|
Grand Forks AFB
Grand Forks Air Force Base (AFB) is a United States Air Force installation in northeastern North Dakota, located north of Emerado and west of Grand Forks. The host unit is the 319th Reconnaissance Wing (319 RW) assigned to the Air Combat Command (ACC) operating E/RQ-4B Global Hawk remotely piloted aircraft (RPA), in the intelligence, surveillance and reconnaissance (ISR) role. During the Cold War, GFAFB was a major installation of the Strategic Air Command (SAC), with B-52 bombers, KC-135 tankers, and Minuteman intercontinental ballistic missiles. History Grand Forks Air Force Base was established on 1 December 1955, with construction beginning in the fall of that year. It was occupied for use on 28 January 1957, and was named after the neighboring city of Grand Forks. Air Defense Command Due to the continuance of the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union, GFAFB was originally an Air Defense Command (ADC) fighter-interceptor air base. The site was chosen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Forks, North Dakota
Grand Forks is the third-largest city in the state of North Dakota (after Fargo and Bismarck) and the county seat of Grand Forks County. According to the 2020 census, the city's population was 59,166. Grand Forks, along with its twin city of East Grand Forks, Minnesota, forms the center of the Grand Forks, ND-MN Metropolitan Statistical Area, which is often called Greater Grand Forks or the Grand Cities. Located on the western banks of the north-flowing Red River of the North, in a flat region known as the Red River Valley, the city is prone to flooding. The Red River Flood of 1997 devastated the city. Originally called ''Les Grandes Fourches'' by French fur traders from Canada, who had long worked and lived in the region, steamboat captain Alexander Griggs platted a community after being forced to winter there. The post office was established in 1870, and the town was incorporated on February 22, 1881. The city was named for its location at the fork of the Red River and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
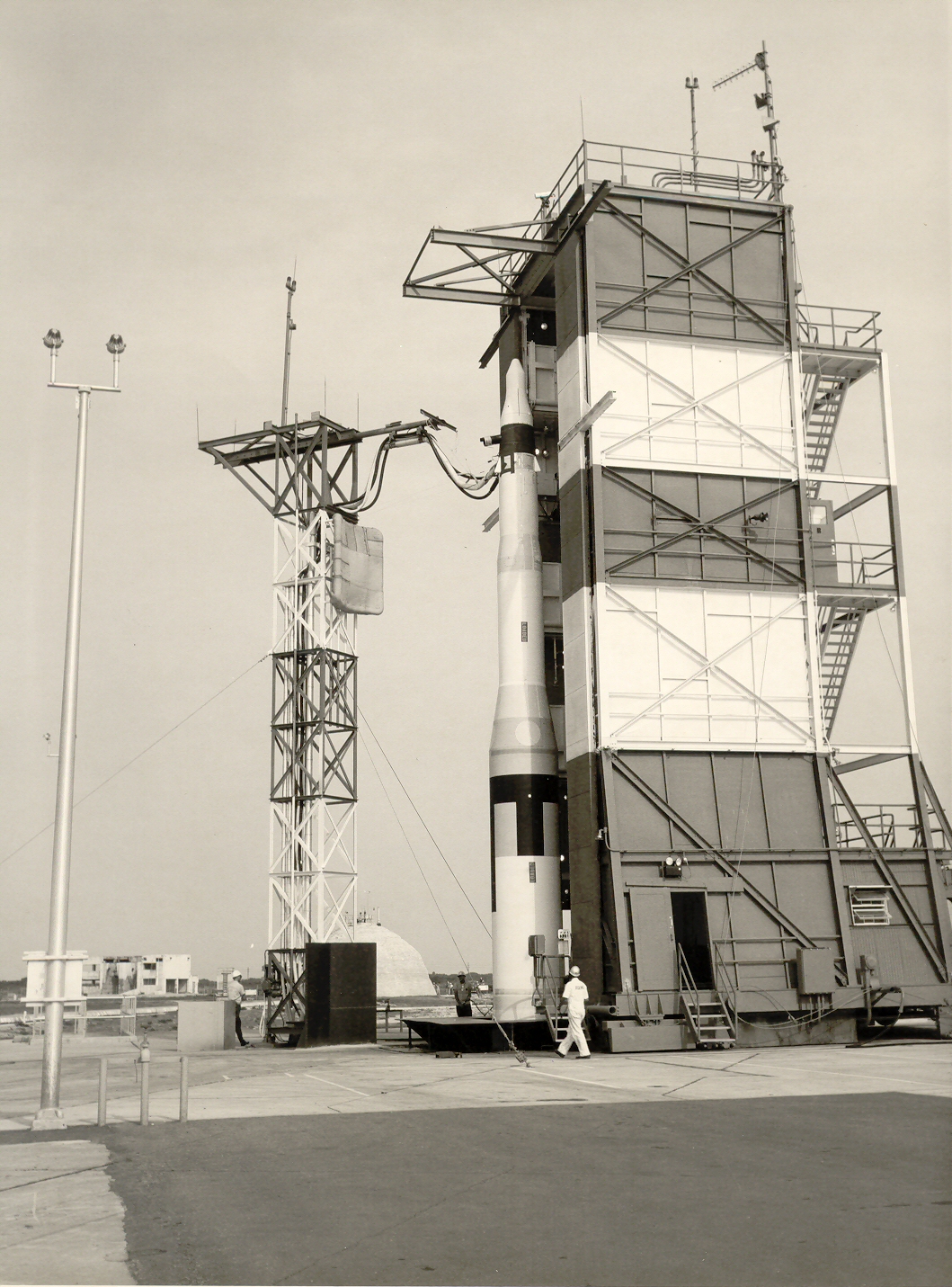
LGM-30 Minuteman
The LGM-30 Minuteman is an American land-based intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) in service with the Air Force Global Strike Command. , the LGM-30G Minuteman III version is the only land-based ICBM in service in the United States and represents the land leg of the U.S. nuclear triad, along with the Trident submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) and nuclear weapons carried by long-range strategic bombers. Development of the Minuteman began in the mid-1950s when basic research indicated that a solid-fuel rocket motor could stand ready to launch for long periods of time, in contrast to liquid-fueled rockets that required fueling before launch and so might be destroyed in a surprise attack. The missile was named for the colonial minutemen of the American Revolutionary War, who could be ready to fight on short notice. The Minuteman entered service in 1962 as a deterrence weapon that could hit Soviet cities with a second strike and countervalue counterattack if the U.S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi Automatic Ground Environment
The Semi-Automatic Ground Environment (SAGE) was a system of large computers and associated networking equipment that coordinated data from many radar sites and processed it to produce a single unified image of the airspace over a wide area. SAGE directed and controlled the NORAD response to a possible Soviet air attack, operating in this role from the late 1950s into the 1980s. Its enormous computers and huge displays remain a part of cold war lore, and after decommissioning were common props in movies such as ''Dr. Strangelove'' and ''Colossus'', and on science fiction TV series such as ''The Time Tunnel''. The processing power behind SAGE was supplied by the largest discrete component-based computer ever built, the IBM-manufactured AN/FSQ-7. Each SAGE Direction Center (DC) housed an FSQ-7 which occupied an entire floor, approximately not including supporting equipment. The FSQ-7 was actually two computers, "A" side and "B" side. Computer processing was switched from "A" s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convair F-106 Delta Dart
The Convair F-106 Delta Dart was the primary all-weather interceptor aircraft of the United States Air Force from the 1960s through to the 1980s. Designed as the so-called "Ultimate Interceptor", it proved to be the last specialist interceptor in U.S. Air Force service to date. It was gradually retired during the 1980s, with the QF-106 drone conversions of the aircraft being used until 1998 under the ''Pacer Six'' program.Winchester 2006, p. 55. Development Antecedents The F-106 was the ultimate development of the USAF's 1954 interceptor program of the early 1950s. The initial winner of this competition had been the F-102 Delta Dagger, but early versions of this aircraft had demonstrated extremely poor performance, limited to subsonic speeds and relatively low altitudes. During the testing program the F-102 underwent numerous changes to improve its performance, notably the application of the area rule to the fuselage shaping and a change of engine, and the dropping of the advan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klamath Falls, Oregon
Klamath Falls ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Klamath County, Oregon, United States. The city was originally called ''Linkville'' when George Nurse founded the town in 1867. It was named after the Link River, on whose falls the city was sited. The name was changed to Klamath Falls in 1893. The population was 21,813 at the 2020 census. The city is on the southeastern shore of the Upper Klamath Lake located about northwest of Reno, Nevada, and approximately north of the California–Oregon border. Logging was Klamath Falls's first major industry. Etymology At its founding in 1867, Klamath Falls was named Linkville. The name was changed to Klamath Falls in 1892–93. The name ''Klamath'' , may be a variation of the descriptive native for "people" Chinookan] used by the indigenous peoples of the Northwest Plateau to refer to the region. Several locatives derived from the Modoc or Achomawi: ''lutuami'', lit: "lake dwellers", ''móatakni'', "tule lake dwellers", respective ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingsley Field Air National Guard Base
Kingsley Field Air National Guard Base is the home base of the Oregon Air National Guard's 173rd Fighter Wing (173 FW). History In 1928, the citizens of Klamath Falls approved the sale of $50,000 worth of bonds to construct an airport. The airport was known as the Klamath Falls Municipal Airport and consisted of gravel runways and one fixed-base operator. In 1942, the airport was selected as a site for a Naval Air Station. Known as NAS Klamath Falls during World War II, the airport was transferred from the U.S. Navy back to civilian use in late 1945. In 1954, the airport was selected as a site for United States Air Force base and the airfield returned to military control. The former naval air station was then placed under the jurisdiction of the Air Defense Command (ADC). The 408th Fighter Group (Air Defense) was activated at Klamath Falls Municipal Airport on 8 April 1956, being assigned to the 28th Air Division. In 1957, the airport was dedicated as Kingsley Field in hono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
460th Fighter-Interceptor Squadron
The 460th Fighter-Interceptor Training Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. Its last assignment was with Tactical Air Command's 325th Fighter Weapons Wing at Tyndall Air Force Base, Florida, where it was inactivated on 15 October 1982. History World War II Established in late 1942 as a ground support squadron. Deployed to the Pacific Theater of Operations in 1943 to Australia where the unit functioned as a ground support unit at Sydney Airport, then at Dobodura in New Guinea. Converted to a P-47 Thunderbolt operational combat unit, engaged in fighter-bomber operations against Japanese positions in New Guinea, Netherlands East Indies and also during the Philippines Campaign (1944–1945). Moved to Okinawa, then Japan after the Japanese Capitulation as part of the Occupation Force, inactivated in 1946. Air defense Reactivated in 1954 as part of the U.S. Air Force Air Defense Command, stationed at Knoxville, for air defense of the Oak Ridge National Labora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McDonnell F-101 Voodoo
The McDonnell F-101 Voodoo is a supersonic jet fighter which served the United States Air Force (USAF) and the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF). Initially designed by McDonnell Aircraft Corporation as a long-range bomber escort (known as a ''penetration fighter'') for the USAF's Strategic Air Command (SAC), the Voodoo was instead developed as a nuclear-armed fighter-bomber for the USAF's Tactical Air Command (TAC), and as a photo reconnaissance aircraft based on the same airframe. An F-101A set a number of world speed records for jet-powered aircraft, including fastest airspeed, attaining per hour on 12 December 1957. They operated in the reconnaissance role until 1979. Delays in the 1954 interceptor project led to demands for an interim interceptor aircraft design, a role that was eventually won by the B model of the Voodoo. This required extensive modifications to add a large radar to the nose of the aircraft, a second crew member to operate it, and a new weapons bay usin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wurtsmith Air Force Base
Wurtsmith Air Force Base is a decommissioned United States Air Force base in Iosco County, Michigan. It operated from 1923 until decommissioned in 1993. On January 18, 1994 it was listed as a Superfund due to extensive groundwater contamination with heavy metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, volatile organic compounds, including trichloroethylene, 1,1-dichloroethane, 1,1,1-trichloroethane, and vinyl chloride. In 2010, Per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances contamination was discovered, and as of 2022 remediation is still ongoing. During the Cold War, it was one of three Strategic Air Command (SAC) bases in Michigan with the B-52 bomber, the others (Kincheloe AFB and Sawyer AFB) were in the Upper Peninsula. The base was named in honor of Major General Paul Wurtsmith, commander of SAC's Eighth Air Force, who was killed when his B-25 Mitchell bomber crashed on Cold Mountain near Asheville, North Carolina, on September 13, 1946. In 2022, Granot Loma was being touted as a potent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
18th Fighter-Interceptor Squadron
The 18th Aggressor Squadron (18 AGRS) is a subordinate unit of the 354th Fighter Wing based at Eielson Air Force Base in Alaska, and flies the Block 30 General Dynamics F-16C/D aircraft. Mission The 18th Aggressor Squadron prepares combat Air Force, joint and allied aircrews through challenging, realistic threat replication, training, test support, academics and feedback. History Activated in 1940 as a Southwest Air District pursuit squadron, equipped with a variety of 1930s-era pursuit aircraft. Re-equipped with P-38 Lightning fighters and deployed to Alaska, engaged in combat during the Aleutian Campaign, 1942–1943. Remained in Alaska as part of the air defense forces until inactivated in August 1946. Air Defense Command Reactivated in 1952 as part of Air Defense Command as an air defense squadron, initially equipped with F-86A Sabre day fighters, initially being assigned to Minneapolis Airport, Minnesota with a mission for the air defense of the Upper Great Lakes re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
478th Fighter Group
478th may refer to: *478th Aeronautical Systems Wing The 478th Aeronautical Systems Wing is an inactive wing of the United States Air Force which was last based at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio, where it was inactivated in 2009. The wing was first organized as the 478th Fighter Group (Two E ... (478 ASW), wing of the United States Air Force based out of Wright-Patterson Air Force Base, Ohio * 478th Bombardment Squadron, inactive United States Air Force unit * 478th Tactical Fighter Squadron, inactive United States Air Force unit See also * 478 (number) * 478, the year 478 (CDLXXVIII) of the Julian calendar * 478 BC {{mil-unit-dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |