LGA 2011-1 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
LGA 2011, also called ''Socket R'', is a
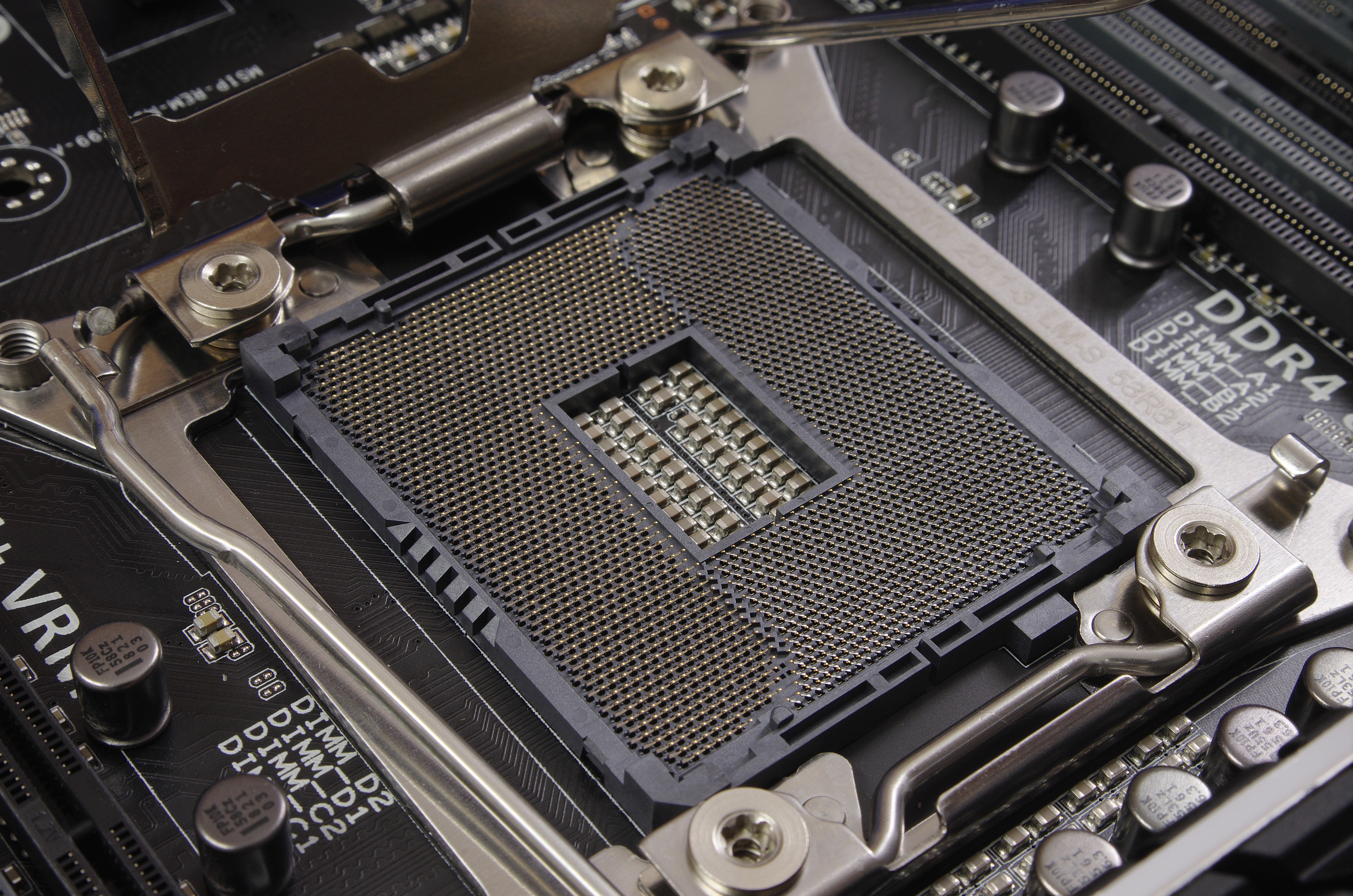 Intel CPU sockets use the so-called ''Independent Loading Mechanism'' (ILM) retention device to apply the specific amount of uniform pressure required to correctly hold the CPU against the socket interface. As part of their design, ILMs have differently placed protrusions which are intended to mate with cutouts in CPU packagings. These protrusions, also known as ''ILM keying'', have the purpose of preventing installation of incompatible CPUs into otherwise physically compatible sockets, and preventing ILMs to be mounted with a 180-degree rotation relative to the CPU socket.
Different variants (or generations) of the LGA 2011 socket and associated CPUs come with different ILM keying, which makes it possible to install CPUs only into generation-matching sockets. CPUs that are intended to be mounted into ''LGA 2011-0'' (R), ''LGA 2011-1'' (R2) or ''LGA 2011-v3'' (R3) sockets are all mechanically compatible regarding their dimensions and ball pattern pitches, but the designations of contacts are different between generations of the LGA 2011 socket and CPUs, which makes them electrically and logically incompatible. Original LGA 2011 socket is used for Sandy Bridge-E/EP and Ivy Bridge-E/EP processors, while LGA 2011-1 is used for Ivy Bridge-EX (Xeon E7 v2) and Haswell-EX (Xeon E7 V3) CPUs, which were released in February 2014 and May 2015, respectively. LGA 2011-v3 socket is used for
Intel CPU sockets use the so-called ''Independent Loading Mechanism'' (ILM) retention device to apply the specific amount of uniform pressure required to correctly hold the CPU against the socket interface. As part of their design, ILMs have differently placed protrusions which are intended to mate with cutouts in CPU packagings. These protrusions, also known as ''ILM keying'', have the purpose of preventing installation of incompatible CPUs into otherwise physically compatible sockets, and preventing ILMs to be mounted with a 180-degree rotation relative to the CPU socket.
Different variants (or generations) of the LGA 2011 socket and associated CPUs come with different ILM keying, which makes it possible to install CPUs only into generation-matching sockets. CPUs that are intended to be mounted into ''LGA 2011-0'' (R), ''LGA 2011-1'' (R2) or ''LGA 2011-v3'' (R3) sockets are all mechanically compatible regarding their dimensions and ball pattern pitches, but the designations of contacts are different between generations of the LGA 2011 socket and CPUs, which makes them electrically and logically incompatible. Original LGA 2011 socket is used for Sandy Bridge-E/EP and Ivy Bridge-E/EP processors, while LGA 2011-1 is used for Ivy Bridge-EX (Xeon E7 v2) and Haswell-EX (Xeon E7 V3) CPUs, which were released in February 2014 and May 2015, respectively. LGA 2011-v3 socket is used for

About the new Intel Xeon E5-2600v3
(Servermeile Wiki) As one of the significant changes from the previous generation, they support DDR4 memory. All processors are released in September 8, 2014, unless noted otherwise.
CPU socket
In computer hardware, a CPU socket or CPU slot contains one or more mechanical components providing mechanical and electrical connections between a microprocessor and a printed circuit board (PCB). This allows for placing and replacing the centr ...
by Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
released on November 14, 2011. It launched along with LGA 1356
LGA 1356, also called Socket B2, is an Intel microprocessor socket released in Q1 2012 with 1356 Land Grid Array pins. It launched alongside LGA 2011 to replace its predecessor, LGA 1366 (Socket B) and LGA 1567. It's compatible with Intel Sandy ...
to replace its predecessor, LGA 1366 (Socket B) and LGA 1567. While LGA 1356 was designed for dual-processor or low-end servers, LGA 2011 was designed for high-end desktops and high-performance servers. The socket has 2011 protruding pins that touch contact points on the underside of the processor.
The LGA 2011 socket uses QPI
The Intel QuickPath Interconnect (QPI) is a point-to-point processor interconnect developed by Intel which replaced the front-side bus (FSB) in Xeon, Itanium, and certain desktop platforms starting in 2008. It increased the scalability and availab ...
to connect the CPU to additional CPUs. DMI 2.0
In computing, Direct Media Interface (DMI) is Intel's proprietary link between the Northbridge (computing), northbridge and Southbridge (computing), southbridge on a computer motherboard. It was first used between the 9xx chipsets and the I/O Con ...
is used to connect the processor to the PCH. The memory controller and 40 PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common ...
(PCIe) lanes are integrated on the CPU. On a secondary processor an extra ×4 PCIe interface replaces the DMI interface. As with its predecessor LGA 1366, there is no provisioning for integrated graphics. This socket supports four DDR3
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth ("double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-speed ...
or DDR4
Double Data Rate 4 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR4 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory with a high bandwidth ("double data rate") interface.
Released to the market in 2014, it is a variant of dynamic rando ...
SDRAM memory channels with up to three unbuffered or registered DIMMs per channel, as well as up to 40 PCI Express 2.0
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e, is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common ...
or 3.0 lanes. LGA 2011 also has to ensure platform scalability beyond eight cores and 20 MB of cache.
The LGA 2011 socket is used by Sandy Bridge-E/EP and Ivy Bridge-E
''Hedera'', commonly called ivy (plural ivies), is a genus of 12–15 species of evergreen climbing or ground-creeping woody plants in the family Araliaceae, native to western, central and southern Europe, Macaronesia, northwestern Africa and ...
/EP processors with the corresponding X79 (E enthusiast class) and C600-series (EP Xeon class) chipsets. It and LGA 1155 are the two last Intel sockets to support Windows XP
Windows XP is a major release of Microsoft's Windows NT operating system. It was released to manufacturing on August 24, 2001, and later to retail on October 25, 2001. It is a direct upgrade to its predecessors, Windows 2000 for high-end and ...
and Windows Server 2003.
LGA 2011-1 (Socket R2), an updated generation of the socket and the successor of LGA 1567, is used for Ivy Bridge-EX (Xeon E7 v2
Xeon ( ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded system markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same ar ...
), Haswell-EX (Xeon E7 v3
Xeon ( ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded system markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same arc ...
) and Broadwell-EX (Xeon E7 v4) CPUs, which were released in February 2014, May 2015 and July 2016, respectively.
LGA 2011-v3 (Socket R3, also referred to as LGA 2011-3) is another updated generation of the socket, used for Haswell-E
Haswell is the List of Intel codenames, codename for a Central processing unit, processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the "fourth-generation core" successor to the Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), Ivy Bridge (which is a die shrink/Tick ...
and Haswell-EP
Xeon ( ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded system markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same arc ...
CPUs and Broadwell-E, which were released in August and September 2014, respectively. Updated socket generations are physically similar to LGA 2011, but different electrical signals, ILM keying and integration of DDR4
Double Data Rate 4 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR4 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory with a high bandwidth ("double data rate") interface.
Released to the market in 2014, it is a variant of dynamic rando ...
memory controller rather than DDR3
Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM) is a type of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) with a high bandwidth ("double data rate") interface, and has been in use since 2007. It is the higher-speed ...
prevent backward compatibility with older CPUs.
In the server market, it was succeeded by LGA 3647, when in high-end desktop and workstation markets its successor is LGA 2066. Xeon E3 family of processors, later renamed Xeon E, uses consumer-grade sockets.
__TOC__
Physical design and socket generations
 Intel CPU sockets use the so-called ''Independent Loading Mechanism'' (ILM) retention device to apply the specific amount of uniform pressure required to correctly hold the CPU against the socket interface. As part of their design, ILMs have differently placed protrusions which are intended to mate with cutouts in CPU packagings. These protrusions, also known as ''ILM keying'', have the purpose of preventing installation of incompatible CPUs into otherwise physically compatible sockets, and preventing ILMs to be mounted with a 180-degree rotation relative to the CPU socket.
Different variants (or generations) of the LGA 2011 socket and associated CPUs come with different ILM keying, which makes it possible to install CPUs only into generation-matching sockets. CPUs that are intended to be mounted into ''LGA 2011-0'' (R), ''LGA 2011-1'' (R2) or ''LGA 2011-v3'' (R3) sockets are all mechanically compatible regarding their dimensions and ball pattern pitches, but the designations of contacts are different between generations of the LGA 2011 socket and CPUs, which makes them electrically and logically incompatible. Original LGA 2011 socket is used for Sandy Bridge-E/EP and Ivy Bridge-E/EP processors, while LGA 2011-1 is used for Ivy Bridge-EX (Xeon E7 v2) and Haswell-EX (Xeon E7 V3) CPUs, which were released in February 2014 and May 2015, respectively. LGA 2011-v3 socket is used for
Intel CPU sockets use the so-called ''Independent Loading Mechanism'' (ILM) retention device to apply the specific amount of uniform pressure required to correctly hold the CPU against the socket interface. As part of their design, ILMs have differently placed protrusions which are intended to mate with cutouts in CPU packagings. These protrusions, also known as ''ILM keying'', have the purpose of preventing installation of incompatible CPUs into otherwise physically compatible sockets, and preventing ILMs to be mounted with a 180-degree rotation relative to the CPU socket.
Different variants (or generations) of the LGA 2011 socket and associated CPUs come with different ILM keying, which makes it possible to install CPUs only into generation-matching sockets. CPUs that are intended to be mounted into ''LGA 2011-0'' (R), ''LGA 2011-1'' (R2) or ''LGA 2011-v3'' (R3) sockets are all mechanically compatible regarding their dimensions and ball pattern pitches, but the designations of contacts are different between generations of the LGA 2011 socket and CPUs, which makes them electrically and logically incompatible. Original LGA 2011 socket is used for Sandy Bridge-E/EP and Ivy Bridge-E/EP processors, while LGA 2011-1 is used for Ivy Bridge-EX (Xeon E7 v2) and Haswell-EX (Xeon E7 V3) CPUs, which were released in February 2014 and May 2015, respectively. LGA 2011-v3 socket is used for Haswell-E
Haswell is the List of Intel codenames, codename for a Central processing unit, processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the "fourth-generation core" successor to the Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), Ivy Bridge (which is a die shrink/Tick ...
and Haswell-EP
Xeon ( ) is a brand of x86 microprocessors designed, manufactured, and marketed by Intel, targeted at the non-consumer workstation, server, and embedded system markets. It was introduced in June 1998. Xeon processors are based on the same arc ...
CPUs, which were released in August and September 2014, respectively.
Two types of ILM exist, with different shapes and heatsink mounting hole patterns, both with M4 x 0.7 threads: ''square ILM'' (80×80 mm mounting pattern), and ''narrow ILM'' (56×94 mm mounting pattern). Square ILM is the standard type, while the narrow one is alternatively available for space-constrained applications. A matching heatsink is required for each ILM type.
Chipsets
Information for the Intel X79 (for desktop) and C600 series (for workstations and servers, codenamed Romley) chipsets is in the table below. The Romley (EP) platform was delayed approximately one quarter, allegedly due to aSAS
SAS or Sas may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''SAS'' (novel series), a French book series by Gérard de Villiers
* ''Shimmer and Shine'', an American animated children's television series
* Southern All Stars, a Japanese rock ba ...
controller bug.
The X79 appears to contain the same silicon as the C600 series, with ECS having enabled the SAS controller for one of their boards, even though SAS is not officially supported by Intel for X79.
Compatible processors
Desktop processors
Desktop processors compatible with LGA 2011, 2011–3 socket are Sandy Bridge-E,Ivy Bridge-E
''Hedera'', commonly called ivy (plural ivies), is a genus of 12–15 species of evergreen climbing or ground-creeping woody plants in the family Araliaceae, native to western, central and southern Europe, Macaronesia, northwestern Africa and ...
, Haswell-E
Haswell is the List of Intel codenames, codename for a Central processing unit, processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the "fourth-generation core" successor to the Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), Ivy Bridge (which is a die shrink/Tick ...
and Broadwell-E
Broadwell is the fifth generation of the Intel Core Processor. It is Intel's codename for the 14 nanometer die shrink of its Haswell microarchitecture. It is a "tick" in Intel's tick–tock principle as the next step in semiconductor fabri ...
.
* Sandy Bridge-E and Ivy Bridge-E processors are compatible with the Intel X79 chipset.
* Haswell-E and Broadwell-E processors are compatible with the Intel X99 chipset.
*All models support: MMX, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. It extends the earlier Streamin ...
, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1
SSE4 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 4) is a SIMD CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 (K8L). It was announced on September 27, 2006, at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper; more ...
, SSE4.2, AVX AVX may refer to:
Technology
* Advanced Vector Extensions, an instruction set extension in the x86 microprocessor architecture
** AVX2, an expansion of the AVX instruction set
** AVX-512, 512-bit extensions to the 256-bit AVX
* AVX Corporation, a m ...
, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST), Intel 64, XD bit (an NX bit
The NX bit (no-execute) is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors. However, the NX bit is ...
implementation), TXT, Intel VT-x, Intel VT-d, Turbo Boost
Intel Turbo Boost is Intel's trade name for central processing units (CPUs) dynamic frequency scaling feature that automatically raises certain versions of its operating frequency when demanding tasks are running, thus enabling a higher resulting ...
, AES-NI, Smart Cache, Hyper-threading, except the C1 stepping models, which lack VT-d.
* Sandy Bridge-E, Ivy Bridge-E and Haswell-E processors are not bundled with standard air-cooled CPU coolers. Intel is offering a standard CPU cooler, and a liquid-cooled
Liquid cooling refers to cooling by means of the convection or circulation of a liquid.
Examples of liquid cooling technologies include:
* Cooling by convection or circulation of coolant, including water cooling
* Liquid cooling and ventilatio ...
CPU cooler, which are both sold separately.
1 The X79 chipset allows for increasing the base clock (BCLK), Intel calls it CPU Strap, by 1.00×, 1.25×, 1.66× or 2.50×. The CPU frequency is derived by the BCLK times the CPU multiplier.
Server processors
Server processors compatible with LGA 2011 socket are Sandy Bridge-EP,Ivy Bridge-E
''Hedera'', commonly called ivy (plural ivies), is a genus of 12–15 species of evergreen climbing or ground-creeping woody plants in the family Araliaceae, native to western, central and southern Europe, Macaronesia, northwestern Africa and ...
, Haswell-E
Haswell is the List of Intel codenames, codename for a Central processing unit, processor microarchitecture developed by Intel as the "fourth-generation core" successor to the Ivy Bridge (microarchitecture), Ivy Bridge (which is a die shrink/Tick ...
and Broadwell-E
Broadwell is the fifth generation of the Intel Core Processor. It is Intel's codename for the 14 nanometer die shrink of its Haswell microarchitecture. It is a "tick" in Intel's tick–tock principle as the next step in semiconductor fabri ...
.
* All models support: MMX, SSE, SSE2
SSE2 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 2) is one of the Intel SIMD (Single Instruction, Multiple Data) processor supplementary instruction sets first introduced by Intel with the initial version of the Pentium 4 in 2000. It extends the earlier Streamin ...
, SSE3, SSSE3, SSE4.1
SSE4 (Streaming SIMD Extensions 4) is a SIMD CPU instruction set used in the Intel Core microarchitecture and AMD K10 (K8L). It was announced on September 27, 2006, at the Fall 2006 Intel Developer Forum, with vague details in a white paper; more ...
, SSE4.2, AVX AVX may refer to:
Technology
* Advanced Vector Extensions, an instruction set extension in the x86 microprocessor architecture
** AVX2, an expansion of the AVX instruction set
** AVX-512, 512-bit extensions to the 256-bit AVX
* AVX Corporation, a m ...
, Enhanced Intel SpeedStep Technology (EIST), Intel 64, XD bit (an NX bit
The NX bit (no-execute) is a technology used in CPUs to segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions or for storage of data, a feature normally only found in Harvard architecture processors. However, the NX bit is ...
implementation), TXT, Intel VT-x, Intel VT-d, AES-NI, Smart Cache. Not all support Hyper-threading and Turbo Boost
Intel Turbo Boost is Intel's trade name for central processing units (CPUs) dynamic frequency scaling feature that automatically raises certain versions of its operating frequency when demanding tasks are running, thus enabling a higher resulting ...
.
Sandy Bridge-EP (Xeon E5)
Ivy Bridge-EP (Xeon E5 v2)
Ivy Bridge-EX (Xeon E7 v2)
All processors are released in February 18, 2014, unless noted otherwise.Haswell-EP (Xeon E5 v3)
Server processors for the LGA 2011-v3 socket are listed in the tables below.(Servermeile Wiki) As one of the significant changes from the previous generation, they support DDR4 memory. All processors are released in September 8, 2014, unless noted otherwise.
Haswell-EX (Xeon E7 v3)
Socket LGA 2011-1 is used for Ivy Bridge-EX (Xeon E7 v2) and Haswell-EX (Xeon E7 V3) CPUs, which were released in February 2014 and May 2015, respectively. All processors are released in May 6, 2015, unless noted otherwise.Broadwell-EP (Xeon E5 v4)
Server processors for the LGA 2011-v3 socket are listed in the tables below. These processors are built onBroadwell-E
Broadwell is the fifth generation of the Intel Core Processor. It is Intel's codename for the 14 nanometer die shrink of its Haswell microarchitecture. It is a "tick" in Intel's tick–tock principle as the next step in semiconductor fabri ...
architecture, 14nM lithography, 4-channel DDR4 ECC with up to 1.5TB and 40-lanes of PCI Express 3.0. E5-16xx v4 do not have QPI links. E5-26xx v4 and E5-46xx 4 processors have 2 QPI links.
Broadwell-EX (Xeon E7 v4)
References
{{Intelsock Intel CPU sockets