|
Larissa (Thrace)
Larissa ( grc, Λάρισσα) was an ancient Greek city located in Thrace, located in the region between the river Nestos to the river Hebros. Larissa was located in the borderland between Elis and Achaian Dyme. It remains unlocated and unidentified.Back Matter: "... sites identified solely by coins' Location Site THESSALY Atrax, Kieron, Larissa THRACE Ainos, Bizye, Byzantium, Deultum, Maroneia, Mesembra, Pantalia (? ... See also *Greek colonies in Thrace Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ... References Greek colonies in Thrace Former populated places in Greece Lost cities and towns {{AncientThrace-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and other territories. Most of these regions were officially unified only once, for 13 years, under Alexander the Great's empire from 336 to 323 BC (though this excludes a number of Greek city-states free from Alexander's jurisdiction in the western Mediterranean, around the Black Sea, Cyprus, and Cyrenaica). In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Roughly three centuries after the Late Bronze Age collapse of Mycenaean Greece, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
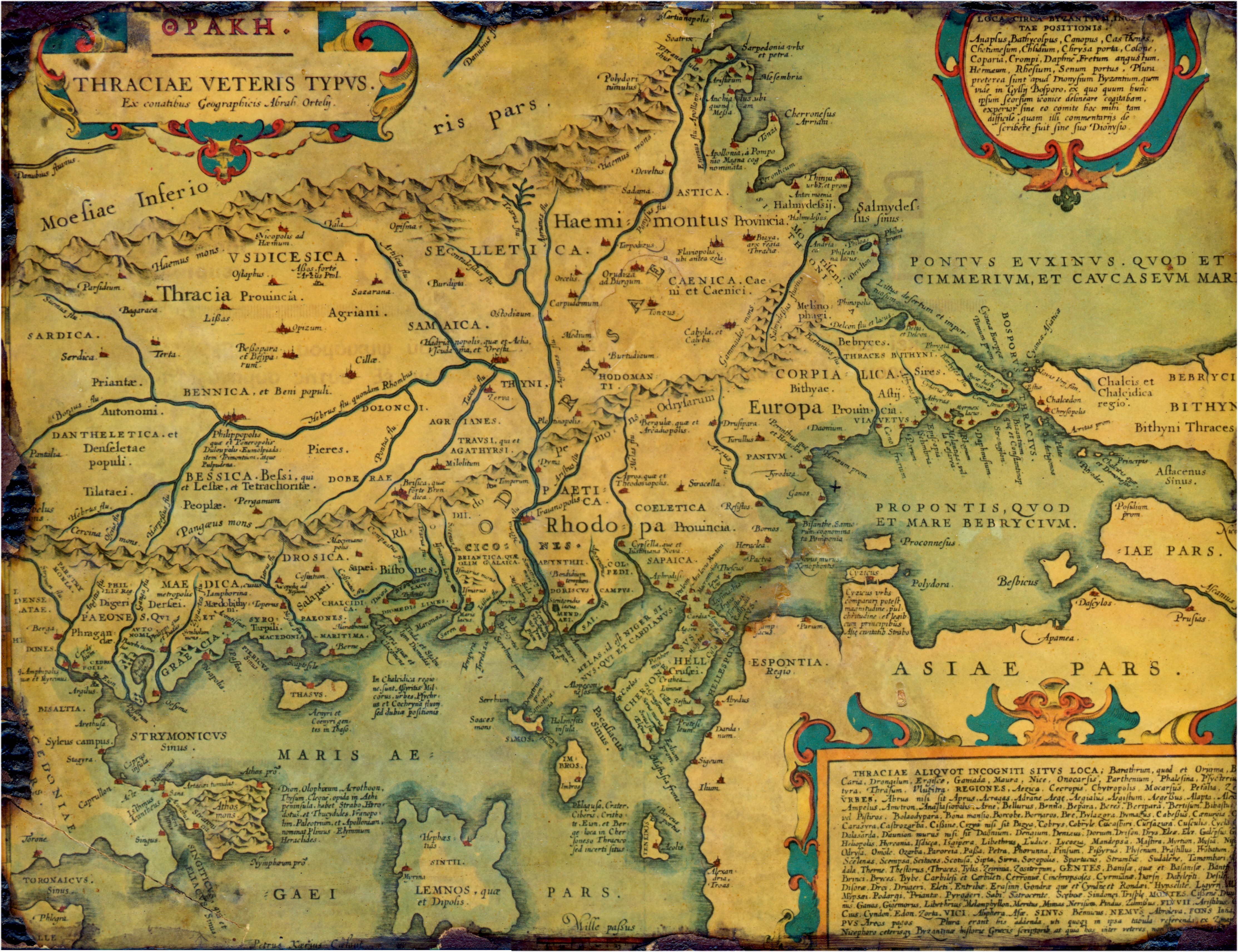
Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. It comprises southeastern Bulgaria (Northern Thrace), northeastern Greece (Western Thrace), and the European part of Turkey ( East Thrace). The region's boundaries are based on that of the Roman Province of Thrace; the lands inhabited by the ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into the region of Macedonia. Etymology The word ''Thrace'' was first used by the Greeks when referring to the Thracian tribes, from ancient Greek Thrake (Θρᾴκη), descending from ''Thrāix'' (Θρᾷξ). It referred originally to the Thracians, an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name ''Europe'' first referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nestos (river)
Nestos ( ), Mesta ( ), or formerly the Mesta Karasu in Turkish (Karasu meaning "black river"), is a river in Bulgaria and Greece. It rises in the Rila Mountains and flows into the Aegean Sea near the island of Thasos. It plunges down towering canyons toward the Aegean Sea through mostly metamorphic formations. At the end, the main stream spreads over the coastal plain of Chrysoupolis and expands as a deltaic system with freshwater lakes and ponds forming the Nestos delta. The length of the river is , of which flow through BulgariaStatistical Yearbook 2017 , p. 17 and the rest in [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebros
Maritsa or Maritza ( bg, Марица ), also known as Meriç ( tr, Meriç ) and Evros ( ell, Έβρος ), is a river that runs through the Balkans in Southeast Europe. With a length of ,Statistical Yearbook 2017 , p. 17 it is the longest river that runs solely in the interior of the Balkan peninsula, and one of the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Elis
Elis () or Eleia ( el, Ήλιδα, Ilida, grc-att, Ἦλις, Ēlis ; Elean: , ethnonym: ) is an ancient district in Greece that corresponds to the modern regional unit of Elis. Elis is in southern Greece on the Peloponnese, bounded on the north by Achaea, east by Arcadia, south by Messenia, and west by the Ionian Sea. Over the course of the archaic and classical periods, the ''polis'' "city-state" of Elis controlled much of the region of Elis, most probably through unequal treaties with other cities; many inhabitants of Elis were Perioeci—autonomous free non-citizens. Perioeci, unlike other Spartans, could travel freely between cities. Thus the polis of Elis was formed. The local form of the name was Valis, or Valeia, and its meaning, in all probability was, "the lowland" (compare with the word "valley"). In its physical constitution Elis is similar to Achaea and Arcadia; its mountains are mere offshoots of the Arcadian highlands, and its principal rivers are fed by Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyme
Dyme ( grc, Δύμη), or Dymae, was a town and polis (city-state) of ancient Achaea, and the most westerly of the 12 Achaean cities, from which circumstance it is said to have derived its name. The location of Dyme is near the modern Kato Achaia. Location It was situated near the coast, according to Strabo 60 stadia from the promontory Araxus, and according to Pausanias 30 stadia from the river Larisus, which separated its territory from Elis. Names It is further said by Strabo to have been formed out of a union of 8 villages, one of which was called Teuthea (Τευθέα); and it is probable, that some of the different names, by which the city is said to have been called, were originally the names of the separate villages. Thus, its more ancient name is stated by Pausanias to have been Paleia (Πάλεια), and by Strabo to have been Stratus or Stratos (Στρατός). The poet Antimachus gave it the epithet Cauconis, which was derived by some from the iron Caucon in the neigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Ancient Cities In Thrace And Dacia
This is a list of ancient cities, towns, villages, and fortresses in and around Thrace and Dacia. A number of these settlements were Dacian and Thracian, but some were Celtic, Greek, Roman, Paeonian, or Persian. A number of cities in Dacia and Thrace were built on or close to the sites of preexisting Dacian or Thracian settlements. Some settlements in this list may have a double entry, such as the Paeonian ''Astibo'' and Latin ''Astibus''. It is believed that Thracians did not build true cities even if they were named as such; the largest Thracian settlements were large villages.The Cambridge Ancient History, Volume 3, Part 2: The Assyrian and Babylonian Empires and Other States of the Near East, from the Eighth to the Sixth Centuries BC by John Boardman, I. E. S. Edwards, E. Sollberger, and N. G. L. Hammond ,, 1992, page 612: "Thrace possessed only fortified areas and cities such as Cabassus would have been no more than large villages. In general the population lived in village ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Colonies In Thrace
Greek may refer to: Greece Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe: *Greeks, an ethnic group. *Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family. **Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor of all known varieties of Greek. **Mycenaean Greek, most ancient attested form of the language (16th to 11th centuries BC). **Ancient Greek, forms of the language used c. 1000–330 BC. **Koine Greek, common form of Greek spoken and written during Classical antiquity. **Medieval Greek or Byzantine Language, language used between the Middle Ages and the Ottoman conquest of Constantinople. **Modern Greek, varieties spoken in the modern era (from 1453 AD). *Greek alphabet, script used to write the Greek language. *Greek Orthodox Church, several Churches of the Eastern Orthodox Church. *Ancient Greece, the ancient civilization before the end of Antiquity. *Old Greek, the language as spoken from Late Antiquity to around 1500 AD. Other uses * '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Greece
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)