|
Theophilos The Indian
Theophilos the Indian ( el, Θεόφιλος) (died 364), also called "the Ethiopian", was an Aetian or Heteroousian bishop who fell alternately in and out of favor with the court of the Roman emperor Constantius II. He is mentioned in the encyclopedia '' Suda''. Originally from Socotra or the island of Divus which could be the Maldive Islands in the Indian Ocean, or an island near the mouth of the Indus. He came to the court of Constantine I as a young man and was ordained a deacon under the Arian bishop Eusebius of Nicomedia. He was later exiled because Constantius believed him to be a supporter of Constantius' rebellious cousin Gallus. Famed for his ability as a healer, Theophilus was later recalled to court to heal Constantius' wife, the empress Eusebia, which he is reputed to have done successfully.Philostorgius. " Chapter 7." ''Ecclesiastical history/Epitome of book IV''. He was exiled again for his support of the disfavored theologian Aëtius whose Anomoean doctrine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aetian
In 4th-century Christianity, the Anomoeans , and known also as Heterousians , Aetians , or Eunomians , were a sect that upheld an extreme form of Arianism, that Jesus Christ was not of the same nature (consubstantial) as God the Father nor was of like nature (homoiousian), as maintained by the semi-Arians. The word "anomoean" comes from Greek 'not' and 'similar': "different; dissimilar". In the 4th century, during the reign of Constantius II, this was the name by which the followers of Aëtius and Eunomius were described. The term "heterousian" derives from the Greek , ''heterooúsios'', "differing in substance" from , ''héteros'', "another" and , ''ousía'', "substance, being". The semi-Arians condemned the Anomoeans in the Council of Seleucia, and the Anomoeans condemned the semi-Arians in their turn in the Councils of Constantinople and Antioch; erasing the word from the formula of Rimini and that of Constantinople and protesting that the Word had not only a different sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anomoeanism
In 4th-century Christianity, the Anomoeans , and known also as Heterousians , Aetians , or Eunomians , were a sect that upheld an extreme form of Arianism, that Jesus Christ was not of the same nature (consubstantial) as God the Father nor was of like nature (homoiousian), as maintained by the semi-Arians. The word "anomoean" comes from Greek language, Greek 'not' and 'similar': "different; dissimilar". In the 4th century, during the reign of Constantius II, this was the name by which the followers of Aëtius (theologian), Aëtius and Eunomius were described. The term "heterousian" derives from the Greek language, Greek , ''heterooúsios'', "differing in substance" from , ''héteros'', "another" and , ''ousía'', "substance, being". The semi-Arians condemned the Anomoeans in the Council of Seleucia, and the Anomoeans condemned the semi-Arians in their turn in the Councils of Council of Constantinople (360), Constantinople and Synods of Antioch, Antioch; erasing the word from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th-century Births
The 4th century (per the Julian calendar and Anno Domini/Common era) was the time period which lasted from 301 ( CCCI) through 400 ( CD). In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fell in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th-century Romans
The 4th century (per the Julian calendar and Anno Domini/Common era) was the time period which lasted from 301 ( CCCI) through 400 ( CD). In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fell in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th-century Bishops
The 4th century (per the Julian calendar and Anno Domini/Common era) was the time period which lasted from 301 ( CCCI) through 400 ( CD). In the West, the early part of the century was shaped by Constantine the Great, who became the first Roman emperor to adopt Christianity. Gaining sole reign of the empire, he is also noted for re-establishing a single imperial capital, choosing the site of ancient Byzantium in 330 (over the current capitals, which had effectively been changed by Diocletian's reforms to Milan in the West, and Nicomedeia in the East) to build the city soon called Nova Roma (New Rome); it was later renamed Constantinople in his honor. The last emperor to control both the eastern and western halves of the empire was Theodosius I. As the century progressed after his death, it became increasingly apparent that the empire had changed in many ways since the time of Augustus. The two emperor system originally established by Diocletian in the previous century fell int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arian Bishops
Arianism ( grc-x-koine, Ἀρειανισμός, ) is a Christological doctrine first attributed to Arius (), a Christian presbyter from Alexandria, Egypt. Arian theology holds that Jesus Christ is the Son of God, who was begotten by God the Father with the difference that the Son of God did not always exist but was begotten within time by God the Father, therefore Jesus was not coeternal with God the Father. Arius's trinitarian theology, later given an extreme form by Aetius and his disciple Eunomius and called anomoean ("dissimilar"), asserts a total dissimilarity between the Son and the Father. Arianism holds that the Son is distinct from the Father and therefore subordinate to him. The term ''Arian'' is derived from the name Arius; it was not what the followers of Arius's teachings called themselves, but rather a term used by outsiders. The nature of Arius's teachings and his supporters were opposed to the theological doctrines held by Homoousian Christians, regarding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
364 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 364 ( CCCLXIV) was a leap year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augustus and Varronianus (or, less frequently, year 1117 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 364 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * February 17 – Emperor Jovian dies after a reign of eight months. He is found dead in his tent at Tyana (Asia Minor) en route back to Constantinople, in suspicious circumstances. * February 26 – Valentinian I is proclaimed Emperor by officers of the Roman army at Nicaea in Bithynia. He addresses the soldiers (who threaten to riot) in a speech. He founds the Valentinianic dynasty and rules the Western Roman Empire, from Caledonia (Scotland) to the Rhine frontier, ensuring it a few years of relativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaleb Of Axum
Kaleb (), also known as Saint Elesbaan, was King of Aksum, which was situated in modern-day Eritrea and Ethiopia. Procopius calls him "Hellestheaeus", a variant of grc-koi, Ελεσβόάς version of his regnal name, gez, እለ አጽብሐ, translit=ʾƎllä ʾAṣbəḥa (''Histories'', 1.20). Variants of his name are Hellesthaeus, Ellestheaeus, Eleshaah, Ellesboas, Elesbaan, and Elesboam. At Aksum, in inscription RIE 191, his name is rendered in unvocalized Gə‘əz as KLB ’L ’ṢBḤ WLD TZN (Kaleb ʾElla ʾAṣbeḥa, son of Tazena). In vocalized Gə‘əz, it is (Kaleb ʾƎllä ʾAṣbəḥa). Kaleb, a name derived from the Biblical character Caleb, was his given name; on both his coins and inscriptions he left at Axum, as well as Ethiopian hagiographical sources and king lists, he refers to himself as the son of Tazena. History Procopius, John of Ephesus, and other contemporary historians recount Kaleb's invasion of Yemen around 520, against the Himyarit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dhu Nuwas
Dhū Nuwās, ( ar, ذُو نُوَاس), real name "Yūsuf Asʾar Yathʾar" ( Musnad: 𐩺𐩥𐩪𐩰 𐩱𐩪𐩱𐩧 𐩺𐩻𐩱𐩧, ''Yws¹f ʾs¹ʾr Yṯʾr''), "Yosef Nu'as" ( he, יוסף נואס), or "Yūsuf ibn Sharhabīl" ( ar, يُوْسُف ٱبْن شَرْحَبِيْل, link=no), also known as "Masruq" in Syriac, and ''Dounaas'' () in Medieval Greek, was a Jewish king of Himyar between 517 and 525–527 AD, who came to renown on account of his persecutions of peoples of other religions, notably Christians, living in his kingdom. History Ibn Hisham's ''Sirat Rasul Allah'' (better known in English as ''the Life of Muhammad''), describes the exploits of Yūsuf Dhū Nuwās. Ibn Hisham explains that Yūsuf was a convert Jew who grew out his sidelocks (''nuwas''), and who became known as "he of sidelocks." The historicity of Dhū Nuwās is affirmed by Philostorgius and by Procopius (in the latter's ''Persian War''). Procopius writes that in 525, the armies of the Chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
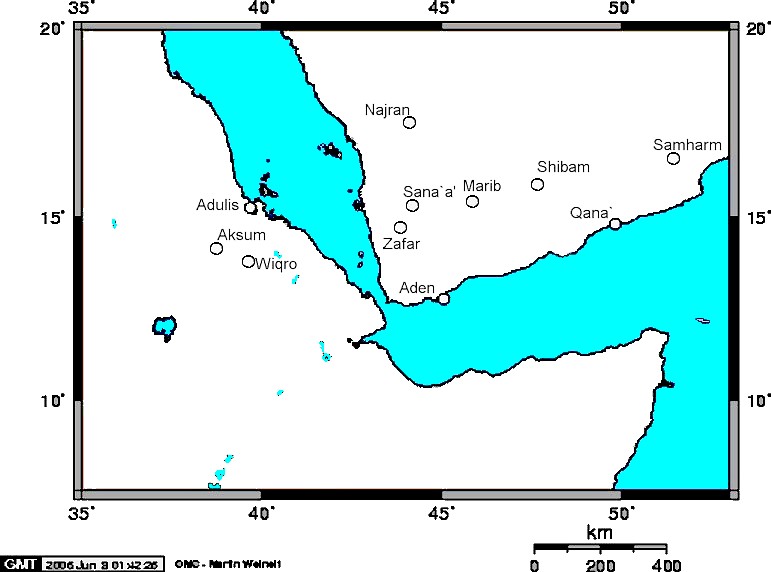
Zafar, Yemen
Ẓafār or Dhafar ( ar, ظفار) is an ancient Himyarite site situated in Yemen, some 130 km south-south-east of today's capital, Sana'a, and c. southeast of Yarim. Given mention in several ancient texts, there is little doubt about the pronunciation of the name. Despite the opinion of local patriots in Oman, this site in Yemen is far older than its namesake there. It lies in the Yemeni highlands at some 2800 m. Zafar was the capital of the Himyarites (110 BCE – 525 CE), which at its peak ruled most of the Arabian Peninsula. For 250 years the tribal confederacy and allies' combined territory extended past Riyadh to the north and the Euphrates to the north-east. History From an archaeological perspective, the settlement's beginnings are not well known. The main sources consist of Old South Arabian Musnad inscriptions dated as early as the 1st century BCE. It is mentioned by Pliny in his Natural History, in the anonymous Periplus of the Erythraean Sea (both 1st centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frumentius
Frumentius ( gez, ፍሬምናጦስ; died c. 383) was a Phoenician Christian missionary and the first bishop of Axum who brought Christianity to the Kingdom of Aksum. He is sometimes known by other names, such as Abuna ("Our Father") and Aba Salama ("Father of Peace"). He was ethnically a Phoenician, according to Rufinus, born in Tyre. As a boy, he was captured with his brother, and they became slaves to the King of Axum. He freed them shortly before his death, and they were invited to educate his young heir. They also began to teach Christianity in the region. Later, Frumentius traveled to Alexandria, Egypt, where he appealed to have a bishop appointed and missionary priests sent south to Axum. Thereafter, he was appointed bishop and established the Church in Ethiopia, converting many local people, as well as the king. His appointment began a tradition that the Patriarch of Alexandria appoint the bishops of Ethiopia. Biography According to the fourth-century historian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Aksum
The Kingdom of Aksum ( gez, መንግሥተ አክሱም, ), also known as the Kingdom of Axum or the Aksumite Empire, was a kingdom centered in Northeast Africa and South Arabia from Classical antiquity to the Middle Ages. Based primarily in what is now northern Ethiopia, and spanning modern-day Eritrea, northern Djibouti, and eastern Sudan, it extended at its height into much of modern-day southern Arabia during the reign of King Kaleb. Axum served as the kingdom's capital for many centuries but relocated to Jarma in the 9th century due to declining trade connections and recurring external invasions. Emerging from the earlier Dʿmt civilization, the kingdom was likely founded in the early 1st century. Pre-Aksumite culture developed in part due to a South Arabian influence, evident in the use of the Ancient South Arabian script and the practice of Ancient Semitic religion. However, the Geʽez script came into use by the 4th century, and as the kingdom became a major power on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)