|
Diode–transistor Logic
Diode–transistor logic (DTL) is a class of digital circuits that is the direct ancestor of transistor–transistor logic. It is called so because the logic gating function (e.g., AND) is performed by a diode network and the amplifying function is performed by a transistor (in contrast with RTL and TTL). Implementations The DTL circuit shown in the picture consists of three stages: an input diode logic stage (D1, D2 and R1), an intermediate level shifting stage (R3 and R4), and an output common-emitter amplifier stage (Q1 and R2). If both inputs A and B are high (logic 1; near V+), then the diodes D1 and D2 are reverse biased. Resistors R1 and R3 will then supply enough current to turn on Q1 (drive Q1 into saturation) and also supply the current needed by R4. There will be a small positive voltage on the base of Q1 (VBE, about 0.3 V for germanium and 0.6 V for silicon). The turned on transistor's collector current will then pull the output Q low (logic 0; VCE(sat), usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Circuit
In theoretical computer science, a circuit is a model of computation in which input values proceed through a sequence of gates, each of which computes a function. Circuits of this kind provide a generalization of Boolean circuits and a mathematical model for digital logic circuits. Circuits are defined by the gates they contain and the values the gates can produce. For example, the values in a Boolean circuit are boolean values, and the circuit includes conjunction, disjunction, and negation gates. The values in an integer circuit are sets of integers and the gates compute set union, set intersection, and set complement, as well as the arithmetic operations addition and multiplication. Formal definition A circuit is a triple (M, L, G), where * M is a set of values, * L is a set of gate labels, each of which is a function from M^ to M for some non-negative integer i (where i represents the number of inputs to the gate), and * G is a labelled directed acyclic graph with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signetics
Signetics Corporation was an American electronics manufacturer specifically established to make integrated circuits. Founded in 1961, they went on to develop a number of early microprocessors and support chips, as well as the widely used 555 timer chip. The company was bought by Philips in 1975 and incorporated in Philips Semiconductors (now NXP). History Signetics was started in 1961, by a group of engineers (David Allison, David James, Lionel Kattner, and Mark Weissenstern) who had left Fairchild Semiconductor. At the time, Fairchild was concentrating on its discrete component business (mostly transistors), and its management felt that by making integrated circuits (ICs) it would lose its customers. Signetics founders believed that ICs were the future of electronics (much like another contemporary Fairchild spinoff, Amelco) and wished to commercialize them. The name of the new company was coined from Signal Network Electronics. The venture was financed by a group organized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-threshold Logic
High-threshold logic (HTL), also known as ''low-speed logic'' (''LSL'') or ''high-level logic'' (''HLL''), is a variant of diode–transistor logic used in environments where noise is very high. Operation The threshold values at the input to a logic gate determine whether a particular input is interpreted as a logic 0 or a logic 1 (e.g. anything less than 1 V is a logic 0, and anything above 3 V is a logic 1; in this example, the threshold values are 1 V and 3 V). HTL incorporates Zener diodes to create a large offset between logic 1 and logic 0 voltage levels. These devices usually ran off a 15 V power supply and were found in industrial control, where the high differential was intended to minimize the effect of noise. Advantages * Increased noise margin * High noise threshold value Disadvantage *Slow speed due to increased supply voltage resulting in use of high value resistors. *High power drawn Usage It is used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diode Logic
Diode logic (DL), or diode-resistor logic (DRL), is the construction of Boolean logic gates from diodes. Diode logic was used extensively in the construction of early computers, where semiconductor diodes could replace bulky and costly active vacuum tube elements. The most common use for diode logic is in diode–transistor logic (DTL) integrated circuits that, in addition to diodes, include inverter logic to provide a NOT function and signal restoration. While diode logic has the advantage of simplicity, the lack of an amplifying stage in each gate limits its application. Not all logical functions can be implemented in diode logic alone; only the non-inverting logical AND and logical OR functions can be realized by diode gates. If several diode logic gates are cascaded, the voltage levels at each stage are significantly changed, so diode logic is normally limited to a single stage, though, in special designs, two-stage systems are sometimes achieved. Simplifying assumpti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fan-in
Fan-in is the number of inputs a logic gate can handle. For instance the fan-in for the AND gate shown in the figure is 3. Physical logic gates with a large fan-in tend to be slower than those with a small fan-in. This is because the complexity of the input circuitry increases the input capacitance Capacitance is the capability of a material object or device to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized a ... of the device. Using logic gates with higher fan-in will help in reducing the depth of a logic circuit; this is because circuit design is realized by the target logic family at a digital level, meaning any large fan-in logic gates are simply the smaller fan-in gates chained together in series at a given depth to widen the circuit instead. Fan-in tree of a node refers to a collection of signals that contribute to the input signal of that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schottky Transistor
A Schottky transistor is a combination of a transistor and a Schottky diode that prevents the transistor from saturating by diverting the excessive input current. It is also called a Schottky-clamped transistor. Mechanism Standard transistor-transistor logic (TTL) uses transistors as saturated switches. A saturated transistor is turned on hard, which means it has a lot more base drive than it needs for the collector current it is drawing. The extra base drive creates a stored charge in the base of the transistor. The stored charge causes problems when the transistor needs to be switched from on to off: while the charge is present, the transistor is on; all the charge must be removed before the transistor will turn off. Removing the charge takes time (called storage time), so the result of saturation is a delay between the applied turn-off input at the base and the voltage swing at the collector. Storage time accounts for a significant portion of the propagation delay in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James R
James is a common English language surname and given name: *James (name), the typically masculine first name James * James (surname), various people with the last name James James or James City may also refer to: People * King James (other), various kings named James * Saint James (other) * James (musician) * James, brother of Jesus Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Arts, entertainment, and media * ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * James the Red Engine, a character in ''Tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baker Clamp
Baker clamp is a generic name for a class of electronic circuits that reduce the storage time of a switching bipolar junction transistor (BJT) by applying a nonlinear negative feedback through various kinds of diodes. The reason for slow turn-off times of saturated BJTs is the stored charge in the base. It must be removed before the transistor will turn off since the storage time is a limiting factor of using bipolar transistors and IGBTs in fast switching applications. The diode-based Baker clamps prevent the transistor from saturating and thereby accumulating a lot of stored charge. Origin The Baker clamp is named after Richard H. Baker, who described it in his 1956 technical report "Maximum Efficiency Transistor Switching Circuits". Baker called the technique "back clamping", but the circuit is now called a Baker clamp. Many sources credit Baker's report for the two-diode clamp circuit. Also in 1956, Baker described the circuit in a patent application; the 1961 issued p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propagation Delay
Propagation delay is the time duration taken for a signal to reach its destination. It can relate to networking, electronics or physics. ''Hold time'' is the minimum interval required for the logic level to remain on the input after triggering edge of the clock pulse. Networking In computer networks, propagation delay is the amount of time it takes for the head of the signal to travel from the sender to the receiver. It can be computed as the ratio between the link length and the propagation speed over the specific medium. Propagation delay is equal to ''d / s'' where ''d'' is the distance and ''s'' is the wave propagation speed. In wireless communication, ''s''=''c'', i.e. the speed of light. In copper wire, the speed ''s'' generally ranges from .59c to .77c. This delay is the major obstacle in the development of high-speed computers and is called the interconnect bottleneck in IC systems. Electronics In electronics, digital circuits and digital electronics, the propaga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
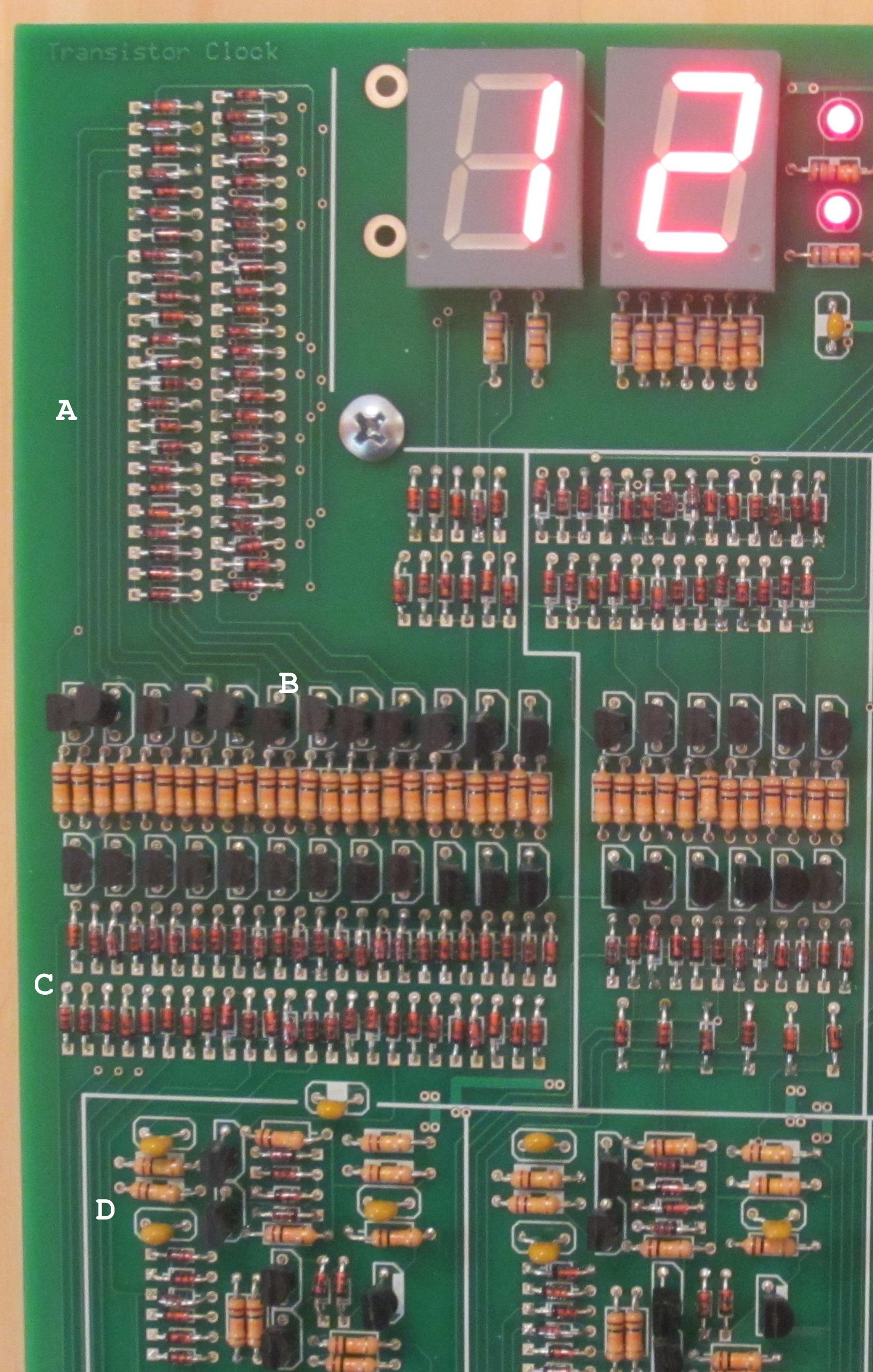
Transistor Clock
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink). A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electrical power, power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transistor in 1926, but it was not possible to actually constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairchild Semiconductor
Fairchild Semiconductor International, Inc. was an American semiconductor company based in San Jose, California. Founded in 1957 as a division of Fairchild Camera and Instrument, it became a pioneer in the manufacturing of transistors and of integrated circuits. Schlumberger bought the firm in 1979 and sold it to National Semiconductor in 1987; Fairchild was spun off as an independent company again in 1997. In September 2016, Fairchild was acquired by ON Semiconductor. The company had locations in the United States at San Jose, California; San Rafael, California; South Portland, Maine; West Jordan, Utah; and Mountaintop, Pennsylvania. Outside the US it operated locations in Australia; Singapore; Bucheon, South Korea; Penang, Malaysia; Suzhou, China; and Cebu, Philippines, among others. History 1950s In 1955, William Shockley founded Shockley Semiconductor Laboratory, funded by Beckman Instruments in Mountain View, California; his plan was to develop a new type of "4-lay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM Standard Modular System
The Standard Modular System (SMS) is a system of standard transistorized circuit boards and mounting racks developed by IBM in the late 1950s, originally for the IBM 7030 Stretch. They were used throughout IBM's second-generation computers, peripherals, the 7000 series, the 1400 series, and the 1620. SMS was superseded by Solid Logic Technology (SLT) introduced with System/360 in 1964, however they remained in use with legacy systems through the 1970s. Overview Many IBM peripheral devices that are part of System/360, but were adapted from second-generation designs, continued to use SMS circuitry instead of the newer SLT. These included the 240x-series tape drives and controllers, the 2540 card reader/punch and 1403N1 printer, and the 2821 Integrated Control Unit for the 1403 and 2540. A few SMS cards used in System/360 peripheral devices even have SLT-type hybrid ICs mounted on them ''(see right)''. SMS cards are constructed of individual discrete components mounted on s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)

