''comarca'' (county) of Berguedà, in the province of Barcelona, Catalonia, Spain. It is bordered by the municipalities of Cercs, Olvan, Avià, Capolat and Castellar del Riu.
History
Berga derives its name from ...
, founded by colonists from Thasos
Thasos or Thassos ( el, Θάσος, ''Thásos'') is a Greek island in the North Aegean Sea. It is the northernmost major Greek island, and 12th largest by area.
The island has an area of and a population of about 13,000. It forms a separate re ...
* Bizone
The Bizone () or Bizonia was the combination of the American and the British occupation zones on 1 January 1947 during the occupation of Germany after World War II. With the addition of the French occupation zone on 1 August 1948J. Robert Weg ...
, founded by colonists from Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' (exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in a ...
, modern Kavarna
* Krutoi, modern Balchik founded by Miletian colonists
* Dionysopolis, modern Balchik, founded by colonists from Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' (exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in a ...
* Heliopolis, modern Obzor
Obzor ( bg, Обзор ) is a small town and seaside resort on the Black Sea coast of Bulgaria. It is part of Nesebar Municipality, Burgas Province. On February 28th, 2021, the citizens of Obzor and six nearby villages voted in a referendum to sepa ...
* Histria, founded by colonists from Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' (exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in a ...
* Kallatis
Mangalia (, tr, Mankalya), ancient Callatis ( el, Κάλλατις/Καλλατίς; other historical names: Pangalia, Panglicara, Tomisovara), is a city and a port on the coast of the Black Sea in the south-east of Constanța County, Northern ...
(''Callatis
Mangalia (, tr, Mankalya), ancient Callatis ( el, Κάλλατις/Καλλατίς; other historical names: Pangalia, Panglicara, Tomisovara), is a city and a port on the coast of the Black Sea in the south-east of Constanța County, Northern D ...
''), founded from colonists from Herakleia Pontike, modern-day Mangalia
Mangalia (, tr, Mankalya), ancient Callatis ( el, Κάλλατις/Καλλατίς; other historical names: Pangalia, Panglicara, Tomisovara), is a city and a port on the coast of the Black Sea in the south-east of Constanța County, Northern D ...
, Romania
* Mesembria, modern Nesebar, settled during the 6th century BC by Dorians
The Dorians (; el, Δωριεῖς, ''Dōrieîs'', singular , ''Dōrieús'') were one of the four major ethnic groups into which the Hellenes (or Greeks) of Classical Greece divided themselves (along with the Aeolians, Achaeans, and Ionians) ...
from Megara
Megara (; el, Μέγαρα, ) is a historic town and a municipality in West Attica, Greece. It lies in the northern section of the Isthmus of Corinth opposite the island of Salamis Island, Salamis, which belonged to Megara in archaic times, befo ...
* Odessos, modern Varna
Varna may refer to:
Places Europe
*Varna, Bulgaria, a city in Bulgaria
**Varna Province
**Varna Municipality
** Gulf of Varna
**Lake Varna
**Varna Necropolis
*Vahrn, or Varna, a municipality in Italy
*Varniai, a city in Lithuania
* Varna (Šaba ...
, founded by colonists from Miletus
Miletus (; gr, Μῑ́λητος, Mī́lētos; Hittite transcription ''Millawanda'' or ''Milawata'' (exonyms); la, Mīlētus; tr, Milet) was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia, near the mouth of the Maeander River in a ...
* Nikonion
Nikonion ( grc, Νικώνιον; la, Niconium) and Nikonia ( grc, Νικωνία) was an ancient Greek city on the east bank of the Dniester estuary. Its ruins are located 300 meters to the northwest of the modern village Roksolany, in the ...
, founded by colonists from Istros
* Salmydessos
Salmydessus or Salmydessos ( grc, Σαλμυδησσός), also Halmydessus or Halmydessos (Ἁλμυδισσός), was a coast-town of ancient Thrace, on the Euxine, about northwest of the entrance of the Bosporus. The eastern offshoots of the Ha ...
(from IE ''*salm-udes'', "salty water"; cf. Greek ''álmē'', "sea water, brine"; ''ýdos'', "water")
* Tomis, modern Constanta, rebuilt Scythia
Scythia (Scythian: ; Old Persian: ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) or Scythica (Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ), also known as Pontic Scythia, was a kingdom created by the Scythians during the 6th to 3rd centuries BC in the Pontic–Caspian steppe.
His ...
n town
Other
* Aison * Brea, founded by colonists fromAthens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
,
* Gazoros Gazoros or Gazorus (Greek: ) was a town mentioned by Ptolemy to be in the region of Edonis or Odomantike and also by inscriptions of Hellenistic and Roman times. Later in the 4th century BC, it was annexed to the Macedonian kingdom and made a polis ...
* Heraclea Sintica
Heraclea Sintica, Heracleia Sintica, Хераклея Синтика in Bulgarian or Herakleia Sintike ( grc, Ἡράκλεια Σιντική), or Heraclea ex Sintiis, also known as Heraclea Strymonus or Herakleia Strymonos (Ἡράκλεια Στ ...
on a tribe of the Sintoi
The Sintians (; grc-gre, Σίντιες), "the Raiders, the Plunderers", from Ancient Greek ''sinteis'', "destructive") were known to the Greeks as pirates and raiders; they are also referred to as a Thracian people who once inhabited the area ...
tribe
* Kossaia
Persian
*Boryza (city) Boryza was a Persian city in Thrace (Achaemenid satrapy of Skudra) founded by King Darius the Great (522–486 BC). Hecataeus of Miletus (died ) mentioned Boryza as being located in the land of the Thynians on the southwestern Black Sea coast to th ...
An Inventory of Archaic and Classical Poleis: An Investigation Conducted by The Copenhagen Polis Centre for the Danish National Research Foundation by Mogens Herman Hansen, 2005, page 891, "Note that the only one which is explicitly called a polis by Hekataios is Boryza (fr.166) and here we learn that it is a polis inhabited by Persians i.e not by Greeks or Thracians."
* Doriscus
Doriscus ( grc-gre, Δορίσκος and Δωρίσκος, ''Dorískos'') was a settlement in ancient Thrace (modern-day Greece), on the northern shores of Aegean Sea, in a plain west of the river Hebrus. It was notable for remaining in Persian h ...
Roman
Acumincum
Acumincum was an ancient Roman settlement, located in the present day town of Stari Slankamen, Serbia.
History
In the 3rd century BC, the area was inhabited by Celtic Scordisci. In the 1st century BC, the fort was conquered by Romans and the s ...
* Ad Medium
* Agura Piatra
''Agura'' (, lit., "foreign/barbarian sitting"; also called ''anza'' ) is the Japanese term for the position normally referred to as sitting cross-legged in English.
Description
The buttocks are on the floor (or on a cushion set on the floor) an ...
( Regianum)
* Appiaria
Ryahovo ( bg, Ряхово) is a village in northern Bulgaria, and as Ancient Ap(p)iaria a former bishopric, remaining a Latin Catholic titular see.
It is located in the municipality of Slivo Pole in Ruse Province.
As of February 2011, it had a p ...
* Apros
Aprus or Apros ( grc, Ἄπρος), also Apri or Aproi (Ἄπροι), was a town of ancient Thrace and, later, a Roman city established in the Roman province of Europa.
History
Stephanus of Byzantium collects a quote of Theopompus that mention ...
* Aquis
* Augustae
* Augusta Traiana
Stara Zagora ( bg, Стара Загора, ) is the sixth-largest city in Bulgaria, and the administrative capital of the homonymous Stara Zagora Province.
Name
The name comes from the Slavic root ''star'' ("old") and the name of the medieva ...
(formerly Beroe, later Stara Zagora)
* Burgenae
Novi Banovci () is a settlement in Serbia by the Danube River. It is situated in the Stara Pazova municipality, in the Srem District, in Vojvodina province. It is located 5 kilometers away from Batajnica and 20 km from the capital, Belgrade. ...
* Camistrum
* Caenophrurium
Caenophrurium (also written as Cenophrurium and Coenophrurium; grc-gre, Καινοφρούριον ) was a settlement in the Roman province of Europa (the southeasternmost part of Thrace), between Byzantium and Heraclea Perinthus. It appears in l ...
* Cypsella
* Deultum
Develtos ( el, Δεβελτός, Δηβελτός, Δεουελτòς, Δεούελτος, Διβηλτóς) or Deultum was an ancient city and bishopric in Thrace. It was located at the mouth of the River Sredetska on the west coast of Lake Mand ...
, rebuilt Debelt
Debelt (Bulgarian: Дебелт) is a village in Burgas Province in southeastern Bulgaria. It is located in the municipality of Sredets.
History
Debelt is located near the ruins of the city of Develtos. During the Russo-Turkish War of 1828-1829, ...
* Deltum
* Diocletianopolis (modern Hisarya
Hisarya ( bg, Хисаря , also known as ''Hisar'', ''Hissar'' or ''Hissarya'', formerly: Toplitsa) is a small resort town in Bulgaria, in Plovdiv Province.
Hisar means 'fort, castle' in Arabic. The word was adopted in Persian and Ottoman Tur ...
)
* Doracium
* Durorstorum, modern Silistra
Silistra ( bg, Силистра ; tr, Silistre; ro, Silistra) is a town in Northeastern Bulgaria. The town lies on the southern bank of the lower Danube river, and is also the part of the Romanian border where it stops following the Danube. Sil ...
* Drobeta
''Drobeta'' is a genus of moths of the family Noctuidae. The genus was erected by Francis Walker (entomologist), Francis Walker in 1858.
Species
* ''Drobeta albicauda'' (Hampson, 1910)
* ''Drobeta albirufa'' (Druce, 1909)
* ''Drobeta andrevia'' ...
* Gensis
* Hadrianople
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
, rebuild Uscudama
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis (Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian borders, ...
* Justiniana Prima
* Margus
* Marcianopolis, modern Devnya
* Maximianopolis
* Morisena
* Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
* Nicopolis ad Istrum
* Nicopolis ad Nestum, rebuilt Alexandrupolis
* Novae
A nova (plural novae or novas) is a transient astronomical event that causes the sudden appearance of a bright, apparently "new" star (hence the name "nova", which is Latin for "new") that slowly fades over weeks or months. Causes of the dramati ...
* Oescus
Oescus, Palatiolon or Palatiolum ( bg, Улпия Ескус, ) was an important ancient city on the Danube river in Roman Moesia. It later became known as ''Ulpia Oescus''. It lay northwest of the modern Bulgarian city of Pleven, near the v ...
* Pautalia, modern Kyustendil
* Pescium, modern Peć
Peja (Definiteness, Indefinite Albanian language, Albanian Albanian morphology#Nouns (declension), form: ''Pejë'' ) or Peć ( sr-Cyrl, Пећ ) is the fourth largest List of cities and towns in Kosovo, city of Kosovo and seat of Peja Municipali ...
* Plotinopolis Plotinopolis ( el, Πλωτινούπολις) is an ancient city founded in Thrace by the Roman emperor Trajan and named after his wife, Pompeia Plotina. In the 6th/7th centuries, it was replaced by the nearby city of Didymoteichon.
History
In ...
, modern Hissarya,
* Porolissum
Porolissum was an ancient Roman city in Dacia. Established as a military camp in 106 during Trajan's Dacian Wars, the city quickly grew through trade with the native Dacians and became the capital of the province Dacia Porolissensis in 124. The sit ...
* Resculum (castra Remesiana)
* Sexagnita Prista, modern Ruse
Ruse may refer to:
Places
*Ruse, Bulgaria, a major city of Bulgaria
**Ruse Municipality
** Ruse Province
** 19th MMC – Ruse, a constituency
*Ruše, a town and municipality in north-eastern Slovenia
* Ruše, Žalec, a small settlement in east-ce ...
* Sirmium
Sirmium was a city in the Roman province of Pannonia, located on the Sava river, on the site of modern Sremska Mitrovica in the Vojvodina autonomous provice of Serbia. First mentioned in the 4th century BC and originally inhabited by Illyrians an ...
* Theranda
)
, settlement_type = Municipality and city
, image_skyline = Prizren Collage.jpg
, imagesize = 290px
, image_caption = View of Prizren
, image_alt = View of Prizren
, image_flag ...
* Traianopolis
* Transmarisca
Tutrakan ( bg, Тутракан , ro, Тurtucaia, tr, Turtukaya) is a town in northeastern Bulgaria, an administrative centre of the homonymous municipality, part of Silistra Province. It is situated on the right bank of the Danube opposite t ...
, modern Tutrakan
* Tropaeum Traiani
* Turres, modern Pirot
Pirot ( sr-cyr, Пирот) is a city and the administrative center of the Pirot District in southeastern Serbia. According to 2011 census, the urban area of the city has a population of 38,785, while the population of the city administrative area ...
* Ulmetum
* Ulpiana
* Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa
Colonia Ulpia Traiana Augusta Dacica Sarmizegetusa was the capital and the largest city of Roman Dacia, later named ''Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa'' after the former Dacian capital, located some 40 km away. Built on the ground of a camp of t ...
* Valve, modern Vratsa
* Vicianum, modern Vučitrn
* Viminacium
* Zaldapa
Zaldapa (''Zeldepa'', grc, Ζάλδαπα, Ζέλδεπα) was a large Late Roman fortified city in Scythia Minor/Moesia, located near today's Abrit, Bulgaria.
It was originally an ancient Thracian settlement from around the 8th century BC. The ...
* Zikideva Zicídeva ( el, Ζικίδεβα) was an Early Byzantine town, tentatively identified with the late antique settlement excavated on the top of Tsarevets hill, near modern Veliko Tarnovo in northern Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, Българи ...
* the rest after conquest
Celtic
*Dunonia
Vidin ( bg, Видин, ; Old Romanian: Diiu) is a port city on the southern bank of the Danube in north-western Bulgaria. It is close to the borders with Romania and Serbia, and is also the administrative centre of Vidin Province, as well as ...
, modern Vidin
* Malata
* Naissus, modern Niš
Niš (; sr-Cyrl, Ниш, ; names in other languages) is the third largest city in Serbia and the administrative center of the Nišava District. It is located in southern part of Serbia. , the city proper has a population of 183,164, while ...
* Noviodunum
* Serdica
Serdika or Serdica (Bulgarian: ) is the historical Roman name of Sofia, now the capital of Bulgaria.
Currently, Serdika is the name of a district located in the city. It includes four neighbourhoods: "Fondovi zhilishta"; "Banishora", "Orlandovts ...
, modern Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, София, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and ha ...
* Singidunum, modern Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
* Taurunum
Zemun ( sr-cyrl, Земун, ; hu, Zimony) is a municipality in the city of Belgrade. Zemun was a separate town that was absorbed into Belgrade in 1934. It lies on the right bank of the Danube river, upstream from downtown Belgrade. The developm ...
* Tylis
See also
* List of ancient tribes in Thrace and Dacia *List of rulers of Thrace and Dacia
This article lists rulers of Thrace and Dacia, and includes Thracian, Paeonian, Celtic, Dacian, Scythian, Persian or Ancient Greek up to the point of its fall to the Roman Empire, with a few figures from Greek mythology.
Mythological
*Haemus, bec ...
* List of ancient cities in Illyria
* List of rulers of Illyria
The Illyrians, ; la, Illyrii}) were a conglomeration of Indo-European peoples and tribes in the Balkan Peninsula, Southeastern Europe. They spoke the Illyrian language and practiced a multitude of common religious and cultural practices. Many o ...
* Dacian Dava
* Dacian Fortresses of the Orăştie Mountains
Dacian, Geto-Dacian, Daco-Getic or Daco-Getian () often refers to something of or relating to:
* Dacia (disambiguation)
* Dacians
* Dacian language
Dacian may also refer to:
* Dacian archaeology
* Dacian art
* Dacia in art
* Dacian culture
* D ...
* Tabula Peutingeriana
* Notitia Dignitatum
The ''Notitia Dignitatum'' (Latin for "The List of Offices") is a document of the late Roman Empire that details the administrative organization of the Western and the Eastern Roman Empire. It is unique as one of very few surviving documents of ...
Notes
References
* * * * *External links
*Sorin Olteanu's Project: Linguae Thraco-Daco-Moesorum - Toponyms Section
Placenames in the Compilation 'notitia dignitatum' (Cnd)
Dacian Map
Thracians and Dacians
Thracians 700-46 BC
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ancient Cities in Thrace And Dacia Geography of ancient Thrace Ancient Thrace Celtic towns Thracian towns Greek colonies in Thrace Greek colonization Former populated places in the Balkans Archaeological sites in Romania Balkans-related lists