History of the Jews in Yemen on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
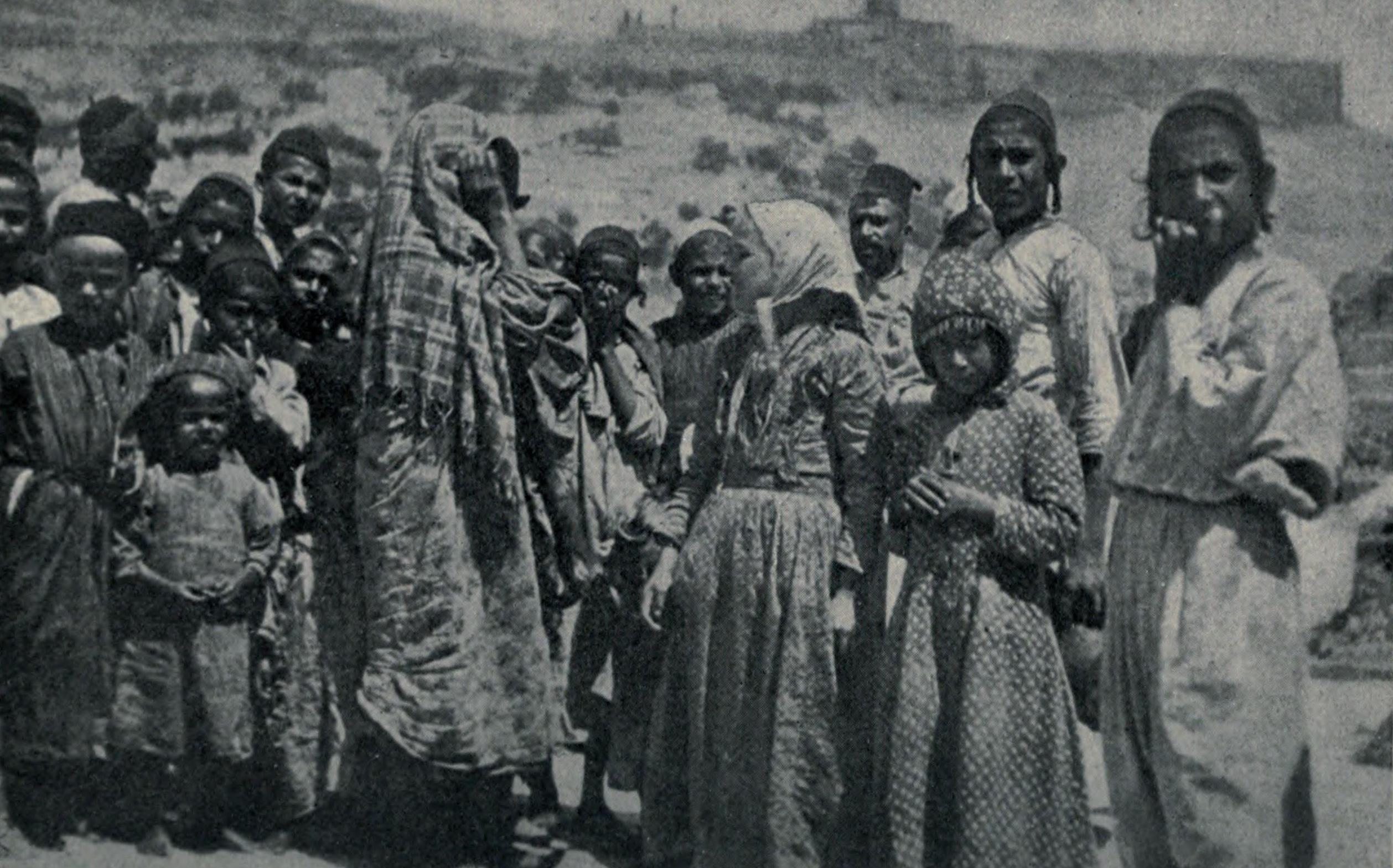

Yemenite Jews or Yemeni Jews or Teimanim (from ''Yehudei Teman''; ar, اليهود اليمنيون) are those
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
who live, or once lived, in
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
, and their descendants maintaining their customs. Between June 1949 and September 1950, the overwhelming majority of Yemen's Jewish population
immigrated
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not natives or where they do not possess citizenship in order to settle as permanent residents or naturalized citizens. Commuters, tourists, and ...
to Israel in
Operation Magic Carpet. After several waves of persecution throughout Yemen, the vast majority of
Yemenite Jews now live in Israel, while smaller communities live in the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
and elsewhere. Only a handful remain in Yemen. The few remaining Jews experience intense, and at times violent,
anti-Semitism
Antisemitism (also spelled anti-semitism or anti-Semitism) is hostility to, prejudice towards, or discrimination against Jews. A person who holds such positions is called an antisemite. Antisemitism is considered to be a form of racism.
Antis ...
on a daily basis.
Yemenite Jews have a unique religious tradition that distinguishes them from
Ashkenazi Jews
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
,
Sephardi Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
, and
other Jewish groups. They have been described as "the most Jewish of all Jews" and "the ones who have preserved the
Hebrew language
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
the best". Yemenite Jews fall within the "
Mizrahi" (eastern) category of Jews, though they differ from other Mizrahi Jews who have undergone a process of total or partial assimilation to
Sephardic liturgy and custom. While the Shami sub-group of Yemenite Jews did adopt a Sephardic-influenced rite, this was mostly due to it being forced upon them, and did not reflect a demographic or general cultural shift among the vast majority of Yemenite Jews.
Family pedigrees
Some Jewish families have preserved traditions relating to their tribal affiliation, based on partial genealogical records passed down generation after generation. In Yemen, for example, some Jews trace their lineage to Judah, others to Benjamin, while yet others to Levi and Reuben. Of particular interest is one distinguished Jewish family of Yemen who traced their lineage to Bani, one of the sons of Peretz, the son of Judah.
Early history
There are numerous accounts and traditions concerning the arrival of Jews in various regions in Southern Arabia. One tradition suggests that
King Solomon sent Jewish merchant marines to Yemen to prospect for gold and silver with which to adorn his
Temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called churches), Hinduism (whose temples ...
in
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
. In 1881, the French vice consulate in Yemen wrote to the leaders of the Alliance (the
Alliance Israelite Universelle
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
) in France, that he read in a book by the Arab historian
Abu-Alfada that the Jews of Yemen settled in the area in 1451 BCE. Another legend says that Yemeni tribes converted to
Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
after the
Queen of Sheba
The Queen of Sheba ( he, מַלְכַּת שְׁבָא, Malkaṯ Šəḇāʾ; ar, ملكة سبأ, Malikat Sabaʾ; gez, ንግሥተ ሳባ, Nəgśətä Saba) is a figure first mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. In the original story, she bring ...
's visit to King Solomon. The
Sanaite Jews have a tradition that their ancestors settled in Yemen forty-two years before the destruction of the
First Temple
Solomon's Temple, also known as the First Temple (, , ), was the Temple in Jerusalem between the 10th century BC and . According to the Hebrew Bible, it was commissioned by Solomon in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited by th ...
. It is said that under the prophet
Jeremiah
Jeremiah, Modern: , Tiberian: ; el, Ἰερεμίας, Ieremíās; meaning " Yah shall raise" (c. 650 – c. 570 BC), also called Jeremias or the "weeping prophet", was one of the major prophets of the Hebrew Bible. According to Jewi ...
some 75,000 Jews, including priests and
Levite
Levites (or Levi) (, he, ''Lǝvīyyīm'') are Jewish males who claim patrilineal descent from the Tribe of Levi. The Tribe of Levi descended from Levi, the third son of Jacob and Leah. The surname ''Halevi'', which consists of the Hebrew de ...
s, traveled to Yemen. Another legend states that when
Ezra
Ezra (; he, עֶזְרָא, '; fl. 480–440 BCE), also called Ezra the Scribe (, ') and Ezra the Priest in the Book of Ezra, was a Jewish scribe ('' sofer'') and priest (''kohen''). In Greco-Latin Ezra is called Esdras ( grc-gre, Ἔσδρα ...
commanded the Jews to return to
Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
they disobeyed, whereupon he pronounced a
ban upon them. According to this legend, as a punishment for this hasty action, Ezra was denied burial in
Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. As a result of this local tradition, which cannot be validated historically, it is said that no Jew of Yemen gives the name of Ezra to a child, although all other Biblical appellatives are used. The Yemenite Jews claim that Ezra cursed them to be a poor people for not heeding his call. This seems to have come true in the eyes of some Yemenites, as Yemen is extremely poor. However, some Yemenite sages in Israel today emphatically reject this story as myth, if not outright blasphemy.
Because of Yemenite Jewry's cultural affiliation with
Babylon, historian Yehuda Ratzaby opines that the Jews of Yemen migrated to Yemen from places in Babylonia. Archaeological records referring to Judaism in Yemen started to appear during the rule of the
Himyarite Kingdom
The Himyarite Kingdom ( ar, مملكة حِمْيَر, Mamlakat Ḥimyar, he, ממלכת חִמְיָר), or Himyar ( ar, حِمْيَر, ''Ḥimyar'', / 𐩹𐩧𐩺𐩵𐩬) (fl. 110 BCE–520s CE), historically referred to as the Homerit ...
, established in Yemen in 110 BCE. Various inscription in
Musnad script in the second century CE refer to constructions of synagogues approved by Himyarite Kings. In the aftermath of the
Bar-Kokhba revolt
The Bar Kokhba revolt ( he, , links=yes, ''Mereḏ Bar Kōḵḇāʾ''), or the 'Jewish Expedition' as the Romans named it ( la, Expeditio Judaica), was a rebellion by the Jews of the Roman province of Judea, led by Simon bar Kokhba, aga ...
, there was significant Jewish emigration from Judea to Yemen, which was then famous in the Greco-Roman world for its prosperous trade, particularly in spices. According to local legends, the kingdom's aristocracy converted to Judaism in the 6th century CE.
The Christian missionary,
Theophilos, who came to Yemen in the mid-fourth century, complained that he had found great numbers of Jews. By 380 CE, Himyarites religious practices had undergone fundamental changes. The inscriptions were no longer addressed to
El Maqah or
'Athtar, but to a single deity called
Rahman. Debate among scholars continues as to whether the Himyarite monotheism was influenced by Judaism or Christianity. Jews became especially numerous and powerful in the southern part of Arabia, a rich and fertile land of incense and spices and a way station on the routes to Africa, India, and East Asia. The Yemeni tribes did not oppose Jewish presence in their country. By 516, tribal unrest broke out, and several tribal elites fought for power. One of those elites was
Joseph Dhu Nuwas or "Yûsuf 'As'ar Yaṯ'ar" as mentioned in ancient south Arabian inscriptions.
[A. Jamme, W.F., ''Sabaean and Ḥasaean Inscriptions from Saudi Arabia'', Instituto di Studi del Vicino Oriente: Università di Roma, Rome 1966, p. 40] The actual story of Joseph is murky. Greek and Ethiopian accounts, portray him as a Jewish zealot.
Some scholars suggest that he was a converted Jew.
Nestorian
Nestorianism is a term used in Christian theology and Church history to refer to several mutually related but doctrinarily distinct sets of teachings. The first meaning of the term is related to the original teachings of Christian theologian ...
accounts claim that his mother was a Jew taken captive from
Nisibis
Nusaybin (; '; ar, نُصَيْبِيْن, translit=Nuṣaybīn; syr, ܢܨܝܒܝܢ, translit=Nṣībīn), historically known as Nisibis () or Nesbin, is a city in Mardin Province, Turkey. The population of the city is 83,832 as of 2009 and is ...
and bought by a king in Yemen, whose ancestors had formerly converted to Judaism. Syriac and Byzantine sources maintain that Yûsuf ’As’ar sought to convert other Yemeni Christians, but they refused to renounce Christianity. The actual picture, however, remains unclear.
Some scholars believe that Syriac sources reflected a great deal of hatred toward Jews. In 2009 a
BBC #REDIRECT BBC #REDIRECT BBC
Here i going to introduce about the best teacher of my life b BALAJI sir. He is the precious gift that I got befor 2yrs . How has helped and thought all the concept and made my success in the 10th board exam. ...
...
broadcast defended a claim that Yûsuf ’As’ar offered villagers the choice between conversion to Judaism or death and then massacred 20,000 Christians. The program's producers stated that, "The production team spoke to many historians over 18 months, among them
, who was our consultant, and Professor Abdul Rahman Al-Ansary
ormer_professor_of_archaeology_at_the_King_Saud_University_in_Riyadh.html" ;"title="King_Saud_University.html" ;"title="ormer professor of archaeology at the King Saud University">ormer professor of archaeology at the King Saud University in Riyadh">King_Saud_University.html" ;"title="ormer professor of archaeology at the King Saud University">ormer professor of archaeology at the King Saud University in Riyadh]."
Inscriptions attributed to Yûsuf ’As’ar himself show the great pride he expressed after killing more than 22,000 Christians in
Ẓafār and
Najran. According to Jamme,
Sabaean inscriptions reveal that the combined war booty (excluding deaths) from campaigns waged against the
Abyssinians in Ẓafār, the fighters in ’Ašʻarān, Rakbān, Farasān, Muḥwān (
Mocha), and the fighters and military units in Najran, amounted to 12,500 war trophies, 11,000 captives and 290,000 camels and bovines and sheep.
Historian
Glen Bowersock
Glen Warren Bowersock (born January 12, 1936 in Providence, Rhode Island) is a historian of ancient Greece, Rome and the Near East, and former Chairman of Harvard’s classics department.
Early life
Bowersock was born in Providence, Rhode Island a ...
described this as a "savage pogrom that the Jewish king of the Arabs launched against the Christians in the city of Najran. The king himself reported in excruciating detail to his Arab and Persian allies about the massacres he had inflicted on all Christians who refused to convert to Judaism." There were also reports of massacres and destruction of places of worship by Christians too.
Francis Edward Peters Francis Edward Peters, SJ (June 23, 1927 – April 30, 2020), who generally published as F. E. Peters, was Professor Emeritus of History, Religion and Middle Eastern and Islamic Studies at New York University (NYU). He died on April 30, 2020 in hosp ...
wrote that while there is no doubt that this was a religious persecution, it is equally clear that a political struggle was going on as well. It is likely that Dhu Nuwas was a leader of a liberation movement seeking to free Yemen from an increasing foreign meddling in the nation's affairs, and Judaism became a vital element in the resistance.
According to ‘Irfan Shahid's ''Martyrs of Najran – New Documents'', Dhu-Nuwas sent an army of some 120,000 soldiers to lay siege to the city of
Najran, which siege lasted for six months, and the city taken and burnt on the 15th day of the seventh month (i.e. the lunar month
Tishri
Tishrei () or Tishri (; he, ''tīšrē'' or ''tīšrī''; from Akkadian ''tašrītu'' "beginning", from ''šurrû'' "to begin") is the first month of the civil year (which starts on 1 Tishrei) and the seventh month of the ecclesiastical yea ...
). The city had revolted against the king and they refused to deliver it up unto the king. About three hundred of the city's inhabitants surrendered to the king's forces, under the assurances of an oath that no harm would come to them, and these were later bound, while those remaining in the city were burnt alive within their church. The death toll in this account is said to have reached about two thousand. However, in the Sabaean inscriptions describing these events, it is reported that by the month Dhu-Madra'an (between July and September) there were “1000 killed, 1500 prisoners
akenand 10,000 head of cattle.”

There are two dates mentioned in the “letter of Simeon of Beit Aršam.” One date indicates the letter was written in Tammuz in the year 830 of Alexander (518/519 CE), from the camp of GBALA (Jebala), king of the ‘SNYA (Ghassanids or the Ġassān clan). In it, he tells of the events that transpired in
Najran, while the other date puts the letter's composition in the year 835 of Alexander (523/524 CE). The second letter, however, is actually a Syriac copy of the original, copied in the year 1490 of the Seleucid Era (= 1178/79 CE). Today, it is largely agreed that the latter date is the accurate one, as it is confirmed by the Martyrium Arethae, as well as by epigraphic records, namely Sabaean inscriptions discovered in the Asir of Saudi-Arabia (Bi’r Ḥimâ), photographed by J. Ryckmans in Ry 507, 8 ~ 9, and by A. Jamme in Ja 1028, which give the old Sabaean year 633 for these operations (said to correspond with 523 CE).
Jacques Ryckmans, who deciphered these inscriptions, writes in his ''La Persécution des Chrétiens Himyarites'', that Sarah'il Yaqbul-Yaz'an was both the tribal chief and the lieutenant of Yûsuf ’As’ar (the king) at the time of the military campaign, and that he was sent out by the king to take the city of
Najran, while the king watched for a possible Abyssinian/Ethiopian incursion along the coastal plains of Yemen near
Mokhā (al-Moḫâ) and the strait known as Bāb al-Mandab. The Ethiopian church in
Ẓafâr, which had been built by the king of Yemen some years earlier, and another church built by him in Aden (see: ''Ecclesiastical History of Philostorgius'', Epitome of Book III, chapter 4), had been seen by
Constantius II
Constantius II (Latin: ''Flavius Julius Constantius''; grc-gre, Κωνστάντιος; 7 August 317 – 3 November 361) was Roman emperor from 337 to 361. His reign saw constant warfare on the borders against the Sasanian Empire and Germanic ...
during the embassage to the land of the Ḥimyarites (i.e. Yemen) in ''circa'' 340 CE. By the 6th-century CE, this church was set on fire and razed to the ground, and its Abyssinian inhabitants killed. Later, foreigners (presumably Christians) living in Haḏramawt were also put to death before the king's army advanced to Najran in the far north and took it.
Byzantine emperor
Justin I
Justin I ( la, Iustinus; grc-gre, Ἰουστῖνος, ''Ioustînos''; 450 – 1 August 527) was the Eastern Roman emperor from 518 to 527. Born to a peasant family, he rose through the ranks of the army to become commander of the imperial ...
sent a fleet to
Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
and
Joseph Dhu Nuwas was killed in battle in 525 CE. The persecutions ceased, and the western coasts of Yemen became a
tributary state
A tributary state is a term for a pre-modern state in a particular type of subordinate relationship to a more powerful state which involved the sending of a regular token of submission, or tribute, to the superior power (the suzerain). This to ...
until Himyarite nobility (also Jews) managed to regain power.
There are also several historical works which suggest that a Jewish kingdom existed in Yemen during pre-Islamic late antiquity. In Yemen, several inscriptions dating back to the 4th and 5th centuries CE have been found in
Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
and
Sabaean praising the ruling house in Jewish terms for "helping and empowering the
People of Israel". In
Bayt al-Ḥāḍir, a village east of
Sana'a
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Gover ...
, German specialist in
Semitic epigraphy,
Walter W. Müller Walter Wilhelm Müller (born 26 September 1933 in Weipert in the Ore Mountains) is a German specialist in the field of Ancient history of Yemen, ancient South Arabia and Semitic languages, Semitic epigraphy.
After studying Semitic and Arabic studie ...
, discovered in the village mosque an important Judeo-Ḥimyarite inscription showing a partial list of the
24-priestly wards described in ''IChronicles 24'', which said inscription happened to be engraved upon a column believed to have formerly belonged to a synagogue. Yet, even here, part of the inscription was embedded in the ground belonging to the mosque. The inscription is believed to date back to the 4th century CE, and attests to the antiquity of the Jews in that area. To that same period belongs another bilingual Sabaean-Hebrew inscription, which orientalist
Giovānnī Garbinī of Naples discovered in 1970. The inscription is found on a column in Bayt al-Ašwāl near
Ẓafār hofār(c. 17 km. from the town of Yarim) and shows, interposed on an earlier writing, the words, "The writing of Judah, of blessed memory, Amen shalom amen," engraved in antiquated Assyrian (Hebrew) script in between larger, sculpted
Sabaean script. The inscription is thought to date back to either the 4th or 5th-century CE.
Jewish–Muslim relations in Yemen


Middle Ages
As ''
Ahl al-Kitab
People of the Book or Ahl al-kitāb ( ar, أهل الكتاب) is an Islamic term referring to those religions which Muslims regard as having been guided by previous revelations, generally in the form of a scripture. In the Quran they are ident ...
'' (lit. "The People of the Scriptures"), Jews were assured freedom of religion only in exchange for payment of a poll-tax (
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
: ''
jizya''), imposed on certain non-Muslim monotheists (people of the Book). Feudal overlords imposed the annual poll-tax upon Jews, which, under Islamic law, was to ensure their status as protected persons of the state. This tax (tribute) was assessed against every male thirteen years and older, and its remittance varied between the wealthy and the poor. In the early 20th century, this amounted to one
Maria Theresa thaler (''riyal'') for a poor man, two thalers in specie for the middle classes, and four or more thalers for the rich. Upon payment, Jews were also exempt from paying the ''
zakat
Zakat ( ar, زكاة; , "that which purifies", also Zakat al-mal , "zakat on wealth", or Zakah) is a form of almsgiving, often collected by the Muslim Ummah. It is considered in Islam as a religious obligation, and by Quranic ranking, is ...
'' which must be paid by Muslims once their residual wealth reaches a certain threshold. Active
persecution of Jews
The persecution of Jews has been a major event in Jewish history, prompting shifting waves of refugees and the formation of diaspora communities. As early as 605 BCE, Jews who lived in the Neo-Babylonian Empire were persecuted and deported. ...
did not gain full force until the Zaydi clan seized power, from the more tolerant
Sunni Muslims, early in the 10th century. The legal status of Jews in Yemen started to deteriorate around the time the
Tahirids
The Tahirid dynasty ( fa, طاهریان, Tâheriyân, ) was a culturally Arabized Sunni Muslim dynasty of Persian dehqan origin, that ruled as governors of Khorasan from 821 to 873 as well as serving as military and security commanders in A ...
took Sana'a from Zaidis, mainly because of new discriminations established by the Muslim rulers. Such laws were not included in Zaidi legal writings till comparatively late with ''Kitab al-Azhar'' of
Imam al-Murtada in the first half of the 15th century. This also led to deterioration of economic and social situation of Jews.
[
Jewish intellectuals wrote in both Hebrew and Arabic and engaged in the same literary endeavours as the Muslim majority. According to a late 9th century document, the first Zaydi imam al-Hadi had imposed limitations and a special tax on land held by Jews and Christians of Najran. In the mid-11th century, Jews from a number of communities in Yemen highlands including ]Sana'a
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Gover ...
appear to have been attracted to Sulayhids' capital of Dhu Jibla. The city was founded by Abdullah bin Muhammad al-Sulaihi in the mid-11th century and according to ''Tarikh al-Yamman'' of the famed Yemenite author Umara al-Yamani (1121–74), was named after a Jewish pottery merchant.
During the 12th century, Aden was first ruled by Fatimids and then Ayyubids
The Ayyubid dynasty ( ar, الأيوبيون '; ) was the founding dynasty of the medieval Sultanate of Egypt established by Saladin in 1171, following his abolition of the Fatimid Caliphate of Egypt. A Sunni Muslim of Kurdish origin, Saladin ...
. The city formed a great emporium on the sea route to India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. Documents of the Cairo Geniza
The Cairo Geniza, alternatively spelled Genizah, is a collection of some 400,000 Jewish manuscript fragments and Fatimid administrative documents that were kept in the ''genizah'' or storeroom of the Ben Ezra Synagogue in Fustat or Old Cairo, ...
pertaining to Aden reflect a thriving Jewish community led by the prominent Bundar family. Abu Ali Hasan ibn Bundar ( Heb. Japheth) served as the head of the Jewish communities in Yemen as well as a representative of the merchants in Aden. His son Madmun was the central figure in Yemenite Jewry during the flourishing of trade with India. The Bundar family produced some celebrated '' negidim'' who exerted authorities over Jews of Yemen as well as Jewish merchants in India and Ceylon. The community developed communal and spiritual connection in addition to business and family ties with other Jewish communities in the Islamic world. They also developed ties with and funded Jewish centers and academies of Babylon, Palestine and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
. Due to the trade, Jews also emigrated to Aden for mercantile and personal reasons.
Yemenite Jews also experienced violent persecution at times. In the late 1160s, the Yemenite ruler 'Abd-al-Nabī ibn Mahdi gave Jews a choice of conversion to Islam or martyrdom
A martyr (, ''mártys'', "witness", or , ''marturia'', stem , ''martyr-'') is someone who suffers persecution and death for advocating, renouncing, or refusing to renounce or advocate, a religious belief or other cause as demanded by an externa ...
.[ Mahdi also imposed his beliefs upon the Muslims besides the Jews. This led to a revival of Jewish messianism, but also led to mass-conversion.]Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Tora ...
sent what is known by the name '' Iggeret Teman'' ("Epistle to Yemen"), requesting that they remain faithful to their religion, but if at all possible, not to cast affronts before their antagonists.[ Wikisource:Epistle to Yemen] The persecution ended in 1173 with the defeat of Ibn Mahdi and conquest of Yemen by Turan-Shah
Shams ad-Din Turanshah ibn Ayyub al-Malik al-Mu'azzam Shams ad-Dawla Fakhr ad-Din known simply as Turanshah ( ar, توران شاه بن أيوب) (died 27 June 1180) was the Ayyubid emir (prince) of Yemen (1174–1176), Damascus (1176–1179), ...
, the brother of Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
, and they were allowed to return to their faith.[ According to two Genizah documents, the Ayyubid ruler of Yemen, al-Malik al-Mu'izz al-Ismail (reigned 1197—1202) attempted to force the Jews of Aden to convert. The second document details the relief of Jewish community after his murder and those who had been forced to convert reverted to Judaism.
The rule of ]Shafi'i
The Shafii ( ar, شَافِعِي, translit=Shāfiʿī, also spelled Shafei) school, also known as Madhhab al-Shāfiʿī, is one of the four major traditional schools of religious law (madhhab) in the Sunnī branch of Islam. It was founded by ...
Rasulids
The Rasulids ( ar, بنو رسول, Banū Rasūl) were a Sunni Muslim dynasty who ruled Yemen from 1229 to 1454.
History
Origin of the Rasulids
The Rasulids took their name from al-Amin's nickname "Rasul". The Zaidi Shi'i Imams of Yemen were ...
which lasted from 1229 to 1474 brought stability to the region. During this period, Jews enjoyed social and economic prosperity. This changed with the rise of the Tahiri dynasty that ruled until the conquest by the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
of Yemen in 1517. A note written in a Jewish manuscript mentions the destruction of the old synagogue in Sana'a in 1457 under the rule of the dynasty's founder Ahmad 'Amir. An important note of the treatment of Jews by Tahirids is found in the colophon of a Jewish manuscript from Yemen in 1505, when the last Tahirid Sultan took Sana'a from the Zaydis. The document describes one kingdom as exploitive and the other as repressive.Messiah
In Abrahamic religions, a messiah or messias (; ,
; ,
; ) is a saviour or liberator of a group of people. The concepts of '' mashiach'', messianism, and of a Messianic Age originated in Judaism, and in the Hebrew Bible, in which a ''mashiach ...
claimant in Bayhan District, mentioned by Hayim bin Yahya Habhush in ''History of the Jews in Yemen'' written in 1893 and Ba'faqia al-Shihri's ''Chronicle'' written in the 16th century. The messiah was acknowledged as a political figure and gathered many people around him into what seemed to be an organized military force. The Tahirid Sultan Amir ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab attacked the messiah, killing many Jews and crushing the movement. He saw it as a violation of the protection agreement and liquidated the Jewish settlement in Hadhramaut
Hadhramaut ( ar, حَضْرَمَوْتُ \ حَضْرَمُوتُ, Ḥaḍramawt / Ḥaḍramūt; Hadramautic: 𐩢𐩳𐩧𐩣𐩩, ''Ḥḍrmt'') is a region in South Arabia, comprising eastern Yemen, parts of western Oman and southern Saud ...
as collective punishment. Presumably some of them were killed, many converted to Islam or migrated to Aden and the adjacent mainland of Yemen. It seems, however, the liquidation wasn't immediate. Jews of the place are recorded by 1527, but not by the 1660s. After the 15th century, Jewish communities only existed in Hadhramaut's western periphery. The oppression at the hands of pious Muslim rulers and endangerment of the community because of the plots of a few Jewish messianists, are common themes in the history of Yemenite Jews.[ The Ottoman conquest allowed Yemenite Jews a chance to have contact with other Jewish communities; contact was established with the ]Kabbalists
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "receiver"). The def ...
in Safed, a major Jewish center, as well as with Jewish communities throughout the Ottoman Empire.[
]
Maimonides
Moses Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Torah s ...
(1138–1204), the 12th-century philosopher, scholar and codifier of Jewish law, was greatly endeared by the Jews of Yemen for his having intervened on their behalf during a time of religious persecution, heresy
Heresy is any belief or theory that is strongly at variance with established beliefs or customs, in particular the accepted beliefs of a church or religious organization. The term is usually used in reference to violations of important religi ...
and heavy taxes levied on the community. When the writings of Maimonides reached the heads of the community, they continued to address their questions unto him and sent emissaries to purchase several copies of his books, just as he, himself, acknowledged. In all the subjects of the Torah, Yemenite Jews customarily base their rule of practice (halakhah) on Maimonides' teachings, and will instruct in accordance with his view, whether in lenient rulings or in strict rulings, even where most other halakhic authorities disagree.Yosef Qafih
Yosef Qafiḥ ( he, יוסף קאפח , ), widely known as Rabbi Yosef Kapach (27 November 1917 – 21 July 2000), was a Yemenite-Israeli authority on Jewish religious law (''halakha''), a dayan of the Supreme Rabbinical Court in Israel, and o ...
.
Early modern period
The Zaydi
Zaydism (''h'') is a unique branch of Shia Islam that emerged in the eighth century following Zayd ibn Ali‘s unsuccessful rebellion against the Umayyad Caliphate. In contrast to other Shia Muslims of Twelver Shi'ism and Isma'ilism, Zaydis, ...
enforced a statute known as the Orphan's Decree, anchored in their own 18th-century legal interpretations and enforced at the end of that century. It obligated the Zaydi state to take under its protection and to educate in Islamic ways any dhimmi (i.e. non-Muslim) child whose parents had died when he was a minor. The Orphan's Decree was ignored during the Ottoman rule (1872–1918), but was renewed during the period of Imam Yahya
, succession1 = King of Yemen
, succession2 = Imam of Yemen
, image = Imam yahya cropped.png
, image_size =
, caption = Portrait of Yahya by Ameen Rihani, 1922. Imam Yahya steadfastly refused to be photographed thro ...
(1918–1948).
Under the Zaydi rule, the Jews were considered to be impure and therefore forbidden to touch a Muslim or a Muslim's food. They were obligated to humble themselves before a Muslim, to walk to the left side, and greet him first. They could not build houses higher than a Muslim's or ride a camel or horse, and when riding on a mule or a donkey, they had to sit sideways. Upon entering the Muslim quarter a Jew had to take off his foot-gear and walk barefoot. If attacked with stones or fists by youth, a Jew was not allowed to fight them. In such situations, he had the option of fleeing or seeking intervention by a merciful Muslim passerby.
 Ottoman rule ended in 1630, when the Zaydis took over Yemen. Jews were once again persecuted. In 1679, under the rule of Al-Mahdi Ahmad, Jews were expelled ''en masse'' from all parts of Yemen to the distant province of Mawza, and many Jews died there of starvation and disease as consequence. As many as two-thirds of the exiled Jews did not survive. Their houses and property were seized, and many synagogues were destroyed or converted into mosques. This event was later known as the
Ottoman rule ended in 1630, when the Zaydis took over Yemen. Jews were once again persecuted. In 1679, under the rule of Al-Mahdi Ahmad, Jews were expelled ''en masse'' from all parts of Yemen to the distant province of Mawza, and many Jews died there of starvation and disease as consequence. As many as two-thirds of the exiled Jews did not survive. Their houses and property were seized, and many synagogues were destroyed or converted into mosques. This event was later known as the Mawza exile
The Exile of Mawzaʻ (the expulsion of Yemenite Jews to Mawza') he, גלות מוזע, ; 1679–1680, is considered the single most traumatic event experienced collectively by the Jews of Yemen, in which Jews living in nearly all cities a ...
, and it is recalled in many writings of the Yemenite Jewish rabbi and poet Shalom Shabazi
Rabbi Shalom ben Yosef ben Avigad Shabazi of the family of Mashtā (1619 – c. 1720), also Abba Sholem Shabazi or Saalem al-Shabazi ( he, שלום שבזי; ar, سالم الشبزي), was a Jewish poet who lived in 17th century Yemen. He i ...
, who experienced it himself. About a year after the expulsion, the survivors were allowed to return for economic reasons; Jews were the majority of craftsmen and artisans, and thus a vital asset in the country's economy. However, they were not allowed to return to their former homes, and found that most of their religious articles had been destroyed. They were instead resettled in special Jewish quarters outside the cities.Al-Mansur
Abū Jaʿfar ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad al-Manṣūr (; ar, أبو جعفر عبد الله بن محمد المنصور; 95 AH – 158 AH/714 CE – 6 October 775 CE) usually known simply as by his laqab Al-Manṣūr (المنصور) w ...
. The community flourished under him because of the part it played in trade with India through Mocha. The German researcher Carsten Niebuhr
Carsten Niebuhr, or Karsten Niebuhr (17 March 1733 Lüdingworth – 26 April 1815 Meldorf, Dithmarschen), was a German mathematician, cartographer, and explorer in the service of Denmark. He is renowned for his participation in the Royal Danish ...
who visited Yemen in 1763, reports that two years before he arrived, Shalom 'Iraqi had been imprisoned and fined while twelve out of fourteen synagogues in a village near Sana'a were shut down. 'Iraqi was released two weeks before his arrival. Jewish sources attribute this to a regime change. The Imam Al-Mahdi Abbas Al-Mahdi Abbas (1719 – 4 September 1775) was an Imam of Yemen who ruled in 1748–1775. He belonged to the Qasimid family, descended from the Islamic prophet Muhammad, which dominated the Zaidiyyah, Zaidi imamate of Yemen in 1597–1962.
Ascensio ...
was extremely religious and his ideological affinity with the clerics created an atmosphere of extreme repression. He however resisted their pressure on him to expel the Jews. The synagogues were reopened by Ali al-Mansur after payment of a heavy fee.
During the 18th century, Yemenite Jews gained a brief respite from their status as second-class citizens when the Imamics came to power. Yemen experienced a resurgence of Jewish life. Synagogues were rebuilt, and some Jews achieved high office. One of them was Rabbi Shalom ben Aharon, who became responsible for minting and for the royal coffers. When the Imamics lost power in the 19th century, Jews were again subjected to persecution. In 1872, the Ottoman Empire again took over, and Ottoman rule would last until Yemeni independence in 1918. Jewish life again improved during Ottoman rule; Jewish freedom of religion was more widely respected, and Yemenite Jews were permitted to have more contact with other Jewish communities.[
]
Chronology of events
Places of Settlement in Yemen
 At the beginning of the nineteenth-century, Yemenite Jews lived principally in
At the beginning of the nineteenth-century, Yemenite Jews lived principally in Sana'a
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Gover ...
(7,000 +), with the largest Jewish population and twenty-eight synagogues, followed by Rada'a, with the second largest Jewish population and nine synagogues, Sa'dah
Saada ( ar, صَعْدَة, translit=Ṣaʿda), a city and ancient capital in the northwest of Yemen, is the capital and largest city of the province of the same name, and the county seat of the county of the same name. The city is located in the ...
(1,000), Dhamar (1,000), Aden (200), the desert of Beda (2,000), Manakhah (3,000), among others. Almost all resided in the interior of the plateau. Carl Rathjens who visited Yemen in the years 1927 and 1931 puts the total number of Jewish communities in Yemen at 371 settlements. Other significant Jewish communities in Yemen were based in the south central highlands in the cities of: Taiz
Taiz ( ar, تَعِزّ, Taʿizz) is a city in southwestern Yemen. It is located in the Yemeni Highlands, near the port city of Mocha on the Red Sea, at an elevation of about above sea level. It is the capital of Taiz Governorate. With a popula ...
(the birthplace of one of the most famous Yemenite Jewish spiritual leaders, ''Mori'' Salem Al-Shabazzi Mashta), Ba'dan, and other cities and towns in the Shar'ab region. Many other Jewish communities in Yemen were long since abandoned by their Jewish inhabitants. Yemenite Jews were chiefly artisans, including gold-, silver- and blacksmiths in the San'a area, and coffee merchants in the south central highland areas.
19th-century Yemenite messianic movements
 During this period messianic expectations were very intense among the Jews of Yemen (and among many Arabs as well). The three pseudo-messiahs of this period, and their years of activity, are:
* Shukr Kuhayl I (1861–65)
*
During this period messianic expectations were very intense among the Jews of Yemen (and among many Arabs as well). The three pseudo-messiahs of this period, and their years of activity, are:
* Shukr Kuhayl I (1861–65)
* Shukr Kuhayl II
Judah ben Shalom (died ca. 1878) (Hebrew: יהודה בן שלום), also known as Mori (Master) Shooker Kohail II or Shukr Kuhayl II (Hebrew: מרי שכר כחיל), was a Yemenite messianic claimant of the mid-19th century.
The rise of Shuk ...
(1868–75)
* Joseph Abdallah (1888–93)
According to the Jewish traveler Jacob Saphir
Jacob Saphir ( he, יעקב הלוי ספיר; 1822–1886) was a 19th-century writer, ethnographer, researcher of Hebrew manuscripts, a traveler and emissary of the rabbis of Eastern European Jewish descent who settled in Jerusalem during hi ...
, the majority of Yemenite Jews during his visit of 1862 entertained a belief in the messianic proclamations of Shukr Kuhayl I. Earlier Yemenite messiah claimants included the anonymous 12th-century messiah who was the subject of Maimonides' famous Iggeret Teman, or ''Epistle to Yemen'',
Religious traditions
 Yemenite Jews and the Aramaic speaking
Yemenite Jews and the Aramaic speaking Kurdish Jews
, image = File:RABBI MOSHE GABAIL.jpg
, caption = Rabbi Moshe Gabai, head of the Jewish community of Zakho, with Israeli President Yitzhak Ben-Zvi in 1951
, pop = 200,000–300,000
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
are the only communities who maintain the tradition of reading the Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the ...
in the synagogue in both Hebrew and the Aramaic Targum
A targum ( arc, תרגום 'interpretation, translation, version') was an originally spoken translation of the Hebrew Bible (also called the ''Tanakh'') that a professional translator ( ''mǝturgǝmān'') would give in the common language of the ...
("translation"). Most non-Yemenite synagogues have a specified person called a Baal Koreh, who reads from the Torah scroll when congregants are called to the Torah scroll for an aliyah. In the Yemenite tradition, each person called to the Torah scroll
A ( he, סֵפֶר תּוֹרָה; "Book of Torah"; plural: ) or Torah scroll is a handwritten copy of the Torah, meaning the five books of Moses (the first books of the Hebrew Bible). The Torah scroll is mainly used in the ritual of Tor ...
for an aliyah reads for himself. Children under the age of Bar Mitzvah are often given the sixth aliyah. Each verse of the Torah read in Hebrew is followed by the Aramaic translation, usually chanted by a child. Both the sixth aliyah and the Targum have a simplified melody, distinct from the general Torah melody used for the other aliyot.
Like most other Jewish communities, Yemenite Jews chant different melodies for Torah, Prophets (Haftara), Megillat Aicha (Book of Lamentations
The Book of Lamentations ( he, אֵיכָה, , from its incipit meaning "how") is a collection of poetic laments for the destruction of Jerusalem in 586 BCE. In the Hebrew Bible it appears in the Ketuvim ("Writings") as one of the Five Megill ...
), Kohelet (Ecclesiastes, read during Sukkot), and Megillat Esther
Esther is the eponymous heroine of the Book of Esther. In the Achaemenid Empire, the Persian king Ahasuerus seeks a new wife after his queen, Vashti, is deposed for disobeying him. Hadassah, a Jewess who goes by the name of Esther, is chosen ...
(the Scroll of Esther read on Purim
Purim (; , ; see Name below) is a Jewish holiday which commemorates the saving of the Jewish people from Haman, an official of the Achaemenid Empire who was planning to have all of Persia's Jewish subjects killed, as recounted in the Book ...
). Unlike Ashkenazic
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
communities, there are melodies for Mishle (Proverbs) and Psalms
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived ...
.
 In larger Jewish communities, such as
In larger Jewish communities, such as Sana'a
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Gover ...
and Sad'a, boys were sent to the ''melamed'' at the age of three to begin their religious learning. They attended the ''melamed'' from early dawn to sunset on Sunday through Thursday and until noon on Friday. Jewish women were required to have a thorough knowledge of the laws pertaining to Kashrut and Taharat Mishpachah (family purity) i.e. Niddah
Niddah (or nidah; he, נִדָּה), in traditional Judaism, describes a woman who has experienced a uterine discharge of blood (most commonly during menstruation), or a woman who has menstruated and not yet completed the associated requirem ...
. Some women even mastered the laws of Shechita
In Judaism, ''shechita'' (anglicized: ; he, ; ; also transliterated ''shehitah, shechitah, shehita'') is slaughtering of certain mammals and birds for food according to ''kashrut''.
Sources
states that sheep and cattle should be slaughtere ...
, thereby acting as ritual slaughterers.
People also sat on the floors of synagogues instead of sitting on chairs, similar to the way many other non-Ashkenazi Jews sat in synagogues. This is in accordance with what Rambam (Maimonides) wrote in his Mishneh Torah
The ''Mishneh Torah'' ( he, מִשְׁנֵה תּוֹרָה, , repetition of the Torah), also known as ''Sefer Yad ha-Hazaka'' ( he, ספר יד החזקה, , book of the strong hand, label=none), is a code of Rabbinic Jewish religious law ('' ...
:
 The lack of chairs may also have been to provide more space for
The lack of chairs may also have been to provide more space for prostration
Prostration is the gesture of placing one's body in a reverentially or submissively prone position. Typically prostration is distinguished from the lesser acts of bowing or kneeling by involving a part of the body above the knee, especiall ...
, another ancient Jewish observance that the Jews of Yemen continued to practise until very recent times.Tachanun
''Tachanun'' or ''Taḥanun'' ( he, תחנון "Supplication"), also called ''nefilat apayim'' ( he, נפילת אפיים "falling on the face"), is part of Judaism's morning (''Shacharit'') and afternoon (''Mincha'') services, after the recitati ...
(Supplication), though such individuals usually do so in privacy. In the small Jewish community that exists today in Bet Harash, prostration is still done during the tachanun prayer. Jews of European origin generally prostrate only during certain portions of special prayers during Rosh Hashanah (Jewish New Year) and Yom Kippur
Yom Kippur (; he, יוֹם כִּפּוּר, , , ) is the holiest day in Judaism and Samaritanism. It occurs annually on the 10th of Tishrei, the first month of the Hebrew calendar. Primarily centered on atonement and repentance, the day' ...
(Day of Atonement). Prostration was a common practise amongst all Jews until some point during the late Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
or Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history
The history of Europe is traditionally divided into four time periods: prehistoric Europe (prior to about 800 BC), classical antiquity (800 BC to AD ...
period.
Like Yemenite Jewish homes, the synagogues in Yemen had to be lower in height than the lowest mosque in the area. In order to accommodate this, synagogues were built into the ground to give them more space without looking large from the outside. In some parts of Yemen, minyanim
In Judaism, a ''minyan'' ( he, מניין \ מִנְיָן ''mīnyān'' , lit. (noun) ''count, number''; pl. ''mīnyānīm'' ) is the quorum of ten Jewish adults required for certain religious obligations. In more traditional streams of Jud ...
would often just meet in homes of Jews, instead of the community having a separate building for a synagogue. Beauty and artwork were saved for the ritual objects in the synagogue and in the home.
Yemenite Jews also wore a distinctive tallit
A tallit ''talit'' in Modern Hebrew; ''tālēt'' in Sephardic Hebrew and Ladino; ''tallis'' in Ashkenazic Hebrew and Yiddish. Mish. pl. טליות ''telayot''; Heb. pl. טליתות ''tallitot'' , Yidd. pl. טליתים ''talleisim''. is a f ...
often found to this day. The Yemenite tallit features a wide ''atara'' and large corner patches, embellished with silver or gold thread, and the fringes along the sides of the tallit are netted. According to the Baladi custom, the tzitzit
''Tzitzit'' ( he, ''ṣīṣīṯ'', ; plural ''ṣīṣiyyōṯ'', Ashkenazi: '; and Samaritan: ') are specially knotted ritual fringes, or tassels, worn in antiquity by Israelites and today by observant Jews and Samaritans. are usuall ...
are tied with seven ''chulyot'' (hitches), based on Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Tora ...
' teaching.
On Sabbath days, the traditional Yemenite bread was not the ''Challah
Challah (, he, חַלָּה or ; plural: or ) is a special bread of Ashkenazi Jewish origin, usually braided and typically eaten on ceremonial occasions such as Shabbat and major Jewish holidays (other than Passover). Ritually acceptable ch ...
'', as found in Western Jewish communities, but the ''Kubaneh
Kubaneh ( he, כֻּבַּאנֶה) is a traditional Yemenite Jewish bread that is popular in Israel. Kubaneh is traditionally baked overnight to be served for Shabbat morning accompanied by haminados (eggs that are baked in their shells along wit ...
'', which was eaten on Sabbath mornings after first making the blessing over two flatbreads
A flatbread is a bread made with flour; water, milk, yogurt, or other liquid; and salt, and then thoroughly rolled into flattened dough. Many flatbreads are unleavened, although some are leavened, such as pizza and pita bread.
Flatbreads ...
baked in an earthen oven
The primitive clay oven, or earthen oven / cob oven, has been used since ancient times by diverse cultures and societies, primarily for, but not exclusive to, baking before the invention of cast-iron stoves, and gas and electric ovens. The genera ...
.
Weddings and marriage traditions
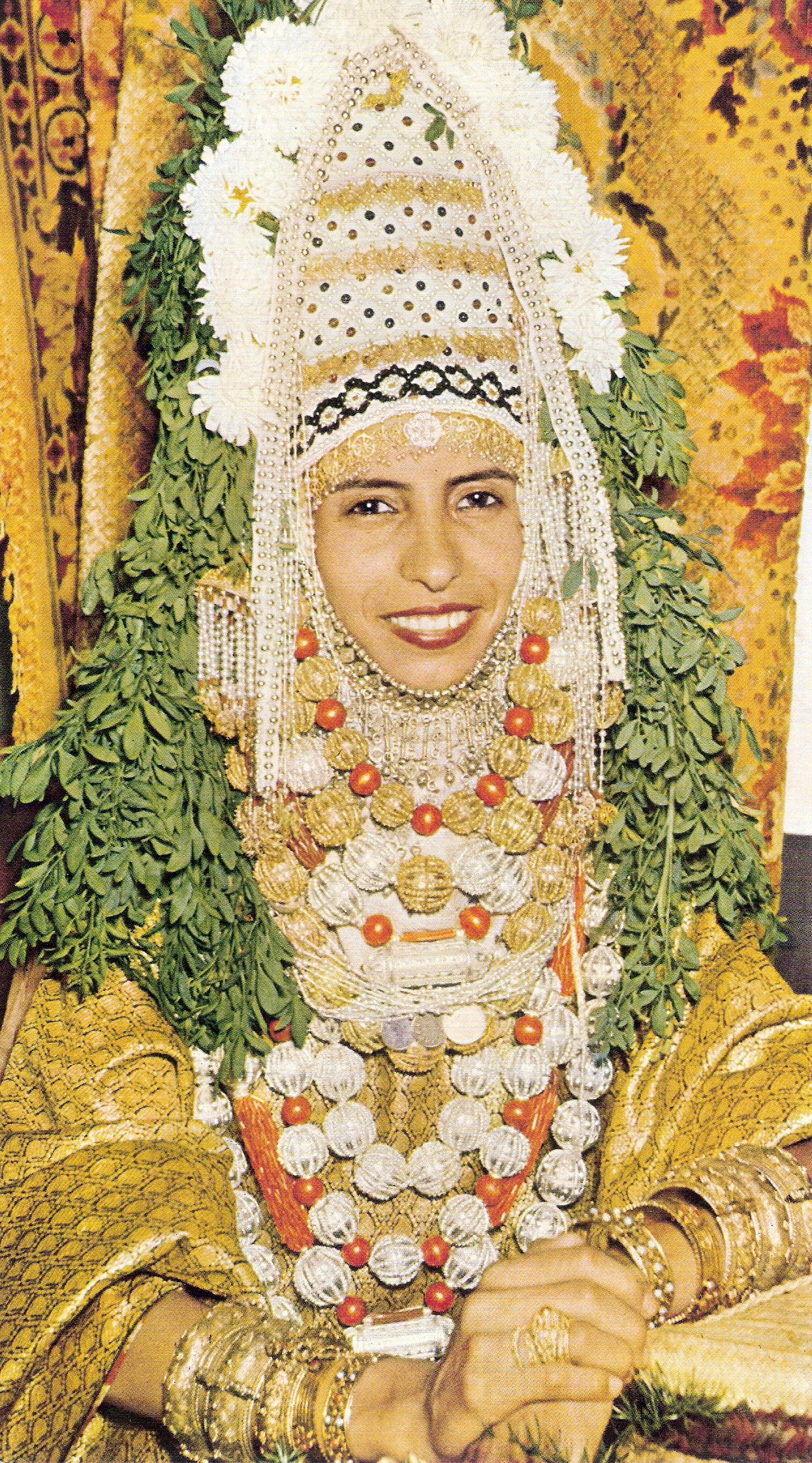 During a Yemenite Jewish wedding, the bride was bedecked with jewelry and wore a traditional wedding costume, including an elaborate headdress decorated with flowers and rue leaves, which were believed to ward off evil. Gold threads were woven into the fabric of her clothing. Songs were sung as part of a seven-day wedding celebration, with lyrics about friendship and love in alternating verses of Hebrew and Arabic.
In Yemen, the Jewish practice was not for the groom and his bride to be secluded in a canopy (''chuppah'') hung on four poles, as is widely practiced today in Jewish weddings, but rather in a bridal chamber that was, in effect, a highly decorated room in the house of the groom. This room was traditionally decorated with large hanging sheets of colored, patterned cloth, replete with wall cushions and short-length mattresses for reclining. Their marriage is consummated when they have been left together alone in this room. This ancient practice finds expression in the writings of Isaac ben Abba Mari (c. 1122 – c. 1193), author of ''Sefer ha-'Ittur'', concerning the Benediction of the Bridegroom: "Now the ''chuppah'' is when her father delivers her unto her husband, bringing her into that house wherein is some new innovation, such as the sheets… surrounding the walls, etc. For we recite in the Jerusalem Talmud, ''Sotah'' 46a (''Sotah'' 9:15), 'Those bridal chambers, (''chuppoth hathanim''), they hang within them patterned sheets and gold-embroidered ribbons,' etc."
During a Yemenite Jewish wedding, the bride was bedecked with jewelry and wore a traditional wedding costume, including an elaborate headdress decorated with flowers and rue leaves, which were believed to ward off evil. Gold threads were woven into the fabric of her clothing. Songs were sung as part of a seven-day wedding celebration, with lyrics about friendship and love in alternating verses of Hebrew and Arabic.
In Yemen, the Jewish practice was not for the groom and his bride to be secluded in a canopy (''chuppah'') hung on four poles, as is widely practiced today in Jewish weddings, but rather in a bridal chamber that was, in effect, a highly decorated room in the house of the groom. This room was traditionally decorated with large hanging sheets of colored, patterned cloth, replete with wall cushions and short-length mattresses for reclining. Their marriage is consummated when they have been left together alone in this room. This ancient practice finds expression in the writings of Isaac ben Abba Mari (c. 1122 – c. 1193), author of ''Sefer ha-'Ittur'', concerning the Benediction of the Bridegroom: "Now the ''chuppah'' is when her father delivers her unto her husband, bringing her into that house wherein is some new innovation, such as the sheets… surrounding the walls, etc. For we recite in the Jerusalem Talmud, ''Sotah'' 46a (''Sotah'' 9:15), 'Those bridal chambers, (''chuppoth hathanim''), they hang within them patterned sheets and gold-embroidered ribbons,' etc."
 After immigration to Israel, the regional varieties of Yemenite bridal jewelry were replaced by a uniform item that became identified with the community: the splendid bridal garb of Sana'a.
Before the wedding, Yemenite and other Eastern Jewish communities perform the henna ceremony, an ancient ritual with
After immigration to Israel, the regional varieties of Yemenite bridal jewelry were replaced by a uniform item that became identified with the community: the splendid bridal garb of Sana'a.
Before the wedding, Yemenite and other Eastern Jewish communities perform the henna ceremony, an ancient ritual with Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second prin ...
origins. The family of the bride mixes a paste derived from the henna plant that is placed on the palms of the bride and groom, and their guests. After the paste is washed off, a deep orange stain remains that gradually fades over the next week.
Yemenites had a special affinity for Henna due to biblical and Talmudic references. Henna, in the Bible, is Camphire, and is mentioned in the Song of Solomon, as well as in the Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law ('' halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the ce ...
. This tradition is also practiced by Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
and Afghan Jews.
:''"My Beloved is unto me as a cluster of Camphire in the vineyards of En-Gedi"'' Song of Solomon, 1:14
A Yemenite Jewish wedding custom specific only to the community of Aden is the Talbis, revolving around the groom. A number of special songs are sung by the men while holding candles, and the groom is dressed in a golden garment.
Religious groups
 The three main groups of Yemenite Jews are the Baladi, Shami, and the Maimonideans or "Rambamists". In addition, the "Rechabites" are a tribe in Sana'a claiming to be descendants of
The three main groups of Yemenite Jews are the Baladi, Shami, and the Maimonideans or "Rambamists". In addition, the "Rechabites" are a tribe in Sana'a claiming to be descendants of Jehonadab
Jehonadab ( he, יְהוֹנָדָב; meaning ''Jehovah is willing''; Latin: Jonadab) was the son of Rechab. He is mentioned in 2 Kings 10:15-31. A Kenite, he was a supporter of Jehu, son of Nimshi, in the elimination of the house of Ahab and in s ...
that was found in 1839 by Reverend Joseph Wolff
Joseph Wolff (1795 – 2 May 1862) was a Jewish Christian missionary born in Weilersbach, near Bamberg, Germany, named Wolff after his paternal grandfather. He travelled widely, and was known as "the missionary to the world". He published sev ...
, who later went to Bukhara to attempt to save Lieutenant Colonel Charles Stoddart and Captain Arthur Conolly
Arthur Conolly (2 July 1807, London – 17 June 1842, Bukhara) was a British intelligence officer, explorer and writer. He was a captain of the 6th Bengal Light Cavalry in the service of the British East India Company. He participated in many r ...
.
The differences between these groups largely concern the respective influence of the original Yemenite tradition, which was largely based on the works of Maimonides, and on the Kabbalistic tradition embodied in the Zohar and in the school of Isaac Luria
Isaac ben Solomon Luria Ashkenazi (1534 Fine 2003, p24/ref> – July 25, 1572) ( he, יִצְחָק בן שלמה לוּרְיָא אשכנזי ''Yitzhak Ben Sh'lomo Lurya Ashkenazi''), commonly known in Jewish religious circles as "Ha'ARI" (mea ...
, which was increasingly influential from the 17th century on.
* The Baladi
Baladi ( ar, بلدي ' relative-adjective 'of town', 'local', 'rural', comparable to English ''folk'', with a lower-class connotation) can refer to an Egyptian musical style, the folk style of Egyptian bellydance (Raqs Baladi), or the Masmou ...
Jews (from Arabic ''balad'', country) generally follow the legal rulings of the ''Rambam'' (Maimonides) as codified in his work the ''Mishneh Torah
The ''Mishneh Torah'' ( he, מִשְׁנֵה תּוֹרָה, , repetition of the Torah), also known as ''Sefer Yad ha-Hazaka'' ( he, ספר יד החזקה, , book of the strong hand, label=none), is a code of Rabbinic Jewish religious law ('' ...
''. Their liturgy was developed by a rabbi known as the Maharitz (''Moreinu Ha-Rav Yiḥya Tzalaḥ''), in an attempt to break the deadlock between the pre-existing followers of Maimonides and the new followers of the mystic, Isaac Luria. It substantially follows the older Yemenite tradition, with only a few concessions to the usages of the Ari. A Baladi Jew may or may not accept the Kabbalah theologically: if he does, he regards himself as following Luria's own advice that every Jew should follow his ancestral tradition.
* The Shami Jews (from Arabic ''ash-Sham'', the north, referring to Greater Syria including Israel) represent those who accepted the Sephardic/Mizrahi rite and lines of rabbinic authority, after being exposed to new inexpensive, typeset siddurs (prayer books) brought from Israel and the Sephardic diaspora by envoys and merchants in the late 17th century and 18th century.Shulchan Aruch
The ''Shulchan Aruch'' ( he, שֻׁלְחָן עָרוּך , literally: "Set Table"), sometimes dubbed in English as the Code of Jewish Law, is the most widely consulted of the various legal codes in Judaism. It was authored in Safed (today in I ...
(Code of Jewish Law). In their interpretation of Jewish law, Shami Yemenite Jews were strongly influenced by Syrian Sephardi Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
, though on some issues, they rejected the later European codes of Jewish law, and instead followed the earlier decisions of Maimonides. Most Yemenite Jews living today follow the Shami customs. The Shami rite was always more prevalent, even 50 years ago.
* The "Rambamists" are followers of, or to some extent influenced by, the Dor Daim
The Dardaim or Dor Daim ( he, דרדעים), are adherents of the Dor Deah movement in Orthodox Judaism . (; Hebrew: "generation of knowledge", an allusion to the Israelites who witnessed the Exodus.) That movement took its name in 1912 in Yemen ...
movement, and are strict followers of Talmudic law as compiled by Maimonides, aka "Rambam". They are regarded as a subdivision of the Baladi Jews, and claim to preserve the Baladi tradition in its pure form. They generally reject the Zohar and Lurianic Kabbalah
Lurianic Kabbalah is a school of kabbalah named after Isaac Luria (1534–1572), the Jewish rabbi who developed it. Lurianic Kabbalah gave a seminal new account of Kabbalistic thought that its followers synthesised with, and read into, the earlie ...
altogether. Many of them object to terms like "Rambamist". In their eyes, they are simply following the most ancient preservation of Torah, which (according to their research) was recorded in the Mishneh Torah.
School reform dispute (Dor Daim vs Iqshim)
 Towards the end of the 19th century, new ideas began to reach Yemenite Jews from abroad. Hebrew newspapers began to arrive, and relations developed with Sephardic Jews, who came to Yemen from various Ottoman provinces to trade with the army and government officials.
Two Jewish travelers,
Towards the end of the 19th century, new ideas began to reach Yemenite Jews from abroad. Hebrew newspapers began to arrive, and relations developed with Sephardic Jews, who came to Yemen from various Ottoman provinces to trade with the army and government officials.
Two Jewish travelers, Joseph Halévy __NOTOC__
Joseph Halévy (15 December 1827, in Adrianople – 21 January 1917, in Paris) was an Ottoman born Jewish-French Orientalist and traveller.
His most notable work was done in Yemen, which he crossed during 1869 to 1870 in search of Saba ...
, a French-trained Jewish Orientalist, and Eduard Glaser, an Austrian-Jewish astronomer and Arabist, in particular had a strong influence on a group of young Yemenite Jews, the most outstanding of whom was Rabbi Yiḥyah Qafiḥ. As a result of his contact with Halévy and Glaser, Qafiḥ introduced modern content into the educational system. Qafiḥ opened a new school and, in addition to traditional subjects, introduced arithmetic, Hebrew and Arabic, with the grammar of both languages. The curriculum also included subjects such as natural science, history, geography, astronomy, sports and Turkish.[''The Jews of the Middle East and North Africa in Modern Times'', by Reeva Spector Simon, Michael Menachem Laskier, Sara Reguer editors, Columbia University Press, 2003, pages 403–404]
The Dor Daim and Iqshim dispute about the Zohar literature broke out in 1912, inflamed Sana'a
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Gover ...
's Jewish community, and split it into two rival groups that maintained separate communal institutions until the late 1940s. Rabbi Qafiḥ and his friends were the leaders of a group of Maimonideans called Dor Daim
The Dardaim or Dor Daim ( he, דרדעים), are adherents of the Dor Deah movement in Orthodox Judaism . (; Hebrew: "generation of knowledge", an allusion to the Israelites who witnessed the Exodus.) That movement took its name in 1912 in Yemen ...
(the "generation of knowledge"). Their goal was to bring Yemenite Jews back to the original Maimonidean method of understanding Judaism that existed in pre-17th-century Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
.
Similar to certain Spanish and Portuguese Jews
Spanish and Portuguese Jews, also called Western Sephardim, Iberian Jews, or Peninsular Jews, are a distinctive sub-group of Sephardic Jews who are largely descended from Jews who lived as New Christians in the Iberian Peninsula during the ...
(Western Sephardi Jews
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
), the Dor Daim
The Dardaim or Dor Daim ( he, דרדעים), are adherents of the Dor Deah movement in Orthodox Judaism . (; Hebrew: "generation of knowledge", an allusion to the Israelites who witnessed the Exodus.) That movement took its name in 1912 in Yemen ...
rejected the Zohar, a book of esoteric mysticism. They felt that the Kabbalah
Kabbalah ( he, קַבָּלָה ''Qabbālā'', literally "reception, tradition") is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal ( ''Məqūbbāl'' "receiver"). The defin ...
which was based on the Zohar was irrational, alien, and inconsistent with the true reasonable nature of Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in t ...
. In 1913, when it seemed that Rabbi Qafiḥ, then headmaster of the new Jewish school and working closely with the Ottoman authorities, enjoyed sufficient political support, the Dor Daim made its views public, and tried to convince the entire community to accept them. Many of the non-Dor Deah elements of the community rejected the Dor Deah concepts. The opposition, the Iqshim, headed by Rabbi Yiḥya Yiṣḥaq, the Hakham Bashi
''Haham Bashi'' (chachampasēs) which is explained as "μεγάλος ραβίνος" or "Grand Rabbi".
* Persian: khākhāmbāšīgarī is used in the Persian version of the Ottoman Constitution of 1876. Strauss stated that there was a possibil ...
, refused to deviate from the accepted customs and from the study of the Zohar. One of the Iqshim's targets in the fight against Rabbi Qafiḥ was his modern Turkish-Jewish school.
Education
Education of children was of paramount importance to Jewish fathers in Yemen, who, as a rule, sent their children from an early age to study the portions of the Torah
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the ...
, usually under the tutelage of a local teacher. Often, such teachings were conducted in the home of their teacher. It was not uncommon for the teacher to be occupied in his trade (coat maker, weaver, etc.) while instructing his students. All instruction consisted of the recital and memorization of sacred texts. The most astute of these students, when they came of age, pursued after a higher Jewish education and which almost always entailed studying ''Shechita
In Judaism, ''shechita'' (anglicized: ; he, ; ; also transliterated ''shehitah, shechitah, shehita'') is slaughtering of certain mammals and birds for food according to ''kashrut''.
Sources
states that sheep and cattle should be slaughtere ...
'' (ritual slaughter), and receiving a license () from a qualified instructor to slaughter domestic livestock.
Baladi-rite and Shami-rite prayer books
* ''Siaḥ Yerushalayim'', ''Baladi'' prayer book in 4 vols, ed. Yosef Qafih
Yosef Qafiḥ ( he, יוסף קאפח , ), widely known as Rabbi Yosef Kapach (27 November 1917 – 21 July 2000), was a Yemenite-Israeli authority on Jewish religious law (''halakha''), a dayan of the Supreme Rabbinical Court in Israel, and o ...
* ''Tefillat Avot'', ''Baladi'' prayer book (6 vols.)
* ''Torat Avot'', ''Baladi'' prayer book (7 vols.)
* ''Tiklal Ha-Mefoar ( Maharitz) ''Nusaḥ Baladi, Meyusad Al Pi Ha-Tiklal Im Etz Ḥayim Ha-Shalem Arukh Ke-Minhag Yahaduth Teiman'': Bene Berak: Or Neriyah ben Mosheh Ozeri'': 2001 or 2002
* ''Siddur Tefillat HaḤodesh — Beit Yaakov'' (Nusaḥ Shami), ''Nusaḥ Sepharadim'', Teiman, and the Edoth Mizraḥ
* Rabbi Shalom Sharabi
Sar Shalom Sharabi ( he, שר שלום מזרחי דידיע שרעבי), also known as the Rashash, the Shemesh or Ribbi Shalom Mizraḥi deyedi`a Sharabi (1720–1777), was a Yemenite Rabbi, Halachist, Chazzan and Kabbalist. In later life, ...
, ''Siddur Kavanot HaRashash'': Yeshivat HaChaim Ve'Hashalom
* ''Hatiklāl Hamevo'ar'' (Baladi-rite), ed. Pinḥas Qoraḥ, Benei Barak 2006
Yemenite rabbis
* Solomon Adeni (1567–1625)
* Yihye Bashiri (died 1661)
* Zechariah Dhahiri
Zechariah (Yaḥya) al-Ḍāhirī ( he, זכריה אלצ'אהרי, , b. ''circa'' 1531 – d. 1608), often spelled Zechariah al-Dhahiri ( ar, زكريا الضاهري) (16th century Yemen), was the son of Saʻīd (Saʻadia) al-Ḍāhirī, from ...
(c. 1531–1608)
* Hayyim Habshush (c. 1833–1899)
* Yihya Yitzhak Halevi
Yiḥya Yitzḥak Halevi, son of Moshe (Musa) Yitzḥak Halevi ( he, יחיא יצחק הלוי also commonly known as ''Mori'' Yiḥya Yitzḥak from the house of Yitzḥak Halevi) (1867 – 1932), was a Yemeni born rabbinical scholar who s ...
(1867–1932)
* Avraham Al-Naddaf Avraham Al-Naddaf () (1866–1940), the son of Ḥayim b. Salem Al-Naddaf, was a Yemenite rabbi and scholar who immigrated to Ottoman Palestine in 1891, eventually becoming one of the members of the Yemenite rabbinical court (''Beit-Din'') estab ...
(1866–1940)
* Yosef Qafih
Yosef Qafiḥ ( he, יוסף קאפח , ), widely known as Rabbi Yosef Kapach (27 November 1917 – 21 July 2000), was a Yemenite-Israeli authority on Jewish religious law (''halakha''), a dayan of the Supreme Rabbinical Court in Israel, and o ...
(1917–2000)
* Yiḥyah Qafiḥ (1850–1931)
* Amram Qorah (1871–1952)
* Mordechai Sharabi (1908–1994)
* Maharitz (Yihya Salah) The following rabbis were known as the Maharitz:
* Yom Tov Tzahalon
* Yosef Tzvi Dushinsky (first Dushinsky rebbe)
Yosef Tzvi Dushinsky (1867 – 17 October 1948), also known as the Maharitz, was the first Rebbe of Dushinsky and Chief Rabbi (' ...
(1713–1805)
* Shalom Shabazi
Rabbi Shalom ben Yosef ben Avigad Shabazi of the family of Mashtā (1619 – c. 1720), also Abba Sholem Shabazi or Saalem al-Shabazi ( he, שלום שבזי; ar, سالم الشبزي), was a Jewish poet who lived in 17th century Yemen. He i ...
(1619-c. 1720)
* Uzi Meshulam
Uzi Meshulam ( he, עוזי משולם; October 30, 1952 - June 21, 2013) was a Rabbi from Yehud who in 1994 was the leader of a group of Yemenite Jews who resisted Israeli law enforcement authorities.
Biography
At the end of the 1970s Meshu ...
(1952–2013)
* Nethanel ben Isaiah (14th century)
* Natan'el al-Fayyumi
Natan'el al-Fayyumi (also known as Nathanel ben Fayyumi), born about 1090 – died about 1165, of Yemen was the twelfth-century author of ''Bustan al-Uqul'' (Hebrew: ''Gan HaSikhlim''; Garden of the Intellects), a Jewish version of Ismaili Shi'i do ...
* Jacob ben Nathanael
* Shalom Sharabi
Sar Shalom Sharabi ( he, שר שלום מזרחי דידיע שרעבי), also known as the Rashash, the Shemesh or Ribbi Shalom Mizraḥi deyedi`a Sharabi (1720–1777), was a Yemenite Rabbi, Halachist, Chazzan and Kabbalist. In later life, ...
Yemenite Hebrew
Yemenite Hebrew has been studied by scholars, many of whom believe it to contain the most ancient phonetic and grammatical features. There are two main pronunciations of Yemenite Hebrew
Yemenite Hebrew ( ''ʿĪvrīṯ Tēmŏnīṯ''), also referred to as Temani Hebrew, is the pronunciation system for Hebrew traditionally used by Yemenite Jews. Yemenite Hebrew has been studied by language scholars, many of whom believe it to retai ...
, considered by many scholars to be the most accurate modern-day form of Biblical Hebrew, although there are technically a total of five that relate to the regions of Yemen. In the Yemenite dialect, all Hebrew letters
The Hebrew alphabet ( he, אָלֶף־בֵּית עִבְרִי, ), known variously by scholars as the Ktav Ashuri, Jewish script, square script and block script, is an abjad script used in the writing of the Hebrew language and other Jewis ...
have a distinct sound, except for ''sāmeḵ'' () and ''śîn'' (), which are both pronounced . The Sanaani Hebrew
Yemenite Hebrew ( ''ʿĪvrīṯ Tēmŏnīṯ''), also referred to as Temani Hebrew, is the pronunciation system for Hebrew traditionally used by Yemenite Jews. Yemenite Hebrew has been studied by language scholars, many of whom believe it to retai ...
pronunciation (used by the majority) has been indirectly critiqued by Saadia Gaon
Saʻadiah ben Yosef Gaon ( ar, سعيد بن يوسف الفيومي ''Saʻīd bin Yūsuf al-Fayyūmi''; he, סַעֲדְיָה בֶּן יוֹסֵף אַלְפַיּוּמִי גָּאוֹן ''Saʿăḏyāh ben Yōsēf al-Fayyūmī Gāʾōn''; ...
since it contains the Hebrew letters ' and ''guf'', which he rules is incorrect. There are Yemenite scholars, such as Rabbi Ratzon Arusi, who say that such a perspective is a misunderstanding of Saadia Gaon's words.
Rabbi Mazuz postulates this hypothesis through the Djerban (Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
) Jewish dialect's use of ''gimmel'' and ''quf'', switching to ' and ''guf'' when talking with Gentiles in the Arabic dialect of Jerba. While Jewish boys learned Hebrew from the age of 3, it was used primarily as a liturgical and scholarly language. In daily life, Yemenite Jews spoke in regional Judeo-Arabic.
Yemenite Jewish literature
 The oldest Yemenite manuscripts are those of the
The oldest Yemenite manuscripts are those of the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;["Tanach"](_blank)
'' Saadia Gaon
Saʻadiah ben Yosef Gaon ( ar, سعيد بن يوسف الفيومي ''Saʻīd bin Yūsuf al-Fayyūmi''; he, סַעֲדְיָה בֶּן יוֹסֵף אַלְפַיּוּמִי גָּאוֹן ''Saʿăḏyāh ben Yōsēf al-Fayyūmī Gāʾōn''; ...
, Rashi
Shlomo Yitzchaki ( he, רבי שלמה יצחקי; la, Salomon Isaacides; french: Salomon de Troyes, 22 February 1040 – 13 July 1105), today generally known by the acronym Rashi (see below), was a medieval French rabbi and author of a compre ...
, Kimhi, Nahmanides
Moses ben Nachman ( he, מֹשֶׁה בֶּן־נָחְמָן ''Mōše ben-Nāḥmān'', "Moses son of Nachman"; 1194–1270), commonly known as Nachmanides (; el, Ναχμανίδης ''Nakhmanídēs''), and also referred to by the acronym Ra ...
, Yehudah ha Levy and Isaac Arama, besides producing a number of exegetes from among themselves. In the 14th century, Nathanael ben Isaiah wrote an Arabic commentary on the Bible; in the second half of the 15th century, Saadia ben David al-Adeni was the author of a commentary on Leviticus, Numbers
A number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. More universally, individual numbers can ...
, and Deuteronomy. Abraham ben Solomon wrote on the Prophets
In religion, a prophet or prophetess is an individual who is regarded as being in contact with a divine being and is said to speak on behalf of that being, serving as an intermediary with humanity by delivering messages or teachings from the s ...
.
Among the midrash
''Midrash'' (;["midrash"]
''Random House Webster's Unabridged Dictionary''. he, מִדְרָשׁ; ...
collections from Yemen mention should be made of the '' Midrash ha-Gadol'' of David bar Amram al-Adeni. Between 1413 and 1430 the physician Yaḥya Zechariah b. Solomon wrote a compilation entitled "Midrash ha-Ḥefeẓ," which included the Pentateuch
The Torah (; hbo, ''Tōrā'', "Instruction", "Teaching" or "Law") is the compilation of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible, namely the books of Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers and Deuteronomy. In that sense, Torah means the ...
, Lamentations
The Book of Lamentations ( he, אֵיכָה, , from its incipit meaning "how") is a collection of poetic laments for the destruction of Jerusalem in 586 BCE. In the Hebrew Bible it appears in the Ketuvim ("Writings") as one of the Five Megillo ...
, Book of Esther, and other sections of the Hebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;["Tanach"](_blank)
'' Judeo-Arabic
Judeo-Arabic dialects (, ; ; ) are ethnolects formerly spoken by Jews throughout the Arabic-speaking world. Under the ISO 639 international standard for language codes, Judeo-Arabic is classified as a macrolanguage under the code jrb, enco ...
copy of Maimonides
Musa ibn Maimon (1138–1204), commonly known as Maimonides (); la, Moses Maimonides and also referred to by the acronym Rambam ( he, רמב״ם), was a Sephardic Jewish philosopher who became one of the most prolific and influential Tora ...
' ''Guide for the Perplexed
''The Guide for the Perplexed'' ( ar, دلالة الحائرين, Dalālat al-ḥā'irīn, ; he, מורה נבוכים, Moreh Nevukhim) is a work of Jewish theology by Maimonides. It seeks to reconcile Aristotelianism with Rabbinical Jewish th ...
'', copied in Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
in 1380, was found in the India Office Library and added to the collection of the British Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom and is one of the largest libraries in the world. It is estimated to contain between 170 and 200 million items from many countries. As a legal deposit library, the British ...
in 1992.
Among the Yemenite poets who wrote Hebrew and Arabic hymns modeled after the Spanish school, mention may be made of Zechariah (Yaḥya) al-Dhahiri and the members of the Shabazi family. Al-Dhahiri's work, which makes use of the poetic genre known as ''maqāmah'', a style inspired by Ḥariri, was written in 1573 under the title ''Sefer ha-Musar
Zechariah (Yaḥya) al-Ḍāhirī ( he, זכריה אלצ'אהרי, , b. ''circa'' 1531 – d. 1608), often spelled Zechariah al-Dhahiri ( ar, زكريا الضاهري) (16th century Yemen), was the son of Saʻīd (Saʻadia) al-Ḍāhirī, from ...
''. Herein, the author describes in 45 chapters his travels throughout India, Iraq, Turkey, Syria, the Land of Israel and Egypt, including a description of Rabbi Yosef Karo
Joseph ben Ephraim Karo, also spelled Yosef Caro, or Qaro ( he, יוסף קארו; 1488 – March 24, 1575, 13 Nisan 5335 A.M.), was the author of the last great codification of Jewish law, the '' Beit Yosef'', and its popular analogue, the ''Shu ...
's seat of learning in Safed. The philosophical writers include: Saadia b. Jabeẓ and Saadia b. Mas'ud, both at the beginning of the 14th century; Ibn al-Ḥawas, the author of a treatise in the form of a dialogue written in rhymed prose, and termed by its author the "Flower of Yemen"; Ḥasan al-Dhamari; and Joseph ha-Levi b. Jefes, who wrote the philosophical treatises "Ner Yisrael" (1420) and "Kitab al-Masaḥah."
Traditional Jewish attire

Men's clothing
 A
A Tunic
A tunic is a garment for the body, usually simple in style, reaching from the shoulders to a length somewhere between the hips and the knees. The name derives from the Latin ''tunica'', the basic garment worn by both men and women in Ancient Rome ...
() and habit (), the latter made with a central hat (), were the traditional items of clothing worn by a married Jewish man in Yemen. Leading rabbinic scholar and sage, Rabbi Yosef Qafih
Yosef Qafiḥ ( he, יוסף קאפח , ), widely known as Rabbi Yosef Kapach (27 November 1917 – 21 July 2000), was a Yemenite-Israeli authority on Jewish religious law (''halakha''), a dayan of the Supreme Rabbinical Court in Israel, and o ...
, described the manner in which they would wrap their habits, saying that the habit was sometimes worn while wrapped around a man's head, or simply partly draped over his head. German ethnographer Erich Brauer
Erich Brauer (28 June 1895, in Berlin – 9 May 1942, in Petah Tikvah) was a German Jewish illustrator, ethnographer, and ethnologist. As an artist he chose to be known as Erich Chiram Brauer. He often signed his art work "Chiram".
Early life
...
(1895–1942) described the differences between Jewish and Gentile garb, making note of the fact that the differences existed only in their outer garments, but not in their undergarments. He also offered the following description:
As noted, some of the men's dress-codes were forced upon them by laws of the State. For example, formerly in Yemen, Jews were not allowed to wear clothing of any color besides blue. Earlier, in Jacob Saphir
Jacob Saphir ( he, יעקב הלוי ספיר; 1822–1886) was a 19th-century writer, ethnographer, researcher of Hebrew manuscripts, a traveler and emissary of the rabbis of Eastern European Jewish descent who settled in Jerusalem during hi ...
's time (1859), they'd wear outer garments that were "utterly black." When German-Danish explorer, Carsten Niebuhr
Carsten Niebuhr, or Karsten Niebuhr (17 March 1733 Lüdingworth – 26 April 1815 Meldorf, Dithmarschen), was a German mathematician, cartographer, and explorer in the service of Denmark. He is renowned for his participation in the Royal Danish ...
, visited Yemen in 1763, the only person he saw wearing the blue-colored tunic was the Jewish courtier, the Minister and Prince, Sālim b. Aharon Irāqi Ha-Kohen, who served under two kings for a period of no less than twenty-eight years.
The traditional Yemenite '' tallīt'' is a full-length ''tallīt'' made from fine wool or goat's hair of a single black or brown color, called ''šämläh'', but it was not unique unto Jews alone. Muslims would also wear similar items of covering, to protect them from the heat or rain.[Erich Brauer, ''Ethnologie der Jemenitischen Juden'', Heidelberg 1934, p. 85] Jewish garments, however, bore the ritual fringes prescribed for such garments. The wearing of such garments was not unique to prayer time alone, but was worn the entire day. Later, decorative black and white striped shawls were imported into the country from Europe, and which were highly valued by the Jews of Yemen who wore them on special occasions and on the Sabbath day. The small ''tallīt'' (''ṭallīt kaṭan'') was introduced into Yemen via Aden from European centers, and principally worn by rabbis and educated persons.
Women's clothing
 Jewish women in Yemen traditionally wore branched pantaloons beneath their long black tunics. The pantaloons were usually made of a jet-black color, tapering close to their ankles, and decorated at the lower seams with a fine embroidered stitch of silver. The tunic served as, both, a dress and long-sleeved blouse, all in one piece. In addition, all young girls wore a black, conical shaped hat upon their heads, which took the place of a scarf. These hats were called in the local vernacular, ''
Jewish women in Yemen traditionally wore branched pantaloons beneath their long black tunics. The pantaloons were usually made of a jet-black color, tapering close to their ankles, and decorated at the lower seams with a fine embroidered stitch of silver. The tunic served as, both, a dress and long-sleeved blouse, all in one piece. In addition, all young girls wore a black, conical shaped hat upon their heads, which took the place of a scarf. These hats were called in the local vernacular, ''gargush
Gargush ( he, גַּרְגּוּשׁ) is a traditional Yemenite Jewish headdress, resembling a hood, which is thought to have originated in the Sanaite community.
History
Yemenite Jews have throughout the ages preserved ancient Jewish modesty t ...
'', and were also decorated with an embroidered sash about its borders, besides being equipped with tapering flaps that extended down to the ears and to the nape of the neck. Older women in Sana'a
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Gover ...
would wear a broad veil-like scarf over their heads, called ''maswan'', especially when going out in public places, and which was traditionally worn above the closer fitting scarves that covered their hair. All women were adorned with black slippers when walking in public places, and only very small girls would walk barefoot.
Jewish women and girls in Haydan a-sham (in the far northern districts of Yemen) did not make use of the gargush
Gargush ( he, גַּרְגּוּשׁ) is a traditional Yemenite Jewish headdress, resembling a hood, which is thought to have originated in the Sanaite community.
History
Yemenite Jews have throughout the ages preserved ancient Jewish modesty t ...
, but would wear a black scarf tied firmly to their foreheads, resembling a black band, along with the covering made by an additional scarf that covered the hair.
Culinary specialties
The Yemenite Jews are known for bringing to Israel certain culinary dishes, now popularly eaten by all ethnic-groups living in Israel, namely, the ''malawach
Malawach or Melawwaḥ, (; literally means "board-like bread"), is a flatbread that is traditional in Yemenite Jewish cuisine. It was brought to Israel by Yemenite Jews. Malawach resembles a thick pancake but consists of thin layers of puff pa ...
'' (itself an adaptation of the Yemeni '' mulawah''), and ''jachnun
Jachnun or Jahnun ( he, גַ'חְנוּן, , ) is a Yemenite Jewish pastry, originating from the Adeni Jews, and traditionally served on ''Shabbat'' morning. Yemenite Jewish immigrants have popularized the dish in Israel.
Preparation
Jahnun is p ...
''. Lesser-known breadstuffs include the ''kubaneh
Kubaneh ( he, כֻּבַּאנֶה) is a traditional Yemenite Jewish bread that is popular in Israel. Kubaneh is traditionally baked overnight to be served for Shabbat morning accompanied by haminados (eggs that are baked in their shells along wit ...
'' (a traditional Sabbath bread), '' luḥūḥ'', '' sabayah'', and ''zalabiyeh
Zalabiyeh ( ar, زلابية) or Pitulici is a fritter or doughnut found in several cuisines across Europe, the Middle East and West Asia. The fritter version is made from a semi-thin batter of wheat flour which is poured into hot oil and deep- ...
''.
Genetics
DNA testing between Yemenite Jews and members of the world's other various Jewish communities shows a common link, with most communities sharing similar paternal genetic profiles. Furthermore, the Y chromosome
The Y chromosome is one of two sex chromosomes (allosomes) in therian mammals, including humans, and many other animals. The other is the X chromosome. Y is normally the sex-determining chromosome in many species, since it is the presence or abse ...
signatures of the Yemenite Jews are also similar to those of other Middle Eastern populations. Recent studies of Yemeni Mitochondrial DNA, indicate the presence of a high frequency of sub-Saharan African L haplogroups. This notable African contribution is lacking in other Jewish diaspora populations, but it does not exclude, in fact it may reflect, potential descent from exiled ancient Israelite individuals who had a shared Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
n and Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
ern ancestry. There is no genetic evidence for the large-scale conversion of local Yemenis.
 The vast majority of Middle Eastern Jewish communities descend from the earliest Assyrian (late 8th Century BCE) and Babylonian (6th Century BCE) Hebrew exiles, whose mtDNA pools virtually lack sub-Saharan L and North and East African-specific M1 and U6 mtDNA variants. Secondly, the Ashkenazi and North African Jews with a low, but still detectable share of L lineages with very low diversity. This low diversity is most easily explained by a limited number of unique Hg L(xM,N) founders. The third example brings together Ethiopian and Yemenite Jews, rich in Hg L(xM,N) and Hg M1 (in particular in Ethiopian Jews) (Tables S1 and Table S3). As far as Ethiopian and Yemenite Jews are concerned, the main observation here is not in the absolute frequency of Hg L(xM,N) among them, but rather its high diversity, in particular among Beta Israel (Tables S1 and Table S3). Furthermore, samples of Ethiopian and Yemenite Jewish mtDNA pools differ considerably in relative abundance of typically West Asian mtDNA lineages such as derivatives of HV1, JT and others (Tables S1 and Table S3), virtually absent in the former...Maternal DNA of Mizrachi Jews is varied, even slightly from other Mizrachim, indicating likely majority Israelite and some non-Israelite origin from among the women of each of the Near Eastern populations; e.g. Yemeni, Mesopotamian, and other local Near Eastern women. DNA markings, however, are irrelevant when considering that, in Jewish law, proselytes who may have joined the religion of Israel and married into Israelite families, will still pass on their DNA readings to their children. According to
The vast majority of Middle Eastern Jewish communities descend from the earliest Assyrian (late 8th Century BCE) and Babylonian (6th Century BCE) Hebrew exiles, whose mtDNA pools virtually lack sub-Saharan L and North and East African-specific M1 and U6 mtDNA variants. Secondly, the Ashkenazi and North African Jews with a low, but still detectable share of L lineages with very low diversity. This low diversity is most easily explained by a limited number of unique Hg L(xM,N) founders. The third example brings together Ethiopian and Yemenite Jews, rich in Hg L(xM,N) and Hg M1 (in particular in Ethiopian Jews) (Tables S1 and Table S3). As far as Ethiopian and Yemenite Jews are concerned, the main observation here is not in the absolute frequency of Hg L(xM,N) among them, but rather its high diversity, in particular among Beta Israel (Tables S1 and Table S3). Furthermore, samples of Ethiopian and Yemenite Jewish mtDNA pools differ considerably in relative abundance of typically West Asian mtDNA lineages such as derivatives of HV1, JT and others (Tables S1 and Table S3), virtually absent in the former...Maternal DNA of Mizrachi Jews is varied, even slightly from other Mizrachim, indicating likely majority Israelite and some non-Israelite origin from among the women of each of the Near Eastern populations; e.g. Yemeni, Mesopotamian, and other local Near Eastern women. DNA markings, however, are irrelevant when considering that, in Jewish law, proselytes who may have joined the religion of Israel and married into Israelite families, will still pass on their DNA readings to their children. According to Simon Schama
Sir Simon Michael Schama (; born 13 February 1945) is an English historian specialising in art history, Dutch history, Jewish history, and French history. He is a University Professor of History and Art History at Columbia University.
He fi ...
, the Israeli geneticist Batsheva Bonne-Tamir established that the ancestry of Yemeni Jews goes back to south-Western Arabian and Bedouin conversions.
The Y chromosome data on Yemenite Jews show greater evidence of shared Jewish ancestry. In particular, four Y haplogroups (A3b2, E3b3a, E3b1, and J2e) are shared between Yemenite and the Ethiopian Jewish population, whereas no exact mitochondrial haplotypes are shared between these two populations. Additionally, four Yemenite Jewish Y haplogroups (E3b1, E3b1b, J1, and R1b10) are also shared with other Jewish populations (including Ashkenazi, Iraqi, Libyan, and Moroccan Jews), as well as Druze and Palestinians. This paternal similarity across Jewish populations is consistent with the theory that most Jewish Diaspora populations share more paternal ancestry than maternal ancestry (Thomas et al., 2002). In sum, neither Yemenite Jewish mtDNA nor Y (chromosome) data support the origin theory of large-scale conversions of Yemeni Arabs to Judaism during the fifth to sixth centuries, based on minimal contribution from the neighboring non-Jewish Yemeni population. In contrast, molecular genetic data support descent from ancient Israeli exiles due to haplotypes shared with other Jewish populations (as seen in the Y chromosome) in addition to shared East African and more generalized Middle Eastern ancestry (supported by both mtDNA and Y).
[
]
In medicine, the mutation SAMD9 (sterile alpha motif domain containing 9), which encodes a protein involved in the regulation of extraosseous calcification, has been found to underlie normophosphatemic familial tumoral calcinosis in families of Jewish Yemenite origin.
Immigration to Israel


Places of origin and 1881-1939 new communities
The three major population centers for Jews in southern Arabia
South Arabia () is a historical region that consists of the southern region of the Arabian Peninsula in Western Asia, mainly centered in what is now the Republic of Yemen, yet it has also historically included Najran, Jizan, Al-Bahah, and 'A ...
were Aden, Habban, and the Hadhramaut
Hadhramaut ( ar, حَضْرَمَوْتُ \ حَضْرَمُوتُ, Ḥaḍramawt / Ḥaḍramūt; Hadramautic: 𐩢𐩳𐩧𐩣𐩩, ''Ḥḍrmt'') is a region in South Arabia, comprising eastern Yemen, parts of western Oman and southern Saud ...
. The Jews of Aden lived in and around the city, and flourished during the British Aden Protectorate
The Aden Protectorate ( ar, محمية عدن ') was a British protectorate in South Arabia which evolved in the hinterland of the port of Aden and in the Hadhramaut following the conquest of Aden by the Bombay Presidency of British India ...
.
The vast majority of Yemenite immigrants counted by the authorities of Mandate Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 i ...
in 1939 had settled in the country prior to that date. Throughout the periods of Ottoman Palestine
Ottoman Syria ( ar, سوريا العثمانية) refers to divisions of the Ottoman Empire within the region of Syria, usually defined as being east of the Mediterranean Sea, west of the Euphrates River, north of the Arabian Desert and south ...
and Mandatory Palestine, Jews from Yemen had settled primarily in agricultural settlements in the country, namely: Petach Tikvah
Petah Tikva ( he, פֶּתַח תִּקְוָה, , ), also known as ''Em HaMoshavot'' (), is a city in the Central District of Israel, east of Tel Aviv. It was founded in 1878, mainly by Haredi Jews of the Old Yishuv, and became a permanent set ...
(Machaneh Yehuda),[Yitzhak Halevi, Aviran (ed.), ''Ish Yemini'', vol. 2, Bnei Barak 2011, p. 565 (Hebrew)] Rishon Lezion (Shivat Zion),Ness Ziona
Ness Ziona ( he, נֵס צִיּוֹנָה, ''Nes Tziyona'') is a town in central Israel. In it had a population of , and its jurisdiction was 15,579 dunams ().
History Early history
Lying within Ness Ziona's city bounds is the ruin of an Arab vi ...
),Beer Yaakov
Be'er Ya'akov ( he, בְּאֵר יַעֲקֹב, ''lit.'' Jacob's Well) is a city in central Israel, near Ness Ziona and Rishon Lezion. The town has an area of 8,580 dunams (~8.6 km²), and had a population of 30,338 in 2022.
History
B ...
,Hadera
Hadera ( he, חֲדֵרָה ) is a city located in the Haifa District of Israel, in the northern Sharon region, approximately 45 kilometers (28 miles) from the major cities of Tel Aviv and Haifa. The city is located along 7 km (5&nb ...
(Nachliel),Zichron Yaakov
Zikhron Ya'akov ( he, זִכְרוֹן יַעֲקֹב, ''lit.'' "Jacob's Memorial"; often shortened to just ''Zikhron'') is a town in Israel, south of Haifa, and part of the Haifa District. It is located at the southern end of the Carmel mounta ...
,Yavne'el
Yavne'el ( he, יַבְנְאֵל, ar, يفنيئيل) is a moshava and local council in the Northern District of Israel. Founded in 1901, it is one of the oldest rural Jewish communities in the country. According to the Israel Central Bureau o ...
,Ben Shemen
Ben Shemen ( he, בֶּן שֶׁמֶן, ''lit.'' very fruitful) is a moshav in central Israel. Located around four kilometres east of Lod, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hevel Modi'in Regional Council. In it had a population of .
Etymolog ...
, Kinneret,[''A Yemenite Portrait'' (2012), pp. 75e–76e] Degania[''A Yemenite Portrait'' (2012), p. 20e] Others chose to live in the urban areas of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
(Silwan
Silwan or Siloam ( ar, سلوان, translit=Silwan; gr, Σιλωὰμ, translit=Siloam; he, כְּפַר הַשִּׁילוֹחַ, translit=''Kfar ha-Shiloaḥ'') is a predominantly Palestinian neighborhood in East Jerusalem, on the outskir ...
, and Nachalat Zvi),Tel Aviv
Tel Aviv-Yafo ( he, תֵּל־אָבִיב-יָפוֹ, translit=Tēl-ʾĀvīv-Yāfō ; ar, تَلّ أَبِيب – يَافَا, translit=Tall ʾAbīb-Yāfā, links=no), often referred to as just Tel Aviv, is the most populous city in the ...
( Kerem Hateimanim), and later, Netanya (Shekhunat Zvi).
First wave of emigration: 1881 to 1918
Emigration from Yemen to the area now known as Israel began in 1881, and continued almost without interruption until 1914. It was during this time that about 10% of the Yemenite Jews left. Due to the changes in the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, citizens could move more freely, and in 1869, travel was improved with the opening of the Suez Canal, which reduced the travel time from Yemen to Palestine. Certain Yemenite Jews interpreted these changes and the new developments in the "Holy Land" as heavenly signs that the time of redemption was near. By settling in the Holy Land, they would play a part in what they believed could precipitate the anticipated messianic era.
From 1881 to 1882, some 30 Jewish families left Sana'a
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Gover ...
and several nearby settlements, and made the long trek by foot and by sea to Jerusalem, where most had settled in Silwan
Silwan or Siloam ( ar, سلوان, translit=Silwan; gr, Σιλωὰμ, translit=Siloam; he, כְּפַר הַשִּׁילוֹחַ, translit=''Kfar ha-Shiloaḥ'') is a predominantly Palestinian neighborhood in East Jerusalem, on the outskir ...
. This wave was followed by other Jews from central Yemen, who continued to move into Palestine until 1914. The majority of these groups would later move into Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
proper and Jaffa. Rabbi Avraham Al-Naddaf Avraham Al-Naddaf () (1866–1940), the son of Ḥayim b. Salem Al-Naddaf, was a Yemenite rabbi and scholar who immigrated to Ottoman Palestine in 1891, eventually becoming one of the members of the Yemenite rabbinical court (''Beit-Din'') estab ...
, who migrated to Jerusalem in 1891, described in his autobiography the hardships the Yemenite Jewish community faced in their new country, where there were no hostelries to accommodate wayfarers and new immigrants. On the other hand, he writes that the Sephardi
Sephardic (or Sephardi) Jews (, ; lad, Djudíos Sefardíes), also ''Sepharadim'' , Modern Hebrew: ''Sfaradim'', Tiberian: Səp̄āraddîm, also , ''Ye'hude Sepharad'', lit. "The Jews of Spain", es, Judíos sefardíes (or ), pt, Judeus sefa ...
''kollel
A kollel ( he, כולל, , , a "gathering" or "collection" f scholars is an institute for full-time, advanced study of the Talmud and rabbinic literature. Like a yeshiva, a kollel features shiurim (lectures) and learning ''sedarim'' (sessions); ...
im'' (seminaries) had taken under their auspices the Yemenite Jews from the moment they set foot in Jerusalem. Later, however, the Yemenites would come to feel discriminated against by the Sephardic community, who compelled them to no longer make use of their own soft, pliable matzah
Matzah or matzo ( he, מַצָּה, translit=maṣṣā'','' pl. matzot or Ashk. matzos) is an unleavened flatbread that is part of Jewish cuisine and forms an integral element of the Passover festival, during which ''chametz'' ( leaven an ...
, but to buy from them only the hard cracker-like matzah made weeks in advance prior to Passover. He also mentions that the Yemenite community would pay the prescribed tax to the public coffers; yet, they were not being allotted an equal share or subsidy as had been given to the Sephardic Jews. By 1910, the Yemenites had broken away from the Sephardic seminaries.
Before World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, there was another wave that began in 1906 and continued until 1914. Hundreds of Yemenite Jews made their way to the Holy Land, and chose to settle in the agricultural settlements. It was after these movements that the World Zionist Organization
The World Zionist Organization ( he, הַהִסְתַּדְּרוּת הַצִּיּוֹנִית הָעוֹלָמִית; ''HaHistadrut HaTzionit Ha'Olamit''), or WZO, is a non-governmental organization that promotes Zionism. It was founded as the ...
sent Shmuel Yavne'eli to Yemen to encourage Jews to emigrate to Palestine. Yavne'eli reached Yemen at the beginning of 1911, and returned in April 1912. Due to Yavne'eli's efforts, about 1,000 Jews left central and southern Yemen, with several hundred more arriving before 1914. The purpose of this immigration was considered by the Zionist Office as allowing the importation of cheap labour. This wave of Yemenite Jewry underwent extreme suffering, physically and mentally, and those who arrived between 1912 and 1918 had a very high incidence of premature mortality, ranging from between 30% and 40% generally and, in some townships, reaching as high as 50%.
Second wave of emigration: 1920 to 1950

 During the
During the British Mandate of Palestine British Mandate of Palestine or Palestine Mandate most often refers to:
* Mandate for Palestine: a League of Nations mandate under which the British controlled an area which included Mandatory Palestine and the Emirate of Transjordan.
* Mandatory P ...
, the total number of persons registered as immigrants from Yemen, between the years April 1939–December 1945, was put at 4,554. By 1947, there were an estimated 35,000 Yemenite Jews living in Mandate Palestine. The largest bulk of immigration to Israel, however, came after the declaration of the state. Israel initiated Operation Magic Carpet in June 1949 and airlifted most of Yemen's Jews to Israel by September 1950.
In 1947, after the partition vote of the British Mandate of Palestine, Arab Muslim rioters, assisted by the local police force, engaged in a pogrom in Aden that killed 82 Jews and destroyed hundreds of Jewish homes. Aden's Jewish community was economically paralyzed, as most of the Jewish stores and businesses were destroyed. Early in 1948, the unfounded rumour of the ritual murder of two girls led to looting.
This increasingly perilous situation led to the emigration of virtually the entire Yemenite Jewish community between June 1949 and September 1950 in Operation Magic Carpet. During this period, over 50,000 Jews migrated to Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
.
Operation Magic Carpet (Yemen)
Operation Magic Carpet is a widely known nickname for Operation On Wings of Eagles ( he, כנפי נשרים, ''Kanfei Nesharim''), an operation between June 1949 and September 1950 that brought 49,000 Yemenite Jews to the new state of Isra ...
began in June 1949 and ended in September 1950.[Tudor Parfitt, ''The Road to Redemption: The Jews of the Yemen, 1900–1950'', (Leiden: E.J. Brill, 1996), pages 229–245] Part of the operation happened during the 1947–48 Civil War in Mandatory Palestine and the 1948 Arab–Israeli War (May 15, 1948 – March 10, 1949). The operation was planned by the American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee
American Jewish Joint Distribution Committee, also known as Joint or JDC, is a Jewish relief organization based in New York City. Since 1914 the organisation has supported Jewish people living in Israel and throughout the world. The organization i ...
. The plan was for the Jews from all over Yemen to make their way to the Aden area. Specifically, the Jews were to arrive in Hashed Camp and live there until they could be airlifted to Israel. Hashed was an old British military camp in the desert, about a mile away from the city of Sheikh Othman
Ash Shaikh Outhman District is a district of the Aden Governorate, Yemen. As of 2003, the district had a population of 105,248 inhabitants.
History
Sheikh Othman derives its name from a religious shrine for Sheikh Othman Al-Zubairi Al-Wahki. The ...
. The operation took longer than was originally planned. Over the course of the operation, hundreds of migrants died in Hashed Camp, as well as on the plane rides to Israel.Alaska Airlines
Alaska Airlines is a major American airline headquartered in SeaTac, Washington, within the Seattle metropolitan area. It is the sixth largest airline in North America when measured by fleet size, scheduled passengers carried, and the num ...
:
In the wake of the 1948 Arab Israeli War
Events January
* January 1
** The General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) is inaugurated.
** The Constitution of New Jersey (later subject to amendment) goes into effect.
** The railways of Britain are nationalized, to form Britis ...
when vast territories were added to the State of Israel, the Jewish Agency
The Jewish Agency for Israel ( he, הסוכנות היהודית לארץ ישראל, translit=HaSochnut HaYehudit L'Eretz Yisra'el) formerly known as The Jewish Agency for Palestine, is the largest Jewish non-profit organization in the world. ...
under the good offices of Levi Eshkol
Levi Eshkol ( he, לֵוִי אֶשְׁכּוֹל ; 25 October 1895 – 26 February 1969), born Levi Yitzhak Shkolnik ( he, לוי יצחק שקולניק, links=no), was an Israeli statesman who served as the third Prime Minister of Israe ...
, then head of the Settlement Department in that Agency, decided to settle many of the new immigrants arriving in Israel in newly founded agricultural communities.[''Levi Eshkol, the Third Prime-Minister: A Selection of Documents Covering his Life'' eb. (לוי אשכול - ראש הממשלה השלישי : מבחר תעודות מפרקי חייו (1895-1969 ed. Y. Rosental, A. Lampron & H. Tzoref, Israel State Archives (publisher): Jerusalem 2002, chapter 6 - ''In the Jewish Agency, During the Years of Mass Immigration'' (Hebrew)] The idea was given further impetus when Yosef Weitz of the Jewish National Fund proposed settling many of the country's new immigrants upon agricultural farms built in the recently acquired territories: in the mountainous regions, in Galilee and in the Jerusalem Corridor, places heretofore sparsely settled.Eshtaol
( he, אֶשְׁתָּאוֹל) is a moshav in central Israel, and a Hebrew Bible, biblical location mentioned in the Book of Joshua, Books of Joshua and Book of Judges, Judges and in the 1 Chronicles, first Book of Chronicles. Located north of ...
, Yish'i, Ajjur, Dayraban Gimel
Zanoah ( he, זָנוֹחַ) is a moshav in central Israel. Located adjacent to Beit Shemesh, it falls under the jurisdiction of Mateh Yehuda Regional Council. In it had a population of .
Modern history
The village was established in 1950 by im ...
, Allar Aleph, Allar-Bet, Kesalon, among other places, although the majority of these frontier places were later abandoned by the new immigrants from Yemen for more urban places in central Israel. This prompted Levi Eshkol to write in a letter to Prime-Minister Ben-Gurion (dated 10 April 1950): "The Yemenite vision doesn't allow him to see what he can do in a place of boulders and rocks. He cannot imagine such a development as Neve Ilan
Neve Ilan ( he, נְוֵה אִילָן, lit. ''Oasis of Ilan'') is a moshav shitufi in central Israel. Located west of Jerusalem, it falls under the jurisdiction of Mateh Yehuda Regional Council. In it had a population of . Previously a kibbutz ...
which sits upon dry rock. Instead, he imagines that he is being deprived..."
Third wave of emigration: 1990 to 2016
 A third wave of emigration from Yemen began in the late 20th-century, with the intercession of Human Rights activist and professor, Hayim Tawil, founder of the International Coalition for the Revival of the Jews of Yemen (ICROJOY) in 1988. Tawil was instrumental in bringing out from Yemen the first Jew to emigrate in 23 years, and who set foot in Israel in September 1990. He was followed by other families in 1992, with the greatest bulk of Jewish families arriving in Israel between 1993 and 1994. These new Yemenite Jewish immigrants settled mainly in Rehovot (''Oshiyot''),
A third wave of emigration from Yemen began in the late 20th-century, with the intercession of Human Rights activist and professor, Hayim Tawil, founder of the International Coalition for the Revival of the Jews of Yemen (ICROJOY) in 1988. Tawil was instrumental in bringing out from Yemen the first Jew to emigrate in 23 years, and who set foot in Israel in September 1990. He was followed by other families in 1992, with the greatest bulk of Jewish families arriving in Israel between 1993 and 1994. These new Yemenite Jewish immigrants settled mainly in Rehovot (''Oshiyot''), Ashkelon
Ashkelon or Ashqelon (; Hebrew: , , ; Philistine: ), also known as Ascalon (; Ancient Greek: , ; Arabic: , ), is a coastal city in the Southern District of Israel on the Mediterranean coast, south of Tel Aviv, and north of the border wit ...
and Beer-Sheva. Other families arrived in 1995 and 1996.
Orphan's decree (Yemen, 1922)
In 1922, the government of Yemen, under Yahya Muhammad Hamid ed-Din
, succession1 = King of Yemen
, succession2 = Imam of Yemen
, image = Imam yahya cropped.png
, image_size =
, caption = Portrait of Yahya by Ameen Rihani, 1922. Imam Yahya steadfastly refused to be photographed t ...
, re-introduced an ancient Islamic law entitled the "orphans decree". The law dictated that if Jewish boys or girls under the age of 12 were orphaned, they were to be forcibly converted to Islam, their connections to their families and communities were to be severed, and they had to be handed over to Muslim foster families. The rule was based on the law that the prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
is "the father of the orphans", and on the fact that the Jews in Yemen were considered "under protection", and the ruler was obligated to care for them.Yemen Arab Republic
The Yemen Arab Republic (YAR; ar, الجمهورية العربية اليمنية '), also known simply as North Yemen or Yemen (Sanaʽa), was a country from 1962 to 1990 in the northwestern part of what is now Yemen.The United States extend ...
, who was alleged to be of Jewish descent by Dorit Mizrahi, a writer in the Israeli ultra-Orthodox weekly ''Mishpaha'', who claimed he was her maternal uncle. According to her recollection of events, he was born ''Zekharia Hadad'' in 1910 to a Yemenite Jewish family in Ibb. He lost his parents in a major disease epidemic at the age of 8 and together with his 5-year-old sister, he was forcibly converted to Islam and they were put under the care of separate foster families. He was raised in the powerful al-Iryani family and adopted an Islamic name. Al-Iryani would later serve as minister of religious endowments under northern Yemen's first national government and he became the only civilian to have led northern Yemen.
Missing children (Israel, 1949-51)
Claims were made that, between 1949 and 1951, up to 1,033 children of Yemenite immigrant families may have disappeared from the immigrant camps. It was said that the parents were told that their children were ill and required hospitalization. Upon later visiting the hospital, it is claimed that the parents were told that their children had died though no bodies were presented and graves which have later proven to be empty in many cases were shown to the parents. Those who believed the theory contended that the Israeli government as well as other organizations in Israel kidnapped the children and gave them for adoption to other, non-Yemenite, families.
Present situation
 Today, the overwhelming majority of Yemenite Jews live in Israel.
Some Yemenite Jews stayed behind during Operation Magic Carpet, many of them not wanting to leave sick or elderly relatives behind. Another wave of emigration took place in 1959, with some 3,000 Yemenite Jews moving to Israel, and some others moving to the
Today, the overwhelming majority of Yemenite Jews live in Israel.
Some Yemenite Jews stayed behind during Operation Magic Carpet, many of them not wanting to leave sick or elderly relatives behind. Another wave of emigration took place in 1959, with some 3,000 Yemenite Jews moving to Israel, and some others moving to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
and United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
. Those Jews that remained behind were forbidden from emigrating and were banned from contacting relatives abroad. They were isolated and scattered throughout the mountainous regions of northern Yemen, and suffered shortages of food, clothing, and medicine, and lacked religious articles. As a result, some converted to Islam. Their existence was unknown until 1976 when an American diplomat stumbled across a small Jewish community in a remote region of northern Yemen. For a short time afterward, Jewish organizations were allowed to travel openly in Yemen, distributing Hebrew books and materials.Raydah
Raydah (sometimes transliterated Raidah or al-Raidah) is a large market town located north of Sana'a, and north of Amran, in northwestern Yemen.Sharp, Jeremy MYemen: Background and U.S. Relations(RL34170, PDF). Congressional Research Service ...
). They had a rabbi, a functioning synagogue, and a mikveh. They also had a boys yeshiva
A yeshiva (; he, ישיבה, , sitting; pl. , or ) is a traditional Jewish educational institution focused on the study of Rabbinic literature, primarily the Talmud and halacha (Jewish law), while Torah and Jewish philosophy are st ...
and a girls seminary, funded by a Satmar
Satmar (Yiddish: סאַטמאַר, Hebrew: סאטמר) is a Hasidic group founded in 1905 by Grand Rebbe Joel Teitelbaum, in the city of Szatmárnémeti, Hungary (now Satu Mare in Romania). The group is an offshoot of the Sighet Hasidic dynasty ...
-affiliated Hasidic organization in Monsey, New York, US. A small Jewish enclave also existed in the town of Raydah
Raydah (sometimes transliterated Raidah or al-Raidah) is a large market town located north of Sana'a, and north of Amran, in northwestern Yemen.Sharp, Jeremy MYemen: Background and U.S. Relations(RL34170, PDF). Congressional Research Service ...
, which lies north of Sana'a. The town hosted a yeshiva
A yeshiva (; he, ישיבה, , sitting; pl. , or ) is a traditional Jewish educational institution focused on the study of Rabbinic literature, primarily the Talmud and halacha (Jewish law), while Torah and Jewish philosophy are st ...
, also funded by a Satmar-affiliated organization.
In spite of hostile conditions in recent years for Jews still living in Yemen, Yemeni security forces have gone to great lengths to try to convince the Jews to stay in their towns. These attempts, however, failed, and the authorities were forced to provide financial aid for the Jews so they would be able to rent accommodations in safer areas.
Despite an official ban on emigration, many Yemenite Jews emigrated to Israel, the United States, and the United Kingdom in the 2000s, fleeing anti-Semitic persecution and seeking better Jewish marriage prospects. Many of them had initially gone there to study but had never returned. There was essentially no Jewish population in Sanaʽa until the Shia insurgency broke out in northern Yemen in 2004. In 2006 it was reported that a Jewish woman in Yemen who had spurned a Muslim suitor had not only been kidnapped and forced to marry
Marriage, also called matrimony or wedlock, is a culturally and often legally recognized union between people called spouses. It establishes rights and obligations between them, as well as between them and their children, and between t ...
him, but had been forced to convert to Islam as well. The Houthis
The Houthi movement (; ar, ٱلْحُوثِيُّون ''al-Ḥūthīyūn'' ), officially called Ansar Allah (' ''Partisans of God'' or ''Supporters of God'') and colloquially simply Houthis, is an Islamist political and armed movement that ...
directly threatened the Jewish community in 2007, prompting the government of President Saleh to offer them refuge in Sanaʽa
Sanaa ( ar, صَنْعَاء, ' , Yemeni Arabic: ; Old South Arabian: 𐩮𐩬𐩲𐩥 ''Ṣnʿw''), also spelled Sana'a or Sana, is the capital and largest city in Yemen and the centre of Sanaa Governorate. The city is not part of the Govern ...
. , around 700 Jews were living in the capital under government protection.
In December 2008, Moshe Ya'ish al-Nahari
Moshe Ya'ish al-Nahari ( he, משה יעיש אל נהרי ar, موشيه يعيش النهاري born 1978 – 11 December 2008) was a Yemeni Jewish Hebrew teacher and kosher butcher in Raydah, Yemen, who was murdered by a Yemeni Muslim who acc ...
, a 30-year-old Hebrew teacher and kosher butcher from Raydah
Raydah (sometimes transliterated Raidah or al-Raidah) is a large market town located north of Sana'a, and north of Amran, in northwestern Yemen.Sharp, Jeremy MYemen: Background and U.S. Relations(RL34170, PDF). Congressional Research Service ...
, was shot and killed by Abed el-Aziz el-Abadi, a former MiG-29 pilot in the Yemeni Air Force
The Yemeni Air Force ( ar, القوات الجوية اليمنية, al-Quwwat al-Jawwiya al-Yamaniya) is the air operations branch of the Yemeni Armed Forces. Numbers of aircraft can not be confirmed but serviceability of these aircraft is low. ...
. Abadi confronted Nahari in the Raydah market, and shouted out, "Jew, accept the message of Islam", and opened fire with an AK-47
The AK-47, officially known as the ''Avtomat Kalashnikova'' (; also known as the Kalashnikov or just AK), is a gas-operated assault rifle that is chambered for the 7.62×39mm cartridge. Developed in the Soviet Union by Russian small-arms d ...
. Nahari was shot five times and died. During interrogation, Abadi proudly confessed his crime, and stated that "these Jews must convert to Islam". Abadi had murdered his wife two years before but had avoided prison by paying her family compensation. The court found Abadi mentally unstable, and ordered him to pay only a fine, but an appeals court sentenced him to death. Following al-Nahari's murder, the Jewish community expressed its feelings of insecurity, claiming to have received hate mail and threats by phone from Islamic extremists. Dozens of Jews reported receiving death threats and said that they had been subjected to violent harassment. Nahari's killing and continual anti-Semitic harassment prompted approximately 20 other Jewish residents of Raydah to emigrate to Israel. In 2009, five of Nahari's children moved to Israel, and in 2012, his wife and four other children followed, having initially stayed in Yemen so she could serve as a witness in Abadi's trial.Wall Street Journal
''The Wall Street Journal'' is an American business-focused, international daily newspaper based in New York City, with international editions also available in Chinese and Japanese. The ''Journal'', along with its Asian editions, is published ...
'' reported that in June 2009, an estimated 350 Jews were left in Yemen, and by October 2009, 60 had emigrated to the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
, and 100 were considering following suit.United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
.Jewish Agency
The Jewish Agency for Israel ( he, הסוכנות היהודית לארץ ישראל, translit=HaSochnut HaYehudit L'Eretz Yisra'el) formerly known as The Jewish Agency for Palestine, is the largest Jewish non-profit organization in the world. ...
and the Israeli Foreign Ministry
The Israeli Ministry of Foreign Affairs ( he, מִשְׂרַד הַחוּץ, translit. ''Misrad HaHutz''; ar, وزارة الخارجية الإسرائيلية) is one of the most important ministries in the Israeli government. The ministry's ...
.Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it ...
. This was reported to be part of a larger operation which was being carried out in order to bring the approximately 400 Jews left in Yemen to Israel in the coming months.
In April 2014 it was reported that the remaining Jewish Population in Yemen numbered 90.Likud
Likud ( he, הַלִּיכּוּד, HaLikud, The Consolidation), officially known as Likud – National Liberal Movement, is a major centre-right to right-wing political party in Israel. It was founded in 1973 by Menachem Begin and Ariel Sha ...
MK Ayoob Kara
Ayoob Kara ( ar, أيوب قرا, he, איוב קרא; born 12 March 1955) is an Israeli Druze politician. He has served as a member of the Knesset for Likud in four spells between 1999 and 2021, and as Minister of Communications.
Biography
...
stated that members of the Yemenite Jewish community had contacted him to say that the Houthi-led Yemen government had given them an ultimatum to convert or leave the country. A spokesman for the party of former President Ali Abdullah Saleh
Ali Abdullah Saleh al-Ahmar (, ''ʿAlī ʿAbdullāh Ṣāliḥ al-Aḥmar;'' 21 March 1947There is a dispute as to Saleh's date of birth, some saying that it was on 21 March 1942. See: However, by Saleh's own confession, he was born in 1947 al ...
denied the reports as incorrect.
On March 21, 2016, a group of 19 Yemenite Jews were flown to Israel in a secret operation, leaving the population at about 50. In April 2016 the Houthis arrested three Yemenite Jews-including Rabbi Yousef. On June 7, 2016 Jews who had been arrested in Yemen after having helped smuggled out a Torah scroll were released.
In May 2017 the Yemeni-based charity Mona Relief (Yemen Organization for Humanitarian Relief and Development) gave aid to 86 members of the Jewish community in Sana'a.
 In a July 2018 interview with a Yemenite rabbi, he claimed that they were definitely treated very well before the recent war in Yemen which has affected all communities in Yemen. He has also said that Yemenite Jews should have never traveled away from Yemen and that he believes thousands of Yemenite Jews will return to Yemen after the war ends.
In 2019, the Mona Relief website reported (February 25): "Mona Relief's team in the capital Sana'a delivered today monthly food aid packages to Jewish minority families in Yemen. Mona Relief has been delivering food aid baskets to Jewish community in the capital Sana'a since 2016. Our project today was funded by Mona Relief's online fundraising campaign in indiegog ..."
As of March 2020, the Jewish Cemetery in Aden was destroyed. On April 28, 2020, Yemenite Minister Moammer al-Iryani remarked the ''fate of the last 50 Jews'' in Yemen is ''unknown''.
A 2020 World Population Review with a Census of Jewish population by country has ''no'' listing of ''any'' Jews in Yemen.
On July 13, 2020, it was reported that the Houthi Militia were capturing the last Jews of Yemen of the Kharif District. In their last mention of the Jews in Yemen in July 2020 the Mona Relief reported on their Website that as of July 19, 2020, of the Jewish Population in Yemen there were only a "handful" of Jews in Sana'a.
According to Yemeni publications published in July 2020, the last two Jewish families were waiting for deportation from the areas controlled by the Houthis, which would make Yemen, for the first time in its modern history, devoid of Jews, with the exception of the families of the brothers Suleiman Musa Salem and Sulaiman Yahya Habib in Sana’a and the family of Salem Musa Mara’bi who moved to the complex owned by the Ministry of Defense near the U.S. embassy in 2007 after the Houthis assaulted them and looted their homes. The publications said that a Jewish woman lives with her brother in the Rayda district and a man and his wife live in the Arhab district of the Sana’a governorate. A source said, “It is now clear that the Houthis want to deport the rest of the Jews, and prevent them from selling their properties at their real prices, and we are surprised that the international community and local and international human rights organizations have remained silent towards the process of forced deportation and forcing the Jews to leave their country and prevent them from disposing of their property.
In August 2020 of an estimated 100 or so remaining Yemen Jews, 42 have migrated to U.A.E. and the rest would also leave.
In a July 2018 interview with a Yemenite rabbi, he claimed that they were definitely treated very well before the recent war in Yemen which has affected all communities in Yemen. He has also said that Yemenite Jews should have never traveled away from Yemen and that he believes thousands of Yemenite Jews will return to Yemen after the war ends.
In 2019, the Mona Relief website reported (February 25): "Mona Relief's team in the capital Sana'a delivered today monthly food aid packages to Jewish minority families in Yemen. Mona Relief has been delivering food aid baskets to Jewish community in the capital Sana'a since 2016. Our project today was funded by Mona Relief's online fundraising campaign in indiegog ..."
As of March 2020, the Jewish Cemetery in Aden was destroyed. On April 28, 2020, Yemenite Minister Moammer al-Iryani remarked the ''fate of the last 50 Jews'' in Yemen is ''unknown''.
A 2020 World Population Review with a Census of Jewish population by country has ''no'' listing of ''any'' Jews in Yemen.
On July 13, 2020, it was reported that the Houthi Militia were capturing the last Jews of Yemen of the Kharif District. In their last mention of the Jews in Yemen in July 2020 the Mona Relief reported on their Website that as of July 19, 2020, of the Jewish Population in Yemen there were only a "handful" of Jews in Sana'a.
According to Yemeni publications published in July 2020, the last two Jewish families were waiting for deportation from the areas controlled by the Houthis, which would make Yemen, for the first time in its modern history, devoid of Jews, with the exception of the families of the brothers Suleiman Musa Salem and Sulaiman Yahya Habib in Sana’a and the family of Salem Musa Mara’bi who moved to the complex owned by the Ministry of Defense near the U.S. embassy in 2007 after the Houthis assaulted them and looted their homes. The publications said that a Jewish woman lives with her brother in the Rayda district and a man and his wife live in the Arhab district of the Sana’a governorate. A source said, “It is now clear that the Houthis want to deport the rest of the Jews, and prevent them from selling their properties at their real prices, and we are surprised that the international community and local and international human rights organizations have remained silent towards the process of forced deportation and forcing the Jews to leave their country and prevent them from disposing of their property.
In August 2020 of an estimated 100 or so remaining Yemen Jews, 42 have migrated to U.A.E. and the rest would also leave.The Jerusalem Post
''The Jerusalem Post'' is a broadsheet newspaper based in Jerusalem, founded in 1932 during the British Mandate of Palestine by Gershon Agron as ''The Palestine Post''. In 1950, it changed its name to ''The Jerusalem Post''. In 2004, the paper ...
'' reported that the remaining Jewish population in Yemen consists of four elderly Jews in Yemen ending the continuous presence of a community that dated back to antiquity.[ According to one report there are six Jews left in Yemen: one woman; her brother; 3 others, and Levi Salem Marhabi (who has been imprisoned for helping smuggle a Torah scroll out of Yemen).]
Yemenite Jewish surnames
The subject of Jewish surnames in Yemen is a complex one. Most surnames are gentilic
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, ...
or toponymic surnames
A toponymic surname or topographic surname is a surname derived from a place name. , meaning, they are derived from an ancestor's place of residence (village or town name, such as Gadasi from al-Gades; Qa'taby from Qa'tabah; Manqadi from Manqadah; Damari from Dhamar, Damti from Damt, etc.), while fewer are eponymous or patronymic surnames
A patronymic, or patronym, is a component of a personal name based on the given name of one's father, grandfather (avonymic), or an earlier male ancestor.
Patronymics are still in use, including mandatory use, in many countries worldwide, alt ...
, being derived from the name of an ancient ancestor.[Moshe Gavra, ''Surnames of Jews in Yemen'' (''shemot ha-mishpahah shel ha-yehudim be-teman''), Benei Barak 2014, Preface p. 6 (Hebrew)] In some cases, surnames are derived from a certain physical characteristic of one's distant ancestor. Some families bear original Spanish surnames, such as Medina and Giyyat. Some names went through additional changes upon emigration to Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
. For example, some who formerly bore the surname of Radha (Judeo-Arabic
Judeo-Arabic dialects (, ; ; ) are ethnolects formerly spoken by Jews throughout the Arabic-speaking world. Under the ISO 639 international standard for language codes, Judeo-Arabic is classified as a macrolanguage under the code jrb, enco ...
: ) have changed their surname to Ratzon (Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
: ), the Hebrew being the direct translation of the word's meaning in Arabic, while yet others have simply changed their names to a more Hebraicized sound, such as the surnames of Al-Nadaf (lit. a stuffer of cushions; carder of cotton), which was later changed to Nadav ("generous"), and 'Urqabi (so-named from a locality in Yemen) which was later changed to Argov; or Sheḥib (Judeo-Arabic
Judeo-Arabic dialects (, ; ; ) are ethnolects formerly spoken by Jews throughout the Arabic-speaking world. Under the ISO 639 international standard for language codes, Judeo-Arabic is classified as a macrolanguage under the code jrb, enco ...
: ), meaning "one whose voice is hoarse," which was changed to Shevach (Hebrew: ), meaning "praise," by a reversal of the last two letters.
Notable Israeli soldiers of Yemenite descent
* Avigdor Kahalani
Tat Aluf (Brigadier General) Avigdor Kahalani ( he, אביגדור קהלני, born 16 June 1944) is a former Israeli soldier and politician.
Early life
Avigdor Kahalani was born in Ness Ziona during the Mandate era. His parents, Moshe and Sa ...
* David Maimon
Yemenite Jews in Israeli culture
Traditional culture
Israeli Yemenite Jews were initially discouraged from practicing their culture from the domination of the Ashkenazi majority, and the practice of using henna before weddings declined. Beginning around the late 1970s there were discussions of honoring ethnic heritage and by 2018 a revival of some Yemenite customs occurred. The cathartic moment was an exhibition of a Yemeni bride was shown at the Israel Museum in 1965.
Music
Yemeni Jews are predominant among Israeli performers of Oriental music.Ofra Haza
Bat-Sheva Ofra Haza ( he, בת-שבע עפרה חזה; 19 November 1957 – 23 February 2000), known as Ofra Haza (), was an Israeli singer, songwriter, actress, and Grammy Award-nominated recording artist commonly known in the Western world as ...
and Achinoam Nini
Achinoam Nini ( he, אחינועם ניני, Aẖinóʿam Nini; born ), also known professionally as Noa (), is an Israeli singer-songwriter, percussionist, poet, composer, and human rights activist working internationally. She is accompanied by ...
(Noa), are of Yemenite origin. At the Eurovision Song Contest, 1998, 1979, and 1978 winners Dana International, Gali Atari, and Izhar Cohen, 1983 runner-up Ofra Haza
Bat-Sheva Ofra Haza ( he, בת-שבע עפרה חזה; 19 November 1957 – 23 February 2000), known as Ofra Haza (), was an Israeli singer, songwriter, actress, and Grammy Award-nominated recording artist commonly known in the Western world as ...
, and 2008 top 10 finalist Boaz Mauda, are Yemenite Jews. Harel Skaat, who competed at Oslo in 2010, is the son of a Yemenite Jewish father. Other Israeli singers and musicians of Yemenite Jewish descent include Zohar Argov, the three sisters of the music group A-WA (Yemenite Jewish father), Inbar Bakal, Mosh Ben-Ari, Yosefa Dahari, Daklon, Eyal Golan, Zion Golan, Yishai Levi, Sara Levi-Tanai (choreographer and songwriter), Bo'az Ma'uda, Avihu Medina, Boaz Sharabi, Pe'er Tasi, Shimi Tavori, Margalit Tzan'ani, and Tomer Yosef of Balkan Beat Box.
Politics
 Israeli Politicians of Yemenite Jewish descent include Gila Gamliel (current member of the Knesset for Likud), Meir Yitzhak Halevi (the Mayor of Eilat), Saadia Kobashi (leader of the Yemenite Jewish community in Israel, and one of the signatories of the country's declaration of independence), and Avraham Taviv.
Israeli Politicians of Yemenite Jewish descent include Gila Gamliel (current member of the Knesset for Likud), Meir Yitzhak Halevi (the Mayor of Eilat), Saadia Kobashi (leader of the Yemenite Jewish community in Israel, and one of the signatories of the country's declaration of independence), and Avraham Taviv.
Sports and media
Becky Griffin, whose mother is Yemenite Jewish, works as a model, TV presenter and actress. Shahar Tzuberi is an Olympic windsurfer.
Linoy Ashram is an Israeli individual rhythmic gymnast. She is the 2020 Olympic All-around Champion.
Further reading
* Abraham Zevi Idelsohn, Idelsohn, Abraham Z. (1914). ''Thesaurus of Hebrew–Oriental Melodies'', vol. 1 (''Songs of the Yemenite Jews''), by Abraham Z. Idelsohn, Leipzig
* Yosef Qafih, Qafih, Yosef (1982). ''Halikhot Teiman — The Life of Jews of Sana'a'', Ben-Zvi Institute: Jerusalem (in Hebrew)
* Amram Qorah, Qorah, Amram (1988). ''Sa‘arat Teiman'', Jerusalem (in Hebrew)
*
* Megillah (Talmud), Megillah (tractate)
The Yemenite MS
of Megillah (Talmud), Megillah in the Library of Columbia University)
* Parfitt, Tudor (1996) ''The Road to Redemption: The Jews of the Yemen 1900–1950''. Brill's Series in Jewish Studies vol. XVII. Leiden: Brill.
* Rohrbacher, Peter (2006)
„Wüstenwanderer“ gegen „Wolkenpolitiker“ – Die Pressefehde zwischen Eduard Glaser und Theodor Herzl
in: Anzeiger der philosophisch-historischen Klasse; 141. Wien: Österreichische Akademie der Wissenschaften, pp. 103–116.
* Simon, Reeva; Laskier, Michael; Reguer, Sara (eds.) (2002). ''The Jews of the Middle East and North Africa In Modern Times'', Columbia University Press, s.v. Chapters 8 and 21
*
* Verskin, Alan (2018). ''A Vision of Yemen: The Travels of a European Orientalist and His Native Guide''. A Translation of Hayyim Habshush's ''Travelogue.'' Stanford, CA. Stanford University Press
See also
* Torah scroll (Yemenite)
* Jews of Hadramaut, Hadhrami Jews
* Habbani Jews
* Adeni Jews
* Arab Jews
* Shara'b As Salam District#Shara'bi Jews, Shara'bi Jews
* History of the Jews in the Arabian Peninsula
* The Jewish community of Saada
* Israel–Yemen relations
* History of the Jews under Muslim rule
* Antisemitism in Islam
* Antisemitism in the Arab world
* Racism in the Arab world
* Islamic–Jewish relations
* Jewish exodus from the Muslim world
* Kfar Tapuach (Apple-village), an Orthodox Judaism, Orthodox Jewish Israeli settlement which is located in the west Bank and was founded by Yemenite Jews in 1978
* List of Jews from the Arab World
* Mizrahi Jews
* Yemenite citron
* Yemenite Hebrew
Yemenite Hebrew ( ''ʿĪvrīṯ Tēmŏnīṯ''), also referred to as Temani Hebrew, is the pronunciation system for Hebrew traditionally used by Yemenite Jews. Yemenite Hebrew has been studied by language scholars, many of whom believe it to retai ...
* Yemenite Jewish poetry
* Yemenite Jewish silversmiths
* Mawza Exile
* Midrash HaGadol
* Nathan ben Abraham I
* Yemenite Children Affair
* Orphans' Decree
* Baladi-rite prayer
* Epistle to Yemen
* Al-Ousta Codex
References
Bibliography
*
External links
Jews of Yemen
Jewish Encyclopedia, 1906
History of the Jews of Yemen
Rabbi Menachem Levine, Aish.com
Yihye Haybi's Collection
now at the Israel Museum
Geniza Project, the Nahum Collection
Television Documentary of Yemen's Jewish Community in 1929
(in Arabic), filmed in Sana'a by Russian film director, Vladimir Shnejderov
Yemenite Jews and Antiquity
*[https://thearabweekly.com/yemen-loses-last-its-jews-israel Yemen loses the Last of its Jews to Israel (Arab Weekly March 2016)]
*[https://www.ynetnews.com/articles/0,7340,L-5068444,00.html Yet News]
*[https://haifa-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/primo-explore/collectionDiscovery?vid=HAU&inst=972HAI_MAIN&collectionId=81198393000002791&lang=en_US Yefet Shlomo Collection] (in Hebrew) on the Digital collections of Younes and Soraya Nazarian Library, University of Haifa
{{Jews and Judaism
Yemenite Jews,
Jewish Yemeni history,
Jewish ethnic groups
History of the Jews in the Middle East
Mizrahi Jews
Ethnic groups in Israel
Ethnic groups in the Middle East
Jewish culture
Religion in Yemen
 Yemenite Jews or Yemeni Jews or Teimanim (from ''Yehudei Teman''; ar, اليهود اليمنيون) are those
Yemenite Jews or Yemeni Jews or Teimanim (from ''Yehudei Teman''; ar, اليهود اليمنيون) are those  There are two dates mentioned in the “letter of Simeon of Beit Aršam.” One date indicates the letter was written in Tammuz in the year 830 of Alexander (518/519 CE), from the camp of GBALA (Jebala), king of the ‘SNYA (Ghassanids or the Ġassān clan). In it, he tells of the events that transpired in Najran, while the other date puts the letter's composition in the year 835 of Alexander (523/524 CE). The second letter, however, is actually a Syriac copy of the original, copied in the year 1490 of the Seleucid Era (= 1178/79 CE). Today, it is largely agreed that the latter date is the accurate one, as it is confirmed by the Martyrium Arethae, as well as by epigraphic records, namely Sabaean inscriptions discovered in the Asir of Saudi-Arabia (Bi’r Ḥimâ), photographed by J. Ryckmans in Ry 507, 8 ~ 9, and by A. Jamme in Ja 1028, which give the old Sabaean year 633 for these operations (said to correspond with 523 CE).
Jacques Ryckmans, who deciphered these inscriptions, writes in his ''La Persécution des Chrétiens Himyarites'', that Sarah'il Yaqbul-Yaz'an was both the tribal chief and the lieutenant of Yûsuf ’As’ar (the king) at the time of the military campaign, and that he was sent out by the king to take the city of Najran, while the king watched for a possible Abyssinian/Ethiopian incursion along the coastal plains of Yemen near Mokhā (al-Moḫâ) and the strait known as Bāb al-Mandab. The Ethiopian church in Ẓafâr, which had been built by the king of Yemen some years earlier, and another church built by him in Aden (see: ''Ecclesiastical History of Philostorgius'', Epitome of Book III, chapter 4), had been seen by
There are two dates mentioned in the “letter of Simeon of Beit Aršam.” One date indicates the letter was written in Tammuz in the year 830 of Alexander (518/519 CE), from the camp of GBALA (Jebala), king of the ‘SNYA (Ghassanids or the Ġassān clan). In it, he tells of the events that transpired in Najran, while the other date puts the letter's composition in the year 835 of Alexander (523/524 CE). The second letter, however, is actually a Syriac copy of the original, copied in the year 1490 of the Seleucid Era (= 1178/79 CE). Today, it is largely agreed that the latter date is the accurate one, as it is confirmed by the Martyrium Arethae, as well as by epigraphic records, namely Sabaean inscriptions discovered in the Asir of Saudi-Arabia (Bi’r Ḥimâ), photographed by J. Ryckmans in Ry 507, 8 ~ 9, and by A. Jamme in Ja 1028, which give the old Sabaean year 633 for these operations (said to correspond with 523 CE).
Jacques Ryckmans, who deciphered these inscriptions, writes in his ''La Persécution des Chrétiens Himyarites'', that Sarah'il Yaqbul-Yaz'an was both the tribal chief and the lieutenant of Yûsuf ’As’ar (the king) at the time of the military campaign, and that he was sent out by the king to take the city of Najran, while the king watched for a possible Abyssinian/Ethiopian incursion along the coastal plains of Yemen near Mokhā (al-Moḫâ) and the strait known as Bāb al-Mandab. The Ethiopian church in Ẓafâr, which had been built by the king of Yemen some years earlier, and another church built by him in Aden (see: ''Ecclesiastical History of Philostorgius'', Epitome of Book III, chapter 4), had been seen by 

 Ottoman rule ended in 1630, when the Zaydis took over Yemen. Jews were once again persecuted. In 1679, under the rule of Al-Mahdi Ahmad, Jews were expelled ''en masse'' from all parts of Yemen to the distant province of Mawza, and many Jews died there of starvation and disease as consequence. As many as two-thirds of the exiled Jews did not survive. Their houses and property were seized, and many synagogues were destroyed or converted into mosques. This event was later known as the
Ottoman rule ended in 1630, when the Zaydis took over Yemen. Jews were once again persecuted. In 1679, under the rule of Al-Mahdi Ahmad, Jews were expelled ''en masse'' from all parts of Yemen to the distant province of Mawza, and many Jews died there of starvation and disease as consequence. As many as two-thirds of the exiled Jews did not survive. Their houses and property were seized, and many synagogues were destroyed or converted into mosques. This event was later known as the  At the beginning of the nineteenth-century, Yemenite Jews lived principally in
At the beginning of the nineteenth-century, Yemenite Jews lived principally in  During this period messianic expectations were very intense among the Jews of Yemen (and among many Arabs as well). The three pseudo-messiahs of this period, and their years of activity, are:
* Shukr Kuhayl I (1861–65)
*
During this period messianic expectations were very intense among the Jews of Yemen (and among many Arabs as well). The three pseudo-messiahs of this period, and their years of activity, are:
* Shukr Kuhayl I (1861–65)
*  Yemenite Jews and the Aramaic speaking
Yemenite Jews and the Aramaic speaking  In larger Jewish communities, such as
In larger Jewish communities, such as  The lack of chairs may also have been to provide more space for
The lack of chairs may also have been to provide more space for  During a Yemenite Jewish wedding, the bride was bedecked with jewelry and wore a traditional wedding costume, including an elaborate headdress decorated with flowers and rue leaves, which were believed to ward off evil. Gold threads were woven into the fabric of her clothing. Songs were sung as part of a seven-day wedding celebration, with lyrics about friendship and love in alternating verses of Hebrew and Arabic.
In Yemen, the Jewish practice was not for the groom and his bride to be secluded in a canopy (''chuppah'') hung on four poles, as is widely practiced today in Jewish weddings, but rather in a bridal chamber that was, in effect, a highly decorated room in the house of the groom. This room was traditionally decorated with large hanging sheets of colored, patterned cloth, replete with wall cushions and short-length mattresses for reclining. Their marriage is consummated when they have been left together alone in this room. This ancient practice finds expression in the writings of Isaac ben Abba Mari (c. 1122 – c. 1193), author of ''Sefer ha-'Ittur'', concerning the Benediction of the Bridegroom: "Now the ''chuppah'' is when her father delivers her unto her husband, bringing her into that house wherein is some new innovation, such as the sheets… surrounding the walls, etc. For we recite in the Jerusalem Talmud, ''Sotah'' 46a (''Sotah'' 9:15), 'Those bridal chambers, (''chuppoth hathanim''), they hang within them patterned sheets and gold-embroidered ribbons,' etc."
During a Yemenite Jewish wedding, the bride was bedecked with jewelry and wore a traditional wedding costume, including an elaborate headdress decorated with flowers and rue leaves, which were believed to ward off evil. Gold threads were woven into the fabric of her clothing. Songs were sung as part of a seven-day wedding celebration, with lyrics about friendship and love in alternating verses of Hebrew and Arabic.
In Yemen, the Jewish practice was not for the groom and his bride to be secluded in a canopy (''chuppah'') hung on four poles, as is widely practiced today in Jewish weddings, but rather in a bridal chamber that was, in effect, a highly decorated room in the house of the groom. This room was traditionally decorated with large hanging sheets of colored, patterned cloth, replete with wall cushions and short-length mattresses for reclining. Their marriage is consummated when they have been left together alone in this room. This ancient practice finds expression in the writings of Isaac ben Abba Mari (c. 1122 – c. 1193), author of ''Sefer ha-'Ittur'', concerning the Benediction of the Bridegroom: "Now the ''chuppah'' is when her father delivers her unto her husband, bringing her into that house wherein is some new innovation, such as the sheets… surrounding the walls, etc. For we recite in the Jerusalem Talmud, ''Sotah'' 46a (''Sotah'' 9:15), 'Those bridal chambers, (''chuppoth hathanim''), they hang within them patterned sheets and gold-embroidered ribbons,' etc."
 After immigration to Israel, the regional varieties of Yemenite bridal jewelry were replaced by a uniform item that became identified with the community: the splendid bridal garb of Sana'a.
Before the wedding, Yemenite and other Eastern Jewish communities perform the henna ceremony, an ancient ritual with
After immigration to Israel, the regional varieties of Yemenite bridal jewelry were replaced by a uniform item that became identified with the community: the splendid bridal garb of Sana'a.
Before the wedding, Yemenite and other Eastern Jewish communities perform the henna ceremony, an ancient ritual with  The three main groups of Yemenite Jews are the Baladi, Shami, and the Maimonideans or "Rambamists". In addition, the "Rechabites" are a tribe in Sana'a claiming to be descendants of
The three main groups of Yemenite Jews are the Baladi, Shami, and the Maimonideans or "Rambamists". In addition, the "Rechabites" are a tribe in Sana'a claiming to be descendants of  Towards the end of the 19th century, new ideas began to reach Yemenite Jews from abroad. Hebrew newspapers began to arrive, and relations developed with Sephardic Jews, who came to Yemen from various Ottoman provinces to trade with the army and government officials.
Two Jewish travelers,
Towards the end of the 19th century, new ideas began to reach Yemenite Jews from abroad. Hebrew newspapers began to arrive, and relations developed with Sephardic Jews, who came to Yemen from various Ottoman provinces to trade with the army and government officials.
Two Jewish travelers,  The oldest Yemenite manuscripts are those of the
The oldest Yemenite manuscripts are those of the 
 A
A  Jewish women in Yemen traditionally wore branched pantaloons beneath their long black tunics. The pantaloons were usually made of a jet-black color, tapering close to their ankles, and decorated at the lower seams with a fine embroidered stitch of silver. The tunic served as, both, a dress and long-sleeved blouse, all in one piece. In addition, all young girls wore a black, conical shaped hat upon their heads, which took the place of a scarf. These hats were called in the local vernacular, ''
Jewish women in Yemen traditionally wore branched pantaloons beneath their long black tunics. The pantaloons were usually made of a jet-black color, tapering close to their ankles, and decorated at the lower seams with a fine embroidered stitch of silver. The tunic served as, both, a dress and long-sleeved blouse, all in one piece. In addition, all young girls wore a black, conical shaped hat upon their heads, which took the place of a scarf. These hats were called in the local vernacular, '' The vast majority of Middle Eastern Jewish communities descend from the earliest Assyrian (late 8th Century BCE) and Babylonian (6th Century BCE) Hebrew exiles, whose mtDNA pools virtually lack sub-Saharan L and North and East African-specific M1 and U6 mtDNA variants. Secondly, the Ashkenazi and North African Jews with a low, but still detectable share of L lineages with very low diversity. This low diversity is most easily explained by a limited number of unique Hg L(xM,N) founders. The third example brings together Ethiopian and Yemenite Jews, rich in Hg L(xM,N) and Hg M1 (in particular in Ethiopian Jews) (Tables S1 and Table S3). As far as Ethiopian and Yemenite Jews are concerned, the main observation here is not in the absolute frequency of Hg L(xM,N) among them, but rather its high diversity, in particular among Beta Israel (Tables S1 and Table S3). Furthermore, samples of Ethiopian and Yemenite Jewish mtDNA pools differ considerably in relative abundance of typically West Asian mtDNA lineages such as derivatives of HV1, JT and others (Tables S1 and Table S3), virtually absent in the former...Maternal DNA of Mizrachi Jews is varied, even slightly from other Mizrachim, indicating likely majority Israelite and some non-Israelite origin from among the women of each of the Near Eastern populations; e.g. Yemeni, Mesopotamian, and other local Near Eastern women. DNA markings, however, are irrelevant when considering that, in Jewish law, proselytes who may have joined the religion of Israel and married into Israelite families, will still pass on their DNA readings to their children. According to
The vast majority of Middle Eastern Jewish communities descend from the earliest Assyrian (late 8th Century BCE) and Babylonian (6th Century BCE) Hebrew exiles, whose mtDNA pools virtually lack sub-Saharan L and North and East African-specific M1 and U6 mtDNA variants. Secondly, the Ashkenazi and North African Jews with a low, but still detectable share of L lineages with very low diversity. This low diversity is most easily explained by a limited number of unique Hg L(xM,N) founders. The third example brings together Ethiopian and Yemenite Jews, rich in Hg L(xM,N) and Hg M1 (in particular in Ethiopian Jews) (Tables S1 and Table S3). As far as Ethiopian and Yemenite Jews are concerned, the main observation here is not in the absolute frequency of Hg L(xM,N) among them, but rather its high diversity, in particular among Beta Israel (Tables S1 and Table S3). Furthermore, samples of Ethiopian and Yemenite Jewish mtDNA pools differ considerably in relative abundance of typically West Asian mtDNA lineages such as derivatives of HV1, JT and others (Tables S1 and Table S3), virtually absent in the former...Maternal DNA of Mizrachi Jews is varied, even slightly from other Mizrachim, indicating likely majority Israelite and some non-Israelite origin from among the women of each of the Near Eastern populations; e.g. Yemeni, Mesopotamian, and other local Near Eastern women. DNA markings, however, are irrelevant when considering that, in Jewish law, proselytes who may have joined the religion of Israel and married into Israelite families, will still pass on their DNA readings to their children. According to 

 During the
During the  A third wave of emigration from Yemen began in the late 20th-century, with the intercession of Human Rights activist and professor, Hayim Tawil, founder of the International Coalition for the Revival of the Jews of Yemen (ICROJOY) in 1988. Tawil was instrumental in bringing out from Yemen the first Jew to emigrate in 23 years, and who set foot in Israel in September 1990. He was followed by other families in 1992, with the greatest bulk of Jewish families arriving in Israel between 1993 and 1994. These new Yemenite Jewish immigrants settled mainly in Rehovot (''Oshiyot''),
A third wave of emigration from Yemen began in the late 20th-century, with the intercession of Human Rights activist and professor, Hayim Tawil, founder of the International Coalition for the Revival of the Jews of Yemen (ICROJOY) in 1988. Tawil was instrumental in bringing out from Yemen the first Jew to emigrate in 23 years, and who set foot in Israel in September 1990. He was followed by other families in 1992, with the greatest bulk of Jewish families arriving in Israel between 1993 and 1994. These new Yemenite Jewish immigrants settled mainly in Rehovot (''Oshiyot''),  Today, the overwhelming majority of Yemenite Jews live in Israel.
Some Yemenite Jews stayed behind during Operation Magic Carpet, many of them not wanting to leave sick or elderly relatives behind. Another wave of emigration took place in 1959, with some 3,000 Yemenite Jews moving to Israel, and some others moving to the
Today, the overwhelming majority of Yemenite Jews live in Israel.
Some Yemenite Jews stayed behind during Operation Magic Carpet, many of them not wanting to leave sick or elderly relatives behind. Another wave of emigration took place in 1959, with some 3,000 Yemenite Jews moving to Israel, and some others moving to the  In a July 2018 interview with a Yemenite rabbi, he claimed that they were definitely treated very well before the recent war in Yemen which has affected all communities in Yemen. He has also said that Yemenite Jews should have never traveled away from Yemen and that he believes thousands of Yemenite Jews will return to Yemen after the war ends.
In 2019, the Mona Relief website reported (February 25): "Mona Relief's team in the capital Sana'a delivered today monthly food aid packages to Jewish minority families in Yemen. Mona Relief has been delivering food aid baskets to Jewish community in the capital Sana'a since 2016. Our project today was funded by Mona Relief's online fundraising campaign in indiegog ..."
As of March 2020, the Jewish Cemetery in Aden was destroyed. On April 28, 2020, Yemenite Minister Moammer al-Iryani remarked the ''fate of the last 50 Jews'' in Yemen is ''unknown''.
A 2020 World Population Review with a Census of Jewish population by country has ''no'' listing of ''any'' Jews in Yemen.
On July 13, 2020, it was reported that the Houthi Militia were capturing the last Jews of Yemen of the Kharif District. In their last mention of the Jews in Yemen in July 2020 the Mona Relief reported on their Website that as of July 19, 2020, of the Jewish Population in Yemen there were only a "handful" of Jews in Sana'a.
According to Yemeni publications published in July 2020, the last two Jewish families were waiting for deportation from the areas controlled by the Houthis, which would make Yemen, for the first time in its modern history, devoid of Jews, with the exception of the families of the brothers Suleiman Musa Salem and Sulaiman Yahya Habib in Sana’a and the family of Salem Musa Mara’bi who moved to the complex owned by the Ministry of Defense near the U.S. embassy in 2007 after the Houthis assaulted them and looted their homes. The publications said that a Jewish woman lives with her brother in the Rayda district and a man and his wife live in the Arhab district of the Sana’a governorate. A source said, “It is now clear that the Houthis want to deport the rest of the Jews, and prevent them from selling their properties at their real prices, and we are surprised that the international community and local and international human rights organizations have remained silent towards the process of forced deportation and forcing the Jews to leave their country and prevent them from disposing of their property.
In August 2020 of an estimated 100 or so remaining Yemen Jews, 42 have migrated to U.A.E. and the rest would also leave.
On November 10, 2020, the U.S. State Department called for the immediate and unconditional release of Levi Salem Musa Marhabi. A press statement said Marhabi has been wrongfully detained by the Houthi militia for four years, despite a court ordering his release in September 2019. On November 25, 2020, it is reported that a total of 38 Jews still remain in Yemen.
In December 2020 an Israeli Rabbi visited the Yemenite Jews who escaped to the UAE. As of January 12, 2021, 7 Jews have left Yemen for UAE leaving 31 Jews in Yemen.
On 28 March 2021, 13 Jews were forced by the Houthis to leave Yemen, ''
In a July 2018 interview with a Yemenite rabbi, he claimed that they were definitely treated very well before the recent war in Yemen which has affected all communities in Yemen. He has also said that Yemenite Jews should have never traveled away from Yemen and that he believes thousands of Yemenite Jews will return to Yemen after the war ends.
In 2019, the Mona Relief website reported (February 25): "Mona Relief's team in the capital Sana'a delivered today monthly food aid packages to Jewish minority families in Yemen. Mona Relief has been delivering food aid baskets to Jewish community in the capital Sana'a since 2016. Our project today was funded by Mona Relief's online fundraising campaign in indiegog ..."
As of March 2020, the Jewish Cemetery in Aden was destroyed. On April 28, 2020, Yemenite Minister Moammer al-Iryani remarked the ''fate of the last 50 Jews'' in Yemen is ''unknown''.
A 2020 World Population Review with a Census of Jewish population by country has ''no'' listing of ''any'' Jews in Yemen.
On July 13, 2020, it was reported that the Houthi Militia were capturing the last Jews of Yemen of the Kharif District. In their last mention of the Jews in Yemen in July 2020 the Mona Relief reported on their Website that as of July 19, 2020, of the Jewish Population in Yemen there were only a "handful" of Jews in Sana'a.
According to Yemeni publications published in July 2020, the last two Jewish families were waiting for deportation from the areas controlled by the Houthis, which would make Yemen, for the first time in its modern history, devoid of Jews, with the exception of the families of the brothers Suleiman Musa Salem and Sulaiman Yahya Habib in Sana’a and the family of Salem Musa Mara’bi who moved to the complex owned by the Ministry of Defense near the U.S. embassy in 2007 after the Houthis assaulted them and looted their homes. The publications said that a Jewish woman lives with her brother in the Rayda district and a man and his wife live in the Arhab district of the Sana’a governorate. A source said, “It is now clear that the Houthis want to deport the rest of the Jews, and prevent them from selling their properties at their real prices, and we are surprised that the international community and local and international human rights organizations have remained silent towards the process of forced deportation and forcing the Jews to leave their country and prevent them from disposing of their property.
In August 2020 of an estimated 100 or so remaining Yemen Jews, 42 have migrated to U.A.E. and the rest would also leave.
On November 10, 2020, the U.S. State Department called for the immediate and unconditional release of Levi Salem Musa Marhabi. A press statement said Marhabi has been wrongfully detained by the Houthi militia for four years, despite a court ordering his release in September 2019. On November 25, 2020, it is reported that a total of 38 Jews still remain in Yemen.
In December 2020 an Israeli Rabbi visited the Yemenite Jews who escaped to the UAE. As of January 12, 2021, 7 Jews have left Yemen for UAE leaving 31 Jews in Yemen.
On 28 March 2021, 13 Jews were forced by the Houthis to leave Yemen, '' Israeli Politicians of Yemenite Jewish descent include Gila Gamliel (current member of the Knesset for Likud), Meir Yitzhak Halevi (the Mayor of Eilat), Saadia Kobashi (leader of the Yemenite Jewish community in Israel, and one of the signatories of the country's declaration of independence), and Avraham Taviv.
Israeli Politicians of Yemenite Jewish descent include Gila Gamliel (current member of the Knesset for Likud), Meir Yitzhak Halevi (the Mayor of Eilat), Saadia Kobashi (leader of the Yemenite Jewish community in Israel, and one of the signatories of the country's declaration of independence), and Avraham Taviv.