|
Penetration Aid
A penetration aid (or "penaid") is a device or tactic used to increase an intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) warhead's chances of penetrating a target's defenses. These can consist of both ''physical devices'' carried within the ICBM (as part of its payload), as well as ''tactics'' that accompany its launch or flight path, operate as either passive or active counters, and may include one or more of the following concepts: * The missile booster can have a short burn time, and/or (if existing) the MIRV bus carrying the nuclear warheads can have some form of stealth technology, thereby hindering detection before the warhead reentry vehicles are released. * MIRV and MRV (instead of single warhead missiles) themselves largely improve penetration since there are many more warheads to destroy than missiles, which may saturate the defensive system's stock of weapons. However, these technologies are very demanding since they require the ability to highly miniaturize both the physics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chevaline2
Chevaline () was a system to improve the penetrability of the warheads used by the British Polaris nuclear weapons system. Devised as an answer to the improved Soviet anti-ballistic missile defences around Moscow, the system increased the probability that at least one warhead would penetrate Moscow's anti-ballistic missile (ABM) defences, something which the Royal Navy's earlier UGM-27 Polaris re-entry vehicles (RV)s were thought to be unlikely to do. Chevaline used a variety of penetration aids and decoys to offer so many indistinguishable targets that an opposing ABM system would be overwhelmed attempting to deal with them all, ensuring that enough warheads would get through an ABM defence to be a reasonable deterrent to a first strike. The project was highly secret, and survived in secrecy through four different governments before being revealed in 1980. The system was in service from 1982 to 1996, when the Polaris A3T missiles it was fitted to were replaced with the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decoy
A decoy (derived from the Dutch ''de'' ''kooi'', literally "the cage" or possibly ''ende kooi'', " duck cage") is usually a person, device, or event which resembles what an individual or a group might be looking for, but it is only meant to lure them. Decoys have been used for centuries most notably in game hunting, but also in wartime and in the committing or resolving of crimes. Hunting In hunting wildfowl, the term decoy may refer to two distinct devices. One, the duck decoy (structure), is a long cone-shaped wickerwork tunnel installed on a small pond to catch wild ducks. After the ducks settled on the pond, a small, trained dog would herd the birds into the tunnel. The catch was formerly sent to market for food, but now these are used only by ornithologists to catch ducks to be ringed and released. The word ''decoy'', also originally found in English as "coy", derives from the Dutch ''de Kooi'' (the cage) and dates back to the early 17th century, when this type of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ballistic Missiles
A ballistic missile is a type of missile that uses projectile motion to deliver warheads on a target. These weapons are guided only during relatively brief periods—most of the flight is unpowered. Short-range ballistic missiles stay within the Earth's atmosphere, while intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs) are launched on a sub-orbital flight. These weapons are in a distinct category from cruise missiles, which are aerodynamically guided in powered flight. Unlike cruise missiles, which are restricted to the atmosphere, it is advantageous for ballistic missiles to avoid the denser parts of the atmosphere and they may travel above the atmosphere into outer space. History The earliest form of ballistic missile dates from the 13th century with its use derived from the history of rockets. In the 14th century, the Ming Chinese navy used an early form of a ballistic missile weapon called the Huolongchushui in naval battles against enemy ships.Needham, Volume 5, Part 7, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chevaline
Chevaline () was a system to improve the penetrability of the warheads used by the British Polaris nuclear weapons system. Devised as an answer to the improved Soviet anti-ballistic missile defences around Moscow, the system increased the probability that at least one warhead would penetrate Moscow's anti-ballistic missile (ABM) defences, something which the Royal Navy's earlier UGM-27 Polaris re-entry vehicles (RV)s were thought to be unlikely to do. Chevaline used a variety of penetration aids and decoys to offer so many indistinguishable targets that an opposing ABM system would be overwhelmed attempting to deal with them all, ensuring that enough warheads would get through an ABM defence to be a reasonable deterrent to a first strike. The project was highly secret, and survived in secrecy through four different governments before being revealed in 1980. The system was in service from 1982 to 1996, when the Polaris A3T missiles it was fitted to were replaced with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maneuverable Reentry Vehicle
The maneuverable reentry vehicle (abbreviated MARV or MaRV) is a type of warhead for ballistic missiles that is capable of maneuvring and changing its trajectory. MaRV can be capable of autonomously tracking ground targets to make sure the missile does not miss the target, because of the frequent trajectory shifts. This often requires some terminal active homing guidance (like Pershing II active radar homing). Advanced Maneuverable Reentry Vehicle The Advanced Maneuverable Reentry Vehicle (AMaRV) was a prototype MARV built by McDonnell Douglas. Four AMaRVs were made and represented a significant leap in reentry vehicle sophistication. Three of the AMaRVs were launched by Minuteman-1 ICBMs on 20 December 1979, 8 October 1980 and 4 October 1981. AMaRV had an entry mass of approximately 470 kg, a nose radius of 2.34 cm, a forward frustum half-angle of 10.4°, an inter-frustum radius of 14.6 cm, aft frustum half angle of 6°, and an axial length of 2.079 meters. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
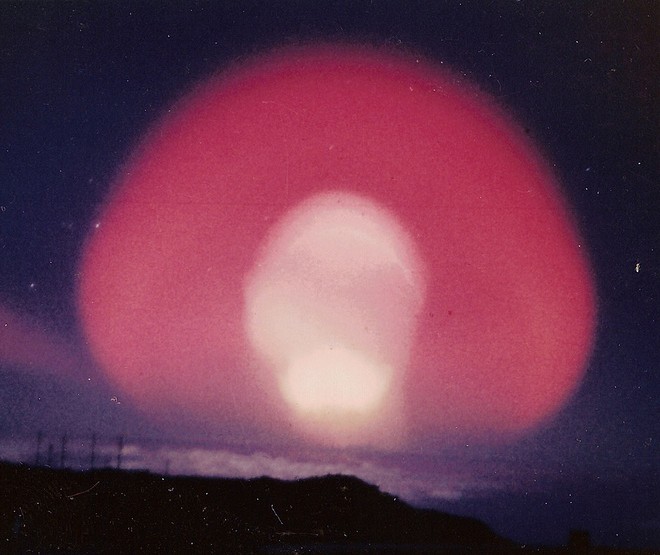
High-altitude Nuclear Explosion
High-altitude nuclear explosions are the result of nuclear weapons testing within the upper layers of the Earth's atmosphere and in outer space. Several such tests were performed at high altitudes by the United States and the Soviet Union between 1958 and 1962. The Partial Test Ban Treaty was passed in October 1963, ending atmospheric and exoatmospheric nuclear tests. The Outer Space Treaty of 1967 banned the stationing of nuclear weapons in space, in addition to other weapons of mass destruction. The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty of 1996 prohibits all nuclear testing; whether over- or underground, underwater or in the atmosphere. EMP generation The strong electromagnetic pulse (EMP) that results has several components. In the first few tenths of nanoseconds, about a tenth of a percent of the weapon yield appears as powerful gamma rays with energies of one to three mega-electron volts ( MeV, a unit of energy). The gamma rays penetrate the atmosphere and collide with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Blackout
Nuclear blackout, also known as fireball blackout or radar blackout, is an effect caused by explosions of nuclear weapons that disturbs radio communications and causes radar systems to be blacked out or heavily refracted so they can no longer be used for accurate tracking and guidance. Within the atmosphere, the effect is caused by the large volume of ionized air created by the energy of the explosion, while above the atmosphere it is due to the action of high-energy beta particles released from the decaying bomb debris. At high altitudes, the effect can spread over large areas, hundreds of kilometers. The effect slowly fades as the fireball dissipates. The effect was known from the earliest days of nuclear testing when radar systems were used to track the nuclear mushroom clouds at very long distances. Its extended effects when exploded outside the atmosphere were first noticed in 1958 as part of the Hardtack and Argus nuclear tests, which caused widespread radio interference exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mylar
BoPET (biaxially-oriented polyethylene terephthalate) is a polyester film made from stretched polyethylene terephthalate (PET) and is used for its high tensile strength, chemical and dimensional stability, transparency, reflectivity, gas and aroma barrier properties, and electrical insulation. A variety of companies manufacture boPET and other polyester films under different brand names. In the UK and US, the best-known trade names are Mylar, Melinex, and Hostaphan. History BoPET film was developed in the mid-1950s,Izard, Emmette Farr"Production of polyethylene terephthalate" U.S. patent no. 2,534,028 (filed: 1948 May 13; issued: 1950 December 12). originally by DuPont, Imperial Chemical Industries (ICI), and Hoechst. In 1955 Eastman Kodak used Mylar as a support for photographic film and called it "ESTAR Base". The very thin and tough film allowed reels to be exposed on long-range U-2 reconnaissance flights. In 1964, NASA launched Echo II, a diameter balloon const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar Jamming
Radar jamming and deception is a form of electronic countermeasures that intentionally sends out radio frequency signals to interfere with the operation of radar by saturating its receiver with noise or false information. Concepts that blanket the radar with signals so its display cannot be read are normally known as jamming, while systems that produce confusing or contradictory signals are known as deception, but it is also common for all such systems to be referred to as jamming. There are two general classes of radar jamming, mechanical and electronic. Mechanical jamming entails reflecting enemy radio signals in various ways to provide false or misleading target signals to the radar operator. Electronic jamming works by transmitting additional radio signals towards enemy receivers, making it difficult to detect real target signals, or take advantage of known behaviors of automated systems like radar lock-on to confuse the system. Various counter-countermeasures can sometimes he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercontinental Ballistic Missile
An intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) is a ballistic missile with a range greater than , primarily designed for nuclear weapons delivery (delivering one or more thermonuclear warheads). Conventional, chemical, and biological weapons can also be delivered with varying effectiveness, but have never been deployed on ICBMs. Most modern designs support multiple independently targetable reentry vehicles (MIRVs), allowing a single missile to carry several warheads, each of which can strike a different target. Russia, the United States, China, France, India, the United Kingdom, and North Korea are the only countries known to have operational ICBMs. Early ICBMs had limited precision, which made them suitable for use only against the largest targets, such as cities. They were seen as a "safe" basing option, one that would keep the deterrent force close to home where it would be difficult to attack. Attacks against military targets (especially hardened ones) still demanded t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a detection system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), angle, and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwaves domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving information about the objects' locations and speeds. Radar was developed secretly for military use by several countries in the period before and during World War II. A key development was the cavity magnetron in the United Kingdom, which allowed the creation of relatively small systems with sub-meter resolution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
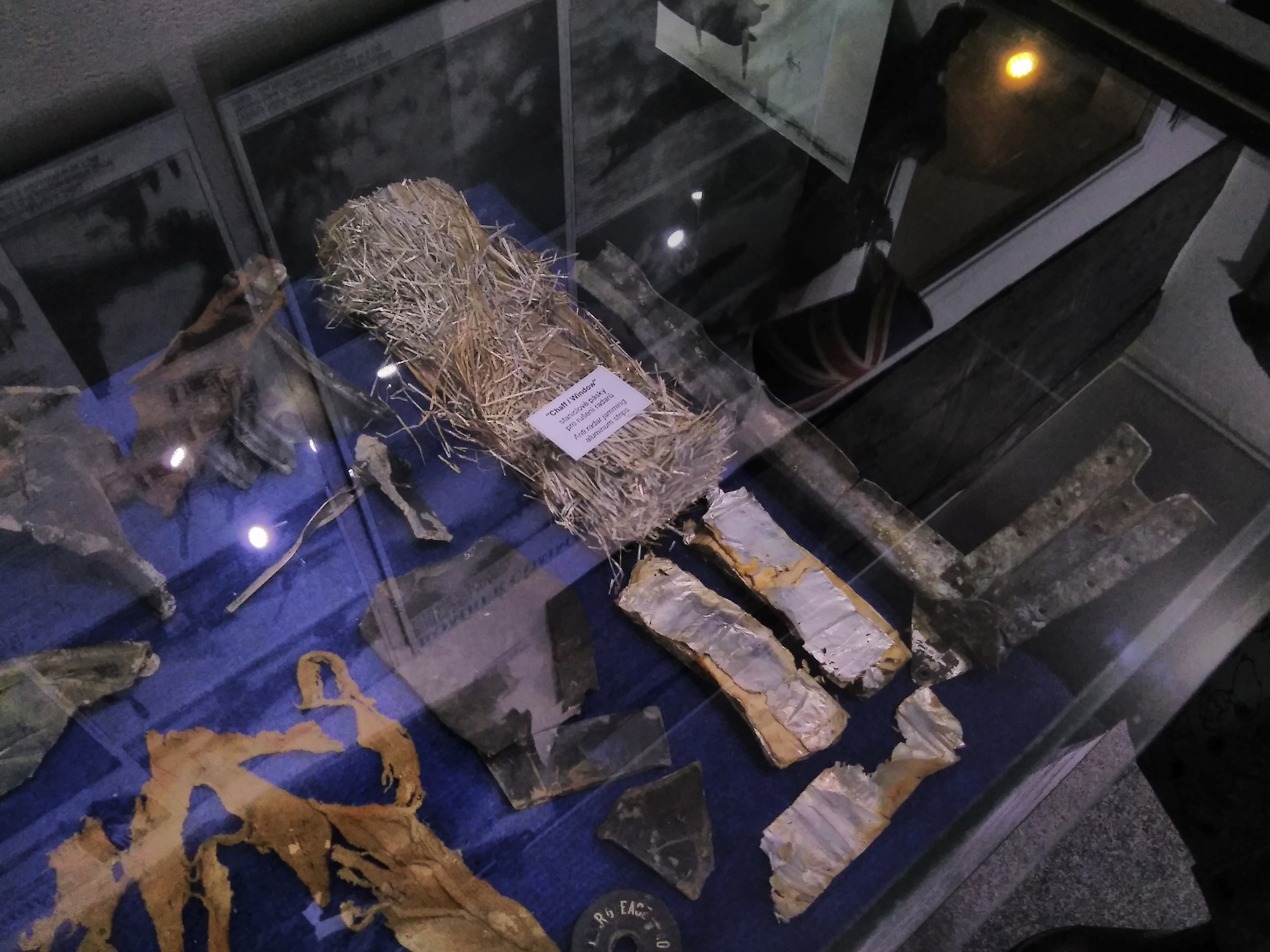
Chaff (radar Countermeasure)
Chaff, originally called Window by the British and ''Düppel'' by the Second World War era German Luftwaffe (from the Berlin suburb where it was first developed), is a radar countermeasure in which aircraft or other targets spread a cloud of small, thin pieces of aluminium, metallized glass fibre or plastic, which either appears as a cluster of primary targets on radar screens or swamps the screen with multiple returns, in order to confuse and distract. Modern armed forces use chaff (in naval applications, for instance, using short-range SRBOC rockets) to distract radar-guided missiles from their targets. Most military aircraft and warships have chaff dispensing systems for self-defense. An intercontinental ballistic missile may release in its midcourse phase several independent warheads as well as penetration aids such as decoy balloons and chaff. Modern radar systems can distinguish chaff from target objects by measuring the Doppler shift; chaff quickly loses speed compar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)