|
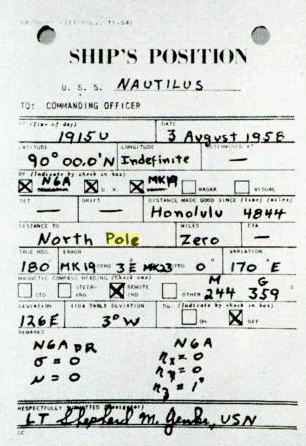
North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distinguish from the Magnetic North Pole. The North Pole is by definition the northernmost point on the Earth, lying antipodally to the South Pole. It defines geodetic latitude 90° North, as well as the direction of true north. At the North Pole all directions point south; all lines of longitude converge there, so its longitude can be defined as any degree value. No time zone has been assigned to the North Pole, so any time can be used as the local time. Along tight latitude circles, counterclockwise is east and clockwise is west. The North Pole is at the center of the Northern Hemisphere. The nearest land is usually said to be Kaffeklubben Island, off the northern coast of Greenland about away, though some perhaps semi-permanent gravel banks lie slightly clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Ocean - En
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia (Murmansk, Siberia, Nenets Okrug, Novaya Zemlya), Sweden and the United States (Alaska). Land within the Arctic region has seasonally varying snow and ice cover, with predominantly treeless permafrost (permanently frozen underground ice) containing tundra. Arctic seas contain seasonal sea ice in many places. The Arctic region is a unique area among Earth's ecosystems. The cultures in the region and the Arctic indigenous peoples have adapted to its cold and extreme conditions. Life in the Arctic includes zooplankton and phytoplankton, fish and marine mammals, birds, land animals, plants and human societies. Arctic land is bordered by the subarctic. Definition and etymology The word Arctic comes from the Greek word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Ice
Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface (as does fresh water ice, which has an even lower density). Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oceans. Much of the world's sea ice is enclosed within the polar ice packs in the Earth's polar regions: the Arctic ice pack of the Arctic Ocean and the Antarctic ice pack of the Southern Ocean. Polar packs undergo a significant yearly cycling in surface extent, a natural process upon which depends the Arctic ecology, including the ocean's ecosystems. Due to the action of winds, currents and temperature fluctuations, sea ice is very dynamic, leading to a wide variety of ice types and features. Sea ice may be contrasted with icebergs, which are chunks of ice shelves or glaciers that calve into the ocean. Depending on location, sea ice expanses may also incorporate icebergs. General features and dynamics Sea ice does not simply grow and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roald Amundsen
Roald Engelbregt Gravning Amundsen (, ; ; 16 July 1872 – ) was a Norwegian explorer of polar regions. He was a key figure of the period known as the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration. Born in Borge, Østfold, Norway, Amundsen began his career as a polar explorer as first mate on Adrien de Gerlache's Belgian Antarctic Expedition of 1897–1899. From 1903 to 1906, he led the first expedition to successfully traverse the Northwest Passage on the sloop ''Gjøa''. In 1909, Amundsen began planning for a South Pole expedition. He left Norway in June 1910 on the ship ''Fram'' and reached Antarctica in January 1911. His party established a camp at the Bay of Whales and a series of supply depots on the Barrier (now known as the Ross Ice Shelf) before setting out for the pole in October. The party of five, led by Amundsen, became the first to successfully reach the South Pole on 14 December 1911. Following a failed attempt in 1918 to reach the North Pole by traversing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norge (airship)
The ''Norge'' was a semi-rigid Italian-built airship that carried out the first verified trip of any kind to the North Pole, an overflight on 12 May 1926. It was also the first aircraft to fly over the polar ice cap between Europe and America. The expedition was the brainchild of polar explorer and expedition leader Roald Amundsen, the airship's designer and pilot Umberto Nobile and American adventurer and explorer Lincoln Ellsworth who, along with the Aero Club of Norway, financed the trip, which was known as the Amundsen-Ellsworth 1926 Transpolar Flight. Design and development ''Norge'' was the first N-class semi-rigid airship designed by Umberto Nobile, and its construction started in 1923. As part of the selling contract s the ''Norge''it was refitted for Arctic conditions. The pressurised envelope was reinforced with metal frames at the nose and tail, with a flexible tubular metal keel connecting the two. This was covered with fabric and used as storage and crew space. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farthest North
Farthest North describes the most northerly latitude reached by explorers, before the first successful expedition to the North Pole rendered the expression obsolete. The Arctic polar regions are much more accessible than those of the Antarctic, as continental land masses extend to high latitudes and sea voyages to the regions are relatively short. Early voyages The most northerly point of Europe, Knivskjellodden in Norway, lies at . War and trade had led to voyages between western Norway and Northern Russia around Knivskjellodden and the North Cape since at least the 15th Century. John Davis on his third voyage to seek the Northwest Passage in 1587 sailed up the Strait that bears his name, between Greenland and Baffin Island, to a latitude of . A Dutch expedition led by Willem Barentz, attempting the Northeast Passage reached on , on the NW coast of Spitsbergen. In 1607, Henry Hudson probably reached Hakluyt's Headland (a little south of the latitude reached by Barentz), but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Climate Change In The Arctic
Major environmental issues caused by contemporary climate change in the Arctic region range from the well-known, such as the loss of sea ice or melting of the Greenland ice sheet, to more obscure, but deeply significant issues, such as permafrost thaw, social consequences for locals and the geopolitical ramifications of these changes. The Arctic is likely to be especially affected by climate change because of the high projected rate of regional warming and associated impacts. Temperature projections for the Arctic region were assessed in 2007: These suggested already averaged warming of about 2 °C to 9 °C by the year 2100. The range reflects different projections made by different climate models, run with different forcing scenarios. Radiative forcing is a measure of the effect of natural and human activities on the climate. Different forcing scenarios reflect things such as different projections of future human greenhouse gas emissions. These effects are wide-rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barneo
Camp Barneo (russian: Лагерь Бaрнео) is a private temporary tourist resort located on Arctic Ocean ice near the North Pole. When it is occupied for a few weeks in April, it is the northernmost inhabited place in the world. It was first established in 2002 and re-occupied annually thereafter, but it has remained vacant since 2018. When operating, the price for a visit starts at about $20,000. History The first Ice Camp Barneo near the North Pole was established in 2002. Since that time, the camp has been rebuilt from scratch every year because of the constantly drifting Arctic ice. For example, in 2007 Ice Camp Barneo was located at about (about 30 miles / 48 kilometers from the North Pole). However, northerly winds caused the Ice Camp to drift towards the southeast at a speed of . The ice camp works under the patronage of the Russian Geographical Society and normally lasts for the month of April. Ice Camp Barneo should not be confused with the sequential Soviet/Ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drifting Ice Station
A drifting ice station is a temporary or semi-permanent facility built on an ice floe. During the Cold War the Soviet Union and the United States maintained a number of stations in the Arctic Ocean on floes such as Fletcher's Ice Island for research and espionage, the latter of which were often little more than quickly constructed shacks. Extracting personnel from these stations proved difficult and in the case of the United States, employed early versions of the Fulton surface-to-air recovery system. Overview Soviet and Russian staffed drifting ice stations are research stations built on the ice of the high latitudes of the Arctic Ocean. They are important contributors to exploration of the Arctic. The stations are named North Pole (NP; russian: Северный полюс, translit=Severny polyus, ), followed by an ordinal number: North Pole-1, etc. NP drift stations carry out the program of complex year-round research in the fields of oceanology, ice studies, meteorology, ae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station
The Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station is the United States scientific research station at the South Pole of the Earth. It is the southernmost point under the jurisdiction (not sovereignty) of the United States. The station is located on the high plateau of Antarctica at above sea level. It is administered by the Office of Polar Programs of the National Science Foundation, specifically the United States Antarctic Program (USAP). It is named in honor of Norwegian Roald Amundsen and Briton Robert F. Scott, who led separate teams that raced to become the first to the pole in the early 1900s. The original Amundsen–Scott Station was built by Navy Seabees for the federal government of the United States during November 1956, as part of its commitment to the scientific goals of the International Geophysical Year, an effort lasting from January 1957 through June 1958 to study, among other things, the geophysics of the polar regions of Earth. Before November ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hague Academy Of International Law
The Hague Academy of International Law (french: Académie de droit international de La Haye) is a center for high-level education in both public and private international law housed in the Peace Palace in The Hague, Netherlands. Courses are taught in English and French and, except for External Programme Courses, are held in the Peace Palace. The academy is notable for its Summer Courses Programme. The academy's alumni, faculty, and administration have included heads of state; foreign ministers; ambassadors; 12 judges of the International Court of Justice; one former secretary-general of the United Nations, Boutros Boutros-Ghali; and two Nobel Prize recipients. History Since its creation in 1923, the Hague Academy of International Law has occupied premises at the Peace Palace. Next to the Peace Palace building the academy's facilities include the Academy Hall built for international conferences, the Peace Palace Library as well as further administrative accommodations. The new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voenizdat
Voenizdat (russian: Воениздат) was a publishing house in Moscow, Russia that was one of the first and largest publishing houses in USSR. The name is a Russian abbreviation for "Voennoe Izdatelstvo", meaning "Military Publication". Voenizdat was established by Revvoyensoviet on 25 October 1919. The initial aim was to publish literature for the needs of Ministry of Defence. It later published both fiction and non-fiction literature, technical manuals and dictionaries A dictionary is a listing of lexemes from the lexicon of one or more specific languages, often arranged alphabetically (or by radical and stroke for ideographic languages), which may include information on definitions, usage, etymologies, p .... The company was absorbed into Red Star in 2009. References External links Worldcat datadase entries ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |