The LGM-30 Minuteman is an American land-based
intercontinental ballistic missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons c ...
(ICBM) in service with the
Air Force Global Strike Command
Air Force Global Strike Command (AFGSC) is a Major Command (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force, headquartered at Barksdale Air Force Base, Louisiana. AFGSC provides combat-ready forces to conduct strategic nuclear deterrence and global stri ...
. , the LGM-30G Minuteman III version is the only land-based ICBM in service in the United States and represents the land leg of the U.S.
nuclear triad, along with the
Trident submarine-launched ballistic missile
A submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) is a ballistic missile capable of being launched from submarines. Modern variants usually deliver multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), each of which carries a nuclear warhead ...
(SLBM) and nuclear weapons carried by long-range
strategic bomber
A strategic bomber is a medium- to long-range penetration bomber aircraft designed to drop large amounts of air-to-ground weaponry onto a distant target for the purposes of debilitating the enemy's capacity to wage war. Unlike tactical bombers, ...
s.
Development of the Minuteman began in the mid-1950s when basic research indicated that a
solid-fuel rocket
A solid-propellant rocket or solid rocket is a rocket with a rocket engine that uses solid propellants ( fuel/oxidizer). The earliest rockets were solid-fuel rockets powered by gunpowder; they were used in warfare by the Arabs, Chinese, Persian ...
motor could stand ready to launch for long periods of time, in contrast to
liquid-fueled rockets that required fueling before launch and so might be destroyed in a surprise attack. The missile was named for the colonial
minutemen
Minutemen were members of the organized New England colonial militia companies trained in weaponry, tactics, and military strategies during the American Revolutionary War. They were known for being ready at a minute's notice, hence the name. Mi ...
of the
American Revolutionary War, who could be ready to fight on short notice.
The Minuteman entered service in 1962 as a
deterrence weapon that could hit
Soviet cities with a
second strike
In nuclear strategy, a retaliatory strike or second-strike capability is a country's assured ability to respond to a nuclear attack with powerful nuclear retaliation against the attacker. To have such an ability (and to convince an opponent of it ...
and
countervalue
In military doctrine, countervalue is the targeting of an opponent's assets that are of value but not actually a military threat, such as cities and civilian populations. Counterforce is the targeting of an opponent's military forces and faciliti ...
counterattack if the U.S. was attacked. However, the development of the
United States Navy (USN)
UGM-27 Polaris, which addressed the same role, allowed the Air Force to modify the Minuteman, boosting its accuracy enough to attack hardened military targets, including Soviet missile silos. The Minuteman II entered service in 1965 with a host of upgrades to improve its accuracy and survivability in the face of an
anti-ballistic missile
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear weapon, nuclear, Chemical weapon, chemical, Bioagent, biological, or conventiona ...
(ABM) system the Soviets were known to be developing. In 1970, the Minuteman III became the first deployed ICBM with
multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle
A multiple independently targetable reentry vehicle (MIRV) is an exoatmospheric ballistic missile payload containing several warheads, each capable of being aimed to hit a different target. The concept is almost invariably associated with in ...
s (MIRV): three smaller warheads that improved the missile's ability to strike targets defended by ABMs.
They were initially armed with the
W62
The W62 was an American thermonuclear warhead designed in the 1960s and manufactured from March 1970 to June 1976. Used on some Minuteman III ICBMs, it was partially replaced by the W78 starting in December 1979, and fully replaced by W87 warhea ...
warhead with a
yield of 170
kilotons
TNT equivalent is a convention for expressing energy, typically used to describe the energy released in an explosion. The is a unit of energy defined by that convention to be , which is the approximate energy released in the detonation of a m ...
.
By the 1970s, 1,000 Minuteman missiles were deployed. This force has shrunk to 400 Minuteman III missiles ,
deployed in
missile silos around
Malmstrom AFB,
Montana;
Minot AFB,
North Dakota; and
Francis E. Warren AFB
Francis E. Warren Air Force Base , shortened as F.E. Warren AFB is a United States Air Force base (AFB) located approximately west of Cheyenne, Wyoming. It is one of three strategic-missile bases in the U.S. It was named in honor of Francis E ...
,
Wyoming.
The Minuteman III will be progressively replaced by the new
Ground Based Strategic Deterrent
The LGM-35 Sentinel, also known as the Ground Based Strategic Deterrent (GBSD), is a future American land-based intercontinental ballistic missile system (ICBM) currently in the early stages of development. It is slated to replace the aging Minu ...
(GBSD) ICBM, to be built by
Northrop Grumman, beginning in 2030.
History
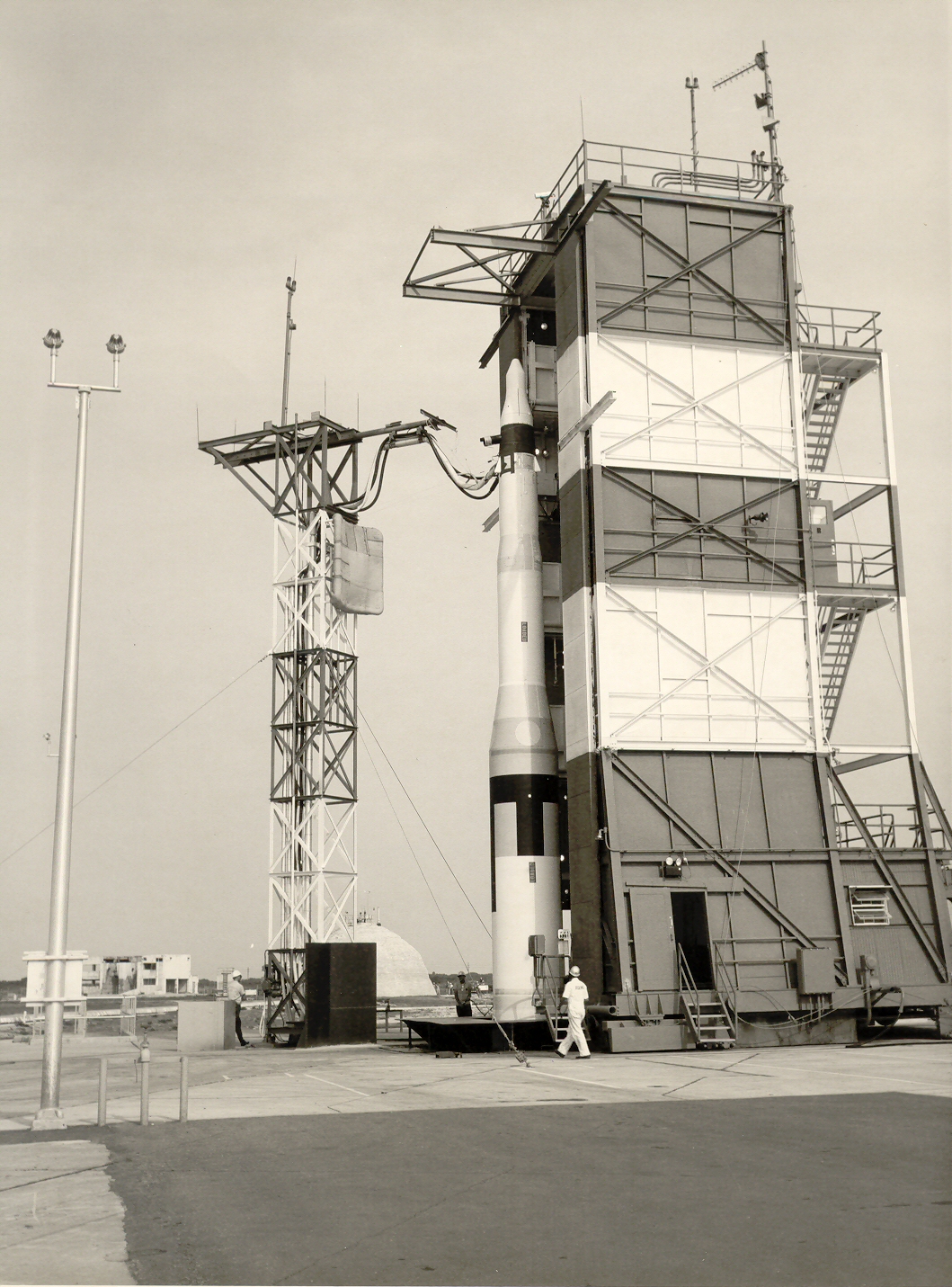

Edward Hall and solid fuels
Minuteman owes its existence largely to Air Force Colonel
Edward N. Hall
Edward Nathaniel Hall (4 August 1914 – 15 January 2006) was a leading missile development engineer working for the United States and its allies in World War II and the late 20th century. He is known as the father of the Minuteman interc ...
, who in 1956 was given charge of the solid-fuel-propulsion division of
General Bernard Schriever's Western Development Division
Space Systems Command (SSC) is the United States Space Force's space development, acquisition, launch, and logistics field command. It is headquartered at Los Angeles Air Force Base, California and manages the United States' space launch r ...
, created to lead development of the
SM-65 Atlas and
HGM-25A Titan I ICBMs. Solid fuels were already commonly used in short-range rockets. Hall's superiors were interested in
short- and
medium-range missiles with solids, especially for use in Europe where the fast reaction time was an advantage for weapons that might be attacked by Soviet aircraft. But Hall was convinced that they could be used for a true ICBM with a range.
To achieve the required energy, that year Hall began funding research at
Boeing and
Thiokol into the use of
ammonium perchlorate composite propellant. Adapting a concept developed in the
UK, they cast the fuel into large cylinders with a star-shaped hole running along the inner axis. This allowed the fuel to burn along the entire length of the cylinder, rather than just the end as in earlier designs. The increased burn rate meant increased thrust. This also meant the heat was spread across the entire motor, instead of the end, and because it burned from the inside out it did not reach the wall of the missile fuselage until the fuel was finished burning. In comparison, older designs burned primarily from one end to the other, meaning that at any instant one small section of the fuselage was being subjected to extreme loads and temperatures.
Guidance of an ICBM is based not only on the direction the missile is traveling but the precise instant that thrust is cut off. Too much thrust and the warhead will overshoot its target, too little and it will fall short. Solids are normally very hard to predict in terms of burn time and their instantaneous thrust during the burn, which made them questionable for the sort of accuracy required to hit a target at intercontinental range. While this initially appeared to be an insurmountable problem, it ended up being solved in an almost trivial fashion. A series of ports were added inside the rocket nozzle that were opened when the guidance systems called for engine cut-off. The reduction in pressure was so abrupt that the remaining fuel broke up and blew out the nozzle without contributing to the thrust.
The first to use these developments was the US Navy. It had been involved in a joint program with the
US Army to develop the liquid-fueled
PGM-19 Jupiter, but had always been skeptical of the system. The Navy felt that liquid fuels were too dangerous to use on board ships, especially submarines. Rapid success in the solids development program, combined with
Edward Teller's promise of much lighter
nuclear warheads during
Project Nobska
Project Nobska was a 1956 summer study on anti-submarine warfare (ASW) for the United States Navy ordered by Chief of Naval Operations Admiral Arleigh Burke. It is also referred to as the Nobska Study, named for its location on Nobska Point near ...
, led the Navy to abandon Jupiter and begin development of their own solid-fuel missile. Aerojet's work with Hall was adapted for their
UGM-27 Polaris starting in December 1956.
Missile farm concept
The US Air Force saw no pressing need for a solid fuel ICBM. Development of the
SM-65 Atlas and
SM-68 Titan The SM-68 Titan (individual variants later designated HGM-25 Titan I and LGM-25 Titan II) was the designation of two intercontinental ballistic missiles developed for the United States Air Force. The Titan I and Titan II missiles were operational be ...
ICBMs was progressing, and "storable" liquids were being developed that would allow missiles to be left in a ready-to-shoot form for extended periods. Hall saw solid fuels not only as a way to improve launch times or safety, but part of a radical plan to greatly reduce the cost of ICBMs so that thousands could be built. He was aware that new computerized
assembly lines would allow continual production, and that similar equipment would allow a small team to oversee operations for dozens or hundreds of missiles. A solid fuel design would be simpler to build, and easier to maintain.
Hall's ultimate plan was to build a number of integrated missiles "farms" that included factories,
missile silos
A missile launch facility, also known as an underground missile silo, launch facility (LF), or nuclear silo, is a vertical cylindrical structure constructed underground, for the storage and launching of intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBM ...
, transport and recycling. Each farm would support between 1,000 and 1,500 missiles being produced in a continuous low rate cycle. Systems in a missile would detect failures, at which point it would be removed and recycled, while a newly built missile would take its place.
The missile design was based purely on lowest possible cost, reducing its size and complexity because "the basis of the weapon's merit was its low cost per completed mission; all other factors – accuracy, vulnerability, and reliability – were secondary."
Hall's plan did not go unopposed, especially by the more established names in the ICBM field.
Ramo-Wooldridge
TRW Inc., was an American corporation involved in a variety of businesses, mainly aerospace, electronics, automotive, and credit reporting.http://www.fundinguniverse.com/company-histories/TRW-Inc-Company-History.html TRW Inc. It was a pioneer ...
pressed for a system with higher accuracy, but Hall countered that the missile's role was to attack Soviet cities, and that "a force which provides numerical superiority over the enemy will provide a much stronger deterrent than a numerically inferior force of greater accuracy."
Hall was known for his "friction with others" and in 1958 Schriever removed him from the Minuteman project, sending him to the UK to oversee deployment of the
Thor IRBM
The PGM-17A Thor was the first operational ballistic missile of the United States Air Force (USAF). Named after the Norse god of thunder, it was deployed in the United Kingdom between 1959 and September 1963 as an intermediate-range ballistic mi ...
.
On his return to the US in 1959, Hall retired from the Air Force, but received his second
Legion of Merit
The Legion of Merit (LOM) is a military award of the United States Armed Forces that is given for exceptionally meritorious conduct in the performance of outstanding services and achievements. The decoration is issued to members of the eight ...
in 1960 for his work on solid fuels.
Although he was removed from the Minuteman project, Hall's work on cost reduction had already produced a new design of diameter, much smaller than the Atlas and Titan at , which meant smaller and cheaper silos. Hall's goal of dramatic cost reduction was a success, although many of the other concepts of his missile farm were abandoned.
Guidance system
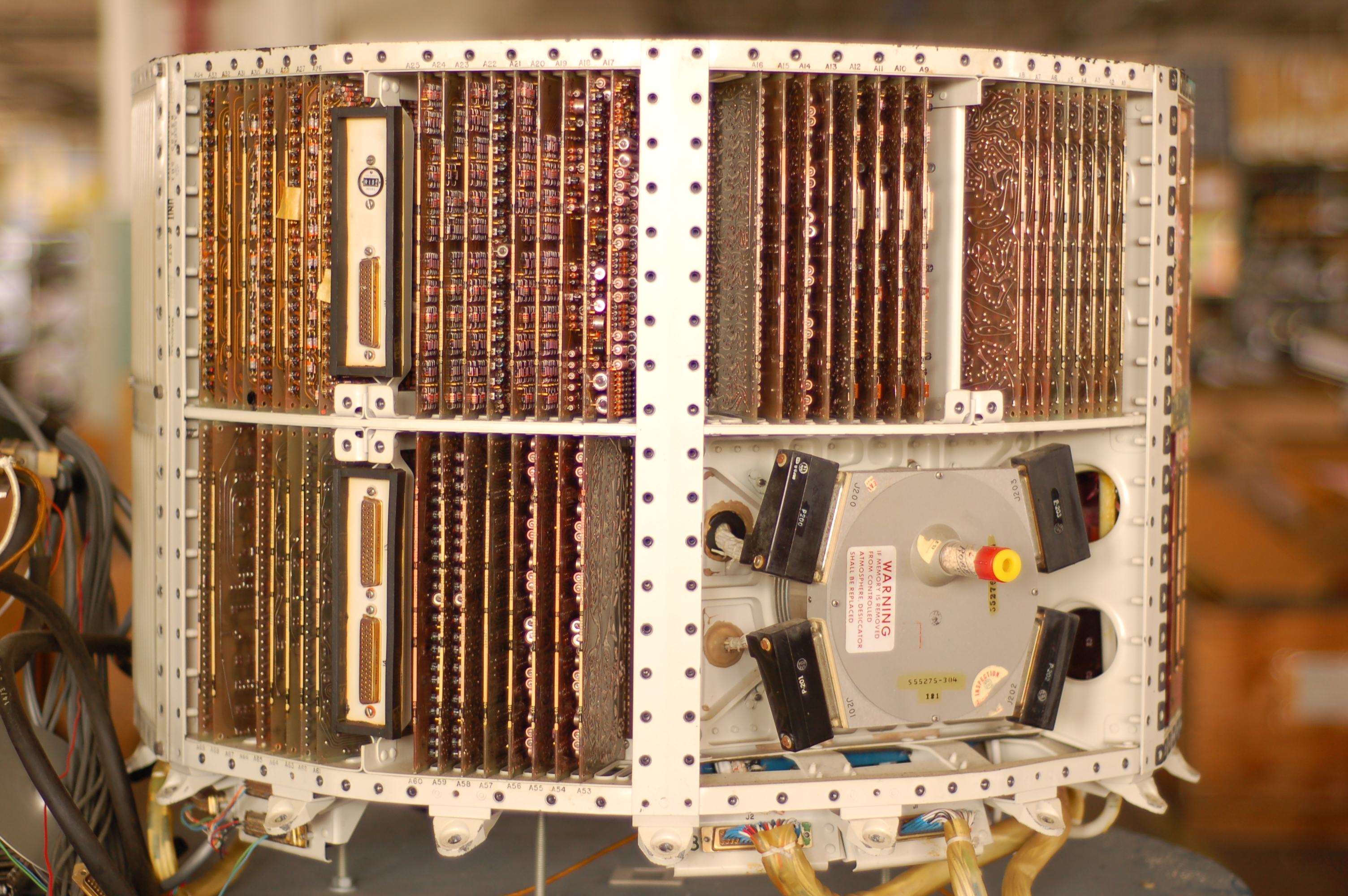
Previous long-range missiles used liquid fuels that could be loaded only just prior to firing. The loading process took from 30 to 60 minutes in typical designs. Although lengthy, this was not considered to be a problem at the time, because it took about the same amount of time to spin up the
inertial guidance system
An inertial navigation system (INS) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors ( gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity (dire ...
, set the initial position, and program in the target coordinates.
Minuteman was designed from the outset to be launched in minutes. While solid fuel eliminated the fueling delays, the delays in starting and aligning the guidance system remained. For the quick launch, the guidance system would have to be kept running and aligned at all times, which was a serious problem for the mechanical systems, especially the gyroscopes which used
ball bearings.
had an experimental design using
air bearing
Air bearings (also known as aerostatic or aerodynamic bearings) are fluid bearings that use a thin film of pressurized gas to provide a low friction load-bearing interface between surfaces. The two surfaces do not touch, thus avoiding the tradit ...
s that they claimed had been running continually from 1952 to 1957.
Autonetics further advanced the
state of the art
The state of the art (sometimes cutting edge or leading edge) refers to the highest level of general development, as of a device, technique, or scientific field achieved at a particular time. However, in some contexts it can also refer to a level ...
by building the platform in the form of a ball which could rotate in two directions. Conventional solutions used a shaft with ball bearings at either end that allowed it to rotate around a single axis only. Autonetics design meant that only two gyros would be needed for the inertial platform, instead of the typical three.
The last major advance was to use a general-purpose digital computer in place of the analog or custom designed digital computers. Previous missile designs normally used two single-purpose and very simple computers; one ran the
autopilot that kept the missile flying along a programmed course, and the second compared the information from the inertial platform to the target coordinates and sent any needed corrections to the autopilot. To reduce the total number of parts used in Minuteman, a single faster computer was used, running separate routines for these functions.
Since the guidance program would not be running while the missile sat in the silo, the same computer was also used to run a program that monitored the various sensors and test equipment. With older designs this had been handled by external systems, requiring miles of extra wiring and many connectors to locations where test instruments could be connected during servicing. Now these could all be accomplished by communicating with the computer through a single connection. In order to store multiple programs, the computer, the
D-17B
The D-17B (D17B) computer was used in the Minuteman I NS-1OQ missile guidance system. The complete guidance system contained a D-17B computer, the associated stable platform, and power supplies.
The D-17B weighed approximately , contained 1,521 ...
, was built in the form of a
drum machine but used a
hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnet ...
in place of the drum.
Building a computer with the required performance, size and weight demanded the use of
transistors, which were at that time very expensive and not very reliable. Earlier efforts to use computers for guidance,
BINAC and the system on the
SM-64 Navaho, had failed and were abandoned. The Air Force and Autonetics spent millions on a program to improve transistor and component reliability 100 times, leading to the "Minuteman high-rel parts" specifications. The techniques developed during this program were equally useful for improving all transistor construction, and greatly reduced the failure rate of transistor production lines in general. This improved yield, which had the effect of greatly lowering production costs, had enormous spin-off effects in the electronics industry.
Using a general-purpose computer also had long-lasting effects on the Minuteman program and the US's nuclear stance in general. With Minuteman, the targeting could be easily changed by loading new trajectory information into the computer's hard drive, a task that could be completed in a few hours. Earlier ICBMs' custom wired computers, on the other hand, could have attacked only a single target, whose precise trajectory information was hard-coded directly in the system's logic.
Missile gap
In 1957, a series of intelligence reports suggested the Soviet Union was far ahead in the missile race and would be able to overwhelm the US by the early 1960s. If the Soviets were building missiles in the numbers being predicted by the CIA and others within the defense establishment, by as early as 1961 they would have enough to attack all SAC and ICBM bases in the US in a single
first strike First strike most commonly refers to:
* Pre-emptive nuclear strike
* Pre-emptive war
First strike may also refer to:
* ''First Strike'' (1996 film), also known as ''Jackie Chan's First Strike'' or ''Police Story 4: First Strike'', an action movie ...
. It was later demonstrated that this "
missile gap" was just as fictional as the "
bomber gap
The bomber gap was the Cold War belief that the Soviet Union's Long Range Aviation department had gained an advantage in deploying jet-powered strategic bombers. Widely accepted for several years, the gap was used as a political talking point in th ...
" of a few years earlier,
but through the late 1950s, it was a serious concern.
The Air Force responded by beginning research into survivable strategic missiles, starting the
WS-199
Weapons System 199 (WS-199) was a weapons development program conducted by the United States Air Force to research and develop new strategic weapons systems for Strategic Air Command. Two air-launched and one ground-launched vehicles were developed ...
program. Initially, this focused on
air-launched ballistic missiles, which would be carried aboard aircraft flying far from the Soviet Union, and thus impossible to attack by either ICBM, because they were moving, or long-range
interceptor aircraft, because they were too far away. In the shorter term, looking to rapidly increase the number of missiles in its force, Minuteman was given crash development status starting in September 1958. Advanced surveying of the potential silo sites had already begun in late 1957.
Adding to their concerns was a Soviet
anti-ballistic missile
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear weapon, nuclear, Chemical weapon, chemical, Bioagent, biological, or conventiona ...
system which was known to be under development at
Sary Shagan. WS-199 was expanded to develop a
maneuvering reentry vehicle
The maneuverable reentry vehicle (abbreviated MARV or MaRV) is a type of warhead for ballistic missiles that is capable of maneuvring and changing its trajectory.
MaRV can be capable of autonomously tracking ground targets to make sure the mis ...
(MARV), which greatly complicated the problem of shooting down a warhead. Two designs were tested in 1957,
Alpha Draco
The Alpha Draco missile, also known as Weapons System 199D (WS-199D), was an experimental ballistic missile developed by McDonnell Aircraft in the late 1950s to investigate the aerodynamic physics of the boost-glide reentry trajectory. Three test ...
and the Boost Glide Reentry Vehicle. These used long and skinny arrow-like shapes that provided aerodynamic lift in the high atmosphere, and could be fitted to existing missiles like Minuteman.
The shape of these reentry vehicles required more room on the front of the missile than a traditional reentry vehicle design. To allow for this future expansion, the Minuteman silos were revised to be built deeper. Although Minuteman would not deploy a
boost-glide warhead, the extra space proved invaluable in the future, as it allowed the missile to be extended and carry more fuel and payload.
Polaris

During Minuteman's early development, the Air Force maintained the policy that the manned
strategic bomber
A strategic bomber is a medium- to long-range penetration bomber aircraft designed to drop large amounts of air-to-ground weaponry onto a distant target for the purposes of debilitating the enemy's capacity to wage war. Unlike tactical bombers, ...
was the primary weapon of nuclear war. Blind bombing accuracy on the order of was expected, and the weapons were sized to ensure even the hardest targets would be destroyed as long as the weapon fell within this range. The USAF had enough bombers to attack every military and industrial target in the USSR and was confident that its bombers would survive in sufficient numbers that such a strike would utterly destroy the country.
Soviet ICBMs upset this equation to a degree. Their accuracy was known to be low, on the order of , but they carried large warheads that would be useful against
Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was both a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile ...
's bombers, which parked in the open. Since there was no system to detect the ICBMs being launched, the possibility was raised that the Soviets could launch a sneak attack with a few dozen missiles that would take out a significant portion of SAC's bomber fleet.
In this environment, the Air Force saw their own ICBMs not as a primary weapon of war, but as a way to ensure that the Soviets would not risk a sneak attack. ICBMs, especially newer models that were housed in silos, could be expected to survive an attack by a single Soviet missile. In any conceivable scenario where both sides had similar numbers of ICBMs, the US forces would survive a sneak attack in sufficient numbers to ensure the destruction of all major Soviet cities in return. The Soviets would not risk an attack under these conditions.
Considering this ''
countervalue
In military doctrine, countervalue is the targeting of an opponent's assets that are of value but not actually a military threat, such as cities and civilian populations. Counterforce is the targeting of an opponent's military forces and faciliti ...
'' attack concept, strategic planners calculated that an attack of "400 equivalent megatons" aimed at the largest Soviet cities would promptly kill 30% of their population and destroy 50% of their industry. Larger attacks raised these numbers only slightly, as all of the larger targets would already have been hit. This suggested that there was a "
finite deterrent In nuclear strategy, minimal deterrence, also known as minimum deterrence and finite deterrence, is an application of deterrence theory in which a state possesses no more nuclear weapons than is necessary to deter an adversary from attacking.Kristen ...
" level around 400 megatons that would be enough to prevent a Soviet attack no matter how many missiles they had of their own. All that had to be ensured was that the US missiles survived, which seemed likely given the low accuracy of the Soviet weapons.
Reversing the problem, the addition of ICBMs to the US Air Force's arsenal did not eliminate the need, or desire, to attack Soviet military targets, and the Air Force maintained that bombers were the only suitable platform in that role.
Into this argument came the Navy's
UGM-27 Polaris. Launched from submarines, Polaris was effectively invulnerable and had enough accuracy to attack Soviet cities. If the Soviets improved the accuracy of their missiles this would present a serious threat to the Air Force's bombers and missiles, but none at all to the Navy's submarines. Based on the same 400 equivalent megatons calculation, they set about building a fleet of 41 submarines carrying 16 missiles each, giving the Navy a finite deterrent that was unassailable.
This presented a serious problem for the Air Force. They were still pressing for the development of newer bombers, like the supersonic
B-70, for attacks against military targets, but this role seemed increasingly unlikely in a nuclear war scenario. A February 1960 memo by
RAND, entitled "The Puzzle of Polaris", was passed around among high-ranking Air Force officials. It suggested that Polaris negated any need for Air Force ICBMs if they were also being aimed at Soviet cities. If the role of the missile was to present an unassailable threat to the Soviet population, Polaris was a far better solution than Minuteman. The document had long-lasting effects on the future of the Minuteman program, which, by 1961, was firmly evolving towards a
counterforce capability.
Kennedy
Minuteman's final tests coincided with
John F. Kennedy entering the White House. His new
Secretary of Defense
A defence minister or minister of defence is a cabinet official position in charge of a ministry of defense, which regulates the armed forces in sovereign states. The role of a defence minister varies considerably from country to country; in som ...
,
Robert McNamara, was tasked with continuing the expansion and modernisation of the US nuclear deterrent while limiting spending. McNamara began to apply
cost/benefit analysis, and Minuteman's low production cost made its selection a foregone conclusion. Atlas and Titan were soon scrapped, and the storable liquid fueled Titan II deployment was severely curtailed.
McNamara also cancelled the
B-70 bomber project.
Minuteman's low cost had spin-off effects on non-ICBM programs. The Army's
Nike Zeus, an interceptor missile capable of shooting down Soviet warheads, provided another way to prevent a sneak attack. This had initially been proposed as a way to defend the SAC bomber fleet. The Army argued that upgraded Soviet missiles might be able to attack US missiles in their silos, and Zeus would be able to blunt such an attack. Zeus was expensive and the Air Force said it was more cost-effective to build another Minuteman missile. Given the large size and complexity of the Soviet liquid-fueled missiles, an ICBM building race was one the Soviets could not afford. Zeus was canceled in 1963.
Counterforce
Minuteman's selection as the primary Air Force ICBM was initially based on the same "
second strike
In nuclear strategy, a retaliatory strike or second-strike capability is a country's assured ability to respond to a nuclear attack with powerful nuclear retaliation against the attacker. To have such an ability (and to convince an opponent of it ...
" logic as their earlier missiles: that the weapon was primarily one designed to survive any potential Soviet attack and ensure they would be hit in return. But Minuteman had a combination of features that led to its rapid evolution into the US's primary weapon of nuclear war.
Chief among these qualities was its digital computer. This could be updated in the field with new targets and better information about the flight paths with relative ease, gaining accuracy for little cost. One of the unavoidable effects on the warhead's trajectory was the mass of the Earth, which contains many
mass concentrations that pull on the warhead as it passes over them. Through the 1960s, the Defense Mapping Agency (now part of
National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency) mapped these with increasing accuracy, feeding that information back into the Minuteman fleet. The Minuteman was initially deployed with a
circular error probable
In the military science of ballistics, circular error probable (CEP) (also circular error probability or circle of equal probability) is a measure of a weapon system's precision. It is defined as the radius of a circle, centered on the mean, wh ...
(CEP) of about , but this had improved to about by 1965.
This was accomplished without any mechanical changes to the missile or its navigation system.
At those levels, the ICBM begins to approach the manned bomber in terms of accuracy; a small upgrade, roughly doubling the accuracy of the INS, would give it the same CEP as the manned bomber. Autonetics began such development even before the original Minuteman entered fleet service, and the Minuteman II had a CEP of . Additionally, the computers were upgraded with more memory, allowing them to store information for eight targets, which the missile crews could select among almost instantly, greatly increasing their flexibility.
From that point, Minuteman became the US's primary deterrent weapon, until its performance was matched by the Navy's
Trident missile of the 1980s.
Questions about the need for the manned bomber were quickly raised. The Air Force began to offer a number of reasons why the bomber offered value, in spite of costing more money to buy and being much more expensive to operate and maintain. Newer bombers with better survivability, like the
B-70, cost many times more than the Minuteman, and, in spite of great efforts through the 1960s, became increasingly vulnerable to
surface-to-air missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft syst ...
s. The
B-1 of the early 1970s eventually emerged with a price tag around $200 million (equivalent to $ million in ) while the Minuteman IIIs built during the 1970s cost only $7 million ($ million in ).
The Air Force countered that having a variety of platforms complicated the defense; if the Soviets built an effective
anti-ballistic missile
An anti-ballistic missile (ABM) is a surface-to-air missile designed to counter ballistic missiles (missile defense). Ballistic missiles are used to deliver nuclear weapon, nuclear, Chemical weapon, chemical, Bioagent, biological, or conventiona ...
system of some sort, the ICBM and SLBM fleet might be rendered useless, while the bombers would remain. This became the
nuclear triad concept, which survives into the present. Although this argument was successful, the number of manned bombers has been repeatedly cut and the deterrent role increasingly passed to missiles.
Minuteman I (LGM-30A/B or SM-80/HSM-80A)
:''See also
W56 Warhead''
Deployment
The LGM-30A Minuteman I was first test-fired on 1 February 1961 at
Cape Canaveral
, image = cape canaveral.jpg
, image_size = 300
, caption = View of Cape Canaveral from space in 1991
, map = Florida#USA
, map_width = 300
, type =Cape
, map_caption = Location in Florida
, location ...
,
and entered into the
Strategic Air Command
Strategic Air Command (SAC) was both a United States Department of Defense Specified Command and a United States Air Force (USAF) Major Command responsible for command and control of the strategic bomber and intercontinental ballistic missile ...
's arsenal in 1962. After the first batch of Minuteman I's were fully developed and ready for stationing, the
United States Air Force (USAF) had originally decided to put the missiles at
Vandenberg AFB in California, but before the missiles were set to officially be moved there it was discovered that this first set of Minuteman missiles had defective boosters which limited their range from their initial to . This defect would cause the missiles to fall short of their targets if launched over the
North Pole as planned. The decision was made to station the missiles at
Malmstrom AFB in
Montana instead.
These changes would allow the missiles, even with their defective boosters, to reach their intended targets in the case of a launch.
The "improved" LGM-30B Minuteman I became operational at
Ellsworth AFB,
South Dakota,
Minot AFB,
North Dakota,
F.E. Warren AFB
Francis E. Warren Air Force Base , shortened as F.E. Warren AFB is a United States Air Force base (AFB) located approximately west of Cheyenne, Wyoming. It is one of three strategic-missile bases in the U.S. It was named in honor of Francis E ...
,
Wyoming, and
Whiteman AFB,
Missouri, in 1963 and 1964. All 800 Minuteman I missiles were delivered by June 1965. Each of the bases had 150 missiles emplaced; F.E. Warren had 200 of the Minuteman IB missiles. Malmstrom had 150 of the Minuteman I, and about five years later added 50 of the Minuteman II similar to those installed at
Grand Forks AFB
Grand Forks Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in northeastern North Dakota, located north of Emerado and west of Grand Forks.
The host unit is the 319th Reconnaissance Wing (319 RW) assigned to the Air Combat C ...
, ND.
Specifications
The Minuteman I's length varied based on which variation one was to look at. The Minuteman I/A had a length of and the Minuteman I/B had a length of . The Minuteman I weighed roughly , had an operational range of
with an accuracy of about .
Guidance
The Minuteman I Autonetics
D-17 flight computer used a rotating air bearing magnetic disk holding 2,560 "cold-stored"
words in 20 tracks (write heads disabled after program fill) of 24 bits each and one alterable track of 128 words. The time for a D-17 disk revolution was 10 ms. The D-17 also used a number of short loops for faster access to intermediate results storage. The D-17 computational minor cycle was three disk revolutions or 30 ms. During that time all recurring computations were performed. For ground operations, the inertial platform was aligned and gyro correction rates updated.
During a flight, filtered command outputs were sent by each minor cycle to the engine nozzles. Unlike modern computers, which use descendants of that technology for
secondary storage
Computer data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
The central processing unit (CPU) of a computer ...
on
hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magnet ...
, the disk was the active
computer memory. The disk storage was considered hardened to radiation from nearby nuclear explosions, making it an ideal storage medium. To improve computational speed, the D-17 borrowed an instruction look-ahead feature from the Autonetics-built Field Artillery Data Computer (
M18 FADAC
The gun data computer was a series of fire control system, artillery computers used by the U.S. Army for coastal artillery, field artillery and anti-aircraft artillery applications. In antiaircraft applications they were used in conjunction with a ...
) that permitted simple instruction execution every word time.
Warhead
At its introduction into service in 1962, Minuteman I was fitted with the
W59 warhead with a yield of 1 Mt. Production for the W56 warhead with a 1.2 Mt yield began in March 1963 and W59 production was ended in July 1963 with a production run of only 150 warheads before being retired in June 1969. The W56 would continue production until May 1969 with a production run of 1000 warheads. Mods 0 to 3 were retired by September 1966 and the Mod 4 version would remain in service until the 1990s.
It's not clear exactly why the W59 was replaced by the W56 after deployment but issues with "... one-point safety" and "performance under aged conditions" were cited in a 1987 Congressional report regarding the warhead.
alleged that all weapons sharing the
"Tsetse" nuclear primary design including the W59 suffered from a critical one-point safety issue and suffered premature tritium aging issues that needed to be corrected after entry into service.
Minuteman II (LGM-30F)
:''See also
W56 warhead''
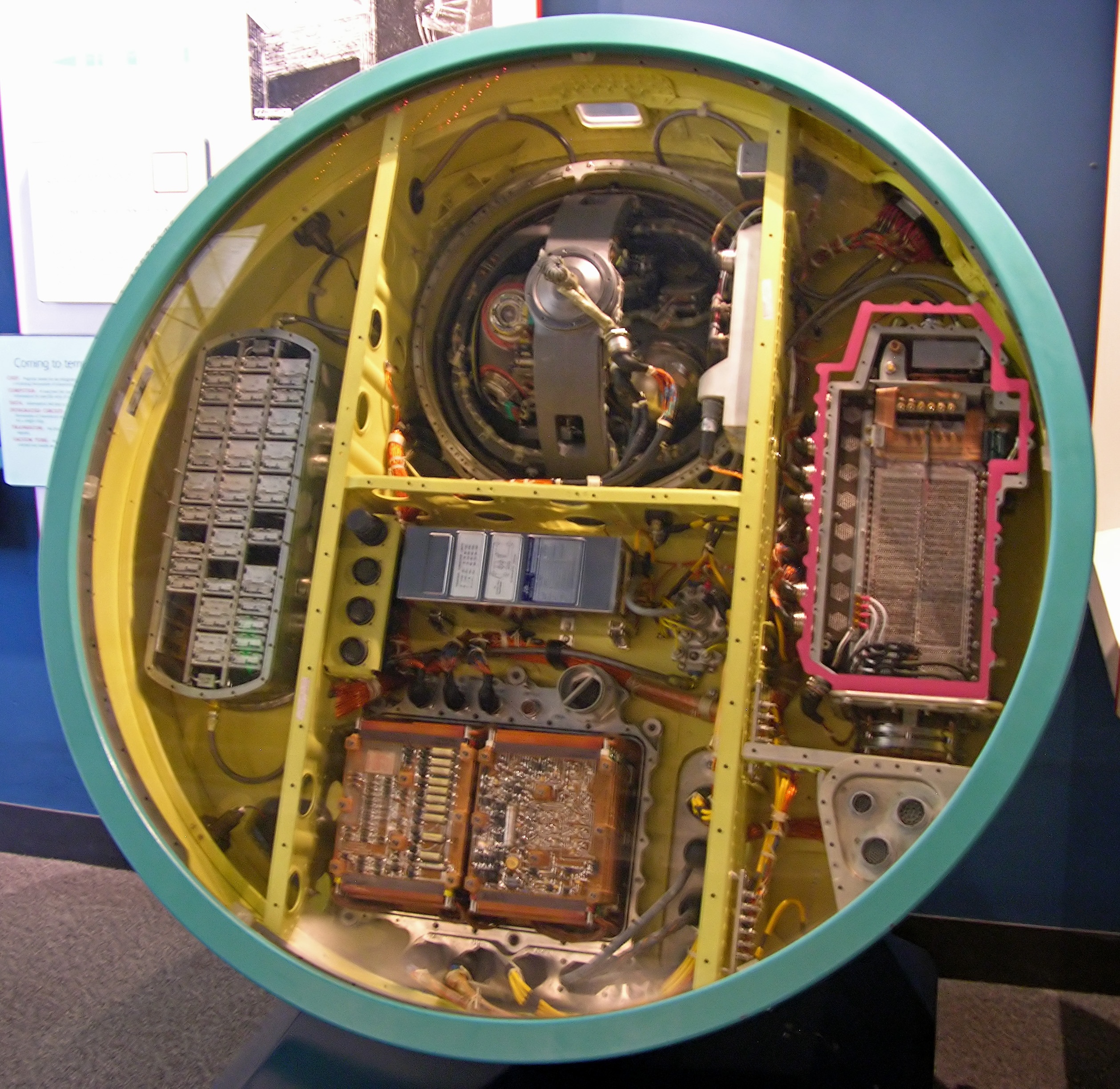
The LGM-30F Minuteman II was an improved version of the Minuteman I missile. Its first test launch took place on September 24, 1964. Development on the Minuteman II began in 1962 as the Minuteman I entered the Strategic Air Command's nuclear force. Minuteman II production and deployment began in 1965 and completed in 1967. It had an increased range, greater
throw weight and guidance system with better azimuthal coverage, providing military planners with better accuracy and a wider range of targets. Some missiles also carried penetration aids, allowing the higher probability of kill against
Moscow's anti-ballistic missile system. The payload consisted of a single Mk-11C reentry vehicle containing a
W56
The W56 (originally called the Mark 56) was an American thermonuclear warhead produced starting in 1963 which saw service until 1993, on the Minuteman I and II ICBMs.
The warhead had a yield of and a demonstrated yield-to-weight ratio of , ve ...
nuclear warhead with a yield of 1.2 megatons of TNT (5
PJ).
Specifications
The Minuteman II had a length of , weighed roughly , had an operational range of with an accuracy of about .
The major new features provided by Minuteman II were:
* An improved first-stage motor to increase reliability.
* A novel, single, fixed
nozzle
A nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a fluid flow (specially to increase velocity) as it exits (or enters) an enclosed chamber or pipe.
A nozzle is often a pipe or tube of varying cross sectional area, a ...
with liquid injection thrust vector control on a larger second-stage motor to increase missile range. Additional motor improvements to increase reliability.
* An improved guidance system (the
D-37 flight computer), incorporating
microchips and miniaturized discrete electronic parts. Minuteman II was the first program to make a major commitment to these new devices. Their use made possible multiple target selection, greater accuracy and reliability, a reduction in the overall size and weight of the guidance system, and an increase in the survivability of the guidance system in a nuclear environment. The guidance system contained 2,000 microchips made by
Texas Instruments.
* A penetration aids system to camouflage the warhead during its reentry into an enemy environment. In addition, the Mk-11C reentry vehicle incorporated stealth features to reduce its radar signature and make it more difficult to distinguish from decoys. The Mk-11C was no longer made of titanium for this and other reasons.
* A larger warhead in the reentry vehicle to increase kill probability.
System modernization was concentrated on
launch facilities and
command and control facilities. This provided decreased reaction time and increased survivability when under nuclear attack. Final changes to the system were performed to increase compatibility with the expected
LGM-118A Peacekeeper. These newer missiles were later deployed into modified Minuteman silos.
The Minuteman II program was the first mass-produced system to use a computer constructed from integrated circuits (the
Autonetics D-37C). The Minuteman II integrated circuits were
diode–transistor logic and
diode logic made by
Texas Instruments. The other major customer of early integrated circuits was the
Apollo Guidance Computer
The Apollo Guidance Computer (AGC) was a digital computer produced for the Apollo program that was installed on board each Apollo command module (CM) and Apollo Lunar Module (LM). The AGC provided computation and electronic interfaces for guidan ...
, which had similar weight and ruggedness constraints. The Apollo integrated circuits were
resistor–transistor logic Resistor–transistor logic (RTL) (sometimes also transistor–resistor logic (TRL)) is a class of digital circuits built using resistors as the input network and bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) as switching devices. RTL is the earliest class o ...
made by
Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. Founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument, it became a pioneer in the manufacturing of transistors and of int ...
. The Minuteman II flight computer continued to use rotating magnetic disks for primary storage. The Minuteman II included
diode
A diode is a two-terminal electronic component that conducts current primarily in one direction (asymmetric conductance); it has low (ideally zero) resistance in one direction, and high (ideally infinite) resistance in the other.
A diode ...
s by
Microsemi Corporation
Microsemi Corporation was an Aliso Viejo, California-based provider of semiconductor and system solutions for aerospace & defense, communications, data center and industrial markets.
In February 2018, it was announced that Chandler, Arizona-base ...
.
Minuteman III (LGM-30G)



:''See also
W62 warhead''
The LGM-30G Minuteman III program started in 1966 and included several improvements over the previous versions. Its first test launch took place on August 16, 1968. It was first deployed in 1970. Most modifications related to the final stage and reentry system (RS). The final (third) stage was improved with a new fluid-injected motor, giving finer control than the previous four-nozzle system.
Performance improvements realized in Minuteman III include increased flexibility in reentry vehicle (RV) and penetration aids deployment, increased survivability after a nuclear attack, and increased payload capacity. The missile retains a
gimballed
inertial navigation system.
Minuteman III originally contained the following distinguishing features:
* Armed with up to three
W62
The W62 was an American thermonuclear warhead designed in the 1960s and manufactured from March 1970 to June 1976. Used on some Minuteman III ICBMs, it was partially replaced by the W78 starting in December 1979, and fully replaced by W87 warhea ...
Mk-12 warheads, having a yield of only 170 kilotons TNT, instead of previous
W56
The W56 (originally called the Mark 56) was an American thermonuclear warhead produced starting in 1963 which saw service until 1993, on the Minuteman I and II ICBMs.
The warhead had a yield of and a demonstrated yield-to-weight ratio of , ve ...
's yield of 1.2 megatons.
* It was the first
missile. A single missile was then able to target three separate locations. This was an improvement from the Minuteman I and Minuteman II models, which were able to carry only one large warhead.
** An RS capable of deploying, in addition to the warheads,
penetration aids such as
chaff
Chaff (; ) is the dry, scaly protective casing of the seeds of cereal grains or similar fine, dry, scaly plant material (such as scaly parts of flowers or finely chopped straw). Chaff is indigestible by humans, but livestock can eat it. In agri ...
and
decoys.
** Minuteman III introduced in the post-boost-stage ("bus") an additional liquid-fuel propulsion system rocket engine (PSRE) that is used to slightly adjust the
trajectory. This enables it to dispense decoys or – with MIRV – dispense individual RVs to separate targets. For the PSRE it uses the bipropellant Rocketdyne RS-14 engine.
* The Hercules M57 third stage of Minuteman I and Minuteman II had thrust termination ports on the sides. These ports, when opened by detonation of shaped charges, reduced the chamber pressure so abruptly that the interior flame was blown out. This allowed a precisely timed termination of thrust for targeting accuracy. The larger Minuteman III third-stage motor also has thrust termination ports although the final velocity is determined by PSRE.
* A fixed nozzle with a liquid injection thrust vector control system on the new third-stage motor (similar to the second-stage Minuteman II nozzle) additionally increased range.
* A flight computer (Autonetics
D37D) with larger disk memory and enhanced capability.
** A Honeywell HDC-701 flight computer which employed non-destructive readout
plated wire memory instead of rotating magnetic disk for primary storage was developed as a backup for the D37D but was never adopted.
** The Guidance Replacement Program, initiated in 1993, replaced the disk-based D37D flight computer with a new one that uses
radiation-resistant
Radiation hardening is the process of making electronic components and circuits resistant to damage or malfunction caused by high levels of ionizing radiation (particle radiation and high-energy electromagnetic radiation), especially for environm ...
semiconductor RAM.
The Minuteman III missiles used D-37D computers and completed the 1,000 missile deployment of this system. The initial cost of these computers ranged from about $139,000 (D-37C) to $250,000 (D-17B).

The existing Minuteman III missiles have been further improved over the decades in service, with more than $7 billion spent in the 2010s to upgrade the 450 missiles.
Specifications
The Minuteman III has a length of ,
weighs ,
an operational range of , and an accuracy of about .
W78 warhead
In December 1979 the higher-yield
W78
The W78 is an American thermonuclear warhead with an estimated yield of , deployed on the LGM-30G Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) and housed in the Mark 12A reentry vehicle. Minuteman III initially carried the older W62 wa ...
warhead (335–350 kilotons) began replacing a number of the W62s deployed on the Minuteman IIIs.
These were delivered in the Mark 12A reentry vehicle. A small, unknown number of the previous Mark 12 RVs were retained operationally, however, to maintain a capability to attack more-distant targets in the south-central Asian republics of the
USSR (the Mark 12 RV weighed slightly less than the Mark 12A).
Guidance Replacement Program
The Guidance Replacement Program replaces the NS20A Missile Guidance Set with the NS50 Missile Guidance Set. The newer system extends the service life of the Minuteman missile beyond the year 2030 by replacing aging parts and assemblies with current, high reliability technology while maintaining the current accuracy performance. The replacement program was completed 25 February 2008.
Propulsion Replacement Program
Beginning in 1998 and continuing through 2009,
the Propulsion Replacement Program extends the life and maintains the performance by replacing the old solid propellant boosters (downstages).
Single Reentry Vehicle
The Single Reentry Vehicle modification enabled the United States ICBM force to abide by the now-voided
START II
START II (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty) was a bilateral treaty between the United States and Russia on the Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms. It was signed by US President George H. W. Bush and Russian President Boris Yelts ...
treaty requirements by reconfiguring Minuteman III missiles from three reentry vehicles down to one. Though it was eventually ratified by both parties, START II never entered into force and was essentially superseded by follow-on agreements such as
SORT
Sort may refer to:
* Sorting, any process of arranging items in sequence or in sets
** Sorting algorithm, any algorithm for arranging elements in lists
** Sort (Unix), a Unix utility which sorts the lines of a file
** Sort (C++), a function in the ...
and
New START
New START (Russian abbrev.: СНВ-III, ''SNV-III'' from ''сокращение стратегических наступательных вооружений'' "reduction of strategic offensive arms") is a nuclear arms reduction treaty between ...
, which do not limit MIRV capability. Minuteman III remains fitted with a single warhead due to the warhead limitations in New START.
Safety Enhanced Reentry Vehicle
Beginning in 2005, Mk-21/
W87
The W87 is an American thermonuclear missile warhead formerly deployed on the LGM-118A Peacekeeper ("MX") ICBM. 50 MX missiles were built, each carrying up to 10 W87 warheads in multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRV), and were ...
RVs from the deactivated
Peacekeeper missile were replaced on the Minuteman III force under the Safety Enhanced Reentry Vehicle (SERV) program. The older
W78
The W78 is an American thermonuclear warhead with an estimated yield of , deployed on the LGM-30G Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) and housed in the Mark 12A reentry vehicle. Minuteman III initially carried the older W62 wa ...
did not have many of the safety features of the newer W87, such as
insensitive high explosives, as well as more advanced safety devices. In addition to implementing these safety features in at least a portion of the future Minuteman III force, the decision to transfer W87s onto the missile was based on two features that improved the targeting capabilities of the weapon: more
fuzing options which allowed for greater targeting flexibility, and the most accurate reentry vehicle available, which provided a greater probability of damage to the designated targets.
Deployment
The Minuteman III missile entered service in 1970, with weapon systems upgrades included during the production run from 1970 to 1978 to increase accuracy and payload capacity. , the USAF plans to operate it until 2030.
The
LGM-118A Peacekeeper (MX) ICBM, which was to have replaced the Minuteman, was retired in 2005 as part of
START II
START II (Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty) was a bilateral treaty between the United States and Russia on the Reduction and Limitation of Strategic Offensive Arms. It was signed by US President George H. W. Bush and Russian President Boris Yelts ...
.
A total of 450 LGM-30G missiles are emplaced at
F.E. Warren Air Force Base
Francis E. Warren Air Force Base , shortened as F.E. Warren AFB is a United States Air Force base (AFB) located approximately west of Cheyenne, Wyoming. It is one of three strategic-missile bases in the U.S. It was named in honor of Francis E ...
,
Wyoming (
90th Missile Wing),
Minot Air Force Base,
North Dakota (
91st Missile Wing
The 91st Missile Wing is a United States Air Force unit assigned to the Air Force Global Strike Command Twentieth Air Force. It is stationed at Minot Air Force Base, North Dakota as a tenant unit.
The 91 MW is one of the Air Force's three inte ...
), and
Malmstrom Air Force Base,
Montana (
341st Missile Wing
The United States Air Force's 341st Missile Wing is an intercontinental ballistic missile unit headquartered at Malmstrom Air Force Base, Montana. Up until 1 July 2008, it was designated as the 341st Space Wing.
Established as a World War II Te ...
). All Minuteman I and Minuteman II missiles have been retired. The United States prefers to keep its MIRV deterrents on submarine-launched
Trident Nuclear Missiles In 2014, the Air Force decided to put fifty Minuteman III silos into "warm" unarmed status, taking up half of the 100 slots in America's allowable nuclear reserve. These can be reloaded in the future if necessary.
Testing
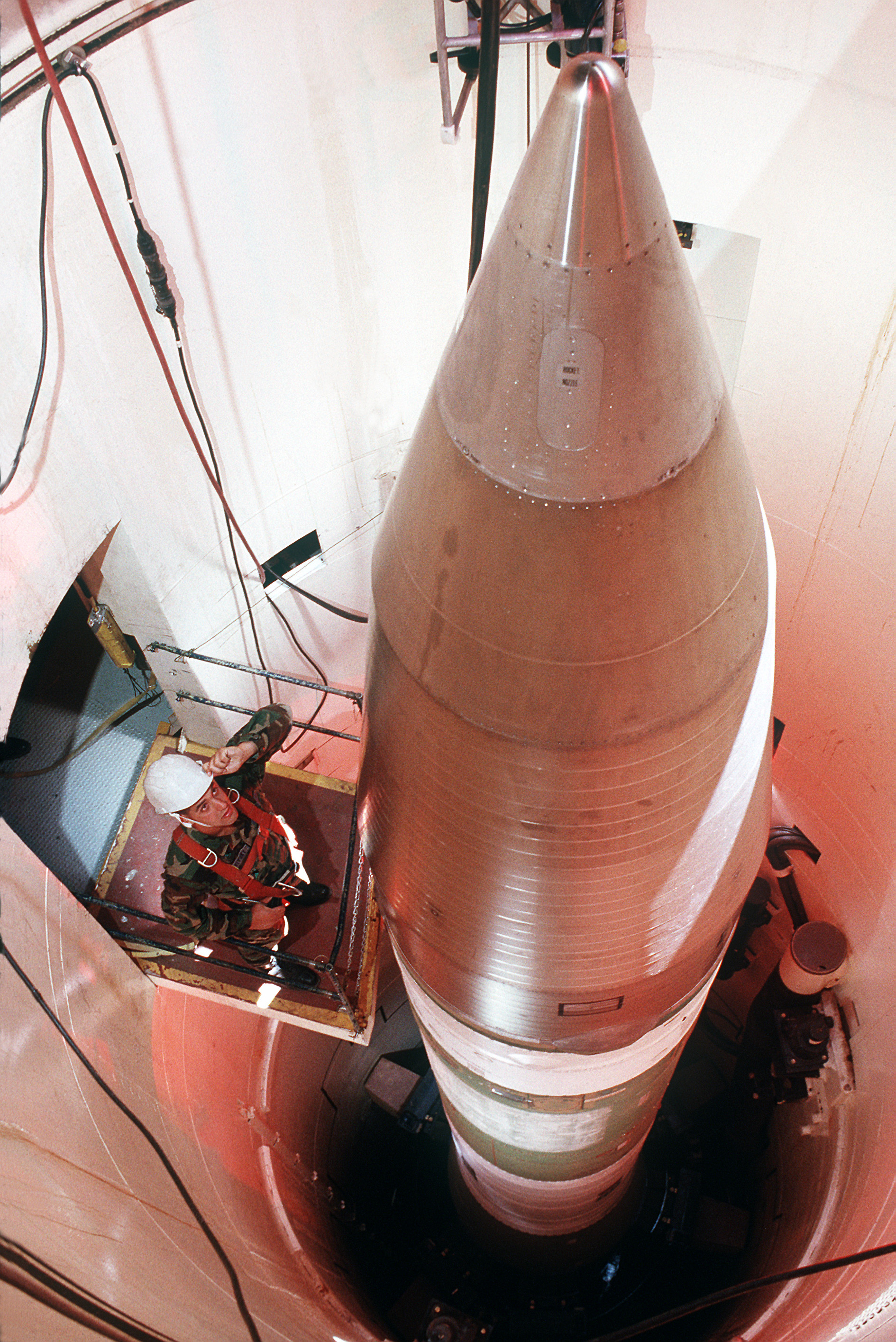
Minuteman III missiles are regularly tested with launches from
Vandenberg Space Force Base in order to validate the effectiveness, readiness, and accuracy of the weapon system, as well as to support the system's primary purpose,
nuclear deterrence
Deterrence theory refers to the scholarship and practice of how threats or limited force by one party can convince another party to refrain from initiating some other course of action. The topic gained increased prominence as a military strategy ...
. The safety features installed on the Minuteman III for each test launch allow the flight controllers to terminate the flight at any time if the systems indicate that its course may take it unsafely over inhabited areas. Since these flights are for test purposes only, even terminated flights can send back valuable information to correct a potential problem with the system.
The
576th Flight Test Squadron
The 576th Flight Test Squadron is a United States Air Force unit assigned to Air Force Global Strike Command. The 576th is stationed at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California. The unit was first established in January 1943 as the 576th Bomba ...
is responsible for planning, preparing, conducting, and assessing all ICBM ground and flight tests.
Airborne Launch Control System (ALCS)
The
Airborne Launch Control System
The Airborne Launch Control System (ALCS) provides a survivable launch capability for the United States Air Force's LGM-30G Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) force. The ALCS is operated by airborne missileers from Air Force G ...
(ALCS) is an integral part of the Minuteman ICBM command and control system and provides a survivable launch capability for the Minuteman ICBM force if ground-based launch control centers (LCCs) are destroyed.
When the Minuteman ICBM was first placed on alert, the Soviet Union did not have the number of weapons, accuracy, nor significant nuclear yield to completely destroy the Minuteman ICBM force during an attack. However, starting in the mid-1960s, the Soviets began to gain parity with the US and now had the potential capability to target and successfully attack the Minuteman force with an increased number of ICBMs that had greater yields and accuracy than were previously available.
Studying the problem, SAC realized that in order to prevent the US from launching all 1,000 Minuteman ICBMs, the Soviets did not have to target all 1,000 Minuteman missile silos. The Soviets needed to launch only a disarming decapitation strike against the 100 Minuteman LCCs – the
command and control sites – in order to prevent the launch of all Minuteman ICBMs. Even though the Minuteman ICBMs would have been left unscathed in their missile silos following an LCC decapitation strike, the Minuteman missiles could not be launched without a command and control capability.
In other words, the Soviets needed only 100 warheads to fully eliminate command and control of the Minuteman ICBMs. Even if the Soviets chose to expend two to three warheads per LCC for assured damage expectancy, the Soviets would have had to expend only up to 300 warheads to disable the Minuteman ICBM force – far less than the total number of Minuteman silos. The Soviets could have then used the remaining warheads to strike other targets they chose.

Faced with only a few Minuteman LCC targets, the Soviets could have concluded that the odds of being successful in a Minuteman LCC decapitation strike were higher with less risk than it would have been having to face the almost insurmountable task of successfully attacking and destroying 1000 Minuteman silos and 100 Minuteman LCCs to ensure Minuteman was disabled. This theory motivated SAC to design a survivable means to launch Minuteman, even if all the ground-based command and control sites were destroyed.
After thorough testing and modification of
EC-135 command post aircraft, the ALCS demonstrated its capability on 17 April 1967 by launching an ERCS configured Minuteman II out of Vandenberg AFB, CA. Afterward, ALCS achieved Initial Operational Capability on 31 May 1967. From that point on, airborne missileers stood alert with
ALCS-capable EC-135 aircraft for several decades. All Minuteman ICBM Launch Facilities were modified and built to have the capability to receive commands from ALCS. With ALCS now standing alert around-the-clock, the Soviets could no longer successfully launch a Minuteman LCC decapitation strike. Even if the Soviets attempted to do so, EC-135s equipped with the ALCS could fly overhead and launch the remaining Minuteman ICBMs in retaliation.
Now that the ALCS was on alert, this complicated Soviet war planning by forcing the Soviets to target not only the 100 LCCs, but also the 1,000 silos with more than one warhead in order to guarantee destruction. This would have required upwards of 3,000 warheads to complete such an attack. The odds of being successful in such an attack on the Minuteman ICBM force would have been extremely low.
Today, the ALCS is operated by airborne missileers from the
Air Force Global Strike Command
Air Force Global Strike Command (AFGSC) is a Major Command (MAJCOM) of the United States Air Force, headquartered at Barksdale Air Force Base, Louisiana. AFGSC provides combat-ready forces to conduct strategic nuclear deterrence and global stri ...
's (AFGSC)
625th Strategic Operations Squadron (STOS) and
United States Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM). The weapon system is now located on board the United States Navy's
E-6B Mercury. The ALCS crew is integrated into the battle staff of the USSTRATCOM "
Looking Glass
A mirror or looking glass is an object that Reflection (physics), reflects an image. Light that bounces off a mirror will show an image of whatever is in front of it, when focused through the lens of the eye or a camera. Mirrors reverse the ...
" Airborne Command Post (ABNCP) and is on alert around-the-clock.
Although the Minuteman ICBM force has been reduced since the end of the Cold War, the ALCS continues to act as a force multiplier by ensuring that an adversary cannot launch a successful Minuteman LCC decapitation strike.
Other roles
Mobile Minuteman

Mobile Minuteman was a program for rail-based ICBMs to help increase survivability and for which the USAF released details on 12 October 1959. The
Operation Big Star
A Minuteman Mobility Test Train was a Cold War train for Strategic Air Command testing before deployment of planned trains for launching Minuteman missiles which were to allow periodic movement for security from targeting by the Soviet missile f ...
performance test was from 20 June to 27 August 1960 at
Hill Air Force Base
Hill Air Force Base is a major U.S. Air Force (USAF) base located in northern Utah, just south of the city of Ogden, and bordering the Cities of Layton, Clearfield, Riverdale, Roy, and Sunset with its largest border immediately adjacent to ...
, and the 4062nd Strategic Missile Wing (Mobile) was organized 1 December 1960 for 3 planned missile train squadrons, each with 10 trains carrying 3 missiles per train. During the
Kennedy/McNamara cutbacks, the Department of Defense announced "that it has abandoned the plan for a mobile Minuteman ICBM. The concept called for 600 to be placed in service—450 in silos and 150 on special trains, each train carrying 5 missiles." Kennedy announced on 18 March 1961 that the 3 squadrons were to be replaced with "fixed-base squadrons", and Strategic Air Command discontinued the 4062nd Strategic Missile Wing on 20 February 1962.

Air Launched ICBM
Air Launched ICBM was a
STRAT-X
STRAT-X, or Strategic-Experimental, was a U.S. government-sponsored study conducted during 1966 and 1967 that comprehensively analyzed the potential future of the U.S. nuclear deterrent force. At the time, the Soviet Union was making significa ...
proposal in which SAMSO (Space & Missile Systems Organization) successfully conducted an Air Mobile Feasibility Test that
airdropped a Minuteman 1b from a
C-5A Galaxy
The Lockheed C-5 Galaxy is a large military transport aircraft designed and built by Lockheed Corporation, Lockheed, and now maintained and upgraded by its successor, Lockheed Martin. It provides the United States Air Force (USAF) with a heavy ...
aircraft from over the
Pacific Ocean. The missile fired at , and the 10-second engine burn carried the missile to 20,000 feet again before it dropped into the ocean. Operational deployment was discarded due to engineering and security difficulties, and the capability was a negotiating point in the
Strategic Arms Limitation Talks
The Strategic Arms Limitation Talks (SALT) were two rounds of bilateral conferences and corresponding international treaties involving the United States and the Soviet Union. The Cold War superpowers dealt with arms control in two rounds of ta ...
.
Emergency Rocket Communications System (ERCS)
From 1963 through 1991 the
National Command Authority National Command Authority may refer to:
* National Command Authority (Pakistan)
* National Command Authority (United States)
National Command Authority (NCA) is a term that was used by the Department of Defense of the United States of America to ...
communication relay system included the
Emergency Rocket Communication System
The Emergency Rocket Communications System (ERCS) was designed to provide a reliable and survivable emergency communications method for the United States National Command Authority, using a UHF repeater placed atop a Blue Scout rocket or Minut ...
(ERCS). Specially designed rockets called BLUE SCOUT carried radio-transmitting payloads high above the continental United States, to relay messages to units within
line-of-sight. In the event of a nuclear attack, ERCS payloads would relay pre-programmed messages giving the "go-order" to SAC units.
BLUE SCOUT launch sites were located at Wisner, West Point and Tekamah,
Nebraska. These locations were vital for ERCS effectiveness due to their centralized position in the US, within range of all missile complexes. In 1968, ERCS configurations were placed on the top of modified Minuteman II ICBMs (LGM-30Fs) under the control of the 510th Strategic Missile Squadron located at
Whiteman Air Force Base,
Missouri.
The Minuteman ERCS may have been assigned the designation LEM-70A.
Satellite launching role
The U.S. Air Force has considered using some decommissioned Minuteman missiles in a satellite launching role. These missiles would be stored in silos, for launch upon short notice. The payload would be variable and would have the ability to be replaced quickly. This would allow a surge capability in times of emergency.
During the 1980s, surplus Minuteman missiles were used to power the Conestoga rocket produced by Space Services Inc. of America. It was the first privately funded rocket, but saw only three flights and was discontinued due to a lack of business. More recently, converted Minuteman missiles have been used to power the Minotaur line of rockets produced by
Orbital Sciences (nowadays
Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems
Northrop Grumman Innovation Systems (NGIS) was a sector (business segment) of Northrop Grumman from 2018 through 2019. It was formed from Orbital ATK Inc. a company which resulted from the merger of Orbital Sciences Corporation and parts of Alli ...
).
Ground and air launch targets
L-3 Communications is currently using SR-19 SRBs, Minuteman II Second Stage Solid Rocket Boosters, as delivery vehicles for a range of different re-entry vehicles as targets for the THAAD and ASIP interceptor missile programs as well as radar testing.
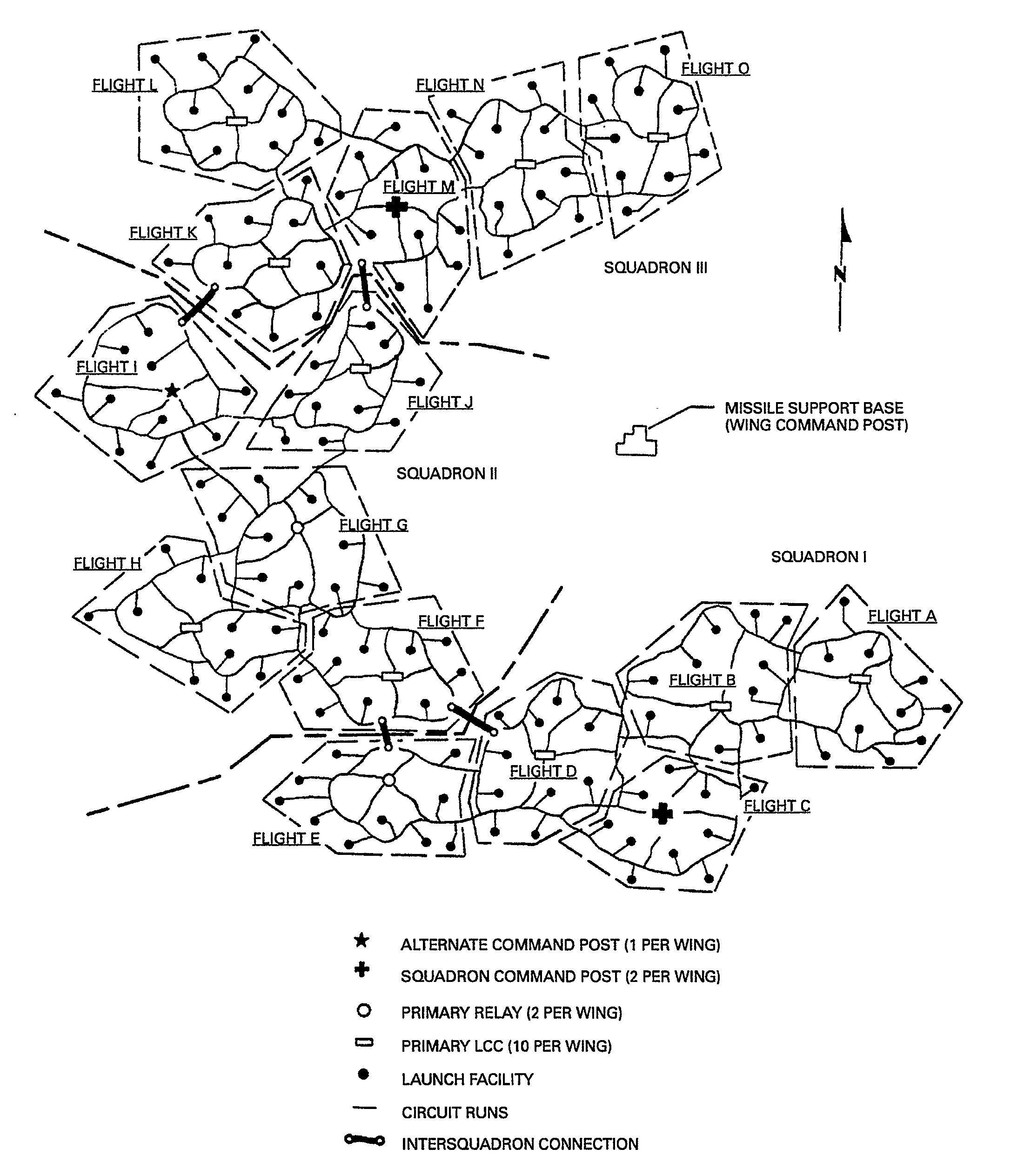
Operators
: The
United States Air Force has been the only operator of the Minuteman ICBM weapons system, currently with three operational wings and one test squadron operating the LGM-30G. The active inventory in FY 2009 is 450 missiles and 45 Missile Alert Facilities (MAF).
Operational units
The basic tactical unit of a Minuteman wing is the squadron, consisting of five flights. Each flight consists of ten unmanned
launch facilities (LFs) which are remotely controlled by a manned
launch control center
The Rocco A. Petrone Launch Control Center (commonly known as just the Launch Control Center or LCC) is a four-story building at NASA's Kennedy Space Center on Merritt Island, Florida, used to manage launches of launch vehicles from Kennedy Space ...
(LCC). A two-officer crew is on duty in the LCC, typically for 24 hours. The five flights are interconnected and status from any LF may be monitored by any of the five LCCs. Each LF is located at least three nautical miles (5.6 km) from any LCC.
Control does not extend outside the squadron (thus the
319th Missile Squadron
The 319th Missile Squadron is a United States Air Force unit assigned to the 90th Operations Group at Francis E. Warren Air Force Base, Wyoming. The squadron is equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile, wit ...
's five LCCs cannot control the
320th Missile Squadron
The 320th Missile Squadron is a United States Air Force unit. It is assigned to the 90th Operations Group, stationed at F.E. Warren AFB, Wyoming. The 320 MS is equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) ...
's 50 LFs even though they are part of the same Missile Wing). Each Minuteman wing is assisted logistically by a nearby Missile Support Base (MSB). If the ground-based LCCs are destroyed or incapacitated, the Minuteman ICBMs can be launched by airborne missileers utilizing the
Airborne Launch Control System
The Airborne Launch Control System (ALCS) provides a survivable launch capability for the United States Air Force's LGM-30G Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) force. The ALCS is operated by airborne missileers from Air Force G ...
.
Active
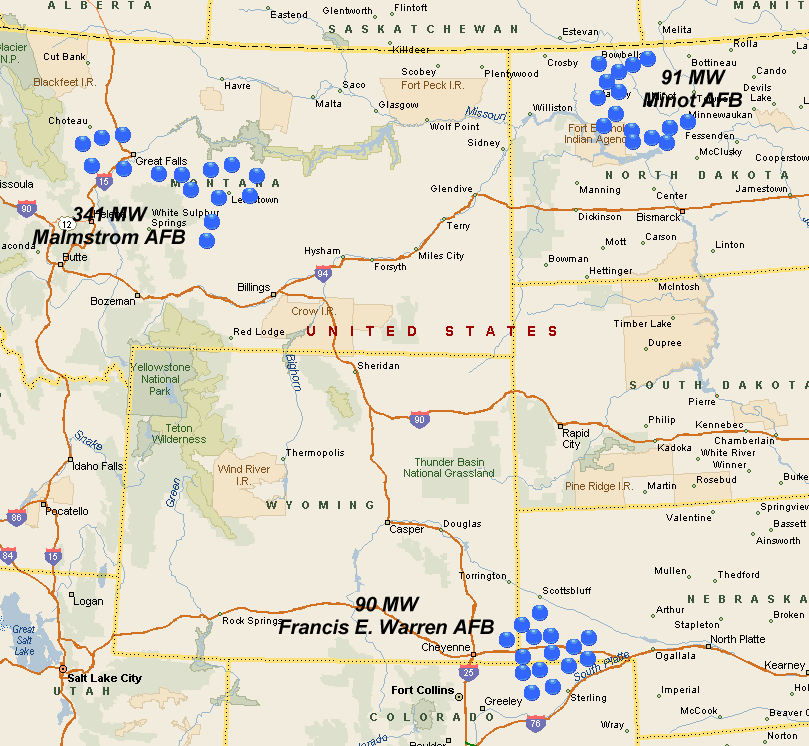
*
90th Missile Wing – "Mighty Ninety"
** at
Francis E. Warren AFB
Francis E. Warren Air Force Base , shortened as F.E. Warren AFB is a United States Air Force base (AFB) located approximately west of Cheyenne, Wyoming. It is one of three strategic-missile bases in the U.S. It was named in honor of Francis E ...
,
Wyoming, (1 July 1963 – present)
** Units:
***
319th Missile Squadron
The 319th Missile Squadron is a United States Air Force unit assigned to the 90th Operations Group at Francis E. Warren Air Force Base, Wyoming. The squadron is equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile, wit ...
– "Screaming Eagles"
***
320th Missile Squadron
The 320th Missile Squadron is a United States Air Force unit. It is assigned to the 90th Operations Group, stationed at F.E. Warren AFB, Wyoming. The 320 MS is equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III Intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) ...
– "G.N.I."
***
321st Missile Squadron
The 321st Missile Squadron is a United States Air Force unit. It is assigned to the 90th Operations Group, stationed at Francis E. Warren Air Force Base, Wyoming. The squadron is equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III Intercontinental ballis ...
– "Greentails"
** 150 missiles, 15 MAF –
Launch sites
*** LGM-30B Minuteman I, 1964–74
*** LGM-30G Minuteman III, 1973–present
*
91st Missile Wing
The 91st Missile Wing is a United States Air Force unit assigned to the Air Force Global Strike Command Twentieth Air Force. It is stationed at Minot Air Force Base, North Dakota as a tenant unit.
The 91 MW is one of the Air Force's three inte ...
– "Roughriders"
** at
Minot AFB,
North Dakota (25 June 1968 – present)
** Units:
***
740th Missile Squadron
The 740th Missile Squadron is a United States Air Force unit stationed at Minot Air Force Base, North Dakota. The squadron is equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile, with a mission of nuclear deterrence.
The ...
– "Vulgar Vultures"
***
741st Missile Squadron
The 741st Missile Squadron is a United States Air Force unit stationed at Minot Air Force Base, North Dakota. The squadron is equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile, with a mission of nuclear deterrence.
The ...
– "Gravelhaulers"
***
742d Missile Squadron
The 742d Missile Squadron is a United States Air Force unit stationed at Minot Air Force Base, North Dakota. The squadron is equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile, with a mission of nuclear deterrence.
The squ ...
– "Wolf Pack"
** 150 Missiles, 15 MAF –
Launch sites
*** LGM-30B Minuteman I, 1968–72
*** LGM-30G Minuteman III, 1972–present
*
341st Missile Wing
The United States Air Force's 341st Missile Wing is an intercontinental ballistic missile unit headquartered at Malmstrom Air Force Base, Montana. Up until 1 July 2008, it was designated as the 341st Space Wing.
Established as a World War II Te ...
** at
Malmstrom AFB,
Montana (15 July 1961 – present)
** Units:
***
10th Missile Squadron
The 10th Missile Squadron is a United States Air Force unit. It is assigned to the 341st Operations Group, stationed at Malmstrom Air Force Base, Montana. The squadron is equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III Intercontinental ballistic mi ...
– "First Aces"
***
12th Missile Squadron
The 12th Missile Squadron is a United States Air Force unit. It is assigned to the 341st Operations Group, stationed at Malmstrom Air Force Base, Montana. The squadron is equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic mis ...
– "Red Dawgs"
***
490th Missile Squadron
The 490th Missile Squadron is a United States Air Force unit. It is assigned to the 341st Operations Group, stationed at Malmstrom AFB, Montana. The 490 MS is equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III Intercontinental ballistic missile, with a mi ...
– "Farsiders"
** 150 Missiles, 15 MAF –
Launch sites
*** LGM-30A Minuteman I, 1962–69
*** LGM-30F Minuteman II, 1967–94
*** LGM-30G Minuteman III, 1975–present
*
625th Strategic Operations Squadron
** at
Offutt AFB,
Nebraska
Historical
*
44th Strategic Missile (later Missile) Wing "Black Hills Bandits"
:
Ellsworth AFB,
South Dakota (24 November 1961 – 5 July 1994)
: LGM-30B Minuteman I, 1963–73
: LGM-30F Minuteman II, 1971–94
:
66th Missile Squadron
The 66th Missile Squadron (66 MS) is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 44th Operations Group, stationed at Ellsworth AFB, South Dakota.
The 66 MS was equipped with the LGM-30F Minuteman II Intercontinental b ...
:
67th Missile Squadron
The 67th Missile Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 44th Operations Group, stationed at Ellsworth AFB, South Dakota.
The 67 MS was equipped with the LGM-30F Minuteman II Intercontinental ballisti ...
:
68th Missile Squadron
The 68th Missile Squadron (68 MS) is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 44th Operations Group, stationed at Ellsworth AFB, South Dakota.
The 68 MS was equipped with the LGM-30F Minuteman II Intercontinental b ...
:
44th Missile Wing LGM-30 Minuteman Missile Launch Sites
This is a list of the LGM-30 Minuteman missile, Missile Alert Facilities and Launch Facilities of the 44th Missile Wing, 20th Air Force, assigned to Ellsworth AFB, South Dakota.
The 44th SMW executed the unique 'Long Life' test of a Minuteman ...
: Inactivated 1994 when Minuteman II phased out of inventory. All retired between 3 December 1991 and April 1994, with destruction of silos and alert facilities finishing in 1996.
*
90th Missile Wing
:
400th Missile Squadron
The 400th Missile Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 90th Operations Group at Francis E. Warren Air Force Base, Wyoming, where it was inactivated in 2005.
The squadron was first activated as the 1 ...
(Converted to
LGM-118A Peacekeeper in 1987. Inactivated 2005. Peacekeepers retired.)
*
321st Strategic Missile (later Missile) Wing (later Group)
:
Grand Forks AFB
Grand Forks Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in northeastern North Dakota, located north of Emerado and west of Grand Forks.
The host unit is the 319th Reconnaissance Wing (319 RW) assigned to the Air Combat C ...
,
North Dakota (14 August 1964 – 30 September 1998)
: LGM-30F Minuteman II, 1965–73
: LGM-30G Minuteman III, 1972–98
:
446th Missile Squadron
The 446th Missile Squadron (446 MS) is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 321st Missile Group, stationed at Grand Forks AFB, North Dakota
The 446 MS was equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III Intercontinent ...
:
447th Missile Squadron
The 447th Missile Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 321st Missile Group, stationed at Grand Forks AFB, North Dakota
The 447 MS was equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III Intercontinental ballist ...
:
448th Missile Squadron
The 448th Missile Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 321st Missile Group at Grand Forks Air Force Base, North Dakota, where it was equipped with the LGM-30G Minuteman III Intercontinental ballisti ...
:
321st Missile Wing LGM-30 Minuteman Missile Launch Sites
This is a list of the LGM-30 Minuteman missile Missile Alert Facilities and Launch Facilities of the 321st Missile Wing, 20th Air Force, assigned to Grand Forks AFB, North Dakota.
Overview
The 321st Strategic Missile Wing was the sixth, and l ...
: Inactivated by
BRAC 1995; missiles reassigned to 341st SMW, however in 1995 it was decided to retire the Grand Forks missiles; the last missile was pulled from its silo in June 1998. Destruction of silos and control facilities began in October 1999; the last silo (H-22) was imploded 24 August 2001 (the last US silo destroyed per the 1991 START-I treaty).
*
341st Missile Wing
The United States Air Force's 341st Missile Wing is an intercontinental ballistic missile unit headquartered at Malmstrom Air Force Base, Montana. Up until 1 July 2008, it was designated as the 341st Space Wing.
Established as a World War II Te ...
:
564th Missile Squadron
The 564th Missile Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 341st Operations Group at Malmstrom Air Force Base, Montana, where it was inactivated on 19 August 2008.
The squadron was first activated durin ...
(Inactivated 2008, WS-133B system retired, missiles recycled into inventory)
*
351st Strategic Missile (later Missile) Wing
:
Whiteman AFB,
Missouri (1 February 1963 – 31 July 1995)
: LGM-30B Minuteman I, 1963–65
: LGM-30F Minuteman II, 1965–95
:
508th Missile Squadron
The 508th Missile Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 351st Operations Group at Whiteman Air Force Base, Missouri. The squadron was equipped with the LGM-30F Minuteman II Intercontinental ballist ...
:
509th Missile Squadron
The 509th Missile Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 351st Operations Group at Whiteman Air Force Base, Missouri. The squadron was equipped with the LGM-30F Minuteman II Intercontinental ballisti ...
:
510th Missile Squadron
The 510th Missile Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 351st Operations Group at Whiteman Air Force Base, Missouri. The squadron was equipped with the LGM-30F Minuteman II Intercontinental ballist ...
:
351st Missile Wing LGM-30 Minuteman Missile Launch Sites
This is a list of the LGM-30 Minuteman missile Missile Alert Facilities and Launch Facilities of the 351st Strategic Missile Wing, 20th Air Force, assigned to Whiteman AFB, Missouri.
Overview
The 351st Strategic Missile Wing was the third Unit ...
: The 510th SMS operated
Emergency Rocket Communication System
The Emergency Rocket Communications System (ERCS) was designed to provide a reliable and survivable emergency communications method for the United States National Command Authority, using a UHF repeater placed atop a Blue Scout rocket or Minut ...
(ERCS) missiles in addition to Minuteman II ICBMs. The 351st SMW was inactivated under START-I. The first silo was imploded on 8 December 1993 and the last on 15 December 1997.
*
455th Strategic Missile Wing 455th may refer to:
*455th Air Expeditionary Wing, provisional United States Air Force USAFCENT unit
*455th Flying Training Squadron, United States Air Force unit of the Air Education and Training Command (AETC)
See also
*455 (number)
*455 (di ...
:
Minot AFB,
North Dakota (28 June 1962 – 25 June 1968)
: LGM-30B Minuteman I, 1962–68
: Replaced by the
91st Strategic Missile Wing in June 1968
* Historical
Airborne Launch Control System
The Airborne Launch Control System (ALCS) provides a survivable launch capability for the United States Air Force's LGM-30G Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) force. The ALCS is operated by airborne missileers from Air Force G ...
Units
:
68th Strategic Missile Squadron
The 68th Missile Squadron (68 MS) is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 44th Operations Group, stationed at Ellsworth AFB, South Dakota.
The 68 MS was equipped with the LGM-30F Minuteman II Intercontinental ...
(Ellsworth AFB, SD: 1967–1970)
:
91st Strategic Missile Wing (Minot AFB, ND: 1967–1969)
[ opkins III, Robert S. 1997. Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker: More Than Just a Tanker. Leicester, England: Midland Publishing Limited, p. 196/ref>
: ]4th Airborne Command and Control Squadron
Fourth or the fourth may refer to:
* the ordinal form of the number 4
* ''Fourth'' (album), by Soft Machine, 1971
* Fourth (angle), an ancient astronomical subdivision
* Fourth (music), a musical interval
* ''The Fourth'' (1972 film), a Sovie ...
(Ellsworth AFB, SD: 1970–1992)[ opkins III, Robert S. 1997. Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker: More Than Just a Tanker. Leicester, England: Midland Publishing Limited, p. 116/ref>]USSTRATCOM
United States Strategic Command (USSTRATCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands in the United States Department of Defense. Headquartered at Offutt Air Force Base, Nebraska, USSTRATCOM is responsible for strategic nuclear deterr ...
(Offutt AFB, NE: 1998–2007)
: Converted to the 625th Strategic Operations Squadron in 2007, where ALCS mission continues to this day
Support
* 532d Training Squadron
The 532d Training Squadron is a United States Air Force unit, assigned to the 82nd Training Group at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California. The squadron was first activated in 1942 as the 532d Bombardment Squadron. After training in the Unit ...
– Vandenberg AFB, California (Missile Maintenance Training and Missile Initial Qualification Course)
* 315th Weapons Squadron
The 315th Weapons Squadron is a United States Air Force unit, assigned to the USAF Weapons School at Nellis Air Force Base, Nevada. It is responsible for training a tactics development for the Air Force's intercontinental ballistic missile forc ...
– Nellis AFB, Nevada (ICBM Weapons Instructor Course)
* 526th ICBM Systems Wing
The 526th Intercontinental Ballistic Missile Systems Group (526 ICBMG) is an inactive United States Air Force (USAF) unit. It was last located at Hill AFB, Utah, where it was inactivated in 2010. The group was first activated during World War I ...
– Hill Air Force Base
Hill Air Force Base is a major U.S. Air Force (USAF) base located in northern Utah, just south of the city of Ogden, and bordering the Cities of Layton, Clearfield, Riverdale, Roy, and Sunset with its largest border immediately adjacent to ...
, Utah
* 576th Flight Test Squadron
The 576th Flight Test Squadron is a United States Air Force unit assigned to Air Force Global Strike Command. The 576th is stationed at Vandenberg Space Force Base, California. The unit was first established in January 1943 as the 576th Bomba ...
– Vandenberg Air Force Base, California – "Top Hand"
* 625th Strategic Operations Squadron – Offutt AFB, Nebraska
Replacement
A request for proposal for development and maintenance of a Ground Based Strategic Deterrent
The LGM-35 Sentinel, also known as the Ground Based Strategic Deterrent (GBSD), is a future American land-based intercontinental ballistic missile system (ICBM) currently in the early stages of development. It is slated to replace the aging Minu ...
(GBSD) next-generation nuclear ICBM, was made by the US Air Force Nuclear Weapons Center, ICBM Systems Directorate, GBSD Division on 29 July 2016. The GBSD would replace MMIII in the land-based portion of the US Nuclear Triad. The new missile to be phased in over a decade from the late 2020s are estimated over a fifty-year life cycle to cost around $86 billion. Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Northrop Grumman were competing for the contract.
On 21 August 2017, the US Air Force awarded 3-year development contracts to Boeing and Northrop Grumman, for $349 million and $329 million, respectively. One of these companies will be selected to produce this ground-based nuclear ICBM in 2020. In 2027, the GBSD program is expected to enter service and remain active until 2075.
On 14 December 2019, it was announced that Northrop Grumman had won the competition to build the future ICBM. Northrop won by default, as their bid was at the time the only bid left to be considered for the GBSD program (Boeing had dropped out of the bidding contest earlier in 2019). The US Air Force said: "The Air Force will proceed with an aggressive and effective sole-source negotiation." in reference to Northrop's bid.
Surviving decommissioned sites
* Oscar One Alert Facility at Whiteman AFB
* Delta One Alert Facility at Minuteman Missile National Historic Site
The Minuteman Missile National Historic Site is an American national historic site established in 1999 near Wall, South Dakota to illustrate the history and significance of the Cold War, the arms race, and intercontinental ballistic missile ...
* Delta Nine Silo at Minuteman Missile National Historic Site
The Minuteman Missile National Historic Site is an American national historic site established in 1999 near Wall, South Dakota to illustrate the history and significance of the Cold War, the arms race, and intercontinental ballistic missile ...
* Minuteman II missile Training Launch Facility at Ellsworth AFB
* Oscar Zero Alert Facility at Ronald Reagan Minuteman Missile State Historic Site
The Ronald Reagan Minuteman Missile State Historic Site consists of two former missile sites around Cooperstown, North Dakota that were part of North Dakota military activities during the Cold War years: the Oscar-Zero Missile Alert Facility and ...
* November 33 Silo (topside only) at Ronald Reagan Minuteman Missile State Historic Site
The Ronald Reagan Minuteman Missile State Historic Site consists of two former missile sites around Cooperstown, North Dakota that were part of North Dakota military activities during the Cold War years: the Oscar-Zero Missile Alert Facility and ...
* Quebec-One Missile Alert Facility
The Quebec-One Missile Alert Facility, also known as Quebec-01 or Q-01, located 30 miles north of Cheyenne, Wyoming, near Chugwater, was a United States Air Force ICBM launch control facility. It was operated by the 400th Missile Squadron cons ...
at Cheyenne, Wyoming (modified for Peacekeeper ICBM in 1986)
Preservation
The Minuteman Missile National Historic Site
The Minuteman Missile National Historic Site is an American national historic site established in 1999 near Wall, South Dakota to illustrate the history and significance of the Cold War, the arms race, and intercontinental ballistic missile ...
in South Dakota preserves a Launch Control Facility (D-01) and a launch facility (D-09) under the control of the National Park Service.Cooperstown
Cooperstown is a village in and county seat of Otsego County, New York, United States. Most of the village lies within the town of Otsego, but some of the eastern part is in the town of Middlefield. Located at the foot of Otsego Lake in the C ...
, North Dakota.
Comparable missiles
* DF-5
The Dongfeng 5 () or DF-5 is a second-generation two stage Chinese intercontinental ballistic missile. It has a length of 32.6 m and a diameter of 3.35 m. It weighs in at 183,000 kilograms and it has an estimated range of 12,000 to 15,000 kilome ...
* DF-41
* PGM-17 Thor
* R-36
* RS-24 Yars
* RT-2
The RT-2 was an intercontinental ballistic missile deployed by the Soviet Union, which was in service from December 1968 until 1976. It was assigned the NATO reporting name SS-13 Savage and carried the GRAU index 8K98. Designed by OKB-1, about 60 ...
* RT-2PM2 Topol-M
* UR-100N
The UR-100N, also known as RS-18A is an intercontinental ballistic missile in service with Soviet and Russian Strategic Missile Troops. The missile was given the NATO reporting name SS-19 Stiletto and carries the industry designation 15A30.
Deve ...
* Agni-V
Agni-V is a nuclear capable intercontinental ballistic missile developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation RDOof India. The missile is believed to have a range of around 5,000 to 5,500 kilometers. Scientists and experts say ...
See also
* Airborne Launch Control Center
* LGM-30 Minuteman chronology
This is a chronology of the LGM-30 Minuteman intercontinental ballistic missile, acquisition and operational.
Program chronology
*1956
**Von Neumann Committee approved Ballistic Missile feasibility program
** R&D programs and contracts authorize ...
* Missile combat crew
A missile combat crew (MCC), is a team of highly trained specialists, often called missileers, staffing Intermediate Range and Intercontinental ballistic missile systems (IRBMs and ICBMs, respectively). In the United States, personnel, officially c ...
* Missile launch control center
* Nuclear weapons and the United States
* Single Integrated Operational Plan
The Single Integrated Operational Plan (SIOP) was the United States' general plan for nuclear war from 1961 to 2003. The SIOP gave the President of the United States a range of targeting options, and described launch procedures and target sets a ...
* List of missiles
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
External links
CSIS Missile Threat – Minuteman III
*
Minuteman Information Site
*
60 Minutes shocked to find 8-inch floppies drive nuclear deterrent
– ''Ars Technica
''Ars Technica'' is a website covering news and opinions in technology, science, politics, and society, created by Ken Fisher and Jon Stokes in 1998. It publishes news, reviews, and guides on issues such as computer hardware and software, sci ...
''
{{DEFAULTSORT:Lgm-30 Minuteman
1974 in spaceflight
Cold War weapons of the United States
Embedded systems
LGM-030
Nuclear weapons of the United States
MIRV capable missiles
Military equipment introduced in the 1960s

 The LGM-30F Minuteman II was an improved version of the Minuteman I missile. Its first test launch took place on September 24, 1964. Development on the Minuteman II began in 1962 as the Minuteman I entered the Strategic Air Command's nuclear force. Minuteman II production and deployment began in 1965 and completed in 1967. It had an increased range, greater throw weight and guidance system with better azimuthal coverage, providing military planners with better accuracy and a wider range of targets. Some missiles also carried penetration aids, allowing the higher probability of kill against Moscow's anti-ballistic missile system. The payload consisted of a single Mk-11C reentry vehicle containing a
The LGM-30F Minuteman II was an improved version of the Minuteman I missile. Its first test launch took place on September 24, 1964. Development on the Minuteman II began in 1962 as the Minuteman I entered the Strategic Air Command's nuclear force. Minuteman II production and deployment began in 1965 and completed in 1967. It had an increased range, greater throw weight and guidance system with better azimuthal coverage, providing military planners with better accuracy and a wider range of targets. Some missiles also carried penetration aids, allowing the higher probability of kill against Moscow's anti-ballistic missile system. The payload consisted of a single Mk-11C reentry vehicle containing a 

 :''See also W62 warhead''
The LGM-30G Minuteman III program started in 1966 and included several improvements over the previous versions. Its first test launch took place on August 16, 1968. It was first deployed in 1970. Most modifications related to the final stage and reentry system (RS). The final (third) stage was improved with a new fluid-injected motor, giving finer control than the previous four-nozzle system.
Performance improvements realized in Minuteman III include increased flexibility in reentry vehicle (RV) and penetration aids deployment, increased survivability after a nuclear attack, and increased payload capacity. The missile retains a gimballed inertial navigation system.
Minuteman III originally contained the following distinguishing features:
* Armed with up to three
:''See also W62 warhead''
The LGM-30G Minuteman III program started in 1966 and included several improvements over the previous versions. Its first test launch took place on August 16, 1968. It was first deployed in 1970. Most modifications related to the final stage and reentry system (RS). The final (third) stage was improved with a new fluid-injected motor, giving finer control than the previous four-nozzle system.
Performance improvements realized in Minuteman III include increased flexibility in reentry vehicle (RV) and penetration aids deployment, increased survivability after a nuclear attack, and increased payload capacity. The missile retains a gimballed inertial navigation system.
Minuteman III originally contained the following distinguishing features:
* Armed with up to three  Minuteman III missiles are regularly tested with launches from Vandenberg Space Force Base in order to validate the effectiveness, readiness, and accuracy of the weapon system, as well as to support the system's primary purpose,
Minuteman III missiles are regularly tested with launches from Vandenberg Space Force Base in order to validate the effectiveness, readiness, and accuracy of the weapon system, as well as to support the system's primary purpose,  Faced with only a few Minuteman LCC targets, the Soviets could have concluded that the odds of being successful in a Minuteman LCC decapitation strike were higher with less risk than it would have been having to face the almost insurmountable task of successfully attacking and destroying 1000 Minuteman silos and 100 Minuteman LCCs to ensure Minuteman was disabled. This theory motivated SAC to design a survivable means to launch Minuteman, even if all the ground-based command and control sites were destroyed.
After thorough testing and modification of EC-135 command post aircraft, the ALCS demonstrated its capability on 17 April 1967 by launching an ERCS configured Minuteman II out of Vandenberg AFB, CA. Afterward, ALCS achieved Initial Operational Capability on 31 May 1967. From that point on, airborne missileers stood alert with ALCS-capable EC-135 aircraft for several decades. All Minuteman ICBM Launch Facilities were modified and built to have the capability to receive commands from ALCS. With ALCS now standing alert around-the-clock, the Soviets could no longer successfully launch a Minuteman LCC decapitation strike. Even if the Soviets attempted to do so, EC-135s equipped with the ALCS could fly overhead and launch the remaining Minuteman ICBMs in retaliation.
Now that the ALCS was on alert, this complicated Soviet war planning by forcing the Soviets to target not only the 100 LCCs, but also the 1,000 silos with more than one warhead in order to guarantee destruction. This would have required upwards of 3,000 warheads to complete such an attack. The odds of being successful in such an attack on the Minuteman ICBM force would have been extremely low.
Today, the ALCS is operated by airborne missileers from the
Faced with only a few Minuteman LCC targets, the Soviets could have concluded that the odds of being successful in a Minuteman LCC decapitation strike were higher with less risk than it would have been having to face the almost insurmountable task of successfully attacking and destroying 1000 Minuteman silos and 100 Minuteman LCCs to ensure Minuteman was disabled. This theory motivated SAC to design a survivable means to launch Minuteman, even if all the ground-based command and control sites were destroyed.
After thorough testing and modification of EC-135 command post aircraft, the ALCS demonstrated its capability on 17 April 1967 by launching an ERCS configured Minuteman II out of Vandenberg AFB, CA. Afterward, ALCS achieved Initial Operational Capability on 31 May 1967. From that point on, airborne missileers stood alert with ALCS-capable EC-135 aircraft for several decades. All Minuteman ICBM Launch Facilities were modified and built to have the capability to receive commands from ALCS. With ALCS now standing alert around-the-clock, the Soviets could no longer successfully launch a Minuteman LCC decapitation strike. Even if the Soviets attempted to do so, EC-135s equipped with the ALCS could fly overhead and launch the remaining Minuteman ICBMs in retaliation.
Now that the ALCS was on alert, this complicated Soviet war planning by forcing the Soviets to target not only the 100 LCCs, but also the 1,000 silos with more than one warhead in order to guarantee destruction. This would have required upwards of 3,000 warheads to complete such an attack. The odds of being successful in such an attack on the Minuteman ICBM force would have been extremely low.
Today, the ALCS is operated by airborne missileers from the  Mobile Minuteman was a program for rail-based ICBMs to help increase survivability and for which the USAF released details on 12 October 1959. The
Mobile Minuteman was a program for rail-based ICBMs to help increase survivability and for which the USAF released details on 12 October 1959. The 
 * 90th Missile Wing – "Mighty Ninety"
** at
* 90th Missile Wing – "Mighty Ninety"
** at