|
Jidava
Jidava was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia. Since 1969, the site has been administered by the Arge»ô County Museum.''Enciclopedia Arge»ôului »ôi Muscelului'' site, p. 123 Gallery File:Jidava - Plan.svg, The plan of the castrum File:Castrul Roman Jidova 3.jpg, The front of reconstructed wall and tower File:Castrul Roman Jidova 2.jpg, The back of reconstructed wall and tower File:Castrul Roman Jidova.jpg, Praetorium File:Castra Jidava - Hipocaust.jpg, Hypocaust room of Praetorium See also *List of castra Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in various places of Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition ... Notes External links *Roman castra from Romania - Google MapsEarth Roman Dacia Archaeological sites in Romania Roman legionary fortresses in Romania History of Muntenia C√¢mpulung Historic monuments in Arge»ô County ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arge»ô County Museum
The Argeș County Museum ( ro, Muzeul Județean Argeș) is a government institution and visitor attraction based in Pitești, Romania. Formally inaugurated in 1955, it is headquartered in an 1890s palace in the city center. Topics of its permanent exhibits include history, ecology, folk art and minerals. Additionally, a fine arts gallery is located in the former city hall, while three other sites elsewhere in the county are also administered by the museum. Background and description The museum is headquartered at 44 Armand Călinescu Street, in the former Argeș County Administrative Palace. The structure was built in 1898–1899 according to the plans of architect Dimitrie Maimarolu, while Mihail Manolescu was Prefect (Romania), prefect. The land previously belonged to the Buliga skete, and the funds for construction came in the form of a loan of 140,000 Romanian leu, lei from a Bucharest bank, guaranteed by the Dimitrie Sturdza-led National Liberal Party (Romania, 1875), Liberal g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C√¢mpulung
Câmpulung (also spelled ''Cîmpulung'', , german: Langenau, Old Romanian ''Dlăgopole'', ''Длъгополе'' (from Middle Bulgarian)), or ''Câmpulung Muscel'', is a municipality in the Argeș County, Muntenia, Romania. It is situated among the outlying hills of the Carpathian mountains, at the head of a long well-wooded glen traversed by the Râul Târgului, a tributary of the Argeș. Its pure air and fine scenery render Câmpulung a popular summer resort. In the city there are more than twenty churches, besides a monastery and a cathedral, which both claim to have been founded in the 13th century by Radu Negru, legendary first Prince of Wallachia. Name "Câmpulung" literally means "Long Field" in Romanian, rendered as "Longus-Campus" in Latin. History Near Câmpulung are the remains of a Roman camp now known as the ''Castra of Jidava (or Jidova)''; and just beyond the gates, vestiges of a Roman colony, variously identified with Romula, Stepenium and Ulpia Traian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
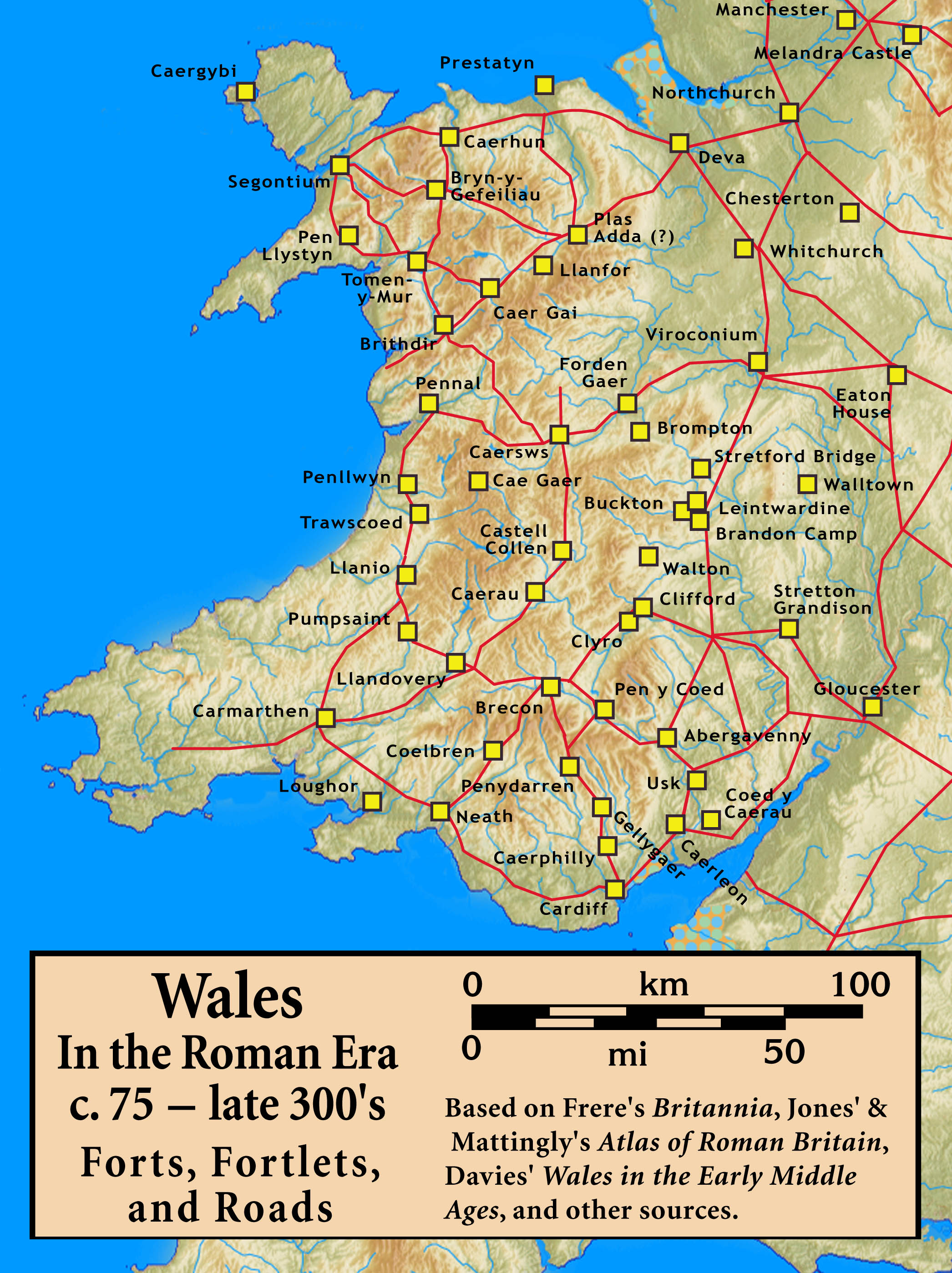
List Of Castra
Castra (Latin, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army throughout the Empire in various places of Europe, Asia and Africa. The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses. Locations The disposition of the castra reflects the most important zones of the empire from a military point of view. Many castra were disposed along frontiers particularly in Northern and Central Europe. Another focal point was the Eastern border, where the Roman Empire confronted one of its long-term enemies, the Persian Empire. Other castra were located in strategically important zones, as in Egypt, from which most of the wealth of the empire came. Finally, other castra were located in zones in which the Romans experienced local unrest, such as Northern Spain and Judea. Provinces where the Roman power was unchallenged, such as Italy, Gaul, Africa and Greece, were provided with few or no castra. In the long history of the Roman Empire, the character of the mil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cohors I Flavia Commagenorum Equitata
Cohors rimaFlavia Commagenorum uingenariaequitata sagittaria? (" stpart-mounted 00 strongcohort of Commagenes") was a Roman auxiliary regiment containing cavalry contingents. The cohort stationed in Dacia at castra Acidava, castra Jidava, castra Romula, castra of Sfârleanca, castra of Slăveni and castra of Drajna de Sus. See also * List of Roman auxiliary regiments This article lists ', non-legionary auxiliary regiments of the imperial Roman army, attested in the epigraphic record, by Roman province of deployment during the reign of emperor Hadrian ( AD 117–138). The index of regimental names explai ... References * Academia Română: Istoria Românilor, Vol. 2, Daco-romani, romanici, alogeni, 2nd. Ed., București, 2010, * Constantin C. Petolescu: Dacia - Un mileniu de istorie, Ed. Academiei Române, 2010, * Cristian M. Vlădescu: Fortificațiile romane din Dacia Inferior, Craiova, 1986 * Petru Ureche: Tactică, strategie și specific de luptă la cohortele e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porta Principalis Sinistra
Porta can refer to: People * Porta (rapper) (born 1988), stagename of Christian Jiménez Bundo, a Spanish rap singer * Bernardo Porta (1758–1829), Italian composer active in France * Bianca Della Porta (born 1991), Canadian ice hockey and rugby player * Carlo Porta (1775–1821), Italian poet in the Milanese dialect * Costanzo Porta (1528–1601), Italian composer of the Renaissance * Giacomo della Porta (1532–1602), Italian sculptor and architect * Giambattista della Porta (1535–1615), Neapolitan physician and playwright * Giovanni Porta (1675–1755), Italian composer * Hugo Porta (born 1951), Argentine rugby union footballer * Livio Dante Porta (1923–2003), Argentine engineer * Luigi Porta (1800–1875), Italian surgeon * Miquel Porta (born 1957), Spanish epidemiologist and scholar * Richard Porta (born 1983), Uruguayan Australian footballer Places * La Porta, a commune in the Haute-Corse department of France on the island of Corsica * Porta (Barcelona) a neighbourhood o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Legionary Fortresses In Romania
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter in the New Testament of the Christian Bible Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television *Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), including a list of people named Roman or Romans *·ø¨œâŒºŒ±· ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Romania
Romanian archaeology begins in the 19th century. Archaeologists * Alexandru Odobescu (1834—1895) * Grigore Tocilescu (1850–1909) * Vasile Pârvan (1882–1927) * Constantin Daicoviciu (1898–1973) ;living * Gheorghe I. Cantacuzino (b. 1938) * Adrian Andrei Rusu (b. 1951) – medieval archaeology, researcher at the Institute of Archaeology and Art History in Cluj-Napoca Institutes * Institute of Archaeology and Art History in Cluj-Napoca * Vasile Pârvan Institute of Archaeology in Bucharest Museums * Archaeology Museum Piatra Neamț * Iron Gates Region Museum * Museum of Dacian and Roman Civilisation * National Museum of Romanian History * National Museum of Transylvanian History Sites * Acidava (Enoşeşti) – Dacian, Roman * Apulon (Piatra Craivii) – Dacian * Apulum (Alba Iulia) – Roman, Dacian * Argedava (Popeşti) – Dacian, possibly Burebista's court or capital * Argidava (Vărădia) – Dacian, Roman * Basarabi (C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypocaust
A hypocaust ( la, hypocaustum) is a system of central heating in a building that produces and circulates hot air below the floor of a room, and may also warm the walls with a series of pipes through which the hot air passes. This air can warm the upper floors as well. The word derives from the Ancient Greek meaning "under" and , meaning "burnt" (as in ''caustic''). The earliest reference to such a system suggests that the temple of Ephesus in 350 BC was heated in this manner, although Vitruvius attributes its invention to Sergius Orata in c. 80 BC. Its invention improved the hygiene and living conditions of citizens, and was a forerunner of modern central heating. Roman operation Hypocausts were used for heating hot baths and other public buildings in Ancient Rome. They were also used in private homes. It was a must for the villas of the wealthier merchant class throughout the Roman Empire. The ruins of Roman hypocausts have been found throughout Europe (for example in Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Pite»ôti
The University of Piteşti ( ro, Universitatea din Pitești, abbreviated ''UPIT'') is a public university in Piteşti, Romania, founded in 1991. History The first Higher Education Institution in Piteşti was founded in 1962 and was called "The 3-year Pedagogical Institute" with pedagogical specialisations in Mathematics, Physics, Biology, Chemistry, Philology and Physical Education and Sports. The opening of the technical specialisations followed, leading to the establishment of the Institute of Sub-Engineers (1969), united in 1974 under the name of the Institute of Higher Education. Subsequently, there were various other forms of organisation, in a period under the subordination of the Bucharest Polytechnic Institute. In 1991, it became autonomous and received the name "University of Pitești". Starting from the beginning, the University of Pitești has polarised the interest of many young people in the region for the programs of study, quality of the education provided by the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castra
In the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire, the Latin word ''castrum'', plural ''castra'', was a military-related term. In Latin usage, the singular form ''castrum'' meant 'fort', while the plural form ''castra'' meant 'camp'. The singular and plural forms could refer in Latin to either a building or plot of land, used as a fortified military base.. Included is a discussion about the typologies of Roman fortifications. In English usage, ''castrum'' commonly translates to "Roman fort", "Roman camp" and "Roman fortress". However, scholastic convention tends to translate ''castrum'' as "fort", "camp", "marching camp" or "fortress". Romans used the term ''castrum'' for different sizes of camps – including large legionary fortresses, smaller forts for cohorts or for auxiliary forces, temporary encampments, and "marching" forts. The diminutive form ''castellum'' was used for fortlets, typically occupied by a detachment of a cohort or a '' centuria''. For a list of known castr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimitrie Butculescu
Dimitrie is the Romanian form of a Slavic given name. Notable persons with that name include: ;First name * Dimitrie Alexandresco (1850–1925), Romanian encyclopedist * Dimitrie Anghel (1872–1914), Romanian poet * Dimitri Atanasescu (1836–1907), Aromanian teacher commonly referred to as Dimitrie Atanasescu * Dimitrie Bogos (1889–1946), Romanian politician * Dimitrie Bolintineanu (1819–1872), Romanian poet, diplomat, politician, and revolutionary * Dimitrie Brândză (1846–1895), Romanian botanist * Dimitrie Brătianu (1818–1892), Romanian politician, Prime Minister of Romania in 1881 * Dimitrie Cantemir (1673–1723), Prince of Moldavia * Dimitrie Călugăreanu (1868-1937), Romanian physician and naturalist * Dimitrie Cărăuş (born 1892), a Bessarabian politician, member of the Moldovan Parliament (1917–1918) * Dimitrie Comșa (1846-1931), Romanian agronomer and activist * Dimitrie Cornea (1816–1884), Romanian politician, and diplomat * Dimitrie Cozacovici (1790 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arge»ô County
Arge»ô County () is a county ('' jude»õ'') of Romania, in Muntenia, with the capital city at Pite»ôti. Demographics On 20 October 2011, it had a population of 612,431 and the population density was 89/km2. * Romanians ‚Äì 97% * Roma (Gypsies) and other ethnic groups ‚Äì 3% Geography This county has a total area of 6,862 km2. The landforms can be split into 3 distinctive parts. In the north side there are the mountains, from the Southern Carpathians group ‚Äì the FƒÉgƒÉra»ô Mountains with Moldoveanu Peak (2,544 m), Negoiu Peak (2,535 m) and V√¢nƒÉtoarea lui Buteanu peak (2,508 m) towering the region, and in the North-East part the LeaotƒÉ Mountains. Between them there is a pass towards Bra»ôov, the RucƒÉr-Bran Passage. The heights decrease, and in the center there are the sub-carpathian hills, with heights around 800 m, crossed with very deep valleys. In the south there is the northern part of the Romanian Plain. The main river that crosses the county is the Arge» ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


