|
D-37C
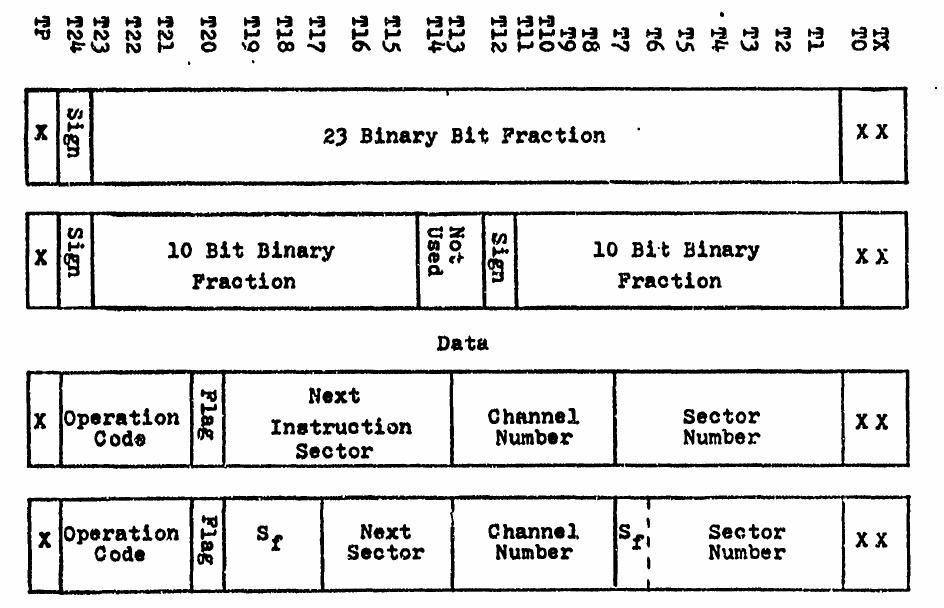
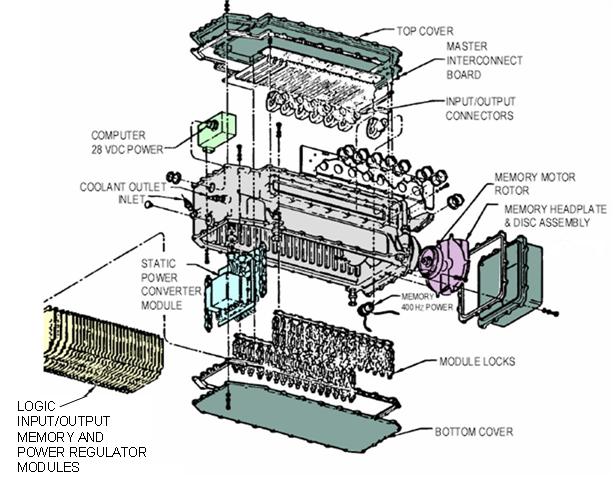
The D-37C (D37C) is the computer component of the all-inertial NS-17 Missile Guidance Set (MGS) for accurately navigating to its target thousands of miles away. The NS-17 MGS was used in the Minuteman II (LGM-30F) ICBM. The MGS, originally designed and produced by the Autonetics Division of North American Aviation, could store multiple preprogrammed targets in its internal memory. Unlike other methods of navigation, inertial guidance does not rely on observations of land positions or the stars, radio or radar signals, or any other information from outside the vehicle. Instead, the inertial navigator provides the guidance information using gyroscopes that indicate direction and accelerometer An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acc ...s that measure changes in speed and direc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D-17B
The D-17B (D17B) computer was used in the Minuteman I NS-1OQ missile guidance system. The complete guidance system contained a D-17B computer, the associated stable platform, and power supplies. The D-17B weighed approximately , contained 1,521 transistors, 6,282 diodes, 1,116 capacitors, and 504 resistors. These components were mounted on double copper-clad, engraved, gold-plated, glass fiber laminate circuit boards. There were 75 of these circuit boards and each one was coated with a flexible polyurethane compound for moisture and vibration protection. The high degree of reliability and ruggedness of the computer were driven by the strict requirements of the weapons system. Design constraints High reliability was required of the D-17B. It controlled a key weapon that would have just one chance to execute its mission. Reliability of the D-17B was achieved through the use of solid-state electronics and a relatively simple design. Simpler DRL (diode–resistor) logic was used ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minuteman (missile)
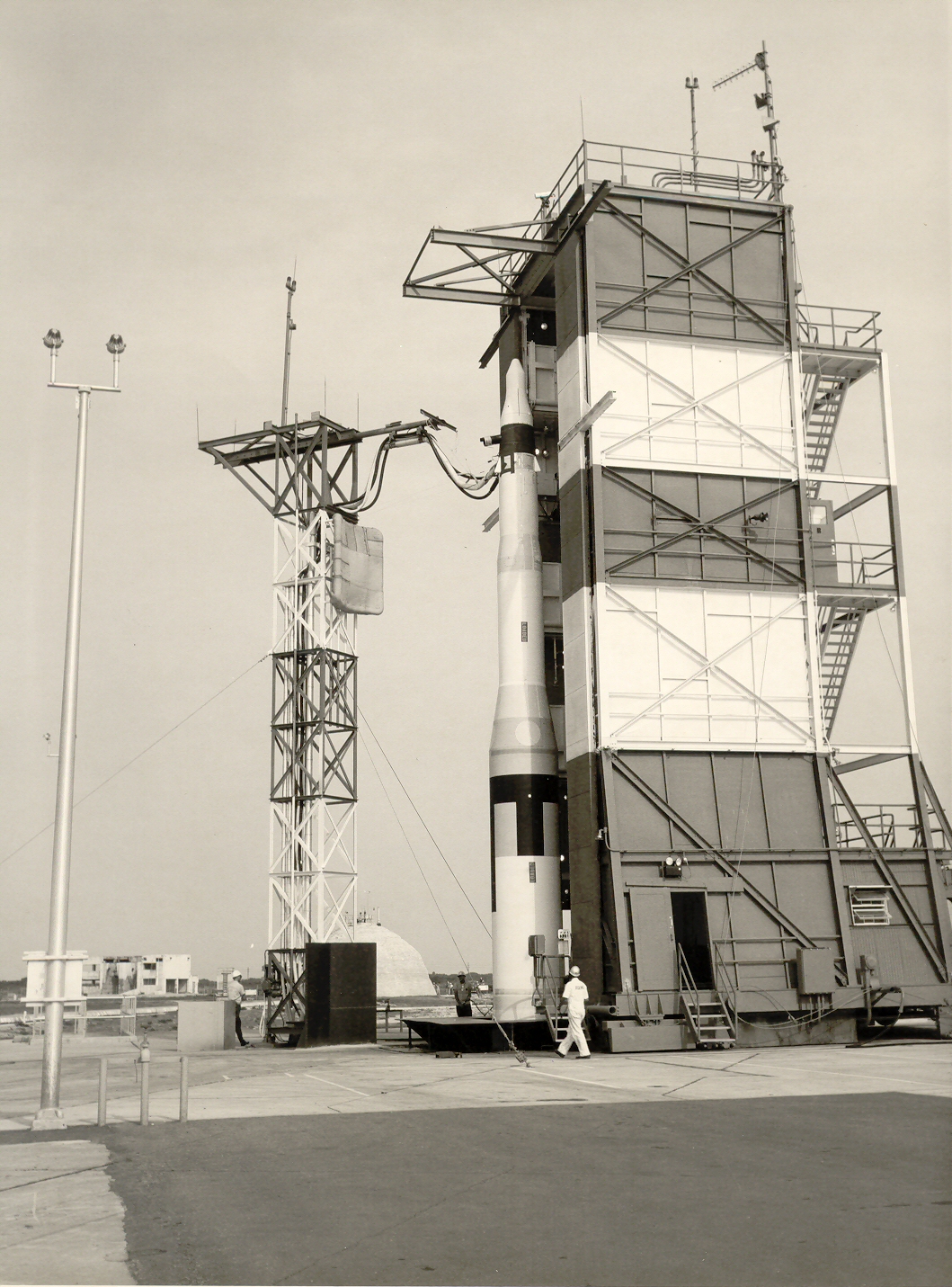
The LGM-30 Minuteman is an American land-based intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) in service with the Air Force Global Strike Command. , the LGM-30G Minuteman III version is the only land-based ICBM in service in the United States and represents the land leg of the U.S. nuclear triad, along with the Trident submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) and nuclear weapons carried by long-range strategic bombers. Development of the Minuteman began in the mid-1950s when basic research indicated that a solid-fuel rocket motor could stand ready to launch for long periods of time, in contrast to liquid-fueled rockets that required fueling before launch and so might be destroyed in a surprise attack. The missile was named for the colonial minutemen of the American Revolutionary War, who could be ready to fight on short notice. The Minuteman entered service in 1962 as a deterrence weapon that could hit Soviet cities with a second strike and countervalue counterattack if the U.S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minuteman II
The LGM-30 Minuteman is an American land-based intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) in service with the Air Force Global Strike Command. , the LGM-30G Minuteman III version is the only land-based ICBM in service in the United States and represents the land leg of the U.S. nuclear triad, along with the Trident submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM) and nuclear weapons carried by long-range strategic bombers. Development of the Minuteman began in the mid-1950s when basic research indicated that a solid-fuel rocket motor could stand ready to launch for long periods of time, in contrast to liquid-fueled rockets that required fueling before launch and so might be destroyed in a surprise attack. The missile was named for the colonial minutemen of the American Revolutionary War, who could be ready to fight on short notice. The Minuteman entered service in 1962 as a deterrence weapon that could hit Soviet cities with a second strike and countervalue counterattack if the U.S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonetics
Autonetics was a division of North American Aviation that produced various avionics but is best known for their inertial navigation systems used in submarines and intercontinental ballistic missiles. Its 188-acre facility in Anaheim, California, with 36,000 employees, was the city's largest employer. Through a series of mergers, Autonetics is now part of Boeing. Origin Autonetics originated in North American Aviation's Technical Research Laboratory, a small unit in the Los Angeles Division's engineering department, in 1945. In 1946, the laboratory won an Army Air Forces contract to develop a 175 to 500 mile range glide missile. The work and the lab expanded, and by June 1948, all of the Aerophysics Laboratory was consolidated at Downey, California. The evolution of the Navaho missile program then resulted in the establishment of Autonetics as a separate division of North American Aviation in 1955, first located in Downey, moving to Anaheim, California in 1963. Divisions Autonetics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D37D
{{Short description, Military flight computer The D37D Minuteman III flight computer was initially supplied with the LGM-30G missile, as part of the NS-20 navigation system. The NS-20 D37D flight computer is a miniaturized general purpose (serial transmission) digital computer. The new NS-50 missile guidance computer (MGC) is built around a 16-bit high-speed microprocessor chip set. They are both designed to solve real-time positional error problems under the adverse conditions encountered in airborne weapon systems. They accept and process data and generate steering signals with sufficient accuracy and speed to meet the requirements of the inertial guidance and flight control systems of the Minuteman ICBMs. Computer operation is controlled by an internally stored program which is loaded from a magnetic tape cartridge at the launch facility (LF). Both the D37D computer and the MGC are designed and programmed to control the Minuteman III missile throughout the powered portion of fli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Computers
This article specifically addresses U.S. armed forces military computers and their use. History Some of the earliest computers were military computers. Military requirements for portability and ruggedness led to some of the earliest transistorized computers, such as the 1958 AN/USQ-17, the 1959 AN/MYK-1 ( MOBIDIC), the 1960 M18 FADAC, and the 1962 D-17B; the earliest integrated-circuit based computer, the 1964 D-37C; as well as one of the earliest laptop computers, the 1982 Grid Compass. Military requirements for a computer small enough to fit through a submarine's hatch led to the AN/UYK-1. Construction Typically a military computer is much more robust than an industrial computer enclosure. Most electronics will be protected with a layer of conformal coating. There will be more structure inside to support the components, the plug-in cards will be individually supported and secured to assure they do not pop out of their sockets, the processor and heat sink will be secured, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emulator
In computing, an emulator is Computer hardware, hardware or software that enables one computer system (called the ''host'') to behave like another computer system (called the ''guest''). An emulator typically enables the host system to run software or use peripheral devices designed for the guest system. Emulation refers to the ability of a computer program in an electronic device to emulate (or imitate) another program or device. Many Printer (computing), printers, for example, are designed to emulate Hewlett-Packard, HP LaserJet printers because so much software is written for HP printers. If a non-HP printer emulates an HP printer, any software written for a real HP printer will also run in the non-HP printer emulation and produce equivalent printing. Since at least the 1990s, many video game enthusiasts and hobbyists have used emulators to play classic arcade games from the 1980s using the games' original 1980s machine code and data, which is interpreted by a current-era s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Navigation System
An inertial navigation system (INS) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors ( gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity (direction and speed of movement) of a moving object without the need for external references. Often the inertial sensors are supplemented by a barometric altimeter and sometimes by magnetic sensors ( magnetometers) and/or speed measuring devices. INSs are used on mobile robots and on vehicles such as ships, aircraft, submarines, guided missiles, and spacecraft. Other terms used to refer to inertial navigation systems or closely related devices include inertial guidance system, inertial instrument, inertial measurement unit (IMU) and many other variations. Older INS systems generally used an inertial platform as their mounting point to the vehicle and the terms are sometimes considered synonymous. Overview Inertial navigation is a self-cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DC-DC Converter
A DC-to-DC converter is an electronic circuit or electromechanical device that converts a source of direct current (DC) from one voltage level to another. It is a type of electric power converter. Power levels range from very low (small batteries) to very high (high-voltage power transmission). History Before the development of power semiconductors, one way to convert the voltage of a DC supply to a higher voltage, for low-power applications, was to convert it to AC by using a vibrator, then by a step-up transformer, and finally a rectifier. Where higher power was needed, a motor–generator unit was often used, in which an electric motor drove a generator that produced the desired voltage. (The motor and generator could be separate devices, or they could be combined into a single "dynamotor" unit with no external power shaft.) These relatively inefficient and expensive designs were used only when there was no alternative, as to power a car radio (which then used thermionic valves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Transistor
A power semiconductor device is a semiconductor device used as a switch or rectifier in power electronics (for example in a switch-mode power supply). Such a device is also called a power device or, when used in an integrated circuit, a power IC. A power semiconductor device is usually used in "commutation mode" (i.e., it is either on or off), and therefore has a design optimized for such usage; it should usually not be used in linear operation. Linear power circuits are widespread as voltage regulators, audio amplifiers, and radio frequency amplifiers. Power semiconductors are found in systems delivering as little as a few tens of milliwatts for a headphone amplifier, up to around a gigawatt in a high voltage direct current transmission line. History The first electronic device used in power circuits was the electrolytic rectifier - an early version was described by a French experimenter, A. Nodon, in 1904. These were briefly popular with early radio experimenters as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globally. It is one of the top 10 semiconductor companies worldwide based on sales volume. The company's focus is on developing analog chips and embedded processors, which account for more than 80% of its revenue. TI also produces TI digital light processing technology and education technology products including calculators, microcontrollers, and multi-core processors. The company holds 45,000 patents worldwide as of 2016. Texas Instruments emerged in 1951 after a reorganization of Geophysical Service Incorporated, a company founded in 1930 that manufactured equipment for use in the seismic industry, as well as defense electronics. TI produced the world's first commercial silicon transistor in 1954, and the same year designed and manufactured t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |